Abstract
Fifty-two GRAS genes are identified in walnut genome. Based on the evolutionary relationship and motif analysis, the walnut GRAS gene family was divided into eight subfamilies, and the sequence features analysis of JrGRAS proteins showed that the JrGRAS protein sequences were both conserved and altered during the evolutionary process. Gene duplication analysis indicated that seven GRAS genes in walnut have orthologous genes in other species, and five of them occurred duplicated events in walnut genome. Expression pattern analysis of the GRAS family genes in walnut showed that two JrGRAS genes (JrCIGRa-b and JrSCL28a) were differentially expressed between flower bud and leaf bud (p < 0.01), and two JrGRAS genes (JrCIGRa-b and JrSCL13b-d) were differentially expressed between the different development stages of flower buds transition (p < 0.01), besides, three hub genes (JrGAIa, JrSCL3f and JrSHRc) were identified by co-expression analysis, which suggested these GRAS genes may play an important role in regulating the development of apical meristem in walnut. This study laid a foundation for further understanding of the function of GRAS family genes in walnut.
Subject terms: Plant molecular biology, Shoot apical meristem
Introduction
GRAS genes, derived from the first three members to be identified as a plant-specific gene family, the GIBBERELLIN-INSENSITIVE (GAI), Repressor of ga1-3 (RGA) and SCARECROW (SCR)1. Among them, GAI proteins and RGA proteins are members of the DELLA proteins, which play important roles in repressing gibberellin responses2 and jasmonate (JA) and light signaling regulation3, and SCR proteins act as a key regulator of Arabidopsis roots4–6.
GRAS proteins share conserved domains in their C-terminus, comprised LHR I, VHIID, LHR II, PFYRE and SAW1,7–9, however, the N-terminus of GRAS proteins show a great divergence, which may result to the functional specificity of each protein10. Although metazoan STATs share similar domain organization with plant GRAS, it is lack of enough support for the hypothesis that GRAS proteins are plant STATS11. Recent structural studies have illustrated that the conserved GRAS domain comprises an α-helical cap and α/β core subdomains, which mediates protein-protein interactions4.
Up to now, more than a dozen of GRAS gene family have been identified, including Arabidopsis thaliana1,7,12, Rice7,13, Populus14, pine15, Chinese cabbage16, tobacco17, tomato18,19, Prunus mume20, Jatropha curcas L.21, Lotus japonicus22, grapevine23,24, Nelumbo nucifera25, Ricinus communis26, Betula kirghisorum27, Isatis indigotica28, apple29, Zea mays L.30, Medicago truncatula31, Camellia sinensis32 and Gossypium hirsutum33. The plant-specific GRAS family of proteins function as transcriptional regulators and play critical roles in development and signaling, such as in signal transduction (gibberellin signal transduction2,34, phytochrome A signal transduction)35,36, stress responses23,37–40, meristem formation and maintenance8,41–44 and promoting flowering9.
Walnut is cultivated worldwide for its nutritious fruits and commercially valuable timber, however, it needs many years before flowering and to become productive45–47. Previous research has shown that some of the GRAS members play important roles in meristem development8,41–44. To better understanding the molecular mechanism of walnut flower bud transition, it is necessary to investigate the GRAS family in walnut. With the availability of walnut genome sequences48 and transcriptome data of the walnut female flower buds and leaf buds, it is possible for us to identify all the GRAS family genes in walnut.
In this study, GRAS family genes in walnut have been identified in genome-wide. The phylogenetic relationship, sequence alignment, conserved motif composition and gene duplication of the JrGRAS genes were systematically analyzed, and their expression patterns in different tissues (flower bud and leaf bud) and different development stages (before, during, after the flower transition period) were explored using transcriptome data and validated by qRT-PCR experiments. Finally, protein-protein interactions analysis was conducted to investigate how they participate in diverse functions by interacting with other proteins. This research lay a foundation for further function investigations of GRAS genes in walnut.
Results
Identification of GRAS family members in walnut
A total of seventy protein sequences (include protein isoforms) encoded by fifty-two genes, which including the GRAS domain were identified as the walnut GRAS proteins for further analysis. Fifty-two GRAS genes locate in 44 scaffolds, and their start position and end position are shown in Table 1. The candidate GRAS members were then uploaded to the CD-search website (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi) and their domain information were listed in Table 1, too. Besides, the gene structures of JrGRAS was presented in Fig. S1, and subcellular location information of the JrGRAS proteins was presented in Table S1.
Table 1.
GRAS gene family identified in Juglans regia.
| Gene name | Gene symbol | Scaff | Scaff rename | Genome location | Strand | Related protein | Protein short name | GRAS domain position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JrNSP2b | LOC108980261 | NW_017388857.1 | Scaff2 | NW_017388857.1: 818600–821800 | + | XP_018806667.1 | JrNSP2b | 119–499 |
