An investigation into the crystallization, crystal structure and packing analysis of the biologically active drug molecule riluzole and its derivative, the riluzolium chloride salt, has been carried out.
Keywords: crystal structure, riluzole, molecular salt, weak interactions, electrostatic potential
Abstract
This study is an investigation into the crystal structure of the biologically active drug molecule riluzole [RZ, 6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amine], C8H5F3N2OS, and its derivative, the riluzolium chloride salt [RZHCl, 2-amino-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-3-ium chloride], C8H6F3N2OS+·Cl−. In spite of repeated efforts to crystallize the drug, its crystal structure has not been reported to date, hence the current study provides a method for obtaining crystals of both riluzole and its corresponding salt, riluzolium hydrochloride. The salt was obtained by grinding HCl with the drug and crystallizing the obtained solid from dichloromethane. The crystals of riluzole were obtained in the presence of l-glutamic acid and d-glutamic acid in separate experiments. In the crystal structure of RZHCl, the –OCF3 moiety is perpendicular to the molecular plane containing the riluzolium ion, as can be seen by the torsion angle of 107.4 (3)°. In the case of riluzole, the torsion angles of the four different molecules in the asymmetric unit show that in three cases the trifluoromethoxy group is perpendicular to the riluzole molecular plane and only in one molecule does the –OCF3 group lie in the same molecular plane. The crystal structure of riluzole primarily consists of strong N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds along with weak C—H⋯F, C—H⋯S, F⋯F, C⋯C and C⋯S interactions, while that of its salt is stabilized by strong [N—H]+⋯Cl− and weak C—H⋯Cl−, N—H⋯S, C—H⋯F, C⋯C, S⋯N and S⋯Cl− interactions.
Chemical Context
Crystals are composed of an infinite array of atoms or molecules arranged in a regular pattern in space. Such crystals form assemblies of supramolecules (Desiraju, 2013 ▸; Yan & Huang, 2010 ▸). These supramolecular assemblies are formed by the involvement of certain intermolecular interactions (Mondal, Kiran et al., 2017 ▸). The study of these intermolecular interactions is significant in both chemistry (Raynal et al., 2014 ▸) and biology (Ball & Maechling, 2009 ▸). Some of the major intermolecular interactions are hydrogen-bonding, dipole–dipole, van der Waals and halogen interactions (Paulini et al., 2005 ▸). Understanding the essential molecular interactions and synthons involved in the early stages of nucleation is very important in determining the formation of crystals (Davey et al., 2013 ▸). These packing trends and supramolecular synthons can also repeat themselves in other crystal structures with similar functional groups. The phenomenon of polymorphism is also a common occurrence because of the possible presence of diverse combinations of intermolecular interactions (Cruz-Cabeza & Bernstein, 2014 ▸).
Riluzole (RZ) is the only available drug used for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and diseases like Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease and other mood and anxiety disorders (Nakane et al., 2016 ▸). Even though riluzole is a most important pharmaceutical drug (Doble, 1996 ▸), no crystal structure of pure riluzole has been obtained to date, although several methods have been tried in the past (Mondal, Rao, et al., 2017 ▸; Mondal et al., 2018 ▸; Thomas et al., 2019 ▸; Yadav et al., 2018 ▸).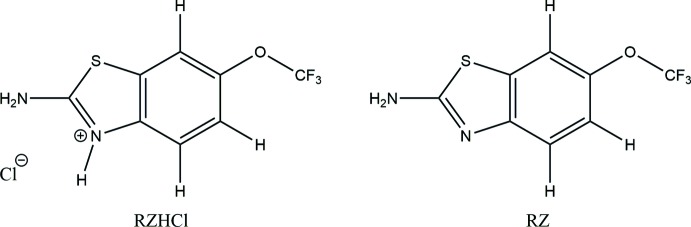
In this work, we have been successful in obtaining crystals of riluzole along with those of its hydrochloride salt. An in-depth analysis of the two crystal structures has been performed and the role of strong hydrogen bonds and weak intermolecular interactions in the crystal lattice has been established.
Structural commentary
The riluzolium chloride salt crystallizes in the P21/c space group with one riluzolium cation (RZH+) and a chloride anion (Cl−) in the asymmetric unit while the riluzole molecule crystallizes in the centrosymmetric triclinic P
 space group with Z′ = 4. The asymmetric unit of riluzolium chloride (Fig. 1 ▸) shows a riluzolium ion with a chloride ion held via [N—H]+⋯Cl− interactions between the riluzolium cation and the chloride anion. On the other hand, the asymmetric unit of riluzole (Fig. 2 ▸) comprises four molecules, wherein each pair is perpendicular to the other pair, with parallel pairs being held together by C⋯C, C⋯O and C⋯S intermolecular contacts and each pair is connected with the other pair via C—H⋯π or C—H⋯S hydrogen-bonding interactions. The conformations of riluzole and of the riluzolium cation in the crystal packing are preserved except for the conformational changes that occur in the –OCF3 group. The main difference between the two molecular structures can be seen from the magnitude of the torsion angles Ci—Cj—Ok—Cl, Table 1 ▸ (Mondal, Rao et al., 2017 ▸; Mondal et al., 2018 ▸; Thomas et al., 2019 ▸; Yadav et al., 2018 ▸). Both the structures in the current study crystallized in a centrosymmetric space group. Hence, only torsion angles within the 0 to 180° range are significant. In the crystal structure of RZHCl, the torsion angle relative to the –OCF3 moiety is 107.4 (3)°, which means that the trifluoromethoxy group is roughly perpendicular to the molecular plane of the riluzolium ion. The corresponding torsion angles for the four different riluzole molecules in the asymmetric unit of the crystal structure of RZ are −86.2 (4), 91.9 (3), −96.4 (3)° (when the –OCF3 group is perpendicular to the molecular plane of riluzole) and 167.6 (2)° (for one molecule when the group is in the same molecular plane).
space group with Z′ = 4. The asymmetric unit of riluzolium chloride (Fig. 1 ▸) shows a riluzolium ion with a chloride ion held via [N—H]+⋯Cl− interactions between the riluzolium cation and the chloride anion. On the other hand, the asymmetric unit of riluzole (Fig. 2 ▸) comprises four molecules, wherein each pair is perpendicular to the other pair, with parallel pairs being held together by C⋯C, C⋯O and C⋯S intermolecular contacts and each pair is connected with the other pair via C—H⋯π or C—H⋯S hydrogen-bonding interactions. The conformations of riluzole and of the riluzolium cation in the crystal packing are preserved except for the conformational changes that occur in the –OCF3 group. The main difference between the two molecular structures can be seen from the magnitude of the torsion angles Ci—Cj—Ok—Cl, Table 1 ▸ (Mondal, Rao et al., 2017 ▸; Mondal et al., 2018 ▸; Thomas et al., 2019 ▸; Yadav et al., 2018 ▸). Both the structures in the current study crystallized in a centrosymmetric space group. Hence, only torsion angles within the 0 to 180° range are significant. In the crystal structure of RZHCl, the torsion angle relative to the –OCF3 moiety is 107.4 (3)°, which means that the trifluoromethoxy group is roughly perpendicular to the molecular plane of the riluzolium ion. The corresponding torsion angles for the four different riluzole molecules in the asymmetric unit of the crystal structure of RZ are −86.2 (4), 91.9 (3), −96.4 (3)° (when the –OCF3 group is perpendicular to the molecular plane of riluzole) and 167.6 (2)° (for one molecule when the group is in the same molecular plane).
Figure 1.
ORTEP view of riluzolium chloride drawn with 50% ellipsoidal probability. The dotted lines depict intermolecular interactions in the asymmetric unit.
Figure 2.
ORTEP view of riluzole drawn with 50% ellipsoidal probability. The dotted lines depict intermolecular interactions in the asymmetric unit.
