FIG 5.
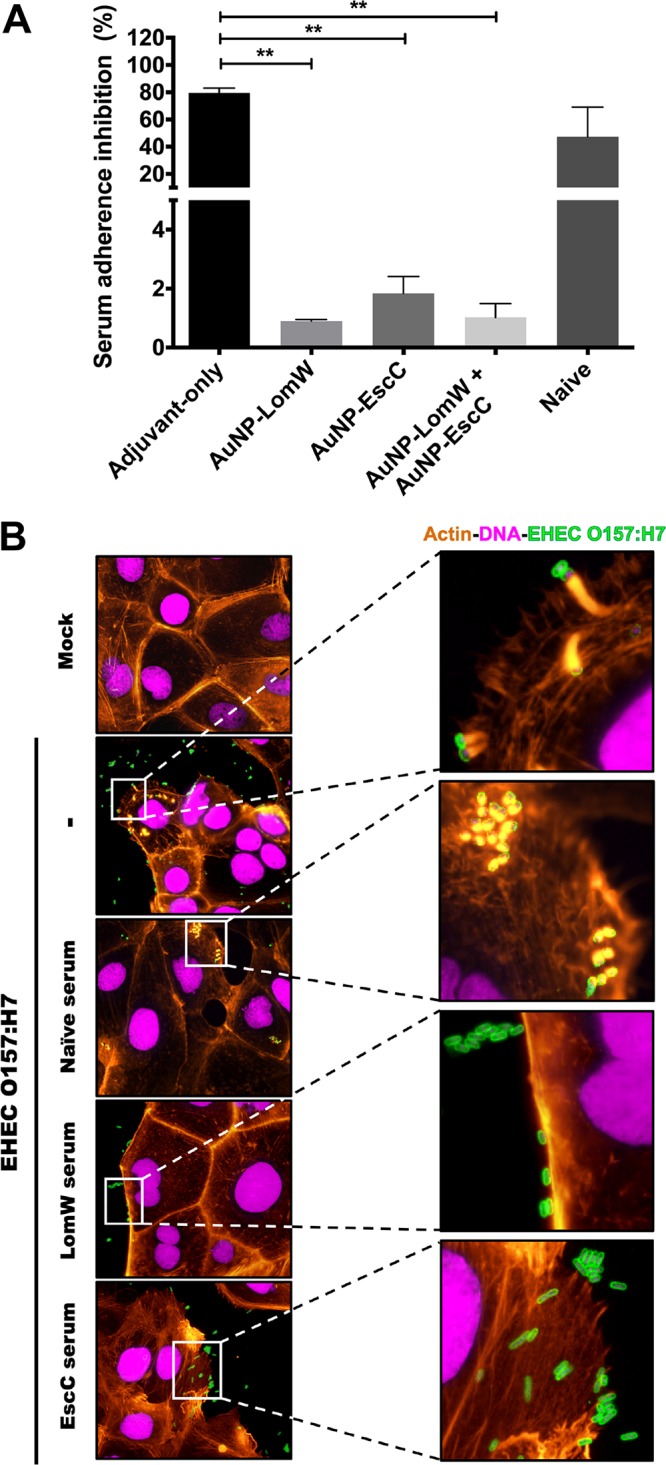
Serum from AuNP-protein-immunized mice reduces EHEC 86-24 adherence and pedestal formation on Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells. EHEC 86-24 bacterial cells (1 × 107 CFU) were incubated in the presence of immunized serum (10% final volume) from AuNP-LomW, AuNP-EscC, and AuNP-LomW plus AuNP-EscC for 1 h at 37°C. Serum from naive mice or mice subjected to adjuvant-only immunization served as controls. After incubation, bacteria were used to infect Caco-2 cells for 2 h. (A) After infection, cell monolayers were washed, detached, and diluted to enable enumeration of adhered bacteria. All adherence data are expressed as mean ± SEM of results from two independent experiments using sera from n = 8 mice per group. Significant differences were determined via one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001). (B) Fluorescence microscopy analysis of Caco-2 cells after EHEC infection in the presence of immune serum (from vaccinated groups). After infection, cells were fixed and stained with phalloidin-rhodamine (actin) or DAPI (bacteria and nuclei) and examined for EHEC by immunofluorescence (anti-EHEC primary antibody conjugated to FITC). Panels on the right present magnifications of the images on the left. The magnified views show the formation of actin pedestals and the bacterial adherence pattern.
