Abstract
Single cell transcriptomics has transformed our ability to characterize cell states, but deep biological understanding requires more than a taxonomic listing of clusters. As new methods arise to measure distinct cellular modalities, a key analytical challenge is to integrate these datasets to better understand cellular identity and function. Here, we develop a strategy to “anchor” diverse datasets together, enabling us to integrate single cell measurements not only across scRNA-seq technologies, but different modalities as well. After demonstrating improvement over existing methods for integrating scRNA-seq data, we anchor scRNA-seq experiments with scATAC-seq to explore chromatin differences in closely related interneuron subsets, and project protein expression measurements onto a bone marrow atlas to characterize lymphocyte populations. Lastly, we harmonize in-situ gene expression and scRNA-seq datasets, allowing transcriptome-wide imputation of spatial gene expression patterns.Our work presents a strategy for the assembly of harmonized references, and transfer of information across datasets.
Graphical Abstract
Introduction
Recent advances in molecular biology, microfluidics, and computation have transformed the growing field of single-cell sequencing beyond routine transcriptomic profiling with single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq)[Svensson et al., 2018, Tanay and Regev, 2017, Stuart and Satija, 2019]. Indeed, new approaches now encompass diverse characterization of a single cell’s immunophenotype [Stoeckius et al., 2017, Peterson et al., 2017], genome sequence [Navin et al., 2011, Vitak et al., 2017], lineage origins [Raj et al., 2018, Spanjaard et al., 2018, Alemany et al., 2018], DNA methylation landscape [Luo et al., 2018, Gavin et al., 2017], chromatin accessibility[Cao et al., 2018, Lake et al., 2018, Preissl et al., 2018], and even spatial positioning [Moffitt et al., 2018, Wang et al., 2018, Codeluppi et al., 2018]. However, each technology has unique strengths and weaknesses, and measures only particular aspects of cellular identity, motivating the need to leverage information in one dataset to improve the interpretation of another.
The importance of data integration is particularly relevant for approaches that aim to measure distinct modalities within single cells. For example, single-cell ATAC-seq (scATAC-seq) can uniquely reveal enhancer regions and regulatory logic, but currently may not achieve the same power for unsupervised cell type discovery as transcriptomics [Cusanovich et al., 2018, Lake et al., 2018]. Similarly, methods for multiplexed spatial RNA profiling using in-situ hybridization can capture the intricate architecture of tissue organization, but are unable to profile the whole transcriptome [Moffitt et al., 2018]. For example, the recently introduced STARmap method enables the measurement of more than 1,000 genes in spatially intact tissue, but forecast this number of genes as an upper limit for such approaches without super-resolution microscopy or the physical expansion of hydrogels [Wang et al., 2018]. The integration of different single-cell technologies with scRNA-seq, such as spatial profiling methods or scATAC-seq, could therefore harmonize these data with transcriptome-wide measurements, allowing not just for the taxonomic listing of cell types, but a deeper understanding of their regulatory logic and spatial organization.
The challenges presented by single-cell data integration can be broadly subdivided into two tasks. First, how can disparate single-cell datasets, produced across individuals, technologies, and modalities be harmonized into a single reference? Second, once a reference has been constructed, how can its data and meta-data improve the analysis of new experiments? These questions are well-suited to established fields in statistical learning. In particular, domain adaptation aims to identify correspondences across domains to combine datasets into a shared space [Blitzer et al., 2006, Wang and Mahadevan, 2010], while transfer learning enables a model trained on a reference dataset to project information onto a query experiment [Raina et al., 2007, Stein-O’Brien et al., 2018]. More broadly, these problems are conceptually similar to reference assembly [Li et al., 2012] and mapping [Langmead et al., 2009] for genomic DNA sequences, and the development of effective tools for single-cell datasets could enable similarly transformative advances in our ability to analyze and interpret single-cell data.
Recent approaches have established the first steps towards effective data integration. In particular, we recently introduced the use of canonical correlation analysis (CCA) [Butler et al., 2018], alongside independent pioneering work leveraging the identification of mutual nearest neighbors (MNNs) [Haghverdi et al., 2018], to identify shared subpopulations across datasets. While these approaches can be highly effective, they can also struggle in cases where only a subset of cell types are shared across datasets, or significant technical variation masks shared biological signal. New probabilistic approaches for scRNA-seq data normalization and analysis using neural networks have also been recently introduced, with the advantage that they scale to very large datasets and explicitly model batch effects [Lopez et al., 2018]. However, these methods focus on scRNA-seq and are not designed to integrate information across different modalities, nor do they enable the transfer of information from one dataset to another.
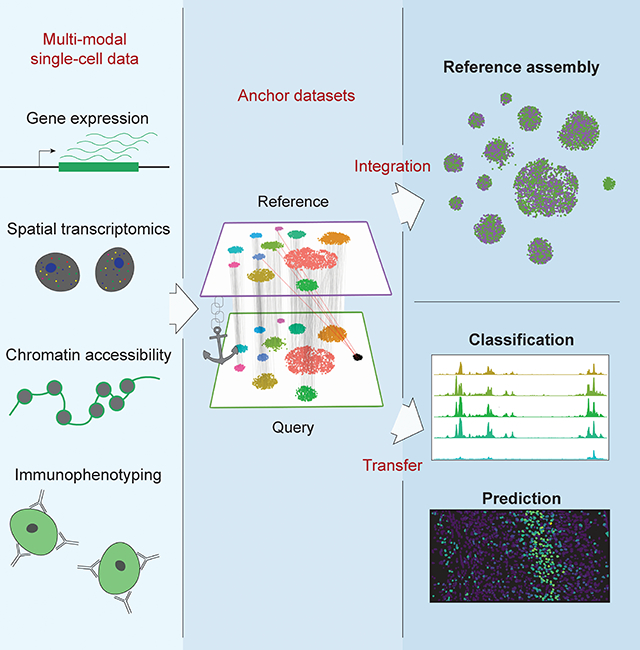
Here, we present a unified strategy for reference assembly and transfer learning for transcriptomic, epigenomic, proteomic, and spatially-resolved single-cell data. Through the identification of cell pairwise correspondences between single cells across datasets, termed “anchors”, we can transform datasets into a shared space, even in the presence of extensive technical and/or biological differences. This enables the construction of harmonized atlases at the tissue or organismal scale, as well as effective transfer of discrete or continuous data from a reference onto a query dataset. Our results, implemented in an updated version 3 of our open-source R toolkit Seurat, present a framework for the comprehensive integration of single-cell data.
Results
Diverse single-cell technologies each measure distinct elements of cellular identity, and are characterized by unique sources of bias, sensitivity, and accuracy [Svensson et al., 2017]. As a result, measurements across datasets may not be directly comparable. For example, expression measurements for scRNA-seq are marred by false negatives (“drop-outs”) due to transcript abundance and protocol-specific biases [Svensson et al., 2017, van Dijk et al., 2018], while expression derived from fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) exhibits probe-specific noise due to sequence specificity and background binding [Torre et al., 2018]. To address this, we developed an unsupervised strategy to “anchor” datasets together to facilitate integration and comparison. Below we briefly summarize the steps in our approach, alongside a complete description in the Methods, and describe its application to diverse published and newly produced single-cell datasets.
Identifying “anchor” correspondences across single-cell datasets
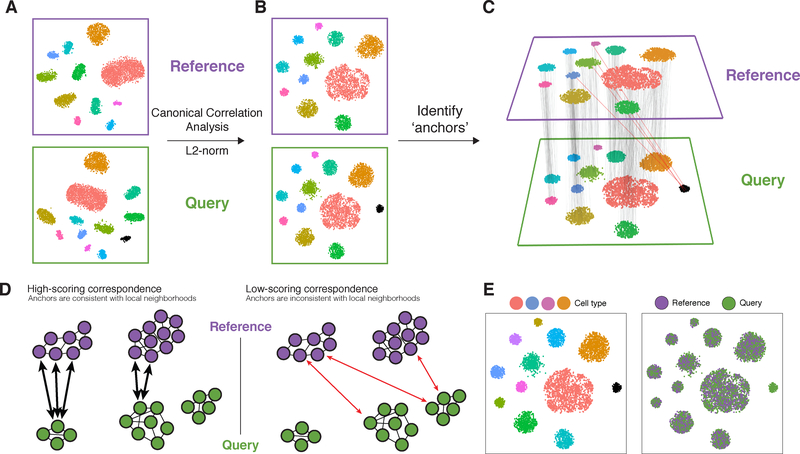
Our motivation for integrating diverse datasets lies in the potential for the information present in one experiment to inform the interpretation of another. In order to relate different experiments to each other, we assume that there are correspondences between datasets, and that at least a subset of cells represent a shared biological state. Inspired by the concept of mutual nearest neighbors (MNNs), we represent these correspondences as two cells (one from each dataset) that we expect to be defined by a common set of molecular features [Haghverdi et al., 2018]. While MNNs have previously been identified using L2-normalized gene expression, significant differences across batches can obscure the accurate identification of MNNs, particularly when the batch effect is on a similar scale to the biological differences between cell states. To overcome this, we first jointly reduce the dimensionality of both datasets using diagonalized canonical correlation analysis (CCA), then apply L2-normalization to the canonical correlation vectors (Figure 1A,B). We next search for MNNs in this shared low-dimensional representation. We refer to the resulting cell pairs as “anchors”, as they encode the cellular relationships across datasets that will form the basis for all subsequent integration analyses (Figure 1C). Our anchors can successfully recover matching cell states even in the presence of significant dataset differences, as CCA can effectively identify shared biological markers and conserved gene correlation patterns [Butler et al., 2018]. However, cells in non-overlapping populations should not participate in anchors, representing an important distinction that extends our previous work.
Figure 1. Schematic overview of reference “assembly” integration in Seurat v3.
(A) Representation of two datasets, reference and query, each of which originates from a separate single-cell experiment. The two datasets share cells from similar biological states, but the query dataset contains a unique population (in black). (B) We perform canonical correlation analysis, followed by L2-normalization of the canonical correlation vectors, to project the datasets into a subspace defined by shared correlation structure across datasets. (C) In the shared space, we identify pairs of mutual nearest neighbors across reference and query cells. These should represent cells in a shared biological state across datasets (grey lines), and serve as “anchors” to guide dataset integration. In principle, cells in unique populations should not participate in anchors, but in practice we observe “incorrect” anchors at low frequency (red lines). (D) For each anchor pair, we assign a score based on the consistency of anchors across the neighborhood structure of each dataset. (E) We utilize anchors and their scores to compute “correction” vectors for each query cell, transforming its expression so it can be jointly analyzed as part of an integrated reference.
Obtaining an accurate set of anchors is paramount to successful integration. Aberrant anchors that form between different biological cell states across datasets are analogous to noisy edges that occur in K-nearest neighbor (KNN) graphs [Bendall et al., 2014], and can confound downstream analyses. This has motivated the use of shared nearest neighbor (SNN) graphs [Levine et al., 2015, Shekhar et al., 2016], where the similarity between two cells is assessed by the overlap in their local neighborhoods. As this measure effectively pools neighbor information across many cells, the result is robust to aberrant connections in the neighbor graph. We introduced an analogous procedure for the scoring of anchors, where each anchor pair was assigned a score based on the shared overlap of mutual neighborhoods for the two cells in a pair (Figure 1D; STAR Methods). High-scoring correspondences therefore represent cases where many similar cells in one dataset are predicted to correspond to the same group of similar cells in a second dataset, reflecting increased robustness in the association between the anchor cells. While we initially identify anchors in low-dimensional space, we also filter out anchors whose correspondence is not supported based on the original untransformed data (STAR Methods). The identification, filtering, and scoring of anchors is the first step for all integration analyses in this manuscript, including reference assembly, classification, and transfer learning.
Constructing integrated atlases at the scale of organs and organisms
To assemble a reference of single-cell datasets in Seurat v3, we aim to identify a non-linear transformation of the underlying data, so that they can be jointly analyzed, in a process conceptually similar to batch correction. We first identify and score anchors between pairs of datasets (referred to as “reference” and “query” datasets) as described above (Figure 1A-D). As introduced by [Haghverdi et al., 2018], the difference in expression profiles between the two cells in each anchor represents a batch vector. Therefore, for each cell in the query dataset, we aim to apply a transformation (correction vector) that represents a weighted average across multiple batch vectors. These weights are determined by two components: a cell similarity score, computed individually for each cell in the dataset, and the anchor score, computed once for each anchor. The cell similarity score is defined by the distance between each query cell and its k nearest anchors in principal component space (STAR Methods), prioritizing anchors representing a similar biological state. Consequently, cells in the same local neighborhood will share similar correction vectors. The anchor score prioritizes robust anchor correspondences, as described above. By subtracting these weighted correction vectors from the query gene expression matrix, we compute a corrected query expression matrix that can then be combined with the original reference dataset, and used as input for all integrated downstream analyses including dimensionality reduction and clustering. To extend this procedure to multiple datasets, we drew inspiration from methods for multiple sequence alignment [Feng and Doolittle, 1987]. Here, we first construct a guide tree based on the similarity between all pairs of datasets and proceed with recursive pairwise correction up the tree. The similarity score used to construct the hierarchy is computed as the total number of anchors between a pair of datasets, normalized to the total number of cells in the smaller dataset of the pair. This extension for multiple dataset integration was independently conceived but conceptually similar to the Scanorama method [Hie et al., 2018].
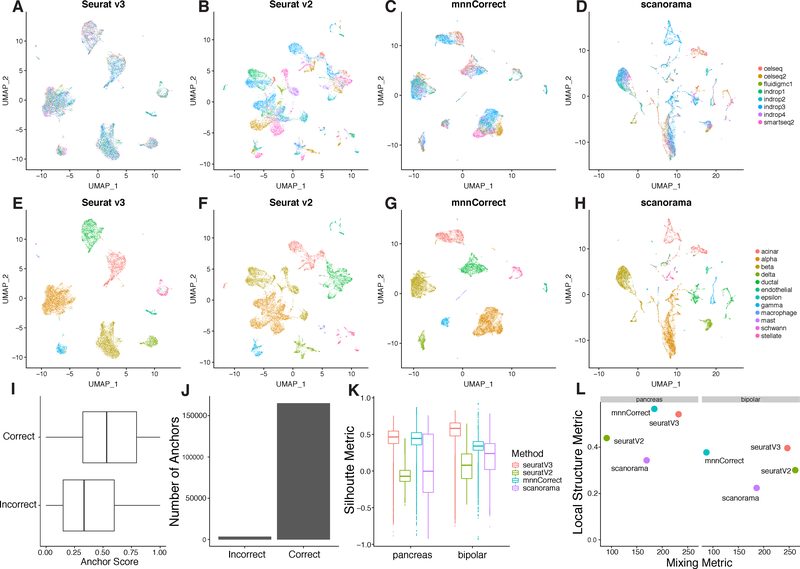
We hypothesized that our anchoring method could be used to create a reference atlas of complex human tissue, by combining diverse datasets across patients, technologies, and laboratories. We examined a collection of eight previously published datasets using tissue from human pancreatic islets, spanning 27 donors, five technologies, and four laboratories [Baron et al., 2016, Lawlor et al., 2017, Grün et al., 2016, Muraro et al., 2016, Segerstolpe et al., 2016]. Before correcting for technical differences, the cells separated by a combination of dataset of origin and cell type, hindering downstream analysis (Figure S1A). After applying our integration procedure, technical distinctions between datasets were effectively removed (Figure S1B), while major and minor cell populations could be identified through unsupervised graph-based clustering (Figure S1C,D). In addition to reliably detecting all major cell classes present in all datasets (alpha, beta, delta, gamma, acinar, and stellate), we also detected a set of extremely rare cell populations in a subset of the datasets that could not be robustly identified through individual unsupervised clustering analyses (epsilon, schwann, mast and macrophage; Figure S1C).
To examine the robustness of our method to non-overlapping populations, we removed all instances of one cell type from each dataset (e.g. we removed all alpha cells from the celseq dataset, all beta cells from the SMART-seq2 dataset, etc.; Table S1A). We then repeated the same integration analysis, and obtained highly concordant results after applying this perturbation (Figure 2A). Our robustness originates in part from the anchor scoring approach, as we observed that erroneous anchors in which the query and reference cells belong to different clusters were assigned lower scores compared to consistent anchors and therefore were given less weight in the resulting transformation (Figure 2I). Furthermore, we observed far fewer “incorrect” anchors compared to correct anchors, reflecting the accuracy of our anchor finding method (Figure 2J).
Figure 2. Comparison of multi-dataset integration methods for scRNA-seq.
(A-H) UMAP plots of eight pancreatic islet cell datasets colored by dataset (A-D) and by cell type (E-H) after integration with Seurat v3, Seurat v2, mnnCorrect, and Scanorama. To challenge the methods’ robustness to non-overlapping populations, a single cell type was withheld from each dataset prior to integration. (I-J) Distribution of anchor scores and counts, separated by incorrect (different cell types in the anchor pair) and correct (same cell type in the anchor pair) anchors. Anchors are from the analysis in Figure S1A. (K-L) Metrics for evaluating integration performance across the four methods on two main properties: cell “mixing” across datasets and the preservation of within-dataset local structure (STAR Methods).
Using these perturbed datasets, we next benchmarked the performance of our Seurat v3 integration procedure against existing methods (Figure 2A-H). For each tool, we aimed to quantify how well mixed the datasets were after integration, and how well they preserved the structure present in the original datasets (STAR Methods). Methods that perform well in both metrics effectively match populations across datasets without blending distinct populations together. We also calculated silhouette coefficients based on our predefined labels, a measure of how similar a cell is to its own cluster compared to other clusters. This gives a score in the range of −1 to +1, where a higher score indicates higher performance. The silhouette coefficient captures elements of both sample mixing and local structure. Seurat v3 exhibited the highest silhouette scores and performed well on all other metrics (Figure 2K,L). We obtained equally positive results and benchmarks when examining six batches of murine bipolar cells, which have previously been demonstrated to exhibit batch effects[Shekhar et al., 2016] (Figure 2J,K; Figure S1E,F). We conclude that our anchoring procedure can effectively integrate diverse scRNA-seq datasets and outperforms existing strategies for data integration.
We also considered the potential for our procedure to construct atlases not only at the level of individual tissues, but across entire organisms. To test this, we considered recently published datasets from Tabula Muris [Schaum et al., 2018], which aimed to profile a diverse set of murine tissues using plate (SMART-seq2) and droplet (10x Genomics) based assays. These data represent an enormously valuable community resource, but the utility of a single atlas requires that the datasets be harmonized. We identified anchors across 97,029 single cells, representing 18 tissues (12 tissues were represented in both datasets, 6 were only profiled using SMART-seq2), and applied these to integrate the datasets. Integrated visualization revealed extensive mixing of shared cell populations across the two technologies (Figure S2A,B), but cells from the six non-overlapping tissues were not mixed and retained their structure from the original dataset (Figure S2C,D). In particular, we note that this harmonized resource provides exceptional power to detect rare populations, such as tissue-resident plasmacytoid dendritic cells (0.07% cells, detected in 9 tissues), and mesothelial cells (0.05% cells, detected in 5 tissues), that could not be robustly identified in individual dataset analysis (Figure S2C,E,F). These results suggest an analytical path forward when similar atlas-scale datasets are generated across human tissues with diverse technologies [Regev et al., 2017].