Table 1. List of torsion angles (°).
| Compound | Ci—Cj—Ok—Cl | Torsion |
|---|---|---|
| RZHCl | C4—C5—O1—C8 | 107.4 (3) |
| RZ | C4—C5—O1—C8 | −86.2 (4) |
| C12—C13—O2—C16 | 91.9 (3) | |
| C20—C21—O3—C24 | 167.6 (2) | |
| C28—C29—O4—C32 | −96.4 (3) |
Supramolecular features
The riluzolium ion forms hydrogen-bonding interactions (Table 2 ▸) with a chloride ion via strong N1—H1A⋯Cl1 (2.15 Å, 154°), N2—H2⋯Cl1 (2.35 Å, 139°) and N1—H1B⋯Cl1 (2.14 Å, 175°) interactions (Motifs I and II, Fig. 3 ▸) along with weak C—H⋯Cl and S⋯Cl interactions (Motif III), forming a molecular sheet down the ab plane. Riluzolinium molecules in parallel planes are connected by weak C⋯C and C⋯S interactions (Motif V, Fig. 4 ▸). Two such chains along the b axis are connected via motif IV, the dimer based on two symmetry-related C—H⋯F–Csp
3 interactions, which yields an  (12) graph-set motif. The importance of such interactions has been evidenced in the crystal structures of –F- and –CF3-containing benzanilides (Panini et al., 2016 ▸). The crystal structure of riluzole consists of strong as well as weak interactions between the corresponding riluzole molecules. Similar types of interactions are grouped together as motifs, in both parallel and perpendicularly aligned molecules in the asymmetric unit. Strong N—H⋯N hydrogen-bonded
(12) graph-set motif. The importance of such interactions has been evidenced in the crystal structures of –F- and –CF3-containing benzanilides (Panini et al., 2016 ▸). The crystal structure of riluzole consists of strong as well as weak interactions between the corresponding riluzole molecules. Similar types of interactions are grouped together as motifs, in both parallel and perpendicularly aligned molecules in the asymmetric unit. Strong N—H⋯N hydrogen-bonded  (8) dimers are obtained (Motifs I to III; Figs. 5 ▸, 6 ▸), leading to the formation of chains along the b-axis direction. [Motifs I(a) and I(b); Fig. 5 ▸]. In addition, the amine nitrogen forms hydrogen-bonding interactions with the amine hydrogen of another riluzole molecule [Motifs II(a) and II(b); Fig. 5 ▸]. The ring nitrogen atom was found to form hydrogen bonds with the amine hydrogens [Motifs III(a) and III(b)] along with other weak C—H⋯F, N—H⋯C, and C⋯S interactions. Molecular motifs IV(a), IV(b), and V(a–f), show the presence of short and highly directional interactions involving organic fluorine, such as the Csp
3—F⋯H–Csp
2 (2.46 Å, 161°; 2.41 Å, 161°) hydrogen bond and the Csp
3—F⋯F—Csp
3 (2.907 Å, 137°, 107°; 2.923 Å, 115°, 120°; 2.845 Å, 127°, 127°) interactions [Figs. 5 ▸ and 6 ▸], in the crystal packing and these structural features are indeed noteworthy. Furthermore, we have also observed sulfur forming weak C—H⋯S and C⋯S interactions (Motifs VII and VIII) in addition to the presence of weak C⋯O, C⋯C (Motif VI), and C—H⋯C interactions (Motif IX) (Fig. 6 ▸).
(8) dimers are obtained (Motifs I to III; Figs. 5 ▸, 6 ▸), leading to the formation of chains along the b-axis direction. [Motifs I(a) and I(b); Fig. 5 ▸]. In addition, the amine nitrogen forms hydrogen-bonding interactions with the amine hydrogen of another riluzole molecule [Motifs II(a) and II(b); Fig. 5 ▸]. The ring nitrogen atom was found to form hydrogen bonds with the amine hydrogens [Motifs III(a) and III(b)] along with other weak C—H⋯F, N—H⋯C, and C⋯S interactions. Molecular motifs IV(a), IV(b), and V(a–f), show the presence of short and highly directional interactions involving organic fluorine, such as the Csp
3—F⋯H–Csp
2 (2.46 Å, 161°; 2.41 Å, 161°) hydrogen bond and the Csp
3—F⋯F—Csp
3 (2.907 Å, 137°, 107°; 2.923 Å, 115°, 120°; 2.845 Å, 127°, 127°) interactions [Figs. 5 ▸ and 6 ▸], in the crystal packing and these structural features are indeed noteworthy. Furthermore, we have also observed sulfur forming weak C—H⋯S and C⋯S interactions (Motifs VII and VIII) in addition to the presence of weak C⋯O, C⋯C (Motif VI), and C—H⋯C interactions (Motif IX) (Fig. 6 ▸).
Table 2. Intermolecular interactions (Å, °) in the crystal structure of the RZHCl salt and RZ.
| Motif number | Symmetry Code | Possible involved interactions | Geometry |
|---|---|---|---|
| RZHCL | |||
| I | x, y, z | N1—H1A⋯Cl1 | 2.15, 154 |
| N2—H2⋯Cl1 | 2.35, 139 | ||
| II | −x,  + y, + y,  − z − z
|
N1—H1B⋯Cl1 | 2.14, 175 |
| III | x, 1 + y, z | C6—H6⋯Cl1 | 2.60, 135 |
| S1⋯Cl1 | 3.340 (2) | ||
| IV | 1 − x, 2 − y, 2 − z | C4—H4⋯F1 | 2.57, 147 |
| V |
x,  − y, − y,  + z + z
|
C5⋯C2 | 3.289 (7) |
| C6⋯C1 | 3.292 (7) | ||
| C7⋯S1 | 3.456 (6) | ||
| RZ | |||
| I(a) | −x, 2 − y, 2 − z | N7—H7B⋯N6 | 1.89, 170 |
| N5—H5B⋯N8 | 2.03, 175 | ||
| I(b) | 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z | N3—H3B⋯N2 | 1.92, 167 |
| N1—H1B⋯N4 | 2.06, 170 | ||
| II(a) | −x, 1 − y, 2 − z | N7—H7A⋯N1 | 2.14, 169 |
| II(b) | 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z | N3—H3A⋯N5 | 2.15, 171 |
| III(a) | 1 + x, −1 + y, z | N1—H1A⋯N8 | 2.49, 155 |
| N1—H1A⋯C25 | 2.77, 130 | ||
| S1⋯C31 | 3.336 (1) | ||
| S1⋯C26 | 3.430 (1) | ||
| III(b) | −1 + x, y, z | N5—H5A⋯N4 | 2.53, 159 |
| N5—H5A⋯C9 | 2.75, 140 | ||
| C10⋯S3 | 3.372 (1) | ||
| C15⋯S3 | 3.311 (1) | ||
| C22—H22⋯F4 | 2.44, 164 | ||
| IV(a) | −1 + x, y, z | C4—H4⋯F4 | 2.46, 161 |
| IV(b) | 1 + x, y, z | C20—H20⋯F12 | 2.41, 161 |
| V(a) | −x, 2 − y, 1 − z | F1⋯F10 | 2.907 (1), 137, 107 |
| V(b) | x, −1 + y, z | F3⋯F10 | 2.923 (1), 115, 120 |
| C27—H27⋯C2 | 2.81, 129 | ||
| V(c) | −x, 2 − y, 1 − z | F9⋯F9 | 2.845 (1), 127, 127 |
| V(d) | 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z | F2⋯F5 | 2.954 (1), 143, 119 |
| V(e) | 1 − x, 2 − y, 1 − z | F6⋯F7 | 2.946 (1), 142, 111 |
| V(f) | −x, 2 − y, 1 − z | F11⋯F9 | 3.071 (1), 129, 97 |
| VI | x, y, z | C5⋯O2 | 3.179 (1) |
| C7⋯C14 | 3.308 (1) | ||
| VII | x, y, z | C3—H3⋯S3 | 2.84, 145 |
| VIII | x, y, z | C17⋯S4 | 3.460 (1) |
| C23⋯C30 | 3.295 (1) | ||
| IX | x, y, z | C12—H12⋯C18 | 2.82, 124 |
| C12—H12⋯C23 | 2.80, 133 |
Figure 3.
A comparative view of the packing of riluzolium chloride represented via N—H⋯Cl, C—H⋯Cl, C—H⋯F, and S⋯Cl intermolecular interactions. Dotted pale-blue lines depict the intermolecular interactions.
Figure 4.
A comparative view of the packing of riluzolium chloride represented via C⋯C and C⋯S intermolecular interactions. Dotted pale-blue lines depict the intermolecular interactions.
Figure 5.
Packing of molecules with strong N—H⋯N dimers formed along the bc plane with weak C—H⋯S and F⋯F interactions in riluzole. Dotted lines depict the intermolecular interactions, and different colours for C atoms have been used for Z′ > 1.
Figure 6.
Packing of molecules with weak C—H⋯F, C—H⋯S, F⋯F, C⋯C, C⋯O, C—H⋯C and C⋯S interactions in riluzole. Dotted lines depict the intermolecular interactions, and different colours for C atoms have been used for Z′ > 1.
