Abstract
Intestinal enterococci indicate the fecal contamination of bathing waters. This study defines the performance characteristics of the reference method ISO 7899–2 (2000) with water samples collected from inland and coastal bathing areas in Finland. From a total of 341 bacterial isolates grown on Slanetz and Bartley medium, 63.6 % were confirmed as intestinal enterococci on bile aesculin agar. The partial 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis clades accounted for 93.1% of the confirmed isolates. The range of the false positive and false negative rate of the ISO 7899–2 was 0.0–18.5% and 5.6–57.1%, respectively, being affected by the presumptive colony count on the membrane. The analysis multiple sample volumes is proposed to reach 10–100 colonies per membrane when 47mm diameter membranes are used to prevent overestimation of low counts and underestimation of the high counts.
Keywords: bathing water quality monitoring, Enterococcus spp, partial 16S rRNA sequencing, ISO 7899–2, slanetz and bartley medium
Introduction
Intestinal enterococci are used as fecal indicator bacteria (FIB) for bathing water quality monitoring in European Union (EU) member countries (European Bathing Water Directive; 2006/7/EC). The presence of intestinal enterococci is considered as a sign of fecal contamination in environmental waters since they are released through feces of warm blooded animals, including human beings (Wheeler et al., 2002). The species distribution of enterococci released from feces of different host animals varies and is thought to be similar between the individuals of the same host species having similar feeding habits (Layton et al., 2010). The prevalence of certain Enterococcus species has been proposed to provide useful information of the fecal contamination sources (Moore et al., 2006). Specifically, Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis are considered the most prevalent Enterococcus species in human feces (Moore et al., 2006; Layton et al., 2010). Pourcher et al. (1991) and Wheeler et al. (2002) reported that the host range of E. faecalis is limited to dogs, humans, and chickens. However, the Enterococcus genus is a large group of bacteria and not all species originate from feces. For example, Enterococcus mundtii, Enterococcus casseliflavus, Enterococcus aquimarinus and Enterococcus sulfureus are often associated with vegetation (Muller et al., 2001; Moore et al., 2006).
Monitoring regulations for bathing water are based on the FIB counts which indicate the extent, but not the source, of fecal contamination. Different contamination sources can cause varying levels of waterborne infection risk for bathers, sometimes without a clear correlation to FIB counts. Some human pathogens such as enteric viruses are host-specific and originate from human feces (Colford et al., 2007). For such agents, contamination of bathing water with human fecal material represents a higher infection risk than contamination from other sources (Colford et al., 2007). However, non-human fecal contamination can also contribute to infection risks at bathing areas due to the possible occurrence of zoonotic pathogens such as Escherichia coli O157:H7, Campylobacter, Salmonella, Leptospira, Cryptosporidium, and Giardia (as reviewed in USEPA, 2009). Thus, identifying sources of contamination is important to accurately estimate the human health risk and eliminate it.
The international standard method ISO 7899–2 (2000) is the reference method for enumeration of intestinal enterococci according to the European Bathing Water Directive (2006/7/EC), focusing on four intestinal Enterococcus species: E. faecalis, E. faecium, Enterococcus durans and Enterococcus hirae. However, the ISO 7899–2 standard does not include specifications of the performance characteristics of the method or specify the reliable counting range for the enterococci enumeration. The present study focused on characterizing the Enterococcus species isolated using the ISO 7899–2 method from the bathing water samples and evaluated the categorical performance characteristics (i.e., sensitivity, specificity, selectivity, false positive rate, false negative rate, and efficiency) of the method. In addition, we applied a combination of fecal source tracking and regulatory bathing water quality monitoring to support the interpretation of FIB count results.
Materials and methods
Bathing water samples
A total of 21 water samples were collected from five bathing areas in the central and western part of Finland during the bathing season of 2013 with the help of local health authorities (Table 1). Collected samples were transported to the laboratory in ice coolers, stored at 3 ± 2 °C and analysed within 24 h.
Table 1.
Public bathing areas sampled in the summer of 2013 in central and western part of Finland. Characteristics of the bathing area are reported by the local health protection authorities (Valvira, 2015).
| Sampling site | Type of bathing area | Estimated number of bathers / day during the bathing season | Bathing water classification* | Identified risks for water quality in the bathing water profile | Beach facilities | Number of samples |
| A | Inland EU bathing area | >100 | Excellent | Runoffs through a nearby stream, waterfowl | Sandy beach, toilets, waste bins | 3 |
| B | Inland EU bathing area | up to 400 | Sufficient | Sewage overflow from a pumping station through rain water pumping station, waterfowl | Sandy beach, toilets, park around the beach | 4 |
| C | Inland EU bathing area | up to 1350 | Good | Cyanobacteria due to the eutrophication, sewage overflows from pumping stations, sewage effluents, runoff from rain water system | Two sandy beaches, toilet, wide parks, playground, tennis court | 3 |
| D | Coastal EU bathing area | >100 | Poor | Waterfowl (gulls), scattered loading, sewage overflows from pumping stations | Sandy beach, toilets, waste bins, camping area beside, different activities for users | 6 |
| E | Coastal small national bathing area | not available | not available | Profile not available. Dense aquatic vegetation in a shallow bay reported, runoffs from nearby streams, waterfowl and sewage discharges | not available | 5 |
The classification excellent> good> sufficient> poor is based on based on quality results in 2009–2012.
Enterococci enumeration
Intestinal enterococci were enumerated using the ISO 7899–2 method as described by Pitkänen et al. (2013). In brief, after filtration of water volumes, membranes (GN6, Pall Life Sciences, Michigan, and USA) were incubated on Slanetz & Bartley medium (S&B, Oxoid Ltd. Basingstoke, Hampshire, UK) at 36±2 °C for 44±4 h. The sample volumes 1, 10, 100 and/or 1000 mL were used with the aim to produce 10–100 presumptive colonies per membrane to follow the principles specified in the standard ISO 8199 (2005). With a few exceptions, the total colony counts ranged from 1 to 149 colonies per membrane. All colonies detected were raised with red, maroon, or pink color and were considered as presumptive enterococci, even when the color was only light or the colony size was very small. After counting the presumptive enterococci, the membranes containing presumptive enterococci colonies were transferred on preheated bile aesculin azide medium (BEA, Scharlau, Barcelona, Spain) and incubated at 44±0.5 °C for 2 h. Black or brown color formation on the BEA medium confirmed the presumptive colony was intestinal enterococci. When no color formation on the BEA was observed, the presumptive colony was defined as unconfire4med. All or at least ten confirmed and ten unconfirmed colonies per each analyzed sampled were sub-cultured on non-selective tryptone soya agar medium (TSA, Oxoid Ltd.) and incubated at 36 ± 2 °C for 2 days. The isolates were stored at −75 °C in nutrient broth containing 15 % glycerol.
Partial 16S rRNA sequencing of the bacteria isolated from Slanetz and Bartley medium
To prepare the total genomic DNA of the isolates for the further analysis, sterile inoculating loops were used to transfer bacterial biomass into 0.1 mL of sterile deionized water and stored at −18 °C. Subsequently, the bacterial suspensions were heat-treated at 95 °C for 10 minutes. The Enterococcus spp. Specific quantitative PCR (qPCR) assay targeting the 23S rRNA gene (Ludwig & Schleifer 2000) was used to confirm the identity of the isolates. The heat-treated suspensions were shipped on dry ice to the laboratory of United States Environmental Protection Agency (Cincinnati, OH) for 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The partial 16S rRNA gene sequences were obtained by using universal bacterial primers 8F (AGAG TTTGATCCTGGCTCAG) and 787R (CGACTACCAGGGTATCT AAT), as described by Ryu et al. (2013).
