The crystal structures of two new isocoumarin derivatives, 8-amino-6-methyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-isochromen-1-one and 8-amino-3,4-diethyl-6-methyl-1H-isochromen-1-one, are described. The intermolecular contacts in the crystals were analysed using Hirshfeld surface analysis and two-dimensional fingerprint plots.
Keywords: crystal structure, chromen, isochromene, hydrogen bonding, N—H⋯π interactions, C—H⋯π interactions, offset π—π interactions, Hirshfeld surface analysis
Abstract
The title compounds, 8-amino-6-methyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-isochromen-1-one, C22H17NO2, (I), and 8-amino-3,4-diethyl-6-methyl-1H-isochromen-1-one, C14H17NO2, (II), are new isocoumarin derivatives in which the isochromene ring systems are planar. Compound II crystallizes with two independent molecules (A and B) in the asymmetric unit. In I, the two phenyl rings are inclined to each other by 56.41 (7)° and to the mean plane of the 1H-isochromene ring system by 67.64 (6) and 44.92 (6)°. In both compounds, there is an intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond present forming an S(6) ring motif. In the crystal of I, molecules are linked by N—H⋯π interactions, forming chains along the b-axis direction. A C—H⋯π interaction links the chains to form layers parallel to (100). The layers are then linked by a second C—H⋯π interaction, forming a three-dimensional structure. In the crystal of II, the two independent molecules (A and B) are linked by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming –A–B–A–B– chains along the [101] direction. The chains are linked into ribbons by C—H⋯π interactions involving inversion-related A molecules. The latter are linked by offset π–π interactions [intercentroid distances vary from 3.506 (1) to 3.870 (2) Å], forming a three-dimensional structure.
Chemical context
In recent years, there has been growing interest in the synthesis of natural products, since they are a tremendous and trustworthy source for the development of new drugs. The isocoumarin nucleus is a rich structural pattern in natural products (Barry, 1964 ▸) that are also constructive intermediates in the synthesis of a range of significant compounds, including some carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds. Many isocoumarins show evidence of attention-grabbing biological properties and a number of pharmacological activities, such as antibacterial, antifungal, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic anti-cancer, anti-virus and anti-HIV (Khan et al., 2010 ▸) activities. Isocoumarins are isolated in a enormous range of microorganisms, plants, insects and show significant biological activity, such the regulation of plant growth (Bianchi et al., 2004 ▸). Isocoumarins and their derivatives are secondary metabolites of an extensive range of microbial plant and insect sources and in the creation of other medicinal compounds (Manivel et al., 2008 ▸; Basvanag et al., 2009 ▸). Depending on their chemical composition and concentration, they can be active either as inhibitors or stimulators in these processes. Isocoumarins and their derivatives (Ercole et al., 2009 ▸; Schnebel et al., 2003 ▸; Schmalle et al., 1982 ▸) have been reported that have a close resemblance as far as isochromane and its attached phenyl ring is considered. The synthesis and pharmacological and other properties of coumarin and isocoumarin derivatives have been studied intensely and reviewed (Jain et al., 2012 ▸; Pal et al., 2011 ▸). Against this background and in view of the importance of their natural occurrence, biological activities, pharmacological activities, medicinal activities and utility as synthetic intermediates, we have synthesized the title compounds, and report herein on their crystal structures.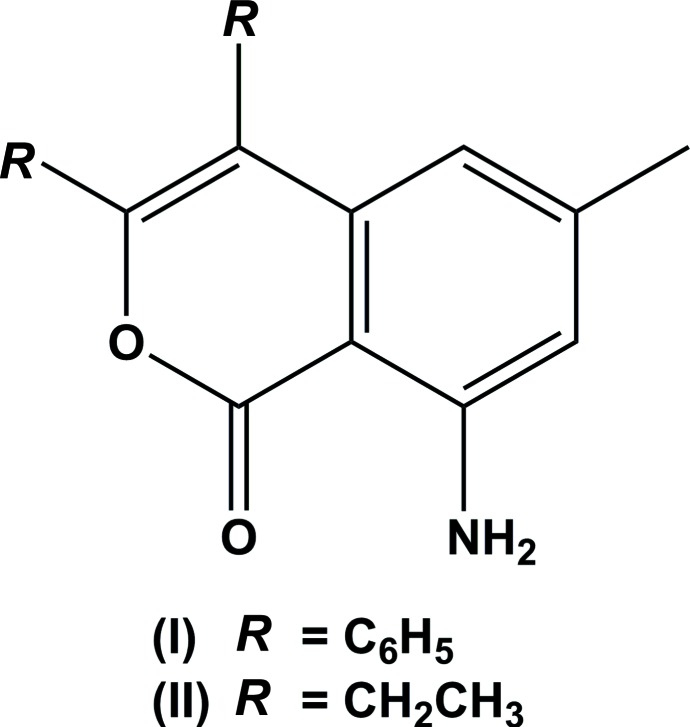
Structural commentary
The molecular structure and conformation of compound I is illustrated in Fig. 1 ▸. It consists of a 1H-isochromen-1-one moiety substituted by two phenyl groups, an amino group and a methyl group. The molecular structures and conformations of the two independent molecules (A and B) of compound II are illustrated in Fig. 2 ▸. Both molecules consist of a 1H-isochromen-1-one moiety substituted by two ethyl groups, an amino group and a methyl group. The bond lengths and angles in the two independent molecules agree with each other within experimental error. The normal probability plot analyses (International Tables for X-ray Crystallography, 1974, Vol. IV, pp. 293–309) for both bond lengths and angles show that the differences between the two symmetry-independent molecules are of a statistical nature. For both compounds, the bond lengths and angles are close to those observed for a similar structure (Mayakrishnan et al., 2018 ▸). In both compounds, there is an intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond present in each molecule forming an S(6) ring motif: see Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 1 ▸ for I, and Table 2 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸ for II.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of I, with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond (Table 1 ▸) is shown as a dashed line.
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of the two independent molecules (A and B) of II, with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Table 2 ▸) are shown as dashed lines.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for I .
Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C17–C22, C11–C16 and C1/C5–C9 rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H2N⋯O2 | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.6915 (19) | 131 |
| N1—H1N⋯Cg1i | 0.86 | 2.81 | 3.631 (2) | 157 |
| C20—H20⋯Cg2ii | 0.93 | 2.70 | 3.588 (2) | 160 |
| C21—H21⋯Cg3iii | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.488 (2) | 128 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for II .
Cg2 is the centroid of the C1A/C5A–C9A ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1A—H1A2⋯O2A | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.701 (3) | 131 |
| N1B—H1B2⋯O2B | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.696 (3) | 131 |
| N1A—H1A1⋯O1B i | 0.86 | 2.57 | 3.328 (3) | 148 |
| N1B—H1B1⋯O1A ii | 0.86 | 2.50 | 3.235 (3) | 143 |
| N1B—H1B1⋯O2A ii | 0.86 | 2.53 | 3.367 (3) | 165 |
| C12A—H12A⋯Cg2iii | 0.96 | 2.99 | 3.773 (2) | 140 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
In I, the phenyl rings (C11–C16 and C17–C22) are inclined to each other by 56.41 (7)° and to the mean plane of the 1H-isochromen-1-one (O1/C1–C9) ring system by 67.64 (6) and 44.92 (6)°, respectively. The 1H-isochromen-1-one moiety is planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.021 Å) and atom O2 deviates from the mean plane by 0.041 (1) Å. In II, the 1H-isochromen-1-one ring system in each molecule (A and B) is also planar (r.m.s. deviations are 0.012 and 0.0321Å, respectively) and atoms O2A and O2B deviate from their respective mean planes by 0.052 (2) and 0.014 (2) Å, respectively.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal of I, molecules are linked by N—H⋯π interactions, forming chains along the b-axis direction (Fig. 3 ▸ and Table 1 ▸). A C—H⋯π interaction (C20—H20⋯Cg2ii; Table 1 ▸) links the chains into layers parallel to (100). The layers are linked by a second C—H⋯π interaction (C21—H21⋯Cg3iii; Table 1 ▸) to form a three-dimensional structure (Fig. 4 ▸). No significant π–π interactions with centroid–centroid distances less than 4 Å are observed.
