CELL BIOLOGY Correction for “Interspecies analysis of MYC targets identifies tRNA synthetases as mediators of growth and survival in MYC-overexpressing cells,” by Jonathan Zirin, Xiaochun Ni, Laura M. Sack, Donghui Yang-Zhou, Yanhui Hu, Roderick Brathwaite, Martha L. Bulyk, Stephen J. Elledge, and Norbert Perrimon, which was first published July 1, 2019; 10.1073/pnas.1821863116 (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 14614–14619).
The authors note that Fig. 5 appeared incorrectly. The corrected figure and its legend appear below.
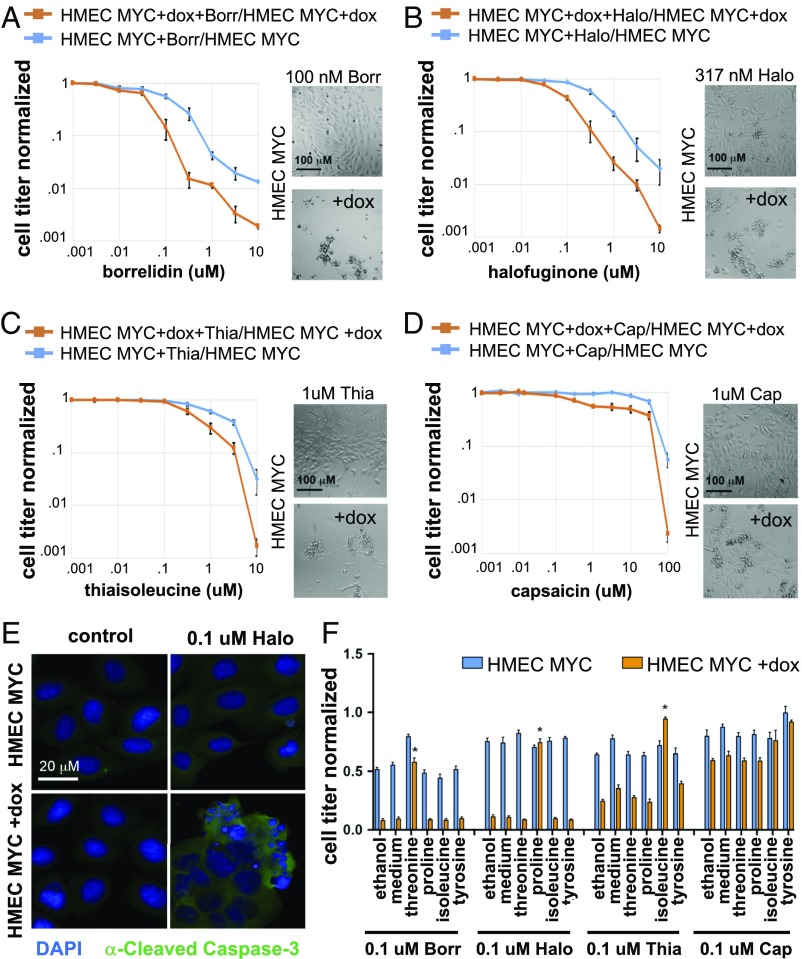
Fig. 5.
aaRS inhibitors selectively kill c-Myc–overexpressing cells. (A–D) Viability curves of control HMEC-MYC cells vs. dox-induced HMEC-MYC cells after 24 h of aaRS inhibition. Cells treated with aaRS inhibitors were normalized to control untreated cells. Representative cell culture images are shown adjacent to curves. (A) At 100 nM and above, borrelidin (Borr) selectively kills dox-induced compared with uninduced HMEC-MYC cells. (B) At 100 nM and above, halofuginone (Halo) selectively kills dox-induced compared with uninduced HMEC-MYC cells. (C) At 1 μM and above, thiaisoleucine (Thia) selectively kills dox-induced compared with uninduced HMEC-MYC cells. (D) Capsaicin does not selectively kill dox-induced compared with uninduced HMEC-MYC cells. (E) Halo treatment triggers cell death of dox-induced HMEC-MYC cells, but not control HMEC-MYC cells. Cells are stained with DAPI (blue) and α-cleaved caspase-3 (green). (F) Viability of HMEC-MYC ± dox cells treated with aaRS inhibitors and supplemented with either controls (ethanol and medium) or amino acids (2 mM). Only the cognate amino acid for the aaRSs targeted by the drugs were able to rescue cell viability (Thr/Borr, Pro/Halo, Ile/Thia) P < 0.01.