Unique phylogenetic contigs were selected on the basis of sequence homology with bioinformatics software CD-hits (98% cutoff value) (Li and Godzik, 2006). The representative contigs were aligned with reference sequences collected from National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) GenBank. A neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree was constructed with Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 6 with 1000 bootstrap value and muscle sequence aligner (Tamura et al., 2013). The species identification of the isolates was initially made on the basis of phylogenetic clades, and was cross-validated in silico with cluster sequence aligner in MEGA-6 with Enterococcus genus specific primer Ent1 targeting to 16S rRNA sequence as additional in silico confirmation. Species-specific primers Faecium1 (E. faecium), Faecalis1 (E. faecalis) and Casseli1 (E. casseliflavus) were also tested in silico as described in Ryu et al. (2013) (Table 2). The species identification was also confirmed with RDP seqmatch (Cole et al. 2013).
Table 2.
The oligonucleotide sequences used in the (RT)-qPCR assays in the study.
| Assay name | Target species | Sequence 5’to 3’ | Length (bp) | Reference |
| Entero1 | Enterococcus spp. | ECST748F: AGAAATTCCAAACGAACTTG
ENC854R: CAGTGCTCTACCTCCATCATT GPL813TQ: 6FAM-TGGTTCTCTCCGAAATAGCTTTAGGGCTA-TAMRA |
92 | Ludwig & Schleifer (2000) |
| Ent1 | Enterococcus spp. | Ent151F: ACACTTGGAAACAGGTGC Ent376R: TCGGTCAGACTTKCGTCC |
243 | Ryu et al. (2013) |
| Faecalis1 | Enterococcus faecalis | FaecalF: CGCTTCTTTCCTCCCGAGT FaecalR: GCCATGCGGCATAAACTG FaecalP: 6FAM-CAATTGGAAA GAGGAGTGGCGGACG-TAMRA |
143 | Ryu et al. (2013) |
| Casseli1 | Enterococcus casseliflavus | CasselF: GGAGCTTGCTCCACCGAA CasselR: TTTCTTCCATGCGGAAAATAGT CasselP: 6FAM-CGAACGGGTGAGTAACACGTGGGTAA-TAMRA |
132 | Ryu et al. (2013) |
| Faecium1 | Enterococcus faecium | CiumF: TTCTTTTTCCACCGGAGCTT CiumR: AACCATGCGGTTTYGATTG CiumP: 6FAM-AGTAACACGTGGGTAACCTGCCCATCAGA-TAMRA |
141 | Ryu et al. (2013) |
| EC23S857 | E. coli | F: GGTAGAGCACTGTTTtGGCA R: TGTCTCCCGTGATAACtTTCTC P: 6FAM-TCATCCCGACTTACCAACCCG-TAMRA |
88 | Chern et al. (2011) |
| GenBac 3 | Bacteroidetes spp. | GenBactF3: GGGGTTCTGAGAGGAAGGT
GenBactR4: CCGTCATCCTTCACGCTACT GenBactP2: 6FAM-CAATATTCCTCACTGCTGCCTCCCGTA-TAMRA |
129 | Siefring et al. (2008) |
| HF183 | Human-specific Bacteroidales | HF183–1: ATCATGAGTTCACATGTCCG
BthetR1: CGTAGGAGTTTGGACCGTGT BthetP1: 6FAM-CTGAGAGGAAGGTCCCCCACATTGGA-TAMRA |
167 | Haugland et al. (2010) |
| Pig-2-Bac | Pig-specific Bacteroidales | Pig-2-Bac41F: GCATGAATTTAGCTTGCTAAATTTGAT
Pig-2-Bac163Rm: ACCTCATACGGTATTAATCCGC Pig-2Bac113MGB: 6FAM-TCCACGGGATAGCC-BHQ1 |
117 | Mieszkin et al. (2009) |
| Rum-2-Bac | Ruminant-specific Bacteroidales | BacB2–590F: ACAGCCCGCGATTGATACTGGTAA
Bac708Rm: CAATCGGAGTTCTTCGTGAT BacB2–626P: 6FAM-ATGAGGTGGATGGAATTCGTGGTGT-BHQ1 |
99 | Mieszkin et al. (2010) |
| Gull4 | Gull-specific Catellicoccus marimammalium |
qGull7F: CTTGCATCGACCTAAAGTTTTGAG
qGull8R: GGT TCT CTG TAT TAT GCG GTA TTA GCA qGull7P: FAM-ACACGTGGGTAACCTGCCCATCAGA-TAMRA |
116 | Ryu et al. (2012) |
| Adenoviruses | Human adenoviruses | JTVXF: GGACGCCTCGGAGTACCTGAG JTVXR: ACIGTGGGGTTTCTGAACTTGTT JTVXP: 6FAM-CTGGTGCAGTTCGCCCGTGCCA-BHQ1 |
96 | Jothikumar et al. (2005) |
| Noroviruses | GI noroviruses | NVGIF: GCYATGTTCCGCTGGATG NVGIR: CCTTAGACGCCATCATCATT NVGIP-MGB: VIC-TGGACAGGAGAYCGC-MGBNFQ |
95 | Kauppinen et al. (2014) |
| Noroviruses | GII noroviruses | QNIF2d:
ATGTTCAGRTGGATGAGRTTCTCWGA COG2R: TCGACGCCATCTTCATTCACA RING2-TP: 6FAM-TGGGAGGGCGATCGCAATCT-BHQ1 |
88 | Loisy et al. (2005); Kageyama et al. (2003) |
Performance analysis of the ISO 7899–2 method for enterococci monitoring
The performance of the standard method ISO 7899–2 for intestinal enterococci enumeration from bathing water samples was tested by calculating false positive rate, false negative rate, sensitivity, specificity, selectivity and efficiency as defined in the standard method ISO 13843 (2017; previous version published as technical report ISO/TR 13843 in 2000) using the Equations (1) to (6). True positive isolates were defined as isolates that were confirmed as intestinal enterococci in the BEA confirmation test (i.e., the primary confirmatory test: ISO 13843:2017) and which belong to either E. faecalis or E. faecium clade using phylogenetic analysis ( i.e., the secondary identification test; ISO 13843:2017). The unconfirmed isolates which belong to E. faecalis or E. faecium clades were defined as false negative isolates. The isolates confirmed as intestinal enterococci, but did not belong to E. faecalis or E. faecium clades, were defined as false positive isolates. True negative isolates were defined as unconfirmed isolates that did not belong to E. faecalis or E. faecium clades
| (Equation 1.) |
| (Equation 2.) |
| (Equation 3.) |
| (Equation 4.) |
| (Equation 5.) |
| (Equation 6.) |
Quantification of the other fecal microbes and source tracking identifiers
Escherichia coli was enumerated using Colilert Quanti-Tray method in the local water laboratories near the bathing water sampling locations according to standard method ISO 9308–2 (2012). All the other microbiological analyses were carried out in the laboratory of National Institute for Health and Welfare (Kuopio, Finland). The primers and probes used in the qPCR and reverse transcriptase (RT)-qPCR assays of this study are listed in the Supplementary material (Table 2).
Noroviruses and adenoviruses were concentrated from 800–2000 mL water samples as previously described (Jalava et al., 2014), and using glass fiber pre-filters (Millipore). Viral nucleic acids were extracted and detected using previously described RT-qPCR and qPCR methods (Kauppinen et al., 2012; 2014), except that Taqman Environmental Master Mix 2.0 (Life Technologies) was used in the adenovirus qPCR assay.