Figure 3.
A partial view along the a axis of the crystal packing of I. The intramolecular hydrogen bond and the N—H⋯π interaction (Table 1 ▸) are shown as dashed lines, and only the H atoms (grey balls) involved in the various interactions have been included.
Figure 4.
A view along the b axis of the crystal packing of I. The intramolecular hydrogen bonds and the N—H⋯π and C—H⋯π interactions (Table 1 ▸) are shown as dashed lines, and only the H atoms (grey balls) involved in the various interactions have been included.
In the crystal of II, the two independent molecules are linked by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds involving the amino H atom of molecule B and the keto and chromen group oxygen atoms, O1A and O2A, of molecule A, forming –A–B–A–B– chains along the [101] direction (see Table 2 ▸ and Fig. 5 ▸). The chains are linked by C—H⋯π interactions involving inversion-related A molecules to form ribbons (Table 2 ▸ and Fig. 5 ▸). The ribbons are linked by offset π–π interactions, forming a three-dimensional structure (Fig. 6 ▸): intercentroid distances Cg1⋯Cg2i = 3.506 (2) Å [α = 0.97 (12)°, β = 15.9°, interplanar distances = 3.356 (1) and 3.373 (1) Å, offset = 0.958 Å] and Cg3⋯Cg4iv = 3.870 (2) Å [α = 6.01 (13)°, β = 16.5°, interplanar distances = 3.611 (1) and 3.711 (1) Å, offset = 1.392 Å]; symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z; (iv) −x, −y +  , z −
, z −  ; Cg1, Cg2, Cg3 and Cg4 are centroids of the (O1A/C1A–C4A/C9A), (C1A/C5A–C9A), (O1B/C1B–C4B/C9B) and (C1B/C5B–C9B) rings, respectively].
; Cg1, Cg2, Cg3 and Cg4 are centroids of the (O1A/C1A–C4A/C9A), (C1A/C5A–C9A), (O1B/C1B–C4B/C9B) and (C1B/C5B–C9B) rings, respectively].
Figure 5.
A partial view of the crystal packing of II (molecule A blue, molecule B red). The intramolecular hydrogen bond (Table 2 ▸) and the C—H⋯π interaction, involving atom H12A (blue ball), are shown as dashed lines, and only the H atoms involved in the various interactions have been included.
Figure 6.
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of II (molecule A blue, molecule B red; O and N atoms are shown as balls). The hydrogen bonds (Table 2 ▸) are shown as dashed lines, and only the H atoms involved in hydrogen bonding have been included.
Hirshfeld surface analysis
The Hirshfeld surface analysis (Spackman & Jayatilaka, 2009 ▸), and the associated two-dimensional fingerprint plots (McKinnon et al., 2007 ▸), to analyse the intermolecular contacts in the crystals, were performed with CrystalExplorer17 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸).
The Hirshfeld surfaces of I and II mapped over d norm are given in Fig. 7 ▸, and the intermolecular contacts are illustrated in Fig. 8 ▸ for I and Fig. 9 ▸ for II. They are colour-mapped with the normalized contact distance, d norm, ranging from red (distances shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii) through white to blue (distances longer than the sum of the van der Waals radii). The d norm surface was mapped over an arbitrary colour scale of −0.125 (red) to 1.528 (blue) for compound I and −0.178 (red) to 1.537 (blue) for compound II. The red spots on the surface indicate the intermolecular contacts involved in hydrogen bonding.
Figure 7.
The Hirshfeld surfaces mapped over d norm, for (a) I and (b) II.
Figure 8.
A view of the Hirshfeld surface mapped over d norm of I, showing the various intermolecular contacts in the crystal.
Figure 9.
A view of the Hirshfeld surface mapped over d norm of II, showing the various intermolecular contacts in the crystal.
The fingerprint plots are given in Figs. 10 ▸ and 11 ▸. For I, they reveal that the principal intermolecular contacts are H⋯H at 48.9% (Fig. 10 ▸ b), O⋯H/H⋯O at 14.0% (Fig. 10 ▸ c), C⋯H/H⋯C contacts at 15.4% (Fig. 10 ▸ d) and H⋯N/N⋯H at 1.4% (Fig. 10 ▸ e) followed by the C⋯C contacts at 2% (Fig. 10 ▸ f). For II, they reveal a similar trend, with the principal intermolecular contacts being H⋯H at 61.7% (Fig. 11 ▸ b), O⋯H/H⋯O at 15.6% (Fig. 11 ▸ c), C⋯H/H⋯C contacts at 14.6% (Fig. 11 ▸ d), and C⋯C contacts at 5.1% (Fig. 11 ▸ e) followed by the H⋯N/N⋯H at 2.2% (Fig. 11 ▸ f). In both compounds, the H⋯H intermolecular contacts predominate, followed by O⋯H/H⋯O contacts. However, the C⋯C contacts are significantly different: 2% cf. 5.1% for I and II, respectively.
Figure 10.
The full two-dimensional fingerprint plot for I, and fingerprint plots delineated into (b) H⋯H, (c) O⋯H/H⋯O, (d) C⋯H/H⋯C, (e) N⋯H/H⋯N contacts and (f) C⋯C.
Figure 11.
The full two-dimensional fingerprint plot for II, and fingerprint plots delineated into (b) H⋯H, (c) O⋯H/H⋯O, (d) C⋯·H/H⋯C, (e) C⋯C and (f) N⋯H/H⋯N contacts.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.40, last update May 2019; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for 8-amino-1H-isochromen-1-ones gave only one hit, viz. 8-amino-3,4-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-isochromen-1-one (CSD refcode NIKMAY; Mayakrishnan et al., 2018 ▸). The conformation of this molecule is slightly different from that of compound (I). The isochromen-1-one ring system is planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.042 Å) and the 4-methoxyphenyl rings are inclined to this mean plane by 67.22 (13) and 71.26 (11)°, and to each other by 66.91 (18)°. The corresponding dihedral angles in compound I are 67.64 (6), 44.92 (6) and 56.41 (7)°. There is an intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond forming an S(6) ring motif as in compound (I). In the crystal, however, molecules are linked by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds into chains along [301], similar to the situation in compound II, rather than by N—H⋯π interactions as in the crystal of compound I.
Synthesis and crystallization
Compound I: An oven-dried round-bottom 25 ml flask with a magnetic stirrer bar was charged with 7-methyl-2H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazine-2,4(1H)-dione (1.0 equiv), diphenylacetylene (1.2 equiv), [RhCp*Cl2]2 (3.0 mol %), Cu(OAc) (1.0 equiv) and dimethylformamide (5 ml). The flask was sealed using a Teflon-coated screw cap and the reaction was continuously heated at 383 K for 24 h. The mixture was then cooled to ambient temperature, diluted with 25 ml of ethyl acetate, filtered through a celite pad, and washed with 40–60 ml of ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases were concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by column chromatography using silica gel which led to the desired product, compound I.
Compound II: An oven-dried round-bottom 25 ml flask with a magnetic stirrer bar was charged with 7-methyl-2H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazine-2,4(1H)-dione (1.0 equiv), hex-3-yne (1.2 equiv), [RhCp*Cl2]2 (3.0 mol %), Cu(OAc) (1.0 equiv) and dimethylformamide (5 ml). The flask was sealed using a Teflon-coated screw cap and the reaction was continuously heated at 383 K for 24 h. The mixture was then cooled to ambient temperature, diluted with 25 ml of ethyl acetate, then filtered through a celite pad and washed with 40–60 ml of ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases were concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by column chromatography using silica gel, which led to the desired product, viz. compound II.
