This cohort study uses data from second-generation participants in the Framingham Heart Study to analyze the association of plasma amylin concentration with Alzheimer disease risk and brain structure.
Key Points
Question
Is plasma amylin concentration associated with Alzheimer disease (AD) risk in humans?
Findings
In this cohort study of 3061 participants in the Framingham Heart Study, the association between plasma amylin concentrations with AD onset and the brain volume was nonlinear and U-shaped. Compared with participants with a low concentration of plasma amylin, participants with a high concentration of plasma amylin had a lower rate of AD incidence but participants with an extremely high concentration of plasma amylin had a higher rate of AD incidence, and a high, but not extremely high, concentration of plasma amylin was positively associated with temporal lobe volumes.
Meaning
Amylin is a neuropeptide that may be beneficial for the aging brain, but an extremely high concentration of plasma amylin, which may lead to amylin aggregation and loss of its protective function for the brain, may be a risk factor for AD.
Abstract
Importance
Preclinical studies suggest that amylin has a U-shaped dose-response association with risk of Alzheimer disease (AD). The association of plasma amylin with AD in humans is unknown.
Objectives
To measure amylin concentration in plasma by using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and to study the association between plasma amylin, incidence of AD, and brain structure in humans.
Design, Setting, and Participants
This cohort study used data from the Framingham Heart Study offspring cohort from 1998 to 2015. Using a Monte Carlo approach, participants were divided into 3 plasma amylin concentration groups: (1) low (<75 pmol/L), (2) high (75-2800 pmol/L), and (3) extremely high (≥2800 pmol/L). Data analyses were conducted October 5, 2017, to December 18, 2018.
Exposures
Baseline plasma amylin concentrations at examination 7.
Main Outcomes and Measures
Incidence of dementia or AD and brain volumetric measures from structural magnetic resonance imaging data.
Results
From the Framingham Heart Study offspring cohort, 3061 participants (mean [SD] age at baseline, 61.0 [9.5] years; 1653 [54.0%] women) who had plasma amylin measurements, dementia incidence, and brain volume measurements on record were included in this study. The distribution of plasma amylin concentrations was highly skewed (median [interquartile range], 7.5 [4.6-18.9] pmol/L; mean [SD], 302.3 [1941.0] pmol/L; range, 0.03-44 623.7 pmol/L). Compared with the low plasma amylin concentration group, the high plasma amylin concentration group had a lower rate of AD incidence (2.3% vs 5.6%; P = .04), but the extremely high plasma amylin concentration group had a higher rate of AD incidence (14.3%; P < .001). After adjusting for age, sex, education, body mass index, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, high-density lipoprotein level, and APOE4, high plasma amylin was not associated with decreased AD risk (hazard ratio, 0.42 [95% CI, 0.16-1.14]; P = .09) but was positively associated with volume of gray matter in the temporal lobe (β = 0.17 [SE, 0.05]; P < .001). In contrast, extremely high plasma amylin concentration was associated with a higher AD risk (hazard ratio, 2.51 [95% CI, 1.38-4.57]; P = .003) but not associated with temporal lobe volume (β = 0.02 [SE, 0.07]; P = .82).
Conclusions and Relevance
This study found that plasma amylin concentration was associated with AD incidence and brain structure with a U-shaped pattern. These findings are consistent with preclinical findings that suggest amylin is a neuropeptide that is physiological; however, at extremely high concentrations, it may lead to amylin aggregation and therefore may be a risk factor for AD.
Introduction
Amylin, also known as islet amyloid polypeptide or IAPP, is a highly conserved 37–amino acid peptide produced and secreted with insulin by the β-cells in the pancreas, and it functions as a gut-brain axis hormone.1,2,3 Amylin binds to the amylin receptor in the brain4,5,6,7 and mediates several important brain functions, including regulating glucose metabolism, modulating inflammatory reactions, and perhaps enhancing neurogenesis.8,9,10,11,12 However, amylin can aggregate when concentrations are high and become neurotoxic in cell cultures.13,14 A 2017 genome-wide interaction study15 showed that an amylin gene polymorphism is associated with brain amyloid burden and cognitive impairment in AD. Amylin aggregations are found colocalized with amyloids in the AD brain.16
Amyloid-β peptide (Aβ), a major pathological factor of the AD brain,17 and amylin share several features, including binding to the amylin receptor.18 Recent preclinical studies19,20,21 demonstrated that peripheral treatment of amylin or its analog reduces amyloid burden, tauopathy, and neuroinflammation in the AD brain. It is possible that in the presence of Aβ and when the plasma amylin concentration is low, amylin cannot bind to the amylin receptor sufficiently to effect a protective function for AD21; however, when the plasma amylin concentration is extremely high, amylin aggregates and loses its ability to bind to the amylin receptor, in addition to being neurotoxic in the aging brain.22 As the longitudinal association of plasma amylin with AD risk and brain structure in humans is unknown, to our knowledge, we hypothesized that the association of plasma amylin concentration with AD risk in humans would be nonlinear.
We used data collected from the Framingham Heart Study (FHS), a large population-based, multigeneration cohort with long and intensive follow-up that includes data on AD development and structural brain volumes.23 Included in this study were the FHS offspring cohort (also called Generation 2 or Gen 2) and the plasma samples from examination 7 to measure amylin concentrations. We examined the association of plasma amylin with dementia or AD risk in the following years and with brain volumes, stratified by plasma amylin concentrations.
