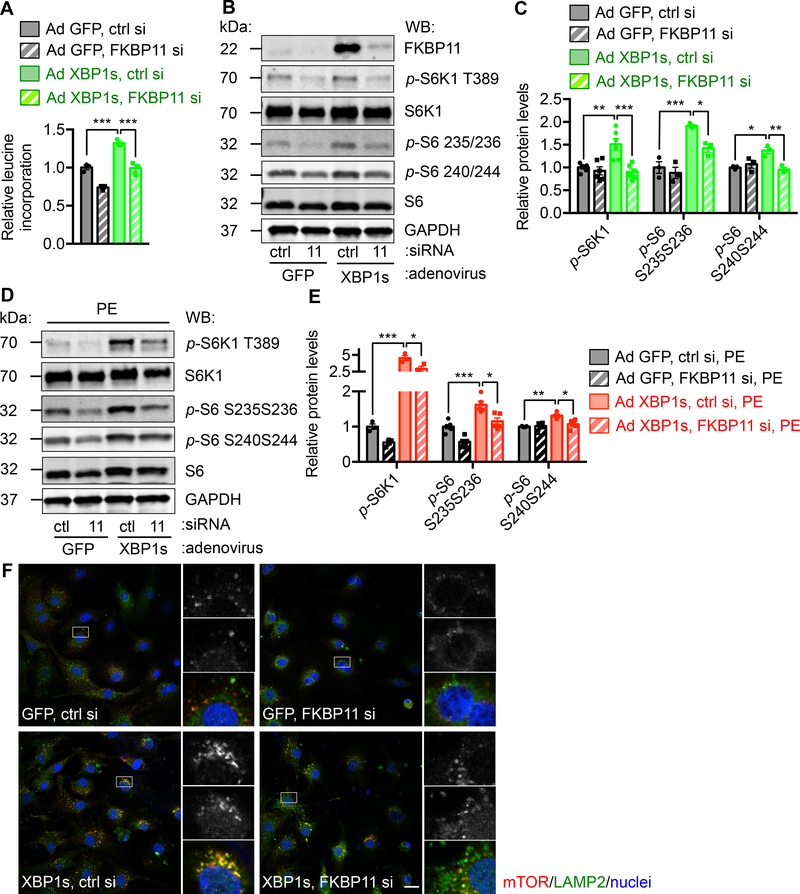
Figure. 8. FKBP11 is required for XBP1s-mediated mTOR activation.
A. FKBP11 was required for XBP1s-induced hypertrophic growth. NRVMs were infected by adenovirus expressing either GFP or XBP1s. FKBP11 was silenced by siRNA transfection. A 3H-leucine incorporation assay was conducted to assess cell growth. N = 3 for each group.
B. FKBP11 knockdown led to a decrease in XBP1s-induced mTOR activation. NRVMs were first infected by adenovirus to overexpression control GFP or XBP1s. FKBP11 siRNA was then used to transfect NRVMs and cell lysates were extracted for immunoblotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control.
C. Induction of mTOR activity by XBP1s was significantly inhibited by FKBP11 silencing as shown by quantification of B. N = 3–6.
D. Silencing of FKBP11 led to a decrease in PE and XBP1s-induced mTOR activation. NRVMs were first infected by adenovirus expressing GFP or XBP1s. FKBP11-specific siRNA was used to transfect the cells. PE treatment was conducted for 24 hrs and immunoblotting was performed to examine the mTOR signaling.
E. Quantification of D. N = 3–6.
F. Overexpression of XBP1s in NRVMs increased colocalization of mTOR and LAMP2, a lysosomal marker. FKBP11 knockdown significantly diminished this effect. Scale bar: 20 μm. Two-way ANOVA analysis was performed, followed by Tukey’s test. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001.