Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of primary site surgery (PSS) on elderly patients (≥65 years) with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (pNET) distant metastasis.
Patients and methods
We reviewed Surveillance Epidemiology and the End Results database for elderly patients with distant pNET from 1973 to 2015. The variables and survival outcomes of patients with PSS were compared with that of patients with no PSS. After propensity score matching, the survival outcome was compared again between the two groups. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard model was used to identify variables associated with cancer-specific and overall survival. Four sub-groups were divided according to the age and differentiation: 1) age 65–74 years+ well or moderately differentiated; 2) age ≥75 years+ well or moderately differentiated; 3) age 65–74 years+ poorly differentiated or undifferentiated; and 4) age ≥75 years+ poorly differentiated or undifferentiated. Cancer-specific survival was compared between the patients with and without PSS in the above each group.
Results
A total of 210 elderly patients with distant pNET were finally confirmed. Of which, 148 patients did not undergo PSS, while 62 patients underwent PSS. Being female (p=0.049), locating on body/tail of pancreas (p=0.006), and well or moderately differentiated (p=0.032) were more likely received PSS. The patients underwent PSS had better survival outcomes both before and after propensity score matching. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard analysis proves PSS and higher histological grade to be protective and risk factors. PSS may improve cancer specific survival in patients of group 1), and no improvement was observed in patients of the other three sub-groups.
Conclusion
Not all elderly patients with pNET distant metastasis could benefit from PSS. Patients aged 65–74 years with well or moderately differentiated may benefit from primary lesion surgery, but should be evaluated carefully. Prospective randomized controlled trials are worth performing.
Keywords: primary site surgery, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, distant metastasis, elderly patients
Introduction
As a rare neoplasm, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (pNET) originates from pancreatic neuroendocrine cells and may occur in various organs, including lung, gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, etc.1,2 pNETs represent approximately 7% of all NETs and account for 1–2% of all pancreatic malignancies.1–3 Over the past several decades, the incidence of pNET has been increasing in the United States.4 pNETs have great variance in biological behavior. Most of the pNETs have low malignant behavior and slow growth rate, but some of them possess high ability of invasiveness.5 Up to 60–80% of patients develop distant metastasis during the course of this disease.6,7 Based on the data from Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database from 1973 to 2015 in the current study, 50.0% of the pNET patients (4212/8422) were distant metastasis at the first diagnosis. Previous studies have revealed that the presence of distant metastatic is one of the strongest predictors for patients’ survival. The 5-year survival rate (13–54%) was significantly worse than patients without liver metastasis (75–99%).8,9
Distant metastatic pNET requires systematic treatment, which includes somatostatin analogs (SSA), molecular targeted therapy, chemotherapy, peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT), etc.10 Previous studies have indicated that the primary site surgery (PSS) can improve the survival of patients with distant metastatic pNET.11,12 With the aggravation of social aging, the number of elderly cancer patients is increasing gradually. Elderly patients account for a considerable proportion of cancerous cases.13,14 In the current study, elderly patients (≥65 years) account for 40.7% (3431/8422) of all pNET patients between 1973 and 2015 in SEER database. In the distant metastatic cases, elderly patients (≥65 years) account for 41.4% (1743/4212) in SEER database. The elderly patients have special physiological and pathological characteristics, such as more complications, poor tolerance to surgery, and high mortality after surgery.15 Is it justifiable to perform the PSS in elderly patients with distant metastasis of pNET, which is seldom elucidated in the existing literature. We performed a study solely focusing on the elderly patients (≥65 years) with pNET distant metastasis based on the SEER database, to investigate the effect of PSS on elderly patients with pNET distant metastasis.
Patients and methods
Patient demographic and clinical data
We queried SEER database for patients with pNET from 1973 to 2015, using SEER*Stat software version 8.3.5. The data accessed from SEER are freely available. PNET was defined as including the following International Classification of Diseases for Oncology third edition (ICD-O3) codes: 8150/3, 8151/3, 8152/3, 8153/3, 8155/3, 8156/3, 8240/2, 8240/3, 8241/3, 8242/3, 8243/3, 8246/2, 8246/3, 8249/3. All pancreatic anatomical sites were included (C25.0-C25.9) in our study. Patients with stage IV pNET diagnosed between 1973 and 2015 were selected. Only the cases with diagnoses based on histological studies were included, while cases whose diagnoses relied only on autopsies or were detailed only on death certificates were excluded. A total of 8422 patients suffered pNET, and 4212 patients have distant metastasis.
