Abstract
Background
With the development and application of endoscopic technology, most pedunculated polyps can be absolutely resected with a complete specimen by hot snare polypectomy (HSP). Brunner’s gland hamartoma (BGH) is a rare benign small bowel tumor. The majority of BGH measuring about 2 cm in diameter, rarely larger than 5 cm. Most patients are asymptomatic, some may present with gastrointestinal hemorrhage or intestinal obstruction. Symptomatic larger lesions leading to bleeding or obstruction should be excised either endoscopically or surgically. Whether it is safe and effective that removing a BGH measuring about 7 cm by HSP is not known.
Case presentation
Here, we reported a rare case of a proximal duodenum pedunculated mass measuring about 7 cm which was responsible for the patient’s severe anemia. we treated it as a pedunculated polyp. After being pretreated the stalk with an endoloop which was placed around the base of the mass to prevent post-polypectomy bleeding (PPB), the pedunculated BGH was removed by HSP completely. The stalk of the mass was negative. We achieved a curative resection.
Conclusion
It is a safe and effective for our patient to treat the pedunculated BGH measuring about 7 cm as a pedunculated polyp and remove it by HSP. And future prospective studies in larger cohorts are needed to confirm it.
Keywords: Brunner’s gland hamartoma, Severe anemia, Hot snare polypectomy, Endoscopy, Case report
Background
For pedunculated polyps, most can be easily removed completely by hot snare polypectomy (HSP). It can not only allow us to obtain a complete specimen, but also can achieve a curative resection [1]. Is this strategy applicable to other pedunculated masses, of which even the size is about 7 cm? Brunner’s gland hamartoma (BGH) is a benign tumor of the duodenum arising from the Brunner’s glands [2]. Most patients are asymptomatic, but some may present with common gastrointestinal symptoms such as bleeding, nausea, vomiting, and chronic abdominal pain [3]. Brunner’s gland hamartoma can be treated either by endoscopic or surgical excision [4]. To our knowledge, up to now, only 4 cases of endoscopic resection of BGH larger than 7 cm have been reported [5–8]. In two cases, the BGH was removed by endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) respectively [5, 6]. In the other two cases being reported 13 years and 18 years ago respectively, neither of them pretreated the stalk, which was very important to the strategy for the treatment of pedunculated mass, to prevent the main adverse event post-polypectomy bleeding (PPB) [7, 8]. Whether it is safe and effective that removing a 7 cm BGH by HSP is not known.
Here, we report a rare case that a pedunculated BGH measuring about 7 cm in proximal duodenum, causing severe anemia, was treated as a pedunculated polyp and being successfully removed by hot snare polypectomy (HSP) in a curable way.
Case presentation
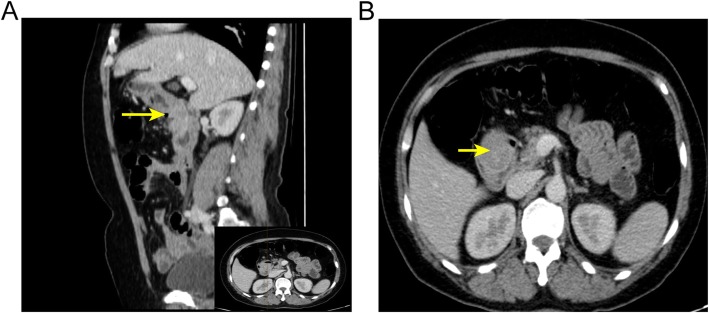
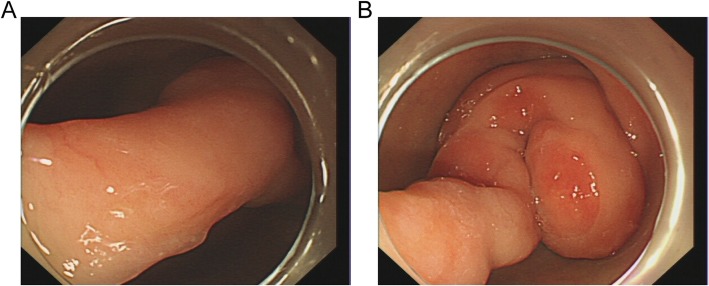
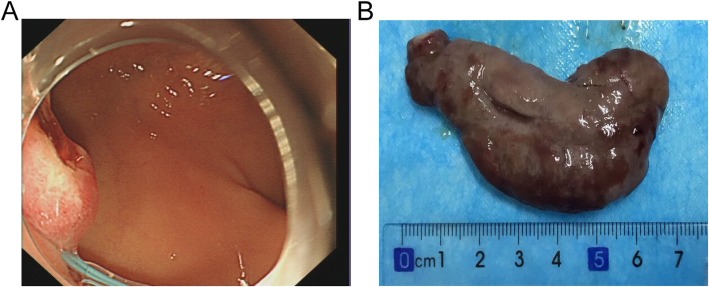