The electrostatic potentials (ESP) (Spackman et al., 2008 ▸) were mapped on the Hirshfeld surfaces for RZHCl (Fig. 7 ▸ a), and for the four molecules in RZ (Fig. 7 ▸ b, front and back views). These were calculated using HF/6-31G** ab initio wave functions via the program Gaussian09 (Frisch et al., 2009 ▸). The ESP map allows a quantitative understanding of the nature of electron-rich and electron-deficient sites in the molecule to be obtained. As expected in all the RZ molecules, the electronegative regions are around the nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and sulfur atoms. The corresponding electropositive regions were observed around the N—H and C—H bonds.
Figure 7.
Electrostatic potential (ESP) mapped on the Hirshfeld surfaces of (a) the RZHCl salt and (b) RZ (four molecules), over the range −0.05 au (red) through 0.0 (white) to 0.05 au (blue).
Database analysis
Recently, Thomas and coworkers (Thomas et al., 2019 ▸) reported the ubiquity of a robust, directional S⋯O chalcogen-bonded synthon and have probed the electronic nature in a series of co-crystals and salts of the drug riluzole. The S⋯O bond order for chalcogen bonding was found to be one-third of a single bond (minimum 0.10 to maximum 0.35), and these are short (2.90 to 3.40 Å) and directional (<C—S⋯O = 160–179°) in nature. In another recent study, performed on the drug riluzole, the riluzole molecules (CCDC codes YEPJIP and YEPJOV; Yadav et al., 2018 ▸) also display the presence of S⋯O chalcogen-bonded synthons (S⋯O distances = 3.39 and 3.42 Å, respectively). However, in the current study, S⋯O chalcogen-bonded synthons were not observed.
Synthesis and crystallization
Riluzole was obtained from Rallis India Ltd, and different solvents were used to crystallize it, along with two additives, namely l-Glutamic acid (LGA) and d-Glutamic acid (DGA), which were obtained from Sigma Aldrich and used directly without further purification. The crystallization of riluzole was conducted with LGA and DGA, by the solvent-drop grinding method. Grinding was carried out for 15-20 minutes, with the dropwise addition of methanol at an interval of 5 min in an agate mortar and pestle. The slow evaporation method was conducted both at low temperature (278 K) in a refrigerator and also at room temperature with 5 mg of granulated material for each crystallization. This resulted in the formation of plate-like crystals of riluzole from methanol. The riluzole crystals were collected from the crystallization beaker under the polarizing microscope and used for single crystal XRD experiments. No further experiments to evaluate the role of additives have been performed and these are not within the scope of the current work.
Riluzolium chloride was obtained by grinding concentrated HCl (35%) with riluzole in a 1:1 molar ratio for 10-15 minutes and the powder obtained was recrystallized from different solvents. 5 mg of granulated material was used for each crystallization. In particular, crystals of riluzolium chloride were obtained from dichloromethane (DCM).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. All hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms and sp 2 nitrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions (C–H = 0.95 Å and Nsp 2—H = 0.88 Å) and refined as riding with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C, Nsp 2). Hydrogen atoms attached to sp 3 nitrogen atoms were located in difference-Fourier maps (Nsp 3—H = 0.81–0.91 Å). The normalized values of hydrogen atoms given by PARST (Nardelli, 1995 ▸) were used for the hydrogen-bonding (Taylor & Kennard, 1983 ▸) analysis.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| RZHCl | RZ | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C8H6ClF3N2OS+·Cl− | C8H5F3N2OS |
| M r | 270.66 | 234.20 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Triclinic, P

|
| Temperature (K) | 100 | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 15.737 (8), 8.526 (4), 7.761 (4) | 8.0824 (19), 11.788 (3), 19.745 (5) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 100.45 (2), 90 | 78.449 (9), 84.378 (8), 89.318 (9) |
| V (Å3) | 1024.0 (9) | 1834.2 (8) |
| Z | 4 | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.60 | 0.37 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.39 × 0.08 × 0.05 | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.03 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.572, 0.746 | 0.553, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 5326, 2037, 1344 | 29801, 6730, 4593 |
| R int | 0.104 | 0.117 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.062, 0.157, 1.08 | 0.056, 0.130, 1.03 |
| No. of reflections | 2037 | 6730 |
| No. of parameters | 153 | 573 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.65, −0.60 | 0.51, −0.47 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) RZHCl, RZ. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009022/xi2017sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) RZHCl. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009022/xi2017RZHClsup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) RZ. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009022/xi2017RZsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009022/xi2017RZHClsup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009022/xi2017RZsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank IISER Bhopal for research facilities and infrastructure.
supplementary crystallographic information
2-Amino-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-3-ium chloride (RZHCl). Crystal data
| C8H6ClF3N2OS+·Cl− | F(000) = 544 |
| Mr = 270.66 | Dx = 1.756 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 15.737 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 2658 reflections |
| b = 8.526 (4) Å | θ = 2.7–29.8° |
| c = 7.761 (4) Å | µ = 0.60 mm−1 |
| β = 100.45 (2)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1024.0 (9) Å3 | Plates, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.39 × 0.08 × 0.05 mm |
2-Amino-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-3-ium chloride (RZHCl). Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 1344 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.104 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Tmin = 0.572, Tmax = 0.746 | h = −19→19 |
