Figure 2.
A Laser Ablation Induced Lesion Can Disconnect Two Neuronal Modules
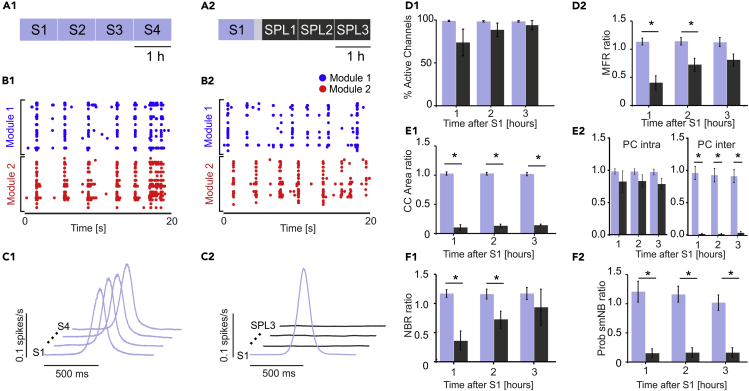
(A–F) (A1) Schematic of the first experimental protocol. Experiments with no lesion: we recorded four consecutive hours of spontaneous activity (S1–S4). (A2) Schematic of the second experimental protocol. Experiments with lesion: we recorded 1 h of spontaneous activity (S1) followed by laser ablation and three consecutive hours of spontaneous activity post lesion (SPL1-SPL3). The gray-shaded area indicates 20 min of no recording due to the execution of the lesion. (B1) A 20-s raster plot of the network bursting activity of one representative experiment during the S1 phase. (B2) A 20-s raster plot of the network bursting activity of one representative experiment during SPL3. (C1) Cross-correlation (CC) function for one representative experiment during the S1–S4 phases. The CC profiles between the spike trains of each module (light blue) in the four phases of the experiment were high and stable (lines shifted for the sake of clarity). Time axis [-500, +500] ms. (C2) CC profile between the spike trains of each module for one representative experiment with lesion. Before the lesion (light blue profile), CC was high; following the lesion (dark gray), CC collapsed to zero (lines shifted for the sake of clarity). Time axis [-500, +500] ms. (D1) Percentage of active channels with respect to S1 for the experiments with no lesions (light blue columns, n = 9) and with lesions (n = 4, dark gray columns). No significant difference was found using the Mann-Whitney test (S2 VS SPL1 p = 0.2042; S3 VS SPL2: p = 0.31608; S4 VS SPL3: p = 0.70769). (D2) Mean firing rate (MFR) ratio with respect to S1 for experiments without (light blue bars) and with lesions (dark gray bars). No significant difference was found during the last hour using the Mann-Whitney test (S2 vs SPL1: p = 0.0028; S3 vs SPL2: p = 0.01119; S4 vs SPL3: p = 0.10629). (E1) Comparison of the CC area ratio with respect to S1 for the experiments without (light blue bars) and with lesions (dark gray bars) (Mann-Whitney test; S2 vs SPL1: p = 0.0028; S3 vs SPL2: p = 0.0028; S4 vs SPL3: p = 0.0028). (E2) On the left, comparison of the intra-module correlation coefficient (i.e., Pearson Correlation, PC) ratio with respect to S1 for the experiments without (light blue bars) and with lesions (dark gray bars). No significant difference was found using the Mann-Whitney test (S2 VS SPL1 p = 0.71049; S3 VS SPL2: p = 0.14825; S4 VS SPL3: p = 0.07552). On the right, the same comparison regarding inter-module PC that showed clear differences between experiments without and with lesion (Mann-Whitney test; S2 vs SPL1: p = 0.0028; S3 vs SPL2: p = 0.0028; S4 vs SPL3: p = 0.0028). (F1) Network burst rate (NBR) ratio with respect to S1 showing significant differences during the first and second hour after the lesion (Mann-Whitney test; S2 vs SPL1: p = 0.0028; S3 vs SPL2: p = 0.01119; S4 vs SPL3: p = 0.26014). (F2) Probability of single-module NB (Prob smNB). The ratio with respect to S1 shows stability for experiments without (light blue bars) and with lesions (dark gray bars) (Mann-Whitney test; S2 vs SPL1: p = 0.0028; S3 vs SPL2: p = 0.0028; S4 vs SPL3: p = 0.0028). Data in the bar graphs is reported as mean ± standard error of the mean.