Thermotolerant Campylobacter spp. (C. jejuni, C. coli, C. lari and C. upsaliensis) were analysed semi-quantitatively as previously described (Hokajärvi et al., 2013) and following the principles in the standard ISO 17995 (2005). In brief, sample volumes of 10, 100 and 1000 mL were concentrated using membranes with 0.45 µm pore size (GN6, Pall Life Sciences, Michigan, USA) and enriched in Bolton and Preston broths. Typical Campylobacter growth on complete modified-charcoal cefoperazone desoxycholate medium (mCCDA, Oxoid Ltd.) was confirmed by Gram staining and motility, the absence of aerobic growth, oxidase and catalase tests. The species identification of thermotolerant Campylobacter isolates from water was achieved by a real-time qPCR method coupled with restriction fragment analysis as previously described by Pitkänen et al. (2008).
Bacteroidetes spp. and source tracking markers of human, gull, pig and ruminant feces were quantified using DNA-based qPCR assays and RNA-based RT-qPCR assays as described earlier by Pitkänen et al. (2013). In brief, a volume of up to 300 mL water was filtered through a polycarbonate membrane with the pore size 0.4 µm (Nuclepore Polycarbonate, Whatman, Kent, UK). The membranes were stored at −75 °C prior to the nucleic acid extraction, cDNA synthesis and the target gene quantification.
Results
Fecal microbes and fecal source identifiers
Bathing areas with prior indication of microbiological quality problems or existing water quality hazards were selected for this study. During the sampling campaign, two coastal bathing areas exceeded the water quality standards (Table 3). The national threshold value for a single sample (STM, 2008a; STM, 2008b) was exceeded in a total of five samples for intestinal enterococci and in two samples for E. coli from the coastal sampling sites D and E. The confirmation rates for intestinal enterococci varied from 8% to 100%, being exceptionally high at site E (small coastal bathing area). In the sampling site B (inland bathing area), the counts of enterococci and E. coli did not exceed the quality standards for the inland waters but the RNA-based qPCR signals of Enterococcus spp. and E. coli specific genetic markers peaked in August (Table 3).
Table 3.
Culturable counts of enterococci and E. coli, RNA and DNA -based gene copy numbers of Enterococcus spp. (Entero1), E. coli (EC23S857), Bacteroidetes spp. (GenBac3), human-specific Bacteroidetes (HF183) and gull-specific Catellicoccus marimammalium (Gull4) generated using RT-qPCR and qPCR, respectively, gene copy numbers of adenoviruses and semi-quantitative count estimates of Campylobacter spp. in bathing waters around Finland.
| Location | Sampling date (2013) | Fecal indicator counts | Fecal indicator genetic markers (gene copy number log10/100ml) | Host-specific source identifiers (gene copy number log10/100ml) | Waterborne pathogens | ||||||||||||
| Presumptive enterococci (CFU/100ml) | Intestinal enterococci
(CFU/100ml) |
Confirmation rate (%) |
E. coli
(MPN/100ml) |
Entero1 | EC23S857 | GenBac3 | HF183 | Gull4 | Adenoviruses (GC/L) |
Campylobacter spp. (CFU/L) | |||||||
| RNA | DNA | RNA | DNA | RNA | DNA | RNA | DNA | RNA | DNA | ||||||||
| A | 4th Jun | 60 | 20 | 33 | 1 | BDL | BDL | BDL | <LOQ | BDL | 3.85 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | 900 | 1–10 a, b |
| 23rd Jul | 27 | 23 | 85 | 19 | 1.88 | BDL | 4.88 | <LOQ | 5.07 | 3.56 | BDL | BDL | 4.83 | 2.75 | BDL | 10–100c | |
| 13th Aug | 12 | 9 | 75 | 5 | BDL | BDL | 4.62 | <LOQ | 5.37 | 3.97 | BDL | BDL | 4.26 | BDL | BDL | 10–100a | |
| B | 5th Jun | 31 | 12 | 39 | 75 | BDL | BDL | BDL | <LOQ | BDL | 4.63 | BDL | 3.59 | BDL | BDL | <LOQ | ND |
| 17th Jun | 55 | 20 | 36 | 110 | 3.61 | BDL | 3.56 | 3.46 | 4.70 | 4.63 | 4.93 | 4.00 | 5.07 | 2.17 | BDL | ND | |
| 10th Jul | 55 | 25 | 45 | 45 | BDL | BDL | 1.95 | <LOQ | 3.90 | 4.44 | 4.52 | 3.48 | BDL | BDL | BDL | 10–100a, d | |
| 6th Aug | 550 | 190 | 35 | 580 | 6.20 | 3.14 | 5.84 | 4.28 | 6.83 | 5.48 | 4.89 | 4.82 | 4.45 | BDL | <LOQ | 1–10a | |
| C | 25th Jul | 37 | 3 | 8 | 150 | 2.00 | BDL | 4.42 | <LOQ | 5.37 | 3.95 | 4.85 | 3.05 | 5.29 | 2.33 | BDL | 10–100a, b |
| 16th Jul | 63 | 46 | 73 | 340 | 2.37 | BDL | 4.65 | 3.79 | 5.51 | 5.24 | 5.58 | 4.63 | 3.32 | BDL | <LOQ | 1–10a | |
| 6th Aug | 8 | 3 | 38 | 15 | BDL | BDL | 3.84 | <LOQ | 5.07 | 4.41 | 3.08 | 3.84 | 4.27 | 2.50 | BDL | 1–10a, c | |
| D | 4th Jun | 250 | 190 | 76 | 2400* | BDL | BDL | BDL | 4.24 | BDL | 4.08 | BDL | BDL | BDL | 3.27 | BDL | BDL |
| 17th Jun | 390 | 140 | 36 | 290 | BDL | BDL | BDL | 3.80 | BDL | 4.03 | BDL | BDL | BDL | 3.85 | BDL | ND | |
| 2nd Jul | 482 | 409* | 85 | NA | 2.11 | BDL | 4.67 | 4.77 | 4.44 | 4.14 | BDL | BDL | 6.17 | 4.43 | BDL | 1–10c, d | |
| 16th Jul | 99 | 71 | 72 | 2400* | 3.98 | 3.98 | 4.75 | 5.11 | 3.55 | 4.72 | BDL | BDL | 5.58 | 5.22 | BDL | 1–10d | |
| 29th Jul | <1 | <1 | NA | 9 | BDL | BDL | 3.56 | BDL | 4.67 | 3.40 | BDL | BDL | 2.48 | 2.79 | BDL | BDL | |
| 12th Aug | 37 | 12 | 32 | 32 | BDL | BDL | BDL | <LOQ | 1.26 | 3.62 | BDL | BDL | BDL | 2.10 | BDL | BDL | |
| E | 5th Aug | 4600 | 4600* | 100 | NA | 2.48 | 2.91 | BDL | <LOQ | 2.98 | 4.16 | BDL | BDL | BDL | 2.35 | BDL | ND |
| 13th Aug | 1600 | 1600* | 100 | 10 | BDL | BDL | BDL | <LOQ | 4.27 | 3.86 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | |
| 19th Aug | 149 | 147 | 99 | <10 | BDL | BDL | 3.92 | <LOQ | 5.44 | 4.16 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | |
| 19th Aug | 1000 | 1000* | 100 | <10 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| 27th Aug | 420 | 420* | 100 | <10 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
BDL- Below the detection limit, <LOQ- Below the limit of quantification, ND- not done, NA- not available.
Campylobacter jejuni
Campylobacter coli
Campylobacter lari
Campylobacter spp.
Exceedance of the national bathing water quality standard for a single sample marked as bold (STM, 2008a, b).
