Abstract
Background
Corticosteroid injection is frequently used for plantar heel pain (plantar fasciitis), although there is limited high-quality evidence to support this treatment. Therefore, this study reviewed randomised trials to estimate the effectiveness of corticosteroid injection for plantar heel pain.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials that compared corticosteroid injection to any comparator. Primary outcomes were pain and function, categorised as short (0 to 6 weeks), medium (7 to 12 weeks) or longer term (13 to 52 weeks).
Results
A total of 47 trials (2989 participants) were included. For reducing pain in the short term, corticosteroid injection was more effective than autologous blood injection (SMD -0.56; 95% CI, − 0.86 to − 0.26) and foot orthoses (SMD -0.91; 95% CI, − 1.69 to − 0.13). There were no significant findings in the medium term. In the longer term, corticosteroid injection was less effective than dry needling (SMD 1.45; 95% CI, 0.70 to 2.19) and platelet-rich plasma injection (SMD 0.61; 95% CI, 0.16 to 1.06). Notably, corticosteroid injection was found to have similar effectiveness to placebo injection for reducing pain in the short (SMD -0.98; 95% CI, − 2.06, 0.11) and medium terms (SMD -0.86; 95% CI, − 1.90 to 0.19). For improving function, corticosteroid injection was more effective than physical therapy in the short term (SMD -0.69; 95% CI, − 1.31 to − 0.07). When trials considered to have high risk of bias were excluded, there were no significant findings.
Conclusions
Based on the findings of this review, corticosteroid injection is more effective than some comparators for the reduction of pain and the improvement of function in people with plantar heel pain. However, corticosteroid injection is not more effective than placebo injection for reducing pain or improving function. Further trials that are of low risk of bias will strengthen this evidence.
Registration
PROSPERO registration number CRD42016053216.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12891-019-2749-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Corticosteroid injection, Plantar heel pain, Plantar fasciitis, Meta-analysis
Background
Plantar heel pain [1] is a common foot condition that occurs in adults, with prevalence estimates between 4 and 7% [2, 3]. Several interventions are used to treat plantar heel pain, although there is limited evidence to suggest which interventions are more effective [4]. Corticosteroid injection is often used to treat plantar heel pain [5] but there is limited high-quality evidence to support its frequent use.
Previous systematic reviews [6–10] have summarised the effectiveness of corticosteroid injection for plantar heel pain but they have limitations, such as; not incorporating meta-analysis [6, 9], only including studies that compared corticosteroid injection to specific comparators [7, 8, 10], and not evaluating the strength of the evidence using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach [6, 7, 10]. In addition, a Cochrane Collaboration review [11] that evaluated corticosteroid injection for plantar heel pain also has limitations. For example, the authors pooled data from the same intervention to different categories (e.g. for one trial, the comparator was categorised both as a control and an orthosis), reported pooled data from different outcome measures using mean differences (not standardised mean differences), and used fixed-effect models when random-effects models would have been more appropriate [12]. When previous reviews are considered together, the limitations outlined above reduce the validity of their findings.
Because corticosteroid injection is frequently used to treat plantar heel pain, it is important to provide healthcare professionals with a robust summary of the findings of randomised trials, including the strength of the evidence from these trials. Accordingly, the objectives of this review were to: (i) conduct a comprehensive review of the effectiveness of corticosteroid injection on pain (including ‘first step’ pain), function, and plantar fascia thickness; (ii) summarise the available evidence and provide pooled effect sizes with meta-analyses; and (iii) use GRADE to evaluate the strength of the evidence.
Methods
This review conforms to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [13], and was prospectively registered on PROSPERO (ID = CRD42016053216).
Selection criteria
Included studies had to be randomised trials (quasi-randomised trials were excluded) published in a peer-reviewed journal. Trials were included if they compared corticosteroid injection for plantar heel pain against any comparator (placebo or active treatment) and included at least one outcome measure for either pain (including ‘first step’ pain) or function. Trials were excluded if they compared two different corticosteroid injection techniques or provided co-interventions that were not provided to all groups.
Search strategy
Electronic databases MEDLINE, CINAHL, SPORTDiscus, Embase and the Cochrane Library were searched for randomised trials published in any language. The search was originally conducted on December 1, 2016 and was updated on April 17, 2019 (Additional file 1). Complementary searches were conducted on Google Scholar and trial registries (e.g. http://clinicaltrials.gov/). Citation tracking was performed for identified trials and reference lists were scanned for trials that may have been missed in the original search.
Data collection
Search results were exported into Endnote X7.2.1 (Thomson Reuters, New York, USA) and duplicates removed. Titles and abstracts of studies were independently screened by two authors (GAW and JMG), and studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria were excluded. Full-text articles were obtained for remaining studies and these were examined for eligibility based on the inclusion criteria.
A data extraction form was used to extract trial characteristics and outcome data. Primary outcomes were pain (including ‘first step’ pain) and function. One secondary outcome was included, which was plantar fascia thickness. Other information including variables affecting bias, adverse effects and characteristics of the corticosteroid injections were also extracted. One author (GAW) extracted data and a random sample of 25% of the trials were analysed by a second author (JMG) to ensure extracted data were error free. The mean, sample size and standard deviation of outcome measures at time-points categorised as short term (0 to 6 weeks), medium term (7 to 12 weeks) and longer term (13 to 52 weeks) were extracted. Attempts were made to obtain missing data by contacting authors. If no response was received, missing standard deviations were calculated based on P values if possible [14]. Any remaining trials for which standard deviations were not available were imputed using pooled standard deviations from other trials in the meta-analysis [15].
Data handling and analysis
All data were synthesised and analysed using RevMan (Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014). Trials were grouped for meta-analysis based on the comparator intervention. For trials that used multiple measures to evaluate the same outcome (such as pain measured on separate questionnaires), the primary outcome measure was used. If more than two trials compared corticosteroid injection to the same comparator with the same time-points for outcome assessment, the data were pooled for a meta-analysis.
Due to the design variability of the included trials, an inverse-variance random-effects model was applied to all meta-analyses [12]. Outcome measures for which a higher score indicated less pain or improved function were multiplied by − 1 to provide common directionality of results. The relative treatment effect for each study was estimated by calculating the standardised mean difference (SMD), even if trials used the same outcome measure, to consistently present findings across different meta-analyses. The SMD was interpreted as having a small effect if approximately 0.2, a moderate effect if 0.5, a large effect if 0.8 and a very large effect if 1.3 [16]. Heterogeneity was investigated using the Chi2 and I2 statistics [17].
Assessment of study quality
Risk of bias assessment was performed independently by two authors (SEM and DRB) using the Cochrane Collaboration tool for assessing risk of bias and disagreements were resolved by consensus meeting [14]. A trial was considered to have a high risk of bias if at least one of the criteria was rated high risk. To be considered low risk of bias, all criteria had to be rated low risk. Any trials not meeting these criteria were considered unclear. The agreement between reviewers was evaluated by calculating a weighted kappa coefficient [18] using the kap command in Stata (version 16.0, StataCorp LLC, College Station, TX). A sensitivity analysis was conducted that excluded trials considered to be at high risk of bias to assess the impact on the original meta-analysis.
Assessment of trial quality at the outcome level was undertaken using GRADE [19]. The criteria used to make judgements for each criterion are outlined in Additional file 2.
Results
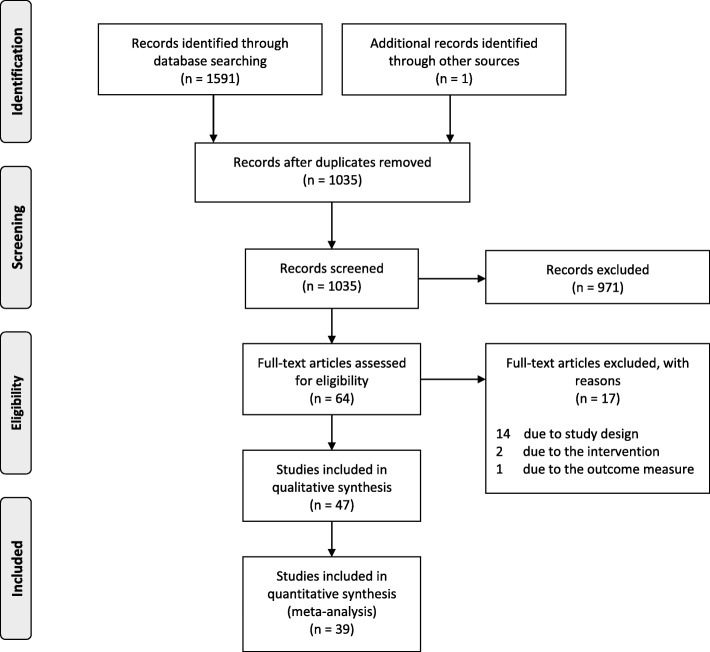
The systematic search identified 47 articles, and at the conclusion of screening, 47 individual trials were included in the final review (Fig. 1) [20–66]. Data were unable to be obtained from three trials [32, 48, 55] after contacting the authors, and five trials [33, 34, 37, 47, 53] could not be included in meta-analyses as the data were from composite outcome measures. Data from a four group trial [56] that sub-divided participants on the presence of perifascial oedema were combined to two groups so the data were similar to other trials. Finally, one trial [33] reported medians and interquartile ranges, which were converted to means and standard deviations [67].
Fig. 1.
Flow of studies through the review
The combined sample size from the included trials was 2989; 65.1% of participants were female, mean age 46.5 years and mean body mass index (BMI) 28.9 kg/m2. Each trial’s intervention, comparator, and participant characteristics are summarised in Table 1. The mean group size from the included trials was 28. Characteristics of the corticosteroid injections are summarised in Table 2; there were eight different types of corticosteroid used, with methylprednisolone acetate the most common (23/47 trials). Most trials (38/47) reported that they mixed a corticosteroid with a local anaesthetic and lidocaine was the most common (25/47 trials). A variety of injection techniques were used, most commonly without ultrasound guidance (35/47 trials) and by injecting at the point of maximal tenderness (14/47 trials).