| 5326 measured reflections | k = −10→10 |
| 2037 independent reflections | l = −9→9 |
2-Amino-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-3-ium chloride (RZHCl). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.062 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.157 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0525P)2 + 1.7896P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2037 reflections | Δρmax = 0.65 e Å−3 |
| 153 parameters | Δρmin = −0.60 e Å−3 |
2-Amino-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-3-ium chloride (RZHCl). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
2-Amino-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-3-ium chloride (RZHCl). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.09861 (8) | 0.78340 (12) | 0.44751 (16) | 0.0149 (3) | |
| Cl1 | 0.12321 (8) | 0.16795 (12) | 0.39066 (17) | 0.0221 (4) | |
| F1 | 0.4624 (2) | 1.1822 (3) | 0.8833 (5) | 0.0363 (9) | |
| O1 | 0.3711 (2) | 0.9930 (3) | 0.8688 (4) | 0.0181 (8) | |
| N2 | 0.1688 (2) | 0.5156 (4) | 0.5297 (5) | 0.0127 (9) | |
| H2 | 0.1770 | 0.4136 | 0.5374 | 0.015* | |
| F2 | 0.3640 (3) | 1.1687 (4) | 0.6555 (5) | 0.0637 (13) | |
| N1 | 0.0427 (3) | 0.4997 (5) | 0.3216 (6) | 0.0207 (10) | |
| H1B | −0.004 (4) | 0.546 (5) | 0.254 (7) | 0.020 (14)* | |
| H1A | 0.051 (4) | 0.396 (7) | 0.319 (8) | 0.040 (17)* | |
| F3 | 0.4660 (3) | 1.0022 (4) | 0.6932 (6) | 0.0696 (15) | |
| C2 | 0.2266 (3) | 0.6230 (5) | 0.6236 (6) | 0.0140 (10) | |
| C7 | 0.1975 (3) | 0.7775 (5) | 0.5902 (6) | 0.0126 (10) | |
| C1 | 0.1005 (3) | 0.5799 (5) | 0.4278 (7) | 0.0147 (11) | |
| C6 | 0.2447 (3) | 0.9045 (5) | 0.6695 (6) | 0.0139 (11) | |
| H6 | 0.2253 | 1.0095 | 0.6492 | 0.017* | |
| C3 | 0.3029 (3) | 0.5914 (5) | 0.7342 (6) | 0.0164 (11) | |
| H3 | 0.3222 | 0.4866 | 0.7567 | 0.020* | |
| C5 | 0.3213 (3) | 0.8689 (5) | 0.7791 (7) | 0.0160 (11) | |
| C4 | 0.3515 (3) | 0.7175 (5) | 0.8127 (7) | 0.0183 (11) | |
| H4 | 0.4050 | 0.6996 | 0.8889 | 0.022* | |
| C8 | 0.4151 (4) | 1.0835 (6) | 0.7748 (8) | 0.0293 (14) |
2-Amino-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-3-ium chloride (RZHCl). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0197 (7) | 0.0091 (5) | 0.0146 (7) | 0.0011 (5) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0011 (4) |
| Cl1 | 0.0307 (8) | 0.0110 (5) | 0.0215 (7) | 0.0016 (5) | −0.0037 (6) | −0.0011 (5) |
| F1 | 0.037 (2) | 0.0304 (16) | 0.039 (2) | −0.0181 (14) | 0.0001 (16) | −0.0117 (15) |
| O1 | 0.022 (2) | 0.0206 (16) | 0.011 (2) | −0.0081 (14) | 0.0011 (15) | −0.0053 (13) |
| N2 | 0.017 (2) | 0.0075 (16) | 0.013 (2) | −0.0012 (15) | −0.0002 (17) | −0.0001 (15) |
| F2 | 0.069 (3) | 0.053 (2) | 0.057 (3) | −0.034 (2) | −0.019 (2) | 0.032 (2) |
| N1 | 0.022 (3) | 0.0119 (19) | 0.025 (3) | −0.0015 (18) | −0.003 (2) | 0.0025 (18) |
| F3 | 0.076 (3) | 0.057 (2) | 0.095 (4) | −0.039 (2) | 0.067 (3) | −0.046 (2) |
| C2 | 0.023 (3) | 0.010 (2) | 0.009 (3) | 0.0002 (18) | 0.004 (2) | 0.0002 (18) |
| C7 | 0.012 (3) | 0.014 (2) | 0.013 (3) | 0.0005 (18) | 0.005 (2) | 0.0038 (18) |
| C1 | 0.020 (3) | 0.008 (2) | 0.017 (3) | −0.0040 (19) | 0.007 (2) | 0.0006 (18) |
| C6 | 0.023 (3) | 0.011 (2) | 0.009 (3) | 0.0013 (18) | 0.007 (2) | 0.0002 (18) |
| C3 | 0.026 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.011 (3) | 0.0027 (19) | 0.003 (2) | 0.0012 (18) |
| C5 | 0.025 (3) | 0.015 (2) | 0.011 (3) | −0.0073 (19) | 0.011 (2) | −0.0031 (18) |
| C4 | 0.015 (3) | 0.024 (2) | 0.015 (3) | 0.003 (2) | 0.002 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C8 | 0.034 (4) | 0.024 (3) | 0.030 (4) | −0.013 (2) | 0.006 (3) | −0.007 (2) |
2-Amino-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-3-ium chloride (RZHCl). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C7 | 1.739 (5) | N1—H1A | 0.89 (6) |
| S1—C1 | 1.742 (4) | F3—C8 | 1.306 (6) |
| F1—C8 | 1.321 (6) | C2—C3 | 1.371 (7) |
| O1—C8 | 1.338 (6) | C2—C7 | 1.403 (6) |
| O1—C5 | 1.422 (5) | C7—C6 | 1.392 (6) |
| N2—C1 | 1.332 (6) | C6—C5 | 1.376 (7) |
| N2—C2 | 1.398 (6) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| N2—H2 | 0.8800 | C3—C4 | 1.393 (7) |
| F2—C8 | 1.328 (7) | C3—H3 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.305 (6) | C5—C4 | 1.384 (6) |
| N1—H1B | 0.91 (6) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C7—S1—C1 | 90.0 (2) | C5—C6—H6 | 122.0 |
| C8—O1—C5 | 117.1 (4) | C7—C6—H6 | 122.0 |
| C1—N2—C2 | 114.7 (4) | C2—C3—C4 | 118.1 (4) |
| C1—N2—H2 | 122.6 | C2—C3—H3 | 121.0 |
| C2—N2—H2 | 122.6 | C4—C3—H3 | 121.0 |
| C1—N1—H1B | 122 (3) | C6—C5—C4 | 123.7 (4) |
| C1—N1—H1A | 116 (4) | C6—C5—O1 | 118.8 (4) |
| H1B—N1—H1A | 121 (5) | C4—C5—O1 | 117.5 (5) |
| C3—C2—N2 | 127.6 (4) | C5—C4—C3 | 119.7 (5) |
| C3—C2—C7 | 121.3 (4) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.2 |
| N2—C2—C7 | 111.0 (4) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.2 |
| C6—C7—C2 | 121.2 (4) | F3—C8—F1 | 108.8 (5) |
| C6—C7—S1 | 127.1 (3) | F3—C8—F2 | 107.4 (5) |
| C2—C7—S1 | 111.7 (3) | F1—C8—F2 | 107.3 (4) |
| N1—C1—N2 | 123.7 (4) | F3—C8—O1 | 112.5 (4) |
| N1—C1—S1 | 123.8 (4) | F1—C8—O1 | 107.9 (5) |
| N2—C1—S1 | 112.5 (3) | F2—C8—O1 | 112.8 (5) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 116.1 (4) |
6-(Trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amine (RZ). Crystal data
| C8H5F3N2OS | Z = 8 |
| Mr = 234.20 | F(000) = 944 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.696 Mg m−3 |
| a = 8.0824 (19) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 11.788 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 7465 reflections |
| c = 19.745 (5) Å | θ = 2.8–28.3° |
| α = 78.449 (9)° | µ = 0.37 mm−1 |
| β = 84.378 (8)° | T = 100 K |
| γ = 89.318 (9)° | Plates, colorless |
| V = 1834.2 (8) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.03 mm |
6-(Trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amine (RZ). Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4593 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| φ and ω scans | Rint = 0.117 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Tmin = 0.553, Tmax = 0.746 | h = −9→8 |
