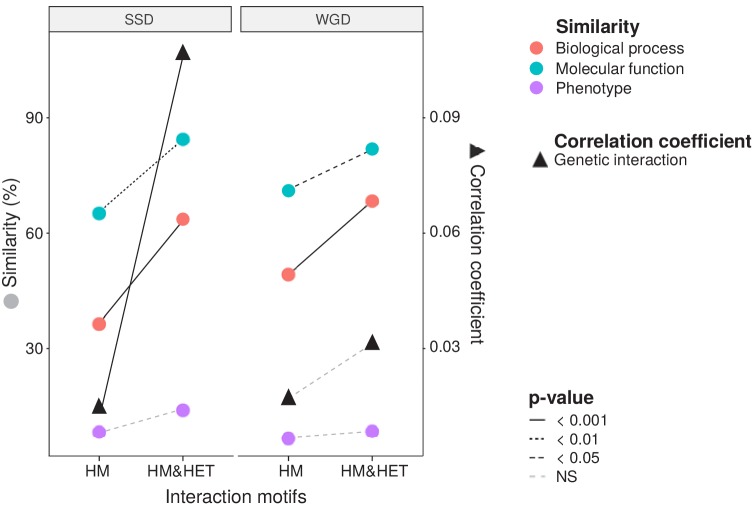
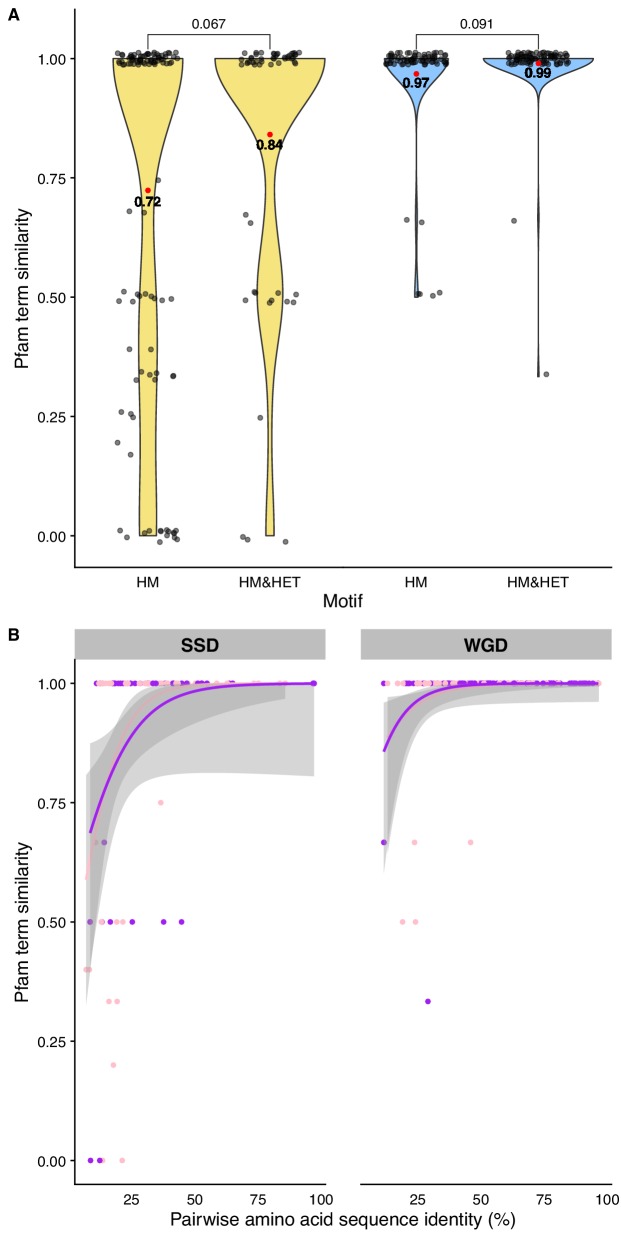
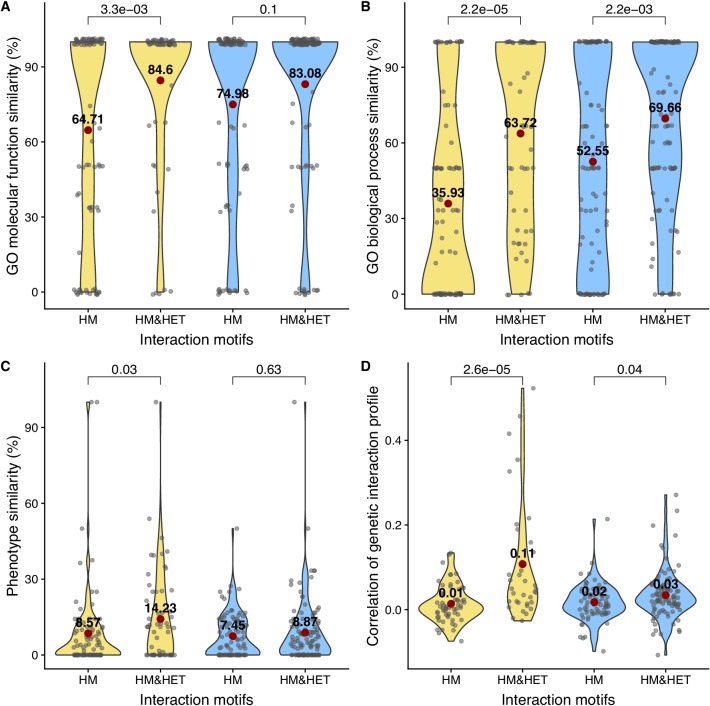
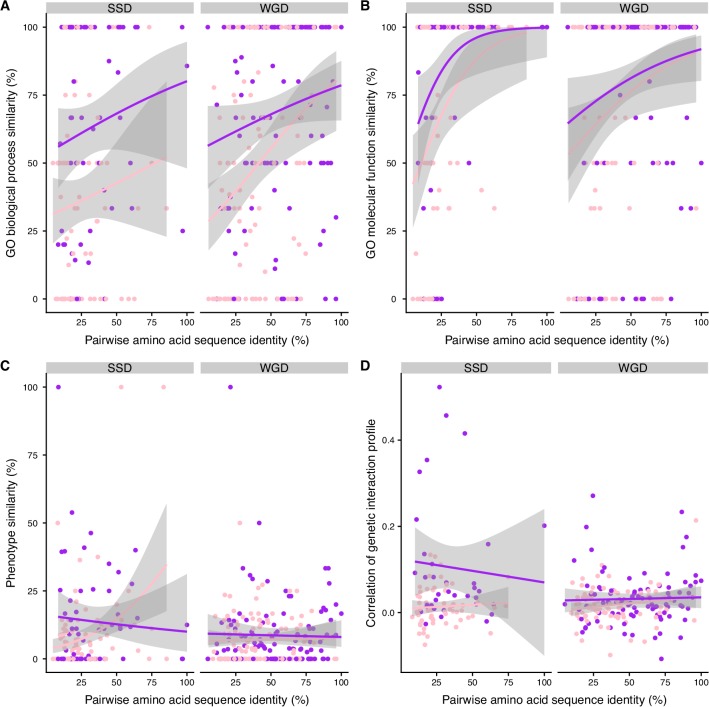
Figure 3. Maintenance of heteromerization between paralogs leads to greater functional similarity.
The similarity score is the average proportion of shared terms (100% * Jaccard's index) across pairs of paralogs for GO molecular functions, GO biological processes and gene deletion phenotypes. The mean values of similarity scores and of the correlation of genetic interaction profiles are compared between HM and HM&HET pairs for SSDs and WGDs. P-values are from Wilcoxon tests.