Significance
Protein kinase A, containing a dimeric regulatory (R)-subunit and 2 catalytic (C)-subunits, is the primary driver of cAMP signaling. The 4 R-subunits (RIα, RIβ, RIIα, RIIβ) form R2C2 holoenzymes with distinct functions. Our 2 RIα holoenzyme states, reflecting the presence and absence of ATP, not only reveal isoform-specific quaternary differences but also provide new insights into understanding of the role of ATP. Combined with biochemical and biophysical analyses, plus molecular dynamics simulations, we show how ATP functions in RIα holoenzymes as an inhibitor that competes with the allosteric activator, cAMP. This is distinct from the RIIβ holoenzyme, where different interfaces lead to distinct allosteric signaling networks. These isoform-specific differences contribute significantly to the combinatorial diversity of PKA signaling in cells.
Keywords: protein kinase A, structural biology, allosteric and orthosteric regulation, isoform-specific quaternary structure, cAMP
Abstract
Protein kinase A (PKA) holoenzyme, comprised of a cAMP-binding regulatory (R)-subunit dimer and 2 catalytic (C)-subunits, is the master switch for cAMP-mediated signaling. Of the 4 R-subunits (RIα, RIβ, RIIα, RIIβ), RIα is most essential for regulating PKA activity in cells. Our 2 RIα2C2 holoenzyme states, which show different conformations with and without ATP, reveal how ATP/Mg2+ functions as a negative orthosteric modulator. Biochemical studies demonstrate how the removal of ATP primes the holoenzyme for cAMP-mediated activation. The opposing competition between ATP/cAMP is unique to RIα. In RIIβ, ATP serves as a substrate and facilitates cAMP-activation. The isoform-specific RI-holoenzyme dimer interface mediated by N3A–N3A′ motifs defines multidomain cross-talk and an allosteric network that creates competing roles for ATP and cAMP. Comparisons to the RIIβ holoenzyme demonstrate isoform-specific holoenzyme interfaces and highlights distinct allosteric mechanisms for activation in addition to the structural diversity of the isoforms.
Protein kinase A (PKA) plays a critical role in regulating biological processes in every mammalian cell, and in canonical cAMP signaling PKA activity is tightly controlled by cAMP. In the absence of cAMP, PKA exists as an inhibited holoenzyme (R2C2) containing a dimer of regulatory (R) subunits and two catalytic (C) subunits; cAMP binding unleashes the activity of the C-subunit (1). The C-subunit, which was the first solved kinase structure (2), defined the conserved kinase core that consists of an N-terminal lobe (N-lobe) dominated by β-strands and a mostly helical C-terminal lobe (C-lobe) (Fig. 1A and SI Appendix, Fig. S1A). Although in the apo C-subunit the N-lobe is highly flexible and assumes an open conformation (3), binding ATP and Mg2+ induces a more closed conformation, where the ATP phosphates are precisely positioned by conserved residues (Lys72C, Glu91C, Asp184C), at the active-site cleft that leaves the γ-phosphate poised for transfer to a protein substrate or trap a high-affinity complex by inhibitory pseudosubstrate proteins (4, 5).
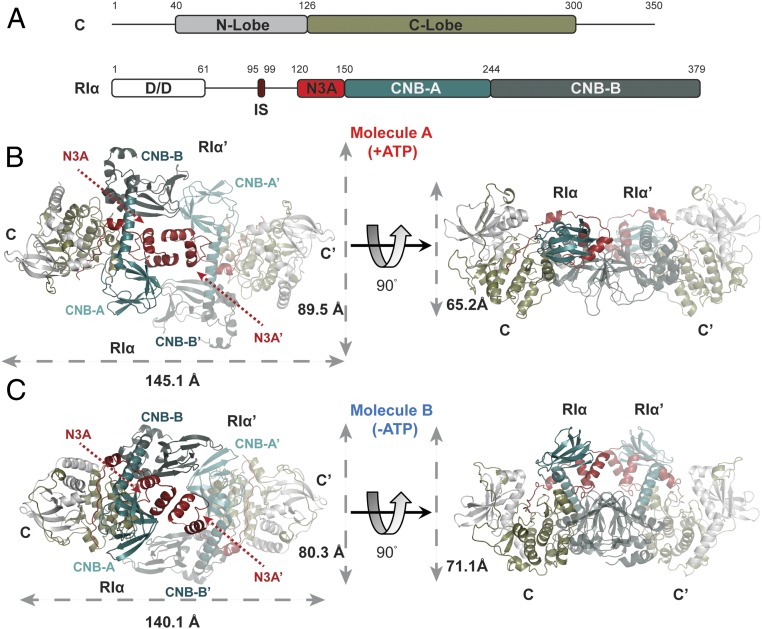
Fig. 1.
Quaternary structure of RIα2C2 holoenzyme. (A) Domain organization and color coding of PKA C-subunit and RIα-subunit. IS: inhibitory sequence. (B) Molecule A of RIα holoenzyme with dimension 145.1 × 89.5 × 65.2 Å. (C) Molecule B of RIα holoenzyme with dimension 140.1 × 80.3 × 71.1 Å.
In humans, there are 4 functionally nonredundant R-subunit isoforms (RIα, RIβ, RIIα, RIIβ) (SI Appendix, Fig. S1B). The same general domain organization is conserved in all R-subunits. Each R-subunit has an N-terminal dimerization/docking (D/D) domain that is connected by a flexible linker to 2 tandem cyclic nucleotide binding (CNB) domains (CNB-A and CNB-B) (Fig. 1A). Embedded within the flexible linker is an inhibitory sequence that binds to the C-subunit active site, thereby preventing substrate binding (1, 6). The D/D domain, a 4-helix bundle, is essential for dimerization and binding to A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) (7, 8). Deletion of the D/D domain creates a monomeric R-subunit, which cannot be properly localized in cells and has also lost most of the allosteric features of cAMP activation (9–12).
The CNB domains, which are conserved from bacteria to humans and translate the second messenger signal into a biological response, consists of α- and β-subdomains. One of the 3 helical motifs, the phosphate-binding cassette (PBC) and the signature motif for cAMP binding, is embedded within the β-barrel subdomain. The α-subdomain has 2 additional helical motifs, the N-terminal N3A-motif (αN-helix, 310-loop, and αA-helix) and the C-terminal αB/C-helix, that flank the ends of the β-barrel but are spatially contiguous with each other and with the PBC. The helical subdomains undergo significant and concerted conformational changes in response to cAMP (12–14). Although in the absence of cAMP the CNB domains dock onto the C-lobe of the C-subunit in every R:C complex, the structures of these R:C complexes are very similar and cannot explain the functional nonredundancy of the isoforms (12, 15, 16). The differences, as well as the full allosteric potential, only become clear with the R2C2 holoenzymes (1). Here we are adding the structure of the full-length RIα holoenzyme to the previously solved structures of the full-length RIIβ and RIβ holoenzymes (17, 18). How do the quaternary structures drive isoform-specific allosteric activation by cAMP, and why are these allosteric networks so different for RIα and RIIβ holoenzymes? Elucidating these differences has been a major challenge.
Different isoforms of full-length PKA holoenzymes not only have distinct allostery, but are also expressed and localized differently in cells. RIα and RIIα are ubiquitously expressed, while RIβ and RIIβ are more tissue-specific. Another important difference is the inhibitory sequence that is embedded in the flexible linker. The phosphorylation site (P-site) in this segment in the RI-subunits, like the cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor, is either Gly or Ala so both proteins function as pseudosubstrates. In contrast, RII-subunits have a Ser at the P-site in the inhibitory sequence, and this site is autophosphorylated in the holoenzyme (1, 19, 20). The R-subunits and their corresponding holoenzymes also differ in their biochemical properties, localization, and cAMP sensitivities (3, 10, 21). The phenotypes that result from depletion of each R-subunit are also quite distinct (22). In mouse models, depletion of RIβ causes memory defects (23), while RIIβ knockout mice have locomotor disorders and a lean phenotype (24, 25). RIα is the only R-subunit that shows embryonic lethality in mouse knockout models (26, 27). Moreover, most PKA-related disease mutations are in RIα. Carney Complex (CNC) disease leads to an increase in PKA activity due to enhanced sensitivity to cAMP (28, 29), while acrodysostosis (ACRDYS) patients show hormone resistance and lower PKA activity (30, 31). These combined data suggest that RIα can be considered as the “master regulator” of PKA signaling; in the absence of sufficient and functionally intact RIα, the activity of the PKA C-subunit cannot be properly regulated.