A 63-year-old woman complained with a 20-days history of melena, epigastric pain and fatigue. A single episode of melena had occurred 5 months ago but no further investigation was performed. The patient has no medical history of taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including no family history of cancer or surgery. Before being referred to our hospital, she initially presented to a clinic and was informed a grant lesion by esophagogastroduodenoscopy. At physical examination of the woman, pallor, sensitivity in the epigastric zone were noted. Vital signs (temperature 36.6 C, pulse 91 beats/minute, pressure of 125/75 mmHg, oximetry saturation100%) were normal. Melena was detected in the rectal examination. Hematological test showed a severe anemia with 32 g/L hemoglobin (normal range, 115-150 g/L), hematocrit 11.7% (mean corpuscular volume 66 fL, mean corpuscular hemoglobin 18.1 pg). Blood iron level was 6.8 ng/ml (normal range, 10-291 ng/mL). Intravenous iron supplement was offered to this lady. Helicobacter pylori test was negative. Due to her microcytic anemia, a colonoscopy was performed and came out to be negative. After 2-unit blood transfusions of erythrocyte concentrates, the woman felt better and refused more transfusions. Computed tomography analysis showed a giant mass near the proximal duodenum (Fig. 1a and b). Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed a giant pedunculated mass with a congested and erosive appearance arising from the duodenal bulb (Fig. 2a and b). No difference was observed between most appearance of the mass and the duodenal normal mucosa. The tumor was not the same as the pedunculated polyp we treated as usual. Because the mass was suspected of being responsible for the patient’s severe anemia, removing the mass was necessary. For the long stalk, the mass could be completely removed by HSP easily like a pedunculated polyp. And a pedunculated specimen could be easily obtained for a further histological examination. We thought the strategy for pedunculated polyps was applicable to this pedunculated mass. After being informed of all approaches to treating this mass, including the risk of endoscopic perforation or bleeding, the patient consented to remove this mass by HSP. We treated this mass as a pedunculated polyp, pretreating the stalk with an endoloop which was placed around the base of the mass to prevent post-polypectomy bleeding (PPB). Then the pedunculated mass was removed by HSP easily. In order to extracting the removed specimen, we used the snare to pull part of the mass into the transparent cap by trapping the smaller end of the mass. Then the specimen was pulled out following the endoscope and a complete specimen was obtained (Fig. 3a). The process was simple and effective, and usually took less time than ESD or EMR. The stalk of the specimen was dealt with carefully for histological examination. The gross endoscopic resection specimen showed a large duodenal lesion measuring 7 × 3 × 1.6 cm3 (Fig. 3b). The resected pedunculated mass was histologically confirmed a giant Brunner’s gland hamartoma (Fig. 4a and b). And the stalk was negative. Epigastric pain and melena of the patient were resolved after the endoscopic treatment and two weeks later, her hemoglobin rose up to 82 g/L. Three months later, her hemoglobin was normalized and no evidence of recurrence or tumor remnants were found by a repeat esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Fig. 1.