Table 1.
Descriptive characteristics of trials included in the review
| Trial | Intervention | Comparator | Cointerventions | Participants per group | Female participants (%) | Mean age (years) | Mean BMI (kg/m2) | Duration of symptoms (weeks)a | Trial duration (weeks) | Trial setting | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention | Comparator | ||||||||||
| Abdihakin (2012) [20] | Corticosteroid injection | Placebo injection |
i) Oral anti-inflammatory drugs three times daily; ii) stretches; iii) foot orthoses; iv) heel splints; v) shoe recommendations |
44 | 38 | 52 | 42.9 | 31.7 | NR | 12 | Outpatient clinic |
| Acosta-Olivo (2017) [21] | Corticosteroid injection | Platelet-rich plasma injection | Plantar fascia stretches | 14 | 14 | 80 | 44.8 | NR | > 12 weeks | 16 | Outpatient clinic |
| Afsar (2015) [22] | Corticosteroid injection | Autologous blood injection | None | 62 | 61 | 57 | 31.8 | NR | > 12 weeks | 24 | Outpatient clinic |
| Babaei-Ghazani (2019) [23] | Corticosteroid injection | Ozone injection | Plantar fascia and calf stretches | 15 | 15 | 90 | 46.3 | 29.0 | > 8 weeks | 12 | Outpatient clinic |
| Ball (2012) [24] | Corticosteroid injection | Placebo injection | Permitted to use analgesia if required | 22 | 19 | 56 | 49.4 | 31.6 | > 8 weeks | 12 | Rheumatology service |
| Celik (2015) [25] | Corticosteroid injection | Physical therapy | None | 21 | 22 | 65 | 45.5 | 30.0 | NR | 52 | Hospital |
| Crawford (1999) [26] | Corticosteroid injection | Local anaesthetic injection | NR | 27 | 27 | 65 | 57.0 | NR | NR | 26 | Hospital |
| Corticosteroid injection + tibial nerve block | Local anaesthetic injection + tibial nerve block | 26 | 26 | ||||||||
| Diaz-Llopis (2012) [27] | Corticosteroid injection | Botulinum toxin-A injection | Plantar fascia and calf stretches | 28 | 28 | 66 | 53.9 | NR | > 26 weeks | 4 | Hospital |
| Elizondo-Rodriguez (2013) [28] | Corticosteroid injection | Botulinum toxin-A injection | Plantar fascia stretches | 17 | 17 | 55 | 43.0 | NR | > 12 weeks | 26 | Hospital |
| Eslamian (2016) [29] | Corticosteroid injection | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy |
i) Foot orthoses and heel pads; ii) plantar fascia and calf stretches |
20 | 20 | 82 | 42.1 | NR | > 8 weeks | 8 | Hospital |
| Guevara Serna (2017) [30] | Corticosteroid injection | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | NR | 24 | 36 | 67 | 51.0 | NR | > 12 weeks | 52 | Hospital |
| Guner (2013) [31] | Corticosteroid injection | Tenoxicam injection | A stretching and strengthening program | 30 | 31 | 77 | 41.4 | 29.5 | > 12 weeks | 52 | NR |
| Hanselman (2015) [32] | Corticosteroid injection | Cryopreserved human amniotic membrane | Plantar fascia and calf stretches | 14 | 9 | 70 | 51.0 | NR | > 12 weeks | 18 | NR |
| Hocaoglu (2017) [33] | Corticosteroid injection | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | NR | 36 | 36 | 87 | 49.0 | 28.7 | > 26 weeks | 26 | Outpatient clinic |
| Hou (2018) [34] | Corticosteroid injection | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | NR | 39 | 38 | 35 | 41.5 | 25.4 | > 12 weeks | 26 | Hospital |
| Jain (2015) [35] | Corticosteroid injection | Platelet-rich plasma injection |
i) Eccentric stretches; ii) foot orthoses |
22 | 24 | 65 | 55.6 | NR | > 52 weeks | 52 | Hospital |
| Jain (2018) [36] | Corticosteroid injection | Platelet-rich plasma injection | Plantar fascia and calf stretches | 40 | 40 | 42 | 38.3 | 24.1 | > 12 weeks | 26 | Hospital |
| Johannsen (2019) [37] | Corticosteroid injection | Physical therapy | NR | 31 | 30 | 58 | 45.0 | 26.2 | > 12 weeks | 104 | University |
| Corticosteroid injection + physical therapy | 29 | ||||||||||
| Karimzadeh (2017) [38] | Corticosteroid injection | Control group | Plantar fascia stretches | 12 | 12 | 67 | 47.5 | NR | > 8 weeks | 12 | NR |
| Autologous blood injection | 12 | ||||||||||
| Kiter (2006) [39] | Corticosteroid injection | Autologous blood injection | NR | 14 | 15 | 69 | 50.7 | NR | > 26 weeks | 26 | University |
| Kriss (2003) [40] | Corticosteroid injection | Foot orthoses | NR | 22 | 26 | 60 | 59.3 | NR | NR | 26 | NR |
| Corticosteroid injection + foot orthoses | 31 | ||||||||||
| Lai (2018) [41] | Corticosteroid injection | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | Acetaminophen as required | 50 | 47 | 56 | 53.5 | NR | > 4 weeks | 12 | Hospital |
| Lee (2007) [42] | Corticosteroid injection | Autologous blood injection | Plantar fascia and calf stretches | 31 | 30 | 93 | 48.7 | 26.1 | > 6 weeks | 26 | Outpatient clinic |
| Li (2014) [43] | Corticosteroid injection | Miniscalpel needle | Participants were permitted to continue with any conservative treatment | 30 | 31 | 72 | 55.8 | NR | > 26 weeks | 52 | Hospital |
| Mahindra (2016) [44] | Corticosteroid injection | Placebo injection | Plantar fascia and calf stretches | 25 | 25 | 58 | 33.4 | NR | > 12 weeks | 12 | NR |
| Platelet-rich plasma injection | 25 | ||||||||||
| Mardani-Kivi (2015) [45] | Corticosteroid injection | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | None | 41 | 40 | 84 | 44.3 | 29.6 | < 6 weeks | 12 | University |
| McMillan (2012) [46] | Corticosteroid injection | Placebo injection | Plantar fascia stretches | 41 | 41 | 48 | 52.6 | 31.1 | > 8 weeks | 12 | University |
| Monto (2014) [47] | Corticosteroid injection | Platelet-rich plasma injection |
i) CAM walker for two weeks; ii) Swedish heel drop program; iii) plantar fascia and calf stretches |
20 | 20 | 57 | 55.0 | 29.2 | > 16 weeks | 104 | NR |
| Mulherin (2009) [48] | Corticosteroid injection | Tibial nerve block | 14 | 12 | 60 | 55 (median) | NR | NR | 26 | Community medical centre | |
| Corticosteroid injection + tibial nerve block | 19 | ||||||||||
| Omar (2012) [49] | Corticosteroid injection | Platelet-rich plasma injection | NR | 15 | 15 | 100 | 43.5 | NR | NR | 6 | Hospital |
| Porter (2005) [50] | Corticosteroid injection | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | Plantar fascia and calf stretches | 64 | 61 | 66 | 39.2 | NR | > 6 weeks | 52 | Hospital |
| Rastegar (2018) [51] | Corticosteroid injection | Dry-needling | NR | 34 | 32 | 58 | 40.9 | NR | > 12 weeks | 52 | University |
| Ryan (2014) [52] | Corticosteroid injection | Physical therapy | Calf stretches | 28 | 28 | 57 | 49.3 | 25.2 | > 52 weeks | 12 | University |
| Saber (2012) [53] | Corticosteroid injection | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | NR | 30 | 30 | 55 | 34.2 | 29.0 | > 26 weeks | 12 | Outpatient clinic |
| Serbest (2013) [54] | Corticosteroid injection | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | NR | 15 | 15 | 53 | 45.2 | 30.5 | > 6 weeks | 12 | Sports medicine clinic |
| Shetty (2019) [55] | Corticosteroid injection | Placebo injection |
i) Oral enterocoxib and paracetamol for 5 days; ii) plantar fascia stretches; iii) eccentric calf strengthening |
30 | 30 | 54 | 44.6 | NR | > 12 weeks | 78 | Hospital |
| Platelet-rich plasma injection | 30 | ||||||||||
| Sorrentino (2008) [56] | Corticosteroid injection in participants with perifascial oedema | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | NR | 16 | 15 | 56 | NR | 27.9 | > 8 weeks | 6 | University |
| Corticosteroid injection in participants without perifascial oedema | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | 15 | 16 | ||||||||
| Tiwari (2013) [57] | Corticosteroid injection | Platelet-rich plasma injection | NR | 30 | 30 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 26 | Hospital |
| Ugurlar (2018) [58] | Corticosteroid injection | Platelet-rich plasma injection | Acetaminophen for 3 days | 40 | 39 | 50 | 38.8 | 26.9 | > 52 weeks | 156 | Hospital |
| Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | Prolotherapy | 39 | 40 | ||||||||
| Uygur (2018) [59] | Corticosteroid injection | Dry-needling | NR | 47 | 49 | 66 | 49.6 | NR | > 12 weeks | 26 | Hospital |
| Vahdatpour (2016) [60] | Corticosteroid injection | Platelet-rich plasma injection | Plantar fascia and calf stretches | 16 | 16 | 72 | 46.2 | 29.6 | > 12 weeks | 26 | Hospital |
| Whittaker (2019) [61] | Corticosteroid injection | Foot orthoses | Plantar fascia and calf stretches | 50 | 53 | 61 | 43.9 | 30.4 | > 4 weeks | 12 | University |
| Yesiltas (2015) [62] | Corticosteroid injection | Autologous blood injection | NR | 21 | 28 | 57 | 45.5 | 30.4 | NR | 26 | Hospital |
| Yucel (2010) [63] | Corticosteroid injection | Extracorporeal shockwave therapy | None permitted other than heel cups | 33 | 27 | 70 | 43.9 | NR | > 26 weeks | 12 | NR |
| Yucel (2013) [64] | Corticosteroid injection | Foot orthoses | Analgesia if required | 20 | 20 | 80 | 46.4 | 30.1 | > 12 weeks | 4 | University |
| Yuzer (2006) [65] | Corticosteroid injection | Laser therapy | NR | 30 | 24 | 85 | 50.5 | 32.3 | > 4 weeks | 26 | NR |
| Zamani (2014) [66] | Corticosteroid injection | Laser therapy | NR | 20 | 20 | 57 | 52.5 | NR | > 6 weeks | 6 | Rheumatology clinic |
Abbreviations: NR Not reported, BMI Body mass index
aThe minimum duration of symptoms that was specified in the inclusion criteria for the trial
Table 2.