Here we captured in crystal structure 2 conformational states of the PKA RIα holoenzyme. These 2 conformations, distinguished by the presence and absence of ATP, show how ATP plays an essential role in allosteric regulation. Because the inhibitor sequence in the RIα is a pseudosubstrate, ATP can be seen as a high-affinity orthosteric inhibitor to facilitate the formation of R:C complex instead of a substrate for phosphate transfer, while cAMP serves as a competing allosteric activator for the RIα holoenzyme. Our structure, together with biochemical studies, show how the opposing competition of 2 nucleotides defines a unique allosteric regulatory mechanism in the RIα holoenzyme. In contrast, for the RII-holoenzymes ATP is a substrate that actually facilitates cAMP activation/dissociation. The quaternary structures, mechanism for cAMP-mediated activation, and the role of ATP are thus quite distinct for RIα and RIIβ. Molecular dynamic (MD) simulations and biochemical assays not only shed further light on the extended allosteric network that leads to activation of the RIα holoenzyme, but also highlight differences with the RIIβ holoenzyme. The N3A–N3A′ dimerization motif in the CNB-A domain is a unique feature of RI holoenzymes and serves as an allosteric hub for communication between the 4 CNB domains (CNB-A, CNB-B, CNB-A′, and CNB-B′). Glu200RIα, a conserved cAMP binding residue in the PBC, also interacts directly with the N3A–N3A′ motif in RIα holoenzymes but not in RIIβ holoenzymes, and this contributes directly to the allosteric mechanism for activation of RIα. Given that the R2C2 holoenzymes represent the relevant physiological complex in vivo, these holoenzyme states provide fundamental insights into isoform-specific cAMP signaling in cells and reveal the potential role of PKA as an energy sensor.
Results
Two Distinct States Are Captured in Crystals of the RIα Holoenzyme.
Crystal of the RIα holoenzyme solved at 3.55 Å captured 2 distinct conformations of holoenzyme in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1 B and C and SI Appendix, Fig. S2). Each is composed of 1 RIα dimer and 2 C-subunits. Although in both holoenzymes the full-length proteins are present in the crystal, based on SDS/PAGE (SI Appendix, Fig. S2D), the D/D domain and part of the N-linker are not visible in the electron density map, most likely because the N-linker is flexible. Both holoenzyme conformations have the same R:C interface in each protomer that was also defined previously in the crystal structure of (Δ1–91)RIα(Arg333RIαLys):C, which represents an R:C complex with a truncated RIα (12). In the full-length holoenzyme structures described here, additional RC:R′C′ interfaces are revealed. Although both molecules are formed by 2 RIα:C complexes with the 2 CNB domains (CNB-A/CNB-B and CNB-A′/CNB-B′) facing each other in an antiparallel orientation, the 2 conformations nevertheless have distinct differences in this interface between the 2 R-subunits. In molecule A, the N3A-motif/N3A′-motif interaction (N3A–N3A′) 4-helix bundle nucleates the dimer interface, and this is the prominent feature that we observed earlier in the RIα dimer (Fig. 1B and SI Appendix, Fig. S3A). The other conformation, molecule B, has a smaller interface, which is mediated by the interactions of αN-helix/αN′-helix (αN–αN′) (Fig. 1C and SI Appendix, Fig. S3B).
Role of ATP/Mg2+ on Holoenzyme Conformation.
The C-subunits in both holoenzyme states all show “closed” conformations, which represent a canonical active-like state. In molecule A, each C-subunit is bound to ATP/Mg2+ and the inhibitory sequence of RIα (SI Appendix, Fig. S3C), while ATP and Mg2+ are missing in molecule B (SI Appendix, Fig. S3D). The hydrodynamic radius (RH), radius of gyration (Rg), and maximum dimension (Dmax) of both holoenzyme states were determined using size-exclusion chromatography and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) (32). To mimic molecule A in solution, the holoenzyme was formed in the presence of excess ATP (“ATP-bound” state) and Mg2+ (SI Appendix, Fig. S4A). When a holoenzyme was formed in the absence of ATP under the same conditions, a reduction in the relative amount of holoenzyme (“ATP-off” state) was observed, confirming that ATP plays a key role in formation of the RIα2C2 complex (Fig. 2A and SI Appendix, Fig. S4B). Based on these 2 chromatography profiles, 2 distinct holoenzyme complexes were observed. Molecule A in the presence of ATP eluted first, suggesting that the conformation of molecule B is more compact. This is consistent with an altered hydrodynamic radius and a more compact structure for molecule B (RH = 48.15 Å), in contrast to the ATP-bound molecule A (RH = 55.39 Å) (SI Appendix, Fig. S5). Molecules A and B have Perrin-shape factors of 1.53 and 1.33, respectively, indicating that both have “oblate” shapes, which is consistent with the crystal structures. The calculated dimensions of molecule A are 145.1 × 89.5 × 65.2 Å, versus 140.1 × 80.3 × 71.1 Å for molecule B (Fig. 1 B and C).
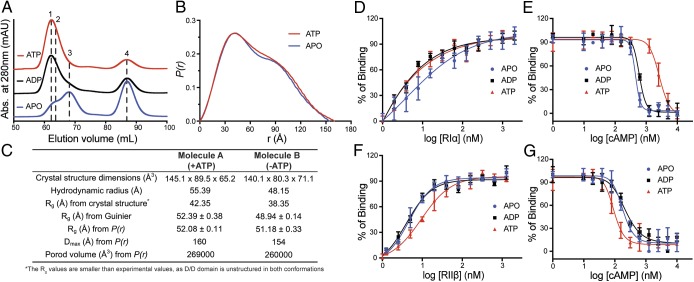
Fig. 2.
The differences of biochemical and biophysical properties between 2 structures. (A) Gel-filtration profiles of RIα2C2 holoenzyme formation in apo (blue), ADP (black), or ATP (red) conditions. Peak 1: holoenzyme molecule A; peak 2: holoenzyme molecule B; peak 3: solely RIα2; and peak 4: solely C-subunit. (B) SAXS P(r) function of RIα 2C2 holoenzyme in apo (blue) or ATP (red) conditions. (C) The structure dimensions, hydrodynamics radius, Rg, Dmax Porod volume comparison between 2 structures. (D) Formation of RIα holoenzyme by titrating C-subunit with RIα in apo (blue), ADP (black), or ATP (red) conditions. (E) Activation of RIα holoenzyme by cAMP in apo (blue), ADP (black), or ATP (red) conditions. (F) Formation of RIIβ holoenzyme by titrating C-subunit with RIIβ in apo (blue), ADP (black), or ATP (red) conditions. (G) Activation of RIIβ holoenzyme by cAMP in apo (blue), ADP (black), or ATP (red) conditions. Data points are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments), and the experiment was repeated 3 times independently with similar result.