| 29801 measured reflections | k = −14→14 |
| 6730 independent reflections | l = −23→23 |
6-(Trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amine (RZ). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.056 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.130 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0541P)2 + 0.7369P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 6730 reflections | Δρmax = 0.51 e Å−3 |
| 573 parameters | Δρmin = −0.47 e Å−3 |
6-(Trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amine (RZ). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
6-(Trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amine (RZ). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.56739 (12) | 0.27424 (7) | 0.80617 (4) | 0.0194 (2) | |
| S2 | 0.83832 (12) | 0.45174 (7) | 0.89575 (4) | 0.0186 (2) | |
| S3 | −0.00146 (12) | 0.76611 (7) | 0.82003 (4) | 0.0193 (2) | |
| S4 | −0.30623 (12) | 0.95409 (7) | 0.89386 (4) | 0.0176 (2) | |
| F1 | 0.2905 (3) | 0.5228 (2) | 0.48186 (10) | 0.0538 (8) | |
| F2 | 0.2508 (4) | 0.3698 (2) | 0.56134 (13) | 0.0681 (9) | |
| F3 | 0.0949 (4) | 0.5160 (3) | 0.56353 (12) | 0.0628 (8) | |
| F4 | 0.9015 (3) | 0.7039 (2) | 0.62797 (11) | 0.0427 (6) | |
| F5 | 0.7172 (3) | 0.7514 (2) | 0.55647 (10) | 0.0405 (6) | |
| F6 | 0.7410 (3) | 0.84532 (19) | 0.63754 (10) | 0.0451 (7) | |
| F7 | 0.3242 (3) | 0.9755 (2) | 0.48390 (10) | 0.0476 (7) | |
| F8 | 0.3079 (4) | 0.8212 (2) | 0.56344 (11) | 0.0504 (8) | |
| F9 | 0.0973 (4) | 0.9316 (2) | 0.54890 (11) | 0.0527 (7) | |
| F10 | −0.1373 (3) | 1.3300 (2) | 0.63105 (11) | 0.0463 (7) | |
| F11 | −0.0685 (3) | 1.2372 (2) | 0.54945 (10) | 0.0422 (7) | |
| F12 | −0.2758 (3) | 1.1814 (2) | 0.62482 (11) | 0.0538 (8) | |
| O1 | 0.3591 (3) | 0.5281 (2) | 0.58387 (11) | 0.0280 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.6333 (3) | 0.6668 (2) | 0.66125 (11) | 0.0231 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.3167 (4) | 0.9962 (2) | 0.58944 (12) | 0.0331 (7) | |
| O4 | −0.0152 (3) | 1.1590 (2) | 0.65325 (11) | 0.0253 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.4995 (5) | 0.2583 (3) | 0.94561 (15) | 0.0191 (7) | |
| H1A | 0.599 (5) | 0.237 (3) | 0.9497 (16) | 0.017 (10)* | |
| H1B | 0.463 (5) | 0.292 (4) | 0.980 (2) | 0.042 (13)* | |
| N2 | 0.3463 (4) | 0.3895 (2) | 0.86966 (13) | 0.0167 (6) | |
| N3 | 0.7894 (4) | 0.4741 (3) | 1.02897 (15) | 0.0215 (7) | |
| H3A | 0.847 (5) | 0.414 (3) | 1.0362 (18) | 0.030 (12)* | |
| H3B | 0.743 (5) | 0.504 (3) | 1.0596 (19) | 0.029 (12)* | |
| N4 | 0.6520 (4) | 0.6036 (2) | 0.94687 (13) | 0.0179 (7) | |
| N5 | 0.0104 (5) | 0.7614 (3) | 0.95743 (15) | 0.0185 (7) | |
| H5A | −0.090 (6) | 0.728 (3) | 0.9646 (18) | 0.033 (12)* | |
| H5B | 0.041 (7) | 0.795 (4) | 0.987 (2) | 0.068 (18)* | |
| N6 | 0.1865 (4) | 0.8916 (2) | 0.87642 (13) | 0.0175 (7) | |
| N7 | −0.2997 (4) | 0.9781 (3) | 1.02592 (15) | 0.0218 (7) | |
| H7A | −0.362 (5) | 0.915 (3) | 1.0386 (16) | 0.016 (9)* | |
| H7B | −0.266 (5) | 1.009 (3) | 1.0575 (18) | 0.027 (11)* | |
| N8 | −0.1349 (4) | 1.1049 (2) | 0.93992 (13) | 0.0171 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.4623 (5) | 0.3124 (3) | 0.88061 (16) | 0.0185 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.3336 (5) | 0.4262 (3) | 0.79884 (16) | 0.0172 (8) | |
| C12 | 0.5408 (5) | 0.7238 (3) | 0.76878 (16) | 0.0192 (8) | |
| H12 | 0.475160 | 0.782215 | 0.744004 | 0.023* | |
| C23 | 0.1382 (4) | 0.8618 (3) | 0.76540 (16) | 0.0160 (8) | |
| C20 | 0.3703 (5) | 1.0258 (3) | 0.69917 (17) | 0.0230 (8) | |
| H20 | 0.450304 | 1.081977 | 0.675480 | 0.028* | |
| C14 | 0.7326 (5) | 0.5640 (3) | 0.76693 (16) | 0.0192 (8) | |
| H14 | 0.796259 | 0.514646 | 0.742027 | 0.023* | |
| C19 | 0.3441 (5) | 1.0046 (3) | 0.77075 (17) | 0.0205 (8) | |
| H19 | 0.405089 | 1.046423 | 0.796581 | 0.025* | |
| C9 | 0.7506 (4) | 0.5159 (3) | 0.96437 (16) | 0.0160 (8) | |
| C30 | −0.1529 (5) | 1.0603 (3) | 0.76231 (16) | 0.0175 (8) | |
| H30 | −0.207468 | 1.010101 | 0.739374 | 0.021* | |
| C31 | −0.1760 (4) | 1.0495 (3) | 0.83368 (16) | 0.0153 (7) | |
| C25 | −0.2392 (4) | 1.0181 (3) | 0.96022 (16) | 0.0156 (7) | |
| C26 | −0.0953 (4) | 1.1236 (3) | 0.86839 (15) | 0.0146 (7) | |
| C11 | 0.5392 (5) | 0.7088 (3) | 0.84009 (16) | 0.0196 (8) | |
| H11 | 0.471794 | 0.756926 | 0.864594 | 0.023* | |
| C10 | 0.6358 (4) | 0.6237 (3) | 0.87584 (16) | 0.0160 (8) | |
| C17 | 0.0717 (5) | 0.8133 (3) | 0.89124 (16) | 0.0173 (8) | |
| C22 | 0.1616 (5) | 0.8820 (3) | 0.69313 (16) | 0.0209 (8) | |
| H22 | 0.099841 | 0.841139 | 0.667017 | 0.025* | |
| C6 | 0.4514 (5) | 0.4040 (3) | 0.68358 (17) | 0.0206 (8) | |
| H6 | 0.526557 | 0.368110 | 0.654413 | 0.025* | |
| C15 | 0.7294 (4) | 0.5499 (3) | 0.83875 (16) | 0.0164 (8) | |
| C32 | −0.1223 (5) | 1.2251 (4) | 0.61556 (18) | 0.0308 (10) | |
| C7 | 0.4453 (5) | 0.3729 (3) | 0.75555 (16) | 0.0174 (8) | |
| C28 | 0.0382 (5) | 1.2201 (3) | 0.75845 (16) | 0.0208 (8) | |
| H28 | 0.112366 | 1.277598 | 0.731590 | 0.025* | |
| C18 | 0.2277 (4) | 0.9216 (3) | 0.80461 (16) | 0.0158 (8) | |
| C16 | 0.7463 (5) | 0.7402 (3) | 0.62168 (17) | 0.0275 (9) | |
| C5 | 0.3445 (5) | 0.4888 (3) | 0.65630 (16) | 0.0202 (8) | |
| C13 | 0.6395 (5) | 0.6524 (3) | 0.73365 (16) | 0.0183 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.2279 (5) | 0.5104 (3) | 0.76902 (17) | 0.0204 (8) | |
| H3 | 0.151349 | 0.546462 | 0.797609 | 0.025* | |
| C29 | −0.0478 (5) | 1.1467 (3) | 0.72619 (16) | 0.0195 (8) | |
| C21 | 0.2789 (5) | 0.9644 (3) | 0.66162 (16) | 0.0216 (8) | |
| C27 | 0.0141 (5) | 1.2081 (3) | 0.82977 (16) | 0.0199 (8) | |
| H27 | 0.071741 | 1.257234 | 0.852371 | 0.024* | |
| C4 | 0.2335 (5) | 0.5424 (3) | 0.69743 (17) | 0.0239 (9) | |
| H4 | 0.161571 | 0.600681 | 0.676698 | 0.029* | |
| C8 | 0.2511 (6) | 0.4824 (4) | 0.54838 (19) | 0.0387 (11) | |
| C24 | 0.2624 (6) | 0.9305 (4) | 0.54759 (18) | 0.0347 (11) |
6-(Trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amine (RZ). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0208 (6) | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0253 (4) | 0.0032 (4) | −0.0030 (4) | −0.0070 (3) |
| S2 | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0232 (4) | 0.0015 (4) | −0.0018 (4) | −0.0061 (3) |