| JrRGL1a | LOC108981380 | NW_017389446.1 | Scaff13 | NW_017389446.1: 52316–54604 | − | XP_018808049.1 | JrRGL1a | 155–526 |
| JrSCL32 | LOC108982343 | NW_017443009.1 | Scaff29 | NW_017443009.1: 2200726–2203181 | + | XP_018809230.1 | JrSCL32 | 51–453 |
| JrSCL28a | LOC108984412 | NW_017442835.1 | Scaff27 | NW_017442835.1: 99273–101699 | + | XP_018811904.1 | JrSCL28a | 303–669 |
| JrSCL1a-b | LOC108984751 | NW_017443020.1 | Scaff30 | NW_017443020.1: 188763–190597 | − | XP_018812342.1 | JrSCL1a | 202–571 |
| XP_018812343.1 | JrSCL1b | 202–571 | ||||||
| JrSCL21a-d | LOC108985037 | NW_017439731.1 | Scaff20 | NW_017439731.1: 8737–10242 | − | XP_018812730.1 | JrSCL21a | 176–546 |
| XP_018812737.1 | JrSCL21b | 176–546 | ||||||
| XP_018812742.1 | JrSCL21c | 176–546 | ||||||
| XP_018812749.1 | JrSCL21d | 176–546 | ||||||
| JrSCL23a | LOC108985505 | NW_017443560.1 | Scaff36 | NW_017443560.1: 1461510–1465205 | + | XP_018813375.1 | JrSCL23a | 73–427 |
| JrSCL14a | LOC108986374 | NW_017389857.1 | Scaff15 | NW_017389857.1: 63443–68155 | + | XP_018814536.1 | JrSCL14a | 369–740 |
| JrGAIc | LOC108986541 | NW_017440525.1 | Scaff21 | NW_017440525.1: 114274–115992 | − | XP_018814727.1 | JrGAIc | 245–603 |
| JrSCLa | LOC108987805 | NW_017443259.1 | Scaff32 | NW_017443259.1: 126697–128229 | − | XP_018816363.1 | JrSCLa | 1–310 |
| JrSCL3a | LOC108988066 | NW_017388959.1 | Scaff7 | NW_017388959.1: 519784–522043 | − | XP_018816712.1 | JrSCL3a | 40–422 |
| JrGAIb | LOC108988158 | NW_017389752.1 | Scaff14 | NW_017389752.1: 468309–470492 | + | XP_018816848.1 | JrGAIb | 238–599 |
| JrNSP2a | LOC108988310 | NW_017442823.1 | Scaff26 | NW_017442823.1: 505495–509211 | + | XP_018817086.1 | JrNSP2a | 117–501 |
| JrSHRa | LOC108988543 | NW_017443543.1 | Scaff34 | NW_017443543.1: 934500–937558 | + | XP_018817374.1 | JrSHRa | 105–484 |
| JrSCL3b | LOC108988679 | NW_017389863.1 | Scaff16 | NW_017389863.1: 241932–244037 | + | XP_018817550.1 | JrSCL3b | 44–457 |
| JrRGL1b | LOC108989561 | NW_017389020.1 | Scaff10 | NW_017389020.1: 713954–717041 | − | XP_018818751.1 | JrRGL1b | 138–508 |
| JrSCL27 | LOC108990734 | NW_017389863.1 | Scaff16 | NW_017389863.1: 270998–273865 | − | XP_018820345.1 | JrSCL27 | 379–740 |
| JrSCL18 | LOC108992395 | NW_017389020.1 | Scaff10 | NW_017389020.1: 724451–727425 | − | XP_018822504.1 | JrSCL18 | 47–445 |
| JrSHRb | LOC108992438 | NW_017389863.1 | Scaff16 | NW_017389863.1: 265516–268446 | − | XP_018822539.1 | JrSHRb | 60–433 |
| JrSCL14b | LOC108992934 | NW_017389020.1 | Scaff10 | NW_017389020.1: 761280–765445 | + | XP_018823200.1 | JrSCL14b | 325–701 |
| JrSCL13a | LOC108993395 | NW_017443546.1 | Scaff35 | NW_017443546.1: 1236377–1240941 | + | XP_018823840.1 | JrSCL13a | 176–546 |
| JrPAT1a-d | LOC108994062 | NW_017443598.1 | Scaff41 | NW_017443598.1: 206015–211096 | − | XP_018824686.1 | JrPAT1a | 168–538 |
| XP_018824687.1 | JrPAT1b | 168–538 | ||||||
| XP_018824688.1 | JrPAT1c | 168–538 | ||||||
| XP_018824689.1 | JrPAT1d | 168–538 | ||||||
| JrSCL3c | LOC108994657 | NW_017443578.1 | Scaff38 | NW_017443578.1: 996644–998749 | + | XP_018825500.1 | JrSCL3c | 46–467 |
| JrSCL4a | LOC108995346 | NW_017388898.1 | Scaff6 | NW_017388898.1: 2412028–2413671 | + | XP_018826448.1 | JrSCL4a | 245–615 |
| JrSCL15 | LOC108995362 | NW_017442540.1 | Scaff24 | NW_017442540.1: 34589–38721 | − | XP_018826470.1 | JrSCL15 | 183–552 |
| JrSCLb-c | LOC108995898 | NW_017388887.1 | Scaff4 | NW_017388887.1: 1355328–1358341 | − | XP_018827109.1 | JrSCLb | 464–816 |
| XP_018827111.1 | JrSCLc | 438–790 | ||||||
| JrSCLd | LOC108995938 | NW_017388969.1 | Scaff8 | NW_017388969.1: 382640–385001 | + | XP_018827159.1 | JrSCLd | 152–507 |
| JrSCL23b | LOC108996381 | NW_017388856.1 | Scaff1 | NW_017388856.1: 1066492–1069818 | − | XP_018827796.1 | JrSCL23b | 73–427 |
| JrSCL13b-d | LOC108996812 | NW_017388861.1 | Scaff3 | NW_017388861.1: 936197–939325 | − | XP_018828372.1 | JrSCL13b | 174–545 |
| XP_018828373.1 | JrSCL13c | 174–545 | ||||||
| XP_018828374.1 | JrSCL13d | 174–545 | ||||||
| JrSCL28b-c | LOC108997020 | NW_017442720.1 | Scaff25 | NW_017442720.1: 50539–52384 | − | XP_018828642.1 | JrSCL28b | 304–670 |
| XP_018828643.1 | JrSCL28c | 304–643 | ||||||
| JrSCL4b | LOC108997571 | NW_017443591.1 | Scaff40 | NW_017443591.1: 871325–873488 | + | XP_018829455.1 | JrSCL4b | 252–623 |
| JrSCL3d-e | LOC108999242 | NW_017388893.1 | Scaff5 | NW_017388893.1: 2740337–2743452 | + | XP_018831643.1 | JrSCL3d | 46–468 |
| XP_018831644.1 | JrSCL3e | 46–468 | ||||||
| JrRGL1c | LOC109001324 | NW_017442404.1 | Scaff23 | NW_017442404.1: 246803–250094 | − | XP_018834108.1 | JrRGL1c | 310–676 |
| JrSCL21e | LOC109001839 | NW_017443600.1 | Scaff42 | NW_017443600.1: 47744–51063 | − | XP_018834825.1 | JrSCL21e | 315–681 |
| JrSHRc | LOC109002462 | NW_017441391.1 | Scaff22 | NW_017441391.1: 33841–36019 | − | XP_018835769.1 | JrSHRc | 110–490 |
| JrSCL33a-b | LOC109002666 | NW_017443009.1 | Scaff29 | NW_017443009.1: 917876–919261 | + | XP_018836065.1 | JrSCL33a | 367–737 |
| XP_018836066.1 | JrSCL33b | 367–737 | ||||||
| JrSCL34a | LOC109002667 | NW_017388893.1 | Scaff5 | NW_017388893.1: 730620–732711 | + | XP_018836067.1 | JrSCL34a | 383–753 |
| JrSCL9 | LOC109002669 | NW_017443569.1 | Scaff37 | NW_017443569.1: 521973–524512 | + | XP_018836069.1 | JrSCL9 | 386–757 |