Leveraging anchor correspondences to classify cell states
We next extended our method to transfer information from a reference to a query dataset. We reasoned that anchors could be used to transfer discrete and continuous data onto query datasets, without modification of the reference. We first considered the problem of cell state classification, where discrete cell labels are learned from reference-derived models, rather than being discovered de novo by unsupervised analysis.
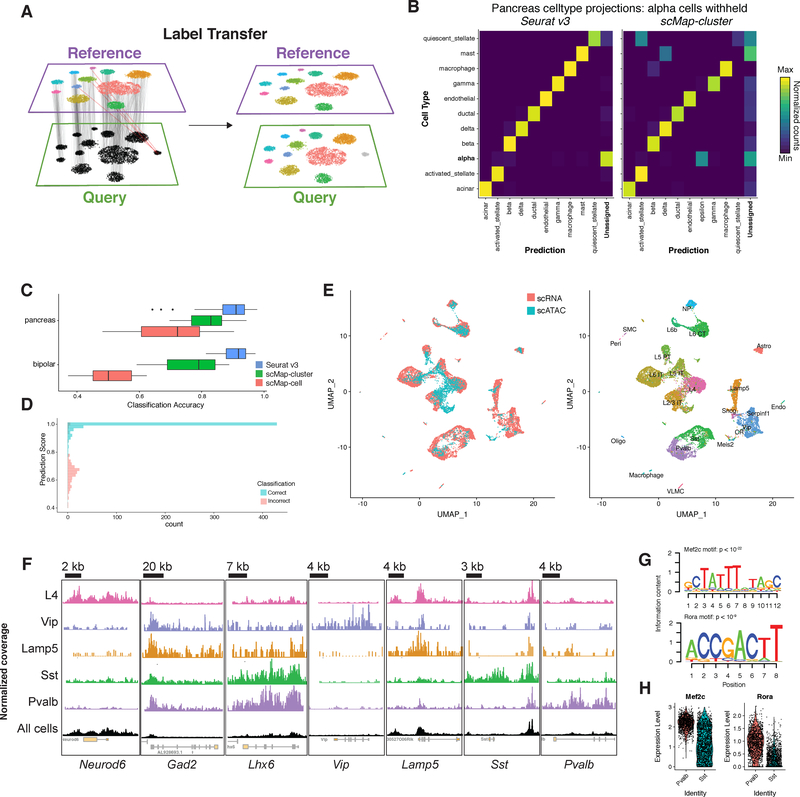
As with dataset integration, we approached the classification problem by first identifying anchors between the reference and query datasets. We use the same procedure to identify anchors, with the option to define our search space by projecting a previously computed reference PCA structure onto the query data as opposed to using CCA (STAR Methods). Projecting a query dataset onto an existing PCA structure is more efficient in cases where the query and reference datasets do not exhibit substantial batch differences, when working with a large reference dataset, or when classifying a homogeneous query population. Once we identified anchors, the annotation of each cell in the query set is achieved using a weighted vote classifier based on the reference cell identities, where the weights are determined by the same criteria used in computing the correction vectors for integration (Figure 3A). Since multiple anchors will contribute to the classification of each query cell, these predictions are informed by a cell’s local neighborhood, increasing the overall robustness of the classification call. Additionally, this approach provides a quantitative score for each cell’s predicted label. Cells that are classified with high confidence will receive consistent votes across anchors whereas cells with low confidence, including cells that are not represented in the reference, should receive inconsistent votes and therefore lower scores.
Figure 3. Transferring cell state classifications across datasets.
(A) Schematic representation where identified anchors allow for the transfer of discrete labels between a reference and query dataset. (B) Confusion matrix for one cell type hold-out evaluation where pancreatic alpha cells were removed from the reference. Cell types with fewer than two cells in the query not shown. Alpha cells in the query consistently receive the lowest classification score, and are labeled as “Unassigned”. (C) Classification benchmarking on 166 test/training datasets from human pancreatic islets and mouse retina. (D) Distribution of prediction scores for one cell type hold-out experiment (as in B). Mis-classification calls are associated with lower prediction scores. (E) Joint visualization of scRNA-seq data with classified scATAC-seq cells (left). We identified anchors between scRNA-seq data (reference) and a gene activity matrix derived from scATAC-seq (query) datasets from the mouse visual cortex, and transferred class annotations (right). (F) We created pseudo-bulk ATAC-seq profiles by pooling together cells with for each cell type. Each cell type showed enriched accessibility near canonical marker genes. Chromatin accessibility tracks are normalized to sequencing depth (RPKM normalization) in each pooled group. Y-axes for each track ranged from 0 to different maxima, due to inherent differences in the maximum read depth at different loci. For each locus, the y-axis maximum shown is: Neurod6 1,500; Gad2, Pvalb, Sst, Vip, Lamp5, and Id2 1,000; Lhx6 600. (G) We searched for overrepresented DNA motifs present in PV-specific accessibility peaks, and identified the Mef2c and Rora motifs as the most highly enriched motifs (p < 10−22 and p < 10−9). (H) Both Mef2c and Rora also exhibit upregulated expression in PV interneurons from scRNA-seq.
We tested our classification in Seurat v3 alongside recently proposed solutions leveraging correlation and nearest-neighbor based classifiers: scMap-cluster and scMap-cell [Kiselev et al., 2018]. Using the pancreatic islet and retinal bipolar datasets previously described (Figure 2), we constructed 166 evaluation cases by splitting data into reference and query sets. In each case, we also removed instances of a single cell population (withheld class; e.g.alpha cells) from the reference, and then proceeded with classification (STAR Methods). We evaluated classification accuracy by considering the percentage of query cells assigned the correct label, but also examined whether query cells in the withheld class received the lowest classification scores (and were therefore classified as “unassigned”). Seurat v3 consistently received the highest classification accuracy (Figure 3B,C), and correctly assigned low classification scores to query cells that were not represented in the reference (Figure 3B). We note that our increased accuracy stems in part from our ability to use the local neighborhood of a cell to increase the robustness of classification, while scMap classifies each cell individually. Additionally, we found that our incorrect predictions were associated with substantially lower classification scores, allowing for the prioritization of high-confidence calls (Figure 3D).
Projecting cellular states across modalities
We next examined the possibility of applying our classification strategy to transfer cell labels across modalities. For example, we explored whether we could classify individual nuclei from a scATAC-seq dataset based on a reference of transcriptomic states. The potential utility of this approach is underscored by recent studies which have found that scATAC-seq does not currently match the power of scRNA-seq for unsupervised discovery of cell states, including a recently generated scATAC-seq landmark resource of >100,000 nuclei from 13 mouse tissues [Cusanovich et al., 2018]. For example, 3,482 cells from the prefrontal cortex revealed a cluster of inhibitory interneurons, representing an exciting resource for studying the chromatin accessibility landscape of inhibitory vs. excitatory neurons, but could not identify well-characterized interneuron subdivisions. Importantly, the authors derive a “gene activity matrix” from the scATAC-seq profiles, utilizing observed reads at gene promoters and enhancers as a prediction of gene activity [Pliner et al., 2018], representing a synthetic scRNA-seq dataset to leverage for integration.
We reasoned that if we could successfully transfer scRNA-seq derived class labels onto scATAC-seq profiles, we may be able to reveal finer distinctions among the cell types. We therefore considered a deeply sequenced SMART-seq2 scRNA-seq reference dataset (14,249 cells) of the mouse visual cortex from the Allen Brain Atlas [Tasic et al., 2016, 2018], and identified anchors between the scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq using the gene activity matrix derived from scATAC-seq profiles. Joint visualization of the two datasets (STAR Methods) suggested that similar levels of diversity could be identified through integration (Figure 3E). Indeed, by transferring the previously published scRNA-seq celltype labels, we were able to confidently classify 2,420 scATAC-seq cells (projection score > 0.5), into 17 clusters, including eight excitatory and four inhibitory populations (Table S1D). Our classifications were consistent with the published labels derived from unsupervised analysis, but revealed substantially increased diversity. For example, 87% of the previously annotated inhibitory neurons were classified as inhibitory in our analysis, but were split into four groups, representing both medial ganglionic eminence (MGE)-derived (SST and PV subsets), and caudal ganglionic eminence (CGE)-derived (Vip and Lamp5) subsets. We also observed a cluster of scATAC-seq cells (highlighted in Figure S3A) that express gene activity markers of multiple neuronal lineages (Figure S3B) and did not have a strong correspondence to an scRNA-seq cluster, likely representing nuclear multiplets. Pooling nuclei within each projected class together, we obtained pseudo-bulk ATAC-seq profiles. This revealed cell-type specific regulatory loci whose accessibility profiles were consistent with expected patterns for all inhibitory cells (Gad2), MGE-derived populations (LHX6), and subset-specific markers (Pvalb, Sst, Vip, Id2; Figure 3F)[Mayer et al., 2018]. We focused on the PV and SST classes, representing to our knowledge the first efforts to derive and compare genome-wide accessibility landscapes for these closely related interneuron subgroups.
We next performed de-novo motif analysis in an attempt to discover cis-regulatory DNA sequences that differentially regulate PV and SST interneurons. While few validated regulators that drive specific interneuron fate decisions are known, we have previously shown that the transcription factor Mef2c is upregulated in embryonic precursors of PV interneurons, and is specifically required for their development [Mayer et al., 2018]. Strikingly, our scATAC-seq analysis revealed a strong enrichment for Mef-family motifs (including Mef2c) in peaks with increased PV-accessibility, representing the highest-scoring motif (Figure 3G). We observed other motifs for putative regulators, including the putative regulator Rora [Sato et al., 2004] (Figure 3G). Intriguingly, as with Mef2c, Rora also exhibits RNA upregulation in PV compared to SST interneurons (Figure 3H), and may also play roles in fate specification. Taken together, these results highlight the role of Mef2c and other transcription factors in establishing or maintaining the chromatin landscape necessary to express the functional receptors and transporters that establish the specific identity of PV cells.
We performed a similar analysis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), integrating scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq datasets produced with the 10x Genomics Chromium system [Zheng et al., 2017]. We classified scATAC-profiles into 13 transcriptional states derived from scRNA-seq clustering (Figure S3C), and co-embed the datasets in a unified visualization (Figure S3D,E). As bulk ATAC-seq data is available for FACS-sorted populations of human immune cell subsets [Corces et al., 2016], we experimentally validated our predictions by comparing FACS-sorted ATAC-seq profiles with pseudo-bulk profiles obtained from our classified scATAC-seq cells. We observed high concordance between bulk and pseudo-bulk accessibility profiles for each of the cell types, both around key marker genes (Figure S3F) and on a genome-wide scale (Figure S3G). However, we also identified rare cases where we were unable to identify correspondences across datasets due to biological, technical, and computational factors. While platelet cells were observed in the scRNA-seq dataset, due to the presence of residual RNA from their mother megakaryocyte cell, these cells are not nucleated and we correctly failed to identify any platelet cells in the scATAC-seq dataset. However, we also observed two populations present in the scATAC-seq data that appeared to have no match in the scRNA-seq dataset. One population displayed a high proportion of reads mapping to genomic blacklist regions (Figure S3H), and so likely represent dead or dying cells, ambient DNA, or a technical artifact specific to scATAC-seq. Another population was predicted to represent CD14+ Monocytes, but were not fully mixed by co-embedding visualization with the CD14+ Monocytes from the scRNA-seq dataset (Figure S3I). However, we did not identify any differences in gene activities between these groups (Figure S3I), and these differences may be an artifact of the integration procedure. In this case the artifact is subtle, and did not prohibit the correct discrete classification of these cells. However, this demonstrates how exploring the underlying molecular data in each dataset independently is an important step in interpreting the results of an integrated analysis.
Our results demonstrate the potential for transferring scRNA-seq derived annotations onto chromatin accessibility data. We emphasize that this strategy requires an initial step where scATAC-seq data is converted to a predicted gene expression matrix [Pliner et al., 2018]. Existing strategies for this task likely assume that chromatin accessibility is positively correlated with gene expression. While this assumption has generally held true and enabled the prior interpretation of scATAC-seq data in the developed brain [Cusanovich et al., 2018, Lake et al., 2018], there may be cases where accessibility is a poor proxy for transcriptional output, particularly in developing systems where chromatin changes may precede gene expression [Lara-Astiaso et al., 2014]. In these cases, we expect that we would not be able to form consistent anchors across datasets. However, effective integration can occur even if only a subset of features exhibit coordinated behavior across RNA and chromatin modalities, similar to how cross-species scRNA-seq datasets can be effectively integrated even when only a subset of gene expression markers are conserved [Butler et al., 2018].
Transferring continuous and multimodal data across experiments
Though we previously demonstrated how anchors could be utilized to transfer discrete classifications across datasets, we reasoned that the same methods could be used to transfer continuous data as well. This is of particular interest for the growing suite of multimodal single-cell technologies that measure multiple aspects of cellular identity. Transfer learning could therefore be used to fill in missing modalites in key datasets. For example, the Human Cell Atlas recently released a freely available resource of 274,932 healthy bone marrow cells from 8 donors [Li et al., 2018]. This represents an extraordinary community resource to study the human immune system, but does not contain cell surface protein measurements, which could substantially improve the ability to interpret and annotate this resource. We hypothesized that by generating a human bone marrow dataset with our recently developed CITE-seq technology [Stoeckius et al., 2017], where immunophenotypes are measured in parallel with transcriptomes, we could effectively transfer protein expression data to the HCA dataset. Additionally, we highlight that this method can be successful even in the absence of correlation between RNA and protein for individual genes (e.g. between Cd4 transcript and CD4 protein), though it does require that a combination of genes exhibit expression patterns that are correlated with cellular immunophenotype (e.g, modules of markers for CD4+ T cells).
Predicting protein expression in human bone marrow cells
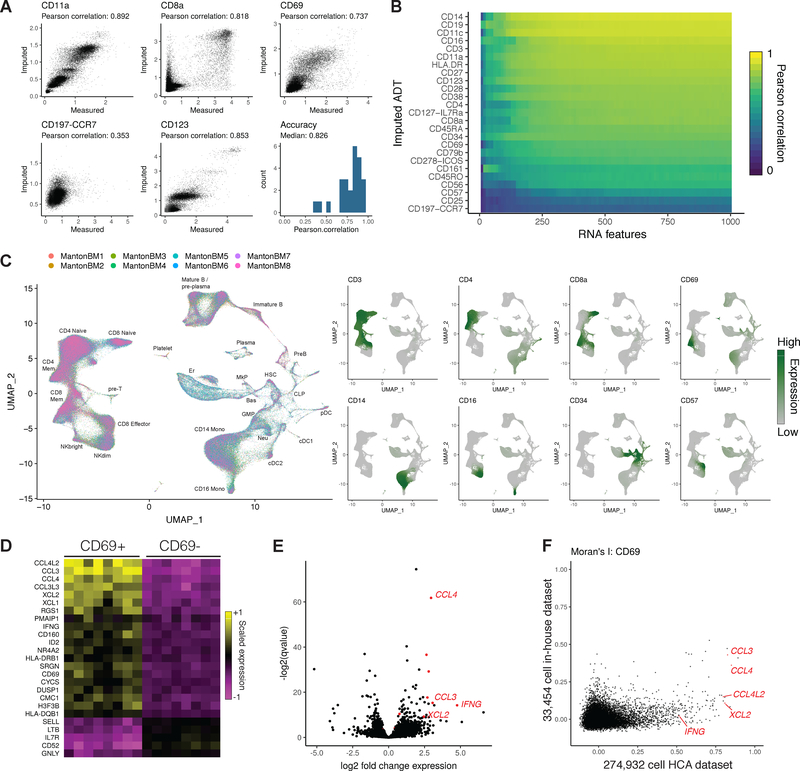
We performed a CITE-seq experiment on human bone marrow cells [Stoeckius et al., 2017], capturing 33,454 cells for which we measured cellular transcriptomes alongside 25 cell-surface proteins representing well-characterized markers (median 4,575 RNA unique molecular identifiers [UMIs] and 2,312 antibody-derived tag [ADT] UMIs per cell; Table S1C, S1D; Supplementary File 1). We first performed cross-validation within the CITE-seq data by randomly assigning cells to a reference or query dataset, and identified anchors between them. As with our discrete classifications, we predicted protein levels in the query dataset using a weighted average of CITE-seq counts from the reference anchor cells, which we then compared with the original measurements (Figure 4A).
Figure 4. Imputing immunophenotypes in a transcriptomic atlas of the human bone marrow.
(A) Cross-validations for immunophenotype imputation, performed using a CITE-seq dataset of 35,543 bone marrow cells and 25 surface proteins. (B) Prediction accuracy as a function of the number of transcriptomic features used to determine anchors. (C) We integrated 274,932 bone marrow cells produced by the Human Cell Atlas and annotated the cell types. Using the CITE-seq bone marrow cells, we predicted protein expression levels in the integrated HCA dataset, and observed expression patterns consistent with the known cell types. (D) Predicted CD8+ CD69+ cells up-regulate a module of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines across all eight donors. Shown are averaged RNA expression values for each human donor. (E) We validated CD69+ marker genes identified in the scRNA-seq data by performing bulk RNA-seq on FACS-isolated CD8+ CD69+/− cells, which revealed a similar set of deferentially expressed genes. (F) We ordered CD8+ memory cells by their CD69 expression in the HCA and CITE-seq datasets, and computed the autocorrelation for each gene along this CD69 axis (Moran’s I). CD69+ marker genes consistently showed a higher Moran’s I value in the HCA dataset, reflecting the increased statistical power accompanying an order-of-magnitude greater cell number.
For most proteins (23/25), we observed strong correlation between the measured and imputed expression levels (Figure 4A,B; median R=0.826), with the remaining residual encompassing background CITE-seq binding (perhaps driven by differences in cell size), stochastic variation in protein expression, or technical noise. In the two cases where we observed poor correlations, either poor antibody specificity or a lack of transcriptomic markers that correlate with immunophenotype could explain these results. Indeed, examination of the patterns of expression for these two proteins (CD25 and CD197-CCR7) show sporadic ADT binding across all cells, indicating a possible non-specific binding of the antibody confounding the biological signal (Supplementary File 1). By downsampling RNA features used to identify anchors and repeating the cross-validations, we found that prediction accuracy began to saturate at approximately 250–500 features (Figure 4B), suggesting that only a subset of shared genes need to be measured across experiments in order to transfer additional modalities across datasets.
Having demonstrated our ability to accurately impute immunophenotypes, we next transferred protein expression data from our CITE-seq experiment to the Human Cell Atlas bone marrow resource of 274,932 cells across eight human donors [Li et al., 2018], after first integrating the eight donor datasets using Seurat v3 to mitigate batch effects (Figure 4C; Figure S2G). Encouragingly, our imputed immunophenotypes were consistent with the well-studied expression patterns of key markers in the hematopoietic system (Supplementary File 1), including high predicted CD34 expression in early hematopoietic progenitors, mutual exclusivity between CD8a and CD4 expression, and canonical marker expression in monocytes (CD14), NK (CD16 / CD56), and B cell (CD19) populations. Intriguingly, we identified a sub-population of CD8+ memory cells marked by sharply elevated predicted expression of CD69 (Figure 4C). While CD69 has been proposed as an early activation marker of T cells[R Testi and Lanier, 1989], the molecular phenotype and significance of CD8+ CD69+ cells in the bone marrow is not well understood. Recent evidence in particular suggests that CD8+ cells upregulate this marker without accompanying changes in the transcriptome, and that the transcriptome of these cells is in a resting state [Okhrimenko et al., 2014]. We therefore sought to identify genes whose measured expression in the HCA data was associated with predicted CD69 expression.
