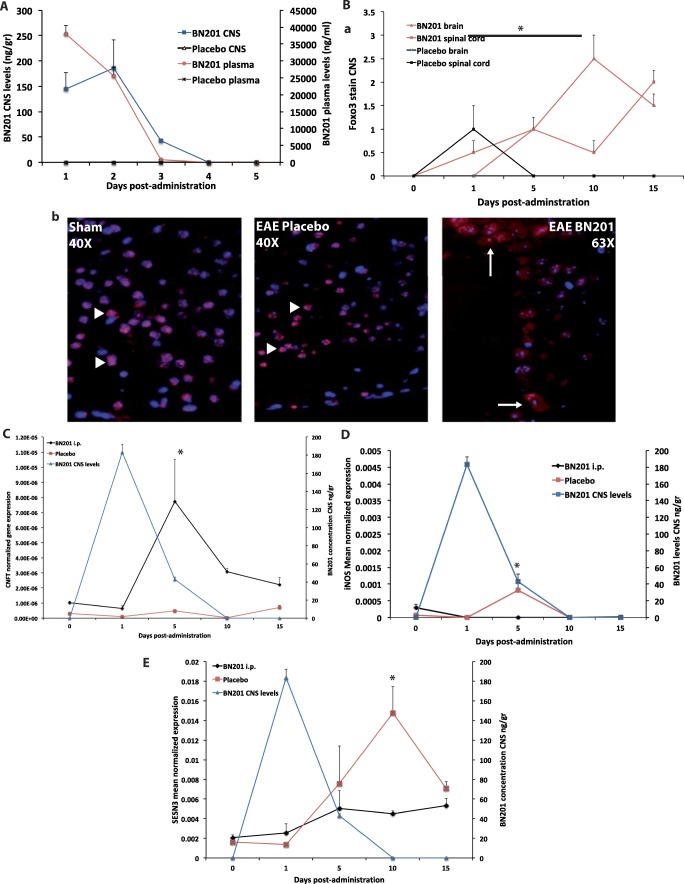
Fig. 5.
Pharmacodynamics of BN201. A Pharmacokinetics of a single administration of BN201 (50 mg/kg/day, i.p.) in plasma and brain in BN201 or placebo-treated animals by HPLC at different time points after injection. B–E The pharmacodynamic properties of BN201 were analyzed in the CNS of EAE animals by assessing the translocation of Foxo3 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in neurons, the expression of the trophic factor CNTF, the antioxidant enzyme SESN3, and the pro-oxidant enzyme iNOS in CNS homogenates. Mice (C57BL6) were immunized with MOG35-55 and treated after clinical onset (clinical score > 1) for 5 days with BN201 50 mg/kg, i.p., or placebo. Results are expressed as the mean of the 5 animals. B Foxo3 translocation to the cytoplasm in cortical and spinal cord neurons: (a) time series of Foxo3 translocation, (b) microphotographs of representative cortical regions showing neuronal nucleus (DAPI, in blue) and Foxo3 (in red) in sham animals, placebo, and BN201-treated mice. Arrowhead shows nuclear Foxo3 (co-localization of Foxo3 stain with DAPI) and arrows indicate cytoplasmic Foxo3 (lack of co-localization of Foxo3 and DAPI). Animals treated with BN201 showed significantly higher levels of Foxo3 translocation than placebo (*p < 0.05 ANOVA test). mRNA levels of CNTF (C), SESN3 (D), and iNOS (E) in the brain homogenates from mice treated with BN201 for 5 days (black line) and the corresponding BN201 CNS levels (in red). *p < 0.05 day 5, 10, or 15 with respect to day 0 of the same treatment group, ANOVA test