| JrSCLe | LOC109004170 | NW_017443629.1 | Scaff44 | NW_017443629.1: 436277–438894 | + | XP_018838179.1 | JrSCLe | 449–801 |
| JrSLN1 | LOC109006296 | NW_017437159.1 | Scaff19 | NW_017437159.1: 15109–18210 | + | XP_018841073.1 | JrSLN1 | 151–518 |
| JrGAIa | LOC109007807 | NW_017443578.1 | Scaff38 | NW_017443578.1: 1317343–1319989 | + | XP_018843202.1 | JrGAIa | 226–585 |
| JrRGL1d | LOC109011259 | NW_017443604.1 | Scaff43 | NW_017443604.1: 879171–881593 | + | XP_018847922.1 | JrRGL1d | 156–525 |
| JrSCL22a | LOC109011601 | NW_017442999.1 | Scaff28 | NW_017442999.1: 59746–62789 | + | XP_018848419.1 | JrSCL22a | 438–793 |
| JrPAT1e-h | LOC109012627 | NW_017443590.1 | Scaff39 | NW_017443590.1: 1210837–1213906 | + | XP_018849898.1 | JrPAT1e | 176–546 |
| XP_018849899.1 | JrPAT1f | 176–546 | ||||||
| XP_018849900.1 | JrPAT1g | 176–546 | ||||||
| XP_018849901.1 | JrPAT1h | 176–546 | ||||||
| JrSCL34b | LOC109013013 | NW_017443590.1 | Scaff39 | NW_017443590.1: 1237365–1238906 | − | XP_018850468.1 | JrSCL34b | 383–758 |
| JrSCL33c-d | LOC109013014 | NW_017389181.1 | Scaff11 | NW_017389181.1: 2256–5719 | − | XP_018850470.1 | JrSCL33c | 385–759 |
| XP_018850471.1 | JrSCL33d | 385–759 | ||||||
| JrSCL14c | LOC109013019 | NW_017417453.1 | Scaff18 | NW_017417453.1: 8–1329 | − | XP_018850477.1 | JrSCL14c | 328–699 |
| JrCIGRa-b | LOC109014308 | NW_017443037.1 | Scaff31 | NW_017443037.1: 144211–146190 | − | XP_018852274.1 | JrCIGRa | 207–576 |
| XP_018852283.1 | JrCIGRb | 207–576 | ||||||
| JrSCL22b | LOC109015811 | NW_017443532.1 | Scaff33 | NW_017443532.1: 1336635–1338234 | + | XP_018853819.1 | JrSCL22b | 386–747 |
| JrSLR1 | LOC109015902 | NW_017389006.1 | Scaff9 | NW_017389006.1: 187337–190408 | + | XP_018853896.1 | JrSLR1 | 151–449 |
| JrSCLf | LOC109017304 | NW_017389344.1 | Scaff12 | NW_017389344.1: 736656–738728 | − | XP_018855146.1 | JrSCLf | 1–309 |
| JrSCL3f | LOC109020246 | NW_017399977.1 | Scaff17 | NW_017399977.1: 832–2407 | + | XP_018858211.1 | JrSCL3f | 46–465 |
Phylogenetic analysis of GRAS members
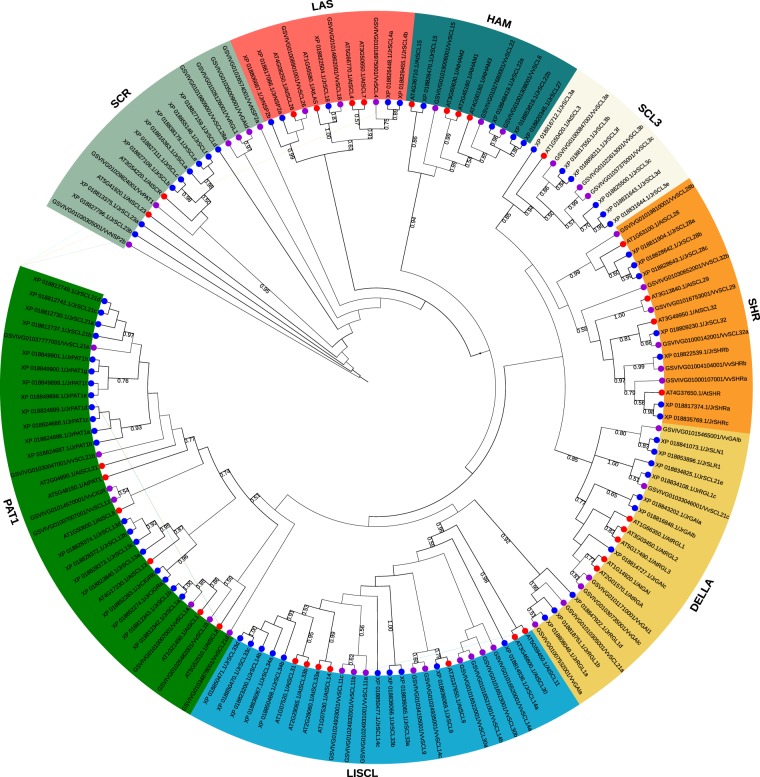
To study the phylogenetic relationships between GRAS family members in walnut, domain sequences of 70 walnut GRAS proteins, 33 Arabidopsis GRAS proteins and 43 grape GRAS proteins were used to construct an unrooted NJ phylogenetic tree in MEGA 6 with 1000 bootstrap replicates (Fig. 1). Based on the phylogenetic analysis and previous research1, all GRAS members were clustered into 8 subfamilies: PAT1, SCL3, DELLA, LAS, SCR, HAM, SHR, LISCL. The distribution of JrGRAS proteins among different subfamilies was as following: PAT1(20), LISCL(14), DELLA (10), SCR(8), SCL3(6), HAM(4), LAS(4), and SHR(4).
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of the domain sequence of GRAS proteins from Arabidopsis, walnut and grape using the Maximum Likelihood method. Genes in Arabidopsis, walnut and grape are labeled in red, blue and purple dots, respectively.
Definition the sequence features of JrGRAS proteins
The GRAS proteins in walnut share a highly conserved C-terminal, which is constituted by five distinct conserved motifs in the following order: LHR I (leucine heptad repeat I), VHIID, LHR II (leucine heptad repeat II), PFYRE and SAW, while the N-terminal region of the sequences seems to be variable (Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
Alignment of the walnut GRAS protein sequences. The highly conserved regions of the JrGRAS proteins were divided into five recognizable motifs.
The presence of leucine heptad repeats in the GRAS proteins suggests that these proteins may function as multimers and a potentially complicated higher order of interaction1. The VHIID sequence consists of valine, histidine, isoleucine and aspartic acid, which is not absolutely conserved although it can be readily recognizable (position: 214–218, Fig. 2). Besides, we noticed the VHIID motif, the P residues (position: 191, Fig. 2) are absolutely conserved in the VHIID motif. The PFYRE motif consists of the P(position: 342)-F(position: 363)-Y(position: 374)-R(position: 366)-E(position: 369) (Fig. 2) residues, the P residues are absolutely conserved in PFYRE motif as well as in motif VHIID. The SAW motif is characterized by the residues S-A-W (position: 481–483, Fig. 2), the W(position: 472,483) residues are absolutely conserved in the other JrGRAS protein sequences, except the JrSLR1 which lack the SAW motif. And the absolute conservation of the residues in the VHIID and SAW motifs indicates that these residues could be necessary for the functions of the GRAS proteins.
Conserved motifs analyses
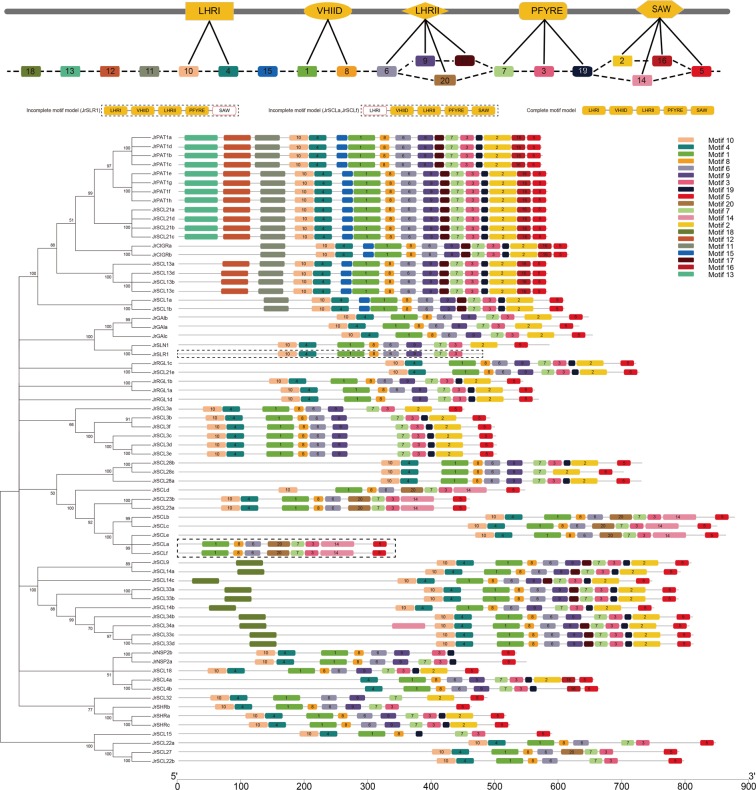
All JrGRAS proteins were subjected to MEME website (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme)49 to identify conserved motifs (Fig. 3). Among the twenty Motifs, Motifs 10 and 4 consisted the LHR I domain, Motifs 1 and 8 consisted the VHIID domain, Motifs 6,9 and 17 or 6 and 20 consisted the LHR II domain, Motifs 7,3 and 19 consisted the PFYRE domain, and Motifs 2, 16 and 5 or 14 and 5 consisted the SAM domain (Fig. 3). Interesting, almost all JrGRAS protein include the complete GRAS motif model, which consists of LHR I, VHIID, LHR II, PFYRE, and SAM domain, and the five domains distribute in the same order, except JrSLR1, JrSCLa and JrSCLf.