We observed a clear module of genes associated with increased CD69 expression across all eight human donors (Figure 4D), including cytokines, chemokines, and granzyme molecules, with ontology analysis revealing striking enrichment for genes involved in IFN-γ responses (P < 10−11; Figure S2H). We validated this finding by sorting CD8+/CD69+ and CD8+/CD69-T cells, performing bulk RNA-seq (four replicates each), and observing differential expression of our top markers (Figure 4E). Importantly, while we observed similar CD69+ heterogeneity in an independent analysis of the original CITE-seq dataset (Supplementary File 1), this dataset contained an order-of-magnitude fewer cells, and as a result exhibited substantially lower power to detect genes associated with CD69 expression. To quantify this, we ordered cells in the CITE-seq and HCA datasets along an axis of CD69 expression, and computed Moran’s I statistic, a measure of spatial autocorrelation, for each gene. We consistently observed substantially higher Moran’s I values in the HCA dataset, and could not identify key inflammatory genes (including IFNG) as outliers from the CITE-seq data alone (Figure 4F). Further experiments are needed to reveal the functional importance of this population, but notably, secretion of inflammatory cytokines like IFN-γ can alter the bone marrow microenvironment and hematopoietic output [de Bruin et al., 2014]. Taken together, these results demonstrate how transfer learning can be used to facilitate biological discovery across datasets, and to impute missing modalities in key resources.
Spatial mapping of single-cell sequencing data in the mouse cortex
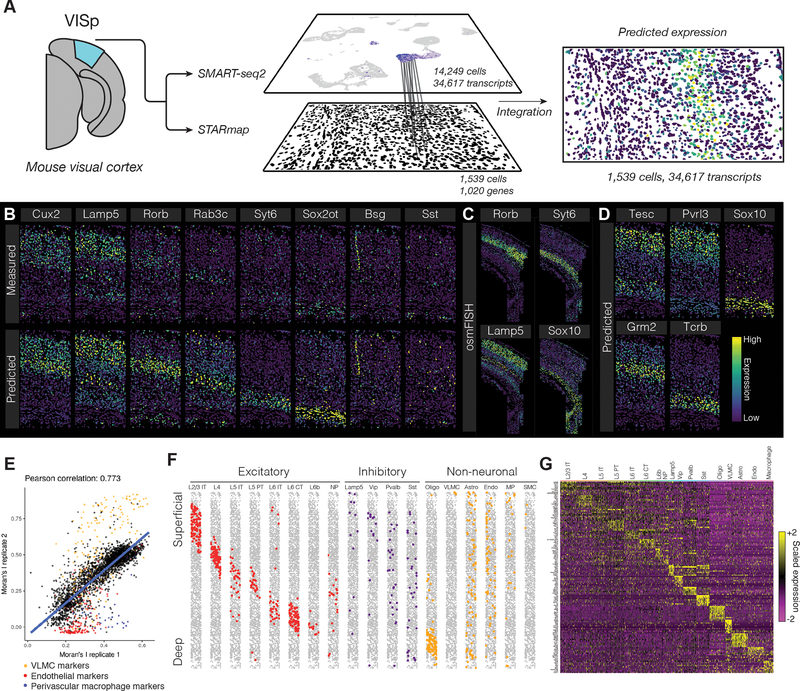
As a final demonstration of transfer learning using our Seurat v3 method, we explored the integration of multiplexed in-situ single-cell gene expression measurements (FISH) with scRNA-seq of dissociated tissue. While we and others [Satija et al., 2015, Achim et al., 2015, Karaiskos et al., 2017, Halpern et al., 2017] have previously demonstrated analytical strategies to map single cells to their original spatial position, these strategies require the tissue to have a stereotypical structure, and rely heavily on transcriptional gradients to facilitate the spatial mapping of cells. In principle, the harmonization of multiplexed FISH or in-situ RNA sequencing with scRNA-seq would enable similar goals to be achieved for any biological system, a challenge that is of paramount importance to understand the spatial organization and regulation of cells and tissues. While imaging datasets have an upper limit on the number of dimensions that can be simultaneously profiled per cell, our previous results indicated that only a subset of transcriptomic features were necessary to facilitate integration (Figure 4B). We therefore considered two complementary datasets of the mouse visual cortex, the deeply sequenced SMART-seq2 (v4 kit) dataset from the Allen Brain Institute [Tasic et al., 2018] (as in Figure 3E; 14,249 cells, 34,617 transcripts), and the recently published STARmap in-situ gene expression datasets of the same tissue (1,539 and 890 cells, 1,020 genes) [Wang et al., 2018].
After identifying anchors between the datasets, we imputed spatial expression patterns across the transcriptome by transferring the expression of all measured scRNA-seq transcripts onto the STARmap datasets (Figure 5A). For genes with well-established spatial patterns of expression (e.g. the layer-specific marker genes Lamp5 and Cux2), our imputed patterns were concordant with the measured STARmap data (Figure 5B; Supplementary File 2). Similarly, genes that were cell-type specific but not spatially restricted (e.g the interneuron subtype marker Sst) also exhibited identical patterns in the imputed and measured data. However, we also observed cases where the original STARmap data exhibited a weak signal that was strengthened in the imputed data (for example, Rorb and Syt6). These cases could reflect stochastic cellular expression, technical noise in the STARmap data, or imputation errors - although our predictions here were further supported by an independently derived, highly sensitive cyclic single molecule FISH (osm-FISH) experiment [Codeluppi et al., 2018] (Figure 5C). By transferring the remaining scRNA-seq genes onto spatially-resolved cells, we were further able to predict spatial patterns for genes that were not originally profiled profiled by STARmap. We identified four representative cases (Figure 5D), each of which contains strong external support in the published literature [Syken and Shatz, 2003, Venkatadri and Lee, 2014], or the Allen Brain Atlas [Tasic et al., 2016, 2018] (Figure S4B). Moreover, when repeating the imputation procedure on a second independent STARmap replicate (890 cells), we found that our gene-level predictions for spatial association were highly reproducible, with the exception of a small group of genes with different Moran’s I values in both replicates (Figure 5E). Further analysis of the genes with higher Moran’s I values in replicate 1 revealed that they largely represented markers of endothelial cells and perivascular macrophages, while genes with a higher Moran’s I in replicate 2 were predominantly markers for VLMC cells. As replicate 1 contained a strip of endothelial cells, and replicate 2 contained a longer spatially restricted section of VLMC cells (Figure S4A), the differences in Moran’s I values between replicates for these genes reflects real biological differences in the spatial structures of the two tissue sections.
Figure 5. Spatial patterns of gene expression in the mouse brain.
(A) Schematic representation of data transfer between scRNA-seq and STARmap datasets. After identifying anchors using the subset of genes measured in both experiments, we subsequently transfer sequencing data to the STARmap cells, predicting new spatial expression patterns. (B) Leave-one-out cross validation for 8 genes, exhibiting predicted expression patterns, and original STARmap measurements. (C) Gene expression patterns for Rorb, Syt6, Lamp5 and Sox10, as measured by osmFISH, a highly sensitive single molecular assay [Codeluppi et al., 2018], in the mouse somatosensory cortex. (D) Predicted expression patterns for four genes not originally profiled by STARmap, with external validation in Supplementary File 2. (E) Correlation between Moran’s I value, a measure of spatial autocorrelation, for each predicted gene expression pattern in two STARmap replicates. Marker genes for VLMC cells, endothelial cells, and perivascular macrophages are highlighted, reflecting rare cell subsets that were spatially restricted in only one replicate. (F) Horizontally-compressed STARmap cells with predicted cell type transferred from the SMART-seq2 dataset. (G) Expression of cell type marker genes in each predicted STARmap cell type (both replicates combined).
We performed the same leave-one-out cross validation imputation procedure using Drop-seq data from the mouse prefrontal cortex, and identified strikingly similar imputed spatial patterns across both scRNA-seq technologies (Supplementary File 2), as well as strong agreement at single-cell resolution when imputing using either dataset (Figure S5A,D). These results indicate that the increased cell number from Drop-seq can compensate for the reduced per-cell sequencing depth, consistent with previous power analyses for cell type discovery [Shekhar et al., 2016]. However, we observed a subset of genes that were too lowly expressed to be accurately quantified by Drop-seq (Figure S5B), resulting in inconsistent spatial imputation results. Moreover, we also observed rare cases where highly expressed genes exhibited subtle differences in their scRNA-seq expression patterns across technologies (i.e. Cux2, Figure S5C), which also drove subtle changes in spatial imputation (Supplementary File 2).
The STARmap dataset measured the expression of 1,020 genes but extensive correlation structure in transcriptomic data suggests that we can achieve similar prediction accuracy using a reduced subset of these genes. We randomly downsampled the STARmap gene set from 50 to 1,000 genes and evaluated the imputation accuracy using the downsampled gene sets (Figure S5E). These results suggested that imputation accuracy starts to saturate between 200–300 features for many genes, particularly those with high expression “redundancy” in the dataset (Figure S5F). Furthermore, when applying a downsampling strategy guided by cluster markers instead of random downsampling, we observed additional improvements when using a reduced feature set (STAR Methods; Figure S5G). Together, these analyses demonstrate that integration can be successful even when using more sparse sequencing approaches, alongside spatial technologies that measure hundreds of markers in-situ [Moffit et al., 2018].
As we previously demonstrated using scATAC-seq data, our anchoring procedure allows us to classify cells across modalities based on scRNA-seq annotations. We therefore transferred cell type labels from the SMART-seq2 dataset to the STARmap cells, classifying 1,915 (79%) of cells with prediction score > 0.5, but conservatively chose to consider the 1,210 (50%) cells with the highest prediction scores for downstream analysis (Figure 5F; STAR Methods). These classifications revealed subdivisions that could not be identified even through iterative clustering of the original dataset (Figure S4C-F). For inhibitory cells, we identified cells from the four major classes (Sst, Pvalb, Lamp5/Id2, Vip), each expressing canonical markers in the original STARmap dataset (Figure 5G). In excitatory cells, we annotated cells from 8 different clusters, representing not only layer-specific populations, but also separating intratelencephalic (IT), pyramidal tract (PT), corticothalamic (CT), and L6b sublayer populations within individual layers (Figure 5F,G).
Lastly, we examined the spatial distribution of our annotated cell-types, searching for non-random patterns. As previously reported, MGE-derived interneurons were enriched in Layers 4/5, CGE-derived interneurons were enriched in Layers 1–3, and excitatory populations were strongly associated with individual layers (Figure 5F) [Tasic et al., 2018]. However, after closely examining the mapping patterns, we observed differences in the laminar distributions for neurons even within the same layer, including IT and PT neurons (Layer 5), and IT and CT neurons (Layer 6), suggesting a complex interplay between excitatory specification and within-layer spatial positioning. These results were reproduced in the second STARmap replicate dataset (Figure S4A, Supplementary File 2), but the functional consequences remain to be explored. We conclude that anchoring imaging and sequencing datasets enables the transcriptome-wide prediction of spatial expression patterns, and the harmonization of scRNA-seq derived cell type labels with in-situ gene expression datasets. As multiplexed image-based single-cell methods and datasets continue to grow and develop, the integration of sequencing and imaging datasets therefore represents a powerful and exciting opportunity to construct high-resolution spatial maps of any biological system.
Discussion
We have developed a strategy for the comprehensive integration of single-cell data, and apply this to derive biological insights jointly from transcriptomic, epigenomic, proteomic, and spatially-resolved single-cell data. Our strategy tackles several technical challenges, starting with the unsupervised identification of cell pairs across datasets, deemed “anchors”, that represent a similar biological state. This enables us to either assemble multiple datasets into an integrated reference, or to transfer data and metadata from one experiment to another. We anticipate that as single-cell RNA-seq experiments have only recently become routine, the challenge of reference assembly will be of particular importance to both small labs and large consortia, as new experiments will continually uncover increasingly rare and subtle biological states. However, as these references begin to stabilize, projecting both discrete labels and continuous data onto new datasets will be of transformative value to the interpretation of new datasets, analogous to how short-read mapping enabled the rise of multiple genomics technologies [Langmead et al., 2009, Trapnell et al., 2009]. Throughout multiple examples in this manuscript, we demonstrate how integrated analysis can reveal biological insights that require the cluster identification and annotation inherent to scRNA-seq analysis, but could not be identified by any single experiment. In particular, we derive in-silico bulk ATAC-seq profiles for finely resolved interneuron subsets whose identities can be classified with the assistance of transcriptomic data, as well as identifying cell surface proteins that can successfully enrich for transcriptomically-defined T cell subsets in human bone marrow. Lastly, we demonstrate how scRNA-seq and in-situ gene expression data can be integrated to robustly predict spatial expression patterns transcriptome-wide, and even to identify high-resolution spatial relationships between closely related neuronal subtypes.
Our integration strategy builds upon previous work in the application of CCA to identify shared sources of variation across experiments [Butler et al., 2018], and the concept of mutual nearest neighbors to identify biologically matched cells in a pair of datasets [Haghverdi et al., 2018]. Furthermore, we leverage ideas from the construction of shared nearest neighbor graphs to score, identify, and downweight the contribution of inaccurate anchors to substantially increase integration robustness. Each of these steps is integral to the improved performance of our method, and in particular, the ability to perform integration across modalities and diverse technologies.
We expect our strategy to be broadly applicable to integrate and transfer a broad spectrum of single-cell data and phenotypes across experiments. These include additional epigenomic [Luo et al., 2018, Gavin et al., 2017, Cao et al., 2018, Lake et al., 2018, Preissl et al., 2018], chromosome conformation [Ramani et al., 2017, Nagano et al., 2013], and RNA modification [Safra et al., 2017] measurements that are increasingly being profiled at the single-cell level, and even computationally derived phenotypes such as RNA velocity [La Manno et al., 2018]. We believe that the integration of sequencing and imaging datasets represents a particularly promising application in the near future. Recent work based on the spatial analysis of protein panels [Goltsev et al., 2018, Keren et al., 2018] has poignantly demonstrated how changes in tissue organization can dramatically shift across disease states. By integrating single-cell transcriptomics with spatial datasets, these analyses can consider not only broadly defined cell types, but subtle alterations in cell state, even for genes that are not directly measured in an imaging probe set. Future extensions could utilize these molecular data to assist in the image alignment of multiple datasets, or even integrate with perturbation screens to help infer causal relationships [Dixit et al., 2016].
These opportunities will ensure the continued development of complementary tools and strategies for single-cell data integration. For example, Welch et al. (2018) [Welch et al., 2018] have recently introduced LIGER, which leverages integrative non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) to identify shared and specific sources of variation across datasets. Both Seurat v3 and LIGER enable batch-effect correction and cross-modality integration, and while the methods have conceptually similar aims, they return complementary outputs. NMF returns factors that characterize biological sources of variation and can be highly interpretable [Welch et al., 2018]. In contrast, Seurat v3 has the ability to return a corrected expression matrix, or to impute query features from a reference dataset - both of which can be used as input to additional methods such as pseudotime or network reconstruction [Qiu et al., 2017, Langfelder and Horvath, 2008]. We anticipate that users, with diverse biological questions and analytical challenges, will find broad utility for both approaches.
Lastly, our results suggest that single-cell RNA-seq can serve as a general mediator for single-cell data integration. Not only is its application commercialized and routinely available, but transcriptome-wide gene expression data encodes multiple aspects of cellular identity and “metadata”, even if they are lost during the experimental process. Moreover, its intermediate position in the central dogma allows for proximity to multiple molecular processes, including both transcriptional, posttranscriptional, and translational regulation. We therefore suggest that scRNA-seq may serve as a “universal adapter plug” for single-cell analysis, facilitating integration across multiple technologies and modalities, and enable a deeper understanding of cellular state, interactions, and behavior.
STAR Methods
Contact for reagent and resource sharing
Further information and requests for resources should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the Lead Contact, Rahul Satija (rsatija@nygenome.org).
Method details
Seurat integration method
The Seurat v3 anchoring procedure is designed to integrate diverse single-cell datasets across technologies and modalities. To facilitate the assembly of datasets into an integrated reference, Seurat returns a corrected data matrix for all datasets, enabling them to be analyzed jointly in a single workflow. To transfer information from a reference to query dataset, Seurat does not modify the underlying expression data, but instead projects either discrete labels or continuous data across experiments. While the use-cases for each approach will depend on the user and particular experiment, the underlying methods are conserved across approaches. When possible in the methods, we specify the function in Seurat where the method is implemented, to facilitate users exploring the source code, which is freely available at https://satijalab.org/seurat.
Our approach consists of four broad steps, as explained in detail below: (1) data preprocessing and feature selection, (2) dimension reduction and identification of “anchor” correspondences between datasets, (3) filtering, scoring, and weighting of anchor correspondences, (4) data matrix correction, or data transfer across experiments.
Parameters for Seurat v3 integration
To exemplify the general utility of our approaches, we aimed to minimize the free parameters that can be tuned for each analysis and to utilize default parameters in all cases. All parameters are described throughout the methods, even when their default values are fixed for all analyses in this manuscript.
One parameter we expect to fluctuate across across datasets represents the estimated “dimensionality” of the data. This affects, for example, the number of principal components or canonical correlation vectors that are calculated during dimensional reduction. Larger datasets will typically have increased dimensionality, particularly if they represent increasingly heterogeneous populations. While we have previously suggested using saturation or statistical-resampling based approaches to estimate dataset dimensionality [Butler et al., 2018], a robust fully unsupervised procedure to identify this value remains a fundamental challenge in the analysis of high-dimensional data. Here, we neglect to finely tune this parameter for each dataset, but still observe robust performance over diverse use cases. For all neuronal, bipolar, and pancreatic analyses we choose a dimensionality of 30. For scATAC-seq analyses in the mouse cortex, we chose a dimensionality of 20. For analyses of human bone marrow and the integration of mouse cell atlases, we choose a dimensionality of 50 and 100 respectively, representing the significant increase in dataset size and heterogeneity for these cases.
We also allow for the use of approximate nearest neighbor methods, using the RANN package in R [Arya et al., 2018, Mount, 2010]. While not enabled by default, the user can set the error bound parameter (eps) to increase the speed of nearest neighbor identification. This parameter is set to 0 by default, but for analyses where more than 50,000 cells are analyzed in total (Figure 4, Figure S2), we set this value to 1. Unless otherwise specified, all other quantitative parameters are fixed to default values.
Data preprocessing
Normalization
For all analyses, we employed standard pre-processing for all single-cell RNA-seq datasets. Unless otherwise specified, we first performed log-normalization of all datasets, using a size factor of 10,000 molecules for each cell. We next standardized expression values for each gene across all cells (z-score transformation), as is standard prior to running dimensional reduction tools such as principal component analysis. These steps are implemented in the NormalizeData and ScaleData functions in Seurat.