Methods
Study Design and Participants
The FHS is a single-site, community-based, prospective cohort study in Framingham, Massachusetts. The design and selection criteria of the FHS offspring cohort have been previously described.24 The baseline for this study was the seventh health examination, which took place from 1998 to 2001, when the enrolled participants underwent cognitive evaluation, medical examination, and blood testing. Follow-up data were collected until 2015.
Participants who did not have dementia, had baseline measurements of plasma amylin, and consented to use of their genetic information (ie, APOE genotype) were included in this study. Participants with both APOE2 and APOE4 genotypes or who had prevalent dementia at baseline were excluded. We examined the distribution of plasma amylin concentration and its associations with other factors, including demographic characteristics, APOE genotype, blood pressure, glucose, and lipid profile. The data on incident dementia, including AD development from examination 7 until 2015, were used to study the association of plasma amylin concentration with AD risk. The data on cardiovascular disease (CVD) and diabetes, in addition to age, sex, and education at examination 7, were used as covariates. Data on a subset of participants who also underwent a brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan after the seventh examination were also used. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants, and the study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Boston University Medical Campus. This study is reported following the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) reporting guideline. Data analyses were conducted October 5, 2017, to December 18, 2018.
Plasma Amylin Measurement
Blood testing was conducted after overnight fasting. Blood samples were centrifuged immediately to isolate plasma. We used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Human Amylin ELISA; EMD Millipore) to measure amylin concentration in plasma according to the manufacturer’s instructions. All samples were assayed in duplicate, and mean final values were generated.
Dementia or AD Diagnoses
Beginning in 1979, all FHS offspring cohort participants have been followed for incident dementia. Consensus diagnostic procedures have been previously described.25 Incidence of dementia, AD, and person-time accruement after the baseline plasma amylin measurement until 2015 were used for analyses.
Brain Measurements
Brain MRI was conducted beginning in March 1999, and only data that were acquired from MRI after the measurement of plasma amylin concentrations were used. The brain MRI protocol has been reported in detail elsewhere.26,27
The semiautomated segmentation protocol for quantifying total cranial volume, total cerebral brain volume, frontal lobar brain volume, parietal lobe brain volume, temporal lobe brain volume, and hippocampal volume has been described elsewhere,28 as has the interrater reliabilities for these methods. For segmentation of white matter hyperintensities from other brain tissues, the first and second echo images from T2 sequences were summed and a log-normal distribution was fitted to the summed data. A segmentation threshold for white matter hyperintensities was determined as 1 SD in pixel intensity greater than the mean of the fitted distribution of brain parenchyma. The units for the brain volumes including total cerebral brain volume, frontal lobar brain volume, temporal lobe brain volume, hippocampal volume, and white matter hyperintensities were computed as the percentage of total cranial volume. Each image set underwent rigorous quality control assessment that included assessment of the original acquisition quality as well as the quality of the image processing. Moreover, each of the analysts was highly trained to maintain rigorous precision with intraclass (analyst) coefficients above 90% for all analyses.
Statistical Analysis
Analyses were performed using SAS statistical software version 9.3 (SAS Institute) and the R statistical environment (R Project for Statistical Computing). Because our preclinical study and others suggested that peripheral amylin treatment is beneficial in mediating the development of AD in the brain,20,21 but an extremely high concentration of amylin in amylin transgenic rats has been shown to increase the degree AD development,29 we hypothesized that plasma amylin concentration would be associated with AD incidence in a nonlinear pattern. To explore if there was a nonlinear association, we conducted analysis of orthogonal polynomial contrasts and found that tended X linear (log), X2 quadratic, X3 cubic, and X4 quartic effects of plasma amylin concentration on AD incidence (eTable 1 in the Supplement). We then conducted exploratory log-rank analyses with different cutoffs higher than 100 pmol/L in the skewed portion of plasma amylin concentration (eFigure 1 in the Supplement).
To address a nonlinear association with a probable U-shape of plasma amylin concentration with AD, we needed at least 2 cutoff values. However, to our knowledge, there are no references to optimize the cutoff values of plasma amylin to date. Given that plasma amylin concentration was a continuous variable, there might be infinite combinations of choosing the 2 cutoff values if the sample size is very large. We applied Monte Carlo methods, which are a broad class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results. In this study, we split the data set into 2 parts: a training data set and a test data set. We first used the Monte Carlo method to randomly draw a set of cutoff values independently (n = 100 000)30 and fit a set of Cox regression models (n = 100 000) based on those randomly chosen cutoff values in the training data set and verified the performance of each model by comparing their area under the curve. We then selected the optimized cutoff values as the ones with maximum area under the curve among all the sets of randomly chosen cutoffs. We estimated 2 optimal cutoff thresholds to generate 3 groups of plasma amylin concentration: (1) low, less than 75 pmol/L; (2) high, 75 to 2800 pmol/L; and (3) extremely high, 2800 pmol/L or more, which were determined by using area under the curve values of an AD incidence prediction model (Cox proportional hazards model) after adjusting for age, sex, and education. We performed 3 analyses for different outcomes. The first analysis was for plasma amylin concentration distribution, demographic characteristics, and medical conditions, in which means and SDs were determined and analysis of variance tests were conducted to compare plasma amylin concentration groups on continuous variables. χ2 tests were used to compare plasma amylin concentration groups for categorical variables. Two-tailed P values less than .05 were used for statistical significance.