Colourless block-like crystals of compounds I and II were obtained by slow evaporation of solutions in ethanol.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. All H atoms were positioned geometrically, with N—H = 0.86 Å, C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C-methyl) and 1.2U eq(N, C) for other H atoms. The crystal of compound II diffracted extremely weakly beyond 20° in θ and the data set was restricted to a maximum θ angle of 23.8°.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| I | II | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C22H17NO2 | C14H17NO2 |
| M r | 327.36 | 231.28 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 296 | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 9.1652 (3), 16.9764 (6), 10.9687 (4) | 10.4844 (8), 26.562 (2), 9.3651 (6) |
| β (°) | 91.156 (1) | 105.367 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 1706.30 (10) | 2514.8 (3) |
| Z | 4 | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.32 × 0.18 × 0.12 | 0.25 × 0.22 × 0.13 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.756, 0.824 | 0.756, 0.824 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 14904, 3628, 2719 | 13067, 3755, 2132 |
| R int | 0.025 | 0.048 |
| θmax (°) | 26.8 | 23.8 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.634 | 0.567 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.040, 0.118, 1.03 | 0.054, 0.168, 1.01 |
| No. of reflections | 3628 | 3755 |
| No. of parameters | 228 | 313 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.22, −0.15 | 0.15, −0.25 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009435/su5498sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009435/su5498Isup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009435/su5498IIsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009435/su5498Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009435/su5498IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the SAIF, IIT, Madras, India, for the data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
8-Amino-6-methyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (I) . Crystal data
| C22H17NO2 | F(000) = 688 |
| Mr = 327.36 | Dx = 1.274 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.1652 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 3001 reflections |
| b = 16.9764 (6) Å | θ = 1.8–26.9° |
| c = 10.9687 (4) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| β = 91.156 (1)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1706.30 (10) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.32 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm |
8-Amino-6-methyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (I) . Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2719 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| ω and φ scans | Rint = 0.025 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | θmax = 26.8°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Tmin = 0.756, Tmax = 0.824 | h = −7→11 |
| 14904 measured reflections | k = −16→21 |
| 3628 independent reflections | l = −13→13 |
8-Amino-6-methyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (I) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.118 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0561P)2 + 0.3498P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3628 reflections | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 228 parameters | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: (SHELXL-2018/3; Sheldrick 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.027 (3) |
8-Amino-6-methyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (I) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
8-Amino-6-methyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (I) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.30517 (11) | 0.50819 (6) | −0.13908 (8) | 0.0428 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.34168 (15) | 0.45740 (7) | −0.31876 (9) | 0.0642 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.29626 (19) | 0.30274 (9) | −0.35783 (12) | 0.0693 (5) | |
| H1N | 0.296082 | 0.260175 | −0.400359 | 0.083* | |
| H2N | 0.321068 | 0.346662 | −0.390514 | 0.083* | |
| C1 | 0.25918 (14) | 0.36948 (8) | −0.16525 (11) | 0.0369 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.30400 (16) | 0.44376 (9) | −0.21526 (12) | 0.0423 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.26388 (14) | 0.50381 (8) | −0.01861 (11) | 0.0343 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.22498 (14) | 0.43536 (8) | 0.03282 (11) | 0.0328 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.18557 (15) | 0.29115 (8) | 0.00781 (13) | 0.0404 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.162684 | 0.287498 | 0.089835 | 0.048* | |
| C6 | 0.18321 (16) | 0.22339 (9) | −0.06446 (14) | 0.0444 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.21712 (16) | 0.22931 (9) | −0.18611 (14) | 0.0466 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.213012 | 0.184295 | −0.234375 | 0.056* | |
| C8 | 0.25737 (16) | 0.30058 (9) | −0.23912 (12) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.22152 (14) | 0.36370 (8) | −0.04094 (11) | 0.0338 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.1460 (2) | 0.14520 (10) | −0.00914 (18) | 0.0717 (6) | |
| H10A | 0.063444 | 0.151158 | 0.042499 | 0.108* | |
| H10B | 0.227983 | 0.126275 | 0.038250 | 0.108* | |
| H10C | 0.122961 | 0.108174 | −0.072811 | 0.108* | |
| C11 | 0.19198 (14) | 0.43298 (7) | 0.16566 (11) | 0.0341 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.05157 (16) | 0.41920 (9) | 0.20535 (13) | 0.0427 (3) | |
| H12 | −0.022264 | 0.406927 | 0.149128 | 0.051* | |
| C13 | 0.02070 (18) | 0.42361 (10) | 0.32806 (14) | 0.0523 (4) | |
| H13 | −0.074106 | 0.415271 | 0.353831 | 0.063* | |
| C14 | 0.1301 (2) | 0.44033 (10) | 0.41240 (13) | 0.0530 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.108969 | 0.443448 | 0.494830 | 0.064* | |
| C15 | 0.27035 (18) | 0.45239 (9) | 0.37447 (13) | 0.0471 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.344296 | 0.463112 | 0.431370 | 0.057* | |
| C16 | 0.30160 (16) | 0.44859 (8) | 0.25200 (12) | 0.0395 (3) | |
| H16 | 0.396814 | 0.456537 | 0.226936 | 0.047* | |
| C17 | 0.27264 (14) | 0.58255 (8) | 0.03882 (12) | 0.0359 (3) | |
| C18 | 0.16250 (17) | 0.60991 (9) | 0.11333 (14) | 0.0465 (4) | |
| H18 | 0.081520 | 0.578437 | 0.127440 | 0.056* | |
| C19 | 0.1727 (2) | 0.68360 (9) | 0.16655 (15) | 0.0556 (4) | |
| H19 | 0.098591 | 0.701582 | 0.216101 | 0.067* | |
| C20 | 0.2924 (2) | 0.73034 (9) | 0.14627 (14) | 0.0547 (4) | |
| H20 | 0.299569 | 0.779622 | 0.182915 | 0.066* | |
| C21 | 0.40126 (18) | 0.70442 (9) | 0.07209 (15) | 0.0527 (4) | |
| H21 | 0.482036 | 0.736185 | 0.058695 | 0.063* | |
| C22 | 0.39120 (16) | 0.63116 (9) | 0.01716 (14) | 0.0447 (4) | |
| H22 | 0.464196 | 0.614417 | −0.034512 | 0.054* |
8-Amino-6-methyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (I) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0583 (6) | 0.0377 (6) | 0.0324 (5) | −0.0033 (5) | 0.0039 (4) | 0.0015 (4) |
| O2 | 0.1014 (10) | 0.0597 (8) | 0.0317 (6) | −0.0104 (7) | 0.0110 (6) | 0.0030 (5) |