Feature selection for individual datasets
In each dataset, we next aimed to identify a subset of features (i.e. genes) exhibiting high variability across cells, and therefore represent heterogeneous features to prioritize for downstream analysis. Choosing genes solely based on their log-normalized single-cell variance fails to account for the mean-variance relationship that is inherent to single-cell RNA-seq. Therefore, we first applied a variance-stabilizing transformation to correct for this, as first outlined by Mayer, Hafemeister & Bandler et al. [Mayer et al., 2018, Hafemeister and Satija, 2019].
To learn the mean-variance relationship from the data, we computed the mean and variance of each gene using the unnormalized data (i.e. UMI or counts matrix), and applied log10-transformation to both. We then fit a curve to predict the variance of each gene as a function of its mean, by calculating a local fitting of polynomials of degree 2 (R function loess, span = 0.3). This global fit provided us with a regularized estimator of variance given the mean of a feature. As such, we could use it to standardize feature counts without removing higher-than-expected variation.
Given the expected variances, we performed the transformation
where zij is the standardized value of feature i in cell j, xij is the raw value of feature i in cell j, is the mean raw value for feature i, and σi is the expected standard deviation of feature i derived from the global mean-variance fit. To reduce the impact of technical outliers, we clipped the standardized values to a maximum value of , where N is the total number of cells. For each gene, we then computed the variance of standardized values across all cells. This variance represents a measure of single-cell dispersion after controlling for mean expression, and we use it directly to rank the features. Unless otherwise noted, we selected the 2,000 genes with the highest standardized variance as “highly variable”. This procedure is implemented in the FindVariableFeatures function in Seurat v3 (selection.method=“vst”).
Feature selection for integrated analysis of multiple datasets
When performing integration across datasets, we aimed to give priority to features that were identified as highly variable in multiple experiments. Therefore, we first performed feature selection on each dataset individually, using the procedure described above. We next prioritized features across multiple experiments by examining the number of datasets in which they were independently identified as highly variable. From this ranked list of features, we took the top 2,000 to use as input for downstream analyses. We broke ties by examining the ranks of the tied features in each original dataset and taking those with the highest median rank. These steps are implemented in the SelectIntegrationFeatures function in Seurat v3.
Identification of anchor correspondences between two datasets
A key step for all integration analyses in this manuscript is the unsupervised identification of anchors between pairs of datasets. These anchors represent two cells (with one cell from each dataset), that we predict to originate from a common biological state. Anchors for reference assembly or transfer learning are calculated using the FindIntegrationAnchors and FindTransferAnchors functions, respectively, in Seurat v3.
We initiate this process through dimension reduction, aiming to place datasets in a shared low-dimensional space. For reference assembly, we utilize canonical correlation analysis (CCA) as an initial dimension reduction. As we have previously demonstrated [Butler et al., 2018], the canonical correlation vectors described by CCA effectively capture correlated gene modules that are present in both datasets, representing genes that define a shared biological state. In contrast, principle component analysis (PCA) will identify sources of variation even if they are only present in an individual experiment, particularly if there are significant technical effects across experiments. We therefore utilize CCA when integrating scRNA-seq datasets into a common reference, or when identifying anchors from single-cell data spanning modalities.
Canonical correlation vectors are calculated as described previously [Butler et al., 2018]. Briefly, let Xf,c be a single-cell dataset of features f1, f2, …, fn by cells c1, c2, …, cm and Yf,d be a single-cell dataset of the same features f1, f2, …, fn by cells d1, d2, …, dp. Because the total number of cells that are measured in these experiments is generally much larger than the total number of features shared between the datasets, we opt for a diagonalized CCA implementation that has shown promising performance in related highdimensional applications [Witten et al., 2009, Dudoit et al., 2002, Tibshirani et al., 2003]. The goal is to find projection vectors u and v such that the correlation between the two indices Xu and Yv is maximized.
To find the canonical correlation vectors, we first standardize X and Y to have a mean of 0 and variance of 1. We use a standard singular value decomposition (SVD) to solve for the canonical correlation vectors u and v as follows:
Let
Decompose K via SVD:
Where
The canonical correlation vectors can then be obtained as the left and right singular values from the SVD for i = 1, …, k.
For computational efficiency, we approximate the SVD using the augmented implicitly restarted Lanczos bidiagonalization algorithm implemented in the irlba R package [Baglama et al., 2018]. This allows us to obtain a user-defined number (k) of singular vectors that approximate the canonical correlation vectors (CCV). As described above, in this manuscript we set k to represent the “dimensionality” of the dataset.
Canonical correlation vectors (CCV) project the two datasets into a correlated low-dimensional space, but global differences in scale (for example, differences in normalization between datasets) can still preclude comparing CCV across datasets. To address this, we perform L2-normalization of the cell embeddings, where N is a vector of cell embeddings across the k CCV.
Following dimensional reduction, we identified the K-nearest neighbors (KNNs) for each cell within its paired dataset, based on the L2-normalized CCV. Finally, we identify mutual nearest neighbors (MNN; pairs of cells, with one from each dataset, that are contained within each other’s neighborhoods). We refer to these pairwise correspondences as “anchors”, and wish to again highlight the foundational work of Haghverdi et al. [Haghverdi et al., 2018] for inspiring this concept. The size of this neighborhood (k.anchor parameter in FindTransferAnchors and FindIntegrationAnchors) was set to 5 for all analyses in this manuscript.
Anchor scoring
The robust identification of anchor correspondences is key for effective downstream integration. Incorrect anchor pairs representing cells from distinct biological states can lead to incorrect downstream conclusions. In particular, cells that represent a biological state unique to one dataset should theoretically not participate in anchor pairs, yet in practice, they will do so with low frequency (Figure 1). Incorrectly identified anchors are similar to aberrant edges that can arise in KNN graphs (deemed ‘short-circuits’ by Bendall et al. [Bendall et al., 2014]) We therefore implement two steps (filtering and scoring anchors) to mitigate the effects of any incorrectly identified anchors.
First, we ensure that the anchors we identify in low-dimensional space also are supported by the underlying high-dimensional measurements. To do this, we return to the original data and examine the nearest neighbors of each anchor query cell in the reference dataset. We perform the search using the max.features (200) genes with the strongest association with previously identified CCV, using the TopDimFeatures function in Seurat, and search in L2-normalized expression space. If the anchor reference cell is found within the first k.filter (200) neighbors, then we retain this anchor. Otherwise, we remove this anchor from further analyses. We do not include a mutual neighborhood requirement for this step, as it is primarily intended as a check to ensure that we do not identify correspondences between reference and query cells with very divergent expression profiles. This procedure is uniformly applied with default parameters (max.features=200, k.filter=200), for all analyses in this manuscript.
Additionally, to further minimize the influence of incorrectly identified anchors, we implemented a method for scoring anchors that is similar to the use of shared nearest neighbor (SNN) graphs in graph-based clustering algorithms. By examining the consistency of edges between cells in the same local neighborhood, SNN metrics add an additional level of robustness to edge identification [Levine et al., 2015]. For each reference anchor cell, we determine its k.score (30) nearest within-dataset neighbors and its k.score nearest neighbors in the query dataset. This gives us four neighbor matrices that we combine to form an overall neighborhood graph. For each anchor correspondence, we compute the shared neighbor overlap between the anchor and query cells, and assign this value as the anchor score. To dampen the potential effect of outlier scores, we use the 0.01 and 0.90 quantiles to rescale anchor scores to a range of 0 to 1.
We find that when ground truth data is available for evaluating anchors, anchors representing reference and cell pairs have significantly higher scores than incorrect anchors (Figure 2I). Therefore, in downstream calculations (see below), anchors with lower scores are downweighted in favor of anchors with higher scores. The k.score parameter is fixed to 30 for all analyses in this manuscript. This procedure is implemented in the ScoreAnchors internal Seurat function, which is called by FindIntegrationAnchors or FindTransfer-Anchors in Seurat.
Anchor weighting
We construct a weight matrix W that defines the strength of association between each query cell c, and each anchor i. These weights are based on two components: the distance between the query cell and the anchor, and the previously computed anchor score. In this way, query cells in distinct biological states (for example alpha cells and gamma cells) will be influenced by distinct sets of anchors, enabling context-specific batch correction. Additionally, robust anchors (with high scores) will gain influence across the query dataset, while inconsistent anchors will be downweighted. For each cell c in the query dataset, we identify the nearest k.weight anchors cells in the query dataset in PCA space. Nearest anchors are then weighted based on their distance to the cell c over the distance to the k.weight-th anchor cell and multiplied by the anchor score (Si). For each cell c and anchor i, we first compute the weighted distances as:
We then apply a Gaussian kernel:
where sd is the Gaussian kernel bandwidth, set to 1 by default. Finally, we normalize across all k.weight anchors:
For identifying anchors for integration, we set k.weight = 100. For identifying transfer anchors, we set k.weight = 50. We reasoned that the batch vector information may be similar for closely related cell types, and so opt to take into account batch information for more anchors in integration analyses. In contrast, label information for different but closely related cell types would not improve the accuracy of cell type predictions, and so we consider a smaller number of anchors surrounding each cell. This procedure is implemented in the FindWeights internal Seurat function, which is called by IntegrateData or TransferData.
Data integration for reference assembly
Once we have identified anchors and constructed the weights matrix, we follow the strategy outlined by Haghverdi et al. [Haghverdi et al., 2018] for batch correction. We first calculate the matrix B, where each column represents the difference between the two expression vectors for every pair of anchor cells, a:
We then calculate a transformation matrix, C, using the previously computed weights matrix and the integration matrix as:
We then subtract the transformation matrix, C, from the original expression matrix, Y, to produce the integrated expression matrix :
This step is implemented in the IntegrateData function in Seurat. The corrected expression matrix can be treated as a single normalized scRNA-seq matrix, and can be processed downstream using any single-cell analytical toolkit. Notably, in Seurat, we continue to store the original uncorrected expression data, to facilitate downstream comparisons across datasets.
Multiple Dataset Integration
Our approach to multiple dataset integration draws inspiration from methods for multiple sequence alignment. Many multiple sequence alignment algorithms begin with the construction of all pairwise alignments and proceed to merge these pairwise alignments to progressively form the final multiple sequence alignment [Feng and Doolittle, 1987]. Here, we use a similar approach where we first identify and score anchors between all pairs of datasets and then progressively build the final integrated dataset.
To integrate multiple datasets, we first determine the order in which to merge the datasets after pairwise anchor identification. To do this we first define a distance between any two datasets as the total number of cells in the smaller dataset divided by the total number of anchors between the two datasets. We compute all pairwise distances between datasets and then perform hierarchical clustering on this distance matrix using the hclust function from the stats R package. This returns a guide tree which we use to iteratively merge the datasets using the integration procedure described above to form the final integrated dataset. This procedure is implemented in the IntegrateData function in Seurat.
Label Transfer
For cell metadata transfer, we create a binary classification matrix L containing the classification information for each anchor cell in the reference dataset. Specifically, each row in L corresponds to a possible class and each column corresponds to a reference anchor. If the reference cell in the anchor belongs to the corresponding class, that entry in the matrix is filled with a 1, otherwise the entry is assigned a 0. We then compute label predictions, Pl, by multiplying the anchor classification matrix L with the transpose of the weights matrix W:
This returns a prediction score for each class for every cell in the query dataset that ranges from 0 to 1, and sums to 1.
Feature Imputation
Our procedure for transferring continuous data is closely related to discrete label transfer. We compute new feature expression predictions, Pf, by multiplying a matrix of anchor features to be transferred, F, with the transpose of the weights matrix W:
This returns a predicted expression matrix for each feature (row) in F for each cell in the query dataset. Feature imputation and label transfer are both implemented in the TransferData function in Seurat.
Quantification and statistical analysis
Processing of single-cell datasets
Data Acquisition and QC
The data used for the majority of the analyses in this paper come from publicly available repositories and data portals, and we are grateful to all the groups and organizations for making their data readily accessible. We obtained the human pancreatic islet datasets from the following accession numbers: GSE81076 (CelSeq), GSE85241 (CelSeq2), GSE86469 (Fluidigm C1), E-MTAB-5061 (SMART-seq2), and GSE84133 (inDrops). We filtered out cells for which fewer than 1,750 unique genes/cell (Celseq) or 2,500 genes/cell (CelSeq2/Fluidigm C1/SMART-seq2) were detected. For the inDrops data sets, we kept all cells with previously annotated cluster information. We obtained the UMI count matrix for the mouse retinal bipolar cell dataset under the accession number GSE81904, keeping only those cells with previously annotated cluster information. The Tabula Muris datasets were obtained from FigShare for the Version 1 release [Consortium, 2018, 2017]. The human bone marrow dataset was obtained from the Human Cell Atlas Data Portal preview site [Li et al., 2018]. We filtered out any cells for which fewer than 500 genes were detected and any genes that were expressed in fewer than 100 cells. The osmFISH data was obtained from the Linnarsson Lab website [Linnarsson, 2018]. The mouse visual cortex SMART-seq2 data was obtained from the Allen Brain Data Portal [Institute, 2018, Tasic et al., 2018]. Any cells that were annotated as either “Low Quality” or “No Class” were removed. The mouse prefrontal cortex scATAC-seq gene activity scores and ATAC peak matrices were obtained from the Seattle Organismal Molecular Atlases (SOMA) Data Portal [SOMA, 2018]. The STARmap 1,020-gene datasets from the mouse visual cortex were downloaded from the original paper’s companion website [Wang, 2018, Wang et al., 2018]. We kept all cortical cells, based on the provided class labels, and did not perform additional filtration based on total RNA counts observed per cell.
Bone marrow mononuclear cells CITE-seq experiment
Bone marrow mononuclear cells from a single human donor were purchased from AllCells (cat #: ABM007F, lot #:3008803). The day of the experiment, cells were thawed according to manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, cell vials were sprayed with ethanol and placed in a 37°C water bath for 2 minutes to thaw. RPMI 10% media was used to wash and resuspend cells. Cell numbers and viability were estimated using trypan blue. Cells were resuspended in CITE-seq [Stoeckius et al., 2017] staining buffer (2%BSA/0.01%Tween in PBS) and incubated with FcX blocking reagent for 10 minutes (BioLegend, cat #: 422302) to block nonspecific antibody binding. Following FcX blocking, cells were incubated with a pool of 25 antibodies (1μg/antibody) for 30 minutes at 4°C. To ensure we can accurately identify cell doublets and distinguish empty droplets from cells with low gene counts, cells were split into 10 tubes each containing a unique hashing antibody from BioLegend [Stoeckius et al., 2018] and were incubated at 4°C for an additional 20 minutes. After incubation, cells were washed three times with 1 mL of staining buffer to remove any unbound antibodies. At the end of the final wash, cells were passed through a 40 μm filter to remove cell clumps (VWR, cat #: 10032–802) and resuspended in 1xPBS at the appropriate cell concentration for 10x Genomics 3’ scRNA-seq [Zheng et al., 2017].
Antibody List
The following human Totalseq BioLegend antibodies were included in the pool: CD3 (cat #: 300475), CD56 (cat #: 362557), CD19 (cat #: 302259), CD11c (cat #: 371519), CD38(cat #: 102733), CD45RA, (cat #: 304157) CD123(cat #: 306037), CD127 (cat #: 351352), CD4 (cat #: 300563), CD8a (cat #: 301067), CD14( cat #: 301855), CD16( cat #: 302061), CD25 (cat #: 302643), CD45RO (cat #: 304255), CD69 (cat #: 310947), CD197 (cat #: 353247), CD161 (cat #: 339945), CD28 (custom made, clone: CD28.2), CD27 (cat #: 302847), HLA-DR (cat #: 307659), CD57 (custom made, clone: QA17A04), CD79b (cat #: 341415), CD11a (cat #: 350615), CD34 (cat #: 343537). For cellular hashing the following TotalSeq hashtag antibodies were purchased from BioLegend: Hashtag 1 (cat #: 394601), Hashtag 2 ( cat #: 394603), Hashtag3 (cat #: 394605), Hashtag 4 (cat #: 394607), Hashtag 5 (cat #: 394609), Hashtag 6 (cat #: 394611), Hashtag 7 (cat #: 394613), Hashtag 8 (cat #: 394615), Hashtag 9 (cat #: 394617), Hashtag 10 ( cat #: 394619). For the complete list of antibody barcode sequences see Tables S1E and S1F.
CITE-seq data preprocessing
CITE-seq RNA reads were mapped to the human genome (GRCh38) and transcripts quantified using CellRanger v2.1.0 [Zheng et al., 2017, Dobin et al., 2012]. Antibody counts for CITE-seq [Stoeckius et al., 2017] and cell hashing [Stoeckius et al., 2018] were counted using CITE-seq-count (https://github.com/Hoohm/CITE-seq-Count). Antibody-derived tags (ADTs) and hashtag oligos (HTOs) for each cell were normalized using a centered log ratio (CLR) transformation across cells, implemented in the function NormalizeData with normalization.method=“CLR”, margin=2 in Seurat v3. Cells were demultiplexed using the HTOdemux function in Seurat, and cell doublets and background empty droplets subsequently removed. RNA counts for each cell were then preprocessed as described above (Data preprocessing).
CITE-seq cross-validation
We separated the 33,454-cell CITE-seq dataset into two equal groups at random to produce a query and reference dataset for cross-validation of protein expression transfer accuracy between experiments. Within the query dataset, we removed and stored the measured protein expression data for each cell. We then ran our transfer workflow on the query and reference dataset with default parameters, transferring the protein expression values from the reference dataset onto the query. We then computed, for each protein in each query cell, the Pearson correlation between the predicted protein expression and the measured expression level.
To assess the relationship between the number of RNA features (genes) used to identify anchors between the datasets and the resulting accuracy, we first ranked each gene in the CITE-seq dataset by it’s contribution to the overall variance in the dataset by multiplying the gene’s PCA loading with the variation explained by the component. We then took increasing subsets for these genes starting with the highest-ranked genes, ranging from 10 to 1,000 genes in steps of 10, and repeated the cross-validation.
Protein expression transfer to the HCA
To transfer cell surface protein expression data to the Human Cell Atlas dataset, we first computationally removed doublets from each scRNA-seq batch using Scrublet [Wolock et al., 2019], then integrated the eight human bone marrow datasets (eight different donors) using the Seurat v3 integration method (FindIntegrationAnchors and IntegrateData functions in Seurat v3) with default parameters, a dimensionality of 50, and an eps=1 as described above. We then transferred protein expression from the 33,454-cell CITE-seq dataset to the 274,932-cell HCA dataset using the FindTransferAnchors and TransferData functions in Seurat v3.
Analysis of CD69+ bone marrow population
We identified a population of predicted CD69+/CD8+ cells in the HCA bone marrow dataset. To identify a gene expression signature associated with this group of cells, we first performed an initial clustering of the data using Louvain clustering based on a shared nearest neighbor graph, as implemented in the FindClusters function in Seurat with default parameters. We then isolated the cluster that contained a mixture of CD69+ and CD69− CD8+ cells. We further subdivided this cluster into CD69-high and CD69-low cells by fitting a three-component mixture model using the predicted CD69 expression data, using the normalmixEM function in the mixtools R package [Benaglia et al., 2009]. After grouping the cells into high- and low-expressing CD69 populations, we searched for differentially expressed genes between the two populations using the original (uncorrected) HCA scRNA-seq data. We used the logistic regression differential expression test [Ntranos et al., 2019] implemented in the FindMarkers function in Seurat, with the donor as a latent variable (latent.vars=“orig.ident”, test.use=“LR”). We retained the top 25 differentially expressed genes based on highest fold-change expression. We performed gene ontology enrichment analysis on this set of genes for both molecular function and biological process, using the R package GOstats with a p-value cutoff of 0.001 [Falcon and Gentleman, 2007].