In our second analysis to examine the association of plasma amylin concentration with AD risk, we first used χ2 tests to examine AD incidence. Then the log-rank test was applied to compare the onset of AD based on the 3 plasma amylin concentration groups. Cox proportional hazards models were used to evaluate AD risk after adjusting for confounders. Two-tailed P values less than .05 were used for statistical significance.
In our third analysis to examine the association of plasma amylin concentration with brain volumes, we used 2148 participants who had brain MRI data from around or after the date of plasma amylin measurement for the brain volume comparisons. We used the mean brain volumes, including gray matter and white matter, measured in centimeters cubed, divided by total cerebral brain volume to study brain atrophy. Using analysis of variance, the association of plasma amylin concentration with brain volume was examined. Next, multivariate linear regression was used to study the association of different plasma amylin concentration with regional brain volume measures as an outcome controlling for confounders. Given multiple testing and the need to minimize the rate of false positives, Bonferroni-corrected 2-tailed P values were used with statistical significance set at less than .004.
While the skewed portion of plasma amylin concentration might have been associated with AD incidence, the normal distributed portion of plasma amylin concentration might have been associated with physiological factors because amylin is a hormone. For additional analysis, we divided the low plasma amylin concentration group into quintiles. Quintiles (Q) were defined as Q1, less than 4.2 pmol/L; Q2, 4.2 to 5.9 mol/L; Q3, 6.0 to 9.4 pmol/L; Q4, 9.5 to 26.9 pmol/L; and Q5, more than 27.0 pmol/L.
Results
Characterization of Plasma Amylin Concentration Among FHS Participants
The FHS offspring cohort at examination 7 enrolled 3539 study participants; 3226 participants (91.2%) underwent blood testing and had plasma amylin measurements; and of them, 3137 participants (97.2%) consented to have their APOE genetic information examined. After excluding 60 individuals with both APOE2 and APOE4 and 16 individuals who had prevalent dementia at baseline, 3061 participants (mean [SD] age, 61.0 [9.5] years; 1653 [54.0%] women) were included in this study (Table 1). The distribution of plasma amylin concentrations was highly skewed toward to the high extreme, with a median (interquartile range) of 7.5 (4.6-18.9) pmol/L, a mean (SD) of 302.3 (1941.0) pmol/L, and a total range of 0.03 pmol/L to 44 623.7 pmol/L. After logarithmizing the plasma amylin data and conducting distribution plots, there were 2752 participants (89.9%) in the low plasma amylin concentration group, 222 participants (7.3%) in the high plasma amylin concentration group, and 87 participants (2.8%) in the extremely high plasma amylin concentration group (eFigure 2 in the Supplement). There was no difference between men and women with respect to the distribution of plasma amylin concentration.
Table 1. Characteristics of the Study Sample Based on Plasma Amylin Concentration.
| Characteristic | Mean (SD) | df | F Score | P Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (N = 3061) | Low Plasma Amylin (n = 2752)a | High Plasma Amylin (n = 222)b | Extremely High Plasma Amylin (n = 87)c | ||||
| Age, y | 61.0 (9.5) | 61.1 (9.5) | 59.8 (9.0) | 61.8 (10.4) | 2 | 2.34 | .10 |
| Education, y | 14.1 (2.6) | 14.1 (2.6) | 14.4 (2.7) | 14.0 (2.6) | 2 | 1.58 | .21 |
| Women, No. (%) | 1653 (54.0) | 1494 (54.3) | 111 (50.0) | 48 (55.2) | 2 | 1.57 | .46 |
| BMI | 28.1 (5.3) | 28.2 (5.4) | 27.8 (5.1) | 27.0 (4.2) | 2 | 2.50 | .08 |
| Waist circumference, cm | 99.8 (14.0) | 99.8 (14.0) | 99.1 (14.0) | 97.0 (11.9) | 2 | 1.94 | .14 |
| Hip circumference, cm | 105.2 (10.4) | 105.2 (10.7) | 105.2 (9.7) | 102.9 (9.1) | 2 | 2.16 | .12 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 126.9 (18.7) | 127.0 (18.8) | 126.0 (18.8) | 127.2 (18.4) | 2 | 0.26 | .77 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 74.0 (9.7) | 74.0 (9.8) | 73.7 (9.6) | 74.2 (9.0) | 2 | 0.13 | .88 |
| Diabetes, No. (%) | 343 (11.2) | 312 (11.3) | 21 (9.5) | 10 (11.5) | 2 | 0.74 | .69 |
| CVD, No. (%) | 300 (11.3) | 273 (11.5) | 21 (10.7) | 6 (7.4) | 2 | 1.40 | .50 |
| Glucose, mg/dL | 104.2 (26.4) | 104.2 (26.3) | 103.1 (26.8) | 105.0 (30.1) | 2 | 0.22 | .80 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 200.5 (36.8) | 200.4 (36.7) | 202.0 (37.8) | 198.2 (36.2) | 2 | 0.36 | .70 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 137.0 (88.7) | 136.8 (88.5) | 139.8 (99.3) | 134.7 (63.3) | 2 | 0.15 | .86 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 119.6 (32.7) | 119.6 (32.7) | 122.5 (33.8) | 120.7 (31.2) | 2 | 0.79 | .45 |
| HDL, mg/dL | 53.9 (17.0) | 54.1 (17.0) | 52.6 (17.4) | 50.4 (15.4) | 2 | 2.64 | .07 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.9 (0.3) | 0.9 (0.3) | 0.9 (0.2) | 0.8 (0.2) | 2 | 0.98 | .37 |
| CRP, mg/L | 4.3 (7.6) | 4.2 (6.2) | 5.3 (17.9) | 3.4 (4.3) | 2 | 2.66 | .07 |
| APOE4, No. (%) | 634 (20.7) | 570 (20.7) | 41 (18.5) | 23 (26.4) | 2 | 2.42 | .30 |
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared); CRP, C-reactive protein; CVD, cardiovascular disease; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
SI conversion factors: To convert glucose to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0555; total cholesterol, LDL, and HDL to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0259; triglycerides to millimoles per liter, multiply by 0.0113; creatinine to micromoles per liter, multiply by 88.4; and CRP to nanomoles per liter, multiply by 9.524.