| N1 | 0.1126 (13) | 0.0608 (9) | 0.0347 (7) | −0.0103 (9) | 0.0097 (7) | −0.0132 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0402 (7) | 0.0394 (8) | 0.0310 (6) | 0.0003 (6) | −0.0027 (5) | −0.0023 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0523 (8) | 0.0445 (8) | 0.0301 (7) | 0.0001 (7) | −0.0013 (6) | −0.0002 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0358 (7) | 0.0364 (7) | 0.0307 (6) | 0.0014 (6) | −0.0008 (5) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0340 (6) | 0.0339 (7) | 0.0305 (6) | 0.0023 (5) | −0.0008 (5) | −0.0023 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0477 (8) | 0.0367 (8) | 0.0370 (7) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0064 (6) | −0.0021 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0440 (8) | 0.0362 (8) | 0.0531 (8) | −0.0033 (6) | 0.0050 (6) | −0.0064 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0508 (8) | 0.0414 (9) | 0.0474 (8) | −0.0016 (7) | −0.0002 (7) | −0.0158 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0486 (8) | 0.0495 (9) | 0.0329 (7) | −0.0003 (7) | −0.0020 (6) | −0.0088 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0347 (7) | 0.0351 (7) | 0.0316 (6) | 0.0009 (6) | −0.0017 (5) | −0.0019 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0957 (14) | 0.0402 (10) | 0.0803 (13) | −0.0122 (9) | 0.0301 (11) | −0.0094 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0424 (7) | 0.0271 (7) | 0.0328 (7) | 0.0027 (6) | 0.0010 (5) | −0.0023 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0422 (7) | 0.0455 (9) | 0.0404 (8) | 0.0012 (6) | 0.0027 (6) | −0.0027 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0547 (9) | 0.0536 (10) | 0.0493 (9) | 0.0054 (8) | 0.0173 (7) | 0.0003 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0782 (11) | 0.0486 (9) | 0.0327 (7) | 0.0133 (8) | 0.0101 (7) | −0.0031 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0650 (10) | 0.0406 (8) | 0.0354 (7) | 0.0070 (7) | −0.0083 (7) | −0.0049 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0444 (7) | 0.0373 (8) | 0.0367 (7) | 0.0019 (6) | −0.0020 (6) | −0.0015 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0401 (7) | 0.0320 (7) | 0.0355 (7) | 0.0032 (6) | −0.0066 (6) | 0.0020 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0486 (8) | 0.0389 (8) | 0.0520 (9) | 0.0026 (7) | 0.0036 (7) | −0.0011 (7) |
| C19 | 0.0721 (11) | 0.0435 (9) | 0.0513 (9) | 0.0128 (9) | 0.0072 (8) | −0.0047 (7) |
| C20 | 0.0816 (12) | 0.0332 (8) | 0.0488 (9) | 0.0013 (8) | −0.0110 (8) | −0.0042 (7) |
| C21 | 0.0570 (9) | 0.0399 (9) | 0.0609 (10) | −0.0069 (7) | −0.0110 (8) | 0.0020 (7) |
| C22 | 0.0440 (8) | 0.0394 (8) | 0.0505 (8) | 0.0015 (7) | −0.0020 (6) | 0.0003 (6) |
8-Amino-6-methyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (I) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C2 | 1.3763 (17) | C11—C12 | 1.3867 (19) |
| O1—C3 | 1.3838 (15) | C11—C16 | 1.3922 (19) |
| O2—C2 | 1.2155 (16) | C12—C13 | 1.383 (2) |
| N1—C8 | 1.3574 (19) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1N | 0.8600 | C13—C14 | 1.380 (2) |
| N1—H2N | 0.8600 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C9 | 1.4167 (18) | C14—C15 | 1.374 (2) |
| C1—C8 | 1.4227 (19) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.438 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.3807 (19) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3430 (18) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C17 | 1.4792 (18) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C9 | 1.4611 (18) | C17—C22 | 1.389 (2) |
| C4—C11 | 1.4947 (17) | C17—C18 | 1.391 (2) |
| C5—C9 | 1.3851 (19) | C18—C19 | 1.383 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.397 (2) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C19—C20 | 1.375 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.380 (2) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C10 | 1.501 (2) | C20—C21 | 1.373 (2) |
| C7—C8 | 1.395 (2) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C21—C22 | 1.384 (2) |
| C10—H10A | 0.9600 | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C10—H10B | 0.9600 | C22—H22 | 0.9300 |
| C10—H10C | 0.9600 | ||
| C2—O1—C3 | 122.56 (11) | C12—C11—C16 | 118.69 (12) |
| C8—N1—H1N | 120.0 | C12—C11—C4 | 121.20 (12) |
| C8—N1—H2N | 120.0 | C16—C11—C4 | 120.04 (12) |
| H1N—N1—H2N | 120.0 | C13—C12—C11 | 120.39 (14) |
| C9—C1—C8 | 119.40 (13) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C9—C1—C2 | 120.31 (12) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C8—C1—C2 | 120.25 (12) | C14—C13—C12 | 120.22 (15) |
| O2—C2—O1 | 114.63 (13) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| O2—C2—C1 | 127.72 (13) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| O1—C2—C1 | 117.64 (11) | C15—C14—C13 | 119.94 (14) |
| C4—C3—O1 | 121.84 (12) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| C4—C3—C17 | 128.00 (12) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| O1—C3—C17 | 110.16 (11) | C14—C15—C16 | 120.08 (14) |
| C3—C4—C9 | 119.40 (11) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—C11 | 119.57 (11) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| C9—C4—C11 | 120.98 (11) | C15—C16—C11 | 120.64 (14) |
| C9—C5—C6 | 120.94 (13) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.7 |
| C9—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C11—C16—H16 | 119.7 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C22—C17—C18 | 118.79 (13) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.18 (14) | C22—C17—C3 | 120.00 (12) |
| C7—C6—C10 | 120.84 (14) | C18—C17—C3 | 121.20 (13) |
| C5—C6—C10 | 119.98 (14) | C19—C18—C17 | 120.41 (15) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 122.20 (13) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.8 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 118.9 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.8 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 118.9 | C20—C19—C18 | 120.06 (15) |
| N1—C8—C7 | 119.99 (14) | C20—C19—H19 | 120.0 |
| N1—C8—C1 | 121.59 (14) | C18—C19—H19 | 120.0 |
| C7—C8—C1 | 118.41 (13) | C21—C20—C19 | 120.17 (15) |
| C5—C9—C1 | 119.84 (12) | C21—C20—H20 | 119.9 |
| C5—C9—C4 | 121.96 (12) | C19—C20—H20 | 119.9 |
| C1—C9—C4 | 118.19 (12) | C20—C21—C22 | 120.21 (15) |
| C6—C10—H10A | 109.5 | C20—C21—H21 | 119.9 |
| C6—C10—H10B | 109.5 | C22—C21—H21 | 119.9 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 | C21—C22—C17 | 120.32 (14) |
| C6—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C21—C22—H22 | 119.8 |
| H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C17—C22—H22 | 119.8 |
| H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 | ||
| C3—O1—C2—O2 | 179.19 (13) | C3—C4—C9—C5 | 178.47 (13) |
| C3—O1—C2—C1 | −0.67 (19) | C11—C4—C9—C5 | 1.05 (19) |
| C9—C1—C2—O2 | 178.61 (15) | C3—C4—C9—C1 | −0.26 (18) |
| C8—C1—C2—O2 | 0.9 (2) | C11—C4—C9—C1 | −177.68 (12) |
| C9—C1—C2—O1 | −1.5 (2) | C3—C4—C11—C12 | 111.95 (15) |
| C8—C1—C2—O1 | −179.26 (12) | C9—C4—C11—C12 | −70.64 (17) |
| C2—O1—C3—C4 | 2.49 (19) | C3—C4—C11—C16 | −64.84 (17) |
| C2—O1—C3—C17 | −178.45 (12) | C9—C4—C11—C16 | 112.57 (14) |
| O1—C3—C4—C9 | −1.94 (19) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 2.2 (2) |
| C17—C3—C4—C9 | 179.17 (12) | C4—C11—C12—C13 | −174.66 (13) |
| O1—C3—C4—C11 | 175.51 (11) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.2 (2) |
| C17—C3—C4—C11 | −3.4 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.2 (2) |
| C9—C5—C6—C7 | −0.1 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.7 (2) |
| C9—C5—C6—C10 | 179.11 (15) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.3 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 1.6 (2) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −1.7 (2) |
| C10—C6—C7—C8 | −177.57 (16) | C4—C11—C16—C15 | 175.14 (13) |
| C6—C7—C8—N1 | 176.95 (15) | C4—C3—C17—C22 | 136.31 (15) |
| C6—C7—C8—C1 | −1.8 (2) | O1—C3—C17—C22 | −42.68 (16) |
| C9—C1—C8—N1 | −178.25 (14) | C4—C3—C17—C18 | −44.8 (2) |
| C2—C1—C8—N1 | −0.5 (2) | O1—C3—C17—C18 | 136.26 (13) |
| C9—C1—C8—C7 | 0.5 (2) | C22—C17—C18—C19 | −1.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—C8—C7 | 178.22 (13) | C3—C17—C18—C19 | 179.82 (13) |
| C6—C5—C9—C1 | −1.2 (2) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −0.2 (2) |
| C6—C5—C9—C4 | −179.90 (13) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 0.7 (2) |
| C8—C1—C9—C5 | 0.97 (19) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 0.1 (2) |
| C2—C1—C9—C5 | −176.77 (12) | C20—C21—C22—C17 | −1.5 (2) |
| C8—C1—C9—C4 | 179.73 (12) | C18—C17—C22—C21 | 2.0 (2) |
| C2—C1—C9—C4 | 1.99 (19) | C3—C17—C22—C21 | −178.99 (13) |
8-Amino-6-methyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (I) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C17–C22, C11–C16 and C1/C5–C9 rings, respectively.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H2N···O2 | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.6915 (19) | 131 |
| N1—H1N···Cg1i | 0.86 | 2.81 | 3.631 (2) | 157 |
| C20—H20···Cg2ii | 0.93 | 2.70 | 3.588 (2) | 160 |
| C21—H21···Cg3iii | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.488 (2) | 128 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) −x, −y+2, −z+1.