| S3 | 0.0192 (6) | 0.0156 (5) | 0.0245 (4) | −0.0047 (4) | −0.0002 (4) | −0.0084 (3) |
| S4 | 0.0187 (6) | 0.0141 (4) | 0.0211 (4) | −0.0028 (4) | −0.0018 (3) | −0.0062 (3) |
| F1 | 0.054 (2) | 0.084 (2) | 0.0219 (12) | 0.0105 (15) | −0.0067 (11) | −0.0060 (12) |
| F2 | 0.123 (3) | 0.0444 (18) | 0.0446 (15) | −0.0135 (17) | −0.0252 (16) | −0.0176 (13) |
| F3 | 0.0352 (19) | 0.114 (3) | 0.0434 (15) | 0.0000 (17) | −0.0094 (12) | −0.0228 (15) |
| F4 | 0.0258 (16) | 0.0544 (16) | 0.0435 (13) | −0.0024 (13) | 0.0007 (11) | −0.0014 (11) |
| F5 | 0.0532 (19) | 0.0484 (15) | 0.0201 (11) | −0.0052 (13) | −0.0036 (10) | −0.0066 (10) |
| F6 | 0.079 (2) | 0.0220 (13) | 0.0322 (12) | −0.0116 (12) | 0.0033 (12) | −0.0042 (10) |
| F7 | 0.066 (2) | 0.0562 (17) | 0.0188 (11) | −0.0080 (14) | 0.0006 (11) | −0.0043 (10) |
| F8 | 0.081 (2) | 0.0370 (15) | 0.0331 (13) | 0.0120 (14) | 0.0028 (12) | −0.0117 (11) |
| F9 | 0.042 (2) | 0.080 (2) | 0.0350 (13) | −0.0092 (15) | −0.0155 (11) | −0.0022 (12) |
| F10 | 0.067 (2) | 0.0360 (15) | 0.0338 (13) | 0.0146 (13) | −0.0077 (12) | −0.0008 (11) |
| F11 | 0.0503 (18) | 0.0570 (16) | 0.0177 (11) | −0.0113 (13) | −0.0014 (10) | −0.0041 (10) |
| F12 | 0.0317 (18) | 0.087 (2) | 0.0378 (13) | −0.0198 (15) | −0.0083 (11) | 0.0024 (13) |
| O1 | 0.0260 (18) | 0.0327 (16) | 0.0232 (13) | −0.0004 (12) | −0.0024 (11) | −0.0001 (11) |
| O2 | 0.0265 (17) | 0.0262 (14) | 0.0180 (12) | −0.0072 (12) | −0.0043 (10) | −0.0059 (10) |
| O3 | 0.043 (2) | 0.0345 (16) | 0.0208 (13) | −0.0110 (14) | 0.0025 (12) | −0.0043 (11) |
| O4 | 0.0307 (18) | 0.0277 (15) | 0.0175 (12) | 0.0016 (12) | −0.0001 (11) | −0.0053 (10) |
| N1 | 0.017 (2) | 0.0176 (17) | 0.0231 (16) | 0.0009 (14) | −0.0057 (13) | −0.0040 (13) |
| N2 | 0.0180 (19) | 0.0115 (15) | 0.0211 (14) | −0.0006 (13) | −0.0026 (12) | −0.0044 (11) |
| N3 | 0.025 (2) | 0.0198 (18) | 0.0203 (17) | 0.0073 (15) | −0.0038 (14) | −0.0047 (14) |
| N4 | 0.0171 (19) | 0.0159 (16) | 0.0211 (14) | −0.0022 (13) | −0.0013 (12) | −0.0049 (11) |
| N5 | 0.020 (2) | 0.0126 (16) | 0.0225 (16) | −0.0034 (14) | 0.0000 (13) | −0.0035 (12) |
| N6 | 0.0194 (19) | 0.0119 (15) | 0.0216 (15) | 0.0002 (13) | −0.0030 (12) | −0.0035 (11) |
| N7 | 0.025 (2) | 0.0221 (18) | 0.0192 (16) | −0.0118 (15) | −0.0006 (13) | −0.0063 (14) |
| N8 | 0.0158 (18) | 0.0155 (15) | 0.0206 (14) | −0.0016 (13) | −0.0003 (12) | −0.0058 (11) |
| C1 | 0.022 (2) | 0.0091 (17) | 0.0248 (18) | −0.0068 (16) | 0.0001 (15) | −0.0051 (14) |
| C2 | 0.020 (2) | 0.0097 (17) | 0.0231 (17) | −0.0044 (15) | −0.0002 (14) | −0.0057 (13) |
| C12 | 0.016 (2) | 0.0176 (19) | 0.0242 (18) | −0.0021 (15) | −0.0072 (14) | −0.0014 (14) |
| C23 | 0.013 (2) | 0.0126 (17) | 0.0223 (17) | −0.0006 (14) | −0.0010 (14) | −0.0045 (14) |
| C20 | 0.023 (2) | 0.0146 (19) | 0.031 (2) | −0.0085 (16) | 0.0002 (16) | −0.0028 (15) |
| C14 | 0.022 (2) | 0.0131 (18) | 0.0241 (18) | −0.0049 (15) | −0.0008 (15) | −0.0086 (14) |
| C19 | 0.019 (2) | 0.0169 (19) | 0.0269 (18) | −0.0057 (16) | −0.0052 (15) | −0.0067 (15) |
| C9 | 0.011 (2) | 0.0144 (18) | 0.0234 (18) | −0.0043 (15) | 0.0009 (14) | −0.0076 (14) |
| C30 | 0.017 (2) | 0.0162 (18) | 0.0224 (18) | 0.0032 (15) | −0.0052 (14) | −0.0096 (14) |
| C31 | 0.016 (2) | 0.0071 (16) | 0.0226 (17) | 0.0007 (14) | −0.0020 (14) | −0.0029 (13) |
| C25 | 0.011 (2) | 0.0148 (18) | 0.0234 (18) | 0.0001 (15) | −0.0042 (14) | −0.0087 (14) |
| C26 | 0.013 (2) | 0.0110 (17) | 0.0211 (17) | 0.0046 (14) | −0.0037 (14) | −0.0048 (13) |
| C11 | 0.018 (2) | 0.0162 (19) | 0.0263 (18) | −0.0031 (16) | −0.0001 (15) | −0.0090 (14) |
| C10 | 0.017 (2) | 0.0096 (17) | 0.0207 (17) | −0.0047 (15) | 0.0005 (14) | −0.0032 (13) |
| C17 | 0.018 (2) | 0.0110 (18) | 0.0242 (18) | 0.0026 (15) | −0.0032 (14) | −0.0055 (14) |
| C22 | 0.021 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.0221 (18) | 0.0004 (16) | −0.0032 (15) | −0.0083 (15) |
| C6 | 0.020 (2) | 0.0185 (19) | 0.0258 (18) | −0.0041 (16) | −0.0014 (15) | −0.0100 (15) |
| C15 | 0.014 (2) | 0.0098 (17) | 0.0252 (18) | −0.0031 (14) | −0.0018 (14) | −0.0033 (13) |
| C32 | 0.031 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.022 (2) | −0.006 (2) | −0.0008 (17) | −0.0034 (17) |
| C7 | 0.014 (2) | 0.0132 (18) | 0.0260 (18) | −0.0011 (15) | −0.0028 (14) | −0.0069 (14) |
| C28 | 0.016 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.0247 (18) | −0.0007 (16) | 0.0038 (14) | −0.0022 (15) |
| C18 | 0.015 (2) | 0.0106 (17) | 0.0230 (17) | 0.0040 (15) | −0.0040 (14) | −0.0054 (13) |
| C16 | 0.035 (3) | 0.025 (2) | 0.0230 (19) | 0.0025 (19) | −0.0042 (16) | −0.0054 (16) |
| C5 | 0.018 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.0207 (17) | −0.0041 (16) | −0.0023 (14) | −0.0020 (14) |
| C13 | 0.018 (2) | 0.0164 (18) | 0.0205 (17) | −0.0068 (15) | −0.0032 (14) | −0.0029 (14) |
| C3 | 0.018 (2) | 0.0160 (19) | 0.0272 (18) | −0.0005 (16) | 0.0005 (15) | −0.0062 (15) |
| C29 | 0.022 (2) | 0.0186 (19) | 0.0182 (17) | 0.0042 (16) | 0.0004 (14) | −0.0060 (14) |
| C21 | 0.020 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.0218 (18) | −0.0005 (16) | 0.0002 (15) | −0.0027 (14) |
| C27 | 0.023 (2) | 0.0149 (18) | 0.0236 (18) | 0.0006 (16) | −0.0042 (15) | −0.0062 (14) |
| C4 | 0.022 (2) | 0.0169 (19) | 0.033 (2) | 0.0006 (16) | −0.0065 (16) | −0.0024 (15) |
| C8 | 0.042 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.022 (2) | 0.001 (2) | −0.0040 (18) | −0.0069 (19) |
| C24 | 0.044 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.021 (2) | 0.000 (2) | −0.0057 (18) | −0.0024 (17) |
6-(Trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amine (RZ). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C7 | 1.739 (4) | N6—C18 | 1.399 (4) |
| S1—C1 | 1.759 (3) | N7—C25 | 1.335 (4) |
| S2—C15 | 1.740 (3) | N7—H7A | 0.88 (4) |
| S2—C9 | 1.766 (3) | N7—H7B | 0.85 (4) |
| S3—C23 | 1.736 (3) | N8—C25 | 1.307 (4) |
| S3—C17 | 1.766 (3) | N8—C26 | 1.391 (4) |
| S4—C31 | 1.742 (3) | C2—C3 | 1.381 (5) |
| S4—C25 | 1.768 (3) | C2—C7 | 1.411 (4) |
| F1—C8 | 1.313 (4) | C12—C11 | 1.383 (4) |
| F2—C8 | 1.300 (5) | C12—C13 | 1.391 (5) |
| F3—C8 | 1.342 (5) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| F4—C16 | 1.330 (5) | C23—C22 | 1.393 (4) |
| F5—C16 | 1.312 (4) | C23—C18 | 1.400 (5) |