Plasma amylin concentration, less than 75 pmol/L.
Plasma amylin concentration, 75 pmol/L to less than 2800 pmol/L.
Plasma amylin concentration, 2800 pmol/L or greater.
Associations of Plasma Amylin Concentrations With Alzheimer Disease Risk
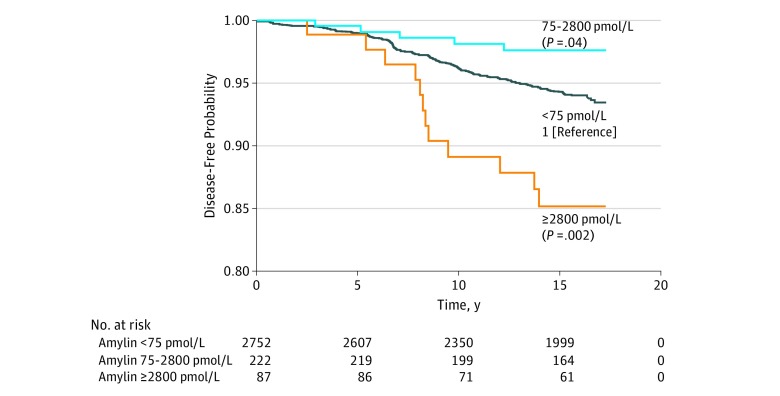
The mean (SD) follow-up for participants after the measurement of plasma amylin was 14.8 (3.8) years. During this time, 210 participants (6.9%) developed dementia and 169 participants (6.6%) had AD. Among the 3 plasma amylin concentration groups, compared with the low plasma amylin concentration group, the high plasma amylin concentration group had lower risks of dementia (6.7% vs 4.5%) and AD (5.6% vs 2.3%), but the extremely high plasma amylin concentration group had higher risks of dementia (17.2%) and AD (14.3%) (Table 2). Using a log-rank test and the low plasma amylin concentration group as the reference, we found that participants with a high concentration of plasma amylin had a lower risk for the onset of AD (P = .04), but participants with an extremely high concentration of plasma amylin had a higher risk of the onset of AD (P = .002) (Figure).
Table 2. Comparisons of AD Incidence Stratified by Plasma Amylin Concentration.
| Subgroup | No. (%) | df | Log-Rank Test | P Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Plasma Amylin (n = 2752)a | High Plasma Amylin (n = 222)b | Extremely High Plasma Amylin (n = 87)c | ||||
| Dementia | 185 (6.7) | 10 (4.5) | 15 (17.2) | 2 | 15.4 | <.001 |
| AD incidence | 152 (5.5) | 5 (2.3) | 12 (13.8) | 2 | 15.7 | <.001 |
| Men | 1258 (45.7) | 111 (50.0) | 39 (44.8) | |||
| AD incidence | 59 (4.7) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (5.1) | 2 | 3.80 | .20 |
| Women | 1494 (54.3) | 111 (50.0) | 48 (55.2) | |||
| AD incidence | 93 (6.2) | 4 (3.6) | 10 (20.8) | 2 | 17.7 | <.001 |
| No diabetes | 2437 (88.7) | 201 (90.5) | 77 (88.5) | |||
| AD incidence | 117 (4.8) | 4 (2.0) | 9 (11.7) | 2 | 11.3 | .004 |
| Diabetes | 312 (11.3) | 21 (9.5) | 10 (11.5) | |||
| AD incidence | 35 (11.2)d | 1 (4.8) | 3 (30.0) | 2 | 4.1 | .10 |
| APOE2 | 380 (13.8) | 24 (10.8) | 9 (10.3) | |||
| AD incidence | 14 (3.7) | 1 (4.2) | 1 (11.1) | 2 | 1.10 | .60 |
| APOE3 | 1802 (65.5) | 157 (70.7) | 55 (63.2) | |||
| AD incidence | 83 (4.6) | 3 (1.9) | 6 (10.9) | 2 | 7.60 | .02 |
| APOE4 | 570 (20.7) | 41 (18.5) | 23 (26.4) | |||
| AD incidence | 55 (9.6)d | 1 (2.4) | 5 (21.7) | 2 | 6.20 | .05 |
Abbreviation: AD, Alzheimer disease.