8-Amino-3,4-diethyl-6-methyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (II) . Crystal data
| C14H17NO2 | F(000) = 992 |
| Mr = 231.28 | Dx = 1.222 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 10.4844 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 3755 reflections |
| b = 26.562 (2) Å | θ = 1.8–26.9° |
| c = 9.3651 (6) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| β = 105.367 (3)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 2514.8 (3) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.25 × 0.22 × 0.13 mm |
8-Amino-3,4-diethyl-6-methyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (II) . Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2132 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| ω and φ scans | Rint = 0.048 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | θmax = 23.8°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Tmin = 0.756, Tmax = 0.824 | h = −11→11 |
| 13067 measured reflections | k = −29→23 |
| 3755 independent reflections | l = −10→7 |
8-Amino-3,4-diethyl-6-methyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (II) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.054 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.168 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.01 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0872P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3755 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 313 parameters | Δρmax = 0.14 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
8-Amino-3,4-diethyl-6-methyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (II) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
8-Amino-3,4-diethyl-6-methyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (II) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1A | 0.19526 (18) | −0.03883 (8) | 0.3169 (2) | 0.0621 (6) | |
| O2A | 0.1114 (2) | −0.10719 (9) | 0.2007 (2) | 0.0765 (7) | |
| N1A | −0.1310 (2) | −0.10445 (9) | 0.0078 (2) | 0.0688 (7) | |
| H1A1 | −0.198031 | −0.117045 | −0.055946 | 0.083* | |
| H1A2 | −0.062249 | −0.122669 | 0.044001 | 0.083* | |
| C1A | −0.0241 (2) | −0.03391 (10) | 0.1564 (2) | 0.0420 (7) | |
| C2A | 0.0926 (3) | −0.06286 (12) | 0.2204 (3) | 0.0529 (8) | |
| C3A | 0.1906 (3) | 0.01162 (12) | 0.3555 (3) | 0.0532 (8) | |
| C4A | 0.0834 (2) | 0.03978 (10) | 0.3010 (3) | 0.0458 (7) | |
| C5A | −0.1438 (3) | 0.04469 (10) | 0.1329 (3) | 0.0493 (7) | |
| H5A | −0.147825 | 0.078312 | 0.159015 | 0.059* | |
| C6A | −0.2512 (3) | 0.02321 (12) | 0.0321 (3) | 0.0538 (8) | |
| C7A | −0.2452 (3) | −0.02619 (13) | −0.0072 (3) | 0.0556 (8) | |
| H7A | −0.317482 | −0.040423 | −0.074901 | 0.067* | |
| C8A | −0.1338 (3) | −0.05578 (11) | 0.0513 (3) | 0.0492 (7) | |
| C9A | −0.0303 (2) | 0.01716 (10) | 0.1956 (2) | 0.0417 (7) | |
| C10A | −0.3711 (3) | 0.05465 (13) | −0.0348 (3) | 0.0806 (10) | |
| H10A | −0.349955 | 0.079114 | −0.100375 | 0.121* | |
| H10B | −0.398847 | 0.071563 | 0.042527 | 0.121* | |
| H10C | −0.441292 | 0.033370 | −0.089177 | 0.121* | |
| C11A | 0.3183 (3) | 0.02507 (13) | 0.4640 (3) | 0.0761 (10) | |
| H11A | 0.326355 | 0.061432 | 0.470382 | 0.091* | |
| H11B | 0.391030 | 0.012236 | 0.428775 | 0.091* | |
| C12A | 0.3281 (3) | 0.00403 (13) | 0.6162 (3) | 0.0828 (11) | |
| H12A | 0.262132 | 0.019401 | 0.656040 | 0.124* | |
| H12B | 0.414351 | 0.010997 | 0.679928 | 0.124* | |
| H12C | 0.314202 | −0.031714 | 0.609490 | 0.124* | |
| C13A | 0.0781 (3) | 0.09389 (11) | 0.3488 (3) | 0.0597 (8) | |
| H13A | 0.033743 | 0.113977 | 0.263609 | 0.072* | |
| H13B | 0.167579 | 0.106592 | 0.385238 | 0.072* | |
| C14A | 0.0062 (3) | 0.09996 (13) | 0.4687 (3) | 0.0818 (10) | |
| H14A | −0.082689 | 0.087702 | 0.433030 | 0.123* | |
| H14B | 0.004438 | 0.134906 | 0.494236 | 0.123* | |
| H14C | 0.051468 | 0.081108 | 0.554672 | 0.123* | |
| O1B | 0.34202 (18) | 0.19483 (8) | 0.14816 (19) | 0.0623 (6) | |
| O2B | 0.4302 (2) | 0.12582 (9) | 0.2580 (2) | 0.0859 (7) | |
| N1B | 0.6446 (2) | 0.13134 (10) | 0.4921 (3) | 0.0786 (8) | |
| H1B1 | 0.705569 | 0.119291 | 0.564264 | 0.094* | |
| H1B2 | 0.591805 | 0.111350 | 0.431977 | 0.094* | |
| C1B | 0.5316 (2) | 0.20312 (11) | 0.3560 (3) | 0.0442 (7) | |
| C2B | 0.4371 (3) | 0.17168 (12) | 0.2564 (3) | 0.0562 (8) | |
| C3B | 0.3370 (3) | 0.24666 (12) | 0.1273 (3) | 0.0532 (8) | |
| C4B | 0.4230 (3) | 0.27743 (10) | 0.2151 (3) | 0.0479 (7) | |
| C5B | 0.6132 (3) | 0.28607 (11) | 0.4388 (3) | 0.0564 (8) | |
| H5B | 0.608867 | 0.320854 | 0.427094 | 0.068* | |
| C6B | 0.7082 (3) | 0.26519 (14) | 0.5561 (3) | 0.0614 (8) | |
| C7B | 0.7174 (3) | 0.21419 (14) | 0.5708 (3) | 0.0628 (9) | |
| H7B | 0.782810 | 0.200493 | 0.648214 | 0.075* | |
| C8B | 0.6315 (3) | 0.18187 (11) | 0.4730 (3) | 0.0531 (8) | |