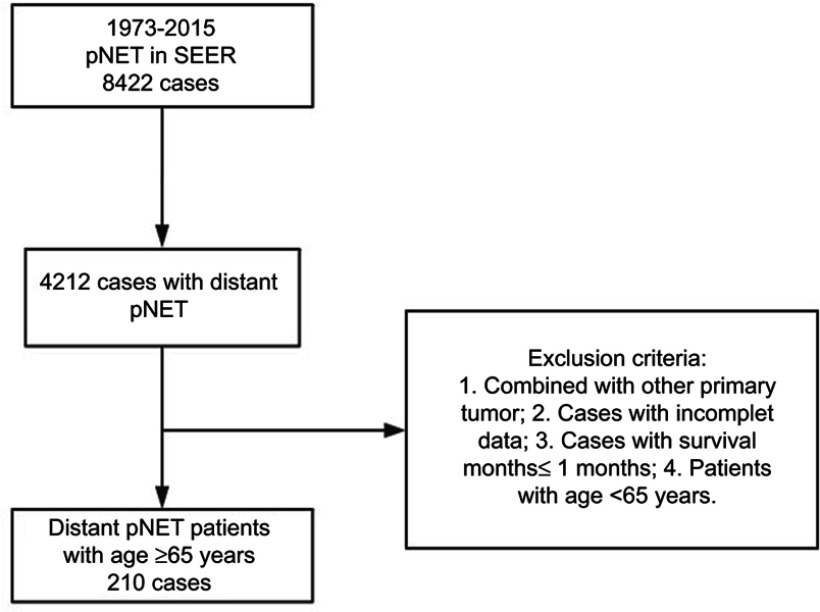
Patients exclusion criteria include (see Figure 1):
Figure 1.
Patient screening process.
Abbreviations: pNET, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; SEER, Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results.
Combined with other primary tumor;
Incomplete data;
Survival month ≤1 month;
Patients with age <65 years.
Patient data collection and outcome measurement
We collected patients demographic and tumor characteristics concerning age, gender, race,primary site of tumor, histological grade, year of diagnosis, tumor size, PSS, marital status, survival months, SEER cause-specific survival, and overall survival. Cancer-specific survival was defined as the duration from diagnosis to death attributable to the pNET. Overall survival was defined as the duration from diagnosis to death from any cause.
The variables of patients with PSS were compared with that of patients with no PSS. The overall survival and cancer-specific survival were also compared with log-rank test between the two groups before and after the propensity score matching of the variables. The primary survival outcome measure was cancer-specific survival. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard model was used to identify variables associated with cancer-specific survival and overall survival before and after propensity score matching.
In order to further study the effects of PSS on different age and differentiation group, patients were further divided into four sub-groups: 1) age 65–74 years+ well or moderately differentiated; 2) age ≥75 years+ well or moderately differentiated; 3) age 65–74 years+ poorly differentiated or undifferentiated; and 4) age ≥75 years+ poorly differentiated or undifferentiated. Cancer-specific survival was compared between the patients with PSS and the patients without PSS using Kaplan–Meier survival analysis with log-rank test and multivariable Cox proportional analysis in the above each group. The cutoff value of age was identified by X-tile.16
The data accessed from SEER are freely available. This study does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. In addition, according to the guidelines of the government of the United States, data released through the SEER database donot require informed patient consent.
Statistical analyses
A two-sided p<0.05 was considered statistically significant and the analyses were performed by IBM SPSS Statistics 22.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and GraphPad Prism version 7.0 (GraphPad Software, USA). Pearson and Fisher chi-square tests were performed before and after PSM to compare the characteristics of patients with and without PSS. To balance the potential baseline confounding variables between the two groups, a propensity score matching method was performed by the “MatchIt” R package and the “nearest neighbor matching” method (ratio=1:1). Kaplan–Meier survival analysis with a log-rank test was performed to plot survival curves and to calculate the cancer-specific survival and overall survival rate. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard model was used to identify variables associated with cancer-specific survival and overall survival before and after propensity score matching. HRs were presented with 95% CI.
Result
Patient clinico-pathological features
A total of 210 patients were finally confirmed after screened out the unqualified patients. Of which, 148 elderly pNET patients with distant metastasis did not undergo PSS, while 62 patients underwent PSS. Being female (p=0.049), locating on body/tail of pancreas (p=0.006), and histological grade of well or moderately differentiated (p=0.032) were more likely received PSS (Table 1). After propensity score matching, all variables were comparable between the two groups (Table 1).
Table 1.