Plasma amylin concentration, less than 75 pmol/L.
Plasma amylin concentration, 75 pmol/L to less than 2800 pmol/L.
Plasma amylin concentration, 2800 pmol/L or greater.
P < .001 for the column comparisons of AD incidence among plasma amylin concentration groups.
Figure. Log-Rank Analysis for Alzheimer Disease–Free or Dementia-Free Survival Among 3 Groups of Plasma Amylin Concentration.
After adjusting for age; sex; education; body mass index (BMI), calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared; diabetes; CVD; APOE4 genotype; and high-density lipoprotein, we found that extremely high plasma amylin concentration was associated with 2- to 3-fold increased AD incidence during the follow-up compared with low plasma amylin concentration (hazard ratio, 2.51 [95% CI, 1.38-4.57]; P = .003) (Table 3). The association of high plasma amylin concentration with AD incidence did not reach statistical significance (hazard ratio, 0.42 [95% CI, 0.16-1.14]; P = .09) (Table 3). Participants were further stratified into men and women; those without or with diabetes; and those with APOE2, APOE3, or APOE4 genotypes. Similar U-shaped associations of the plasma amylin cutoffs with AD risk were found in these analyses, except for APOE2 (Table 2).
Table 3. Association of Plasma Amylin Concentration With Risk of Alzheimer Disease in Multivariate Cox Regression Model .
| Plasma Amylin Concentration | Hazard Ratio (95% CI)a | P Value |
|---|---|---|
| Highb | 0.42 (0.16-1.14) | .09 |
| Extremely highc | 2.51 (1.38-4.57) | .003 |
Low plasma amylin concentration (<75 pmol/L) was used as a reference level. Cox regression was adjusted for confounders, including age, sex, education, APOE4, body mass index, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and high-density lipoprotein.
75 pmol/L to less than 2800 pmol/L.
2800 pmol/L or greater.
Other variables among the 3 amylin groups did not show statistical significance (Table 1). In contrast, across the quintiles of plasma amylin, there were statistically significant differences of mean (SD) BMI (Q1, 27.6 [5.0]; Q2, 28.2 [5.2]; Q3, 28.7 [5.8]; Q4, 28.4 [5.6]; Q5, 27.7 [4.9]; P = .001), waist circumference (Q1, 98.6 [13.7] cm; Q2, 99.8 [13.7] cm; Q3, 101.3 [14.7] cm; Q4, 100.3 [14.2] cm; Q5, 98.6 [13.7] cm; P = .002), diastolic blood pressure (Q1, 72.9 [9.4] mm Hg; Q2, 74.1 [9.7] mm Hg; Q3, 74.4 [9.6] mm Hg; Q4, 74.6 [10.2] mm Hg; Q5, 74.0 [9.6] mm Hg; P = .02), triglyceride (Q1, 121.8 [71.9] mg/dL; Q2, 142.3 [78.7] mg/dL; Q3, 144.6 [98.1] mg/dL; Q4, 138.5 [93.6] mg/dL; Q5, 137.7 [96.7] mg/dL; P < .001), and high-density lipoprotein (Q1, 56.8 [16.6] mg/dL; Q2, 53.0 [16.0] mg/dL; Q3, 52.9 [17.2] mg/dL; Q4, 53.6 [17.6] mg/dL; Q5, 53.1 [17.2] mg/dL; P < .001) (eTable 2 in the Supplement). However, the associations among amylin quintiles and these variables were nonlinear with a slight U or inverted U shape, eg, the plasma amylin concentration quintile with the lowest or largest mean was not the lowest or the highest plasma amylin concentration. We did not find statistically significant differences in AD incidence among the quintiles (eTable 3 in the Supplement), possibly owing to the U-shaped association of plasma amylin concentration with AD risk.
Associations of Plasma Amylin and Brain Volumes
The study participants who had undergone brain MRI were younger compared with those who had not (mean [SD] age, 60.6 [9.4] years vs 62.1 [9.6] years; P < .001) and had no statistically significant difference in sex (1151 women [54.0%] of 2148 participants with brain MRI data vs 502 women [47.9%] of 913 participants without brain MRI data; P = .50). There was no statistically significant difference in cumulative AD incidence between participants who had or had not undergone brain MRI (124 of 2148 participants [5.8%] with brain MRI data vs 45 of 913 participants [5.0%] without brain MRI data; P = .40). Using the Monte Carlo approach for cutoffs of plasma amylin concentration, we also found an inverted U– or U-shaped association of plasma amylin concentration with brain volume. Compared with participants with low plasma amylin concentration, participants with high plasma amylin concentration had higher mean (SD) volumes as percentages of total cerebral brain volume for temporal lobe brain volume (13.8% [0.7%] vs 13.6% [0.8%]) and temporal lobe gray matter volume (8.5% [0.5%] vs 8.4% [0.5%]) and lower median (interquartile range) volume of white matter hyperintensities (0.8% [0.4%-1.6%] vs 1.1% [0.5%-2.2%]), but participants with an extremely high plasma amylin concentration had similar volumes of these brain regions (eTable 4 in the Supplement). Using multivariate linear regression analyses after adjusting for age, sex, education, BMI, diabetes, CVD, and APOE4, the high concentration of plasma amylin cutoff remained positively associated with temporal lobe brain gray matter volume (β = 0.17 [SE, 0.05]; P < .001) (Table 4). In the same models, extremely high plasma amylin concentration was not found to be associated with temporal lobe brain volume or white matter hyperintensities.