Validation of CD69+ T cell population
To validate the CD69+/CD8+ T-cell population identified through our integration method, we performed bulk RNA-seq experiments on FACS-sorted cell populations from the same bone marrow cell sample. Bone marrow mononuclear cells were thawed as described above. Cells were resuspended in MACS buffer (2%BSA/2mM EDTA in PBS) and incubated with FcX blocking reagent for 10 minutes (BioLegend, cat #: 422302) to block nonspecific antibody binding. Cells were stained with the following FACS antibodies: FITC-CD3 (clone HIT3a, 300306), APC-CD4 (clone RPA-T4, cat #: 300514), APCCy7-CD8 (clone RPA-T8, cat #: 301015) and PE-CD69 (clone FN50, cat #: 310905). DAPI was used to exclude dead cells (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat #: D1306). CD4−/CD8+/CD3+/CD69+ and CD4− /CD8+/CD3+/CD69− cells were sorted into tubes (4 replicates per population, 300–3000 cells per replicate) containing RLT lysis buffer (Giagen, cat #: 79216) using the SONY SH800 sorter. To remove cellular debris, AmPure bead cleanup was performed on all sample lysates. Reverse transcription, cDNA amplification and RNA-seq libraries were prepared as described previously [Bracken, 2018]. To identify differentially-expressed genes between the CD69+ and CD69− sorted populations, we used DESeq2 [Love et al., 2014] and filtered for significant genes with a log2-fold change in expression greater than 1.5 and a q-value of less than 0.01 [Storey and Tibshirani, 2003].
Calculation of Moran’s I
To calculate Moran’s I statistic, a measure of spatial autocorrelation, we compute:
Where N is the number of spatial units (i and j for 2-dimensional space), x is the gene of interest, is the mean expression of gene x, wij is a spatial weight matrix with zeros on the diagonal, and W is the sum of all wij. We computed the spatial weight matrix using the function dist in the R package stats, and applied a Gaussian kernel to the distance matrix to produce a smooth distribution. We used the implementation of Moran’s I available in the R package ape [Paradis et al., 2004], and acknowledge the Trapnell Lab Monocle 3 tutorials for suggesting the use of Moran’s I to estimate spatial autocorrelation in single-cell data. We applied Moran’s I in two analyses: examining spatial (2D) patterns of gene expression in the mouse brain, and examining the dependence of gene expression on a 1D axis defined by CD69 expression in human bone marrow cells. In each case, we binned gene expression values for cells in small spatial regions before calculating spatial weights and Moran’s I.
Assignment of cell type labels for pancreatic islet cells
To assign a set of consistent cell type labels to the pancreatic islet cell datasets, we based our classifications on the labels provided in the inDrops dataset. We first computed a PCA on the scaled integrated data matrix and used the first 30 PCs to build an SNN graph using the FindNeighbors function in Seurat with k.param set to 20. We then clustered the data using FindClusters in Seurat with the resolution parameter set to 1.5. For each resulting cluster, we assigned a label based on the most frequently occurring cell type in that cluster from the inDrops dataset (Table S1B).
Identification of rare subtypes in the Tabula Muris dataset
We integrated the two Tabula Muris datasets using the Seurat v3 integration method (FindAnchors and IntegrateData) with a chosen dimensionality of 100. We then normalized, scaled, and performed PCA on the integrated data as described in the Data preprocessing section above. The first 100 PCs were then used to construct an SNN matrix using the FindNeighbors function in Seurat v3 with k.param set to 20. We then identified clusters using the FindClusters command with the resolution parameter set to 4, identifying 132 total clusters. We annotated cluster 121 as mesothelial cells and cluster 114 as plasmacytoid dendritic cells based on the expression of known cell type markers (Figure S2C,E,F).
Integration with simulated cell type holdouts
For both the pancreas and bipolar datasets, we performed a simulated holdout experiment where one cell type was completely removed from each dataset being integrated. These combinations are detailed in Table S1A. After the cell type removal, highly variable genes were recalculated and integration features were selected. These features were then used as input to the integration procedure with the same default parameter settings as used in the full dataset integration.
We also tested the following existing integration methods on the same holdout datasets: Seurat v2 [Butler et al., 2018], mnnCorrect [Haghverdi et al., 2018], and scanorama [Hie et al., 2018]. For Seurat v2, we used the same feature set as determined for Seurat v3 to run a multi-CCA analysis followed by alignment (RunMultiCCA and AlignSubspace in Seurat v2). We used the first 30 aligned CCs to define the integrated subspace for clustering, visualization, and computing the integration metrics.
For mnnCorrect, we used the mnnCorrect function from the scran [Lun et al., 2016] R package with the log-normalized data matrices as input, subset to include the same variable integration features we used for Seurat v3, and setting the pc.approx parameter to TRUE. This returned a corrected gene expression matrix on which we performed principle component analysis and kept the first 30 PCs as input for clustering, visualization, and computing the integration metrics.
For scanorama, we used the “correct” function with default parameter settings to batch correct the data and return an integrated expression matrix. The downstream processing here was kept the same as for mnnCorrect.
Integration Metrics
To compare the results of the holdout integration experiments, we computed three measures of integration quality: the silhouette coefficient [Rousseeuw, 1987], a mixing metric, and a local structure metric.
Silhouette coefficient
We computed the silhouette coefficient using the cluster package in R. Here, distances were computed in PCA space defined by the first 30 components for all methods except for Seurat v2, where we used the first 30 aligned CCs to define cluster distances. Clusters were defined using the previously assigned cell-type labels (Assignment of cell type labels for pancreatic islet cells). The silhouette coefficient gives a score for each cell that assesses the separation of cell types, with a high score suggesting that cells of the same cell type are close together and far from other cells of a different type. The silhouette score s(i) is defined for each cell i as follows. Let a(i) be the average distance of cell i to all other cells within i’s cluster and b(i) be the average distance of i to all cells in the nearest cluster to which i does not belong. s(i) can then be computed as:
Mixing metric
We designed a “mixing metric” to evaluate how well mixed the input datasets were after integration. We first considered using a metric based on dataset entropy within an individual cell’s local neighborhood [Büttner et al., 2017]. However, the assumptions of these methods are violated in cases where the distribution of cell type frequencies differs significantly across datasets, as is the case in many of our experiments. As an alternative, we reasoned that if the local neighborhood for a cell is well mixed, its closest neighbors should contain at least a small number (k = 5) of cells from each dataset. If the cell is poorly mixed, then its closest neighbors will likely stem only from a small subset of datasets (perhaps only its own). For each cell, we therefore examine the (k.max = 300) ranked nearest neighbors across all datasets. We also compute the k=5 closest neighbors for each dataset individually. We then ask which rank in the overall neighborhood list corresponds to the 5th neighbor in each dataset (with a max of 300), and took a median over all these values. This corresponds to a mixing metric per cell, and we averaged across all cells to obtain an overall mixing metric for each method. We found that this metric accurately reflected the the mixing of shared biological states across datasets, even when cluster frequencies differed. This metric is implemented in the MixingMetric function in Seurat v3.
Local structure metric
We computed a metric designed to determine how well the original structure of each dataset was preserved after integration. Here, we split the data back into its original datasets, re-compute an principal component analysis on the uncorrected data, and identify the k=100 closest nearest neighbors. We also computed the 100 nearest neighbors based on a principal component analysis of the integrated dataset. For every cell, we then looked at the intersection of these two neighborhoods and computed the fraction of overlap. For an overall score, we took the mean overlap fraction for all cells. This metric is implemented in the LocalStruct function in Seurat v3.
Transferring cell type labels onto scRNA-seq data
In order to benchmark the projection of new data onto an existing reference, we performed the following experiments with the pancreas and bipolar datasets:
We generated 166 evaluation datasets for benchmark comparison. For each case, we removed one dataset from the reference to use as a query. We also removed all instances of one celltype from the reference (‘withheld class’). We did this for all possible combinations of holdout datasets and cell types.
To ensure that a single cell type did not dominate in downstream evaluation, we downsampled the query dataset to contain a maximum of 100 cells per celltype. We then added or subtracted additional instances of cells in the “withheld” class, so that it composed 20% of the query.
We then integrated the reference using the same default workflow and parameter settings as for all previous integrations.
To classify cells using the Seurat v3 workflow, we first integrated the reference dataset using default parameters. We then classified query cells using the FindTransferAnchors and TransferData functions in Seurat with default parameters. We examined projection scores and assigned the cells with the lowest 20% of values to be “Unassigned”.
We also repeated the classification using two functions from the scMAP R package: scmapCluster and scmapCell [Kiselev et al., 2018]. For these tests, we selected features using the selectFeatures function in scMap with n_features specified as 500. For scmapCluster, we set the similarity threshold parameter to -Inf to force assignments where possible. We then took the cells with the lowest 20% of similarity values and called them “Unassigned”.
scATAC-seq analysis
Preprocessing scATAC-seq data
We obtained scATAC-seq gene activity score and binarized peak count matrices for the mouse prefrontal cortex [Cusanovich et al., 2018]. For all integration with scRNA-seq data, we used the gene activity score matrix. For finding differentially accessible peaks between groups of cells, we used the binarized peak count matrix. The authors instruct that scATAC-seq gene activity score matrix must be preprocessed and filtered, so we applied log-CPM (counts-per-million) normalization, and removed cells with less than 5,000 total peaks detected in the binary peak matrix.
Latent semantic indexing
We reduced the dimensionality of the scATAC-seq data by performing latent semantic indexing (LSI) on the scATAC-seq peak matrix, as suggested by Cusanovich and Hill et at. [Cusanovich et al., 2018]. We first computed the term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) of the peak matrix by dividing the accessibility of each peak in each cell by the total accessibility in the cell (the “term frequency”), and multiplied this by the inverse accessibility of the peak in the cell population. This step ‘upweights’ the contribution of highly variable peaks and downweights peaks that are accessible in all cells. We then computed to log of this TF-IDF matrix, adding a pseudocount of 1 to avoid computing the log of 0. We decomposed the TF-IDF matrix via SVD to return LSI components, and scaled LSI loadings for each cell to mean 0 and standard deviation 1. These steps are used for learning the weighting of anchors within the scATAC-seq dataset, and are implemented in the RunLSI function in Seurat.
Transferring cell type labels onto scATAC-seq cells
We found anchors between the pre-processed scATAC-seq cells (gene activity matrix) for the mouse prefrontal cortex and scRNA-seq cells from the mouse visual cortex [Tasic et al., 2016, 2018]. We first found highly variable features in the scRNA-seq data using the FindVariableFeatures function in Seurat v3, as described above (Data preprocessing). We used the top 5,000 variable features that were also present in the scATAC-seq data as input to the integration, resulting in ~3,000 variable features as recommended by the original authors for downstream analysis [Cusanovich et al., 2018]. We found anchors between the two datasets using the FindTransferAnchors function in Seurat v3, with the parameters dims=1:20 and reduction=“cca”. We transferred cell type labels from the scRNA-seq dataset to the scATAC-seq cells using the TransferData function in Seurat v3, setting the parameter weight.reduction=atac[[“lsi”]] to specify the previously computed LSI dimensional reduction when calculating anchor weights.
To visualize the two datasets together, we transferred scRNA-seq data onto the scATAC-seq cells, using the same anchors as previously identified. We accomplished this by applying the same procedure used to impute transcriptome-wide expression in the STARmap dataset (see below). After imputation, we concatenated this matrix with the scRNA-seq dataset, performed a single PCA on both datasets, projected to two dimensions with UMAP, and colored the cells by their classification label. We emphasize that step is intended only for visual interpretation, and it is not necessary for us to jointly visualize the datasets, or transfer scRNA-seq data, in order to classify the scATAC-seq cells.
Identification of differentially accessible peaks and overrepresented motifs
We identified differentially accessible peaks between groups of scATAC-seq cells simply by ordering peaks by their fold-change accessibility between the groups, and retaining the top 1,000 peaks that displayed the greatest fold-change in accessibility. We searched for overrepresented DNA sequence motifs in accessible regions using the Homer package [Heinz et al., 2010], using the findMotifsGenome.pl program with default parameters, and the mm9 genome.
Psuedo-bulk ATAC-seq data collation
We split the scATAC-seq binary sequence/alignment map (BAM) file for the prefrontal cortex into individual files for each predicted cell type to create pseudo-bulk ATAC seq datasets for each celltype. To extract scATAC-seq reads by their cell barcode, we used the filterbarcodes command in the Python package sinto (v0.1, https://github.com/timoast/sinto), which depends heavily on the pysam package [Li et al., 2009]. We created normalized read coverage tracks (bigwig format) for each BAM file using the program bamCoverage in the deepTools package [Ramírez et al., 2016] with the bin-Size parameter set to 1 and using the reads per kilobase per million mapped reads (RPKM) normalization option.
Pre-processing of 10X scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq data
We downloaded a human peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) scRNA-seq dataset generated with the 10× Genomics Chromium system (v3 chemistry, 10k dataset; https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-gene-expression/datasets/3.0.0/pbmc_10k_v3), and a human PBMC scATAC-seq dataset, also generated with the 10× Genomics Chromium system (v1 chemistry; 10k dataset; https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-atac/datasets/1.0.1/atac_v1_pbmc_10k).
We pre-processed the scRNA-seq dataset, retaining cells with over 2,000 and under 20,000 genes detected, with fewer than 20% mitochondrial transcripts. We identified and removed doublets using Scrublet [Wolock et al., 2019], removing cells with a doublet score greater than 0.1. We clustered the scRNA-seq cells by first identifying the top 3,000 highly variable genes, scaling and centering the expression of these genes, computing PCA on the scaled expression values, and performing graph-based cluster detection using the top 30 principal components with the Louvain algorithm for community detection. We annotated clusters as cell types according to the expression of canonical marker genes.
We pre-processed the scATAC-seq data, retaining cells with over 5,000 peaks, and peaks detected in at least 100 cells. As proposed by [Cusanovich et al., 2018], we performed latent semantic indexing on the scATAC-seq dataset to reduce dimensionality. To link the scATAC-seq accessibility peaks to genes, we simply summed peaks intersecting the gene body and 2 kilobase upstream region to give a gene activity score for each gene in each cell. This procedure is implemented in the CreateGeneActivityMatrix in Seurat v3, though our procedure can also run on Cicero-derived gene activity matrices [Pliner et al., 2018].
Classification of scATAC-seq profiles based on scRNA-seq clusters
We transferred cell type annotations from the scRNA-seq dataset to the scATAC-seq dataset using the same procedure as described above for the integration of scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq data from the mouse cortex, and using a dimensionality of 30. To visualize cells from each dataset in the same space, we also transferred gene expression data from the scRNA-seq cells to the scATAC-seq cells using the same set of anchors as was used to transfer cell type annotations, then performed PCA and UMAP on the combined RNA and ATAC object. We note that this is only necessary for the purposes of visualization.
Experimental validation using ATAC-seq from FACS-sorted populations
We downloaded bulk ATAC-seq peak accessibility data for all available cell types (NK cells, CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, Monocytes) from the UCSC Genome Browser https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/chang-public-data/2016_NatGen_ATAC-AML/hub.txt and GEO (GSE74912 [Corces et al., 2016]). Monocyte tracks were available from the UCSC genome browser, but peak-level quantifications were not available on GEO. To create pseudo-bulk ATAC-seq datasets for each PBMC cell type, we computationally grouped reads from the 10x Genomics data according to their predicted cell type as described above for the mouse brain data. We compared accessibility patterns between the FACS-sorted bulk ATAC-seq and computationally-sorted scATAC-seq cells through visualization of coverage at canonical marker loci using the Gviz R package [Hahne and Ivanek, 2016]. To compare global patterns of chromatin accessibility, we identified variable peaks among the bulk ATAC-seq samples and computed the peak coverage of each pseudo-bulk scATAC-seq population using bedtools multicov [Quinlan and Hall, 2010]. We then computed the Pearson correlation between peak accessibility in each bulk ATAC-seq population and the different pseudo-bulk scATAC-seq populations.
Projecting gene expression and cell type labels onto spatially-resolved cells
Preprocessing STARmap data
We obtained STARmap gene count matrices and cell position information for two combinatorially-encoded 1,020-gene experiments from the STARmap companion website (https://www.starmapresources.com/data/ [Wang et al., 2018]), and preprocessed the gene expression matrices as described above (Data preprocessing), with a normalization scaling factor equal to the median RNA counts per cell. To visualize spatial patterns of gene expression, we identified cell locations and morphologies using Python code provided by the original authors (https://github.com/weallen/STARmap [Wang et al., 2018]). Before transferring transcriptome-wide gene expression data from the SMART-seq2 dataset [Tasic et al., 2016, 2018] to the STARmap cells, we first integrated the two STARmap replicates using the Seurat v3 integration method. First, we identified anchors between the STARmap datasets using the FindIntegrationAnchors function in Seurat v3, using all 1,020 genes as input to the CCA. We then integrated the datasets using the IntegrateData function.
Data transfer
We then transferred transcriptome-wide gene expression data from the SMART-seq2 dataset to the integrated STARmap datasets using the FindTransferAnchors (reduction=“cca”) and TransferData functions in Seurat v3. We ran TransferData twice, once to transfer transcriptome-wide gene expression measurements, and again to transfer cell type labels from the SMART-seq2 dataset, using the same set of anchors. For all genes shown in Figure 5B (Cux2, Lamp5, Rorb, Rab3c, Syt6, Sox2ot, Bsg and Sst), imputations represent leave-one-out cross-validation of the STARmap data transfer. Specifically, we performed feature transfer independently for each gene, each time removing the gene of interest from the set of genes used to identify anchor cells between the STARmap and SMART-seq2 datasets.
Analysis of integrated STARmap data
After predicting cell type labels in the STARmap cells by transferring labels from the SMART-seq2 dataset, we observed 1,915 cells with high-confidence cell type predictions (prediction score > 0.5). To be more conservative, we chose to filter the predicted celltype labels to retain only the highest 50% scoring cells for each transferred cell type, retaining a total of 1,210 classified cells. We then performed differential expressed to identify gene expression markers that were upregulated in each classified cell type. We used a logistic regression test for differential expression [Ntranos et al., 2019] on the uncorrected data with replicate as a latent variable, implemented in the FindMarkers function in Seurat (method=“LR”, latent.vars=“orig.ident”, assay=“RNA”).
To assess the robustness of our data transfer method, we first re-computed variable genes in each STARmap dataset, using the predicted gene expression data. Here, we selected the top 3,000 highly variable genes based on mean-variance dispersion. We did not use the variance-stabilizing transformation described above (Data preprocessing), as the predicted expression data are not discrete counts. For each gene identified as highly variable in either STARmap replicate, we calculated Moran’s I (see Calculation of Moran’s I, above), to estimate the relationship between predicted gene expression and spatial distribution for each gene. We then compared the Moran’s I value for each gene in the two replicates by calculating the Pearson correlation between Moran’s I values.
