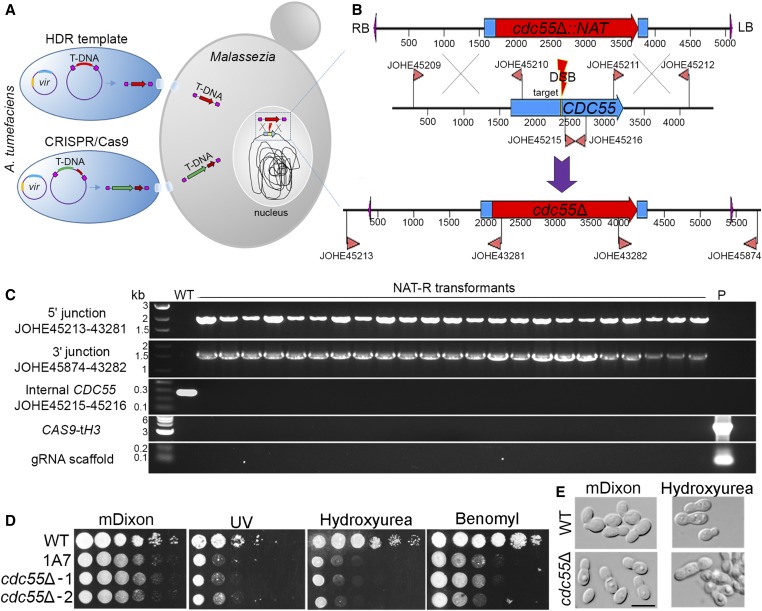
Figure 5.
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated target mutagenesis of M. furfur CDC55. (A) Cotransformation of M. furfur mediated by two A. tumefaciens strains, one that delivers a T-DNA including the HDR template (i.e., cdc55Δ::NAT deletion construct in red), and another that includes the CAS9 cassette (in green) and the gene-specific gRNA (dark red). Also depicted are the vir plasmids present in A. tumefaciens cells that are necessary for T-DNA excision and transfer to the M. furfur nucleus where HR occurs. (B) Magnification of the HR event that occurs in the M. furfur nucleus. The top construct represents the T-DNA of the plasmid pGI41 bearing the cdc55Δ::NAT HDR template. The middle panel represents the native M. furfur CDC55 locus, the primers used to amplify the 5ʹ and 3ʹ regions for HR, the internal primer for the CDC55 gene, and the 20-nt target sequence (yellow). The gRNA guides Cas9 to the target site to generate a DSB that is repaired using the deletion allele as template, resulting in the targeted replacement of CDC55 with a NAT dominant marker (lower panel). Primers outside the region in which HR events occur are used in combination with primers for the NAT marker to identify cdc55Δ mutants. (C) Diagnostic PCR analyses of M. furfur WT and NAT-resistant transformants for the identification of cdc55Δ mutants. Each panel used the indicated combination of primers, whose position can be found in (B). PCR primers for CAS9 and gRNA are reported in Table S1. (D) Phenotypic analysis of M. furfur WT, insertional mutant 1A7, and two independent cdc55Δ mutants on mDixon (control), UV (300 µJ/cm2 × 100), hydroxyurea (50 mM), and benomyl (50 µM); 1.5 µl of 10-fold serial dilutions were spotted on the agar plates, incubated at 30° for 3–7 days, and then photographed. (E) Microscopic analysis of cell morphology of WT and a representative cdc55Δ mutant, after growth on mDixon and mDixon supplemented with hydroxyurea (50 mM). The black bar indicates 5 µm. CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; DSB, double-strand break; gRNA, guide RNA; HDR, homology-directed repair; HR, homologous recombination; mDixon; modified Dixon’s media; NAT, nourseothricin; T-DNA, transfer DNA; WT, wild-type.