Table 4. General Linear Regression Analyses of the Association of Plasma Amylin Concentration With Brain Volumea.
| Plasma Amylin Concentration | Temporal Lobe Brain Gray Matter Volume, %b | Logarithm of White Matter Hyperintensities, %b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β Estimate (SE) | P Valuec | β Estimate (SE) | P Valuec | |
| Highd | 0.17 (0.05) | <.001 | −1.85 (0.70) | .008 |
| Extremely highe | 0.02 (0.07) | .82 | 0.63 (1.09) | .57 |
The models were adjusted for age, sex, education, smoking, body mass index, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, APOE4, and high-density lipoprotein. Low plasma amylin concentration (<75 pmol/L) was used as the reference.
Given as a percentage of total cerebral brain volume.
P values adjusted using conventional Bonferroni correction (P < .004).
75 pmol/L to less than 2800 pmol/L.
2800 pmol/L or greater.
The brain volumes among plasma amylin concentration quintiles were also compared (eTable 5 in the Supplement). Using analysis of variance, we found that the median (interquartile range) volume of white matter hyperintensities was negatively associated with increasing quintiles of plasma amylin (Q1, 1.1 [0.5-2.3]; Q2, 1.2 [0.5-2.4]; Q3, 0.93 [0.4-2.0]; Q4, 1.1 [0.5-2.1]; Q5, 1.0 [0.5-2.1]; P = .007). Using multivariate linear regression analyses after adjusting for age, sex, education, BMI, diabetes, CVD, and APOE4, the largest amylin quintile, Q5, remained positively associated with temporal lobe brain gray matter volume (β = 0.10 [SE, 0.04]; P = .007) (eTable 6 in the Supplement). In the same model, we found that Q5 was negatively associated with the logarithm of white matter hyperintensities (β = −1.12 [SE, 0.57]; P = .05). However, these were not statistically significant after Bonferroni correction.
Discussion
The U-shaped association of plasma amylin concentration with AD incidence was consistent with previous preclinical findings. Compared with low plasma amylin concentration, participants with high plasma amylin concentration had a lower rate of AD incidence. Consistently, high plasma amylin concentration had a protective association for temporal lobe brain volume. Although the mechanism of amylin’s beneficial effects for the brain is still unclear, amylin is a gut-brain axis hormone that is produced by β-cells in the pancreas31 and crosses the blood-brain barrier.4,5,6 The beneficial effects of amylin for AD are likely through binding to the amylin receptor,21 which is one type of G-protein coupled receptor and is composed of the calcitonin receptor combined with different receptor activity–modifying proteins.7,32
In contrast to the high range of plasma amylin, the extremely high range of plasma amylin concentration was associated with increased AD risk in long-term follow-up and did not show any association with temporal lobe brain volume. There are 2 possible mechanisms for this: (1) amylin aggregates and causes neurotoxic effects, or (2) aggregated amylin cannot bind to its cognate amylin receptor to mediate the protective function against AD.33 Our recent in vitro study showed that exogenously adding human amylin was beneficial to antagonize the neurotoxic effects caused by aggregated Aβ1-42, but adding an extremely high concentration of human amylin was ineffective and synergetic with Aβ’s neurotoxicity in primary rat cortical neurons.34 Meanwhile, a 2017 study35 demonstrated that low amylin concentrations vs high amylin concentrations bind to different receptors, and we contend that one is neurophysiological and the other neurotoxic, each through independent pathways. At an extremely high plasma amylin concentration, probably in nanomole-per-liter ranges, for a long duration, there may be an independent pathway for AD pathogenesis stemming from amylin’s physiological effects as a hormone. The extremely high plasma amylin concentrations were associated with increased AD incidence during the study follow-up. Since case-control studies have shown that patients with AD have a lower concentration of plasma amylin than controls19,33 and amylin aggregates are found in the AD brain,16 it is possible that an extremely high plasma amylin concentration declines owing to its aggregation and deposition in the brain during neurodegeneration processed in the brain occurring for longer than 10 years.
It has been overwhelmingly illustrated in multiple cohort studies with large and small sample sizes36 that APOE4 is a major genetic risk factor, while APOE2 is a protecting factor for AD. In our study, when plasma amylin concentration was high and beneficial, APOE4 was not a risk factor for AD; when plasma amylin concentration was extremely high and was associated with increased risk of AD, APOE2 was not associated with protection from AD. A 2008 in vitro experiment37 found that APOE4 could bind amylin, which suggests that amylin may be an important player interacting with the APOE genotype in the pathogenesis of late-onset AD. In contrast, being a woman was a risk factor for AD across the 3 amylin groups. It has been widely demonstrated that rat amylin, with 3 amino acid differences from human amylin, does not have aggregating characteristics.13 Pramlintide, an amylin analog based on rat amylin sequence so that it cannot aggregate, is a US Food and Drug Administration–approved and effective drug for type 2 diabetes38 with a favorable safety profile in clinical use.39 Thus, pramlintide could be investigated as a repurposed drug for AD for patients who have a low plasma amylin concentration.