Similar results were observed with SAXS where RIα holoenzyme scattering profiles were measured in the absence and presence of ATP (Fig. 2B and SI Appendix, Fig. S6). Holoenzyme in the presence of ATP is slightly larger (Rg = 52.08 Å, Dmax = 160 Å, and Porod volume = 269,000 Å3), based on pair-distance distribution functions P(r), than the apo holoenzyme (Rg = 51.18 Å, Dmax = 154 Å, Porod volume = 260,000 Å3). Similar Rg values can also be obtained from Guinier analysis (Rg = 52.39 Å and Rg = 48.94 Å for molecule A and molecule B, respectively). The SAXS analyses are consistent with the hydrodynamic radius and theoretical Rg calculations based on the crystal structures. Both crystal and solution state structures thus confirm that ATP induces a small but significant conformational change in the RIα holoenzyme (Fig. 2C), and that ATP specifically promotes a more extended conformation. The importance of ATP and Mg2+ ions has been discussed in prior studies. The ATP dissociation rate, for example, is in the same time range as R–C dissociation (9, 33), indicating that these 2 processes are probably linked. In the absence of ATP, the R–C dissociation rate is significantly reduced. However, the detailed mechanism and the exact role of ATP for RIα holoenzyme homeostasis is not yet clear.
ATP Regulation of the RIα Holoenzyme.
To further understand the allosteric features of how ATP regulates the conformational state and cAMP activation of the RIα holoenzyme, we used a fluorescence polarization (FP) assay. By titrating a fluorophore-labeled C-subunit with RIα, the ratio of holoenzyme formation can be determined from the FP changes. R–C association was measured under apo conditions or in the presence of ADP or ATP. RIα showed strong binding with the C-subunit in the presence of ADP or ATP (EC50 = 4.6 or 5.0 nM), in contrast to holoenzyme formed in the absence of nucleotide (EC50 = 12.5 nM) (Fig. 2D and SI Appendix, Fig. S4D). Although this assay is sufficient to show that interactions of the subunits are reduced in the absence of nucleotide, due to the limits of detection (5 nM), this assay cannot discriminate between the actual dissociation constants (Kd) in the presence of ADP vs. ATP, which, based on surface plasmon resonance measurements, are predicted to be subnanomolar (9). Both our results and previous studies indicate that ATP influences RIα holoenzyme formation (9)
Nucleotide also plays a significant role in cAMP-mediated holoenzyme dissociation. Starting from 100% inactive holoenzyme, cAMP was titrated in under apo conditions or in the presence of ADP or ATP. RIα holoenzyme is less sensitive to cAMP in the presence of ATP; the holoenzyme is easier to dissociate by the trigger of cAMP when there is no ATP or ADP present (Fig. 2E and SI Appendix, Fig. S4D). Interestingly, even though the R- and C-subunit in the holoenzyme show strong affinity in the presence of ADP, the RIα holoenzyme is more easily activated by cAMP in the presence of ADP. It is ATP and an excess of Mg2+ that specifically facilitates RIα holoenzyme formation and causes it to have a higher threshold for cAMP activation. This also supports earlier Biacore measurements that show a significant difference between ATP and ADP as well as the importance of the second metal ion (34).
Our functional studies indicate that molecule B (ATP-off state) represents a conformation that is easier to activate with cAMP while molecule A (ATP-bound state) is more resistant to activation by cAMP. Thus, both nucleotides (ATP and cAMP) contribute in opposing ways to regulation of cAMP-mediated dissociation of the RIα holoenzyme.
ATP Regulation of PKA Holoenzymes Is Isoform-Specific.
ATP plays a different role in regulation of the RIIβ holoenzyme. In addition to being an inhibitor of the C-subunit activity, RIIβ is also a single-turnover substrate since in the RIIβ holoenzyme the P-site in the inhibitory sequence is phosphorylated when ATP is present (19). Using the FP assay, RIIβ displayed weaker affinity for the C-subunit in the presence of ATP (EC50 = 10 nM), compared with the apo and ADP conditions (EC50 ∼ 5 nM) (Fig. 2F and SI Appendix, Fig. S4D). This is opposite to the RIα holoenzyme and indicates that affinity is modulated by phosphorylation of the substrate site. Considering the FP assay’s detection limit, the difference in Kd in the absence of ATP is likely to be at least an order-of-magnitude (0.6 nM vs. 5 nM) for the full-length protein (21). In cAMP activation assays, the RIIβ holoenzyme is less sensitive to cAMP in the presence of ADP or apo conditions (EC50 ∼ 200 nM), while dissociation is more readily triggered by cAMP in the presence of ATP (EC50 = 94 nM) (Fig. 2G and SI Appendix, Fig. S4D). ATP thus primes the RIIβ holoenzyme for cAMP-mediated dissociation by phosphorylation of the substrate site in contrast to the stabilizing effects of ATP on the RIα holoenzyme.
In contrast to RIα holoenzyme, size-exclusion chromatography showed that all RIIβ holoenzymes eluted at the same elution volume; there are no ATP-dependent conformational changes and ATP is not required to form a stable RIIβ holoenzyme complex (SI Appendix, Fig. S4C). Previous crystal structures also showed similar results; apo RIIβ2C2 (PDB ID code 3TNP) and ADP-bound/phosphorylated RIIβ2C2 (PDB ID code 3TNQ) have essentially the same quaternary structures (17). ATP thus plays a critical role in both RIα and RIIβ, yet the effects are different.
The 2 Conformations of the RIα Holoenzyme Show Different Subunit Dynamics.
C-subunit.
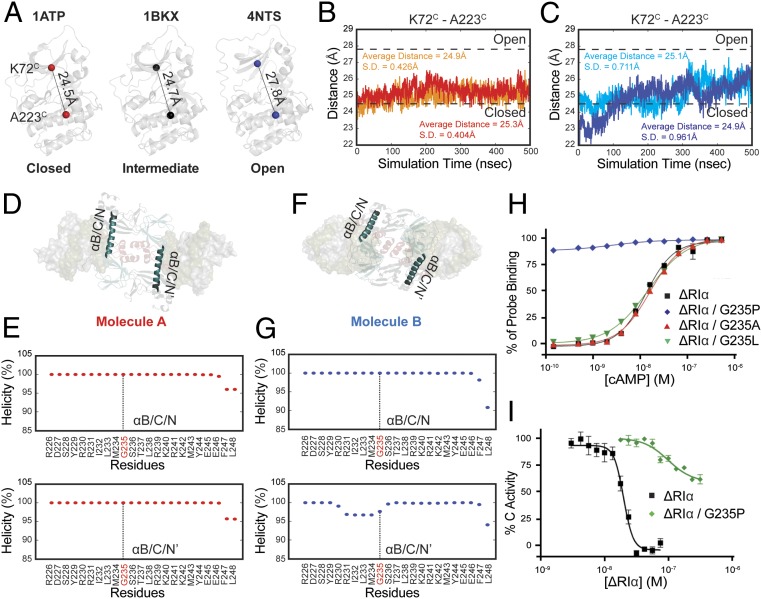
To further investigate the dynamic differences between the 2 RIα holoenzyme conformations, 500-ns MD simulations were carried out (SI Appendix, Fig. S7 A and B). The C-subunits in each conformation have different propensities to stay in open or closed states. Kinases’ open and closed conformations represent their substrate recognition and release states. Here, the closed, intermediate, and open conformations are defined by the distance of the α-carbon from Lys72C on the β3-strand to Ala223C on the αF-helix (Fig. 3A) (35–37). The Lys72C-Ala223C distance of each C-subunit in the 2 holoenzymes were determined throughout the trajectories. In molecule A, which has the N3A–N3A′ interface, both C-subunits remained stable with low fluctuation (SD = 0.404 and 0.426 Å) (Fig. 3B). In contrast, the distance of Lys72C-Ala223C on each C-subunit of molecule B showed significantly greater fluctuations (SD = 0.961 and 0.711 Å), suggesting that the C-subunits are more dynamic and that the open state is more accessible (Fig. 3C). The higher flexibility of C-subunits in molecule B further validates the experimentally observed weaker binding with the inhibitory site of the R-subunit in the absence of ATP.
Fig. 3.