Characteristics of patients older than 65 years included in the study
| Variables | Before PSM | After PSM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPSS, N=148 | PSS, N=62 | p | NPSS, N=62 | PSS, N=62 | p | |
| Age | 0.265 | 0.091 | ||||
| 65–75 years | 95 (64.2%) | 45 (72.6%) | 35 (56.5%) | 45 (72.6%) | ||
| ≥75 years | 53 (35.8%) | 17 (27.4%) | 27 (43.5%) | 17 (27.4%) | ||
| Gender | 0.049 | 0.281 | ||||
| Male | 89 (60.1%) | 28 (45.2%) | 35 (56.5%) | 28 (45.2%) | ||
| Female | 59 (39.9%) | 34 (54.8%) | 27 (43.5%) | 34 (54.8%) | ||
| Race | 0.247 | 0.161 | ||||
| White | 123 (83.1%) | 57 (91.9%) | 50 (80.6%) | 57 (91.9%) | ||
| Black | 16 (10.8%) | 3 (4.8%) | 9 (14.5%) | 3 (4.8%) | ||
| Other | 9 (6.1%) | 2 (3.2%) | 3 (4.8%) | 2 (3.2%) | ||
| Marital status | 0.639 | 0.855 | ||||
| Married | 96 (64.9%) | 38 (61.3%) | 36 (58.1%) | 38 (61.3%) | ||
| Unmarried | 52 (35.1%) | 24 (38.7%) | 26 (41.9%) | 24 (38.7%) | ||
| Year of diagnosis | 0.875 | 0.699 | ||||
| 1973–2009 | 53 (35.8%) | 21(33.9%) | 18 (29.0%) | 21 (33.9%) | ||
| 2010–2015 | 95 (64.2%) | 41 (66.1%) | 44 (71.0%) | 41 (66.1%) | ||
| Tumor site | 0.006 | 0.517 | ||||
| Head | 58 (39.2%) | 12 (19.4%) | 16 (25.8%) | 12 (19.4%) | ||
| Body/tail | 62 (41.9%) | 42(67.7%) | 35 (56.5%) | 42 (67.7%) | ||
| Overlap | 21 (14.2%) | 7 (11.3%) | 8 (12.9%) | 7 (11.3%) | ||
| Other | 7 (4.7%) | 1 (1.6%) | 3 (4.8%) | 1 (1.6%) | ||
| Tumor size | 0.000 | 0.097 | ||||
| ≤4 cm | 48 (32.4%) | 21 (33.9%) | 29 (46.8%) | 21 (33.9%) | ||
| >4 cm | 67 (45.3%) | 41 (66.1%) | 31 (50.0%) | 41 (66.1%) | ||
| Unknown | 33 (22.3%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (3.2%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Histological grade | 0.032 | 1.000 | ||||
| Well/moderately | 97(65.5%) | 50 (80.6%) | 50 (80.6%) | 50 (80.6%) | ||
| Poorly/undifferentiated | 51(34.5%) | 12 (19.4%) | 12 (19.4%) | 12 (19.4%) | ||
Notes: Race: other included American Indian/AK, Native Asian/Pacific Islander. Marital status: unmarried included divorced/separated/single (never married)/unmarried or domestic partner/widowed. Tumor site: “Other” included Islets of langerhans+other specific parts of pancreas+NOS of pancreas.
Abbreviations: PSM, propensity score matching; NPSS, no primary site surgery; PSS, primary site surgery; cm, centimeter.
Logistic regression analysis of characteristics associated with elderly patients (≥65 years) who underwent PSS
The univariate regression analysis for PSS was performed to patients with age ≥65 years (Table 2). The variables with univariate logistic analysis p<0.1 were further analyzed using multivariate logistic regression. Being female (p=0.012, OR: 2.329, 95% CI: 1.204–4.503), and tumor locating at body/tail of pancreas (p=0.001, OR: 3.780, 95% CI: 1.749–8.170) were more likely received PSS, while tumor with histological grade of poorly differentiated/undifferentiated (p=0.040, OR: 0.455, 95% CI: 0.215–0.964) had decreased possibility of receipt of PSS (Table 2).
Table 2.
Logistic regression analysis of characteristics for PSS in elderly patients (≥65 years)
| Variables | Univariate analysis for PSS | Multivariate analysis for PSS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p | OR | 95% CI | p | |
| Age | ||||||
| 65–75 years | 1 (Referent) | |||||
| >75 years | 0.677 | 0.353–1.299 | 0.241 | |||
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Female | 1.832 | 1.007–3.333 | 0.048 | 2.329 | 1.204–4.503 | 0.012 |
| Race | ||||||
| White | 1 (Referent) | |||||
| Black | 0.405 | 0.113–1.444 | 0.163 | |||
| Other | 0.480 | 0.100–2.291 | 0.357 | |||
| Marital status | ||||||
| Married | 1 (Referent) | |||||
| Unmarried | 1.166 | 0.632–2.151 | 0.623 | |||
| Year of diagnosis | ||||||
| 1973–2009 | 1 (Referent) | |||||
| 2010–2015 | 1.089 | 0.584–2.033 | 0.788 | |||
| Tumor site | ||||||
| Head | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Body/tail | 3.274 | 1.570–6.826 | 0.002 | 3.780 | 1.749–8.170 | 0.001 |
| Overlap | 1.611 | 0.560–4.638 | 0.377 | 1.241 | 0.418–3.681 | 0.697 |
| Other | 0.690 | 0.078–6.142 | 0.740 | 0.711 | 0.077–6.535 | 0.763 |
| Histological grade | ||||||
| Well/moderately | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Poorly/undifferentiated | 0.456 | 0.223–0.934 | 0.032 | 0.455 | 0.215–0.964 | 0.040 |
| Tumor size | ||||||
| ≤4 cm | 1 (Referent) | |||||
| >4 cm | 1.399 | 0.735–2.662 | 0.485 | |||
| Unknown | NA | |||||
Note: Variables with univariate analysis p<0.1 underwent further multivariate analysis.
Abbreviation: PSS, primary site surgery.
Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank test, and multivariable Cox proportional hazard analysis before propensity score matching and after propensity score matching
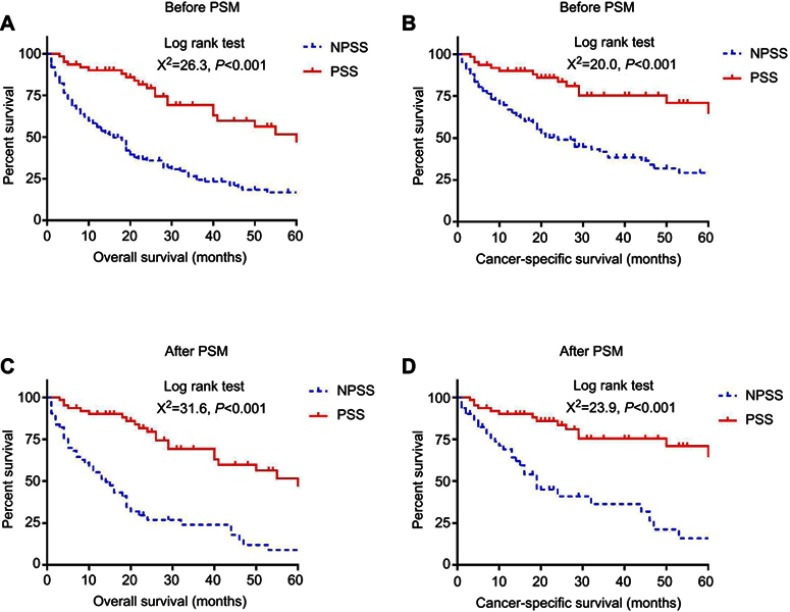
The Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank test proved that PSS in distant metastatic pNET patients with age ≥65 years had better cancer-specific survival and overall survival both before and after propensity score matching (Figure 2). Multivariable Cox proportional hazard analysis was performed for all 210 patients before propensity score matching. Histological grade of poorly differentiated/undifferentiated was risk factor for both overall survival (HR: 3.062, 95% CI: 2.118–4.425, p<0.001) and cancer-specific survival (HR 3.641, 95% CI 2.351–5.640, p<0.001), and PSS was proved to be protective factor for overall survival (HR: 0.392, 95% CI: 0.252–0.612, p<0.001) and cancer-specific survival (HR: 0.362, 95% CI: 0.206–0.637, p<0.001) (see Table 3). After propensity score matching, multivariable Cox proportional hazard analysis was performed for 124 patients. Histological grade of poorly differentiated/undifferentiated was also proved to be risk factor for both overall survival (HR: 4.020, 95% CI: 2.203–7.336, p<0.001) and cancer-specific survival (HR: 6.574, 95% CI: 3.261–13.251, p<0.001), and PSS was also proved to be protective factor for overall survival (HR: 0.212, 95% CI: 0.125–0.360, p<0.001) and cancer-specific survival (HR: 0.210, 95% CI: 0.110–0.403, p<0.001). (See Table 4)
Figure 2.
Overall survival and cancer-specific survival in elderly patients (≥65 years) with metastatic pNET who underwent primary site surgery (PSS) and no primary site surgery (NPSS), before and after propensity score matching (PSM).
Notes: (A) Kaplan–meier analysis for overall survival in elderly patients (≥65 years) who underwent PSS and NPSS before PSM; (B) Kaplan–meier analysis for cancer-specific survival in elderly patients (≥65 years) who underwent PSS and NPSS before PSM; (C) Kaplan–meier analysis for overall survival in elderly patients (≥65 years) who underwent PSS and NPSS after PSM; (D) Kaplan–meier analysis for cancer-specific survival in elderly patients (≥65 years) who underwent PSS and NPSS after PSM.
Table 3.
Multivariate regression analysis of characteristics for survival in elderly patients (≥65 years) before PSM
| Variables | Multivariate analysis for OS | Multivariate analysis for CSS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | |
| Age | ||||||
| 65–75 years | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| >75 years | 1.373 | 0.954–1.977 | 0.088 | 1.231 | 0.775–1.955 | 0.378 |
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Female | 1.028 | 0.678–1.557 | 0.898 | 0.939 | 0.571–1.544 | 0.803 |
| Race | ||||||
| White | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Black | 1.367 | 0.726–2.572 | 0.333 | 1.333 | 0.621–2.859 | 0.460 |
| Other | 1.598 | 0.782–3.269 | 0.199 | 1.767 | 0.777–4.018 | 0.175 |
| Marital status | ||||||
| Married | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Unmarried | 1.228 | 0.852–1.770 | 0.271 | 1.417 | 0.906–2.217 | 0.127 |
| Year of diagnosis | ||||||
| 1973–2009 | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| 2010–2015 | 0.931 | 0.634–1.365 | 0.714 | 1.027 | 0.638–1.651 | 0.913 |
| Tumor site | ||||||
| Head | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Body/tail | 1.104 | 0.734–1.661 | 0.635 | 0.872 | 0.538–1.415 | 0.580 |
| Overlap | 1.226 | 0.692–2.171 | 0.485 | 0.859 | 0.422–1.749 | 0.676 |
| Other | 1.709 | 0.784–3.729 | 0.178 | 1.758 | 0.773–3.997 | 0.178 |
| Histological grade | ||||||
| Well/moderately | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Poorly/undifferentiated | 3.062 | 2.118–4.425 | 0.000 | 3.641 | 2.351–5.640 | 0.000 |
| Tumor size | ||||||
| ≤4 cm | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| >4 cm | 0.862 | 0.568–1.308 | 0.485 | 0.790 | 0.476–1.310 | 0.361 |
| Unknown | 0.798 | 0.463–1.375 | 0.416 | 0.812 | 0.423–1.558 | 0.531 |
| Primary site surgery | ||||||
| No | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Yes | 0.392 | 0.252–0.612 | 0.000 | 0.362 | 0.206–0.637 | 0.000 |
Note: Variables with univariate analysis p<0.1 underwent further multivariate analysis.