Characteristics of the corticosteroid injection used in each trial
| Trial | Drug | Local anaesthetic | Ultrasound guidance | Needle placement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdihakin (2012) [20] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocaine 1% | No | NR |
| Acosta-Olivo (2017) [21] | Dexamethasone isonicotinate | Lidocainea | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Afsar (2015) [22] | NR | Lidocaine 1% | No | NR |
| Babaei-Ghazani (2019) [23] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocaine 1% | Yes | Within the plantar fascia |
| Ball (2012) [24] | Methylprednisolone acetate | None. Skin anesthetized | Yes | Superficial to the plantar fascia enthesis |
| Celik (2015) [25] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Prilocaine 2% | No | Around the plantar fascia |
| Crawford (1999) [26] | Prednisolone acetate | Lidocaine 1% | No | Within flexor digitorum brevis |
| Diaz-Llopis (2012) [27] | Betamethasone acetate and betamethasone disodium phosphate | Mepivacaine 1% | No | Deep to quadratus plantae, near the plantar fascia insertion |
| Elizondo-Rodriguez (2013) [28] | Dexamethasone isonicotinate | Lidocaine 2% | No | Superior to the plantar fascia |
| Eslamian (2016) [29] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocaine 2% | No | NR |
| Guevara Serna (2017) [30] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocainea | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Guner (2013) [31] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocaine 2% | No | Peppering the plantar fascia |
| Hanselman (2015) [32] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Bupivacaine 0.5% | No | Inserted to calcaneal periosteum then ‘dragged’ across plantar fascia |
| Hocaoglu (2017) [33] | Betamethasone sodium phosphate | Prilocainea | Yes | Into the thickest part of the plantar fascia, distal to its insertion on the calcaneus |
| Huo (2018) [34] | Betamethasonea | Lidocaine 2% | Yes | Within the thickest part of the plantar fascia |
| Jain (2015) [35] | Triamcinolone acetonide | Levobupivacainea | No | Peppering the plantar fascia |
| Jain (2018) [36] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocaine 2% | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Johannsen (2019) [37] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocaine 1% | Yes | NR |
| Karimzadeh (2017) [38] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocainea | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Kiter (2006) [39] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Prilocaine 2% | No | NR |
| Kriss (2003) [40] | Triamcinolone hexacetonide | NR | No | NR |
| Lai (2018) [41] | Triamcinolone acetonide | Lidocaine 2% | No | NR |
| Lee (2007) [42] | Triamcinolone acetonide | Lidocaine 1% | No | Origin of the plantar fascia |
| Li (2014) [43] | Triamcinolone acetonide | Lidocaine 2% | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Mahindra (2016) [44] | Methylprednisolone acetate | NR | No | Peppering the plantar fascia |
| Mardani-Kivi (2015) [45] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocaine 2% | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| McMillan (2012) [46] | Dexamethasone sodium phosphate | Nil – provided tibial block | Yes | Within the plantar fascia |
| Monto (2014) [47] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Field block to the skin of bupivacaine 0.5% | Yes | NR |
| Mulherin (2009) [48] | Methylprednisolonea | Lidocaine 1% | No | Within the plantar fascia |
| Omar (2012) [49] | NR | NR | No | NR |
| Porter (2005) [50] | Betamethasonea | Lidocaine 1% | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Rastegar (2018) [51] | Methylprednisolone acetate | NR | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Ryan (2014) [52] | Dexamethasonea | Lidocaine 1% | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Saber (2012) [53] | Betamethasone diproprionate and betamethasone sodium phosphate | Lidocaine 0.5% | Yes | Within the plantar fascia |
| Serbest (2013) [54] | Betamethasone acetate and betamethasone sodium phosphate | Prilocaine 2% | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Shetty (2019) [55] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocaine 1% | No | Peppering the point of maximal tenderness |
| Sorrentino (2008) [56] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Mepivacaine 3% | Yes | Within the plantar fascia |
| Tiwari (2013) [57] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocaine 2% | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Ugurlar (2018) [58] | Betamethasonea | Bupivacaine 0.5% | Yes | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Uygur (2018) [59] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Bupivacaine 0.5% | No | Between the plantar fascia and the periosteum, with peppering |
| Vahdatpour (2016) [60] | Methylprednisolone acetate | Lidocainea | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Whittaker (2019) [61] | Betamethasone acetate and betamethasone sodium phosphate | Bupivacaine 0.5% | Yes | Deep and superficial to the plantar fascia |
| Yesiltas (2015) [62] | Triamcinolonea (mixed with distilled water) | NR | No | NR |
| Yucel (2010) [63] | Betamethasone diproprionate and betamethasone sodium phosphate | Prilocaine 2% | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Yucel (2013) [64] | Betamethasone diproprionate and betamethasone sodium phosphate | Lidocainea | Yes | Within the plantar fascia |
| Yuzer (2006) [65] | Betamethasone diproprionate and betamethasone sodium phosphate | Prilocaine 2% | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
| Zamani (2014) [66] | Methylprednisolone acetate | NR | No | Point of maximal tenderness |
Abbreviations: NR Not reported
aNo other information provided
Risk of bias assessment (Fig. 2) revealed that 1/47 of the included trials was low risk, 41/47 were high risk, and 5/47 were of unclear risk. A frequent contributor (39/47 trials) to high risk of bias was not blinding participants/personnel and outcome assessors. There was a moderate [18] level of agreement between the authors (SEM and DRB) who assessed risk of bias (κ = 0.46; 95% CI, 0.40 to 0.50, P < 0.001).
Fig. 2.
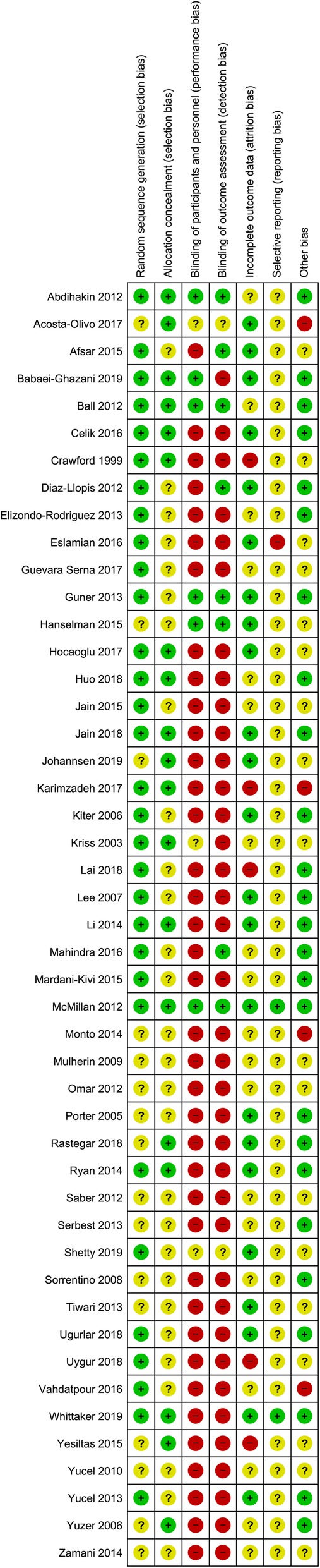
Risk of bias summary for each included trial
GRADE evidence profiles are presented in Tables 3 and 4. Ratings were made at short, medium and longer term-time points for comparisons that had sufficient data to conduct meta-analyses. Ratings were only made for the primary outcomes of pain and function as they were considered the most important outcomes for patients [68].
Table 3.