MD simulations of 2 RIα holoenzyme molecules. (A) The distance from Lys72C to Ala223C in closed (PDB ID code 1ATP), intermediate (PDB ID code 1BKX), and open (PDB ID code 4NTS) conformations of C-subunit. (B) Distance fluctuations of Lys72C to Ala223C in C-subunit (red) and C′-subunit (orange) of molecule A holoenzyme. (C) Distance fluctuations of Lys72C to Ala223C in C-subunit (blue) and C′-subunit (cyan) of molecule B holoenzyme. (D) The representation of αB/C/N-helix and αB/C/N′-helix locations in molecule A. (E) The helical propensity of αB/C/N-helix (Upper) and αB/C/N′-helix (Lower) in molecule A. (F) The representation of αB/C/N-helix and αB/C/N′-helix locations in molecule B. (G) The helical propensity of αB/C/N-helix (Upper) and αB/C/N′-helix (Lower) in molecule B. (H) cAMP activation. (1–91Δ)RIα (black square), (1–91Δ)RIα G235P (blue diamond), (1–91Δ)RIα G235A (red triangle), (1–91Δ)RIα G235L (green inverted triangle). (I) Kinase activity inhibition. (1–91Δ)RIα (black square), (1–91Δ)RIα G235P (green diamond). Data points are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments), and the experiment was repeated 3 times independently with similar results.
R-subunit.
R-subunit dynamics are important for holoenzyme activation, as highlighted by the extended αB/C/N-helix in the holoenzyme in contrast to the kinked helices in the cAMP-bound R-subunits. Several studies have characterized the dynamic features of the αB/C/N-helix, including a “flipped-back” model for PKA activation (38–40). The thermodynamic properties of the 2 CNB domains are critically intertwined and sensitive to ligand binding as well as mutation of the neighbor (41). Both mutagenesis and simulations have shown that the helical propensity of the αB/C/N-helix correlates with R–C dissociation in the (Δ1–91)RIα:C complex (42). The “flip-back” model of the R–C complex, which has been observed in long MD simulations, also highlights the dynamic properties of the αB/C/N-helix and the CNB domains for PKA activation (43).
The R-subunits in each molecule also show distinct dynamic features. Although the extended αB/C/N-helix is strengthened by the RC:R′C′ interface in both states of our structure, and we did not observe a flip-back conformation in the simulation, different αB/C/N-helix dynamics were observed in the 2 conformations. In molecule A, the R-subunits are less dynamic, and their αB/C/N-helices remain 100% helical throughout the simulation, which likely keeps the holoenzyme in an inactive locked-state (Fig. 3 D and E). However, 1 of the αB/C/N-helices in the molecule B simulations shows partial unwinding indicating the αB/C/N-helix is more flexible (Fig. 3 F and G). For this reason, we think that molecule B can be considered as an intermediate state, which can be activated more readily by cAMP.
The holoenzyme interface in molecule B not only shows a lower proportion of helicity of the αB/C/N-helix, but also contributes to the CNB domain dynamics. To examine the dynamic features of the CNB domains, differences in the interchain CNB domain positions were represented by measuring the distance from the α-carbon of Arg209RIα to the neighboring Arg333RIα’ in the other protomer (R209RIα-R333RIα′/R333RIα-R209RIα′). Residues Arg209RIα and Arg333RIα have been identified as crucial amino acids for cAMP binding, and we use them here to represent the core of the CNB-A and CNB-B domains, respectively (11). In molecule A, the distance between the 2 domains remains stable throughout the simulation with an SD = 3.22 and 2.43 Å (SI Appendix, Fig. S7 C and D). The distance fluctuation in molecule B (SD = 4.61 and 3.97 Å) is larger than in molecule A, indicating the positions of CNB domains are more dynamic in molecule B (SI Appendix, Fig. S7 E and F). Taking these data together, we find that the conformation specific dynamic and biochemical properties support the conclusion that molecule A is in a fully inhibited more locked-state, while molecule B can be considered to be an intermediate structure that can be activated more readily by cAMP.
Gly235 in RIα Serves as Pivot Point for PKA Activation.
A main feature that distinguishes cAMP bound R-subunits (B-form) from the holoenzyme (H-form) is the αB/C/N-helix. In the holoenzyme, the αB- and αC-helices from CNB-A form a long contiguous helix with the αN-helix from CNB-B, whereas in the cAMP-bound B-form, the αB/C/N-helix is split into 3 separated segments. Gly235RIα lies at the junction between the αB- and αC-helix and serves as the pivot point for the transition from the B- to H-form (13, 44). The strong helix propensity of the region corresponding to the αC/N-helix is also a unique feature of RIα. To further understand the importance of the αB/C/N-helix for PKA activation, Gly235RIα was mutated to Ala/Leu/Pro.
While the effects of the Leu and Ala mutations were negligible, the inhibitory effect of RIα was abolished by introducing the helix-disrupting proline mutation (Gly235RIαPro) (Fig. 3 H and I and SI Appendix, Fig. S8 A and B). Even though this mutant can still form complex with C-subunit (SI Appendix, Fig. S8C), it presumably cannot form a contiguous helix and catalytic activity is no longer inhibited. These results suggest that an extended αB/C/N-helix is critical for inhibition of the catalytic activity. Once the extended αB/C/N-helix is disrupted, the holoenzyme is much easier to activate while the inhibitory potential is reduced (Fig. 3 H and I).
The N3A-N3A′ Motif Nucleates the R:C/R′:C′ Interface in Molecule A.
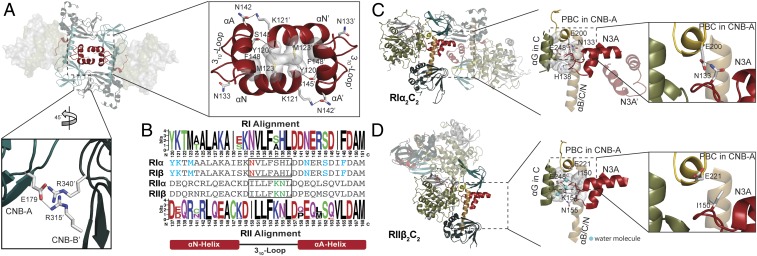
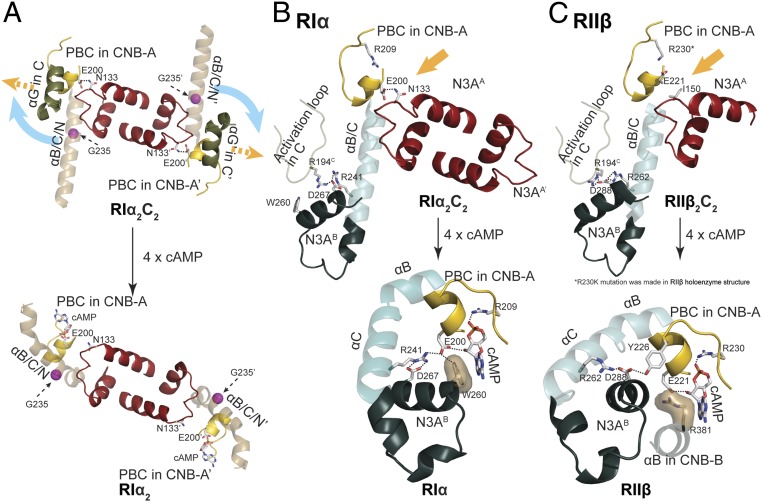
Molecule A features an N3A–N3A′ interface similar to what was described earlier in the RIα homodimer (13), and this was also seen in a recent holoenzyme structure with a cancer-driving fusion protein of the C-subunit (45). Hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding interactions both contribute to the N3A–N3A′ interface. The N3A-motif in each RIα protomer makes symmetric contacts with the N3A-motif in the other protomer, forming a compact 4-helix bundle. In molecule A, the antiparallel alignment of Met123RIα, Tyr120RIα, and Phe148RIα on each protomer creates a hydrophobic core, while the interactions of Lys121RIα to Asn142RIα′, and Ser145RIα to the main chain of Tyr120RIα′ form the hydrogen bond network that holds the 2 N3A motifs together (Fig. 4A). The smaller interface between CNB-A and CNB-B′ in molecule A lies outside of the N3A–N3A′ interface where Glu179RIα in CNB-A forms hydrogen bonds with Arg315RIα and Arg340RIα in CNB-B′ from the other protomer (Fig. 4A).