| F6—C16 | 1.337 (4) | C20—C19 | 1.381 (4) |
| F7—C24 | 1.315 (4) | C20—C21 | 1.398 (5) |
| F8—C24 | 1.320 (5) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| F9—C24 | 1.332 (5) | C14—C13 | 1.374 (5) |
| F10—C32 | 1.334 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.392 (4) |
| F11—C32 | 1.315 (4) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| F12—C32 | 1.331 (5) | C19—C18 | 1.387 (5) |
| O1—C8 | 1.351 (5) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C5 | 1.406 (4) | C30—C29 | 1.371 (5) |
| O2—C16 | 1.342 (5) | C30—C31 | 1.383 (4) |
| O2—C13 | 1.411 (4) | C30—H30 | 0.9500 |
| O3—C24 | 1.345 (5) | C31—C26 | 1.413 (5) |
| O3—C21 | 1.403 (4) | C26—C27 | 1.393 (5) |
| O4—C32 | 1.337 (5) | C11—C10 | 1.386 (5) |
| O4—C29 | 1.417 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.374 (4) | C10—C15 | 1.414 (4) |
| N1—H1A | 0.84 (4) | C22—C21 | 1.376 (5) |
| N1—H1B | 0.88 (4) | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C1 | 1.301 (4) | C6—C5 | 1.375 (5) |
| N2—C2 | 1.392 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.391 (5) |
| N3—C9 | 1.338 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| N3—H3A | 0.84 (4) | C28—C27 | 1.381 (4) |
| N3—H3B | 0.82 (4) | C28—C29 | 1.400 (5) |
| N4—C9 | 1.309 (4) | C28—H28 | 0.9500 |
| N4—C10 | 1.394 (4) | C5—C4 | 1.383 (5) |
| N5—C17 | 1.374 (4) | C3—C4 | 1.384 (5) |
| N5—H5A | 0.89 (5) | C3—H3 | 0.9500 |
| N5—H5B | 0.82 (5) | C27—H27 | 0.9500 |
| N6—C17 | 1.288 (4) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C7—S1—C1 | 88.72 (16) | N6—C17—N5 | 124.8 (3) |
| C15—S2—C9 | 88.86 (16) | N6—C17—S3 | 116.1 (2) |
| C23—S3—C17 | 88.43 (16) | N5—C17—S3 | 119.0 (3) |
| C31—S4—C25 | 88.76 (16) | C21—C22—C23 | 116.4 (3) |
| C8—O1—C5 | 116.5 (3) | C21—C22—H22 | 121.8 |
| C16—O2—C13 | 115.7 (3) | C23—C22—H22 | 121.8 |
| C24—O3—C21 | 120.0 (3) | C5—C6—C7 | 117.4 (3) |
| C32—O4—C29 | 115.5 (3) | C5—C6—H6 | 121.3 |
| C1—N1—H1A | 117 (2) | C7—C6—H6 | 121.3 |
| C1—N1—H1B | 116 (3) | C14—C15—C10 | 121.6 (3) |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 110 (4) | C14—C15—S2 | 128.8 (3) |
| C1—N2—C2 | 110.8 (3) | C10—C15—S2 | 109.6 (2) |
| C9—N3—H3A | 119 (2) | F11—C32—F12 | 108.3 (3) |
| C9—N3—H3B | 116 (3) | F11—C32—F10 | 108.5 (3) |
| H3A—N3—H3B | 124 (4) | F12—C32—F10 | 105.5 (3) |
| C9—N4—C10 | 110.5 (3) | F11—C32—O4 | 108.7 (3) |
| C17—N5—H5A | 120 (2) | F12—C32—O4 | 113.5 (3) |
| C17—N5—H5B | 112 (4) | F10—C32—O4 | 112.2 (3) |
| H5A—N5—H5B | 119 (4) | C6—C7—C2 | 121.2 (3) |
| C17—N6—C18 | 110.7 (3) | C6—C7—S1 | 129.0 (3) |
| C25—N7—H7A | 123 (2) | C2—C7—S1 | 109.7 (2) |
| C25—N7—H7B | 118 (3) | C27—C28—C29 | 119.2 (3) |
| H7A—N7—H7B | 118 (3) | C27—C28—H28 | 120.4 |
| C25—N8—C26 | 110.3 (3) | C29—C28—H28 | 120.4 |
| N2—C1—N1 | 123.7 (3) | C19—C18—N6 | 125.9 (3) |
| N2—C1—S1 | 116.0 (2) | C19—C18—C23 | 119.3 (3) |
| N1—C1—S1 | 120.2 (3) | N6—C18—C23 | 114.8 (3) |
| C3—C2—N2 | 126.0 (3) | F5—C16—F4 | 108.6 (3) |
| C3—C2—C7 | 119.2 (3) | F5—C16—F6 | 108.1 (3) |
| N2—C2—C7 | 114.7 (3) | F4—C16—F6 | 105.8 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.4 (3) | F5—C16—O2 | 108.7 (3) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 120.3 | F4—C16—O2 | 112.8 (3) |
| C13—C12—H12 | 120.3 | F6—C16—O2 | 112.7 (3) |
| C22—C23—C18 | 122.5 (3) | C6—C5—C4 | 122.6 (3) |
| C22—C23—S3 | 127.6 (3) | C6—C5—O1 | 118.0 (3) |
| C18—C23—S3 | 109.9 (2) | C4—C5—O1 | 119.2 (3) |
| C19—C20—C21 | 119.9 (3) | C14—C13—C12 | 122.9 (3) |
| C19—C20—H20 | 120.1 | C14—C13—O2 | 119.0 (3) |
| C21—C20—H20 | 120.1 | C12—C13—O2 | 117.9 (3) |
| C13—C14—C15 | 117.0 (3) | C2—C3—C4 | 119.9 (3) |
| C13—C14—H14 | 121.5 | C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 |
| C15—C14—H14 | 121.5 | C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 |
| C20—C19—C18 | 119.4 (3) | C30—C29—C28 | 123.0 (3) |
| C20—C19—H19 | 120.3 | C30—C29—O4 | 119.3 (3) |
| C18—C19—H19 | 120.3 | C28—C29—O4 | 117.6 (3) |
| N4—C9—N3 | 124.9 (3) | C22—C21—C20 | 122.6 (3) |
| N4—C9—S2 | 115.9 (2) | C22—C21—O3 | 123.8 (3) |
| N3—C9—S2 | 119.2 (3) | C20—C21—O3 | 113.6 (3) |
| C29—C30—C31 | 117.0 (3) | C28—C27—C26 | 119.7 (3) |
| C29—C30—H30 | 121.5 | C28—C27—H27 | 120.2 |
| C31—C30—H30 | 121.5 | C26—C27—H27 | 120.2 |
| C30—C31—C26 | 122.0 (3) | C5—C4—C3 | 119.6 (3) |
| C30—C31—S4 | 128.6 (3) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.2 |
| C26—C31—S4 | 109.3 (2) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.2 |
| N8—C25—N7 | 124.8 (3) | F2—C8—F1 | 110.3 (3) |
| N8—C25—S4 | 116.0 (2) | F2—C8—F3 | 107.3 (4) |
| N7—C25—S4 | 119.2 (3) | F1—C8—F3 | 107.0 (3) |
| N8—C26—C27 | 125.4 (3) | F2—C8—O1 | 113.1 (4) |
| N8—C26—C31 | 115.6 (3) | F1—C8—O1 | 107.9 (4) |
| C27—C26—C31 | 119.0 (3) | F3—C8—O1 | 111.2 (3) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 120.0 (3) | F7—C24—F8 | 109.2 (3) |
| C12—C11—H11 | 120.0 | F7—C24—F9 | 107.8 (3) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.0 | F8—C24—F9 | 107.4 (4) |
| C11—C10—N4 | 125.7 (3) | F7—C24—O3 | 107.2 (4) |
| C11—C10—C15 | 119.0 (3) | F8—C24—O3 | 113.3 (3) |
| N4—C10—C15 | 115.2 (3) | F9—C24—O3 | 111.9 (3) |
| C2—N2—C1—N1 | −178.1 (3) | N2—C2—C7—C6 | −177.6 (3) |
| C2—N2—C1—S1 | −0.9 (4) | C3—C2—C7—S1 | 178.1 (3) |
| C7—S1—C1—N2 | 0.8 (3) | N2—C2—C7—S1 | 0.2 (4) |
| C7—S1—C1—N1 | 178.1 (3) | C1—S1—C7—C6 | 177.0 (3) |
| C1—N2—C2—C3 | −177.3 (4) | C1—S1—C7—C2 | −0.6 (3) |
| C1—N2—C2—C7 | 0.4 (4) | C20—C19—C18—N6 | −179.3 (3) |
| C17—S3—C23—C22 | −179.0 (3) | C20—C19—C18—C23 | −0.6 (5) |
| C17—S3—C23—C18 | −0.2 (3) | C17—N6—C18—C19 | 178.7 (3) |
| C21—C20—C19—C18 | 0.5 (5) | C17—N6—C18—C23 | −0.1 (4) |
| C10—N4—C9—N3 | −179.1 (3) | C22—C23—C18—C19 | 0.2 (5) |
| C10—N4—C9—S2 | 1.7 (4) | S3—C23—C18—C19 | −178.6 (3) |
| C15—S2—C9—N4 | −1.2 (3) | C22—C23—C18—N6 | 179.0 (3) |
| C15—S2—C9—N3 | 179.6 (3) | S3—C23—C18—N6 | 0.2 (4) |
| C29—C30—C31—C26 | −0.1 (5) | C13—O2—C16—F5 | −175.2 (3) |
| C29—C30—C31—S4 | 177.0 (3) | C13—O2—C16—F4 | 64.3 (4) |
| C25—S4—C31—C30 | −178.7 (3) | C13—O2—C16—F6 | −55.4 (4) |
| C25—S4—C31—C26 | −1.3 (3) | C7—C6—C5—C4 | −0.2 (6) |
| C26—N8—C25—N7 | 179.3 (3) | C7—C6—C5—O1 | 174.7 (3) |
| C26—N8—C25—S4 | −2.5 (4) | C8—O1—C5—C6 | 98.8 (4) |
| C31—S4—C25—N8 | 2.3 (3) | C8—O1—C5—C4 | −86.2 (4) |