GRADE evidence profile of the effect of corticosteroid injection on pain
| Quality assessment | Summary of findings | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison | No. of trials | Limitations | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Publication bias | Participants | Effect size (95% CI)a |
GRADE | |
| Corticosteroid injection | Comparator | |||||||||
| Corticosteroid injection vs placebo injection | ||||||||||
| Short term | 4 [20, 24, 44, 46] | No serious limitations | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisionc | Undetected | 132 | 123 |
-0.98 (−2.06, 0.11)f |
Moderate |
| Medium term | 4 [20, 24, 44, 46] | No serious limitations | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisionc | Undetected | 126 | 122 |
-0.86 (− 1.90, 0.19)f |
Moderate |
| Corticosteroid injection vs physical therapy | ||||||||||
| Short term | 2 [25, 52] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisione | Undetected | 49 | 50 |
-1.07 (−2.75, 0.60)f |
Very low |
| Medium term | 3 [25, 37, 52] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | Undetected | 80 | 79 |
-0.74 (− 1.51, 0.03)f |
Low |
| Longer term | 2 [25, 37] | Very serious limitationsd | No serious inconsistency | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisionc | Undetected | 52 | 51 |
0.00 (−0.39, 0.38) |
Very low |
| Corticosteroid injection vs foot orthoses | ||||||||||
| Short term | 3 [40, 61, 64] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | Undetected | 92 | 99 |
−0.91 (−1.69, − 0.13)f |
Low |
| Medium term | 3 [40, 61, 64] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | Serious indirectnessg | Serious imprecisionc | Undetected | 72 | 79 |
−0.17 (− 1.30, 0.97) |
Very low |
| Corticosteroid injection vs dry needling | ||||||||||
| Short term | 2 [51, 59] | Very serious limitationsd | Very serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisionc | Undetected | 81 | 81 |
−0.86 (−3.70, 1.97)f |
Very low |
| Longer term | 2 [51, 59] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | Undetected | 81 | 81 | 1.45 (0.70, 2.19)f | Low |
| Corticosteroid injection vs extracorporeal shockwave therapy | ||||||||||
| Short term | 8 [29, 33, 34, 41, 45, 54, 56, 58] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | Undetected | 269 | 265 |
−0.32 (−0.77, 0.12) |
Very low |
| Medium term | 10 [29, 30, 33, 34, 41, 45, 50, 54, 58, 63] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisionc | Undetected | 354 | 354 |
−0.05 (−0.60, 0.49) |
Very low |
| Longer term | 5 [30, 33, 34, 50, 58] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | Undetected | 202 | 211 |
0.45 (−0.09, 0.99) |
Very low |
| Corticosteroid injection vs laser therapy | ||||||||||
| Short term | 2 [65, 66] | Very serious limitationsd | No serious inconsistency | Serious indirectnessg | Serious imprecisionc | Undetected | 50 | 44 |
−0.20 (−0.61, 0.20) |
Very low |
| Corticosteroid injection vs autologous blood injection | ||||||||||
| Short term | 4 [22, 38, 42, 62] | Very serious limitationsd | No serious inconsistency | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | Undetected | 126 | 131 |
−0.56 (−0.86, − 0.26) |
Low |
| Medium term | 4 [22, 38, 42, 62] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisionc | Undetected | 126 | 131 |
−0.31 (−0.83, 0.21) |
Very low |
| Longer term | 4 [22, 39, 42, 62] | Very serious limitationsd | No serious inconsistency | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisionc | Undetected | 128 | 134 |
−0.05 (−0.31, 0.21) |
Very low |
| Corticosteroid injection vs platelet-rich plasma injection | ||||||||||
| Short term | 8 [21, 35, 36, 44, 49, 57, 58, 60] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisionc | Undetected | 202 | 203 |
−0.16 (−0.70, 0.38) |
Very low |
| Medium term | 7 [21, 35, 36, 44, 57, 58, 60] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisionc | Undetected | 187 | 188 |
0.32 (−0.19, 0.83) |
Very low |
| Longer term | 6 [21, 35, 36, 57, 58, 60] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | Serious indirectnessh | No serious imprecision | Undetected | 162 | 163 | 0.61 (0.30, 1.06) | Very low |
| Corticosteroid injection vs botulinum toxin-A injection | ||||||||||
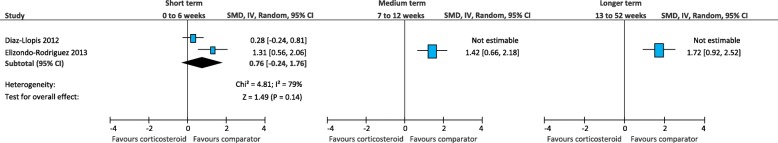
| Short term | 2 [27, 28] | Very serious limitationsd | Serious inconsistencyb | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisione | Undetected | 45 | 45 |
0.67 (−0.04, 1.38) |
Very low |
Abbreviations: CI Confidence interval, GRADE Grading Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation
a Negative values indicate that the effect size (SMD) favours corticosteroid injection
b Rated down 1 level for consistency as there was significant heterogeneity (i.e. I2 greater than 40%)
c Rated down 1 level as the upper and lower boundaries of the confidence intervals represent different conclusions
d All participants for this outcome were from trials rated at high risk of bias
e The total sample for this outcome is less than 100
f Rated up 1 level due to large effect size
g The interventions differed between studies
h Outcome measures were obtained at significantly different time points
Table 4.
GRADE evidence profile of the effect of corticosteroid injection on function
| Quality assessment | Summary of findings | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison | No. of trials | Limitations | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Publication bias | Participants | Effect size (95% CI)a |
GRADE | |
| Corticosteroid injection | Comparator | |||||||||
| Corticosteroid injection vs physical therapy | ||||||||||
| Short term | 2 [25, 52] | Very serious limitationsb | Serious inconsistencyc | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | Undetected | 49 | 50 | −0.69 (−1.31, − 0.07) | Low |
| Medium term | 2 [25, 52] | Very serious limitationsb | Serious inconsistencyc | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisiond | Undetected | 49 | 50 | −0.55 (− 1.14, 0.03) | Very low |
| Corticosteroid injection vs foot orthoses | ||||||||||
| Short term | 2 [61, 64] | Very serious limitationsb | Serious inconsistencyc | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisiond | Undetected | 70 | 73 | −0.78 (−1.81, 0.25) | Very low |
| Corticosteroid injection vs extracorporeal shockwave therapy | ||||||||||
| Short term | 2 [41, 58] | Very serious limitationsb | No serious inconsistency | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisiond | Undetected | 90 | 86 | 0.11 (−0.18, 0.41) | Very low |
| Medium term | 2 [41, 58] | Very serious limitationsb | No serious inconsistency | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisiond | Undetected | 90 | 86 | 0.21 (−0.08, 0.51) | Very low |
| Corticosteroid injection vs platelet-rich plasma injection | ||||||||||
| Short term | 3 [21, 36, 58] | Very serious limitationsb | No serious inconsistency | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | Undetected | 94 | 93 | −0.18 (−0.47, 0.10) | Low |
| Medium term | 3 [21, 36, 58] | Very serious limitationsb | No serious inconsistency | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisiond | Undetected | 94 | 93 | 0.10(−0.18, 0.39) | Very low |
| Longer term | 3 [21, 36, 58] | Very serious limitationsb | No serious inconsistency | No serious indirectness | No serious imprecision | Undetected | 94 | 93 | 0.21 (−0.08, 0.49) | Low |
| Corticosteroid injection vs botulinum toxin-A injection | ||||||||||
| Short term | 2 [27, 28] | Very serious limitationsb | Serious inconsistencyc | No serious indirectness | Serious imprecisiond | Undetected | 45 | 45 | 0.76 (−0.24, 1.76) | Very low |
Abbreviations: CI Confidence interval, GRADE Grading Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation
a Negative values indicate that the effect size (SMD) favours corticosteroid injection
b All participants for this outcome were from trials rated at high risk of bias
c Rated down 1 level for consistency as there was significant heterogeneity (i.e. I2 greater than 40%)
d Rated down 1 level as the upper and lower boundaries of the confidence intervals represent different conclusions
Primary outcomes
Pain
Results of trials that could not be pooled in meta-analyses are summarised in Additional file 3. Pooled point estimates with negative values indicate an effect in favour of corticosteroid injection.
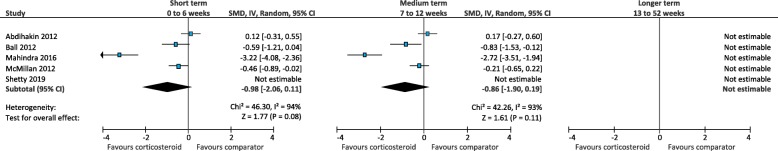
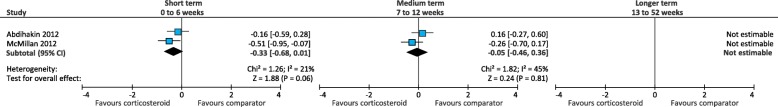
Data for the comparison of corticosteroid injection to placebo injection were available from four trials [20, 24, 44, 46] in the short and medium terms, and no data were available in the longer term (Fig. 3). There was moderate quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is similar to placebo injection in the short (SMD -0.98; 95% CI, − 2.06 to 0.11) and medium terms (SMD -0.86; 95% CI, − 1.90 to 0.19).