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic relationship, motifs and gene structures of GRAS members in walnut.
Synteny analysis and gene duplication of JrGRAS genes
Synteny analysis between different species
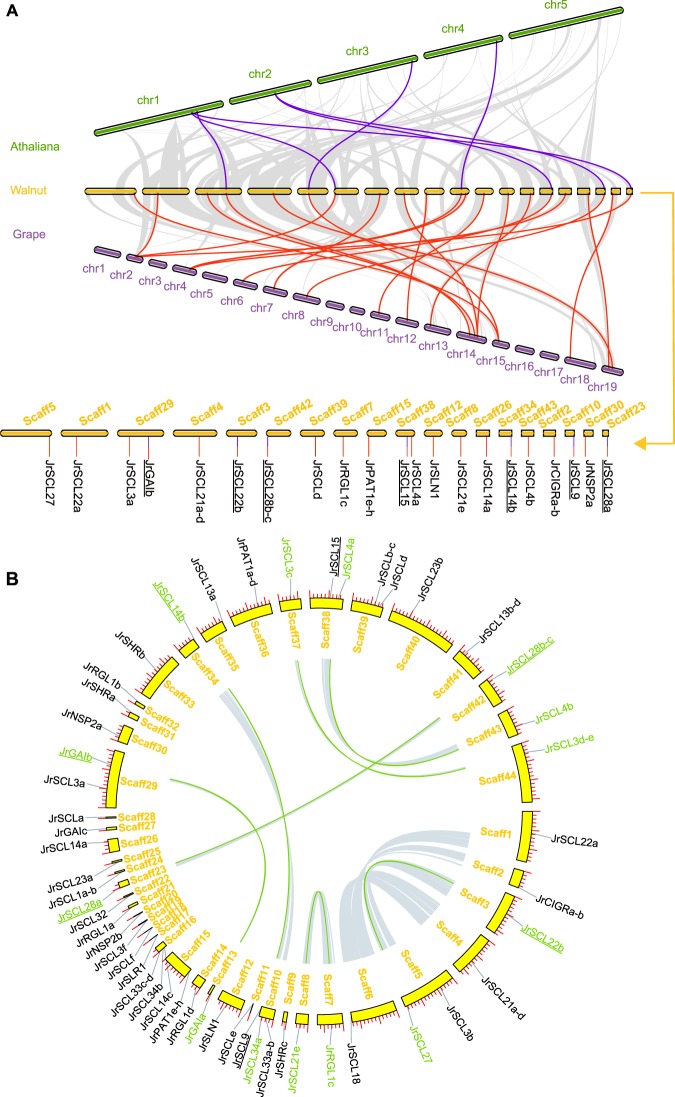
To deduce the evolutionary relationship of GRAS genes between different species, syntenic analysis was performed for three plants (A. thaliana, Vitis vinifera and Juglans regia) (Fig. 4A). The result showed that there are many synteny blocks between Arabidopsis, grape and walnut. Among these blocks, seven walnut GRAS genes (JrGAIb/JrSCL22b/JrSCL28b-c/JrSCL15/JrSCL14b/JrSCL9/JrSCL28a) showed pairwise synteny with genes in Aradiposis genome, and twenty-one walnut GRAS genes (JrSCL27/JrSCL22a/JrSCL3a/JrGAIb/JrSCL21a-d/JrSCL22b/JrSCL28b-c/JrSCLd/JrRGL1c/JrPAT1e-h/JrSCL15/JrSCL4a/JrSLN1/JrSCL21e/JrSCL14a/JrSCL14b/JrSCL4b/JrCIGRa-b/JrSCL9/JrNSP2a/JrSCL28a) showed pairwise synteny with genes in grape genome. What is more, the seven walnut GRAS genes (JrGAIb/JrSCL22b/JrSCL28b-c/JrSCL15/JrSCL14b/JrSCL9/JrSCL28a) were identified to have orthologous genes within Aradiposis genome and within grape genome, simultaneously. These data indicated that the GRAS genes might have evolved from the common ancestor in different plants (The gene name with an underline means this gene was identified as the orthologous gene between different species).
Figure 4.
(A) Synteny analysis of GRAS genes between Arabidopsis, walnut and grape. The gray lines in the background indicate the collinear blocks within walnut and other plant genomes, while the blue and red lines highlight the syntenic GRAS gene pairs. (B) Synteny analysis of JrGRAS genes. Gray lines indicate all synteny blocks in the walnut genome, whereas the green lines suggest duplicated GRAS gene pairs. The gene name with an underline means this gene was identified as the synteny gene between different species.
Gene duplication in walnut genome
Gene duplication events were surveyed to explore the evolutionary patterns of the GRAS gene family in walnut genome (Fig. 4B). Physical locations of 52 JrGRAS genes in walnut were investigated by analysis of genomic distribution on scaffolds. Fifty-two JrGRAS genes were distributed unevenly across the 44 scaffolds in the walnut genome (Fig. 4B). Analysis of walnut GRAS family genes revealed seven paralogous gene pairs (JrGAIa&JrGAIb/JrRGL1c& JrSCl21e/JrSCL14b&JrSCL34a/JrSCL22b&JrSCL27/JrSCL28a&JrSCL28b-c/JrSCL3c&JrSCL3d-e/JrSCL4a&JrSCL4b) existed in walnut GRAS family genes. Among the 14 GRAS paralogous genes, 5 of them were orthologous genes identified between species, which indicated they were involved in the duplication event in walnut genome. (The gene name with an underline means this gene was identified as the orthologous gene between different species and the ‘&’ means connector between duplicated gene pairs).
Expression profiles of GRAS members
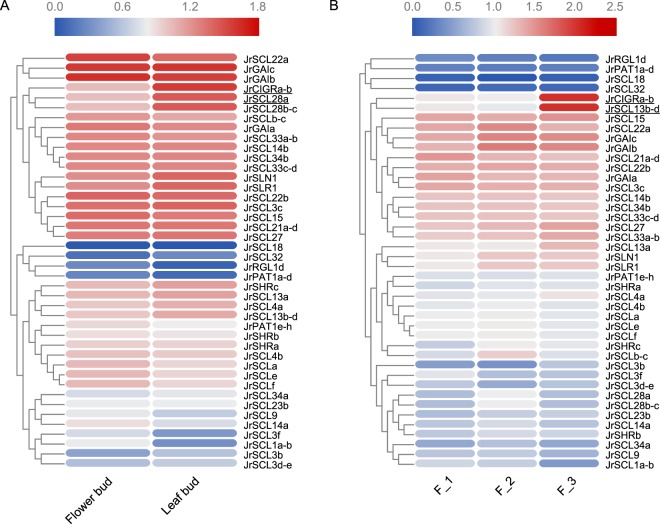
We used the FPKM values of 52 JrGRAS genes to investigate the expression profiles of the JrGRAS family genes. Ten of the JrGRAS genes were excluded to draw the heatmap for their FPKM value were zero in both flower bud and leaf bud.