Abbreviations: OS, overall survival; CSS, cancer-specific survival; PSM, propensity score matching.
Table 4.
Multivariate regression analysis of characteristics for survival in elderly patients (Table 4: Multfter PSM)
| Variables | Multivariate analysis for OS | Multivariate analysis for CSS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | |
| Age | ||||||
| 65–75 years | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| >75 years | 1.442 | 0.852–2.442 | 0.173 | 1.224 | 0.648–2.311 | 0.533 |
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Female | 1.591 | 0.880–2.877 | 0.125 | 1.378 | 0.688–2.758 | 0.366 |
| Race | ||||||
| White | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Black | 1.371 | 0.602–3.124 | 0.452 | 1.031 | 0.377–2.817 | 0.953 |
| Other | 2.705 | 0.959–7.628 | 0.060 | 3.864 | 1.340–11.143 | 0.012 |
| Marital status | ||||||
| Married | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Unmarried | 1.309 | 0.750–2.288 | 0.344 | 1.370 | 0.694–2.703 | 0.364 |
| Year of diagnosis | ||||||
| 1973–2009 | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| 2010–2015 | 0.909 | 0.482–1.714 | 0.769 | 0.931 | 0.413–2.100 | 0.863 |
| Tumor site | ||||||
| Head | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Body/tail | 0.649 | 0.347–1.214 | 0.176 | 0.664 | 0.303–1.456 | 0.307 |
| Overlap | 0.694 | 0.288–1.670 | 0.414 | 0.530 | 0.164–1.706 | 0.287 |
| Other | 0.423 | 0.129–1.384 | 0.155 | 0.602 | 0.167–2.171 | 0.438 |
| Histological grade | ||||||
| Well/moderately | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Poorly/undifferentiated | 4.020 | 2.203–7.336 | 0.000 | 6.574 | 3.261–13.251 | 0.000 |
| Tumor size | ||||||
| ≤4 cm | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| >4 cm | 1.058 | 0.618–1.813 | 0.836 | 1.087 | 0.548–2.157 | 0.811 |
| Unknown | 0.701 | 0.114–4.324 | 0.702 | 1.070 | 0.162–7.080 | 0.944 |
| Primary site surgery | ||||||
| No | 1 (Referent) | 1 (Referent) | ||||
| Yes | 0.212 | 0.125–0.360 | 0.000 | 0.210 | 0.110–0.403 | 0.000 |
Note: Variables with univariate analysis p<0.1 underwent further multivariate analysis.
Abbreviations: OS, overall survival; CSS, cancer-specific survival; PSM, propensity score matching.
Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank test and multivariable Cox proportional analysis for sub-groups of elderly patients with pNET distant metastasis
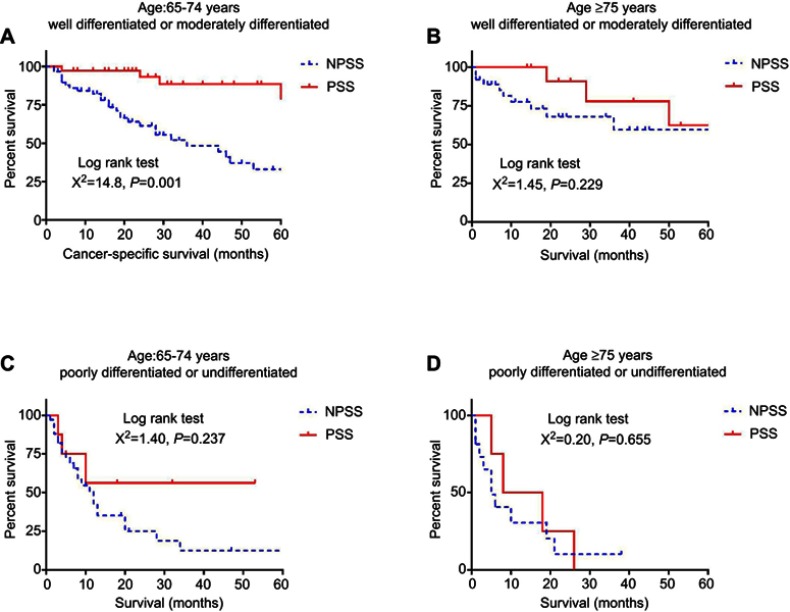
Cases with PSS had a cancer-specific survival advantage comparing with cases with no PSS in the sub-group of 1) age 65–74 years+ well or moderately differentiated (p<0.001) (Figure 3A). However, no differences were observed regarding cancer-specific survival in the sub-groups of 2) age ≥75 years+ well or moderately differentiated (p=0.229) (Figure 3B), 3) age 65–74 years+ poorly differentiated or undifferentiated (p=0.237) (Figure 3C), and 4) age ≥75 years+ poorly differentiated or undifferentiated (p=0.655) (Figure 3D). Multivariable Cox proportional analysis was performed for the four sub-groups, and PSS was an independent protective factor only in cases with age of 65–74 years and well or moderately differentiated tumors (HR 0.142, 95% CI 0.053–0.379, p<0.001) (supplemental materials).