Fig. 3.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to placebo injection for the outcome of pain. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
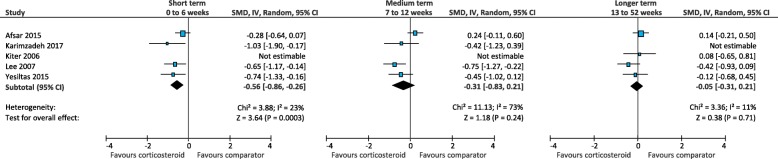
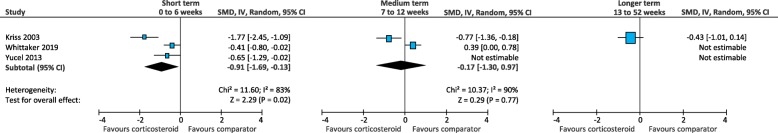
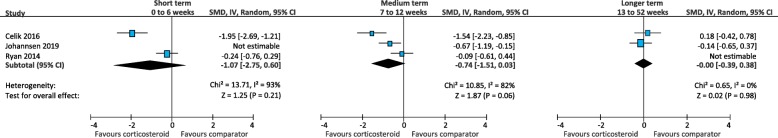
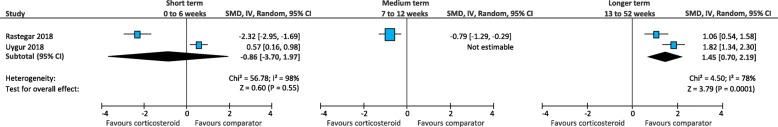
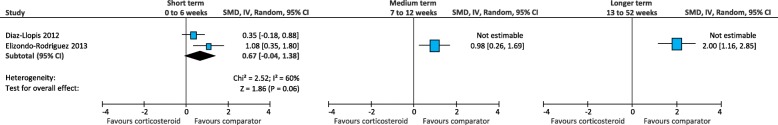
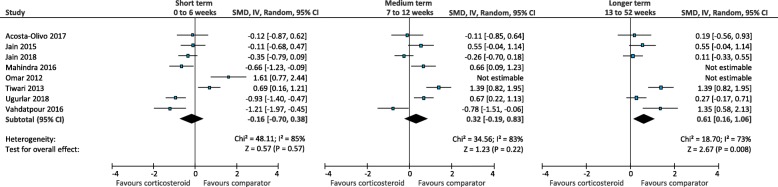
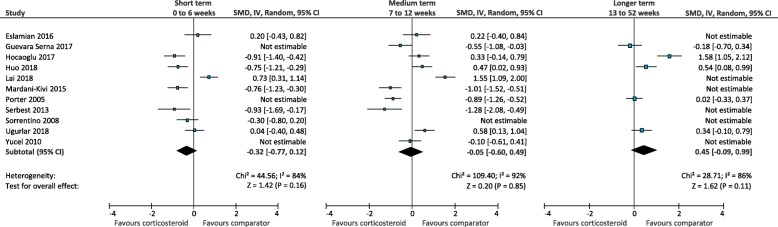
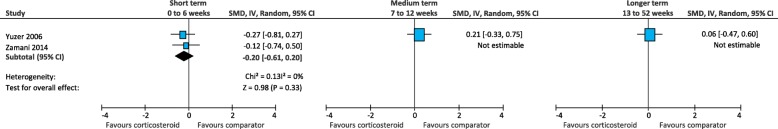
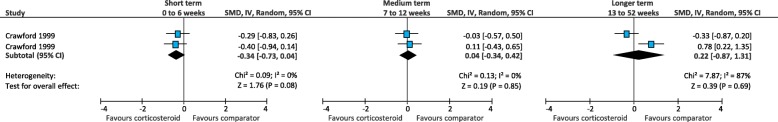
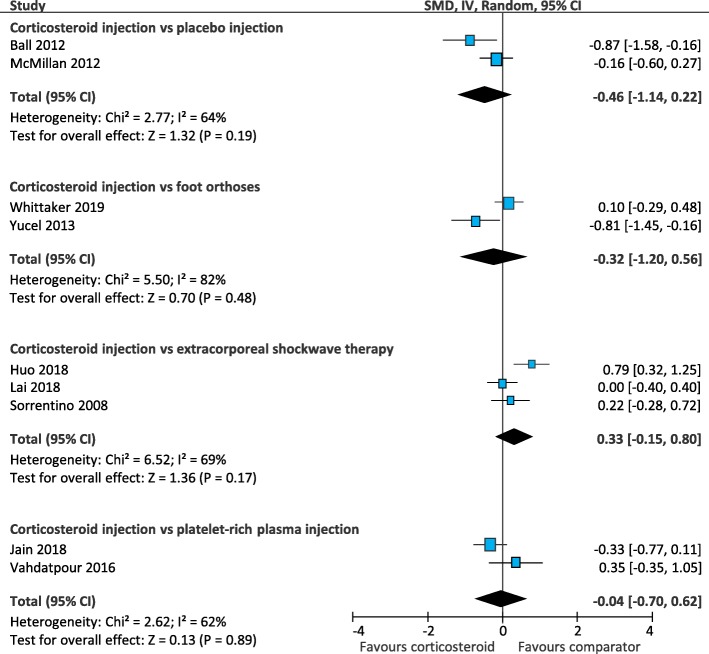
When corticosteroid injection was compared to other comparators in the short term (0 to 6 weeks), there was low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is more effective than autologous blood injection (SMD -0.56; 95% CI, − 0.86 to − 0.26) (Fig. 4) [22, 38, 42, 62] and foot orthoses (SMD -0.91; 95% CI, − 1.69 to − 0.13) (Fig. 5) [40, 61, 64]. There was very-low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is similar to physical therapy (SMD -1.07; 95% CI, − 2.75 to 0.60) (Fig. 6) [25, 52], dry needling (SMD -0.86; 95% CI, − 3.70 to 1.97) (Fig. 7) [51, 59], botulinum toxin-A injection (SMD 0.67; 95% CI, − 0.04 to 1.38) (Fig. 8) [27, 28], platelet-rich plasma injection (SMD -0.16; 95% CI, − 0.70 to 0.38) (Fig. 9) [21, 35, 36, 44, 49, 57, 58, 60], extracorporeal shockwave therapy (SMD -0.32; 95% CI, − 0.77 to 0.12) (Fig. 10) [29, 33, 34, 41, 45, 54, 56, 58], laser therapy (SMD -0.20; 95% CI, − 0.61 to 0.20) (Fig. 11) [65, 66], and local anaesthetic injection (SMD -0.34; 95% CI, − 0.73 to 0.04) (Fig. 12) [26].
Fig. 4.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to autologous blood injection for the outcome of pain. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 5.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to foot orthoses for the outcome of pain. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 6.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to physical therapy for the outcome of pain. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 7.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to dry needling for the outcome of pain. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 8.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to botulinum toxin-A injection for the outcome of pain. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 9.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to platelet-rich plasma injection for the outcome of pain. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 10.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to extracorporeal shockwave therapy for the outcome of pain. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 11.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to laser therapy for the outcome of pain. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 12.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to local anaesthetic injection for the outcome of pain. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
In the medium term (7 to 12 weeks), there was low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is similar to physical therapy (SMD -0.74; 95% CI, − 1.51 to 0.03) [25, 37, 52], and very-low quality evidence corticosteroid injection is similar to autologous blood injection (SMD -0.31; 95% CI, − 0.83 to 0.21) [22, 38, 42, 62], foot orthoses (SMD -0.17; 95% CI; − 1.30 to 0.97) [40, 61], platelet-rich plasma injection (SMD 0.32; 95% CI, − 0.19 to 0.83) [21, 35, 36, 44, 57, 58, 60], extracorporeal shockwave therapy (SMD -0.05; 95% CI, − 0.60 to 0.49) [29, 30, 33, 34, 41, 45, 50, 54, 58, 63], and local anaesthetic injection (SMD 0.04; 95% CI, − 0.34 to 0.42) [26].
In the longer term (13 to 52 weeks), there was low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is less effective than dry needling (SMD 1.45; 95% CI, 0.70 to 2.19) [51, 59], and very low-quality evidence corticosteroid injection is less effective than platelet-rich plasma injection (SMD 0.61; 95% CI, 0.16 to 1.06) [21, 35, 36, 57, 58, 60]. There was very-low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is similar to physical therapy (SMD -0.00; 95% CI − 0.39 to 0.38) [25, 37] autologous blood injection (SMD -0.05; 95% CI, − 0.31 to 0.21) [22, 39, 42, 62], extracorporeal shockwave therapy (SMD 0.45; 95% CI, − 0.09 to 0.99) [30, 33, 34, 50, 58], and local anaesthetic injection (SMD 0.22; 95% CI, − 0.87 to 1.31) [26].
For ‘first-step’ pain, meta-analyses were possible for trials that compared corticosteroid injection to placebo injection in the short and medium terms (Fig. 13). Corticosteroid injection was similar to placebo injection in the short (SMD -0.33; 95% CI, − 0.68 to 0.01) and medium terms (SMD -0.05; 95% CI, − 0.46 to 0.36) [20, 46]. Results from trials that could not be pooled in meta-analyses are summarised in Additional file 4.
Fig. 13.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to placebo injection for the outcome of ‘first step’ pain. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
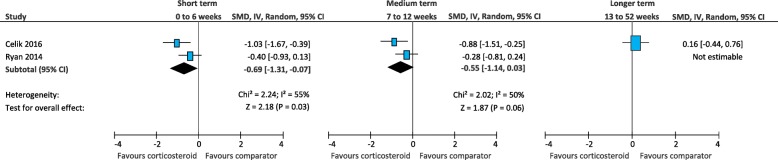
Function
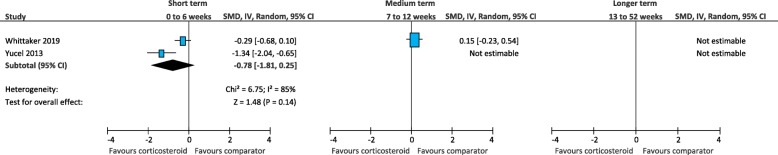
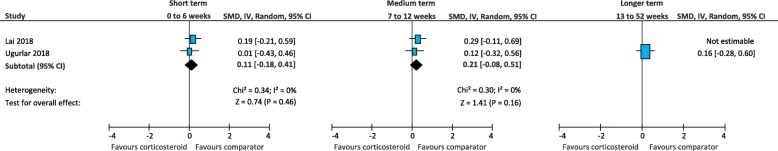
In the short term, there was low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is more effective than physical therapy (SMD -0.69; 95% CI, − 1.31 to − 0.07) (Fig. 14) [25, 52]. There was very-low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is similar to foot orthoses (SMD -0.78; 95% CI, − 1.81 to 0.25) (Fig. 15) [61, 64], extracorporeal shockwave therapy (SMD 0.11; 95% CI, − 0.18 to 0.41) (Fig. 16) [41, 58], and botulinum toxin-A injection (SMD 0.76; 95% CI, − 0.24 to 1.76) (Fig. 17) [27, 28]. There was low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is similar to platelet-rich plasma injection (SMD -0.18; 95% CI − 0.47 to 0.10) (Fig. 18) [21, 36, 58],
Fig. 14.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to physical therapy for the outcome of function. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 15.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to foot orthoses for the outcome of function. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 16.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to extracorporeal shockwave therapy for the outcome of function. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 17.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to botulinum toxin-A injection for the outcome of function. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Fig. 18.
Meta-analyses comparing corticosteroid injection to platelet-rich plasma injection for the outcome of function. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
In the medium term, there was very-low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is similar to physical therapy (SMD -0.55; 95% CI, − 1.14 to 0.03) [25, 52], extracorporeal shockwave therapy (SMD 0.21; 95% CI − 0.08 to 0.51) [41, 58], and platelet-rich plasma injection (SMD 0.10; 95% CI, − 0.18 to 0.39) [21, 36, 58].