(a) Contrast-enhanced sagittal and (b) axial computed tomography scan shows a large polypoid mass in the duodenal bulb (arrows)
Fig. 2.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy shows a tortuous pedunculated mass occupying the lumen of the duodenal bulb. (a) The long and thick pedicle of the tumor. (b) The tumor is coiled around the duodenal bulb
Fig. 3.
(a) The appearance after polypectomy (b) The complete endoscopic resection specimen showed a large duodenal lesion measuring 7 × 3 × 1.6 cm3
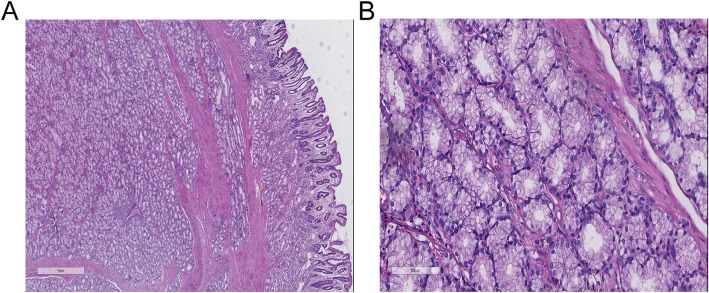
Fig. 4.
Microscopic pictures. (a) Light microscopy showed hyperplastic lobules of proliferating Brunner’s glands separated by fibrous. H&E staining, scale bar: 1 mm. (b) Brunner’s gland hyperplasia composed of variable size of Brunner’s glands can be observed. H&E staining, scale bar: 100 μm
Discussion and conclusion
Brunner’s glands were first described by Brunner in 1688 [9]. They locate in duodenal submucosa and secrete some alkaline fluid which can avoid gastric acid eroding duodenal epithelium [2]. The benign hyperplastic lesions of Brunner glands are described as Brunner gland hyperplastic nodules/polyps or Brunner gland hamartomas [10]. As a rule, lesions smaller than 2 cm defined as Brunner’s gland hyperplastic nodules/polyps, while lesions larger than 2 cm termed Brunner’s gland hamartoma [11]. The pathogenesis of BGH remains obscure. Chronic pancreatitis and Helicobacter pylori infection are suspected to be involved [2, 6]. Because BGH was usually covered with normal mucosa, the value of pinch biopsies might be limited. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) may be helpful in the diagnosis and treatment of BGH [12]. In our case, taking into account that a complete specimen for histological examination could be obtained easily by HSP, we did not perform a EUS. However, we believe that the endoscopic resection should been much safer if we had performed a EUS which could offer us some information about the nature of the mass and submucosal vascular. Usually, asymptomatic small Brunner’s gland hamartomas require no treatment. While symptomatic and larger lesions leading to bleeding or obstruction should be excised either endoscopically or surgically [11].
Endoscopic treatments for large Brunner’s hamartomas with relatively low complication and mortality rates is effective and safe [5, 6]. But not all the large BGH could be removed endoscopically. As Table 1 shows, in reported cases of Brunner’s gland hamartomas larger than 5 cm, all the exophytic BGH and sessile BGH are removed surgically, while Endoscopic resection was only performed in the pedunculated BGH. In addition, surgical treatment was also chosen in the pedunculated mass in the following cases: [1] Malignancy of the mass can not be excluded; [2] some emergency complications like intussusception; [3] The mass was too large, or the stalk was too thick to be removed endoscopically. Therefore, preoperative diagnosis and endoscopic evaluation are important to proper selection of the interventional approach.
Table 1.