RNA-based RT-qPCR and DNA-based qPCR assays were used to detect the molecular source identifiers (Table 3). The GenBac3 marker of Bacteroidetes spp. was detected in all water samples. Based on the HF183 genetic marker, human-specific fecal contamination was prevalent at bathing sites B and C but remained absent from other areas. The gull-specific Gull4 marker was detected at least once in all the bathing areas with site D showing the highest relative abundance. Swine and ruminant specific contamination (Pig-2-Bac and Rum-2-Bac markers) were not detected in any of the samples. RNA-based RT-qPCR resulted in higher marker copy numbers more often than the DNA-based qPCR (Table 4).
Table 4.
Comparison of the molecular source identifier copy numbers generated by RNA-based RT-qPCR and DNA-based qPCR methods using of Enterococcus spp. (Entero1), E. coli (EC23S857), Bacteroidetes spp. (GenBac3), human-specific Bacteroidetes (HF183) and gull-specific Catellicoccus marimammalium (Gull4) assays.
| Assay | RNA-based signal higher | Equal or non-detect | DNA-based signal higher |
| Entero1 | 6/19 (32%) | 12/19 (63%) | 1/19 (5%) |
| EC23S857 | 10/19 (53%) | 0/19 (0%) | 9/19 (47%) |
| GenBac3 | 11/19 (58%) | 0/19 (0%) | 8/19 (42%) |
| HF183 | 5/19 (26%) | 12/19 (63%) | 2/19 (11%) |
| Gull4 | 9/19 (47%) | 5/19 (26%) | 5/19 (26%) |
While noroviruses were not detected in any of the samples, four samples collected from the inland bathing areas were positive for adenoviruses (three out of four detections were below the quantification limit of the method) (Table 3). Campylobacter was abundant in all eight studied samples taken from the inland bathing areas, but only in two of the seven studied samples in coastal bathing areas (Table 3). C. jejuni and C. coli were found only from inland bathing areas, C. jejuni being more common. C. lari was found from inland bathing areas A and C and also from coastal bathing area D.
Species distribution of bacteria isolated using the ISO 7899–2 method
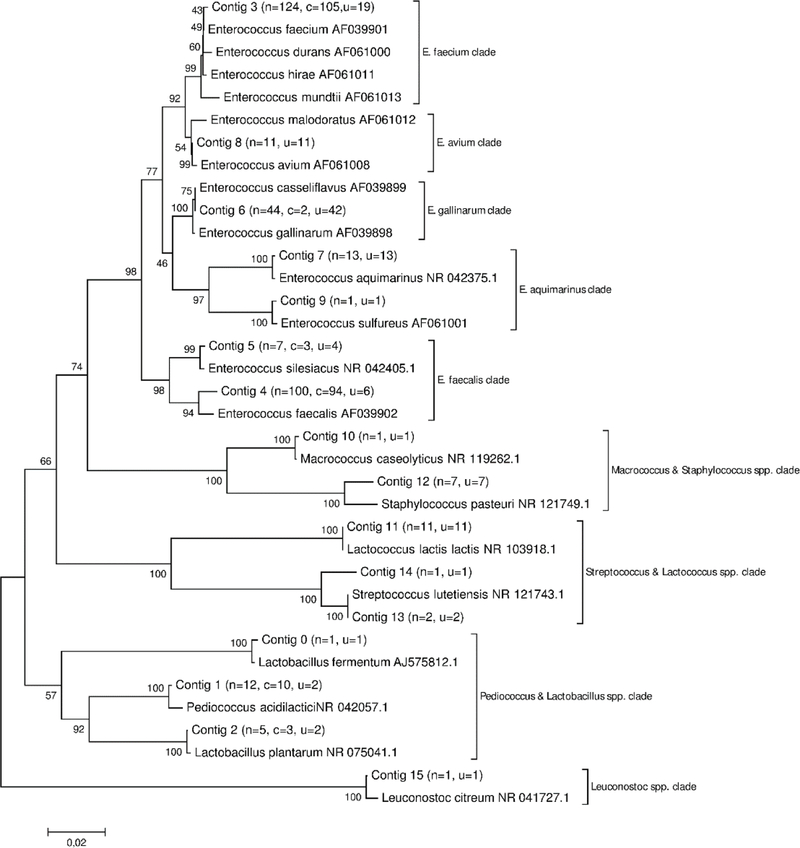
A partial 16S rRNA sequence was successfully obtained for a total of 341 bacterial colonies grown on Slanetz and Bartley medium, among them, 217 were confirmed as intestinal enterococci on BEA agar, and 124 of the isolates remained unconfirmed (Table 5). The colonies were collected from a total of 27 membrane filters from two to nine membranes on BEA medium from each bathing water site (A-B). Based on phylogenetic analysis, the confirmed isolates were grouped into three bacterial genera: Enterococcus spp., Pediococcus spp. and Lactobacillus spp. (Figure 1). Among the unconfirmed bacterial isolates, eight different genera were identified: Enterococcus spp., Lactococcus spp., Staphylococcus spp., Lactobacillus spp., Staphylococcus spp., Pediococcus spp., Leuconostoc spp. and Macrococcus spp. (Figure 1). Intestinal enterococci clades (E. faecium and E. faecalis clades) represented 67.7 % of the isolates (231 out of 341). Altogether, 88.0 % (300 out of 341) of the bacteria isolated from the colonies grown on the S&B medium in the bathing water analysis belonged to the genus Enterococcus spp. The rest of the isolates (12.0 %, n=41) were non-enterococci Gram-positive bacteria.
Table 5.
Distribution of confirmed and unconfirmed enterococci isolates of the ISO 7899–2 method in the intestinal enterococci, environmental enterococci and non-enterococci clades based on the phylogenetic analysis of the partial 16S rRNA sequences.
| Intestinal enterococci | Environmental enterococci | Non-enterococci | ||||||||
| Site | E. faecium clade | E. faecalis clade | E. avium clade | E. gallinarum clade | Other enterococci | Macrococcus spp. & Staphylococcus spp. clade | Streptococcus spp. & Lactococcus spp. clade | Lactobacillus spp. & Pediococcus spp. clade | Leuconostoc spp. clade | Total |
| Number of confirmed isolates | ||||||||||
| A | 12 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 27 |
| B | 31 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 44 |
| C | 13 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| D | 47 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 70 |
| E | 2 | 54 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 56 |
| Total (confirmed) | 105 | 97 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 217 |
| Number of unconfirmed isolates | ||||||||||
| A | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| B | 4 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 35 |
| C | 4 | 1 | 2 | 13 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27 |
| D | 10 | 5 | 1 | 20 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 43 |
| E | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Total (unconfirmed) | 19 | 10 | 11 | 42 | 14 | 8 | 14 | 6 | 1 | 124 |
| Total (all) | 124 | 107 | 11 | 44 | 14 | 8 | 14 | 18 | 1 | 341 |
Figure 1.
Unrooted neighbor-joining tree of bacterial 16S rRNA gene sequences obtained during bathing water monitoring using ISO 7899–2 method. n; the total number of isolates in each contig. c; the total number of confirmed isolates. u; the total number of unconfirmed isolates.