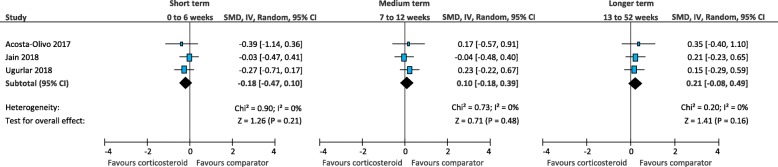
In the longer term, there was low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is similar to platelet-rich plasma injection (SMD 0.21; 95% CI, − 0.08 to 0.49) [21, 36, 58]. Results of trials that could not be pooled in meta-analyses are summarised in Additional file 5.
Secondary outcomes
Plantar fascia thickness
Values extracted for plantar fascia thickness were from the last time point reported in each trial. Corticosteroid injection was similar to placebo injection (SMD -0.46; 95% CI, − 1.14 to 0.22) [24, 46], foot orthoses (SMD-0.32; 95% CI − 1.20 to 0.56) [61, 64], extracorporeal shockwave therapy (SMD 0.33; 95% CI, − 0.15 to 0.80) [34, 41, 56], and platelet-rich plasma injection (SMD -0.04; 95% CI, − 0.70 to 0.62) [36, 60] (Fig. 19). Results from trials that could not be pooled in meta-analyses are summarised in Additional file 6.
Fig. 19.
Meta-analyses for the outcome of plantar fascia thickness. SMD = standard mean difference; IV = inverse variance; CI = confidence interval
Sensitivity analysis
A sensitivity analysis was conducted that excluded trials considered to have high risk of bias. For pain, there was sufficient data for meta-analysis from three trials [20, 24, 46], which found corticosteroid injection is similar to placebo injection in the short (SMD -0.28; 95% CI, − 0.71 to 0.16) and medium terms (SMD -0.23; 95% CI, − 0.72 to 0.28). No data were available for meta-analysis from other comparators. The findings for ‘first step’ pain were unchanged with the sensitivity analysis. For function, no data were available, so a sensitivity analysis was not conducted. Finally, the findings for the secondary outcome measure of plantar fascia thickness were unchanged with sensitivity analysis for the comparison to placebo injection only.
Adverse events
Adverse events were assessed in 30/47 trials [21–24, 27–32, 34–38, 40, 42, 43, 46, 50, 55–59, 61–65]. In 25 of the 30 trials where adverse events were assessed [21, 22, 24, 25, 27–32, 35, 40, 43, 46, 53, 56, 57, 62–65], no adverse events were reported. In the remaining 5 trials, the only adverse event that was reported was post-injection pain [37, 38, 42, 50, 63].
Discussion
The findings of this systematic review indicate that for the outcome of pain, corticosteroid injection is more effective than autologous blood injection and foot orthoses in the short term (up to 6 weeks), but platelet-rich plasma and dry needling are more effective in the longer term (greater than 12 weeks). For the outcome of function, corticosteroid injection is more effective than physical therapy in the short term. Notably, corticosteroid injection is similar to placebo injection for pain and function.
The finding that corticosteroid injection is similar to placebo injection for the outcome of pain is notable. Many health professionals would perceive a discordance between this finding and reductions in pain observed in clinical practice following corticosteroid injection. However, this may be explained by non-specific effects from influences such as natural resolution, regression to the mean, the placebo effect, or expectancy effects [69, 70]. These non-specific effects cannot be disregarded and our findings may suggest that any specific effect from the corticosteroid drug itself is small. Indeed, in similar work relating to knee osteoarthritis, non-specific effects account for almost half of the overall effect observed for corticosteroid injection [71].
For comparators other than placebo injection, we found corticosteroid injection to be more effective for the reduction of pain than autologous blood injection and foot orthoses in the short term. Although meta-analyses for the remaining comparators in the short term were not statistically significant, there was a general trend for corticosteroid injection to be more effective (based on meaningful effect sizes). However, this trend diminished in the medium to longer term. Statistically significant findings, with moderate to large effect sizes, were found for the comparison to dry needling (SMD of 1.45) and platelet-rich plasma injection (SMD of 0.61). Therefore, compared to the variety of other comparators included in this review, corticosteroid injection is more effective compared to comparators in the short term but not in the longer term. Further research will improve the precision of these estimates and the conclusions that can be drawn, especially regarding the effectiveness of corticosteroid injection in the short term.
For ‘first-step’ pain, few trials reported this outcome and a meta-analysis was only possible for the comparison between corticosteroid injection and placebo injection, which found that corticosteroid injection was similar to placebo injection in the short term. However, this finding was close to being statistically significant with the upper confidence limit just including zero (SMD -0.33; 95% CI, − 0.68 to 0.01). This finding remained unchanged after excluding trials considered to have a high risk of bias. Given ‘first step’ pain is a principal complaint of patients with plantar heel pain, it is important that future clinical trials evaluate ‘first step’ pain as an outcome.
There were few trials that reported function as an outcome, and meta-analyses were only possible for comparisons to physical therapy, foot orthoses, extracorporeal shockwave therapy, platelet-rich plasma injection, and botulinum toxin-A injection. The only significant finding was for the comparison between corticosteroid injection and physical therapy, which found corticosteroid injection to be more effective in the short term. Single trials, and meta-analyses that were not significantly different, tended to find corticosteroid injection was more effective in the short term, but the comparator intervention was found to be more effective in the medium and longer term.
We also investigated the secondary outcome of plantar fascia thickness – a biological outcome rather than a patient-reported outcome. Meta-analyses found corticosteroid injection was not more effective than other comparators for the reduction of plantar fascia thickness. However, there was a trend for corticosteroid injection to be more effective than placebo injection and for extracorporeal shockwave therapy to be more effective than corticosteroid injection. It is important to note, however, that because this was a secondary outcome, it was not included in our original search strategy, so there is a small chance that additional trials that measured this outcome may have been missed.
The findings above should be interpreted with regard to the quality of the trials that investigated the effectiveness of corticosteroid injection. According to GRADE, the findings of these studies ranged from very-low to moderate quality, which means we have limited confidence in the findings and they are likely to change when future trials are conducted. Furthermore, most trials (39/47) were at high risk of bias, and when a sensitivity analysis was performed that excluded these trials, there were no significant findings.
Clinical importance
To provide a sense of the clinical worth of these findings, statistically significant results for pain were back-transformed to a 0–100 point visual analogue scale [14], and compared to the previously calculated minimal important difference value of 8 points (on a 0–100 point scale) [72] using a pooled standard deviation [15]. Although this method provides a sense of whether the difference between these interventions is clinically worthwhile, these estimates can be misleading and should be interpreted with caution [73]. In the short term, corticosteroid injection provided a clinically worthwhile effect when compared to foot orthoses (between-group difference of 12.2 points) and autologous blood injection (between-group difference of 14.8 points). In the longer term, dry needling (between-group difference of 18.9 points) and platelet-rich plasma injection (between-group difference of 10.0 points) provided a clinically worthwhile effect when compared to corticosteroid injection. For function, the clinical worth of corticosteroid injection compared to physical therapy could not be estimated as the minimal important difference values have not been calculated for the outcome measures used by trials in that meta-analysis.
Importantly, these findings were all from trials at high risk of bias, which may exaggerate clinical effectiveness. An example of the influence of bias is the comparison between corticosteroid injection and placebo injection in the short term. After excluding trials at high risk of bias, the estimate of the clinical importance of this comparison (although not statistically significant) reduced from 18.0 points to 4.7 points (on a 0–100 point scale). This reduction should be noted by health professionals, and it reiterates our earlier comment that non-specific effects may influence the reporting of pain.
Limitations and directions for future research
There was substantial heterogeneity (as indicated by the high I2 values) for most meta-analyses conducted, and this may reflect several recurring methodological issues. First, there were a variety of corticosteroids, combined anaesthetics, injection techniques, and comparators used in the included trials. Second, the mean group size for trials was 28 participants, and most trials did not report a priori sample size calculations. Finally, there was a lack of participant and investigator blinding, which was a common reason that trials were considered to have a high risk of bias. For trials with interventions such as physical therapy, it is almost impossible to blind the participant, however for injectable therapeutic solutions (e.g. autologous blood or platelet-rich plasma), it is possible to achieve participant and investigator blinding [74]. With these shortcomings in mind, the strength of the overall body of evidence is reduced and the recommendations that can be made are limited.
We found that corticosteroid injection was a safe intervention, with post-injection pain the only reported adverse effect. Two case-series studies published in the 1990s suggested there may be an increased risk of plantar fascia rupture following corticosteroid injection [75, 76], although no plantar fascia ruptures have been reported for participants who received a corticosteroid injection in the randomised trials included in our review. Long-term adverse effects of a corticosteroid injection are unclear, as few trials reported outcomes beyond 12 weeks. This is an important consideration as there are reports that corticosteroid injection has a deleterious long-term effect on tendon [77], and one trial that followed participants with lateral epicondylitis for 1 year found that the group that received a corticosteroid injection had more pain than a ‘wait and see’ group at the conclusion of the trial [78]. Worryingly, some trials [20, 26, 33, 39, 41, 44, 45, 47–49, 51–54, 60] included in our review did not report adverse events, and few reported whether they actively questioned participants about adverse events.
Conclusions
For the outcome of pain in the short term, we found low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is more effective than autologous blood injection and foot orthoses. In the longer term, we found very-low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is less effective than dry needling and platelet-rich plasma injection. These findings were greater than minimal important difference values, indicating that they are clinically worthwhile. For the outcome of function, we found low quality evidence that corticosteroid injection is more effective than physical therapy, but this was only in the short term. Notably, corticosteroid injection was found to have similar effectiveness to placebo injection for pain and function. The impact of bias on these findings was assessed with a sensitivity analysis, which found that corticosteroid injection had similar effectiveness to placebo injection. Further trials that are of low risk of bias will strengthen this evidence.