Figure 3.
Kaplan–Meier analysis of cancer-specific survival for elderly patients (≥65 years) in sub-groups.
Notes: (A) Kaplan–meier analysis for cancer-specific survival in patients with age between 65 and 74 years and tumor of well or moderately differentiation; (B) Kaplan–meier analysis for cancer-specific survival in patients with age ≥75 years and tumor of well or moderately differentiation; (C) Kaplan–meier analysis for cancer-specific survival in patients with age between 65 and 74 years and tumor of poorly differentiation or undifferentiation; (D) Kaplan–meier analysis for cancer-specific survival in patients with age ≥75 years and tumor of poorly differentiation or undifferentiation.
Discussion
Patients with distant metastasis of pNET are often treated with comprehensive therapy, including SSA, molecular targeted therapy, chemotherapy, PRRT, etc.10 Many studies advocate PSS in the setting of metastatic pNET for reasons that PSS can improve the control of endocrine-related symptoms, relieve the symptoms of compression and may prolong the survival time of patients.11,12,17,18 However, with the increase of the elderly population, there is still few clinical evidence on the suitability of the elderly with metastatic pNET to accept PSS. The elderly patients usually have a higher incidence of comorbidities, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and diabetes mellitus, which may increase the death rate and reduce the possibility of receipt of endocrine therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and surgery.15 Given the absence of clinical evidence, the study focusing on the suitability of PSS for elderly patients with metastatic pNET is necessary.
In the current study, female patients are more likely to receive PSS, which may be associated with fewer comorbidities in elderly women. There are more tumors receiving PSS in the body/tail of the pancreas than in the head of the pancreas. This may be related to the fact that the complexity of surgery of pancreatic body/tail is less than that of the surgery of pancreatic head. After all, the tumors locating on the head of pancreas need pancreaticoduodenectomy, whereas the former only needs the resection of pancreatic body and tail. In addition, it is not surprising that poorly differentiated and undifferentiated tumors are less likely to undergo surgery than well-differentiated tumors, because the patients with poorly differentiated and undifferentiated tumors have worse prognosis and are more likely receiving conservative treatment options. However, the rate of PSS in the greater elderly patients (≥75 years) is not different from that in the elderly patients (65–74 years) (see Table 2).
Both before and after propensity score matching, tumor histological grade of poorly differentiation and undifferentiation is an independent risk factor for overall survival and cancer-specific survival, whereas PSS is an independent protective factor (see Tables 3, 4 and Figure 2). Then, in order to further explore whether elderly patients with metastatic pNET are suitable for PSS, a further sub-grouping of age and differentiation was performed. The reason for choosing 75 years for further grouping is that WHO stipulates that the older elderly are over 75 years old.15 In addition, X-tiles are also used to determine the cutoff value of age. From the results of the present study, patients with age ≥65 years with poorly differentiated and undifferentiated pNETs are not suitable to receive PSS. For well and moderately differentiated metastatic pNETs, only those aged 65–74 are suitable for PSS, while those aged ≥75 are not suitable for PSS, because there is no difference in cancer-specific survival between PSS and no PSS patients. The physical condition of the patients with age≥75 years is worse than that of other patients, and their physical state, surgical tolerance, and antineoplastic immunity are decreased. These may be the explanation of the fact that even accepting PSS does not improve cancer-specific survival for cases with age ≥75 years and histological grade of well and moderately differentiation.
It should be pointed out that selection bias may exist in the present study. Firstly, patients who have not undergone surgery may be too ill to perform surgery. Secondly, it is impossible to determine whether the two groups are completely balanced in other treatments (such as SSA, chemotherapy, molecular targeted therapy or PRRT, etc.) due to the lack of other treatment information. In addition, there are other limitations that need to be addressed. First, there is a lack of information related to surgery. We can not obtain the duration of surgery, blood loss, complications, and so on. Secondly, the number of patients administrated in the study was relatively small, especially after further divided sub-groups. Thirdly, we can not know the exact reason for the surgery due to the lack of relevant information.