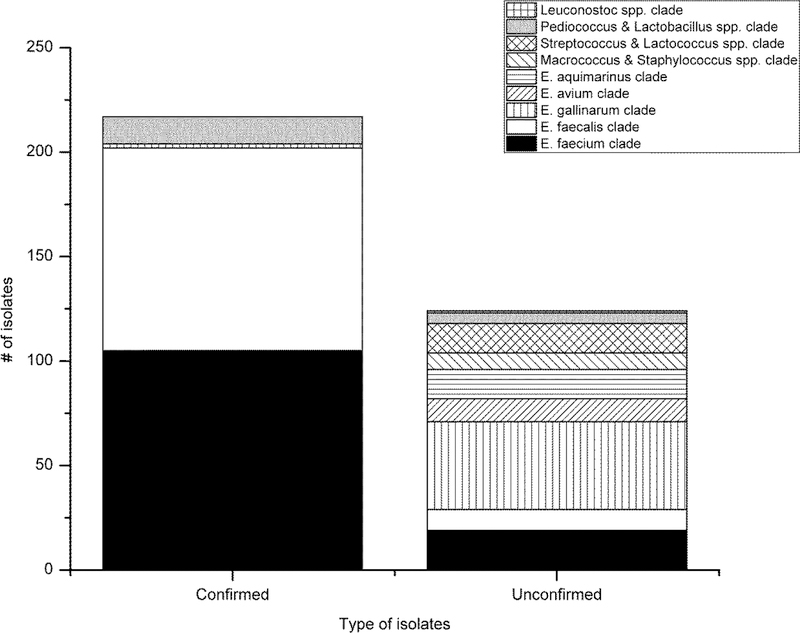
Out of the 217 isolates confirmed as intestinal enterococci in BEA agar, 202 isolates (93.1%) were classified to E. faecalis and E. faecium clades and were considered as true positives (Table 5, Figure 2.a). The other confirmed isolates (n=15) were classified as E. gallinarum, Pediococcus spp. and Lactobacillus spp. and were considered as false positive results. Among the 124 unconfirmed isolates; 29 were E. faecalis and E. faecium and were considered as false negative results (Table 5, Figure 2.a). A total of 76.6 % of the unconfirmed isolates were considered as true negatives as they belonged to clades associated with environmental enterococci and non-enterococci species. The true negatives identified (i.e. isolates being able to grow on Slanetz and Bartley medium, but remaining unconfirmed on BEA medium) included environmental enterococci species Enterococcus avium, E. casseliflavus, E. aquimarinus and E. sulfureus and other genera like Lactococcus, Staphylococcus, Leuconostoc and Macrococcus (Figure 1).
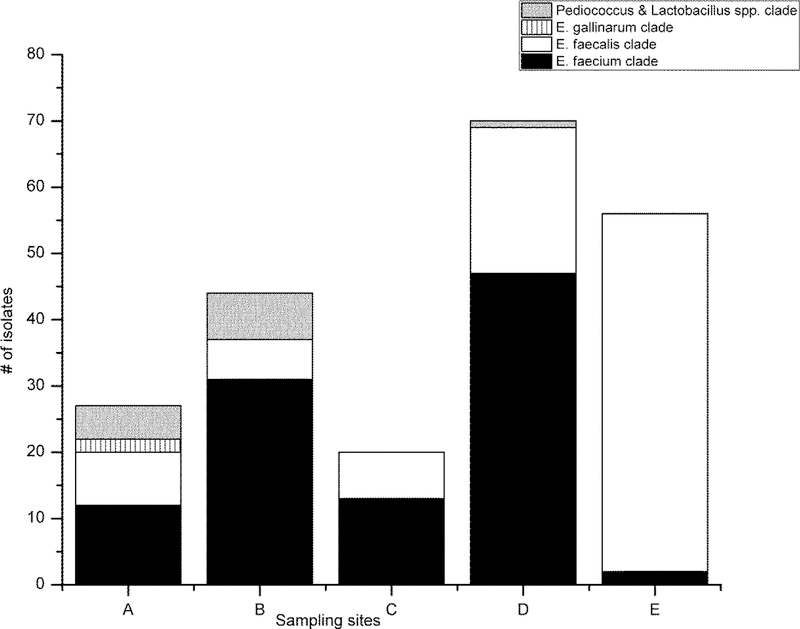
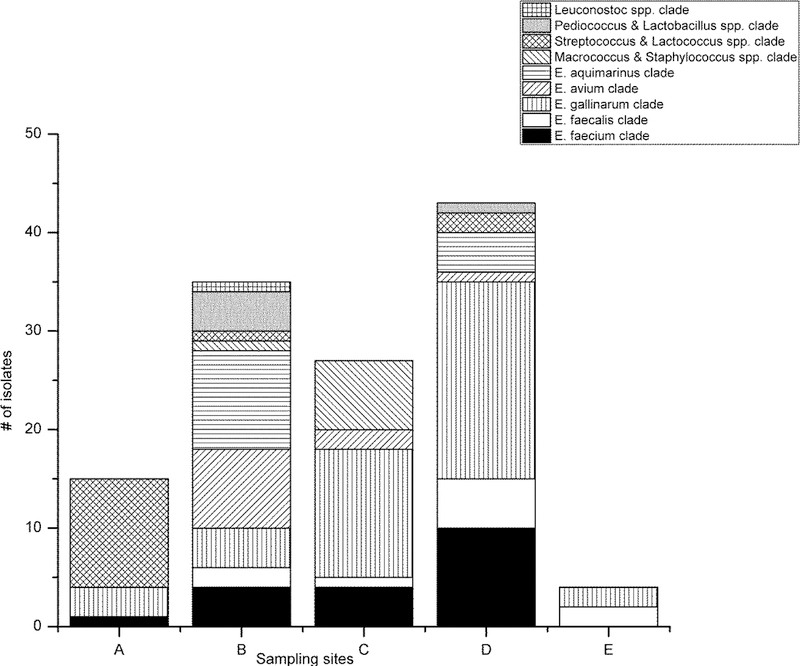
Figure 2.
Distribution of (a) the total confirmed and unconfirmed isolates in the bacterial clades, and the bacterial clade identification of (b) the confirmed isolates and (c) the unconfirmed isolates from the study sites (A-E).
The isolates identified as false positives (n=15) or false negatives (n=29) were re-streaked from the storage stock and sub-cultured on TSA medium (at 36 ± 2 °C for 2 days) prior to streaking on the BEA medium. The repetition of the BEA confirmation from the pure cultures showed that only three isolates out of 15 false positives (two Lactobacillus spp. isolates and one Pediococcus spp. isolate) were truly able to produce blackish color on the BEA medium. All the unconfirmed 29 isolates identified as false negatives according to method ISO 7899–2 were positive and confirmed to be intestinal enterococci when re-streaked from the pure culture on the BEA.
To further confirm the phylogenetic clustering, the isolates were challenged against 23S rRNA based Enterococcus spp. specific qPCR assay Entero1 (Ludwig and Schleifer, 2000) and the corresponding partial 16S rRNA sequence was tested in silico against 16S rRNA based Enterococcus spp. specific Ent1 primer (Ryu et al., 2013). All the isolates classified as Enterococcus species in the phylogenetic analysis were amplified in the Entero1 assay and their corresponding partial 16S rRNA sequences aligned (100%) with the Ent1 primer in silico. Of the non-enterococci isolates, three out of 13 false positive Pediococcus spp. and Lactobacillus spp. isolates amplified with the Entero1 assay. However, none of the non-enterococci the partial 16S rRNA sequences aligned with the Ent1 primer in silico.
Furthermore, the partial 16S rRNA sequences of the isolates classified to the E. faecium, E. faecalis and E. gallinarum clades were tested in silico against the species-specific primers Faecium1, Faecalis1 and Casseli1 (Ryu et al., 2013), respectively. Faecium1 primer aligned with the sequences associated with the E. faecium clade (n= 124) except for one sequence that was associated with Enterococcus mundtii when further analysed with RDP seqmatch. Faecalis1 and Casseli1 primers aligned with the sequences associated with the E. faecalis and E. gallinarum clades, respectively (n=107 and n=44). In addition, Casseli1 primer aligned with the isolates classified into the E. avium clade (n=11).