STARmap imputation with Drop-seq data
To investigate whether we could achieve accurate imputation results with a dataset generated using a droplet-based scRNA-seq technology, we repeated our STARmap imputation analysis using a recent Drop-seq scRNA-seq dataset from the mouse brain [Saunders et al., 2018]. We downloaded Drop-seq data for the mouse prefrontal cortex from the Drop-viz website (https://storage.googleapis.com/dropviz-downloads/static/regions/F_GRCm38.81.P60Cortex_noRep5_FRONTALonly.raw.dge.txt.gz). We pre-processed the Drop-seq data using Seurat as described above, choosing a dimensionality of 50. We repeated the STARmap imputation analysis exactly as described above for the Smart-seq2 dataset, using the Drop-seq data [Saunders et al., 2018].
STARmap feature downsampling and calculation of gene expression redundancy
To assess the number of features required for accurate gene expression prediction in the STARmap dataset, we first randomly chose subsets of STARmap genes ranging from 50–1,000 genes retained, and repeated the transcriptional imputations described above with each downsampling set. We evaluated the performance of each downsampling by computing the Pearson correlation in gene expression between the downsampled prediction values and prediction values obtained using the entire STARmap dataset. For each gene, we calculated its correlation in the scRNA-seq data with each of the features in the measured feature set, and took the third highest value as an estimate of “expression redundancy”. To repeat our gene downsampling analysis in a way that would minimize redundancy among genes in the measured set, we chose an equal number of markers from Figure 5G per cluster, ranked by highest average log-fold change. Once we had exhausted cluster markers, we picked remaining genes based on their stabilized variance values, computed with FindVariableFeatures in Seurat.
Data and software availability
Our integration methods are implemented in Seurat v3, available on CRAN (https://cran.r-project.org/package=Seurat) and GitHub (https://github.com/satijalab/seurat). Raw CITE-seq and bulk RNA-seq reads are available through SRA (SRP188993), and processed expression matrices through GEO (GSE128639).
Additional resources
Documentation, tutorials, and vignettes for Seurat v3 can be found on the Satija lab website (https://satijalab.org/seurat/).
Supplementary Material
Data File S1, related to Figure 4. Protein and gene expression patterns in Human bone marrow cells.
Page 2 represents the expression level of all 25 measured proteins in human bone marrow CITE-seq experiment. Cells are projected into two dimensions using UMAP, and colored based on normalized antibody-derived tag (ADT) counts for each protein (range 10th-99th expression percentile for each protein). Page 3 represents the predicted protein expression for all 25 proteins measured in the CITE-seq experiment in the Human Cell Atlas bone marrow dataset. Cells are projected into two dimensions using UMAP, and colored based on predicted normalized antibody-derived tag (ADT) counts for each protein (range 40th-99th expression percentile for each protein). Page 4 represents the expression of celltype marker genes in HCA bone marrow cells. AVP: marker of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC). LMO4: basophil progenitor (Bas). PF4: megakaryocyte progenitor (MkP). BLVRB: erythroid progenitor (Er). MME: common lymphoid progenitor (CLp). DERL3: plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC). CLEC9A: conventional dendritic cell 1 (cDC1). CDC1: convensional dendritic cell 2 (cDC2). MPO: granulocyte macrophage progenitor (GMP). AZU1: neutrophil progenitor (Neu). CD14: CD14+ monocyte (CD14 Mono). FCGR3A: CD16+ monocyte (CD16 Mono). VREB3: immature B cell (Immature B). MS4A1: mature B cell (Mature B). CD79A: immature / mature B cell (Immature/Mature B). IGKC: plasma cell (Plasma). PF4: megakaryocytes (Mk). XCL1: CD56+ natural killer cells (NK Bright). CD8A: CD8+ T cells (CD8 T). CD4: CD4+ T cells (CD4 T). SH2D1A: pre-T cell (pre-T). Cells are projected into two dimensions using UMAP, and colored based on normalized RNA counts for each gene (range 0–99th expression percentile for each gene).
Data File S2, related to Figure 5. Spatial gene expression patterns in the mouse brain.
Page 2 represents the spatial patterns of gene expression in the mouse brain (STARMap replicate 2) (A) Measured and predicted gene expression patterns for a subset of genes measured in the STARmap experiment, for the second biological replicate (as for Figure 5B). (B) Gene expression patterns for four genes not measured by STARmap (as for Figure 5C). Page 3 represents the spatial imputation of gene expression using either the Drop-seq or SMART-seq2 dataset as the scRNA-seq reference. Predicted gene expression patterns for leave-one-out cross validations of 8 genes (same genes shown in 5B) for STARmap replicate 1 (A) and replicate 2 (B).
Figure S1, related to Figure 2. Integration of human pancreatic islet and mouse retinal bipolar cells
(A-C) UMAP plots of 14,890 human pancreatic islet cells across 8 datasets before (A) and after (B) integration. After integration, cells were clustered and labeled based on a previously annotated reference dataset (C), allowing for detection of both common and rare subpopulations of islet cells across integrated datasets. (D) For verification of the cell type labels, we plot the top differentially expressed gene markers for each cluster, broken down by original dataset and observe consistent patterns of cell-type specific expression. To facilitate the visualization of rare populations, we downsample the heatmap to show at most 25 cells per cluster per dataset. (E, F) tSNE plots of 23,725 mouse retinal bipolar cells after integration with Seurat V3, Seurat V2, mnnCorrect, and Scanorama. For each of these analyses, a single cell type was removed from each of the 6 replicates prior to integration (Table S1A).
Figure S2, related to Figure 2. Integration of Tabula Muris mouse cell atlas datasets
(A-C) tSNE plots of the integrated mouse cell atlas datasets grouped by (A) technology, (B) tissue, and (C) whether the tissue was profiled by SMART-Seq (FACS) only. After integration, cells from tissues profiled by both 10x and FACS-sorted SMART-seq cluster together, where as cells from tissues uniquely profiled by FACS are not blended into other tissue types, demonstrating robustness to non-overlapping populations. (D) Further underscoring robustness, cells from tissues profiled across technologies achieve high mixing whereas cells profiled using only one technology have substantially lower scores. The internal dataset structure for both subsets is preserved in integrated analysis. (E-F) By integrating the datasets we can detect exceedingly rare cell populations that are present in multiple tissues, such as (E) mesothelial cells and (F) plasmacytoid dendritic cells. We can also identify both shared and divergent gene expression markers for these populations across tissues. (G) Integration of 274,932 human bone marrow cells generated by the Human Cell Atlas project, from eight different human donors. (H) Enriched gene ontology terms for gene biological processes and molecular functions for CD69+ marker genes identified from HCA bone marrow scRNA-seq data. Gene ontology analysis was performed using GOstats.
Figure S3, related to Figure 3. Examination of non-overlapping scATAC-seq cells in multi-modal co-embedding
(A) UMAP visualization of scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq cells following multimodal integration. Cells are colored by dataset of origin (left), and the unknown group of scATAC-seq cells that failed to mix with the scRNA-seq cells are highlighted in red (right). (B) Expression of cell-type-specific marker genes in the unknown population and in other groups of cells, as annotated by the original authors (Cusanovich et al. (2018), Cell). The unknown population of scATAC-seq cells co-express gene activity markers that are otherwise mutually exclusive, suggesting that they may represent scATAC-seq multiplets. (C) UMAP embedding of human PBMCs profiled using 10x Genomics scRNA-seq, with cells colored by their annotated cell type. (D) Joint visualization of scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq PBMCs, with cells colored by their predicted cell type. (E) As for (D), with cells colored by their dataset of origin. (F) Chromatin accessibility profiles for computationally-sorted human PBMC subsets. X-axis scale is indicated by scale bars above each genomic region. Y-axis limits were set individually for each locus to enhance visualization. However, within each locus all pseudo-bulk tracks are on a consistent scale, and all FACS-sorted bulk tracks are on a consistent scale, to enable a visual comparison. (G) Genome-wide agreement between experimentally and computationally-sorted immune cell chromatin accessibility profiles. Pearson correlation between peak accessibility (normalized coverage within peak) between cell types sorted experimentally (by FACS; Corces et al. [2016]) and computationally. Corresponding cell types in the single-cell and bulk datasets are highlighted in black boxes. (H) Examination of non-overlapping scATAC-seq cells in the joint visualization with scRNA-seq cells. Genomic blacklist region read counts for the non-overlapping cluster are shown, in comparison to counts for all other cells in the dataset combined. (I) Examination of a second non-overlapping scATAC-seq population, showing mean expression for each gene in the non-overlapping population and all other CD14+ Monocytes.
Figure S4, related to Figure 5. Validation of predicted gene expression patterns and cell type labels.
(A) Horizontally-compressed STARmap cells with predicted cell type transferred from the SMART-seq4 dataset (as for Figure 5F). (B) External validation of predicted gene expression patterns. in-situ hybridization images from the Allen Brain Atlas for Tesc and Pvrl3 alongside predictions for the same genes in STARmap cells. (C) UMAP co-embedding of scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq cells following multi-modal integration, colored by predicted cell type in each dataset. (D) As for (C), colored by dataset of origin. (E) UMAP on original STARmap data, with cells colored by the annotation given by the original authors (Wang et al. (2018), Science). (F) As for (E), with cells colored by their predicted identity. For the UMAP plots using the original STARmap data only, we are not able to recover the same level of structure that is suggested by the heatmap in Figure 5G, demonstrating the value of transferring cell type classifications.
Figure S5, related to Figure 5. Considerations for the integration of scRNA-seq and STARmap data
(A) Distribution of correlations between SMART-seq2 and Drop-seq-based gene expression predictions for cell type marker genes. (B) Genes that exhibited low agreement (correlation <0.5) between the two predictions tended to be lowly expressed, and rarely detected (<10% cells) in the Drop-seq dataset. Boxplot shows the detection rate of genes with greater or less than 0.5 correlation. (C) Normalized expression values for Cux2 in both the Drop-seq and the SMART-seq2 datasets showing different relative expression in the L2/3 IT and L4 clusters. (D) Representative scatter plots showing the correlation of Drop-seq and SMART-seq2 imputed values. (E) Correlation of imputed gene expression measurements computed using a downsampled number of genes versus the full set of genes under a random downsampling approach. (F) Scatter plot showing a strong positive relationship between how accurately a gene can be imputed versus its redundancy in the scRNA-seq dataset. (G) Comparison of a random versus guided feature downsampling approach in terms of the correlation of imputed expression measurement saturation.
Table S1, related to Figure 2. Cell type holdout information for integration evaluation cases.
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| CD3 | BioLegend | Cat# 300475 |
| CD56 | BioLegend | Cat# 363557 |
| CD19 | BioLegend | Cat# 302259 |
| CD11c | BioLegend | Cat# 371519 |
| CD38 | BioLegend | Cat# 102733 |
| CD45RA | BioLegend | Cat# 304157 |
| CD123 | BioLegend | Cat# 306037 |
| CD127 | BioLegend | Cat# 351352 |
| CD4 | BioLegend | Cat# 300563 |
| CD8a | BioLegend | Cat# 301067 |
| CD14 | BioLegend | Cat# 301855 |
| CD16 | BioLegend | Cat# 302061 |
| CD25 | BioLegend | Cat# 302643 |
| CD45RO | BioLegend | Cat# 304255 |
| CD69 | BioLegend | Cat# 310947 |
| CD197 | BioLegend | Cat# 353247 |
| CD161 | BioLegend | Cat# 339945 |
| CD28 | Custom made | Clone CD28.2 |
| CD27 | BioLegend | Cat# 302847 |
| HLA-DR | BioLegend | Cat# 307659 |
| CD57 | Custom made | Clone QA17A04 |
| CD79b | BioLegend | Cat# 341415 |
| CD11a | BioLegend | Cat# 350615 |
| CD34 | BioLegend | Cat# 343537 |
| Hashtag 1 Cell Hashing antibody | BioLegend | Cat# 394601 |
| Hashtag 2 Cell Hashing antibody | BioLegend | Cat# 394603 |
| Hashtag 3 Cell Hashing antibody | BioLegend | Cat# 394605 |
| Hashtag 4 Cell Hashing antibody | BioLegend | Cat# 394607 |
| Hashtag 5 Cell Hashing antibody | BioLegend | Cat# 394609 |
| Hashtag 6 Cell Hashing antibody | BioLegend | Cat# 394611 |
| Hashtag 7 Cell Hashing antibody | BioLegend | Cat# 394613 |
| Hashtag 8 Cell Hashing antibody | BioLegend | Cat# 394615 |
| Hashtag 9 Cell Hashing antibody | BioLegend | Cat# 394617 |
| Hashtag 10 Cell Hashing antibody | BioLegend | Cat# 394619 |
| Biological Samples | ||
| Human bone marrow cells | AllCells | Cat# ABM007F, lot 3008803 |
| Critical Commercial Assays | ||
| 3’ scRNA-seq kit | 10x Genomics | V2 chemistry |
| Deposited Data | ||
| Human bone marrow – CITE-seq | This paper | GEOXXXXXX |
| Pancreas – CelSeq | Grün et al., 2016 | GSE81076 |
| Pancreas – CelSeq2 | Muraro et al., 2016 | GSE85241 |
| Pancreas – FluidigmC1 | Lawlor et al., 2017 | GSE86469 |
| Pancreas – SMART-seq2 | Segerstolpe et al., 2016 | E-MTAB-5061 |
| Pancreas – InDrops | Baron et al., 2016 | GSE84133 |
| Retinal bipolar cells – Drop-seq | Shekhar et al., 2016 | GSE81904 |
| Tabula muris – SMART-seq2 | The Tabula Muris Consortium, 2018 | https://figshare.com/articles/Single-cell_RNA-seq_data_from_Smart-seq2_sequencing_of_FACS_sorted_cells_v2_/5829687/1 |
| Tabula muris – 10x Genomics | The Tabula Muris Consortium, 2018 | https://figshare.com/articles/Single-cell_RNA-seq_data_from_microfluidic_emulsion_v2_/5968960/1 |
| Bone marrow – 10x Genomics | The Human Cell Atlas | https://preview.data.humancellatlas.org/ |
| osmFISH | Codeluppi et al., 2018 | http://linnarssonlab.org/osmFISH/availability/ |
| STARmap | Wang et al., 2018 | https://www.starmapresources.com/data/ |
| Mouse prefrontal cortex – SMART-seq2 | The Allen Institute for Brain Science | http://celltypes.brain-map.org/api/v2/well_known_file_download/694413985. |
| Mouse cortex – sci-ATAC-seq | Cusanovich et al., 2018 | http://atlas.gs.washington.edu/mouse-atac/data/ |
| Human PBMCs – scATAC-seq | 10x Genomics | https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-atac/datasets/1.0.1/atac_v1_pbmc_10k |
| Human PBMCs – scRNA-seq | 10x Genomics | https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-gene-expression/datasets/3.0.0/pbmc_10k_v3 |
| Mouse cortex – Drop-seq | Saunders et al., 2018 | http://dropviz.org/ |
| Software and Algorithms | ||
| Seurat v3.0.0.9000 | This paper | https://github.com/satijalab/seurat/tree/release/3.0 |
| Seurat v2.3.3 | Butler et al., 2018 | https://github.com/satijalab/seurat/releases/tag/v2.3.3 |
| Scran v1.6.9 | Lun et al., 2016 | https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/scran.html |
| Scanorama commit b83e1ba87e6635825e155046b884dee2154c5d34 | Hie et al., 2018 | https://github.com/brianhie/scanorama |
| scmap v1.1.5 | Kiselev et al., 2018 | http://bioconductor.org/packages/scmap |
| Scrublet v0.1 | Wolock et al., 2018 | https://github.com/AllonKleinLab/scrublet |
| CellRanger v2.2.0 | 10x Genomics | https://support.10xgenomics.com/single-cell-gene-expression/software/pipelines/latest/installation |
| CITE-seq-count v1.2 | Patrick Roelli | https://github.com/Hoohm/CITE-seq-Count |
| Drop-seq tools v2.0.0 | McCarroll Lab | https://github.com/broadinstitute/Drop-seq |
| deepTools v3.1.2 | Ramirez et al., 2016 | https://github.com/deeptools/deepTools |
| GOstats v2.44.0 | Falcon and Gentleman, 2007 | https://github.com/deeptools/deepTools |
| Homer v4.10 | Heinz et al., 2010 | http://homer.ucsd.edu/homer/ |
| R | R Core | https://www.r-project.org/ |
| Python | Python Software Foundation | https://www.python.org/ |
Highlights.
Seurat v3 identifies correspondences between cells in different experiments
These ‘anchors’ can be used to harmonize datasets into a single reference
Reference labels and data can be projected onto query datasets
Extends beyond RNA-seq to single-cell protein, chromatin, and spatial data
A platform that integrates diverse modalities associated with single cell sequencing datasets can be used to better understand cellular identity and function.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by an NIH New Innovator Award (1DP2HG009623-01; R.S.) NIH Human Biomolecular Atlas Program Award (1OT2OD026673-01) and R01 (5R01MH071679-12; R.S.), Chan Zuckerberg Awards HCA-A-1704-01895 (R.S. and P.S.) and HCA2-A-1708-02755 (R.S) and an NSF Graduate Fellowship (DGE1342536; A.B.). We acknowledge members of the Satija Lab, NYGC Technology Innovation lab, Claude Desplan, Dan Littman, and Gord Fishell for helpful comments and discussion, and Josh Batson and Will Allen for sharing data and metadata.
Footnotes
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Achim K, Pettit J-B, Saraiva LR, Gavriouchkina D, Larsson T, Arendt D, Marioni JC, 2015. High-throughput spatial mapping of single-cell RNA-seq data to tissue of origin. Nature Biotechnology 33 (5), 503–509. URL http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/nbt.3209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alemany A, Florescu M, Baron CS, Peterson-Maduro J, Van Oudenaarden A, 2018. Whole-organism clone tracing using single-cell sequencing. Nature 556 (7699), 108–112. URL 10.1038/nature25969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya S, Mount D, Kemp SE, Jefferis G, 2018. RANN: Fast Nearest Neighbour Search (Wraps ANN Library) Using L2 Metric . R package version 2.6. URL https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=RANN [Google Scholar]
- Baglama J, Reichel L, Lewis BW, 2018. irlba: Fast Truncated Singular Value Decomposition and Principal Components Analysis for Large Dense and Sparse Matrices. R package version 2.3.2. URL https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=irlba [Google Scholar]
- Baron M, Veres A, Wolock SL, Faust AL, Gaujoux R, Vetere A, Ryu JH, Wagner BK, Shen-Orr SS, Klein AM, Melton DA, Yanai I, October 2016. A Single-Cell transcriptomic map of the human and mouse pancreas reveals inter- and intra-cell population structure. Cell Syst 3 (4), 346–360.e4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benaglia T, Chauveau D, Hunter DR, Young D, 2009. mixtools: An R package for analyzing finite mixture models. Journal of Statistical Software 32 (6), 1–29. URL http://www.jstatsoft.org/v32/i06/ [Google Scholar]
- Bendall SC, Davis KL, Amir EAD, Tadmor MD, Simonds EF, Chen TJ, Shenfeld DK, Nolan GP, Pe’Er D, 2014. Single-cell Trajectory Detection Uncovers Progression and Regulatory Coordination in Human B Cell Development. Cell 157 (3), 714–725. URL 10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer J, McDonald R, Pereira F, 2006. Domain adaptation with structural correspondence learning. Proceedings of the 2006 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (July), 120–128. URL http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=1610075.1610094 [Google Scholar]
- Bracken B, 2018. Barcoded plate-based single cell rna-seq. [Google Scholar]
- Butler A, Hoffman P, Smibert P, Papalexi E, Satija R, April 2018. Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions technologies, and species. Nature Biotechnology 36 (5), 411–420. URL https://doi.org/10.1038%2Fnbt.4096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büttner M, Miao Z, Wolf FA, Teichmann SA, Theis FJ, 2017. Assessment of batch-correction methods for scRNA-seq data with a new test metric. bioRxiv. [Google Scholar]
- Cao J, Cusanovich DA, Ramani V, Aghamirzaie D, Pliner HA, Hill AJ, Daza RM, McFaline-Figueroa JL, Packer JS, Christiansen L, Steemers FJ, Adey AC, Trapnell C, Shendure J, 2018. Joint profiling of chromatin accessibility and gene expression in thousands of single cells. Science 361 (6409), 1380–1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codeluppi S, Borm LE, Zeisel A, La Manno G, van Lunteren JA, Svensson CI, Linnarsson S, October 2018. Spatial organization of the somatosensory cortex revealed by osmFISH . Nat. Methods, 1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consortium, T. M., 2017. Single-cell rna-seq data from microfluidic emulsion (figshare).