Fig. 4.
Holoenzyme interface in RIα2C2 structure. (A) N3A–N3A′ and CNB-A/CNB-B′ interfaces in molecule A. (B) Sequence alignment of N3A motifs in different R-isoforms shows the essential residues for forming N3A–N3A′ interface (blue), RI-specific Glu200RIα–Asn133RIα interaction (red), and RII-specific 310-loop, αB/C/N-helix, and C-subunit interface (green). Upper alignment: consensus sequence alignment of RI. Lower alignment: consensus sequence alignment of RII. (C) The 310-loop, αB/C/N-helix, and C-subunit interface in RIα holoenzyme. Glu200RIα forms hydrogen bond with Asn133RIα. (D) The 310-loop, αB/C/N-helix, and C-subunit interface in RIIβ holoenzyme. Asn133RIIβ is solvent-exposed, and not forming a hydrogen bond with Glu221RIIβ. Water molecules are shown as cyan balls.
Molecule B Shows a Distinct αN–αN′ Interface.
Molecule B has a distinct αN–αN′ interface. Compared with molecule A, the interactions are solely between the αN- and αN′-helix (SI Appendix, Fig. S8D); the αA-helix is not involved. In molecule B, Lys121 forms a hydrogen bond with Thr122′ on the other protomer. Moreover, the pairwise Tyr120/Tyr120′ hydrophobic interaction is broken and instead forms a smaller hydrophobic core together with Ala124RIα and Ala125RIα between the αN–αN′ interface. Lys128RIα and Lys121RIα form hydrogen bonds with Tyr120RIα and Thr122RIα/Tyr176RIα on the other protomer, respectively.
N3A Motifs Display Isoform-Specific Features.
Sequence differences.
Although all 4 R-subunit isoforms share the same domain organizations, their quaternary structures are distinct (17), and sequence alignment shows that the critical residues for forming the N3A–N3A′ interfaces are RI-specific (Fig. 4B). The sequence of the N3A-motif in RI was analyzed across more than 130 different species, and residues involved in the N3A–N3A′ interface—such as Tyr120RIα, Met123RIα, and Phe148RIα for hydrophobic interactions and Lys121RIα, Asn142RIα, and Ser145RIα for the hydrogen bonding/electrostatic network—are conserved across nearly all species (Fig. 4B). Interestingly, from our sampling the conserved sequences in the N3A-motif of RI only appear for the first time in coelomates (SI Appendix, Fig. S8E and Dataset S1). Other species, such as Caenorhabditis elegans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, do not have a conserved sequence in the αN- or αA-helix, but they can be phosphorylated on their inhibitor site (P-site). Based on our sequence analysis and the structure they are more RI-like; thus, they appear to be somewhat of a hybrid (46). Since N3A–N3A′ is the main interface in RIα, it is possible that higher species need more complex systems for allosteric regulation. The N3A-motif in RII-subunits also share similar sequences across most of the species, but they are different from RI-subunits, and they lack the residues necessary for forming the N3A–N3A′ interface. This can explain why the RIIβ holoenzyme has a different quaternary structure where the N3A-motifs are solvent-exposed (17), potentially providing a docking site for an as yet unknown protein partner. A smaller CNB-A/CNB-B′ interaction that lies outside of the N3A–N3A′ interface is also isoform-specific (SI Appendix, Fig. S8F). The highly conserved N3A motif sequences within but not between type I and type II R-subunits demonstrates another isoform-specific feature of the PKA holoenzyme structures.
310-loop.
In addition to residues in the αN- and αA-helices, the sequences in the 310-loop that connects the αA-helix to the αN-helix are also highly conserved across species. However, this loop that also contributes to the R:C interface is different in RI and RII. In the RIα holoenzyme, the hydrophobic residues in the 310-loop, Val134RIα, Leu135RIα, Phe136RIα, and His138RIα, interact with other hydrophobic residues from the αB/C/N-helix and the αG-helix in the C-subunit forming a ternary motif interface (Fig. 4C and SI Appendix, Fig. S9 A and B) (14). Even though hydrophobic interactions can also be observed in the RIIβ holoenzyme (Fig. 4D), Lys154RIIβ and Asn155RIIβ in the 310-loop of RIIβ form water-mediated hydrogen bonds between the ternary motif interface. This solvent-accessible interface would be weaker than the strongly hydrophobic interactions that dominate the RIα holoenzyme.
Role of Glu200.
In the RIα holoenzyme, Asn133RIα in the αN-helix forms a hydrogen bond with Glu200RIα in the PBC of CNB-A. Glu200RIα is essential for cAMP binding (44, 47) and is conserved in all PKA R-subunits, while Asn133RIα is only conserved in RI-subunits. The same hydrogen bond is found in both the RIβ holoenzyme and (Δ1–91)RIα:C structures (SI Appendix, Fig. S9C). However, there is no hydrogen bond between the PBC of CNB-A and the 310-loop in RIIβ (Fig. 4D). The equivalent positions of Asn133RIα and Glu200RIα in RIIβ are Ile150RIIβ and Glu221RIIβ, respectively. While Glu221RIIβ is still important for binding to cAMP, it cannot hydrogen bond to Ile150RIIβ, and instead is solvent exposed in the holoenzyme; there is no direct link between the 310-loop and the PBC. Ile150RIIβ, Glu221RIIβ, Lys154RIIβ, and Asn155RIIβ are conserved in all RII- subunits. Glu221RIIβ is also solvent-exposed in the (Δ1–89)RIIα:C structure (SI Appendix, Fig. S9C). These sequence differences likely explain why cAMP binding to the RIα holoenzyme is strictly ordered with cAMP binding first to CNB-B, which is designated as the “gatekeeper” for cAMP access. In contrast, cAMP can bind to the CNB-A domain readily in the RIIβ holoenzyme independent of cAMP binding to the CNB-B domain although allostery is severely compromised (21, 48). The sequence differences between isoforms thus not only help to explain the distinct quaternary structures, but also highlight different potential mechanisms for allosteric cross-talk between the CNB-B and CNB-A domains in a single protomer as well as for CNB domain cross-talk between the 2 protomers.
N3A–N3A′ Is a Central Hub for Allosteric Regulation of the RI Holoenzyme.
The N3A–N3A′ interface forms a cross-talk network and serves as a central hub for mediating allosteric communication in both the RIα holoenzyme and RIα dimer. The N3A-motif interacts with several other motifs and links all them together. The residues on the αN-helix and αA-helix are essential to form the N3A–N3A′ interface and bring the 2 protomers together. The 310-loop is also the crucial motif for interacting with both the αB/C/N-helix and the C-subunit (12). Finally, and perhaps most importantly, in RIα the 310-loop also anchors directly to the PBC in the CNB-A domain and thus is a sensor for cAMP binding (Fig. 5A). Our structures reveal that the other protomer can also be influenced through interactions of the N3A–N3A′ motifs. The multidomain cross-talk network nucleated by the N3A–N3A′ interface is thus a central hub that provides a mechanistic model for the tightly regulated PKA RIα holoenzyme system.
Fig. 5.
PKA holoenzyme activation. (A) The N3A–N3A′ motifs serve as central hub for RIα activation. (Upper) RIα2C2 holoenzyme; (Lower) RIα dimer. (B) Allosteric nodes in RIα holoenzyme (Upper) and RIα (Lower). (C) Allosteric nodes in RIIβ holoenzyme (Upper) and RIIβ (Lower).