Categorical performance characteristics of the ISO 7899–2 method
The categorical performance characteristics of the ISO 7899–2 method are presented in Table 4. Overall, the results indicate that the method is sufficiently sensitive, specific, selective, and efficient for the enumeration of intestinal enterococci. The confirmed isolates belonging to the E. gallinarum clade and genera Pediococcus and Lactobacillus created false positive results for the ISO 7899–2 method with a rate of 18.5% when less than ten presumptive colonies per membrane were counted and with a rate of 7.0% when the presumptive colony counts ranged from 12 to 62 per membrane (Table 4). When the colony count exceeded 100 per membrane, the false positives were no longer detected. The false positive intestinal enterococci findings originated from bathing areas of the sites A, B and D (Figure 2(b).
False negative findings were detected using the ISO 7899–2 method from all bathing areas. The number of E. faecalis and E. faecium isolates that remained unconfirmed was the highest at bathing area D (Figure 2(c), the site where the FIB counts exceeded the water quality standards. When taking into account the number of presumptive colonies on the membrane filter of the ISO 7899–2 method, it was seen that the presumptive colony count affected the false negative rates of the method (Table 4). The false negative rate was as high as 57.1% when analyzing isolates from membranes exceeding the limit of reliable counting, being more than 100 colonies per membrane. When the presumptive colony counts ranged from 12 to 62 per membrane, the false negative rate was still relatively high, being 20.9 %.
Discussion
This study confirmed that ISO 7899–2 method is a reliable method and can be applied for the enumeration of intestinal enterococci from bathing water. Most of the confirmed intestinal enterococci isolates from bathing water in Finland (i.e., 93.1%) were identified as members of E. faecalis or E. faecium clades based on their partial 16S rRNA gene sequences. E. gallinarum, Pediococcus spp. and Lactobacillus spp. isolates were false positives on the BEA medium used for Enterococcus confirmation in the ISO 7899–2 method. The false positive rate was as high as 18.5% when the presumptive colony count on Slanetz and Bartley medium membranes was less than 10 CFU, suggesting that interpreting the blackening of the BEA medium is prone to subjective errors. Even small traces of color were mistakenly interpreted as a positive result when only a few colonies were present. However, this does not explain all the false positive findings as only two Lactobacillus spp. isolates and one Pediococcus spp. isolate were able to produce blackish color on the BEA medium when BEA confirmation was repeated with the pure cultures.
As the presumptive colony count affects the method performance, it is important to determine the reliable working range of the colony counting methods. In the ISO 7899–2 method, membrane filters (usually 47 mm in diameter) with the presumptive enterococci colonies are transferred from the Slanetz and Bartley medium to the pre-heated BEA medium for confirmation. In our study, it was observed that membranes having more than 100 presumptive colonies had a false negative rate as high as 57.1%. This is because when the colonies are too dense it is difficult to see the blackening on the BEA medium correctly. In our data, presumptive colony counts ranging from 10 to 62 colonies per membrane were considered reliable for enumeration based on the recommendations presented in the standard ISO 8199 (2005). As compared to other water microbiology methods based on membrane filtration, in ISO 9308–1:2012 for coliform bacteria and E. coli enumeration, the range of quantitative determination (colonies per 47-mm membrane filter) was defined as 10–100 (Lange et. al., 2013) and in ISO 14189 (2013) for enumeration of Clostridium perfringens the validated range was 10–80.
Different media have unique ingredients for selective growth of targeted species and means to inhibit growth of non-targeted species (Ferguson et al., 2005). Enterococcus species are known to reduce triphenyltetrazolium chloride of Slanetz and Bartley medium to formazan to form red colored bacterial colonies (Slanetz and Bartley, 1957). In ISO 7899–2 method, the change in colony color is used for the presumptive enterococci identification. However, Slanetz and Bartley medium does not have any inhibitor for Gram-positive bacteria. Previously, Svec and Sedlacek (1999) have reported that other bacteria than enterococci are able to grow on the Slanetz and Bartley medium. The growth of Gram-positive bacteria other than enterococci was clearly seen in our study. In addition to the Enterococcus species, we identified Pediococcus spp., Lactobacillus spp., Lactococcus spp., Staphylococcus spp., Leuconostoc spp. and Macrococcus spp. from the colonies grown on the Slanetz and Bartley medium.
At a bathing area, the measured enterococci counts can be accumulated from multiple sources like urban runoff, wastewater treatment plants, wildlife defecation, and even from environmental sources (as reviewed in Byappanahalli et al., 2012). In our study, both intestinal and environmental species of the enterococci were detected from all studied bathing areas, although the number of environmental enterococci isolates was very low and consisted solely of E. gallinarum clade members at study sites A and E.
As noted before (Savichtcheva and Okabe, 2006; Hokajärvi et al., 2013), the FIB counts did not show relation to the presence of adenoviruses or Campylobacter spp. In addition, a recent study describes the poor indicator value of FIB in bathing waterborne norovirus outbreaks (Kauppinen et al., 2017). In our study, the exceedances of the quality standards were seen without detection of these pathogens and vice versa (i.e., these pathogens were detected when the water quality standards were not exceeded). It has been proposed that adenoviruses could be used as bathing water quality indicators, potentially indicating the presence of enteric viruses that are infectious to humans (Wyn-Jones et al., 2011). We found adenoviruses from sites B and C from where human-specific source identifier HF183 was found and adenoviruses remained absent at sites D and E where HF183 was not detected. However, site A was the exception; adenoviruses were detected but not HF183.
Besides the detection of Campylobacter species causing campylobacteriosis in humans (C. jejuni and C. coli), the third Campylobacter species identified was C. lari which is associated with waterfowl feces such as seagulls (Ryu et al., 2014). C. lari and the Gull4 marker specific for gull feces were detected at sites A, C and D. The highest Gull4 copy number (6.17 log10/100 mL) was recorded at the beginning of July from site D using the RNA-based RT-qPCR. The higher target copy numbers generated using RNA-based RT-qPCR compared to the DNA-based qPCR is in agreement with the previous studies, and the rRNA:rDNA ratio may indicate the overall activity levels of the targets (Pitkänen et al., 2013; Kapoor et al., 2014). The simultaneous exceedance of the intestinal enterococci quality standard and detection of C. lari/Gull4 indicate fresh gull feces as a source to bathing water quality deterioration at sites A, C, and D. Indeed, gull feces are a potential source of E. faecalis, as Pourcher et al. (1991) reported that 70% of the total Enterococcus isolates from seagulls were E. faecalis. However, many other enterococci species like E. avium, E. gallinarum, E. durans, E. hirae, and E. casseliflavus have been reported from gull feces (Fogarty et al., 2003).