| C9B | 0.5246 (2) | 0.25581 (11) | 0.3387 (3) | 0.0447 (7) | |
| C10B | 0.8005 (3) | 0.29914 (14) | 0.6652 (4) | 0.0914 (12) | |
| H10D | 0.861250 | 0.279047 | 0.737701 | 0.137* | |
| H10E | 0.750228 | 0.320132 | 0.713663 | 0.137* | |
| H10F | 0.848950 | 0.319861 | 0.613864 | 0.137* | |
| C11B | 0.2212 (3) | 0.25846 (13) | 0.0000 (3) | 0.0767 (10) | |
| H11C | 0.226498 | 0.238303 | −0.084589 | 0.092* | |
| H11D | 0.225174 | 0.293610 | −0.026570 | 0.092* | |
| C12B | 0.0907 (3) | 0.24846 (15) | 0.0340 (4) | 0.1083 (14) | |
| H12D | 0.090713 | 0.214998 | 0.072749 | 0.162* | |
| H12E | 0.020240 | 0.251665 | −0.055014 | 0.162* | |
| H12F | 0.078047 | 0.272358 | 0.105949 | 0.162* | |
| C13B | 0.4150 (3) | 0.33380 (11) | 0.1925 (3) | 0.0604 (8) | |
| H13C | 0.374007 | 0.340940 | 0.088909 | 0.073* | |
| H13D | 0.503755 | 0.347615 | 0.217150 | 0.073* | |
| C14B | 0.3362 (3) | 0.35947 (11) | 0.2865 (3) | 0.0731 (9) | |
| H14D | 0.247412 | 0.346648 | 0.260456 | 0.110* | |
| H14E | 0.334475 | 0.395109 | 0.269095 | 0.110* | |
| H14F | 0.376919 | 0.352867 | 0.389239 | 0.110* |
8-Amino-3,4-diethyl-6-methyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (II) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1A | 0.0559 (13) | 0.0674 (16) | 0.0564 (12) | 0.0158 (11) | 0.0035 (10) | 0.0115 (11) |
| O2A | 0.1035 (18) | 0.0453 (15) | 0.0803 (14) | 0.0221 (13) | 0.0241 (12) | 0.0094 (12) |
| N1A | 0.0866 (19) | 0.0476 (18) | 0.0742 (17) | −0.0169 (14) | 0.0249 (14) | −0.0101 (13) |
| C1A | 0.0511 (17) | 0.0357 (18) | 0.0386 (13) | −0.0001 (13) | 0.0105 (12) | 0.0057 (12) |
| C2A | 0.064 (2) | 0.049 (2) | 0.0463 (16) | 0.0100 (17) | 0.0163 (15) | 0.0123 (15) |
| C3A | 0.0533 (19) | 0.056 (2) | 0.0485 (16) | −0.0012 (16) | 0.0103 (14) | 0.0049 (14) |
| C4A | 0.0430 (16) | 0.049 (2) | 0.0427 (14) | −0.0015 (14) | 0.0061 (13) | 0.0024 (13) |
| C5A | 0.0508 (17) | 0.0438 (19) | 0.0486 (15) | 0.0030 (14) | 0.0049 (14) | 0.0003 (13) |
| C6A | 0.0471 (18) | 0.059 (2) | 0.0502 (16) | 0.0017 (16) | 0.0046 (14) | 0.0033 (15) |
| C7A | 0.0494 (18) | 0.067 (2) | 0.0456 (16) | −0.0171 (17) | 0.0040 (13) | −0.0008 (15) |
| C8A | 0.067 (2) | 0.0393 (19) | 0.0470 (15) | −0.0117 (16) | 0.0243 (15) | −0.0002 (14) |
| C9A | 0.0415 (16) | 0.0449 (19) | 0.0371 (13) | −0.0023 (13) | 0.0078 (12) | 0.0049 (12) |
| C10A | 0.055 (2) | 0.092 (3) | 0.081 (2) | 0.0079 (19) | −0.0065 (16) | 0.0077 (19) |
| C11A | 0.0516 (19) | 0.096 (3) | 0.070 (2) | −0.0024 (18) | −0.0020 (16) | 0.0106 (19) |
| C12A | 0.087 (2) | 0.090 (3) | 0.0563 (19) | 0.007 (2) | −0.0078 (17) | −0.0083 (18) |
| C13A | 0.0571 (18) | 0.059 (2) | 0.0587 (17) | −0.0130 (15) | 0.0078 (14) | −0.0117 (15) |
| C14A | 0.093 (2) | 0.083 (3) | 0.073 (2) | −0.002 (2) | 0.0271 (18) | −0.0218 (18) |
| O1B | 0.0632 (13) | 0.0536 (15) | 0.0614 (12) | −0.0025 (11) | 0.0012 (10) | −0.0087 (11) |
| O2B | 0.1026 (18) | 0.0414 (16) | 0.1027 (17) | −0.0062 (13) | 0.0079 (14) | −0.0060 (13) |
| N1B | 0.0833 (19) | 0.056 (2) | 0.093 (2) | 0.0262 (15) | 0.0168 (15) | 0.0176 (15) |
| C1B | 0.0418 (16) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0457 (14) | 0.0047 (14) | 0.0097 (13) | 0.0033 (13) |
| C2B | 0.0595 (19) | 0.046 (2) | 0.0612 (18) | −0.0001 (17) | 0.0132 (16) | −0.0027 (16) |
| C3B | 0.0580 (19) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0506 (16) | 0.0081 (16) | 0.0120 (14) | 0.0028 (15) |
| C4B | 0.0540 (17) | 0.0415 (19) | 0.0477 (15) | 0.0049 (14) | 0.0125 (14) | 0.0031 (14) |
| C5B | 0.0607 (19) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0632 (17) | −0.0024 (15) | 0.0131 (16) | −0.0019 (15) |
| C6B | 0.0448 (18) | 0.074 (3) | 0.0608 (18) | −0.0025 (17) | 0.0062 (15) | −0.0052 (18) |
| C7B | 0.0483 (18) | 0.081 (3) | 0.0538 (17) | 0.0108 (18) | 0.0049 (14) | 0.0059 (18) |
| C8B | 0.0516 (18) | 0.048 (2) | 0.0620 (18) | 0.0109 (15) | 0.0197 (15) | 0.0048 (15) |
| C9B | 0.0437 (16) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0479 (15) | 0.0016 (13) | 0.0124 (13) | 0.0002 (13) |
| C10B | 0.066 (2) | 0.109 (3) | 0.087 (2) | −0.010 (2) | −0.0018 (19) | −0.024 (2) |
| C11B | 0.075 (2) | 0.086 (3) | 0.0574 (18) | 0.0129 (19) | −0.0039 (17) | −0.0030 (17) |
| C12B | 0.063 (2) | 0.118 (4) | 0.125 (3) | 0.013 (2) | −0.009 (2) | 0.008 (3) |
| C13B | 0.073 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0570 (16) | 0.0107 (16) | 0.0178 (15) | 0.0086 (15) |
| C14B | 0.092 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.083 (2) | 0.0184 (18) | 0.0329 (19) | 0.0023 (17) |
8-Amino-3,4-diethyl-6-methyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (II) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1A—C2A | 1.366 (3) | O1B—C2B | 1.365 (3) |
| O1A—C3A | 1.392 (3) | O1B—C3B | 1.389 (3) |
| O2A—C2A | 1.216 (3) | O2B—C2B | 1.221 (3) |
| N1A—C8A | 1.358 (3) | N1B—C8B | 1.356 (3) |