Discussion
Our crystal structure of the RIα holoenzyme in the presence and absence of ATP reveal an ATP-dependent allosteric mechanism that is isoform-specific (49). The role of ATP as an orthosteric inhibitor that controls the conformation of the RIα holoenzyme is supported by biochemical and SAXS data. ATP is an essential cofactor for all kinases serving as a substrate that donates its γ-phosphate either to water or to a protein substrate. However, because both RIα and the protein kinase inhibitor function as pseudosubstrates due to the absence of an acceptor residue at the P-site, ATP plays a different role; in this case it can be thought of as an orthosteric inhibitor. While pseudokinases have been highlighted recently, less attention has been devoted to pseudosubstrates. In the RIα holoenzyme there is a competition between 2 nucleotides, cAMP and ATP, that allosterically control the activity of the C-subunits that are tethered to the RIα dimer.
Our holoenzyme structure also highlights the unique importance of the N3A-mediated dimer motif in CNB-A. The 4-helix bundle created by the N3A–N3A′ node nucleates a major interface between the 2 R:C heterodimers, and this serves as a finely regulated central hub not only for the RIα dimer but also for the RIα holoenzyme (13). While RIα interacts with the C-subunit to form a high-affinity RIα:C complex, this RIα:C complex does not allow us to appreciate the full extent of allosteric activation that is embedded in the tetrameric holoenzyme. The N3A–N3A′ interaction introduces a direct R:C/R’:C′ pathway that allows the CNB-A domain from 1 protomer to communicate not only with its own CNB-B domain, but also directly with the CNB-B′ domain. This helps to explain why the full allosteric potential for cAMP-mediated activation with a high cooperativity (Hill coefficient 1.75) is achieved only in the full-length holoenzyme (13). Our further dissection of this allosteric node also shows how Glu200RIα, a residue that is essential for binding to cAMP in the PBC, also contributes directly to the N3A–N3A′ cross-talk in RIα but not in RIIβ, and this is another key difference between the 2 holoenzymes. The allosteric implications of this node are discussed below, followed by the differences between the RIα and RIIβ holoenzymes.
The idea that N3A–N3A′ serves as central hub and can pass activation signals to different domains now reveals new levels of domain cross-talk in the RIα holoenzyme. This cross-talk network of 4 CNB domains underlines how finely regulated the RIα system is, and helps to explain the high cAMP activation cooperativity of RIα. Two interacting residues, Arg241RI and Asp267RI, have been shown previously to be important for allosteric activation of PKA. Arg241RIα in the αB-helix in CNB-A interacts directly with Asp267RIα at the end of the αAB-helix in CNB-B (Fig. 5B) (50), and this node (Arg241RIα-Asp267RIα) that links CNB-A to CNB-B is universally conserved in all holoenzymes and in all cAMP-bound conformations (Fig. 5 B and C). The exception is the ACRDYS mutant of RIα holoenzyme, where residues 366 to 379 are deleted when Asp267RIα is ordered differently (50). The 2 key residues for binding to cAMP in the PBC are Arg209RIα and Glu200RIα in CNB-A, and these are also conserved in all of the CNB domains. Although each bound cAMP also has a hydrophobic capping residue, the origin of the capping residue is not only different for CNB-A and CNB-B but is also different in RI- and RII-subunits (51). For cAMP bound to the RIα CNB-A, the capping residue is Trp260RIα, which also lies in the αAB-helix. Another residue in the αAB-helix is Glu261RIα, which is anchored to Arg366RIα in the αC-helix of CNB-B in the holoenzyme. These electrostatic interactions are conserved in all PKA holoenzymes and in the R:C complexes (Fig. 5 B and C). If we now consider the N3A–N3A′ node, we see an additional interaction that is RIα-specific. Asn133RIα in the 310-loop of the N3A motif in RIα interacts with Glu200RIα in the PBC of CNB-A′, and this link is missing in the RIIβ holoenzyme where both Arg230RIIβ and Glu221RIIβ are solvent-exposed (Fig. 5C). Each N3A motif in RIα is thus linked directly to its own PBC as well as to the N3A′ motif. What are the consequences for allosteric activation and how do the CNC disease mutations emphasize the importance of these contacts?
Allosteric Regulation.
Although Glu200RIα/Glu221RIIβ both contribute directly to cAMP binding in CNB-A, they play different allosteric roles in the cAMP-bound B-Form in RIα and RIIβ (Fig. 5 B and C). In RIα, Glu200RIα nucleates an extended allosteric node that involves Arg241RIα, Asp267RIα, and cAMP, and this node is stabilized by the capping residue Trp260RIα. In the B-form of RIIβ, Glu221RIIβ interacts only with cAMP, while the capping residue (Arg262RIIβ), which in this case is in the αB-helix of CNB-B and still anchored to Asp288RIIβ, now interacts with Tyr226RIIβ in the PBC of CNB-A. This shows how specific residues can multitask and also highlights how a few amino acids can completely change allosteric signaling and domain interactions.
Disease Mutations.
Disease mutations associated with CNC (Arg144RIαSer and Ser145RIαGly) as well as critical residues in the N3A–N3A′ interface (Lys121RIαAla and Tyr120RIαAla) further highlight the physiological and allosteric importance of this node, which is unique to RI holoenzymes. Tyr120RIα and Lys121RIα anchor the N terminus of the αN-helix to the C terminus of the αA′-helix, and mutation of either residues almost completely abolishes all cooperativity (Hill coefficient = 1 to 1.1 vs. 1.75 in wild-type) (13). CNC mutations in the αA-helix (Arg144RIαSer and Ser145RIαGly) that flank the hydrophobic interface between the αA- and αA′-helix reduce the Hill coefficient to 1.45. These will likely weaken the hydrophobic interface while mutation of Lys121RIα will likely break the dimer interface. Based on SAXS, these mutations also affect the shape of the RIα dimers; both types of mutation create a more extended conformation that resembles the RII dimer (13). Tyr120RIαAla, which abolishes cooperativity, is the most extended while the Ser145RIαGly dimer is intermediate. We predict that these mutations will also likely influence the compact vs. extended conformation of the RIα holoenzyme as they do for the RIα dimer.
Our holoenzymes show how an additional level of cross-talk can occur through CNB-B and CNB-A′, and this is highly significant because previous studies established that the first cAMP that binds to the RIα holoenzyme binds to the CNB-B domain (11, 48). With our structure we can see how binding to the CNB-B domain cannot only communicate a signal to its own CNB-A domain through the αB/C/N-helix, but will also give an immediate signal to the opposite CNB-A′ domain. Our structure of the apo holoenzyme shows furthermore how the removal of ATP dramatically changes the dynamic portrait of the holoenzyme, poising it for activation/dissociation. Weakening of the specific CNB-B:CNB-A′ interface will likely be the first step in the signaling process following binding of cAMP to CNB-B, which will essentially release Glu200RIα from the N3A–N3A′ interface. Does this lead to activation of the C′-subunit, or at least release of the inhibitor site that blocks substrate binding to the C′-subunit, by a mechanism that will not require dissociation of the holoenzyme? This is a future challenge. If the holoenzyme is tethered in close proximity to the tail of a receptor or channel or transporter that contains the site of PKA phosphorylation, then all that would be required is that the peptide harboring the phosphorylation site has access to the active-site cleft of 1 C-subunit. While the first step following cAMP binding would be transmitted to CNB-A′, subsequent steps leading to the actual dissociation of the R- and C-subunits would involve signaling to the αB/C/N-helix, which would need to bend. The extended αB/C/N-helix is well protected in this holoenzyme conformation. This model for communication between CNB-B and CNB-A′ would also provide an explanation for why the point mutations associated with ACRDYS and CNC diseases are dominant. It also suggests that there is an inherent asymmetry in the signaling process.