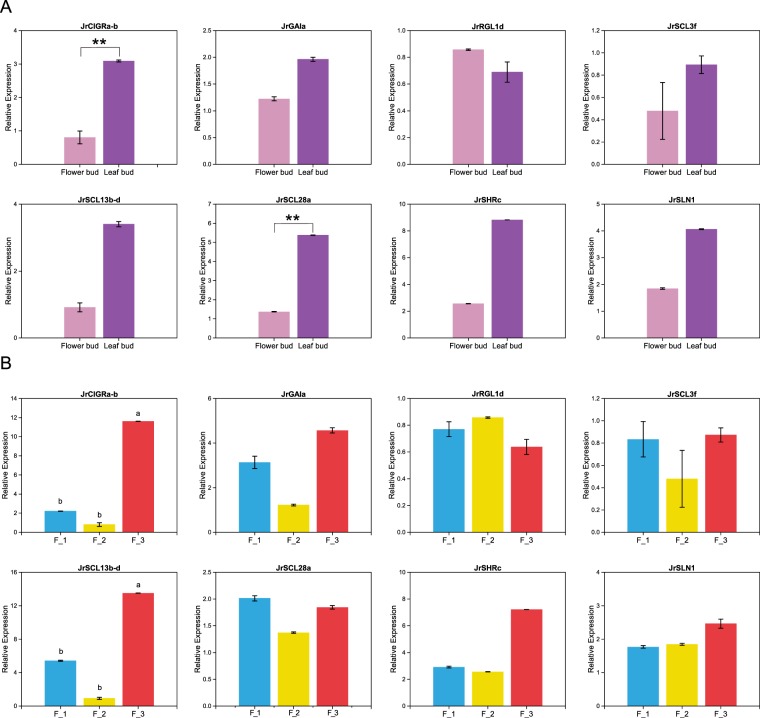
First, expression levels of JrGRAS genes in female flower bud and in leaf bud were compared (Fig. 5A). Three JrGRAS genes (JrSCL22a/JrGAIb/JrGAIc) were highly expressed in both flower bud and leaf bud, and four JrGRAS genes (JrSCL18/JrSCL32/JrRGL1d/JrPAT1a-d) were lowly expressed in both flower bud and leaf bud. Besides, two JrGRAS genes (JrCIGRa-b/JrSCL28a) were differentially expressed between flower bud and leaf bud (p < 0.01).
Figure 5.
(A) Heatmap of the JrGRAS genes between flower buds and leaf buds. (B) Heatmap of JrGRAS genes expressed differently in three development periods of flower buds (F_1, F_2, and F_3).
Next, expression levels of the JrGRAS genes in female flower buds before, during, and after flower transition (F_1/F_2/F_3) were compared (Fig. 5B). Four JrGRAS genes (JrSCL18/JrSCL32/JrRGL1d/JrPAT1a-d) were lowly expressed in F_1, F_2 and F_3, and four JrGRAS genes (JrSCL15/JrSCL22a/JrGAIb/JrGAIc) were highly expressed in both flower bud and leaf bud. Besides, two JrGRAS genes (JrCIGRa-b and JrSCL13b-d) were differentially expressed between F_1, F_2 and F_3 (p < 0.01).
GO enrichment
The GO enrichment analysis based on the 70 JrGRAS proteins annotated in the GO database. In the biological process category, significantly enriched terms were associated with biological regulation, cellular process, metabolic process, and response to stimulus. In the cellular component category, cell, cell part, and organelle were significantly enriched. In the molecular function category, GO terms related to binding and nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity were highly represented. Besides, GO: 003674 (molecular function) was the most GO term enriched by the JrGRAS members (Fig. S2).
Co-expression networks analysis of the JrGRAS family genes
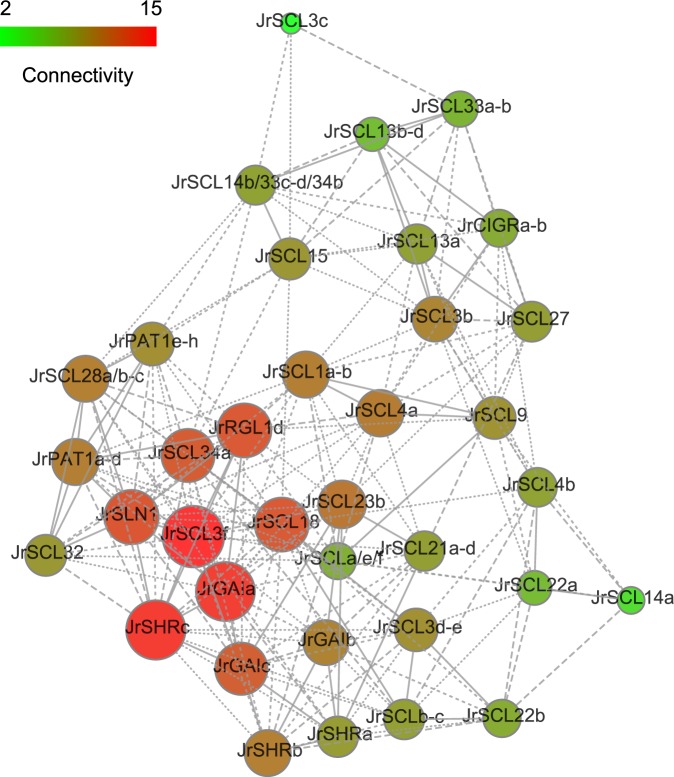
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) is a biology method for interaction analysis and correlation networks resolving50. To search for the genes involved in flowering time regulation in walnut, JrGRAS family genes were used to construct a co-expression network with the method of WGCNA, the result was presented in Fig. 6. In the co-expression network, many of the key genes that participate in walnut flower bud transition were identified, such as JrGAIa, JrSCL3f, JrSHRc, JrSCL34a, JrSLR1, JrRGL1d, JrSLN1, JrSCL18 and the hub genes with the highest edge numbers were JrGAIa, JrSCL3f and JrSHRc.
Figure 6.
Co-expression networks of 58 JrGRAS genes. In the drawn weight network graph, the weight between genes will be divided into four parts, which are represented by point lines, short dotted lines, long dotted lines and real lines from small to large weights. The larger node and the redder color mean the greater connectivity of the gene in the network graph.
Validation expression patterns of JrGRASs by qRT-PCR
The top five JrGRAS genes (JrSCL3f/JrSHRc/JrGAIa/JrSLN1/JrRGL1d) in the co-expression network and three DEGs (JrCIGRa-b, JrSCL13b-d and JrSCL28a) were used to conduct a qRT-PCR experiment (Fig. 7). The results were similar to those of our RNA-seq analysis and the DEGs were evidently differentially expressed among different tissues and development stages (P < 0.01). In leaf bud, JrCIGRa-b and JrSCL28a were all significantly up-regulated than that in flower bud (P < 0.01). As for flower bud transition periods, JrCIGRa-b and JrSCL13b-d were up-regulated in F_3 than that in F_1 and F_2 (P < 0.01). Among the DEGs, JrCIGRa-b differentially expressed in different tissues and different development period of flower buds, suggesting that this gene should work as the candidate gene for flower bud transition in walnut.
Figure 7.
qRT-PCR analysis of JrGRAS genes in different tissues and different development period of flower buds.