Judging from the common sense, patients undergoing surgery should be in better physical conditions and are more likely to receive a variety of treatment options. The no prolonged survival time after surgery may be more indicative of the ineffectiveness of PSS for these patients. Patients in the three sub-groups (age ≥75 years+ well or moderately differentiated, age 65–74 years+ poorly differentiated or undifferentiated, and age ≥75 years+ poorly differentiated or undifferentiated) did not have a better prognosis after surgery, which suggests that patients of these three sub-groups are less likely to benefit from PSS. Patients in the sub-group of age 65–74 years+ well or moderately differentiated achieved a prolonged survival after surgery. However, given the possible existing selection bias, the prolonged survival after surgery may not be entirely attributed to surgery. Careful evaluation should be performed before surgery and various treatment options should be in consideration. In a word, the results of this study have some implications for the treatment of these patients, but prospective randomized controlled studies are still necessary for concluding a decision of surgery.
Conclusion
Not all elderly patients with distant metastatic pNET could benefit from PSS. Patients aged 65–74 with well or moderately differentiated tumor may benefit from primary lesion surgery, but should be evaluated carefully and in consideration of various treatment options. Patients aged ≥75 years with well or moderately differentiated tumor, and patients aged ≥65 years with poorly differentiated and undifferentiated tumor may not benefit from PSS. Prospective randomized controlled trials are worth performing.
Supplementary materials
Table S1.
Multivariate regression analysis of characteristics for cancer-specific survival in patients with age 65–74 years+ well or moderately differentiated
| Variables | Multivariate analysis for CSS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p | |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Female | 1.887 | 0.794–4.485 | 0.151 |
| Race | |||
| White | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Black | 0.676 | 0.183–2.492 | 0.556 |
| Other | 0.919 | 0.111–7.615 | 0.937 |
| Marital status | |||
| Married | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Unmarried | 1.677 | 0.736–3.823 | 0.219 |
| Year of diagnosis | |||
| 1973–2009 | 1(Referent) | ||
| 2010–2015 | 2.286 | 0.944–5.534 | 0.068 |
| Tumor site | |||
| Head | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Body/tail | 0.963 | 0.398–2.329 | 0.933 |
| Overlap | 1.266 | 0.415–3.863 | 0.679 |
| Other | 2.908 | 0.816–10.367 | 0.100 |
| Tumor size | |||
| ≤4 cm | 1(Referent) | ||
| >4 cm | 1.835 | 0.822–4.096 | 0.138 |
| Unknown | 0.620 | 0.216–1.782 | 0.375 |
| Primary site surgery | |||
| No | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Yes | 0.142 | 0.053–0.379 | 0.000 |
Table S2.
Multivariate regression analysis of characteristics for cancer-specific survival in patients with age ≥75 years+ well or moderately differentiated
| Variables | Multivariate analysis for CSS | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | ||
| Gender | |||
| Male | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Female | 1.899 | 0.270–13.335 | 0.519 |
| Race | |||
| White | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Black | |||
| Other | 28.922 | 1.998–418.6 | 0.014 |
| Marital status | |||
| Married | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Unmarried | 0.582 | 0.103–3.289 | 0.582 |
| Year of diagnosis | |||
| 1973–2009 | 1(Referent) | ||
| 2010–2015 | 0.408 | 0.097–1.719 | 0.222 |
| Tumor site | |||
| Head | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Body/tail | 2.483 | 0.447–13.785 | 0.307 |
| Overlap | |||
| Other | 17.690 | 0.918–340.8 | 0.057 |
| Tumor size | |||
| ≤4 cm | 1 (Referent) | ||
| >4 cm | 0.166 | 0.036–0.764 | 0.037 |
| Unknown | 1.213 | 0.179–8.215 | 0.843 |
| Primary site surgery | |||
| No | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Yes | 1.150 | 0.130–10.165 | 0.900 |
Table S3.
Multivariate regression analysis of characteristics for cancer-specific survival in patients with age 65–74 years+ poorly differentiated or undifferentiated
| Variables | Multivariate analysis for CSS | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | ||
| Gender | |||
| Male | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Female | 1.143 | 0.349–3.746 | 0.825 |
| Race | |||
| White | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Black | 3.047 | 0.748–12.406 | 0.120 |
| Other | 0.656 | 0.066–6.505 | 0.719 |
| Marital status | |||
| Married | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Unmarried | 1.444 | 0.520–4.014 | 0.481 |
| Year of diagnosis | |||
| 1973–2009 | 1 (Referent) | ||
| 2010–2015 | 0.802 | 0.304–2.118 | 0.656 |
| Tumor site | |||
| Head | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Body/tail | 0.914 | 0.330–2.531 | 0.863 |
| Overlap | 0.719 | 0.168–3.090 | 0.658 |
| Other | 0.760 | 0.068–8.540 | 0.824 |
| Tumor size | |||
| ≤4 cm | 1 (Referent) | ||
| >4 cm | 0.841 | 0.302–2.341 | 0.740 |
| Unknown | 0.986 | 0.285–3.413 | 0.983 |
| Primary site surgery | |||
| No | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Yes | 0.621 | 0.174–2.218 | 0.463 |
Table S4.