The characteristics of Brunner’s gland hamartomas larger than 5 cm and interventional approaches in reported cases
| Reference | Size (cm) | Growth pattern | PeduncuLated or sessile | Reasons for choosing different interventional approaches | The interventional approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [13] | 8 × 10 | exophytic type | not applicable | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [14] | 5 X 6 | exophytic type | not applicable | Malignancy could not be excluded. | Surgery |
| [15] | 7.9 | exophytic type | not applicable | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [16] | 5–6 | exophytic type | not applicable | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [17] | 6 | exophytic type | not applicable | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [18] | 6.6 × 4.5 | exophytic type | not applicable | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [19] | 5.5 × 3.3× 2.2 | intraluminal type | sessile | Malignancy could not be excluded | Surgery |
| [20] | 5.5 | intraluminal type | sessile | unknown nature of the mass | Surgery |
| [21] | 10.5 | intraluminal type | sessile | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [22] | 7.3 × 3.4× 2.9 | intraluminal type | sessile | The suspicion for malignancy was high | Surgery |
| [23] | 7.5 × 6.5× 6.5 | intraluminal type | sessile | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [24] | 10 × 6 × 8 | intraluminal type | sessile | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [25] | 12 × 10 × 8 | intraluminal type | sessile | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [3] | 8 × 4 × 8 | intraluminal type | sessile | uncertain malignant potential | Surgery |
| [26] | 6 × 2.4 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [27] | 6 × 3 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [28] | 5 × 3、6 × 3.5 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [29] | 6 × 4 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | the large size of the tumor | Surgery |
| [30] | 7.3 × 3.4 × 2.9 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [31] | 8 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [32] | 3 × 10 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | intussusception | Surgery |
| [33] | 10–12 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | suspected malignant transformation | Surgery |
| [2] | 10 × 2 × 1.5 | intraluminal type | peduncuLated | large size and the difficulty in gaining access to the head of the polyp for snaring. | Surgery |
| [34] | 6.4 × 3 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | The stalk was too thick | Surgery |
| [35] | 5.5 × 4.2 × 4.3 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | The polyp was too large | Surgery |
| [36] | 6x5x3 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Surgery |
| [5] | 7 × 2 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Endoscopic polypectomy |
| [6] | 9.3 × 2 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Endoscopic polypectomy |
| [7] | 7 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Endoscopic polypectomy |
| [8] | 10.5 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Endoscopic polypectomy |
| [37] | 6.5 × 4 × 4 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | no invasion andintraluminal type | Endoscopic polypectomy |
| [38] | 6 × 0.9 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | For both the diagnosis and the treatment. | Endoscopic polypectomy |
| [39] | 6.0 × 0.4 × 0.2 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Endoscopic polypectomy |
| [40] | 5 | intraluminal type | pedunculated | Not given clearly | Endoscopic polypectomy |
Large pedunculated polyps have an increased risk of PPB because of the presence of a large blood vessel within the stalk [41]. Pretreatment of the stalk is a recommended method to prevent it [1]. In our case, the giant pedunculated mass measuring about 7 cm was suspected of being responsible for the patient’s severe anemia. We treated it as a pedunculated polyp. After being pretreated the stalk to prevent PPB, the pedunculated BGH was removed by HSP completely. The stalk of the mass was negative. We achieve a curative resection. For our patient, removing a pedunculated by HSP is safe and effective. Future prospective studies in larger cohorts are necessary for further verification.
Acknowledgements
We thank Xiaoli Ren for her assistance in providing imaging consultation.
Abbreviations
- BGH
Brunner’s gland hamartoma
- EMR
Endoscopic mucosal resection
- ESD
Endoscopic submucosal dissection
- EUS
Endoscopic ultrasound
- HSP
Hot snare polypectomy
- PPB
Post-polypectomy bleeding
Authors’ contributions
LZY, ZYC, TW, KL and HQ collected the information of the patient and wrote the manuscript. JJY performed the histological examination. LZY was also a major contributor in writing the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate√
A case report is intended to develop information to be shared for medical and educational purposes and do not meet the definition of “research”. Ethical approval was not necessary. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Consent for publication
Written consent for publication was obtained from the patient.
Competing interests
The authors have disclosed that they have no significant relationships with, or financial interest in, any commercial companies pertaining to this article.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Lizhi Yi, Zhengyu Cheng and Huarong Qiu contributed equally to this work.
