Figure 3.
Bidirectional Bridging Is Effective in Reconnecting Functionally and Anatomically Disconnected Neuronal Modules
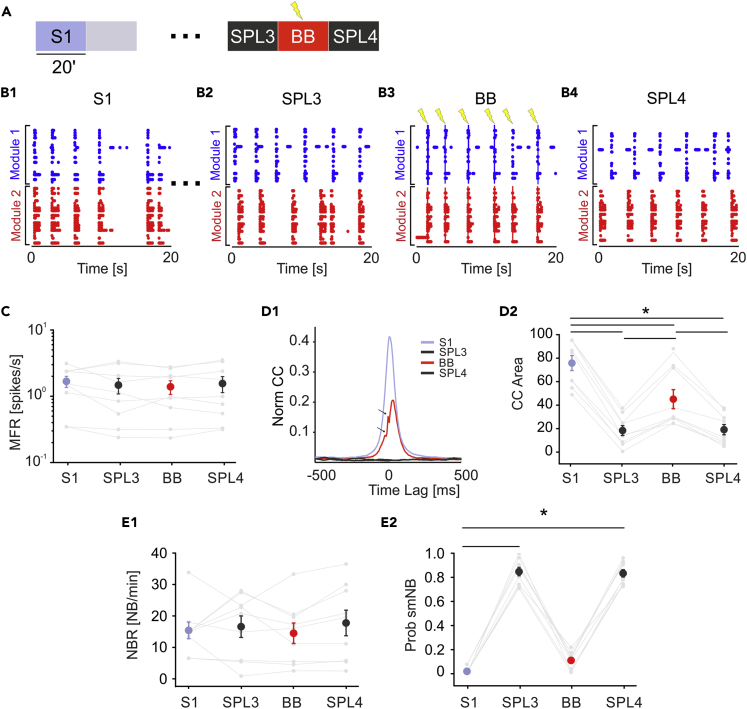
(A and B) (A) Schematic of the experimental protocol. We recorded 20 min of spontaneous activity (S1) followed by laser ablation. The gray-shaded area indicates 20 min of no recording during ablation. Dots represent 2 h of no recording after the lesion to maintain a stable activity in both modules. Then, we recorded 20 min of SPL activity (SPL3) followed by 20 min of the bidirectional bridging (BB) protocol and another 20 min of spontaneous activity (SPL4). (B1–B4) The 20-s-long raster plots of representative experiments (respectively, from phases S1, SPL1, BB, and SPL4). In (B3) blue and red lines represent electrical stimulation pulses delivered from module 1 to module 2 and vice versa, respectively.
(C–E) (C) MFR during the four experimental phases was stable (color code as in panel A: S1: light blue dot; SPL3, SPL4: dark gray dots; BB: red dot). No significant difference was found (one-way RM ANOVA, p = 0.469, DF = 3, F = 0.872). (D1) CC function during the four experimental phases. Small arrows indicate the blanking period of 8 ms following each stimulation. Color code, the same as that in panel A. Note that during BB, the cross-correlation function (red) recovers even if not completely with respect to the initial profile (light blue), whereas it stays at zero during the spontaneous activity phases post lesion (SPL3 and SPL4, dark gray profiles). (D2) CC area was highly reduced during the post-lesion phases. The CC area partially recovered during the BB protocol and collapsed again when stimulation was switched off (one-way repeated measures analysis of variance; degrees of freedom = 3; F = 101,832. S1 vs SPL3 p = 5.67 × 10−13; S1 vs SPL4 p = 7.54 × 10−13; S1 vs BB p = 1.60 × 10−7; BB vs SPL3 p = 1.77 × 10−6; BB vs SPL4 p = 2.81 × 10−6; SPL4 vs SPL3 p = 1). (E1) NBR remained stable during the experiments. No significant difference was found (one-way repeated measures analysis of variance: p = 0.501, DF = 3; F = 0.810). (E2) Probability of the single-module NB (Prob smNB) was close to one after the lesion. During the BB protocol, the probability was similar to the pre-lesion condition (Friedman's repeated measures analysis of variance; p < 0.001, DF = 3, Chi-square = 24.3. SPL4 vs S1 and SPL3 vs S1: p < 0.001). Data in the plots is reported as mean ± standard error of the mean.