Multivariate regression analysis of characteristics for cancer-specific survival in patients with age ≥75 years+ poorly differentiated or undifferentiated
| Variables | Multivariate analysis for CSS | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | ||
| Gender | |||
| Male | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Female | 0.640 | 0.141–2.898 | 0.563 |
| Race | |||
| White | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Black | |||
| Other | 8.373 | 1.036–67.700 | 0.046 |
| Marital status | |||
| Married | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Unmarried | 1.562 | 0.316–7.708 | 0.584 |
| Year of diagnosis | |||
| 1973–2009 | 1 (Referent) | ||
| 2010–2015 | 0.380 | 0.064–2.266 | 0.288 |
| Tumor site | |||
| Head | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Body/tail | 2.483 | 0.447–13.785 | 0.307 |
| Overlap | |||
| Other | 17.690 | 0.918–340.8 | 0.057 |
| Tumor size | |||
| ≤4 cm | 1 (Referent) | ||
| >4 cm | 0.458 | 0.119–1.766 | 0.257 |
| Unknown | 5.879 | 0.296–116.8 | 0.245 |
| Primary site surgery | |||
| No | 1 (Referent) | ||
| Yes | 0.469 | 0.091–2.407 | 0.364 |
Acknowledgment
We are deeply grateful to Ye-li Huang and Hui-yu Jin from the Nursing Department of The Sixth Medical Center of People’s Liberation Army General Hospital for their contributions to the revision of this article.
Ethical approval
This study does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. In addition, according to the guidelines of the government of the United States, data released through the SEER database does not require informed patient consent.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Dasari A, Shen C, Halperin D, et al. Trends in the incidence, prevalence, and survival outcomes in patients with neuroendocrine tumors in the United States. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1335–1342. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0589 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhu LM, Tang L, Qiao XW, et al. Differences and similarities in the clinicopathological features of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in china and the United States: a multicenter study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:e2836. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shimata K, Sugawara Y, Hibi T. Liver transplantation for unresectable pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors with liver metastases in an era of transplant oncology. Gland Surgery. 2018;7:42–46. doi: 10.21037/gs.2017.12.11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hallet J, Law CH, Cukier M, Saskin R, Liu N, Singh S. Exploring the rising incidence of neuroendocrine tumors: a population-based analysis of epidemiology, metastatic presentation, and outcomes. Cancer. 2015;121:589–597. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29099 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Halfdanarson TR, Rabe KG, Rubin J, Petersen GM. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs): incidence, prognosis and recent trend toward improved survival. Ann Oncol. 2008;19:1727–1733. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdn351 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bilimoria KY, Talamonti MS, Tomlinson JS, et al. Prognostic score predicting survival after resection of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: analysis of 3851 patients. Ann Surg. 2008;247:490–500. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31815b9cae [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bertani E, Fazio N, Botteri E, et al. Resection of the primary pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor in patients with unresectable liver metastases: possible indications for a multimodal approach. Surgery. 2014;155:607–614. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2013.12.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Frilling A, Clift AK. Therapeutic strategies for neuroendocrine liver metastases. Cancer. 2015;121:1172–1186. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28760 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rindi G, D’Adda T, Froio E, Fellegara G, Bordi C. Prognostic factors in gastrointestinal endocrine tumors. Endocr Pathol. 2007;18:145–149. doi: 10.1007/s12022-007-0020-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Auernhammer CJ, Spitzweg C, Angele MK, et al. Advanced neuroendocrine tumours of the small intestine and pancreas: clinical developments, controversies, and future strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:404–415. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30401-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Frilling A, Modlin IM, Kidd M, et al. Recommendations for management of patients with neuroendocrine liver metastases. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e8–e21. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70362-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chawla A, Williams RT, Sich N, et al. Pancreaticoduodenectomy and metastasectomy for metastatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Surg Oncol. 2018;118:983–990. doi: 10.1002/jso.25219 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cheng KK, Lim EY, Kanesvaran R. Quality of life of elderly patients with solid tumours undergoing adjuvant cancer therapy: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e018101. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1605–1617. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0901557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shamali A, De’Ath HD, Jaber B, et al. Elderly patients have similar short term outcomes and five-year survival compared to younger patients after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Int J Surg. 2017;45:138–143. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.07.106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Camp RL, Dolled-Filhart M, Rimm DL. X-tile: a new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7252–7259. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0713 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Falconi M, Eriksson B, Kaltsas G, et al. ENETS consensus guidelines update for the management of patients with functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Neuroendocrinology. 2016;103:153–171. doi: 10.1159/000443171 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pavel M, O’Toole D, Costa F, et al. ENETS consensus guidelines update for the management of distant metastatic disease of intestinal, pancreatic, bronchial Neuroendocrine Neoplasms (NEN) and NEN of unknown primary site. Neuroendocrinology. 2016;103:172–185. doi: 10.1159/000443167 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]