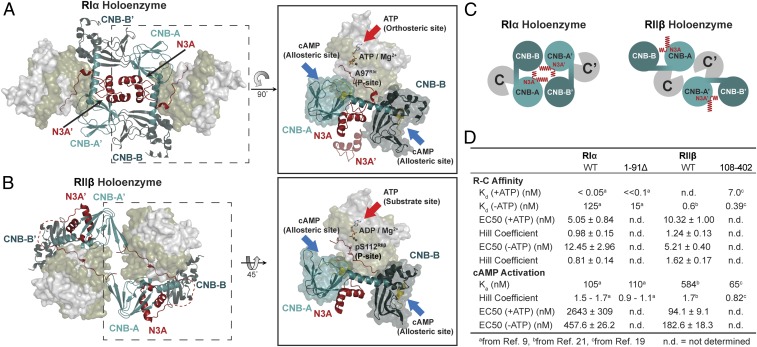
The RIα and RIIβ holoenzymes have distinct quaternary structures (Fig. 6 A and B and Movies S1 and S2). In both of our RIα holoenzymes and the RIα dimer, the interacting N3A–N3A′ motifs are the dominant feature of the protein interface (Fig. 6C). In contrast, in RIIβ holoenzymes, the N3A domains are exposed to solvent and do not contribute to the major interface between RC and R′C′ (Fig. 6C). Instead in the RIIβ holoenzyme structure, the major holoenzyme interface is based on the interaction of the β4-β5 loop in the CNB-A domain of RIIβ with the adjacent C′-subunit (17).
Fig. 6.
The diverse quaternary structure and allostery of RIα and RIIβ holoenzyme. (A) RIα holoenzyme structure. ATP serves as an orthosteric inhibitor, and cAMP docks to CNB domains as an allosteric activator in RIα. CNB-A domain is in teal, CNB-B domain is in deep teal, N3A motif is in red, PBC motif is in gold. (B) RIIβ holoenzyme structure. ATP serves as a substrate and its γ-phosphate can be transferred to Ser112 in RIIβ, while cAMP docks to CNB domains as an allosteric activator. CNB-A domain is in teal, CNB-B domain is in deep teal, N3A motif is in red, PBC motif is in gold. (C) Cartoon representation of PKA holoenzymes. (C, Left) RIα holoenzyme structure with N3A–N3A′ motifs as holoenzyme interface. (Right) RIIβ holoenzyme structure with solvent exposed N3A motifs. (D) The R–C affinity and cAMP activation of full-length and D/D domain truncated RIα and RIIβ.
The 2 RIα holoenzyme states described here allow us to appreciate not only how cAMP controls PKA activation, but also show how ATP can serve as an allosteric cofactor, and this is in striking contrast to the RIIβ holoenzyme. Even though all PKA R-subunit isoforms share the same domain organization, the role that is played by ATP is fundamentally different (Fig. 6D). In the RIα holoenzyme, ATP induces a more extended conformation and enhances the affinity of the R- and C-subunits (<0.05 nM in the presence of ATP, and 125 nM in the absence of ATP) (9). In addition, the ATP-bound conformation (molecule A) is less dynamic and more resistant to activation by cAMP. In contrast, the MD simulations of molecule B show both a kink in the αB/C/N-helix and a more open conformation of the active-site cleft, which further suggests a correlation between these 2 sites. The 2 nucleotides, ATP and cAMP, thus are competing in the RIα holoenzyme. ATP controls the inhibitor sequence in the linker segment; it serves as an orthosteric inhibitor that locks the protein substrate into the active-site cleft, while cAMP docking first to the CNB-B domain of the R-subunit facilitates activation by promoting release of the inhibitory sequence (Fig. 6A).
In the RIIβ holoenzyme, ATP has a different role. The dimensions of the RIIβ holoenzyme are the same in the presence and absence of ATP, and ATP is not required to form a stable complex (17). For the RIIβ holoenzyme, ATP is a substrate that controls the phosphorylation state of the inhibitor sequence and enhances opening and closing of the active-site cleft by a single-turnover mechanism (Fig. 6B). When the RIIβ holoenzyme is phosphorylated, it is easier for cAMP to release the inhibitor sequence from the active-site cleft of the C-subunit (19). Since RIα and RIIβ localize differently and ATP concentrations vary in different cellular compartments, it is likely that the 2 holoenzymes have very distinct ATP-dependent roles (10). The sensitivity of the RIα holoenzyme to ATP is especially relevant for localization to mitochondria where RIα-related signaling would be triggered by depressing the levels of ATP and Mg2+. Elevating ATP levels could turn on RIIβ-related signaling pathways, while RIα-related signaling would be triggered by reducing the levels of ATP. This also highlights the potential importance of the RIα holoenzyme as a stress-responsive holoenzyme; it is not required when energy levels are high. The ATP-dependent holoenzyme activation allows the PKA holoenzyme to serve as an energy sensor, which is consistent with recent studies showing that PKA can be activated more by metabolic stress, such as glucose deprivation, than by cAMP stimulation; lowering the energy levels may be sufficient to influence PKA activation (52). Since the second Mg2+ ion is essential for the high-affinity ATP binding to the RIα holoenzyme, we hypothesize that this holoenzyme can be also tightly regulated by metal homeostasis in cells (53, 54).
In summary, our holoenzyme states, together with biochemistry and simulations, provide insights into the biological function and complex regulation of the full-length RIα holoenzyme. We show how ATP, by serving as a high-affinity orthosteric inhibitor, plays a crucial role in influencing not only the RIα holoenzyme conformation but also its biological properties. We have also captured the cross-talk between the CNB and CNB′ domains and show how the N3A–N3A′ interface in CNB-A serves as a central hub for allosteric regulation, in contrast to the RIIβ holoenzyme, where these N3A motifs are solvent exposed (Fig. 6 A–C). Our results, together with previous studies, further confirm that the allosteric regulation of the RIα and RIIβ holoenzymes are quite distinct (Fig. 6D). In addition to localization, we can see that isoform diversity of the PKA holoenzymes extends to function, allostery, and quaternary structure. We can also now better appreciate how isoform diversity is controlled in mechanistically distinct ways by ATP. Our enhanced allosteric portrait of the RIα holoenzyme also lays the foundation for further tackling the pathogenic mechanisms that underlie diseases such as CNC and ACRDYS, which highlight the unique importance of the RIα holoenzyme as a general sensor for stress.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank all members of the S.S.T. laboratory; Dr. Rodrigo Maillard, Dr. Giuseppe Melacini, and Dr. Friedrich Herberg for helpful discussions; Dr. Alexandr Kornev for help in making movies; and all the staff/scientists at Advanced Light Source (ALS) for the help with beam access and data collection/analysis. The small-angle X-ray scattering and single crystal data collection were conducted at ALS, a national user facility operated by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory on behalf of the Department of Energy (DOE), Office of Basic Energy Sciences; also a DOE Office of Science User Facility under Contract DE-AC02-05CH11231, through the Integrated Diffraction Analysis Technologies program, supported by DOE Office of Biological and Environmental Research. Additional support comes from the National Institute of Health project ALS-ENABLE (P30 GM124169) and High-End Instrumentation Grant S10OD018483. The computational work used the Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment SDSC at the Comet GPU through allocation TG-MCB170143. This work was supported by a Taiwan MOE scholarship (to T.-W.L.), Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award NIH/NCI T32 CA009523 (to P.C.A.), and NIH grant GM34921 (to S.S.T.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Data deposition: The atomic coordinates have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank, www.pdb.org (PDB ID code 6NO7).