References
- 1.Ferlitsch M, Moss A, Hassan C, et al. Colorectal polypectomy and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR): European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) clinical guideline. Endoscopy. 2017;49:270–297. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-102569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tan YM, Wong WK. Giant brunneroma as an unusual cause of upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage: report of a case. Surg Today. 2002;32:910–912. doi: 10.1007/s005950200179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Frenkel NC, Laclé MM, Borel Rinkes IH, Molenaar IQ, Hagendoorn J. A Giant Brunneroma causing gastrointestinal bleeding and severe Anemia requiring transfusion and surgery. Case Rep Surg. 2017;2017:6940649. doi: 10.1155/2017/6940649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jung Y, Chung IK, Lee TH, et al. Successful endoscopic resection of large pedunculated Brunner's gland hamartoma causing gastrointestinal bleeding arising from the pylorus. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2013;7(2):304–307. doi: 10.1159/000354138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kitagawa Y, Osumi H, Kawachi H, et al. Giant duodenal Brunner’s gland hamartoma successfully treated via endoscopic mucosal resection. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2018;19:125–129. doi: 10.1016/j.ajg.2018.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lee JH, Jo KM, Kim TO et al. Giant Brunner's gland hamartoma of the duodenal bulb presenting with upper gastrointestinal bleeding and obstruction. Clin Endosc. 2016;49:570–574. doi: 10.5946/ce.2016.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Stermer E, Elias N, Keren D, Rainis T, et al. Acute pancreatitis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding as presenting symptoms of duodenal Brunner's gland hamartoma. Can J Gastroenterol. 2006;20:541–542. doi: 10.1155/2006/806926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tai M, Yoshikawa I, Kume K, et al. A large Brunner’s gland hamartoma resected by endoscopicpolypectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;53:207–208. doi: 10.1067/mge.2001.112041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gao YP, Zhu JS, Zheng WJ. Brunner's gland adenoma of duodenum: a case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10:2616–2617. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kim K, Jan SJ, Song HJ, Yu E. Clinicopathologic characteristics and mucin expression in Brunner’s gland proliferating lesions. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:194–201. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Collins K, Ligato S. Duodenal epithelial polyps: a Clinicopathologic review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2019;143:370–385. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2018-0034-RA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Xu GQ, Wu YQ, Wang LJ, Chen HT. Values of endoscopic ultrasonography for diagnosis and treatment of duodenal protruding lesions. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2008;9:329–334. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B0710546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gupta V, Singh V, Kalra N, Vaiphei K. Pancreas sparing resection for giant hamartoma of Brunner’s glands. JOP. 2009;10:196–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Limi L, Liew NC, Badrul RH, Faisal MJ, Daniel YP. Duodenal intussusception of Brunner’s glandadenoma mimicking a pancreatic tumour. Med J Malaysia. 2010;65(4):311–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pandey A, Chandra A, Wahal A. Brunneroma with duodenojejunal intussusception: a rare cause of gastric outlet obstruction. BMJ Case Reports. 2013;2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Mayoral W, Salcedo JA, Montgomery E, Al-Kawas FH. Biliary obstruction and pancreatitis caused by Brunner’s gland hyperplasia of the ampulla of water: a case report and review of the literature. Endoscopy. 2000;32:998–1001. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-9623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stoos-Veic T, Tadic M, Aralica G. EUS-FNA of Brunner’s gland hamartoma: a case report. Cytopathology. 2013;24:194–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2303.2011.00932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mumtaz R, Shah IA, Ramirez FC. Brunner’s gland hamartoma simulating a pancreatic mass with duodenal obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:932–934. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5107(02)70380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yadav D, Hertan H, Pitchumoni CS. A giant Brunner’s gland adenoma presenting as gastrointestinal hemorrhage. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001;32:448–450. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200105000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Iusco D, Roncoroni L, Violi V, Donadei E, Sarli L. Brunner's gland hamartoma: ‘over-treatment’ of a voluminous mass simulating a malignancy of the pancreatic-duodenal area. JOP. 2005;6:348–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Stewart ZA, Hruban RH, Fishman EF, Wolfgang CL. Surgical management of giant Brunner’s gland hamartoma: case report and literature review. World J Surg Oncol. 