The origin of the extremely high E. faecalis counts on the small national bathing area (coastal site E) suffering repeatedly from peaking enterococci levels remained unidentified. At this site, the high counts of enterococci were detected at the end of bathing season (in July-August). In our investigation, the E. coli counts were absent or very low and no human fecal contamination or waterborne pathogens were detected. The local environmental health authorities have had to close the bathing area due to the high counts, even though the true human health risk was questioned. In one sample, a low number of Gull4 marker specific for gull feces was seen using the DNA-based qPCR assay. The absence of Gull4 marker in the RNA-based RT-qPCR may indicate the absence of metabolically active target cells and that the contamination did not originate from fresh feces. The traces of DNA may originate from dormant, inactive, and dead cells or naked DNA occurring in the surface waters (Keer and Birch, 2003). Further, the absence of E. coli at site E supports the avian contamination source as the enterococci count per gram feces have been reported to be high on feces of wild birds while E. coli was not detected or the counts were low (Moriarty et al., 2008). However, although the presence of intestinal enterococci in the environmental water is considered as a sign of fecal contamination, environmental sources of E. faecalis and E. faecium like soil, sediments and vegetation have been reported (Badgley et al. 2011; Byappanahalli et al. 2012). Instead of fecal contamination, the blooming of aquatic plants may provide an alternative explanation for the increased enterococci counts. Indeed, green algae have been suggested to play role in the enterococci ecology as Cladophora was a source and sink of enterococci in coastal waters in the United States (Whitman et al. 2003; Verhougstraete et al. 2010). At site E of our study, the abundance of aquatic plants such as Myriophyllum spp. was noted. The invasion of common watermilfoil Myriophyllum sibiricum Komarov 1914 (Magnoliophyta: Haloragaceae) has been previously identified as a problem in shallow Åland lakes in southwestern Finland (Lindholm et al. 2008). The growth was reported as a new environmental problem resembling an underwater jungle with the surface water pH exceeding 10 without any simple solution to lake restoration. The impacts of this vegetation include oxygen deprivation due to the accumulation of decaying plant material, but its link to the growth of environmental enterococci remains unknown.
CONCLUSION
ISO 7899–2 method can be considered as a reliable method for the intestinal enterococci enumeration from bathing waters. The use of multiple sample volumes is recommended to reach the reliable counting range even in cases of peaking enterococci counts. However, intestinal enterococci counts alone was insufficient for water quality assessments. Even on the occasions of low intestinal enterococci counts, the presence of fecal pathogens was observed in some inland samples of the study. Therefore, identifying of the presence of fecal pathogens and the contaminant source at the bathing area is important for developing microbial infection risk estimates, preventing contamination events and protecting public health.
Supplementary Material
Table 6.
Performance characteristics of ISO 7899–2 method for bathing water monitoring.
| Colonies/ membrane | Median (min-max) of presumptive colony count/membrane | Number of isolates | False positive rate (%) | False negative rate (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Selectivity (%) | Efficiency (%) |
| <10 colonies | 4.5 (1–8) | 45 | 18.5 | 5.6 | 95.7 | 77.3 | 48.9 | 86.7 |
| 10–100 | 42.0 (12–62) | 234 | 7.0 | 20.9 | 87.5 | 87.5 | 56.8 | 87.6 |
| >100 colonies | 137.0 (106–149) | 42 | 0.0 | 57.1 | 77.8 | 100.0 | 66.7 | 81.0 |
| Unknown | NA | 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Total | 40.5 (1–149) | 341 | 9.0 | 18.5 | 90.1 | 82.9 | 59.2 | 87.7 |
NA; not available.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express special thanks to the local health authorities for providing the water samples for the study. Dr. Outi Zacheus, Ms. Sallamaari Siponen, Mrs. Tiina Heiskanen and Mrs. Marjo Tiittanen from the National Institute for Health and Welfare, Water Health Unit, Kuopio are acknowledged for their valuable contribution to the study. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, through its Office of Research and Development, partially funded and managed the research described herein. This work has been subjected to the agency’s administrative review and has been approved for external publication. Any opinions expressed in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the agency; therefore, no official endorsement should be inferred. Any mention of trade names or commercial products does not constitute endorsement or recommendation for use.
References
- 1.Byappanahalli MN, Nevers MB, Korajkic A, Staley ZR, and Harwood VJ, 2012. Enterococci in the Environment. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 76 (4), 685–706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chern EC, Siefring S, Paar J, Doolittle M, Haugland RA, 2011. Comparison of quantitative PCR assays for Escherichia coli targeting ribosomal RNA and single copy genes. Lett. Appl. Microbiol 52, 298–306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cole JR, Wang Q, Fish JA, Chai B, McGarrell DM, Sun Y, Brown T, Porras-Alfaro A, Kuske CR, Tiedje JM, 2013. Ribosomal database project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucl. Acids Res, 42, D633–D642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Colford JM Jr, Wade TJ, Schiff KC, Wright CC, Griffith JF Sandhu SK, Burns S, Sobsey M, Lovelace G, Weisberg SB, 2007. Water quality indicators and the risk of illness at beaches with nonpoint sources of fecal contamination. Epidemiology 18, 27–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Directive 2006/7/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 February 2006 concerning the management of bathing water quality and repealing directive 76/160/EEC. Official Journal of the European Union, L 64, 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ferguson DM, Griffith JF, McGee CD, Weisberg SB, Hagedorn C, 2013. Comparison of Enterococcus species diversity in marine water and wastewater using Enterolert and EPA method 1600. J. Environ. Public Health (Article ID 848049), 1–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ferguson DM, Moore DF, Getrich MA, Zhowandai MH, 2005. Enumeration and speciation of enterococci found in marine and intertidal sediments and coastal water in southern California. J. Appl. Microbiol 99, 598–608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fogarty LR, Haack SK, Wolcott MJ, Whitman RL, 2003. Abundance and characteristics of the recreational water quality indicator bacteria Escherichia coli and enterococci in gull faeces. J. Appl. Microbiol, 94(5), 865–78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Haugland RA, Varma M, Sivaganesan M, Kelty C, Peed L, Shanks OC, 2010. Evaluation of genetic markers from the 16S rRNA gene V2 region for use in quantitative detection of selected Bacteroidales species and human fecal waste by qPCR. Syst. Appl. Microbiol 33, 348–357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hokajärvi A Pitkänen T, Siljanen H, Nakari U, Torvinen E, Siitonen A, Miettinen I, 2013. Occurrence of thermotolerant Campylobacter spp. and adenoviruses in Finnish bathing waters and purified sewage effluents. J. Water Health, 11 (1), 120–134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.ISO 17995, 2005. Water quality- Detection and enumeration of thermotolerant Campylobacter species International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- 12.ISO 7899–2, 2000. Water quality- Detection and enumeration of intestinal enterococci – Part 2: membrane filtration method International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- 13.ISO 9308–2, 2012. Water quality - enumeration of Escherichia coli and coliform bacteria, Part 2: most probable number method International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- 14.ISO/TR 13843, 2000. Water quality - guidance on validation of microbiological methods International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jalava K, Rintala H, Ollgren J, Maunula L, Gomez-Alvarez V, Revez J, Palander M, Antikainen J, Kauppinen A, Räsänen P, Siponen S, Nyholm O, Kyyhkynen A, Hakkarainen S, Merentie J, Pärnänen M, Loginov R, Ryu H, Kuusi M, Siitonen A, Miettinen I, Santo Domingo JW, Hänninen ML, Pitkänen T, 2014. Novel microbiological and spatial statistical methods to improve strength of epidemiological evidence in a community-wide waterborne outbreak. PLoS One 9(8):e104713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jothikumar N, Cromeans TL, Hill VR, Lu X, Sobsey MD & Erdman DD, 2005. Quantitative real-time PCR assays for detection of human adenoviruses and identification of serotypes 40 and 41. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 71, 3131–3136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kageyama T, Kojima S, Shinohara M, Uchida K, Fukushi S, Hoshino FB, Takeda N, Katayama K, 2003. Broadly reactive and highly sensitive assay for Norwalk-like viruses based on real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol 41, 1548–1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kapoor V, Pitkänen T, Ryu H, Elk M, Wendell D, Santo Domingo JW, 2014. Distribution of human-specific Bacteroidales and fecal indicator bacteria in an urban watershed impacted by sewage pollution distributed using RNA- and DNA- based quantitative PCR assays. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 81, 91–99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kauppinen A, Al-Hello H, Zacheus O, Kilponen J, Maunula L, Huusko S, Lappalainen M, Miettinen I, Blomqvist S, Rimhanen-Finne R, 2017. Increase in outbreaks linked to bathing water in the summer of 2014 in Finland Submitted May 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kauppinen A, Ikonen J, Pursiainen A, Pitkänen T, Miettinen IT, 2012. Decontamination of a drinking water pipeline system contaminated with adenovirus and Escherichia coli utilizing peracetic acid and chlorine. J. Water Health 10(3), 406–418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kauppinen A, Martikainen K, Matikka V, Veijalainen A-M., Pitkänen T, Heinonen-Tanski H, Miettinen IT, 2014. Sand filters for removal of microbes and nutrients from wastewater during a one-year pilot study in a cold temperate climate. J. Environ. Manage 133, 206–213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Keer JT, Birch L, 2003 Molecular methods for the assessment of bacterial viability. J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 53, 175–183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Layton BA, Walters SP Lam LH, Boehm AB, 2010. Enterococcus species distribution among human and animal hosts using multiplex PCR. J. Appl Microbiol 109, 539–547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li W and Godzik A, 2006. Cd-hit: a fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 22, 1658–1659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lindholm T, Rönnholm E, Häggqvist K (2008). Change due to invasion of Myriophyllum sibiricum in shallow lake in Åland, SW Finland. Aquatic Invasions (3) 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Loisy F, Atmar RL, Guillon P, Cann PL, Pommepuy M, Guyader F.S.Le, 2005. Real-time RT-PCR for norovirus screening in shellfish. J. Virol. Meth, 123, 1–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ludwig W and Schleifer K 2000. How quantitative is quantitative PCR with respect to cell counts? Syst. Appl. Microbiol 23, 556–562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mieszkin S, Furet JP, Corthier G, Gourmelon M, 2009. Estimation of pig fecal contamination in a river catchment by real-time PCR using two pig-specific Bacteroidales 16S rRNA genetic markers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 75(10), 3045–3054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mieszkin S, Yala JF, Joubrel R, Gourmelon M, 2010. Phylogenetic analysis of Bacteroidales 16S rRNA gene sequences from human and animal effluents and assessment of ruminant fecal pollution by real-time PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol 108 (3) 1365–2672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Moore DF, Zhowandai MH, Ferguson DM, McGee C, Mott JB, Stewart JC, 2006. Comparison of 16S rRNA sequencing with conventional and commercial phenotypic techniques for identification of enterococci from the marine environment. J. Appl. Microbiol 100, 1272–1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Moriarty E, Nourozi F, Robson B, Wood D, Gilpin B, 2008. Evidence for growth of enterococci in municipal oxidation ponds, obtained using antibiotic resistance analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 74, 7204–7210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Muller T, Ulrich A, Ott EM, Muller M, 2001. Identification of plant-associated enterococci. J. Appl Microbiol 91, 268–278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pitkänen T, Paakkari P, Miettinen IT, Heinonen-Tanski H, Paulin L, Hänninen M, 2007. Comparison of media for enumeration of coliform bacteria and Escherichia coli in non-disinfected water. J. microbial. methods, 68, 522–529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pitkänen T, Ryu H, Elk M, Hokajärvi A, Siponen S, Vepsäläinen A, Räsänen P, Domingo JWS, 2013. Detection of fecal bacteria and source tracking identifiers in environmental waters using rRNA-based RT-qPCR and rDNA-based qPCR assays. Environ. Sci Technol 47, 13611–13620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pitkänen T, Miettinen IT, Nakari UM, Takkinen J, Nieminen K, Siitonen A, Kuusi M, Holopainen A, Hanninen ML, 2008. Faecal contamination of a municipal drinking water distribution system in association with Campylobacter jejuni infections. J. Water Health 6, 365–376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pourcher AM, Devriese LA, Hernandez JF Delattre JM, 1991. Enumeration by a miniaturized method of Escherichia coli, Streptococcus bovis and enterococci as indicators of the origin of fecal pollution of waters. J. Appl Bacteriol 70, 525–530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ryu H, Henson M, Elk M, Toledo-Hernandez C, Griffith J, Blackwood D, Noble R, Gourmelon M, Glassmeyer S, Domingo JS, 2013. Development of quantitative PCR assays targeting 16S rRNA gene of Enterococcus spp. and their application to the identification of Enterococcus species in environmental samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 79, 196–204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ryu H, Griffith JF, Khan IUH, Hill S, Edge TA, Toledo-Hernandez C, Gonzalez-Nieves J, Domingo JS, 2012. Comparison of Gull Feces-Specific Assays Targeting the 16S rRNA Genes of Catellicoccus marimammalium and Streptococcus spp.. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 78, 1909–1916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ryu H, Grond K, Verheijen B, Elk M, Buehler DM, Santo Domingo JW, 2014. Intestinal microbiota and species diversity of Campylobacter and Helicobacter spp. in migrating shorebirds in Delaware Bay. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(6):1838–47. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03793-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Savichtcheva O, Okabe S, 2006. Alternative indicators of fecal pollution: Relations with pathogens and conventional indicators, current methodologies for direct pathogen monitoring and future application perspectives, Water Res, 40(13): 2463–2476, 10.1016/j.watres.2006.04.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Siefring S, Varma M, Atikovic E, Wymer L, Haugland RA, 2008. Improved real-time PCR assays for the detection of fecal indicator bacteria in surface waters with different instrument and reagent systems. J. Water Health 6, 225–237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Slanetz LW and Bartley CH (1957). Numbers of enterococci in water, sewage, and feces determined by the membrane filter technique with an improved medium. J. Bact 74, 591–595 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.STM, 2008a. Decree of the Ministry of Social Affairs and Health concerning the quality requirements and surveillance of bathing water in public bathing areas (177/2008) http://www.finlex.fi/fi/laki/alkup/2008/20080177 (accessed 29.03.16).
- 44.STM, 2008b. Decree of the Ministry of Social Affairs and Health concerning the quality requirements and surveillance of bathing water in small public bathing areas (354/2008) http://www.finlex.fi/fi/laki/alkup/2008/20080354 (accessed 29.03.16).
- 45.Svec P and Sedlacek (1999). Occurrence of Enterococci spp. in water. Folia Microbiologica 44(1):3–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, and Kumar S (2013). MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol 30(12): 2725–2729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.USEPA, 2009. United States Environmental Protection Agency, February 2009; Review of Zoonotic pathogens in ambient waters USEPA Office of Water, Health and Ecological Criteria Division. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Valvira, 2015. Identified bathing waters in Finland in 2015 http://www.valvira.fi/ymparistoterveys/terveydensuojelu/uimavesi (accessed 29.03.16).
- 49.Wheeler AL, Hartel PG, Godfrey DG, Hill JL & Segars WI, 2002. Potential of Enterococcus faecalis as a human fecal indicator for microbial source tracking. J. Environ. Qual 31(4), 1286–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wyn-Jones AP, Carducci A, Cook N, D’Agostino M, Divizia M, Fleischer J, Gantzer C, Gawler A, Girones R, Holler C, Husman AMD, Kay D, Kozyra I, Lopez-Pila J, Muscillo M, Nascimento MS, Papageorgiou G, Rutjes S, Sellwood J, Szewzyk R, Wyer M, 2011. Surveillance of adenoviruses and noroviruses in European recreational waters. Water Res 45, 1025–38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.