- Consortium, T. M., 2018. Single-cell RNA-seq data from Smart-seq2 sequencing of FACS sorted cells (v2; figshare).
- Corces MR, Buenrostro JD, Wu B, Greenside PG, Chan SM, Koenig JL, Snyder MP, Pritchard JK, Kundaje A, Greenleaf WJ, Majeti R, Chang HY, August 2016. Lineage-specific and single-cell chromatin accessibility charts human hematopoiesis and leukemia evolution. Nat. Genet. 48 (10), 1193–1203. URL http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/ng.3646 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusanovich DA, Hill AJ, Aghamirzaie D, Daza RM, Pliner HA, Berletch JB, Filippova GN, Huang X, Christiansen L, DeWitt WS, Lee C, Regalado SG, Read DF, Steemers FJ, Disteche CM, Trapnell C, Shendure J, August 2018. A Single-Cell atlas of in vivo mammalian chromatin accessibility. Cell 174 (5). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin AM, Voermans C, Nolte MA, 2014. Impact of interferon-g on hematopoiesis. Blood 124 (16), 2479–2486. URL http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/110009758699/en/ [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit A, Parnas O, Li B, Chen J, Fulco CP, Jerby-Arnon L, Marjanovic ND, Dionne D, Burks T, Raychowdhury R, Adamson B, Norman TM, Lander ES, Weissman JS, Friedman N, Regev A, 2016. Perturb-Seq: Dissecting Molecular Circuits with Scalable Single-Cell RNA Profiling of Pooled Genetic Screens. Cell 167 (7), 1853–1866.e17. URL 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.038 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M, Gingeras TR, December 2012. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29 (1), 15–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudoit S, Fridlyans J, Speed TP, 2002. Comparison of discrimination methods for the classification of tumors using gene expression data. Journal of the American Statistical Association 97 (457), 77–87. URL http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.114.5140 [Google Scholar]
- Falcon S, Gentleman R, January 2007. Using GOstats to test gene lists for GO term association. Bioinformatics 23 (2), 257–258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D-F, Doolittle RF, 1987. Progressive Sequence Alignment as a Prerequisite to Correct Phylogenetic Trees. J Mol Evol, 351–360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin K, Stegle O, Reik W, 2017. Single-cell epigenomics: Recording the past and predicting the future. Science 358 (6359), 60–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goltsev Y, Samusik N, Kennedy-Darling J, Bhate S, Hale M, Vazquez G, Black S, Nolan GP, 2018. Deep Profiling of Mouse Splenic Architecture with CODEX Multiplexed Imaging. Cell 174 (4), 968–981.e15. URL 10.1016/j.cell.2018.07.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grün D, Muraro MJ, Boisset J-C, Wiebrands K, Lyubimova A, Dharmadhikari G, van den Born M, van Es J, Jansen E, Clevers H, de Koning EJP, van Oudenaarden A, August 2016. De novo prediction of stem cell identity using Single-Cell transcriptome data. Cell Stem Cell 19 (2), 266–277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafemeister C, Satija R, March 2019. Normalization and variance stabilization of single-cell RNA-seq data using regularized negative binomial regression. URL https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/576827v1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haghverdi L, Lun ATL, Morgan MD, Marioni JC, April 2018. Batch effects in single-cell RNA-sequencing data are corrected by matching mutual nearest neighbors. Nature Biotechnology 36 (5), 421–427. URL https://doi.org/10.1038%2Fnbt.4091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahne F, Ivanek R, 2016. Statistical Genomics: Methods and Protocols Springer New York, New York, NY, Ch: Visualizing Genomic Data Using Gviz and Bioconductor, pp. 335–351. URL 10.1007/978-1-4939-3578-9_16 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern KB, Shenhav1 R, Matcovitch-Natan O, Toth B, Lemze D, Golan M, Massasa EE, Baydatch S, Landen S, Moor AE, Brandis A, Giladi A, Stokar-Avihail A, David E, Amit I, Itzkovitz S, 2017. Single-cell spatial reconstruction reveals global division of labour in the mammalian liver. Nature 542, 352–356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz S, Benner C, Spann N, Bertolino E, Lin YC, Laslo P, Cheng JX, Murre C, Singh H, Glass CK, May 2010. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol. Cell 38 (4), 576–589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hie BL, Bryson B, Berger B, July 2018. Panoramic stitching of heterogeneous single-cell transcriptomic data. bioRvix. URL https://doi.org/10.1101%2F371179 [Google Scholar]
- Institute, A., 2018. Allen Brain Data Portal. http://celltypes.brain-map.org/api/v2/well_known_file_download/694413985, accessed: 2018–10-25.
- Karaiskos N, Wahle P, Alles J, Boltengagen A, Ayoub S, Kipar C, Kocks C, Rajewsky N, Zinzen RP, 2017. The Drosophila embryo at single-cell transcriptome resolution. Science. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren L, Bosse M, Marquez D, Angoshtari R, Jain S, Varma S, Yang SR, Kurian A, Van Valen D, West R, Bendall SC, Angelo M, 2018. A Structured Tumor-Immune Microenvironment in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Revealed by Multiplexed Ion Beam Imaging. Cell 174 (6), 1373–1387.e19. URL 10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiselev VY, Yiu A, Hemberg M, April 2018. scmap: projection of singlecell RNA-seq data across data sets. Nature Methods 15 (5), 359–362. URL https://doi.org/10.1038%2Fnmeth.4644 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Manno G, Soldatov R, Zeisel A, Braun E, Hochgerner H, Petukhov V, Lidschreiber K, Kastriti ME, Lonnerberg P, Furlan A, Fan J, Borm LE, Liu Z, van Bruggen D, Guo J, He X, Barker R, Sundstrom E, Castelo-Branco G, Cramer P, Adameyko I, Linnarsson S, Kharchenko PV, 2018. RNA velocity of single cells. Nature 560 (7719), 494–498. URL 10.1038/s41586-018-0414-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake BB, Chen S, Sos BC, Fan J, Kaeser GE, Yung YC, Duong TE, Gao D, Chun J, Kharchenko PV, Zhang K, 2018. Integrative single-cell analysis of transcriptional and epigenetic states in the human adult brain. Nature Biotechnology 36 (1), 70–80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langfelder P, Horvath S, January 2008. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 9 (1), 559 URL 10.1186/1471-2105-9-559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL, 2009. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biology 10 (3). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lara-Astiaso D, Weiner A, Lorenzo-Vivas E, Zaretsky I, Jaitin DA, David E, Keren-Shaul H, Mildner A, Winter D, Jung S, Friedman N, Amit I, August 2014. Immunogenetics. chromatin state dynamics during blood formation. Science 345 (6199), 943–949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor N, George J, Bolisetty M, Kursawe R, Sun L, Sivakamasundari V, Kycia I, Robson P, Stitzel ML, February 2017. Single-cell transcriptomes identify human islet cell signatures and reveal cell-type-specific expression changes in type 2 diabetes. Genome Res. 27 (2), 208–222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine JH, Simonds EF, Bendall SC, Davis KL, Amir EAD, Tadmor MD, Litvin O, Fienberg HG, Jager A, Zunder ER, Finck R, Gedman AL, Radtke I, Downing JR, Pe’er D, Nolan GP, 2015. Data-Driven Phenotypic Dissection of AML Reveals Progenitor-like Cells that Correlate with Prognosis. Cell 162 (1), 184–197. URL 10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B, Kowalczyk MS, Dionne K, Ashenberg O, Tabaka M, Tickle T, Lee J, Shekhar K, Slyper M, Waldman J, Rozenblatt-Rosen O, Regev A, 2018. HCA Data Portal - Census of Immune Cells. https://preview.data.humancellatlas.org, accessed: 2018–10-25. [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup, August 2009. The sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25 (16), 2078–2079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R, Zhu H, Ruan J, Qian W, Fang X, Shi Z, Li Y, Li S, Shan G, Kristiansen K, Li S, Yang H, Wang J, Wang J, 2012. De novo assembly of human genomes with massively parallel short read sequencing. Genome Research, 265–272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnarsson S, 2018. Linnarsson Lab - Data and code availability. http://linnarssonlab.org/osmFISH/availability, accessed: 2018–10-25. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez R, Regier J, Cole MB, Jordan MI, Yosef N, December 2018. Deep generative modeling for single-cell transcriptomics. Nat. Methods 15 (12), 1053–1058. URL 10.1038/s41592-018-0229-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love MI, Huber W, Anders S, January 2014. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15 (12), 550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lun ATL, McCarthy DJ, Marioni JC, 2016. A step-by-step workflow for low-level analysis of single-cell rna-seq data with bioconductor. F1000Res. 5, 2122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo C, Rivkin A, Zhou J, Sandoval JP, Kurihara L, Lucero J, Castanon R, Nery JR, Pinto-Duarte A, Bui B, Fitzpatrick C, O’Connor C, Ruga S, Van Eden ME, Davis DA, Mash DC, Behrens MM, Ecker JR, 2018. Robust single-cell DNA methylome profiling with snmC-seq2. Nature Communications 9 (1), 7–12. URL 10.1038/s41467-018-06355-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer C, Hafemeister C, Bandler RC, Machold R, Brito RB, Jaglin X, Allaway K, Butler A, Fishell G, Satija R, March 2018. Developmental diversification of cortical inhibitory interneurons. Nature 555 (7697), 457–462. URL https://doi.org/10.1038%2Fnature25999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffit JR, Bambah-Mukku D, Eichhorn SW, Vaughn E, Shekhar K, Perez JD, Rubinstein ND, Hao J, Regev A, Dulac C, Zhuang X, 2018. Molecular, spatial, and functional single-cell profiling of the hypothalamic preoptic region. Science 5324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffitt JR, Bambah-Mukku D, Eichhorn SW, Vaughn E, Shekhar K, Perez JD, Rubinstein ND, Hao J, Regev A, Dulac C, Zhuang X, November 2018. Molecular, spatial and functional single-cell profiling of the hypothalamic preoptic region. Science. URL 10.1126/science.aau5324 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount DM, 2010. ANN: A library for approximate nearest neighbor searching. http://www.cs.umd.edu/~mount/ANN/. [Google Scholar]
- Muraro MJ, Dharmadhikari G, Grün D, Groen N, Dielen T, Jansen E, van Gurp L, Engelse MA, Carlotti F, de Koning EJP, van Oudenaarden A, October 2016. A Single-Cell transcriptome atlas of the human pancreas. Cell Syst 3 (4), 385–394.e3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano T, Lubling Y, Stevens TJ, Schoenfelder S, Yaffe E, Dean W, Laue ED, Tanay A, Fraser P, October 2013. Single-cell Hi-C reveals cell-to-cell variability in chromosome structure. Nature 502 (7469), 59–64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navin N, Kendall J, Troge J, Andrews P, Rodgers L, Mclndoo J, Cook K, Stepansky A, Levy D, Esposito D, Muthuswamy L, Krasnitz A, McCombie WR, Hicks J, Wigler M, 2011. Tumour evolution inferred by single-cell sequencing. Nature 472 (7341), 90–95. URL 10.1038/nature09807 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ntranos V, Yi L, Melsted P, Pachter L, February 2019. A discriminative learning approach to differential expression analysis for single-cell RNA-seq. Nat. Methods 16 (2), 163–166. URL 10.1038/s41592-018-0303-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okhrimenko A, Grün JR, Westendorf K, Fang Z, Reinke S, von Roth P, Wassilew G, Kühl AA, Kudernatsch R, Demski S, Scheibenbogen C, Tokoyoda K, McGrath MA, Raftery M, Serra A, Chang HD, Radbruch A, Dong J, 2014. Human memory T cells from the bone marrow are resting and maintain long-lasting systemic memory. PNAS 111 (25), 9229–9234. URL http://ard.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-205124.184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradis E, Claude J, Strimmer K, January 2004. APE: Analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 20 (2), 289–290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson VM, Zhang KX, Kumar N, Wong J, Li L, Wilson DC, Moore R, Mcclanahan TK, Sadekova S, Klappenbach JA, 2017. Multiplexed quantification of proteins and transcripts in single cells. Nature Biotechnology 35 (10), 936–939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pliner HA, Packer JS, McFaline-Figueroa JL, Cusanovich DA, Daza RM, Aghamirzaie D, Srivatsan S, Qiu X, Jackson D, Minkina A, Adey AC, Steemers FJ, Shendure J, Trapnell C, September 2018. Cicero predicts cis-regulatory DNA interactions from Single-Cell chromatin accessibility data. Mol. Cell 71 (5), 858–871.e8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissl S, Fang R, Huang H, Zhao Y, Raviram R, Gorkin DU, Zhang Y, Sos BC, Afzal V, Dickel DE, Kuan S, Visel A, Pennacchio LA, Zhang K, Ren B, 2018. Single-nucleus analysis of accessible chromatin in developing mouse forebrain reveals cell-type-specific transcriptional regulation. Nature Neuroscience 21 (3), 432–439. URL http://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-018-0079-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu X, Mao Q, Tang Y, Wang L, Chawla R, Pliner HA, Trapnell C, October 2017. Reversed graph embedding resolves complex single-cell trajectories. Nat. Methods 14 (10), 979–982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan AR, Hall IM, March 2010. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 26 (6), 841–842. URL mailto:http://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&id=20110278&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks?subject=http://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&id=20110278&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- R Testi JHP, Lanier LL, 1989. T cell activation via Leu-23 (CD69). J Immunol 143, 1123–1128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raina R, Battle A, Lee H, Packer B, Ng AY, 2007. Self-taught Learning: Transfer Learning from Unlabeled Data. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning. [Google Scholar]
- Raj B, Wagner DE, McKenna A, Pandey S, Klein AM, Shendure J, Gagnon JA, Schier AF, 2018. Simultaneous single-cell profiling of lineages and cell types in the vertebrate brain. Nature Biotechnology 36 (5), 442–450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramani V, Deng X, Qiu R, Gunderson KL, Steemers FJ, Disteche CM, Noble WS, Duan Z, Shendure J, January 2017. Massively multiplex single-cell Hi-C. Nat. Methods 14 (3), 1–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez F, Ryan DP, Grüning B, Bhardwaj V, Kilpert F, Richter AS, Heyne S, Dündar F, Manke T, July 2016. deeptools2: a next generation web server for deep-sequencing data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 44 (W1), W160–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regev A, Teichmann S, Lander E, Amit I, Benoist C, Birney E, Bodenmiller B, Campbell P, Carninci P, Clatworthy M, Clevers H, Deplancke B, Dunham I, Eberwine J, Eils R, Enard W, Farmer A, Fugger L, Göttgens B, Hacohen N, Haniffa M, Hemberg M, Kim S, Klenerman P, Kriegstein A, Lein E, Linnarsson S, Lundberg E, Lundeberg J, Majumder P, Marioni J, Merad M, Mhlanga M, Nawijn M, Netea M, Nolan G, Pe’er D, Phillipakis A, Ponting C, Quake S, Reik W, Rozenblatt-Rosen O, Sanes J, Satija R, Schumacher T, Shalek A, Shapiro E, Sharma P, Shin J, Stegle O, Stratton M, Stubbington M, Theis F, Uhlen M, van OA, Wagner A, Watt F, Weissman J, Wold B, Xavier R, Yosef N, December 2017. The Human Cell Atlas. Elife 6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw PJ, November 1987. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Safra M, Sas-Chen A, Nir R, Winkler R, Nachshon A, Bar-Yaacov D, Erlacher M, Rossmanith W, Stern-Ginossar N, Schwartz S, 2017. The mlA landscape on cytosolic and mitochondrial mRNA at single-base resolution. Nature 551 (7679), 251–255. URL 10.1038/nature24456 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satija R, Farrell J. a., Gennert D, Schier AF, Regev A, 2015. Spatial reconstruction of single-cell gene expression data. Nature Biotechnology 33 (5). URL http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/nbt.3192 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato TK, Panda S, Miraglia LJ, Reyes TM, Rudic RD, McNamara P, Naik KA, FitzGerald GA, Kay SA, Hogenesch JB, August 2004. A functional genomics strategy reveals Rora as a component of the mammalian circadian clock. Neuron 43 (4), 527–537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A, Macosko EZ, Wysoker A, Brumbaugh S, Kulp D, Mccarroll SA, Saunders A, Macosko EZ, Wysoker A, Goldman M, Krienen FM, 2018. Molecular Diversity and Specializations among the Cells of the Adult Mouse Brain. Cell 174 (4), 1015–1030.e16. URL 10.1016/j.cell.2018.07.028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaum N, Karkanias J, Neff NF, May AP, Quake SR, Wyss-Coray T, Darmanis S, Batson J, Botvinnik O, Chen MB, Chen S, Green F, Jones RC, Maynard A, Penland L, Pisco AO, Sit RV, Stanley GM, Webber JT, Zanini F, Baghel AS, Bakerman I, Bansal I, Berdnik D, Bilen B, Brownfield D, Cain C, Chen MB, Chen S, Cho M, Cirolia G, Conley SD, Darmanis S, Demers A, Demir K, de Morree A, Divita T, du Bois H, Dulgeroff LBT, Ebadi H, Espinoza FH, Fish M, Gan Q, George BM, Gillich A, Green F, Genetiano G, Gu X, Gulati GS, Hang Y, Hosseinzadeh S, Huang A, Iram T, Isobe T, Ives F, Jones RC, Kao KS, Karnam G, Kershner AM, Kiss BM, Kong W, Kumar ME, Lam JY, Lee DP, Lee SE, Li G, Li Q, Liu L, Lo A, Lu W-J, Manjunath A, May AP, May KL, May OL, Maynard A, McKay M, Metzger RJ, Mignardi M, Min D, Nabhan AN, Neff NF, Ng KM, Noh J, Patkar R, Peng WC, Penland L, Puccinelli R, Rulifson EJ, Schaum N, Sikandar SS, Sinha R, Sit RV, Szade K, Tan W, Tato C, Tellez K, Travaglini KJ, Tropini C, Waldburger L, van Weele LJ, Wosczyna MN, Xiang J, Xue S, Youngyunpipatkul J, Zanini F, Zardeneta ME, Zhang F, Zhou L, Bansal I, Chen S, Cho M, Cirolia G, Darmanis S, Demers A, Divita T, Ebadi H, Genetiano G, Green F, Hosseinzadeh S, Ives F, Lo A, May AP, Maynard A, McKay M, Neff NF, Penland L, Sit RV, Tan W, Waldburger L, Youngyunpipatkul J, Batson J, Botvinnik O, Castro P, Croote D, Darmanis S, DeRisi JL, Karkanias J, Pisco AO, Stanley GM, Webber JT, Zanini F, Baghel AS, Bakerman I, Batson J, Bilen B, Botvinnik O, Brownfield D, Chen MB, Darmanis S, Demir K, de Morree A, Ebadi H, Espinoza FH, Fish M, Gan Q, George BM, Gillich A, Gu X, Gulati GS, Hang Y, Huang A, Iram T, Isobe T, Karnam G, Kershner AM, Kiss BM, Kong W, Kuo CS, Lam JY, Lehallier B, Li G, Li Q, Liu L, Lu W-J, Min D, Nabhan AN, Ng KM, Nguyen PK, Patkar R, Peng WC, Penland L, Rulifson EJ, Schaum N, Sikandar SS, Sinha R, Szade K, Tan SY, Tellez K, Travaglini KJ, Tropini C, van Weele LJ, Wang BM, Wosczyna MN, Xiang J, Yousef H, Zhou L, Batson J, Botvinnik O, Chen S, Darmanis S, Green F, May AP, Maynard A, Pisco AO, Quake SR, Schaum N, Stanley GM, Webber JT, Wyss-Coray T, Zanini F, Beachy PA, Chan CKF, de Morree A, George BM, Gulati GS, Hang Y, Huang KC, Iram T, Isobe T, Kershner AM, Kiss BM, Kong W, Li G, Li Q, Liu L, Lu W-J, Nabhan AN, Ng KM, Nguyen PK, Peng WC, Rulifson EJ, Schaum N, Sikandar SS, Sinha R, Szade K, Travaglini KJ, Tropini C, Wang BM, Weinberg K, Wosczyna MN, Wu SM, Yousef H, Barres BA, Beachy PA, Chan CKF, Clarke MF, Darmanis S, Huang KC, Karkanias J, Kim SK, Krasnow MA, Kumar ME, Kuo CS, May AP, Metzger RJ, Neff NF, Nusse R, Nguyen PK, Rando TA, Sonnenburg J, Wang BM, Weinberg K, Weissman IL, Wu SM, Quake SR, Wyss-Coray T, The Tabula Muris Consortium, Overall coordination, Logistical coordination, Organ collection and processing, Library preparation and sequencing, Computational data analysis, Cell type annotation, Writing group, Supplemental text writing group, Principal investigators, October 2018. Single-cell transcriptomics of 20 mouse organs creates a tabula muris. Nature. URL 10.1038/s41586-018-0590-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segerstolpe Å, Palasantza A, Eliasson P, Andersson EM, Andréasson AC, Sun X, Picelli S, Sabirsh A, Clausen M, Bjursell MK, Smith DM, Kasper M, Ämmälä C, Sandberg R, 2016. Single-Cell Transcriptome Profiling of Human Pancreatic Islets in Health and Type 2 Diabetes . Cell Metabolism 24 (4), 593–607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar K, Lapan S, Whitney I, Tran N, Macosko E, Kowalczyk M, Adiconis X, Levin J, Nemesh J, Goldman M, McCarroll S, Cepko C, Regev A, Sanes J, August 2016. Comprehensive Classification of Retinal Bipolar Neurons by Single-Cell Transcriptomics. Cell 166, 1308–1323.e30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOMA, 2018. Seattle Organismal Molecular Atlases (SOMA) Data Portal - Mouse sci-ATAC-seq Atlas. http://atlas.gs.washington.edu/mouse-atac/data/, accessed: 2018–10-25.