2009;7:68. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-7-68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Qayed E, Wehbi M, Rutherford R. Gastrointestinal bleeding from Brunner gland hamartoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;9:e4–e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Namikawa T, Kobayashi M, Hanazaki K. An unusual giant duodenal mass lesion. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:e5–e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.10.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cheung TT, Ip EWK, Poon RTP, Trendell-Smith N. Brunner's gland adenoma: unusual cause of duodenal haemorrhage and obstruction. Hong Kong Medical Journal. 2013;19(5):460.e1-460.e2. doi: 10.12809/hkmj133776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.de Silva S, Chandrasoma P. Chandrasoma. Giant duodenal hamartoma consisting mainly of Brunner's glands. Am J Surg. 1977;133:240–243. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Silverman L, Waugh JM, Huizenga KA, Harrison EG. Large adenomatous polyp of Brunner’s glands. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961;36:438–443. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.5.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liu J, Li YQ, Xu H, Tang TY. Significant upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage and intussusception due to a giant Brunners gland adenoma. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2014;25:446–447. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2014.5996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Takeuchi M, Cho H, Sugimoto M, Ohira T, Usuki N, Morimoto Y. CT and MRI findings for Brunner's gland hamartoma: report of three cases. Jpn J Radiol. 2015;33:375–379. doi: 10.1007/s11604-015-0425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Adell-Carceller R, Salvador-Sanchís JL, Navarro-Navarro J, et al. Laparoscopically treated duodenal hamartoma of Brunner's glands. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1997;7(4):298–300. doi: 10.1097/00019509-199708000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lu L, Li R, Zhang G, Zhao Z, Fu W, Li W. Brunner’s gland adenoma of duodenum: report of two cases. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:7565–7569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bayan K, Tüzün Y, Yilmaz S, Yilmaz G, Bilici A. Pyloric giant brunner’s gland hamartoma as a cause of both duodenojejunal intussusception and obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2009;20:52–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nakabori T, Shinzaki S, Yamada T, et al. Atypical duodenal ulcer and invagination caused by a large pedunculated duodenal Brunner's gland hamartoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79:679–680. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2013.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Verma I, Jha R, Parikh M, Agrawal A. Giant Brunner’s gland hamartoma! BMJ Case Rep. 2015;2015. pii: bcr2015210670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Akaki M1, Taniguchi S, Hatakeyama K, Kushima R, Kataoka H. Duodenal mucosal damage is associated with proliferative activity of Brunner’s gland hamartoma: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014;14:14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 35.Vyas S, Skipworth JR. Lytras Det al. Rare presentation of brunner’s gland adenoma: another differentiation in patients with recurrent “idiopathic” pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2012;11:107–110. doi: 10.1016/S1499-3872(11)60133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gupta V, Gupta P, Jain A. Giant Brunner’s glandadenoma of the duodenal bulb presenting with ampullary and duodenal obstruction mimicking pancreatic malignancy. JOP. 2011;12:413–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ohba R, Otaka M, Jin M, et al. Large Brunner’s gland hyperplasia treated with modified endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52:170–172. doi: 10.1007/s10620-006-9607-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Itaba S, Iwasa T, Sadamoto Y, Nasu T, Misawa T, Nakamura K. An unusual duodenal polyp: pedunculated Brunner’s glands hyperplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:1070–1071. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2005.11.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chen YY, Su WW, Soon MS, Yen HH. Hemoclip-assisted polypectomy of large duodenal Brunner's gland hamartoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2006;51(9):1670–1672. doi: 10.1007/s10620-005-9039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Desai G, Yadav K, Pande P, Sali P, Tampi C, Wagle P. Brunner gland adenoma masquerading as duodenal gastrointestinal stromal tumor with intussusception: CASE report. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2017;30:71–72. doi: 10.1590/0102-6720201700010020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dobrowolski S, Dobosz M, Babicki A, et al. Blood supply of colorectal polyps correlates with risk of bleeding after colonoscopic polypectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:1004–1009. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2005.11.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.