| C31—S4—C25—N7 | −179.4 (3) | C15—C14—C13—C12 | −2.1 (5) |
| C25—N8—C26—C27 | −179.1 (3) | C15—C14—C13—O2 | −177.3 (3) |
| C25—N8—C26—C31 | 1.4 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 2.3 (5) |
| C30—C31—C26—N8 | 177.9 (3) | C11—C12—C13—O2 | 177.5 (3) |
| S4—C31—C26—N8 | 0.2 (4) | C16—O2—C13—C14 | −92.6 (4) |
| C30—C31—C26—C27 | −1.7 (5) | C16—O2—C13—C12 | 92.0 (4) |
| S4—C31—C26—C27 | −179.3 (3) | N2—C2—C3—C4 | 177.0 (3) |
| C13—C12—C11—C10 | 0.3 (5) | C7—C2—C3—C4 | −0.6 (5) |
| C12—C11—C10—N4 | 176.5 (3) | C31—C30—C29—C28 | 1.8 (5) |
| C12—C11—C10—C15 | −2.7 (5) | C31—C30—C29—O4 | 177.8 (3) |
| C9—N4—C10—C11 | 179.1 (3) | C27—C28—C29—C30 | −1.8 (5) |
| C9—N4—C10—C15 | −1.6 (4) | C27—C28—C29—O4 | −177.8 (3) |
| C18—N6—C17—N5 | 176.4 (3) | C32—O4—C29—C30 | 87.5 (4) |
| C18—N6—C17—S3 | −0.1 (4) | C32—O4—C29—C28 | −96.3 (4) |
| C23—S3—C17—N6 | 0.2 (3) | C23—C22—C21—C20 | −0.3 (5) |
| C23—S3—C17—N5 | −176.5 (3) | C23—C22—C21—O3 | −179.3 (3) |
| C18—C23—C22—C21 | 0.3 (5) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 0.0 (6) |
| S3—C23—C22—C21 | 178.8 (3) | C19—C20—C21—O3 | 179.0 (3) |
| C13—C14—C15—C10 | −0.5 (5) | C24—O3—C21—C22 | −13.4 (6) |
| C13—C14—C15—S2 | −177.1 (3) | C24—O3—C21—C20 | 167.6 (4) |
| C11—C10—C15—C14 | 2.9 (5) | C29—C28—C27—C26 | −0.1 (5) |
| N4—C10—C15—C14 | −176.5 (3) | N8—C26—C27—C28 | −177.7 (3) |
| C11—C10—C15—S2 | −179.9 (3) | C31—C26—C27—C28 | 1.7 (5) |
| N4—C10—C15—S2 | 0.7 (4) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | −0.1 (6) |
| C9—S2—C15—C14 | 177.1 (3) | O1—C5—C4—C3 | −174.9 (3) |
| C9—S2—C15—C10 | 0.2 (3) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.5 (5) |
| C29—O4—C32—F11 | 174.4 (3) | C5—O1—C8—F2 | −53.5 (5) |
| C29—O4—C32—F12 | −65.1 (4) | C5—O1—C8—F1 | −175.7 (3) |
| C29—O4—C32—F10 | 54.4 (4) | C5—O1—C8—F3 | 67.2 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | 0.1 (5) | C21—O3—C24—F7 | −175.9 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—S1 | −177.3 (3) | C21—O3—C24—F8 | −55.4 (5) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | 0.3 (5) | C21—O3—C24—F9 | 66.1 (4) |
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, India grant . Science and Engineering Research Board grant .
References
- Ball, V. & Maechling, C. (2009). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 10, 3283–3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker, (2009). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cruz-Cabeza, A. J. & Bernstein, J. (2014). Chem. Rev. 114, 2170–2191. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Davey, R. J., Schroeder, S. L. M. & ter Horst, J. H. (2013). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 2166–2179. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Desiraju, G. R. (2013). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 9952–9967. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Doble, A. (1996). Neurology, 47, S233–S241. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Frisch, M. J., Trucks, G. W., Schlegel, H. B., Scuseria, G. E., Robb, M. A., Cheeseman, J. R., Scalmani, G., Barone, V., Mennucci, B., Petersson, G. A., Nakatsuji, H., Caricato, M., Li, X., Hratchian, H. P., Izmaylov, A. F., Bloino, J., Zheng, G., Sonnenberg, J. L., Hada, M., Ehara, M., Toyota, K., Fukuda, R., Hasegawa, J., Ishida, M., Nakajima, T., Honda, Y., Kitao, O., Nakai, H., Vreven, T., Montgomery, J. J. A., Peralta, J. E., Ogliaro, F., Bearpark, M., Heyd, J. J., Brothers, E., Kudin, K. N., Staroverov, V. N., Kobayashi, R., Normand, J., Raghavachari, K., Rendell, A., Burant, J. C., Iyengar, S. S., Tomasi, J., Cossi, M., Rega, N., Millam, J. M., Klene, M., Knox, J. E., Cross, J. B., Bakken, V., Adamo, C., Jaramillo, J., Gomperts, R., Stratmann, R. E., Yazyev, O., Austin, A. J., Cammi, R., Pomelli, C., Ochterski, J. W., Martin, R. L., Morokuma, K., Zakrzewski, V. G., Voth, G. A., Salvador, P., Dannenberg, J. J., Dapprich, S., Daniels, A. D., Farkas, O., Foresman, J. B., Ortiz, J. V., Cioslowski, J. & Fox, D. J. (2009). Gaussian09. Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, Connecticut, USA.
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Mondal, P. K., Kiran, M. S. R. N., Ramamurty, U. & Chopra, D. (2017). Chem. Eur. J. 23, 1023–1027. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mondal, P. K., Rao, V. & Chopra, D. (2018). CrystEngComm, 20, 2079–2083.
- Mondal, P. K., Rao, V., Mittapalli, S. & Chopra, D. (2017). Cryst. Growth Des. 17, 1938–1946.
- Nakane, S., Izumi, Y., Oda, M., Kaji, R. & Matsuo, H. (2016). Intern. Med. 55, 1985–1990. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- Panini, P., Gonnade, R. G. & Chopra, D. (2016). New J. Chem. 40, 4981–5001.
- Paulini, R., Müller, K. & Diederich, F. (2005). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44, 1788–1805. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Raynal, M., Ballester, P., Vidal-Ferran, A. & van Leeuwen, P. W. N. M. (2014). Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 1660–1733. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008a). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spackman, M. A., McKinnon, J. J. & Jayatilaka, D. (2008). CrystEngComm, 10, 377–388.
- Taylor, R. & Kennard, O. (1983). Acta Cryst. B39, 133–138.
- Thomas, S. P., Kumar, V., Alhameedi, K. & Guru Row, T. N. (2019). Chem. Eur. J. 25, 3591–3597. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yadav, B., Balasubramanian, S., Chavan, R. B., Thipparaboina, R., Naidu, V. G. M. & Shastri, N. R. (2018). Cryst. Growth Des. 18, 1047–1061.
- Yan, Y. & Huang, J. (2010). Coord. Chem. Rev. 254, 1072–1080.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) RZHCl, RZ. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009022/xi2017sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) RZHCl. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009022/xi2017RZHClsup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) RZ. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009022/xi2017RZsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009022/xi2017RZHClsup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009022/xi2017RZsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report