- Spanjaard B, Hu B, Mitic N, Olivares-Chauvet P, Janjuha S, Ninov N, Junker JP, 2018. Simultaneous lineage tracing and cell-type identification using CrIsPr-Cas9-induced genetic scars. Nature Biotechnology 36 (5), 469–473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein-O’Brien GL, Clark BS, Sherman T, Zibetti C, Hu Q, Sealfon R, Liu S, Qian J, Colantuoni C, Blackshaw S, Goff LA, Fertig EJ, 2018. Decomposing cell identity for transfer learning across cellular measurements, platforms, tissues, and species. bioRxiv. [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckius M, Hafemeister C, Stephenson W, Houck-Loomis B, Chattopadhyay PK, Swerdlow H, Satija R, Smibert P, July 2017. Simultaneous epitope and transcriptome measurement in single cells. Nature Methods 14 (9), 865–868. URL https://doi.org/10.1038%2Fnmeth.4380 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckius M, Zheng S, Houck-Loomis B, Hao S, Yeung BZ, Mauck WM, Smibert P, Satija R, December 2018. Cell hashing with barcoded antibodies enables multiplexing and doublet detection for single cell genomics Genome Biol. 19 (1), 224 URL 10.1186/s13059-018-1603-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey JD, Tibshirani R, August 2003. Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 100 (16), 9440–9445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart T, Satija R, January 2019. Integrative single-cell analysis. Nat. Rev. Genet URL 10.1038/s41576-019-0093-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson V, Natarajan KN, Ly L-H, Miragaia RJ, Labalette C, Macaulay IC, Cvejic A, Teichmann SA, 2017. Power analysis of single-cell RNA-sequencing experiments. Nature Methods 14 (4), 381–387. URL http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/nmeth.4220 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson V, Vento-Tormo R, Teichmann SA, 2018. Exponential scaling of single-cell RNA-seq in the past decade. Nature Protocols 13 (4), 599–604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syken J, Shatz CJ, October 2003. Expression of T cell receptor beta locus in central nervous system neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 100 (22), 13048–13053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanay A, Regev A, 2017. Scaling single-cell genomics from phenomenology to mechanism. Nature 541 (7637), 331–338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasic B, Menon V, Nguyen TN, Kim TK, Jarsky T, Yao Z, Levi B, Gray LT, Sorensen SA, Dolbeare T, Bertagnolli D, Goldy J, Shapovalova N, Parry S, Lee C, Smith K, Bernard A, Madisen L, Sunkin SM, Hawrylycz M, Koch C, Zeng H, 2016. Adult mouse cortical cell taxonomy revealed by single cell transcriptomics. Nature Neuroscience 19 (2), 335–346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasic B, Yao Z, Graybuck LT, Smith KA, Nguyen TN, Bertagnolli D, Goldy J, Garren E, Economo MN, Viswanathan S, Penn O, Bakken T, Menon V, Miller J, Fong O, Hirokawa KE, Lathia K, Rimorin C, Tieu M, Larsen R, Casper T, Barkan E, Kroll M, Parry S, Shapovalova NV, Hirschstein D, Pendergraft J, Sullivan HA, Kim TK, Szafer A, Dee N, Groblewski P, Wickersham I, Cetin A, Harris JA, Levi BP, Sunkin SM, Madisen L, Daigle TL, Looger L, Bernard A, Phillips J, Lein E, Hawrylycz M, Svoboda K, Jones AR, Koch C, Zeng H, November 2018. Shared and distinct transcriptomic cell types across neocortical areas. Nature 563 (7729), 72–78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani R, Hastie T, Narasimhan B, Chu G, 2003. Class prediction by nearest shrunken centroids, with applications to DNA microarrays. Statistical Science 18 (1), 104–117. [Google Scholar]
- Torre E, Dueck H, Shaffer S, Gospocic J, Gupte R, Bonasio R, Kim J, Murray J, Raj A, 2018. Rare Cell Detection by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing as Guided by Single-Molecule RNA FISH. Cell Systems 6 (2), 171–179.e5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL, 2009. TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25 (9), 1105–1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk D, Sharma R, Nainys J, Yim K, Kathail P, Carr AJ, Burdziak C, Moon KR, Chaffer CL, Pattabiraman D, Bierie B, Mazutis L, Wolf G, Krishnaswamy S, Pe’er D, 2018. Recovering Gene Interactions from Single-Cell Data Using Data Diffusion. Cell 174 (3), 716–729.e27. URL https://doi.org/10.10167j.cell.2018.05.061 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatadri PS, Lee CC, July 2014. Differential expression of mGluR2 in the developing cerebral cortex of the mouse. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng 7 (13), 1030–1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitak SA, Torkenczy KA, Rosenkrantz JL, Fields AJ, Christiansen L, Wong MH, Carbone L, Steemers FJ, Adey A, 2017. Sequencing thousands of single-cell genomes with combinatorial indexing. Nature Methods 14 (3), 302–308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, 2018. Data-STARmap Resources. https://www.starmapresources.com/data/, accessed: 2018–10-25.
- Wang C, Mahadevan S, 2010. Heterogeneous Domain Adaptation Using Manifold Alignment. In: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence pp. 1541–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, Allen W, Wright M, Sylwestrak E, Samusik N, Vesuna S, Evans K, Liu C, Ramakrishnan C, Liu J, Nolan G, Bava F, Deisseroth K, July 2018. Three-dimensional intact-tissue sequencing of single-cell transcriptional states. Science 361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch J, Kozareva V, Ferreira A, Vanderburg C, Martin C, Macosko E, November 2018. Integrative inference of brain cell similarities and differences from single-cell genomics. URL https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2018/11/02/459891 [Google Scholar]
- Witten DM, Tibshirani R, Hastie T, 2009. A penalized matrix decomposition, with applications to sparse principal components and canonical correlation analysis. Biostatistics 10 (3), 515–534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolock SL, Lopez R, Klein AM, April 2019. Scrublet: Computational identification of cell doublets in Single-Cell transcriptomic data. Cell Systems 0 (0). URL http://www.cell.com/article/S2405471218304745/abstract [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng GXY, Terry JM, Belgrader P, Ryvkin P, Bent ZW, Wilson R, Ziraldo SB, Wheeler TD, McDermott GP, Zhu J, Gregory MT, Shuga J, Montesclaros L, Underwood JG, Masquelier DA, Nishimura SY, Schnall-Levin M, Wyatt PW, Hindson CM, Bharadwaj R, Wong A, Ness KD, Beppu LW, Deeg HJ, McFarland C, Loeb KR, Valente WJ, Ericson NG, Stevens EA, Radich JP, Mikkelsen TS, Hindson BJ, Bielas JH, January 2017. Massively parallel digital transcriptional profiling of single cells. Nat. Commun 8, 1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data File S1, related to Figure 4. Protein and gene expression patterns in Human bone marrow cells.
Page 2 represents the expression level of all 25 measured proteins in human bone marrow CITE-seq experiment. Cells are projected into two dimensions using UMAP, and colored based on normalized antibody-derived tag (ADT) counts for each protein (range 10th-99th expression percentile for each protein). Page 3 represents the predicted protein expression for all 25 proteins measured in the CITE-seq experiment in the Human Cell Atlas bone marrow dataset. Cells are projected into two dimensions using UMAP, and colored based on predicted normalized antibody-derived tag (ADT) counts for each protein (range 40th-99th expression percentile for each protein). Page 4 represents the expression of celltype marker genes in HCA bone marrow cells. AVP: marker of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC). LMO4: basophil progenitor (Bas). PF4: megakaryocyte progenitor (MkP). BLVRB: erythroid progenitor (Er). MME: common lymphoid progenitor (CLp). DERL3: plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC). CLEC9A: conventional dendritic cell 1 (cDC1). CDC1: convensional dendritic cell 2 (cDC2). MPO: granulocyte macrophage progenitor (GMP). AZU1: neutrophil progenitor (Neu). CD14: CD14+ monocyte (CD14 Mono). FCGR3A: CD16+ monocyte (CD16 Mono). VREB3: immature B cell (Immature B). MS4A1: mature B cell (Mature B). CD79A: immature / mature B cell (Immature/Mature B). IGKC: plasma cell (Plasma). PF4: megakaryocytes (Mk). XCL1: CD56+ natural killer cells (NK Bright). CD8A: CD8+ T cells (CD8 T). CD4: CD4+ T cells (CD4 T). SH2D1A: pre-T cell (pre-T). Cells are projected into two dimensions using UMAP, and colored based on normalized RNA counts for each gene (range 0–99th expression percentile for each gene).
Data File S2, related to Figure 5. Spatial gene expression patterns in the mouse brain.
Page 2 represents the spatial patterns of gene expression in the mouse brain (STARMap replicate 2) (A) Measured and predicted gene expression patterns for a subset of genes measured in the STARmap experiment, for the second biological replicate (as for Figure 5B). (B) Gene expression patterns for four genes not measured by STARmap (as for Figure 5C). Page 3 represents the spatial imputation of gene expression using either the Drop-seq or SMART-seq2 dataset as the scRNA-seq reference. Predicted gene expression patterns for leave-one-out cross validations of 8 genes (same genes shown in 5B) for STARmap replicate 1 (A) and replicate 2 (B).
Figure S1, related to Figure 2. Integration of human pancreatic islet and mouse retinal bipolar cells
(A-C) UMAP plots of 14,890 human pancreatic islet cells across 8 datasets before (A) and after (B) integration. After integration, cells were clustered and labeled based on a previously annotated reference dataset (C), allowing for detection of both common and rare subpopulations of islet cells across integrated datasets. (D) For verification of the cell type labels, we plot the top differentially expressed gene markers for each cluster, broken down by original dataset and observe consistent patterns of cell-type specific expression. To facilitate the visualization of rare populations, we downsample the heatmap to show at most 25 cells per cluster per dataset. (E, F) tSNE plots of 23,725 mouse retinal bipolar cells after integration with Seurat V3, Seurat V2, mnnCorrect, and Scanorama. For each of these analyses, a single cell type was removed from each of the 6 replicates prior to integration (Table S1A).
Figure S2, related to Figure 2. Integration of Tabula Muris mouse cell atlas datasets
(A-C) tSNE plots of the integrated mouse cell atlas datasets grouped by (A) technology, (B) tissue, and (C) whether the tissue was profiled by SMART-Seq (FACS) only. After integration, cells from tissues profiled by both 10x and FACS-sorted SMART-seq cluster together, where as cells from tissues uniquely profiled by FACS are not blended into other tissue types, demonstrating robustness to non-overlapping populations. (D) Further underscoring robustness, cells from tissues profiled across technologies achieve high mixing whereas cells profiled using only one technology have substantially lower scores. The internal dataset structure for both subsets is preserved in integrated analysis. (E-F) By integrating the datasets we can detect exceedingly rare cell populations that are present in multiple tissues, such as (E) mesothelial cells and (F) plasmacytoid dendritic cells. We can also identify both shared and divergent gene expression markers for these populations across tissues. (G) Integration of 274,932 human bone marrow cells generated by the Human Cell Atlas project, from eight different human donors. (H) Enriched gene ontology terms for gene biological processes and molecular functions for CD69+ marker genes identified from HCA bone marrow scRNA-seq data. Gene ontology analysis was performed using GOstats.
Figure S3, related to Figure 3. Examination of non-overlapping scATAC-seq cells in multi-modal co-embedding
(A) UMAP visualization of scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq cells following multimodal integration. Cells are colored by dataset of origin (left), and the unknown group of scATAC-seq cells that failed to mix with the scRNA-seq cells are highlighted in red (right). (B) Expression of cell-type-specific marker genes in the unknown population and in other groups of cells, as annotated by the original authors (Cusanovich et al. (2018), Cell). The unknown population of scATAC-seq cells co-express gene activity markers that are otherwise mutually exclusive, suggesting that they may represent scATAC-seq multiplets. (C) UMAP embedding of human PBMCs profiled using 10x Genomics scRNA-seq, with cells colored by their annotated cell type. (D) Joint visualization of scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq PBMCs, with cells colored by their predicted cell type. (E) As for (D), with cells colored by their dataset of origin. (F) Chromatin accessibility profiles for computationally-sorted human PBMC subsets. X-axis scale is indicated by scale bars above each genomic region. Y-axis limits were set individually for each locus to enhance visualization. However, within each locus all pseudo-bulk tracks are on a consistent scale, and all FACS-sorted bulk tracks are on a consistent scale, to enable a visual comparison. (G) Genome-wide agreement between experimentally and computationally-sorted immune cell chromatin accessibility profiles. Pearson correlation between peak accessibility (normalized coverage within peak) between cell types sorted experimentally (by FACS; Corces et al. [2016]) and computationally. Corresponding cell types in the single-cell and bulk datasets are highlighted in black boxes. (H) Examination of non-overlapping scATAC-seq cells in the joint visualization with scRNA-seq cells. Genomic blacklist region read counts for the non-overlapping cluster are shown, in comparison to counts for all other cells in the dataset combined. (I) Examination of a second non-overlapping scATAC-seq population, showing mean expression for each gene in the non-overlapping population and all other CD14+ Monocytes.
Figure S4, related to Figure 5. Validation of predicted gene expression patterns and cell type labels.
(A) Horizontally-compressed STARmap cells with predicted cell type transferred from the SMART-seq4 dataset (as for Figure 5F). (B) External validation of predicted gene expression patterns. in-situ hybridization images from the Allen Brain Atlas for Tesc and Pvrl3 alongside predictions for the same genes in STARmap cells. (C) UMAP co-embedding of scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq cells following multi-modal integration, colored by predicted cell type in each dataset. (D) As for (C), colored by dataset of origin. (E) UMAP on original STARmap data, with cells colored by the annotation given by the original authors (Wang et al. (2018), Science). (F) As for (E), with cells colored by their predicted identity. For the UMAP plots using the original STARmap data only, we are not able to recover the same level of structure that is suggested by the heatmap in Figure 5G, demonstrating the value of transferring cell type classifications.
Figure S5, related to Figure 5. Considerations for the integration of scRNA-seq and STARmap data
(A) Distribution of correlations between SMART-seq2 and Drop-seq-based gene expression predictions for cell type marker genes. (B) Genes that exhibited low agreement (correlation <0.5) between the two predictions tended to be lowly expressed, and rarely detected (<10% cells) in the Drop-seq dataset. Boxplot shows the detection rate of genes with greater or less than 0.5 correlation. (C) Normalized expression values for Cux2 in both the Drop-seq and the SMART-seq2 datasets showing different relative expression in the L2/3 IT and L4 clusters. (D) Representative scatter plots showing the correlation of Drop-seq and SMART-seq2 imputed values. (E) Correlation of imputed gene expression measurements computed using a downsampled number of genes versus the full set of genes under a random downsampling approach. (F) Scatter plot showing a strong positive relationship between how accurately a gene can be imputed versus its redundancy in the scRNA-seq dataset. (G) Comparison of a random versus guided feature downsampling approach in terms of the correlation of imputed expression measurement saturation.
Table S1, related to Figure 2. Cell type holdout information for integration evaluation cases.
Data Availability Statement
Our integration methods are implemented in Seurat v3, available on CRAN (https://cran.r-project.org/package=Seurat) and GitHub (https://github.com/satijalab/seurat). Raw CITE-seq and bulk RNA-seq reads are available through SRA (SRP188993), and processed expression matrices through GEO (GSE128639).