| N1A—H1A1 | 0.8600 | N1B—H1B1 | 0.8600 |
| N1A—H1A2 | 0.8600 | N1B—H1B2 | 0.8600 |
| C1A—C9A | 1.411 (3) | C1B—C9B | 1.409 (3) |
| C1A—C8A | 1.425 (3) | C1B—C8B | 1.417 (3) |
| C1A—C2A | 1.435 (4) | C1B—C2B | 1.435 (4) |
| C3A—C4A | 1.334 (3) | C3B—C4B | 1.328 (4) |
| C3A—C11A | 1.494 (4) | C3B—C11B | 1.492 (4) |
| C4A—C9A | 1.461 (3) | C4B—C9B | 1.467 (3) |
| C4A—C13A | 1.511 (4) | C4B—C13B | 1.511 (4) |
| C5A—C6A | 1.386 (3) | C5B—C6B | 1.388 (4) |
| C5A—C9A | 1.387 (3) | C5B—C9B | 1.388 (3) |
| C5A—H5A | 0.9300 | C5B—H5B | 0.9300 |
| C6A—C7A | 1.369 (4) | C6B—C7B | 1.363 (4) |
| C6A—C10A | 1.501 (4) | C6B—C10B | 1.507 (4) |
| C7A—C8A | 1.393 (4) | C7B—C8B | 1.396 (4) |
| C7A—H7A | 0.9300 | C7B—H7B | 0.9300 |
| C10A—H10A | 0.9600 | C10B—H10D | 0.9600 |
| C10A—H10B | 0.9600 | C10B—H10E | 0.9600 |
| C10A—H10C | 0.9600 | C10B—H10F | 0.9600 |
| C11A—C12A | 1.509 (4) | C11B—C12B | 1.509 (4) |
| C11A—H11A | 0.9700 | C11B—H11C | 0.9700 |
| C11A—H11B | 0.9700 | C11B—H11D | 0.9700 |
| C12A—H12A | 0.9600 | C12B—H12D | 0.9600 |
| C12A—H12B | 0.9600 | C12B—H12E | 0.9600 |
| C12A—H12C | 0.9600 | C12B—H12F | 0.9600 |
| C13A—C14A | 1.517 (4) | C13B—C14B | 1.519 (4) |
| C13A—H13A | 0.9700 | C13B—H13C | 0.9700 |
| C13A—H13B | 0.9700 | C13B—H13D | 0.9700 |
| C14A—H14A | 0.9600 | C14B—H14D | 0.9600 |
| C14A—H14B | 0.9600 | C14B—H14E | 0.9600 |
| C14A—H14C | 0.9600 | C14B—H14F | 0.9600 |
| C2A—O1A—C3A | 123.1 (2) | C2B—O1B—C3B | 122.9 (2) |
| C8A—N1A—H1A1 | 120.0 | C8B—N1B—H1B1 | 120.0 |
| C8A—N1A—H1A2 | 120.0 | C8B—N1B—H1B2 | 120.0 |
| H1A1—N1A—H1A2 | 120.0 | H1B1—N1B—H1B2 | 120.0 |
| C9A—C1A—C8A | 119.1 (2) | C9B—C1B—C8B | 119.3 (2) |
| C9A—C1A—C2A | 120.0 (2) | C9B—C1B—C2B | 119.8 (2) |
| C8A—C1A—C2A | 120.9 (3) | C8B—C1B—C2B | 120.8 (3) |
| O2A—C2A—O1A | 115.0 (3) | O2B—C2B—O1B | 115.1 (3) |
| O2A—C2A—C1A | 127.6 (3) | O2B—C2B—C1B | 127.3 (3) |
| O1A—C2A—C1A | 117.5 (3) | O1B—C2B—C1B | 117.6 (3) |
| C4A—C3A—O1A | 121.6 (2) | C4B—C3B—O1B | 121.9 (2) |
| C4A—C3A—C11A | 129.7 (3) | C4B—C3B—C11B | 129.8 (3) |
| O1A—C3A—C11A | 108.7 (3) | O1B—C3B—C11B | 108.3 (3) |
| C3A—C4A—C9A | 118.8 (3) | C3B—C4B—C9B | 118.6 (3) |
| C3A—C4A—C13A | 120.9 (2) | C3B—C4B—C13B | 121.3 (2) |
| C9A—C4A—C13A | 120.3 (2) | C9B—C4B—C13B | 120.0 (2) |
| C6A—C5A—C9A | 121.5 (3) | C6B—C5B—C9B | 121.0 (3) |
| C6A—C5A—H5A | 119.3 | C6B—C5B—H5B | 119.5 |
| C9A—C5A—H5A | 119.3 | C9B—C5B—H5B | 119.5 |
| C7A—C6A—C5A | 119.4 (3) | C7B—C6B—C5B | 119.6 (3) |
| C7A—C6A—C10A | 121.0 (3) | C7B—C6B—C10B | 120.7 (3) |
| C5A—C6A—C10A | 119.7 (3) | C5B—C6B—C10B | 119.7 (3) |
| C6A—C7A—C8A | 121.9 (3) | C6B—C7B—C8B | 121.9 (3) |
| C6A—C7A—H7A | 119.0 | C6B—C7B—H7B | 119.0 |
| C8A—C7A—H7A | 119.0 | C8B—C7B—H7B | 119.0 |
| N1A—C8A—C7A | 120.1 (3) | N1B—C8B—C7B | 119.8 (3) |
| N1A—C8A—C1A | 121.2 (3) | N1B—C8B—C1B | 121.6 (3) |
| C7A—C8A—C1A | 118.7 (3) | C7B—C8B—C1B | 118.6 (3) |
| C5A—C9A—C1A | 119.3 (2) | C5B—C9B—C1B | 119.5 (2) |
| C5A—C9A—C4A | 121.6 (3) | C5B—C9B—C4B | 121.5 (3) |
| C1A—C9A—C4A | 119.1 (2) | C1B—C9B—C4B | 119.0 (2) |
| C6A—C10A—H10A | 109.5 | C6B—C10B—H10D | 109.5 |
| C6A—C10A—H10B | 109.5 | C6B—C10B—H10E | 109.5 |
| H10A—C10A—H10B | 109.5 | H10D—C10B—H10E | 109.5 |
| C6A—C10A—H10C | 109.5 | C6B—C10B—H10F | 109.5 |
| H10A—C10A—H10C | 109.5 | H10D—C10B—H10F | 109.5 |
| H10B—C10A—H10C | 109.5 | H10E—C10B—H10F | 109.5 |
| C3A—C11A—C12A | 112.3 (3) | C3B—C11B—C12B | 112.7 (3) |
| C3A—C11A—H11A | 109.1 | C3B—C11B—H11C | 109.1 |
| C12A—C11A—H11A | 109.1 | C12B—C11B—H11C | 109.1 |
| C3A—C11A—H11B | 109.1 | C3B—C11B—H11D | 109.1 |
| C12A—C11A—H11B | 109.1 | C12B—C11B—H11D | 109.1 |
| H11A—C11A—H11B | 107.9 | H11C—C11B—H11D | 107.8 |
| C11A—C12A—H12A | 109.5 | C11B—C12B—H12D | 109.5 |
| C11A—C12A—H12B | 109.5 | C11B—C12B—H12E | 109.5 |
| H12A—C12A—H12B | 109.5 | H12D—C12B—H12E | 109.5 |
| C11A—C12A—H12C | 109.5 | C11B—C12B—H12F | 109.5 |
| H12A—C12A—H12C | 109.5 | H12D—C12B—H12F | 109.5 |
| H12B—C12A—H12C | 109.5 | H12E—C12B—H12F | 109.5 |
| C4A—C13A—C14A | 112.6 (2) | C4B—C13B—C14B | 112.5 (2) |
| C4A—C13A—H13A | 109.1 | C4B—C13B—H13C | 109.1 |
| C14A—C13A—H13A | 109.1 | C14B—C13B—H13C | 109.1 |
| C4A—C13A—H13B | 109.1 | C4B—C13B—H13D | 109.1 |
| C14A—C13A—H13B | 109.1 | C14B—C13B—H13D | 109.1 |
| H13A—C13A—H13B | 107.8 | H13C—C13B—H13D | 107.8 |
| C13A—C14A—H14A | 109.5 | C13B—C14B—H14D | 109.5 |
| C13A—C14A—H14B | 109.5 | C13B—C14B—H14E | 109.5 |
| H14A—C14A—H14B | 109.5 | H14D—C14B—H14E | 109.5 |
| C13A—C14A—H14C | 109.5 | C13B—C14B—H14F | 109.5 |
| H14A—C14A—H14C | 109.5 | H14D—C14B—H14F | 109.5 |
| H14B—C14A—H14C | 109.5 | H14E—C14B—H14F | 109.5 |
| C3A—O1A—C2A—O2A | −178.6 (2) | C3B—O1B—C2B—O2B | −178.2 (2) |
| C3A—O1A—C2A—C1A | 0.4 (3) | C3B—O1B—C2B—C1B | 2.8 (4) |
| C9A—C1A—C2A—O2A | 177.9 (3) | C9B—C1B—C2B—O2B | −179.6 (3) |