Limitations
This study has limitations. Since participants were relatively young and only a small number had dementia when plasma amylin concentrations were measured, we did not have enough power to study the prevalent association of plasma amylin with AD for this study. We also did not have longitudinal measurements of plasma amylin; thus, we were unable to determine whether plasma amylin concentration changes during AD pathogenesis. Another limitation is that this study sample did not include people of different ethnicities. This U-shaped association between plasma amylin and long-term risk of AD needs to be examined in other human study populations.
Conclusions
The distribution of plasma amylin concentration was skewed in humans and associated with AD and brain structures in a U-shaped manner. It is important to monitor plasma amylin concentration for elderly patients, especially APOE4 carriers, women, and people with diabetes, for the sequela of AD development. Future studies are needed to determine whether the similar associations of plasma amylin with AD that have been found in other cohort studies and whether amylin analogs can be repurposed as a therapeutic for AD, especially people with APOE4, women, and people with diabetes.
eTable 1. Analysis of Orthogonal Polynomial Contrasts and Cox Proportional Hazard Regression on the Association of Plasma Amylin Concentration With Risk of Alzheimer Disease
eTable 2. General Characterization of the Study Sample Based on Plasma Amylin Concentration Quintiles
eTable 3. Association of Plasma Amylin Concentration Quintiles With Alzheimer Disease
eTable 4. Brain Volume Comparisons Among Patients With a Low, High, or Extremely High Plasma Amylin Concentration
eTable 5. Characterization of Brain Volume Based on Plasma Amylin Concentration Quintiles
eTable 6. General Linear Regression Analyses on the Association of Plasma Amylin Concentration With Brain Volume
eFigure 1. Accumulative Alzheimer Disease Incidence Rates Based on Different Cutoffs for Plasma Amylin Concentration
eFigure 2. Distribution of Plasma Amylin Concentrations Among the Population of the Framingham Heart Study
References
- 1.Nishi M, Sanke T, Seino S, et al. . Human islet amyloid polypeptide gene: complete nucleotide sequence, chromosomal localization, and evolutionary history. Mol Endocrinol. 1989;3(11):-. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-11-1775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lutz TA. The interaction of amylin with other hormones in the control of eating. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15(2):99-111. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2012.01670.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mietlicki-Baase EG. Amylin-mediated control of glycemia, energy balance, and cognition. Physiol Behav. 2016;162:130-140. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.02.034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Maness LM, Huang W, Jaspan JB. Permeability of the blood-brain barrier to amylin. Life Sci. 1995;57(22):1993-2001. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(95)02197-Q [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Banks WA, Kastin AJ. Differential permeability of the blood-brain barrier to two pancreatic peptides: insulin and amylin. Peptides. 1998;19(5):883-889. doi: 10.1016/S0196-9781(98)00018-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Olsson M, Herrington MK, Reidelberger RD, Permert J, Arnelo U. Comparison of the effects of chronic central administration and chronic peripheral administration of islet amyloid polypeptide on food intake and meal pattern in the rat. Peptides. 2007;28(7):1416-1423. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2007.06.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hay DL, Chen S, Lutz TA, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Amylin: pharmacology, physiology, and clinical potential. Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(3):564-600. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.010629 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Westfall TC, Curfman-Falvey M. Amylin-induced relaxation of the perfused mesenteric arterial bed: meditation by calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1995;26(6):932-936. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199512000-00012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Edvinsson L, Goadsby PJ, Uddman R. Amylin: localization, effects on cerebral arteries and on local cerebral blood flow in the cat. ScientificWorldJournal. 2001;1:168-180. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2001.23 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Trevaskis JL, Turek VF, Wittmer C, et al. . Enhanced amylin-mediated body weight loss in estradiol-deficient diet-induced obese rats. Endocrinology. 2010;151(12):5657-5668. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0590 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Roth JD. Amylin and the regulation of appetite and adiposity: recent advances in receptor signaling, neurobiology and pharmacology. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2013;20(1):8-13. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e32835b896f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Roth JD, Erickson MR, Chen S, Parkes DG. GLP-1R and amylin agonism in metabolic disease: complementary mechanisms and future opportunities. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;166(1):121-136. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01537.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.May PC, Boggs LN, Fuson KS. Neurotoxicity of human amylin in rat primary hippocampal cultures: similarity to Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta neurotoxicity. J Neurochem. 1993;61(6):2330-2333. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb07480.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lorenzo A, Razzaboni B, Weir GC, Yankner BA. Pancreatic islet cell toxicity of amylin associated with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1994;368(6473):756-760. doi: 10.1038/368756a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Roostaei T, Nazeri A, Felsky D, et al. ; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) . Genome-wide interaction study of brain beta-amyloid burden and cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22(2):287-295. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.35 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jackson K, Barisone GA, Diaz E, Jin LW, DeCarli C, Despa F. Amylin deposition in the brain: a second amyloid in Alzheimer disease? Ann Neurol. 2013;74(4):517-526. doi: 10.1002/ana.23956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297(5580):353-356. doi: 10.1126/science.1072994 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fu W, Ruangkittisakul A, MacTavish D, Shi JY, Ballanyi K, Jhamandas JH. Amyloid β (Aβ) peptide directly activates amylin-3 receptor subtype by triggering multiple intracellular signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(22):18820-18830. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.331181 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Adler BL, Yarchoan M, Hwang HM, et al. . Neuroprotective effects of the amylin analogue pramlintide on Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and cognition. Neurobiol Aging. 2014;35(4):793-801. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.10.076 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhu H, Wang X, Wallack M, et al. . Intraperitoneal injection of the pancreatic peptide amylin potently reduces behavioral impairment and brain amyloid pathology in murine models of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry. 2015;20(2):252-262. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhu H, Xue X, Wang E, et al. . Amylin receptor ligands reduce the pathological cascade of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology. 2017;119:170-181. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.03.030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Qiu WQ. Amylin and its G-protein-coupled receptor: a probable pathological process and drug target for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience. 2017;356:44-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.05.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wilson PW, Nam BH, Pencina M, D’Agostino RB Sr, Benjamin EJ, O’Donnell CJ. C-reactive protein and risk of cardiovascular disease in men and women from the Framingham Heart Study. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(21):2473-2478. doi: 10.1001/archinte.165.21.2473 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kannel WB, Feinleib M, McNamara PM, Garrison RJ, Castelli WP. An investigation of coronary heart disease in families: the Framingham offspring study. Am J Epidemiol. 1979;110(3):281-290. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112813 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Seshadri S. Elevated plasma homocysteine levels: risk factor or risk marker for the development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease? J Alzheimers Dis. 2006;9(4):393-398. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2006-9404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.DeCarli C, Massaro J, Harvey D, et al. . Measures of brain morphology and infarction in the Framingham Heart Study: establishing what is normal. Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26(4):491-510. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.05.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jefferson AL, Himali JJ, Beiser AS, et al. . Cardiac index is associated with brain aging: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2010;122(7):690-697. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.905091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.DeCarli C, Reed T, Miller BL, Wolf PA, Swan GE, Carmelli D. Impact of apolipoprotein E epsilon4 and vascular disease on brain morphology in men from the NHLBI twin study. Stroke. 1999;30(8):1548-1553. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.30.8.1548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Verma N, Ly H, Liu M, et al. . Intraneuronal amylin deposition, peroxidative membrane injury and increased IL-1β synthesis in brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients with type-2 diabetes and in diabetic HIP rats. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;53(1):259-272. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Reibnegger G, Schrabmair W. Optimum binary cut-off threshold of a diagnostic test: comparison of different methods using Monte Carlo technique. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2014;14:99. doi: 10.1186/s12911-014-0099-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Westermark P, Wernstedt C, Wilander E, Hayden DW, O’Brien TD, Johnson KH. Amyloid fibrils in human insulinoma and islets of Langerhans of the diabetic cat are derived from a neuropeptide-like protein also present in normal islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84(11):3881-3885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3881 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gebre-Medhin S, Mulder H, Pekny M, et al. . Increased insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in mice lacking islet amyloid polypeptide (amylin). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;250(2):271-277. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.9308 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Qiu WQ, Zhu H. Amylin and its analogs: a friend or foe for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease? Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:186. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gan Q, Yao H, Na H, et al. . Amylin’s effects against Aβ induced tauopathy and synapse loss in primary neurons. J Alzheimers Dis. In press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang N, Yang S, Wang C, et al. . Multiple target of hAmylin on rat primary hippocampal neurons. Neuropharmacology. 2017;113(Pt A):241-251. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.07.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tanzi RE. A genetic dichotomy model for the inheritance of Alzheimer’s disease and common age-related disorders. J Clin Invest. 1999;104(9):1175-1179. doi: 10.1172/JCI8593 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lei P, Wu WH, Li RW, et al. . Prevention and promotion effects of apolipoprotein E4 on amylin aggregation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;368(2):414-418. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.01.103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gebre-Medhin S, Olofsson C, Mulder H. Islet amyloid polypeptide in the islets of Langerhans: friend or foe? Diabetologia. 2000;43(6):687-695. doi: 10.1007/s001250051364 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Aronne L, Fujioka K, Aroda V, et al. . Progressive reduction in body weight after treatment with the amylin analog pramlintide in obese subjects: a phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(8):2977-2983. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eTable 1. Analysis of Orthogonal Polynomial Contrasts and Cox Proportional Hazard Regression on the Association of Plasma Amylin Concentration With Risk of Alzheimer Disease
eTable 2. General Characterization of the Study Sample Based on Plasma Amylin Concentration Quintiles
eTable 3. Association of Plasma Amylin Concentration Quintiles With Alzheimer Disease
eTable 4. Brain Volume Comparisons Among Patients With a Low, High, or Extremely High Plasma Amylin Concentration
eTable 5. Characterization of Brain Volume Based on Plasma Amylin Concentration Quintiles
eTable 6. General Linear Regression Analyses on the Association of Plasma Amylin Concentration With Brain Volume
eFigure 1. Accumulative Alzheimer Disease Incidence Rates Based on Different Cutoffs for Plasma Amylin Concentration
eFigure 2. Distribution of Plasma Amylin Concentrations Among the Population of the Framingham Heart Study