Additional files
Search strategy. The search strategy used for the systematic search. (PDF 61 kb)
Criteria used for judgements of GRADE. (PDF 64 kb)
Results of single trials that investigated pain. A summary of the findings from single trials that investigated pain but were not included in a meta-analysis. (PDF 95 kb)
Results of single trials that investigated ‘first step’ pain. A summary of the findings from single trials that investigated ‘first step’ pain but were not included in a meta-analysis. (PDF 109 kb)
Results of single trials that investigated function. A summary of the findings from single trials that investigated function but were not included in a meta-analysis. (PDF 82 kb)
Results of single trials that investigated plantar fascia thickness. A summary of the findings from single trials that investigated plantar fascia thickness but were not included in a meta-analysis. (PDF 65 kb)
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- BMI
Body mass index
- CI
Confidence interval
- GRADE
Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses
- SMD
Standardised mean difference
Authors’ contributions
GAW designed the study, conducted the systematic search and study selection, statistical analysis and interpretation, and prepared the manuscript. SEM designed the study, conducted the quality appraisal, reviewed and interpreted the statistical analysis. HBM designed the study, reviewed and interpreted the statistical analysis. DRB conducted the quality appraisal. JMG conducted the systematic search and study selection. KBL designed the study, reviewed and interpreted the statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
The review received no direct funding support. GAW is a recipient of an Australian Government Research Training Program scholarship. HBM is a National Health and Medical Research Senior Fellow (ID: 1135995).
Availability of data and materials
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is available in the figshare repository:
Whittaker, Glen; Munteanu, Shannon; Menz, Hylton; Bonanno, Daniel; Gerrard, James; Landorf, Karl (2018): Extracted data for a systematic review and meta-analyses of corticosteroid injection for plantar heel pain. Figshare. Dataset. 10.4225/22/5afa8ad63d93d
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
GAW, SEM, HBM, JMG and KBL and are authors of randomised trials included in this review. The other authors have disclosed no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Glen A. Whittaker, Phone: +613 9479 5785, Email: g.whittaker@latrobe.edu.au
Shannon E. Munteanu, Email: s.munteanu@latrobe.edu.au
Hylton B. Menz, Email: h.menz@latrobe.edu.au
Daniel R. Bonanno, Email: d.bonanno@latrobe.edu.au
James M. Gerrard, Email: j.gerrard@latrobe.edu.au
Karl B. Landorf, Email: k.landorf@latrobe.edu.au
References
- 1.Riel H, Cotchett M, Delahunt E, Rathleff MS, Vicenzino B, Weir A, et al. Is ‘plantar heel pain’ a more appropriate term than ‘plantar fasciitis’? Time to move on. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51:1576–1577. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2017-097519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hill CL, Gill TK, Menz HB, Taylor AW. Prevalence and correlates of foot pain in a population-based study: the north West Adelaide health study. J Foot Ankle Res. 2008;1:2. doi: 10.1186/1757-1146-1-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dunn JE, Link CL, Felson DT, Crincoli MG, Keysor JJ, McKinlay JB. Prevalence of foot and ankle conditions in a multiethnic community sample of older adults. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;159:491–498. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwh071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Babatunde OO, Legha A, Littlewood C, Chesterton LS, Thomas MJ, Menz HB, et al. Comparative effectiveness of treatment options for plantar heel pain: a systematic review with network meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2019;53:182–194. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2017-098998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hansen Liselotte, Krogh Thøger Persson, Ellingsen Torkell, Bolvig Lars, Fredberg Ulrich. Long-Term Prognosis of Plantar Fasciitis: A 5- to 15-Year Follow-up Study of 174 Patients With Ultrasound Examination. Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine. 2018;6(3):232596711875798. doi: 10.1177/2325967118757983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Atkins D., Crawford F., Edwards J., Lambert M. A systematic review of treatments for the painful heel. Rheumatology. 1999;38(10):968–973. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.10.968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Uden H, Boesch E, Kumar S. Plantar fasciitis - to jab or to support? A systematic review of the current best evidence. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2011;4:155. 10.2147/JMDH.S20053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.Li Z, Yu A, Qi B, Zhao Y, Wang W, Li P, et al. Corticosteroid versus placebo injection for plantar fasciitis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9:2263–2268. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Landorf KB. Plantar heel pain and plantar fasciitis. BMJ Clin Evid. 2015;11:1111. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Chen C-M, Lee M, Lin C-H, Chang C-H, Lin C-H. Comparative efficacy of corticosteroid injection and non-invasive treatments for plantar fasciitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2018;8:4033. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22402-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.David JA, Sankarapandian V, Christopher PR, Chatterjee A, Macaden AS. Injected corticosteroids for treating plantar heel pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;Issue 6 Art:No. CD009348. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009348.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein HR. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. 2010;1:97–111. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration; 2011. Available from http://handbook.cochrane.org.
- 15.Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta-analyses can provide accurate results. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006;59:7–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sedgwick P. Cohen’s coefficient. BMJ. 2012;344:e1178. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e1178. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, et al. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 2004;328:1490. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7454.1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Abdihakin M, Wafula K, Hasan S, MacLeod J. A randomised controlled trial of steroid injection in the management of plantar fasciitis. SA Orthop J. 2012;11:33–38. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Acosta-Olivo C, Elizondo-Rodriguez J, Lopez-Cavazos R, Vilchez-Cavazos F, Simental-Mendia M, Mendoza-Lemus O. Plantar fasciitis. A comparison of treatment with intralesional steroids versus platelet-rich plasma (PRP). A randomized, blinded study. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2017;107:490–496. doi: 10.7547/15-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Afsar SS, Khan A, Idrees M. Comparison of autologous blood injection and corticosteroid injection in the treatment of plantar fasciitis, randomized controlled trial. Pakistan J Surg. 2015;31:238–241. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Babaei-Ghazani A, Karimi N, Forogh B, Madani SP, Ebadi S, Fadavi HR, et al. Comparison of ultrasound-guided local ozone (O2-O3) injection vs corticosteroid injection in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis: a randomized clinical trial. Pain Med. 2019;20:314–322. doi: 10.1093/pm/pny066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ball EM, McKeeman HM, Patterson C, Burns J, Yau WH, Moore OA, et al. Steroid injection for inferior heel pain: a randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72:996–1002. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Celik D, Kus G, Sırma SÖ. Joint mobilization and stretching exercise vs steroid injection in the treatment of plantar fasciitis: a randomized controlled study. Foot Ankle Int. 2016;37:150–156. doi: 10.1177/1071100715607619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Crawford F., Atkins D., Young P., Edwards J. Steroid injection for heel pain: evidence of short-term effectiveness. A randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology. 1999;38(10):974–977. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.10.974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Diaz-Llopis IV, Rodriguez-Ruiz CM, Mulet-Perry S, Mondejar-Gomez FJ, Climent-Barbera JM, Cholbi-LLobel F. Randomized controlled study of the efficacy of the injection of botulinum toxin type a versus corticosteroids in chronic plantar fasciitis: results at one and six months. Clin Rehabil. 2012;26:594–606. doi: 10.1177/0269215511426159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Elizondo-Rodriguez J, Araujo-Lopez Y, Moreno-Gonzalez JA, Cardenas-Estrada E, Mendoza-Lemus O, Acosta-Olivo C. A comparison of botulinum toxin a and intralesional steroids for the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. 2013;34:8–14. doi: 10.1177/1071100712460215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Eslamian F, Shakouri SK, Jahanjoo F, Hajialiloo M, Notghi F. Extra corporeal shock wave therapy versus local corticosteroid injection in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis, a single blinded randomized clinical trial. Pain Med. 2016;17:1722–1731. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnw113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Guevara Serna JA, Acosta Morón JA. Terapia de ondas de choque frente a infiltración corticosteroidea en el tratamiento de la fascitis plantar crónica. Rev Colomb Ortop y Traumatol. 2017;32:43–49. doi: 10.1016/j.rccot.2017.07.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guner S, Onder H, Guner SI, Ceylan MF, Gökalp MA, Keskin S. Effectiveness of local tenoxicam versus corticosteroid injection for plantar fasciitis treatment. Orthopedics. 2013;36:e1322–e1326. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20130920-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hanselman AE, Tidwell JE, Santrock RD. Cryopreserved human amniotic membrane injection for plantar fasciitis: a randomized, controlled, double-blind pilot study. Foot Ankle Int. 2015;36:151–158. doi: 10.1177/1071100714552824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hocaoglu S, Vurdem UE, Cebicci MA, Sutbeyaz ST, Guldeste Z, Yunsuroglu SG. Comparative effectiveness of radial extracorporeal shockwave therapy and ultrasound-guided local corticosteroid injection treatment for plantar fasciitis. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2017;107:192–199. doi: 10.7547/14-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Huo X-L, Wang K-T, Zhang X-Y, Yang Y-T, Cao F-Y, Yang J, et al. Prognostic analysis of plantar fasciitis treated by pneumatic ballistic extracorporeal shock wave versus ultrasound guided intervention. J South Med Univ. 2018;38:135–140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2018.02.03. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jain K, Murphy PN, Clough TM. Platelet rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection for plantar fasciitis: a comparative study. Foot. 2015;25:235–237. doi: 10.1016/j.foot.2015.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jain SK, Suprashant K, Kumar S, Yadav A, Kearns SR. Comparison of plantar fasciitis injected with platelet-rich plasma vs corticosteroids. Foot Ankle Int. 2018;39:780–786. doi: 10.1177/1071100718762406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Johannsen FE, Herzog RB, Malmgaard-Clausen NM, Hoegberget-Kalisz M, Magnusson SP, Kjaer M. Corticosteroid injection is the best treatment in plantar fasciitis if combined with controlled training. Knee Surg Sport Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27:5–12. doi: 10.1007/s00167-018-5234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Karimzadeh A, Raeissadat SA, Erfani Fam S, Sedighipour L, Babaei-Ghazani A. Autologous whole blood versus corticosteroid local injection in treatment of plantar fasciitis: a randomized, controlled multicenter clinical trial. Clin Rheumatol. 2017;36:661–669. doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3484-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kiter E, Çelikbaş E, Akkaya S, Demirkan F, Kiliç BA. Comparison of injection modalities in the treatment of plantar heel pain. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2006;96:293–296. doi: 10.7547/0960293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kriss S. Injectable steroids in the management of heel pain. A prospective randomised trial. Br J Pod. 2003;6:40–42. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lai T, Ma H, Lee M, Chen P, Ku M. Ultrasonography and clinical outcome comparison of extracorporeal shock wave therapy and corticosteroid injections for chronic plantar fasciitis: a randomized controlled trial. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2018;18:47–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lee TG, Ahmad TS. Intralesional autologous blood injection compared to corticosteroid injection for treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Foot Ankle Int. 2007;28:984–990. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2007.0984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Li Shuming, Shen Tong, Liang Yongshan, Zhang Ying, Bai Bo. Miniscalpel-Needle versus Steroid Injection for Plantar Fasciitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial with a 12-Month Follow-Up. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2014;2014:1–7. doi: 10.1155/2014/164714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mahindra P, Yamin M, Selhi HS, Singla S, Soni A. Chronic plantar fasciitis: effect of platelet-rich plasma, corticosteroid, and placebo. Orthopedics. 2016;39:e285–e289. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20160222-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mardani-Kivi M, Karimi Mobarakeh M, Hassanzadeh Z, Mirbolook A, Asadi K, Ettehad H, et al. Treatment outcomes of corticosteroid injection and extracorporeal shock wave therapy as two primary therapeutic methods for acute plantar fasciitis: a prospective randomized clinical trial. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2015;54:1047–1052. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2015.04.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.McMillan AM, Landorf KB, Gilheany MF, Bird AR, Morrow AD, Menz HB. Ultrasound guided corticosteroid injection for plantar fasciitis: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2012;344:e3260. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e3260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Monto RR. Platelet-rich plasma efficacy versus corticosteroid injection treatment for chronic severe plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;35:313–318. doi: 10.1177/1071100713519778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mulherin D, Price M. Efficacy of tibial nerve block, local steroid injection or both in the treatment of plantar heel pain syndrome. Foot. 2009;19:98–100. doi: 10.1016/j.foot.2009.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Omar AS, Ibrahim ME, Ahmed AS, Said M. Local injection of autologous platelet rich plasma and corticosteroid in treatment of lateral epicondylitis and plantar fasciitis: randomized clinical trial. Egypt Rheumatol. 2012;34:43–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ejr.2011.12.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Porter MD, Shadbolt B. Intralesional corticosteroid injection versus extracorporeal shock wave therapy for plantar fasciopathy. Clin J Sport Med. 2005;15:119–124. doi: 10.1097/01.jsm.0000164039.91787.dc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rastegar S, Baradaran Mahdavi S, Hoseinzadeh B, Badiei S. Comparison of dry needling and steroid injection in the treatment of plantar fasciitis: a single-blind randomized clinical trial. Int Orthop. 2018;42:109–116. doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3681-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ryan M, Hartwell J, Fraser S, Newsham-West R, Taunton J. Comparison of a physiotherapy program versus dexamethasone injections for plantar fasciopathy in prolonged standing workers. Clin J Sport Med. 2014;24:211–217. doi: 10.1097/JSM.0000000000000021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Saber N, Diab H, Nassar W, Razaak HA. Ultrasound guided local steroid injection versus extracorporeal shockwave therapy in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Alexandria J Med. 2012;48:35–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ajme.2011.11.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Serbest MO, Kaya Hİ, Demir MH, Ercan S, Cetin C. Comparison of effectiveness of the extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) and steroid injection at plantar fasciitis treatment. Med Sport. 2013;9:2185–2190. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Shetty SH, Dhond A, Arora M, Deore S. Platelet-rich plasma has better long-term results than corticosteroids or placebo for chronic plantar fasciitis: randomized control trial. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;58:42–46. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2018.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sorrentino F, Iovane A, Vetro A, Vaccari A, Mantia R, Midiri M. Role of high-resolution ultrasound in guiding treatment of idiopathic plantar fasciitis with minimally invasive techniques. Radiol Med. 2008;113:486–495. doi: 10.1007/s11547-008-0277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Tiwari M, Bhargava R. Platelet rich plasma therapy: a comparative effective therapy with promising results in plantar fasciitis. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2013;4:31–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2013.01.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Uğurlar M, Sönmez MM, Uğurlar ÖY, Adıyeke L, Yıldırım H, Eren OT. Effectiveness of four different treatment modalities in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis during a 36-month follow-up period: a randomized controlled trial. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2018;57:913–918. doi: 10.1053/J.JFAS.2018.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Uygur E, Aktaş B, Eceviz E, Yilmazoğlu EG, Poyanli O. Preliminary report on the role of dry needling versus corticosteroid injection, an effective treatment method for plantar fasciitis: a randomized controlled trial. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2018;58:301–305. doi: 10.1053/J.JFAS.2018.08.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Vahdatpour B, Kianimehr L, Moradi A, Haghighat S. Beneficial effects of platelet-rich plasma on improvement of pain severity and physical disability in patients with plantar fasciitis: a randomized trial. Adv Biomed Res. 2016;5:179. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.192731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Whittaker GA, Munteanu SE, Menz HB, Gerrard JM, Elzarka A, Landorf KB. Effectiveness of foot orthoses versus corticosteroid injection for plantar heel pain: the SOOTHE randomized clinical trial. J Orthop Sport Phys Ther. 2019;49:491–500. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2019.8807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yesiltas F, Aydogan U, Parlak A, Sari O, Akgun V, Kurklu M, et al. The comparison of intralesionary steroid injection and autologous venous blood injection in patients with plantar fasciitis. Acta Medica Mediterr. 2015;31:711–716. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Yucel I, Ozturan KE, Demiraran Y, Degirmenci E, Kaynak G. Comparison of high-dose extracorporeal shockwave therapy and intralesional corticosteroid injection in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2010;100:105–110. doi: 10.7547/1000105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Yucel Ufuk, Kucuksen Sami, Cingoz Havva T, Anlıacik Emel, Ozbek Orhan, Salli Ali, Ugurlu Hatice. Full-length silicone insoles versus ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection in the management of plantar fasciitis: A randomized clinical trial. Prosthetics and Orthotics International. 2013;37(6):471–476. doi: 10.1177/0309364613478328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yuzer S, Sever A, Gurcay E, Unlu E, Cakci A. Comparison of the effectiveness of laser therapy and steroid injection in epin calcanei. Turkiye Fiz Tip ve Rehabil Derg. 2006;52:68–71. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Zamani B, Hadizadeh-Moghdam M, Moravveji SA. Comparing the effect of low-power laser therapy with methylprednisolone injection in unilateral plantar fasciitis. J Kashan Univ Med Sci. 2014;17:545–552. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2005;5. 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 68.Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Atkins D, Brozek J, Vist G, et al. GRADE guidelines: 2. Framing the question and deciding on important outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64:395–400. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Di Blasi Z, Harkness E, Ernst E, Georgiou A, Kleijnen J. Influence of context effects on health outcomes: a systematic review. Lancet. 2001;357:757–762. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zhang W, Doherty M. Efficacy paradox and proportional contextual effect (PCE) Clin Immunol. 2018;186:82–86. doi: 10.1016/J.CLIM.2017.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Zou K, Wong J, Abdullah N, Chen X, Smith T, Doherty M, et al. Examination of overall treatment effect and the proportion attributable to contextual effect in osteoarthritis: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75:1964–1970. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Landorf KB, Radford JA, Hudson S. Minimal important difference (MID) of two commonly used outcome measures for foot problems. J Foot Ankle Res. 2010;3:7. doi: 10.1186/1757-1146-3-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Scholten RJPM, de Beurs E, Bouter LM. From effect size into number needed to treat. Lancet. 1999;354:598. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)77952-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Boutron I, Tubach F, Giraudeau B, Ravaud P. Blinding was judged more difficult to achieve and maintain in nonpharmacologic than pharmacologic trials. J Clin Epidemiol. 2004;57:543–550. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2003.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Acevedo JI, Beskin JL. Complications of plantar fascia rupture associated with corticosteroid injection. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19:91–97. doi: 10.1177/107110079801900207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Sellman JR. Plantar fascia rupture associated with corticosteroid injection. Foot Ankle Int. 1994;15:376–381. doi: 10.1177/107110079401500706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Dean BJF, Lostis E, Oakley T, Rombach I, Morrey ME, Carr AJ. The risks and benefits of glucocorticoid treatment for tendinopathy: a systematic review of the effects of local glucocorticoid on tendon. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43:570–576. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Smidt N, van der Windt DA, Assendelft WJ, Devillé WL, Korthals-de Bos IB, Bouter LM. Corticosteroid injections, physiotherapy, or a wait-and-see policy for lateral epicondylitis: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;359:657–662. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07811-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Search strategy. The search strategy used for the systematic search. (PDF 61 kb)
Criteria used for judgements of GRADE. (PDF 64 kb)
Results of single trials that investigated pain. A summary of the findings from single trials that investigated pain but were not included in a meta-analysis. (PDF 95 kb)
Results of single trials that investigated ‘first step’ pain. A summary of the findings from single trials that investigated ‘first step’ pain but were not included in a meta-analysis. (PDF 109 kb)
Results of single trials that investigated function. A summary of the findings from single trials that investigated function but were not included in a meta-analysis. (PDF 82 kb)
Results of single trials that investigated plantar fascia thickness. A summary of the findings from single trials that investigated plantar fascia thickness but were not included in a meta-analysis. (PDF 65 kb)
Data Availability Statement
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is available in the figshare repository:
Whittaker, Glen; Munteanu, Shannon; Menz, Hylton; Bonanno, Daniel; Gerrard, James; Landorf, Karl (2018): Extracted data for a systematic review and meta-analyses of corticosteroid injection for plantar heel pain. Figshare. Dataset. 10.4225/22/5afa8ad63d93d