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1906036116/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Taylor S. S., Ilouz R., Zhang P., Kornev A. P., Assembly of allosteric macromolecular switches: Lessons from PKA. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 646–658 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Knighton D. R., et al. , Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science 253, 407–414 (1991). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Taylor S. S., Zhang P., Steichen J. M., Keshwani M. M., Kornev A. P., PKA: Lessons learned after twenty years. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1834, 1271–1278 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Johnson D. A., Akamine P., Radzio-Andzelm E., Madhusudan M., Taylor S. S., Dynamics of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Chem. Rev. 101, 2243–2270 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McClendon C. L., Kornev A. P., Gilson M. K., Taylor S. S., Dynamic architecture of a protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, E4623–E4631 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Knighton D. R., et al. , Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science 253, 414–420 (1991). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kinderman F. S., et al. , A dynamic mechanism for AKAP binding to RII isoforms of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol. Cell 24, 397–408 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sarma G. N., et al. , Structure of D-AKAP2:PKA RI complex: Insights into AKAP specificity and selectivity. Structure 18, 155–166 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Herberg F. W., Dostmann W. R. G., Zorn M., Davis S. J., Taylor S. S., Crosstalk between domains in the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase: Influence of amino terminus on cAMP binding and holoenzyme formation. Biochemistry 33, 7485–7494 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Day M. E., et al. , Isoform-specific targeting of PKA to multivesicular bodies. J. Cell Biol. 193, 347–363 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Herberg F. W., Taylor S. S., Dostmann W. R., Active site mutations define the pathway for the cooperative activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry 35, 2934–2942 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kim C., Cheng C. Y., Saldanha S. A., Taylor S. S., PKA-I holoenzyme structure reveals a mechanism for cAMP-dependent activation. Cell 130, 1032–1043 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bruystens J. G., et al. , PKA RIα homodimer structure reveals an intermolecular interface with implications for cooperative cAMP binding and Carney complex disease. Structure 22, 59–69 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kornev A. P., Taylor S. S., Ten Eyck L. F., A generalized allosteric mechanism for cis-regulated cyclic nucleotide binding domains. PLoS Comput. Biol. 4, e1000056 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wu J., Brown S. H., von Daake S., Taylor S. S., PKA type IIalpha holoenzyme reveals a combinatorial strategy for isoform diversity. Science 318, 274–279 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Brown S. H., Wu J., Kim C., Alberto K., Taylor S. S., Novel isoform-specific interfaces revealed by PKA RIIbeta holoenzyme structures. J. Mol. Biol. 393, 1070–1082 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhang P., et al. , Structure and allostery of the PKA RIIβ tetrameric holoenzyme. Science 335, 712–716 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ilouz R., et al. , Localization and quaternary structure of the PKA RIβ holoenzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 12443–12448 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhang P., et al. , Single turnover autophosphorylation cycle of the PKA RIIβ holoenzyme. PLoS Biol. 13, e1002192 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Isensee J., et al. , PKA-RII subunit phosphorylation precedes activation by cAMP and regulates activity termination. J. Cell Biol. 217, 2167–2184 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zawadzki K. M., Taylor S. S., cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit type IIbeta: Active site mutations define an isoform-specific network for allosteric signaling by cAMP. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 7029–7036 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kirschner L. S., Yin Z., Jones G. N., Mahoney E., Mouse models of altered protein kinase A signaling. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 16, 773–793 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Brandon E. P., et al. , Hippocampal long-term depression and depotentiation are defective in mice carrying a targeted disruption of the gene encoding the RI beta subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 8851–8855 (1995). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brandon E. P., et al. , Defective motor behavior and neural gene expression in RIIbeta-protein kinase A mutant mice. J. Neurosci. 18, 3639–3649 (1998). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cummings D. E., et al. , Genetically lean mice result from targeted disruption of the RII beta subunit of protein kinase A. Nature 382, 622–626 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kirschner L. S., et al. , A mouse model for the Carney complex tumor syndrome develops neoplasia in cyclic AMP-responsive tissues. Cancer Res. 65, 4506–4514 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Amieux P. S., et al. , Increased basal cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity inhibits the formation of mesoderm-derived structures in the developing mouse embryo. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 27294–27304 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kirschner L. S., et al. , Mutations of the gene encoding the protein kinase A type I-alpha regulatory subunit in patients with the Carney complex. Nat. Genet. 26, 89–92 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Greene E. L., et al. , In vitro functional studies of naturally occurring pathogenic PRKAR1A mutations that are not subject to nonsense mRNA decay. Hum. Mutat. 29, 633–639 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Linglart A., et al. , Recurrent PRKAR1A mutation in acrodysostosis with hormone resistance. N. Engl. J. Med. 364, 2218–2226 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Elli F. M., et al. , Screening of PRKAR1A and PDE4D in a large Italian series of patients clinically diagnosed with Albright hereditary osteodystrophy and/or pseudohypoparathyroidism. J. Bone Miner. Res. 31, 1215–1224 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hura G. L., et al. , Robust, high-throughput solution structural analyses by small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). Nat. Methods 6, 606–612 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Herberg F. W., Taylor S. S., Physiological inhibitors of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase: Effect of MgATP on protein-protein interactions. Biochemistry 32, 14015–14022 (1993). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Herberg F. W., Doyle M. L., Cox S., Taylor S. S., Dissection of the nucleotide and metal-phosphate binding sites in cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry 38, 6352–6360 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Narayana N., Cox S., Nguyen-huu X., Ten Eyck L. F., Taylor S. S., A binary complex of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase and adenosine further defines conformational flexibility. Structure 5, 921–935 (1997). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bastidas A. C., Wu J., Taylor S. S., Molecular features of product release for the PKA catalytic cycle. Biochemistry 54, 2–10 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zheng J., et al. , 2.2 A refined crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase complexed with MnATP and a peptide inhibitor. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 49, 362–365 (1993). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Akimoto M., et al. , Mapping the free energy landscape of PKA inhibition and activation: A double-conformational selection model for the tandem cAMP-binding domains of PKA RIα. PLoS Biol. 13, e1002305 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Malmstrom R. D., Kornev A. P., Taylor S. S., Amaro R. E., Allostery through the computational microscope: cAMP activation of a canonical signalling domain. Nat. Commun. 6, 7588 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.McNicholl E. T., Das R., SilDas S., Taylor S. S., Melacini G., Communication between tandem cAMP binding domains in the regulatory subunit of protein kinase A-Ialpha as revealed by domain-silencing mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 15523–15537 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.England J. P., et al. , Switching of the folding-energy landscape governs the allosteric activation of protein kinase A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115, E7478–E7485 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.P Barros E., et al. , Electrostatic interactions as mediators in the allosteric activation of protein kinase A RIα. Biochemistry 56, 1536–1545 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hirakis S. P., Malmstrom R. D., Amaro R. E., Molecular simulations reveal an unresolved conformation of the type IA protein kinase A regulatory subunit and suggest its role in the cAMP regulatory mechanism. Biochemistry 56, 3885–3888 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Su Y., et al. , Regulatory subunit of protein kinase A: Structure of deletion mutant with cAMP binding domains. Science 269, 807–813 (1995). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cao B., et al. , Structures of the PKA RI alpha holoenzyme with the FLHCC driver J-PKAc alpha or wild-type PKAc alpha. Structure 27, 816–828.e4 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rinaldi J., et al. , Structure of yeast regulatory subunit: A glimpse into the evolution of PKA signaling. Structure 18, 1471–1482 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ringheim G. E., Taylor S. S., Effects of cAMP-binding site mutations on intradomain cross-communication in the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase I. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 19472–19478 (1990). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Boras B. W., Kornev A., Taylor S. S., McCulloch A. D., Using Markov state models to develop a mechanistic understanding of protein kinase A regulatory subunit RIα activation in response to cAMP binding. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 30040–30051 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lu T., Wu J., Taylor S. S. (2019) Crystal structure of the full-length wild-type PKA RIa holoenzyme. Protein Data Bank. https://www.rcsb.org/structure/6NO7. Deposited 15 January 2019.
- 50.Bruystens J. G., et al. , Structure of a PKA RIα recurrent acrodysostosis mutant explains defective cAMP-dependent activation. J. Mol. Biol. 428, 4890–4904 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Berman H. M., et al. , The cAMP binding domain: An ancient signaling module. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 45–50 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ferretti A. C., et al. , AMPK and PKA interaction in the regulation of survival of liver cancer cells subjected to glucose starvation. Oncotarget 7, 17815–17828 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Knape M. J., et al. , Divalent metal ions control activity and inhibition of protein kinases. Metallomics 9, 1576–1584 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Khavrutskii I. V., Grant B., Taylor S. S., McCammon J. A., A transition path ensemble study reveals a linchpin role for Mg(2+) during rate-limiting ADP release from protein kinase A. Biochemistry 48, 11532–11545 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.