Interaction network of JrGRAS proteins
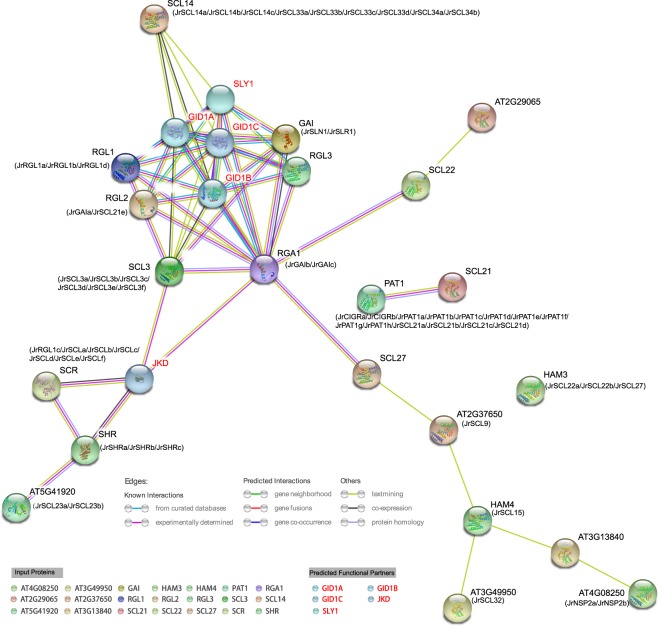
Because the interaction of walnut GRAS proteins is little known, we constructed the interaction network of the JrGRAS proteins based on interaction relationship of the homologous GRAS proteins in Arabidopsis. The walnut GRAS proteins corresponded with the Arabidopsis GRAS proteins are listed below them (Fig. 8). The result showed that several JrGRASs (such as JrGAIb/JrGAIc) were predicted to be core nodes in the network, which suggested that they might participate in diverse functions by interacting with other proteins.
Figure 8.
Predicted protein-protein interaction network of JrGRAS proteins. The network nodes represent proteins, the 3D structure of the proteins is shown inside the nodes and the colors of the line indicate different data sources.
Discussion
In general, analysis of whole genome location and evolution rely on the available information of species genome assembled in Chromosomes-level. However, the walnut genome was assembled only in scaffold-level, and there is no access to the information of walnut Chromosomes until now. In this article, the 44 scaffolds which including the 52 JrGRAS genes were used to represent the walnut genome in the synteny and gene duplication analysis, and this may provide a new insight to the analysis of whole genome evolution for the species whose genome assembled in scaffold-level.
Evolution of divergence and conservation
Divergence and conservation always come together with the process of species evolution. Phylogenetic analysis divided the JrGRAS family into eight subgroups based on the evolutionary relationship, and each subgroup always function differently (Fig. 1). However, sequence alignment indicated that it was high conserved for the distribution of five motifs (LHR I, VHIID, LHR II, PFYRE, SAW motif) in JrGRAS family members, and the order of these motifs within each protein is the same (Figs 2 and 3). Besides, in VHIID and SAW motifs, the absolute conserved residues suggested that these residues could be necessary for the activity of the GRAS proteins (Fig. 2).
The duplication of GRAS genes between species and in walnut genome
Gene duplication between species indicated that Arabidopsis, walnut, and grape share the same seven ancestral GRAS genes. The number of orthologous genes of GRAS family genes in the three species showed a ratio of 7:21:21 (Arabidopsis: walnut: grape), which suggest a triplication event could occur in the GRAS family gene of walnut and grape. These caused us to further investigate the expansion of GRAS family gene in the walnut genome.
However, duplication analysis in walnut genome indicated that the triplicated speculation was invalid. Besides, duplicate genes face fates as follow: non-functionalization, neo-functionalization (evolving novel functions), or sub-functionalization (partition of gene functions)51. The seven orthologous GRAS genes (JrGAIb/JrSCL22b/JrSCL28b-c/JrSCL15/JrSCL14b/JrSCL9/JrSCL28a) occurred gene duplication event with function divergent in walnut genome, five of them duplicated with their pair genes (JrGAIb&JrGAIa/JrSCL22b&JrSCL27/JrSCL28b-c&JrSCL28a/JrSCL14b&JrSCL34a) still belong to the GRAS gene family. As for one of the five duplicated gene pairs mentioned above, (JrSCL28b-c&JrSCL28a), it seems that both of JrSCL28b-c and JrSCL28a come from the orthologous GRAS genes and this suggests that the duplication of them could be earlier than that in the other four duplicated gene pairs. What’s more, not all of the seven orthologous GRAS genes occurred gene duplication event, two of them (JrSCL15/JrSCL9) showed that they have no duplicated gene pairs in this research.
Expression and function analysis of JrGRAS genes
JrCIGRa-b and JrSCL28a were identified to have a lower expression level in flower bud than that in leaf bud, which suggested these JrGRAS genes may negatively control the flower buds transition. And expression levels of JrCIGRa-b and JrSCL13b-d were detected up-regulated after flower buds transition (F_3) compared to that in (i) before the flower buds transition (F_1) and (ii) during the flower buds transition (F_2), which indicated that these JrGRAS genes may positively participate in the regulation of walnut flower organs development. Besides, three hub JrGRAS genes (JrSCL3f/JrGAIa/JrSHRc) were predicted by co-expression analysis, which suggested that they may involve in the regulation network of walnut flower buds transition, too.
Functional analysis of the JrGRAS proteins seems to accord with the result of expression analysis. The GRAS domains are interacting with other domains identified by forming the heterodimer or homodimer structure. Up to now, two models of the GRAS domain interacting with other domains have been reported: (i) SHR-SCR heterodimeric structure; (ii) the homodimeric structure of the SCL7 GRAS domain4. And in this study, the SCR proteins (JrSCLa/b/c/d/e/f) were predicted to interact with the SHR proteins (JrSHRa/b/c) (Fig. 8), which consist with the SHR-SCR heterodimeric structure model. Besides, protein-protein interaction analysis showed that three hub JrGRASs (JrSCL3f/JrGAIa/JrSHRc) identified by expression analysis also have many interaction partners in the JrGRAS protein-protein interaction network (Fig. 8), these results illustrate how JrGRAS family proteins might form functional complexes, mediating the expression of flower bud transition genes in walnut.
Importantly, the LAS subfamily is involved and necessary in the growth regulation of the meristem formation41,43,44. A differentially expressed JrGRAS gene (JrSCL28a) in the LAS subfamily was found expressed both in leaf bud and flower bud, however, its expression level in leaf bud was significantly higher than that in flower bud (P < 0.01), the mechanism is still unclear. PAT1 is involved in phytochrome A signal transduction in Arabidopsis35. In this study, two DEGs (JrCIGRa-b and JrSCL13b-d, P < 0.01), identified (i) before, (ii) during and (iii) after flower bud transition (F_1, F_2 and F_3), were classified into the PAT subfamily, which indicated light signaling via the phytochrome A photoreceptor controls basic plant developmental processes, including flower bud development. Recently, a single walnut GRAS gene, JrGRAS2 (LOC108996381, JrSCL23b, belongs to the SCL subfamily in this article), was reportedly involved in high-temperature stress tolerance40, which offer new insights to the functional diversity of walnut GRAS family members.
In summary, our work laid a foundation for future function investigation of the GRAS members in walnut and provides valuable information about the gene functions of GRAS family in the development of walnut flower bud transition.