| C8A—C1A—C2A—O2A | −3.1 (4) | C8B—C1B—C2B—O2B | −0.2 (4) |
| C9A—C1A—C2A—O1A | −0.9 (3) | C9B—C1B—C2B—O1B | −0.7 (4) |
| C8A—C1A—C2A—O1A | 178.1 (2) | C8B—C1B—C2B—O1B | 178.7 (2) |
| C2A—O1A—C3A—C4A | 0.8 (4) | C2B—O1B—C3B—C4B | −2.0 (4) |
| C2A—O1A—C3A—C11A | 179.3 (2) | C2B—O1B—C3B—C11B | 179.9 (2) |
| O1A—C3A—C4A—C9A | −1.5 (4) | O1B—C3B—C4B—C9B | −1.0 (4) |
| C11A—C3A—C4A—C9A | −179.6 (2) | C11B—C3B—C4B—C9B | 176.7 (3) |
| O1A—C3A—C4A—C13A | 177.5 (2) | O1B—C3B—C4B—C13B | −179.1 (2) |
| C11A—C3A—C4A—C13A | −0.6 (4) | C11B—C3B—C4B—C13B | −1.4 (4) |
| C9A—C5A—C6A—C7A | −0.4 (4) | C9B—C5B—C6B—C7B | 2.1 (4) |
| C9A—C5A—C6A—C10A | −179.1 (2) | C9B—C5B—C6B—C10B | −178.3 (3) |
| C5A—C6A—C7A—C8A | 0.1 (4) | C5B—C6B—C7B—C8B | −1.7 (4) |
| C10A—C6A—C7A—C8A | 178.7 (3) | C10B—C6B—C7B—C8B | 178.8 (3) |
| C6A—C7A—C8A—N1A | −179.0 (2) | C6B—C7B—C8B—N1B | −180.0 (3) |
| C6A—C7A—C8A—C1A | 0.8 (4) | C6B—C7B—C8B—C1B | −0.5 (4) |
| C9A—C1A—C8A—N1A | 178.5 (2) | C9B—C1B—C8B—N1B | −178.3 (2) |
| C2A—C1A—C8A—N1A | −0.5 (4) | C2B—C1B—C8B—N1B | 2.3 (4) |
| C9A—C1A—C8A—C7A | −1.3 (3) | C9B—C1B—C8B—C7B | 2.2 (4) |
| C2A—C1A—C8A—C7A | 179.7 (2) | C2B—C1B—C8B—C7B | −177.2 (2) |
| C6A—C5A—C9A—C1A | −0.2 (4) | C6B—C5B—C9B—C1B | −0.3 (4) |
| C6A—C5A—C9A—C4A | 179.6 (2) | C6B—C5B—C9B—C4B | 179.4 (2) |
| C8A—C1A—C9A—C5A | 1.0 (3) | C8B—C1B—C9B—C5B | −1.8 (3) |
| C2A—C1A—C9A—C5A | −180.0 (2) | C2B—C1B—C9B—C5B | 177.6 (2) |
| C8A—C1A—C9A—C4A | −178.7 (2) | C8B—C1B—C9B—C4B | 178.5 (2) |
| C2A—C1A—C9A—C4A | 0.2 (3) | C2B—C1B—C9B—C4B | −2.2 (3) |
| C3A—C4A—C9A—C5A | −178.8 (2) | C3B—C4B—C9B—C5B | −176.7 (2) |
| C13A—C4A—C9A—C5A | 2.2 (4) | C13B—C4B—C9B—C5B | 1.4 (4) |
| C3A—C4A—C9A—C1A | 1.0 (3) | C3B—C4B—C9B—C1B | 3.0 (3) |
| C13A—C4A—C9A—C1A | −178.1 (2) | C13B—C4B—C9B—C1B | −178.9 (2) |
| C4A—C3A—C11A—C12A | 103.6 (4) | C4B—C3B—C11B—C12B | −109.5 (4) |
| O1A—C3A—C11A—C12A | −74.7 (3) | O1B—C3B—C11B—C12B | 68.5 (3) |
| C3A—C4A—C13A—C14A | −98.1 (3) | C3B—C4B—C13B—C14B | 93.8 (3) |
| C9A—C4A—C13A—C14A | 80.9 (3) | C9B—C4B—C13B—C14B | −84.3 (3) |
8-Amino-3,4-diethyl-6-methyl-1H-isochromen-1-one (II) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1A/C5A–C9A ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1A—H1A2···O2A | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.701 (3) | 131 |
| N1B—H1B2···O2B | 0.86 | 2.05 | 2.696 (3) | 131 |
| N1A—H1A1···O1Bi | 0.86 | 2.57 | 3.328 (3) | 148 |
| N1B—H1B1···O1Aii | 0.86 | 2.50 | 3.235 (3) | 143 |
| N1B—H1B1···O2Aii | 0.86 | 2.53 | 3.367 (3) | 165 |
| C12A—H12A···Cg1iii | 0.96 | 2.99 | 3.773 (2) | 140 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (iii) −x+2, −y+1, −z.
References
- Barry, R. D. (1964). Chem. Rev. 64, 239–241.
- Basvanag, U. M. V., Roopan, S. M. & Khan, F. N. (2009). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd, 45, 1276–1278.
- Bianchi, D. A., Blanco, N. E., Carrillo, N. & Kaufman, T. S. (2004). J. Agric. Food Chem. 52, 1923–1927. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Ercole, F., Davis, T. P. & Evans, R. A. (2009). Macromolecules, 42, 1500–1511.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Jain, P. K. & Joshi, H. (2012). J. Appl. Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2, 236–240.
- Khan, K. M., Ambreen, N., Mughal, U. R., Jalil, S., Perveen, S. & Choudhary, M. I. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 4058–4064. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Manivel, P., Roopan, S. M. & Khan, F. N. (2008). J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 53, 1609–1610.
- Mayakrishnan, S., Arun, Y., Maheswari, N. U. & Perumal, P. T. (2018). Chem. Commun. 54, 11889–11892. [DOI] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, J. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2007). Chem. Commun. pp. 3814–3816. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Pal, S., Chatare, V. & Pal, M. (2011). Curr. Org. Chem. 15, 782–800.
- Schmalle, H. W., Jarchow, O. H., Hausen, B. M. & Schulz, K.-H. (1982). Acta Cryst. B38, 2938–2941.
- Schnebel, M., Weidner, I., Wartchow, R. & Butenschön, H. (2003). Eur. J. Org. Chem. pp. 4363–4372.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spackman, M. A. & Jayatilaka, D. (2009). CrystEngComm, 11, 19–32.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). CrystalExplorer17. University of Western Australia. http://hirshfeldsurface.net
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009435/su5498sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009435/su5498Isup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009435/su5498IIsup5.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009435/su5498Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019009435/su5498IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report