Methods
Identification of GRAS family members in walnut
The latest protein sequences file (GCF_001411555.1_wgs.5d_protein.faa) of walnut genome was downloaded from the NCBI website (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/GCF/001/411/555/GCF_001411555.1_wgs.5d/GCF_001411555.1_wgs.5d_protein.faa.gz). The hmm model of GRAS domain was constructed based on the PF03514 (PFAM website, http://pfam.xfam.org/family/pf03514) by the hmmbuild program HMMER 3.252. Then, we used the hmm model mentioned above to search against the protein databases of walnut genomes with the hmmsearch program in HMMER 3.252, the E-value cutoff was 1e−10. The candidate GRAS members were then uploaded to the CD-search website (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi) to further confirm if they include the proper GRAS domains (sequences included GRAS domain and length of domain sequences was more than 150aa). Gene structures of the JrGRAS genes were drawn by the Biosequence Structure Illustrator program of the TBtools software53. Subcellular location information of the JrGRAS proteins was predicted by online software WoLF PSORT II (https://www.genscript.com/wolf-psort.html?src=leftbar).
Multiple alignments and phylogenetic analyses
The domain sequences of the GRAS proteins in Arabidopsis, walnut and grape were downloaded from the Plant Transcription Factor Database (http://planttfdb.cbi.pku.edu.cn/) and aligned using Clustal X 2.154. Then these sequences were used to conduct phylogenetic analyses using MEGA 6 software55 with 1000 bootstrap replicates. Motifs in the JrGRAS family members were identified by MEME program (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme)49 with a maximum of 20 motifs shown in the result.
Synteny and gene duplication analysis
Analysis of gene duplication events using MCScanX toolkit56, paralogous genes in walnut genome were identified by the duplicate_gene_classifier program with the default parameters of the MCScanX toolkit, and orthologous genes between species were identified by the detect_collinear_tandem_arrays program with the default parameters of the MCScanX toolkit56. The genome sequences files and annotation files of Arabidopsis (RefSeq assembly accession: GCF_000001735.2, ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/GCF/000/001/735/GCF_000001735.4_TAIR10.1), walnut (RefSeq assembly accession: GCF_001411555.1) and grape (RefSeq assembly accession: GCF_000003745.3, ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/GCF/000/003/745/GCF_000003745.3_12X/) were downloaded from NCBI website (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). The circle map of syntenic analysis maps in walnut genome was constructed by TBtools software53. Because of the walnut genome was assembled only in scaffold-level, the 44 scaffolds which including the 52 JrGRAS genes were used to represent the walnut genome in the synteny and gene duplication analysis.
Expression analysis of GRAS members
Transcriptome sequencing and library construction were reported in our previous study57. Expression analysis of walnut GRAS members was evaluated using the walnut RNA-sequence data among different tissues (leaf bud and female flower bud), development stages (F_1, F_2, F_3). The FPKM values were normalized with the treatment of log10(FPKM), and the results were then used to generate heatmap using the HemI software58.
RNA isolation and qRT-PCR analysis
The female flower buds were collected before, during, and after flower transition (F_1, F_2 and F_3), and leaf buds were collected during the floral transition period. The Leaf buds and female flower buds (F_1, F_2 and F_3) were collected and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. Total RNA was extracted with RNAout 1.0 (Tianenze, China) as described by the manufacturer and cDNA was reversed reverse-transcribed using the PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit (Takara, China). The real-time PCR analysis was performed using CFX Manager (Bio-Rad, USA) with SYBR Green mixture (Toyobo, Japan), and the walnut actin gene and walnut gadph gene were used for normalization, the amplification was applied using the cycling parameter as described previously45. The results were evaluated by the 2−ΔCt method according to Livak and Schmittgen59.
GO enrichment
The Blast2GO60–63 software was employed to perform the GO annotation. First, protein sequences of the JrGRAS were used to perform the blastp search against the Swissport database with the E-Value of 1E-05, number of blast hits was 5. Then the result was conducted a GO mapping, and after that the GO annotation program was used to get the GO annotation of the JrGRAS members. Finally, the GO enrichment analysis was conducted by the online GO enrichment program on the omicshare website (https://www.omicshare.com/tools/Home/Soft/gogsea).
Interaction network of JrGRAS proteins
The blastp program was used between the walnut GRAS proteins and the Arabidopsis GRAS proteins, each walnut GRAS protein matched a homologous Arabidopsis GRAS protein with the highest score (Table S7). Thirty-three Arabidopsis GRAS proteins which represent the 70 walnut GRAS proteins were uploaded to the String website (https://string-db.org/)64 to predict protein interactions. Except the 33 input proteins, five predicted functional partners of the input proteins were used to construct the network. The walnut GRAS proteins corresponded with the Arabidopsis GRAS proteins are listed below them. The online program ran with default parameters.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the important National Science and Technology Specific projects of Xinjiang (No. 201130102-1-4) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30560090).
Author Contributions
J.X.N. led and coordinated the project, J.X.N. and S.W.Q. designed the study, S.W.Q., L.Z., H.X., L.M. and Y.Q. collected the plant materials and isolated the RNA. S.W.Q. and L.Z. conducted the real-time quantitative PCR. S.W.Q. conducted the bioinformatics analysis and wrote the paper. All authors have read and agree with the final manuscript. J.X.N. is the corresponding author and is responsible for all contact and correspondence.
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41598-019-48287-x.
References
- 1.Pysh LD, Wysocka-Diller JW, Camilleri C, Bouchez D, Benfey PN. The GRAS gene family in Arabidopsis: sequence characterization and basic expression analysis of the SCARECROW-LIKE genes. Plant J. 1999;18:111–119. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Silverstone AL, Ciampaglio CN, Sun T. The Arabidopsis RGA gene encodes a transcriptional regulator repressing the gibberellin signal transduction pathway. The Plant cell. 1998;10:155–169. doi: 10.1105/tpc.10.2.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sun TP. The molecular mechanism and evolution of the GA-GID1-DELLA signaling module in plants. Curr Biol. 2011;21:R338–345. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.02.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hakoshima T. Structural basis of the specific interactions of GRAS family proteins. FEBS letters. 2018;592:489–501. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pauluzzi G, et al. Surfing along the root ground tissue gene network. Dev Biol. 2012;365:14–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Petricka JJ, Winter CM, Benfey PN. Control of Arabidopsis root development. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2012;63:563–590. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042811-105501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tian C, Wan P, Sun S, Li J, Chen M. Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant molecular biology. 2004;54:519–532. doi: 10.1023/b:Plan.0000038256.89809.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bolle C. The role of GRAS proteins in plant signal transduction and development. Planta. 2004;218:683–692. doi: 10.1007/s00425-004-1203-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhou S, et al. Manipulation of plant architecture and flowering time by down-regulation of the GRAS transcription factor SlGRAS26 in Solanum lycopersicum. Plant science: an international journal of experimental plant biology. 2018;271:81–93. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sun X, et al. A functionally required unfoldome from the plant kingdom: intrinsically disordered N-terminal domains of GRAS proteins are involved in molecular recognition during plant development. Plant Mol Biol. 2011;77:205–223. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9803-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Richards DE, Peng J, Harberd NP. Plant GRAS and metazoan STATs: one family? Bioessays. 2000;22:573–577. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1521-1878(200006)22:6<573::Aid-bies10>3.0.Co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee MH, et al. Large-scale analysis of the GRAS gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant molecular biology. 2008;67:659–670. doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Day RB, Shibuya N, Minami E. Identification and characterization of two new members of the GRAS gene family in rice responsive to N-acetylchitooligosaccharide elicitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1625:261–268. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4781(02)00626-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Liu X, Widmer A. Genome-wide Comparative Analysis of the GRAS Gene Family in Populus, Arabidopsis and Rice. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter. 2014;32:1129–1145. doi: 10.1007/s11105-014-0721-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Abarca D, et al. The GRAS gene family in pine: transcript expression patterns associated with the maturation-related decline of competence to form adventitious roots. BMC Plant Biol. 2014;14:354. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0354-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Song XM, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis) Genomics. 2014;103:135–146. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2013.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chen YQ, et al. Homology-based analysis of the GRAS gene family in tobacco. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14:15188–15200. doi: 10.4238/2015.November.25.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huang W, Xian Z, Kang X, Tang N, Li Z. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of GRAS gene family in tomato. BMC Plant Biol. 2015;15:209. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0590-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Niu Y, Zhao T, Xu X, Li J. Genome-wide identification and characterization of GRAS transcription factors in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) PeerJ. 2017;5:e3955. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lu J, Wang T, Xu Z, Sun L, Zhang Q. Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in Prunus mume. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015;290:303–317. doi: 10.1007/s00438-014-0918-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wu ZY, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in physic nut (Jatropha curcas L.) Genet Mol Res. 2015;14:19211–19224. doi: 10.4238/2015.December.29.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Xue L, et al. Network of GRAS transcription factors involved in the control of arbuscule development in Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol. 2015;167:854–871. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.255430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Grimplet J, Agudelo-Romero P, Teixeira RT, Martinez-Zapater JM, Fortes AM. Structural and Functional Analysis of the GRAS Gene Family in Grapevine Indicates a Role of GRAS Proteins in the Control of Development and Stress Responses. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:353. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sun X, et al. A characterization of grapevine of GRAS domain transcription factor gene family. Funct Integr Genomics. 2016;16:347–363. doi: 10.1007/s10142-016-0479-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhao H, et al. Comprehensive analysis of multi-tissue transcriptome data and the genome-wide investigation of GRAS family in Phyllostachys edulis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27640. doi: 10.1038/srep27640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Xu Wei, Chen Zexi, Ahmed Naeem, Han Bing, Cui Qinghua, Liu Aizhong. Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary Analysis, and Stress Responses of the GRAS Gene Family in Castor Beans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016;17(7):1004. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yang, C. J., Li, G. Y. & Cui, Y. L. Bioinformatic analyses of GRAS genes in Betula kirghisorum based on transcriptome data. Genet Mol Res15, 10.4238/gmr.15038321 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28.Zhang L, Li Q, Chen JF, Chen WS. Computational identification and systematic classification of novel GRAS genes in Isatis indigotica. Chinese journal of natural medicines. 2016;14:161–176. doi: 10.1016/s1875-5364(16)30013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fan S, et al. Identification, Classification, and Expression Analysis of GRAS Gene Family in Malus domestica. Frontiers in physiology. 2017;8:253. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Guo Y, et al. Identification and expression of GRAS family genes in maize (Zea mays L.) Plos One. 2017;12:e0185418. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhang H, et al. Genome-wide characterization of GRAS family genes in Medicago truncatula reveals their evolutionary dynamics and functional diversification. Plos One. 2017;12:e0185439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wang YX, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of GRAS family transcription factors in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) Sci Rep. 2018;8:3949. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22275-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhang B, et al. Genome-wide analysis of GRAS transcription factor gene family in Gossypium hirsutum L. BMC Genomics. 2018;19:348. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4722-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Peng J, et al. The Arabidopsis GAI gene defines a signaling pathway that negatively regulates gibberellin responses. Gene Dev. 1997;11:3194–3205. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.23.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bolle C, Koncz C, Chua NH. PAT1, a new member of the GRAS family, is involved in phytochrome A signal transduction. Genes Dev. 2000;14:1269–1278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Torres-Galea P, Hirtreiter B, Bolle C. Two GRAS proteins, Scarecrow-Like21 and Phytochrome a Signal Transduction1, function cooperatively in phytochrome A signal transduction. Plant Physiol. 2013;161:291–304. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.206607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mayrose M, Ekengren SK, Melech-Bonfil S, Martin GB, Sessa G. A novel link between tomato GRAS genes, plant disease resistance and mechanical stress response. Molecular plant pathology. 2006;7:593–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2006.00364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yuan Y, et al. Overexpression of VaPAT1, a GRAS transcription factor from Vitis amurensis, confers abiotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2016;35:655–666. doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1910-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Xu K, et al. OsGRAS23, a rice GRAS transcription factor gene, is involved in drought stress response through regulating expression of stress-responsive genes. BMC Plant Biol. 2015;15:141. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0532-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yang G, et al. The walnut transcription factor JrGRAS2 contributes to high temperature stress tolerance involving in Dof transcriptional regulation and HSP protein expression. BMC Plant Biol. 2018;18:367. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1568-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Stuurman J, Jaggi F, Kuhlemeier C. Shoot meristem maintenance is controlled by a GRAS-gene mediated signal from differentiating cells. Genes Dev. 2002;16:2213–2218. doi: 10.1101/gad.230702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Li X, et al. Control of tillering in rice. Nature. 2003;422:618–621. doi: 10.1038/nature01518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Greb T, et al. Molecular analysis of the Lateral Suppressor gene in Arabidopsis reveals a conserved control mechanism for axillary meristem formation. Genes Dev. 2003;17:1175–1187. doi: 10.1101/gad.260703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Engstrom EM, et al. Arabidopsis homologs of the petunia hairy meristem gene are required for maintenance of shoot and root indeterminacy. Plant Physiol. 2011;155:735–750. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.168757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Quan S, et al. Identification and characterization of NF-Y gene family in walnut (Juglans regia L.) BMC Plant Biol. 2018;18:255. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1459-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pollegioni P, et al. Rethinking the history of common walnut (Juglans regia L.) in Europe: Its origins and human interactions. Plos One. 2017;12:e0172541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Abdallah IB, et al. Content of carotenoids, tocopherols, sterols, triterpenic and aliphatic alcohols, and volatile compounds in six walnuts (Juglans regia L.) varieties. Food Chemistry. 2015;173:972–978. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Martinez-Garcia PJ, et al. The walnut (Juglans regia) genome sequence reveals diversity in genes coding for the biosynthesis of non-structural polyphenols. Plant J. 2016;87:507–532. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bailey TL, et al. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic acids research. 2009;37:W202–208. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Presson A.P, et al. Integrated Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis with an Application to Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. BMC Systems Biology. 2008;2:95–95. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-2-95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Prince VE, Pickett FB. Splitting pairs: the diverging fates of duplicated genes. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:827–837. doi: 10.1038/nrg928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Eddy SR. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics. 1998;14:755–763. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chen, C., Xia, R., Chen, H. & He, Y. TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various HTS-data handling tools with a user-friendly interface, 10.1101/289660 (2018).
- 54.Thompson Julie D., Gibson Toby. J., Higgins Des G. Multiple Sequence Alignment Using ClustalW and ClustalX. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics. 2002;00(1):2.3.1-2.3.22. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0203s00. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:2725–2729. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wang Y, et al. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic acids research. 2012;40:e49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Quan S, et al. Stages identifying and transcriptome profiling of the floral transition in Juglans regia. Sci Rep. 2019;9:7092. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43582-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Deng W, Wang Y, Liu Z, Cheng H, Xue Y. HemI: a toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. Plos One. 2014;9:e111988. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods (San Diego, Calif.) 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gotz S, et al. High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic acids research. 2008;36:3420–3435. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Gotz S, et al. B2G-FAR, a species-centered GO annotation repository. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:919–924. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ana C, Stefan Gt. Blast2GO: A Comprehensive Suite for Functional Analysis in Plant Genomics. International Journal of Plant Genomics. 2008;2008:619832. doi: 10.1155/2008/619832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Conesa A, et al. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3674–3676. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Szklarczyk D, et al. The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic acids research. 2017;45:D362–D368. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article.