Abstract
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tb) is a highly successful pathogen that has co-existed with humans for 1,000's of years. As the cornerstone of the immune system, macrophages are a key part of innate immunity. They ingest and degrade foreign substances including aging cells and microorganisms, coordinate the inflammatory process, and are the first line of defense against M. tb infection. Recent advances in cellular mycobacteriology have indicated that M. tb uses an remarkably complex strategy to disrupt macrophage function, in order to counteract the antimicrobial mechanisms of the innate and adaptive immune responses, thereby achieving immune escape. With the popularity of microarray technology, a variety of public platforms have provided a variety of gene expression data associated with physiological and disease conditions. Meta-analysis can systematically and quantitatively analyze multiple independent data concerning the same disease, greatly improving the statistical significance and credibility of the gene expression data analysis performed. In the present study, 6 microarray expression datasets of human acute monocytic leukemia THP-1 cell line infected by M. tb H37Rv strain were collected from the GEO database. A total of 4 high-quality datasets were identified using meta-analysis methods in R language, and 306 differentially expressed genes with statistical significance were obtained. Then, a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of these differentially expressed genes was constructed on the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins Database online tool and visualized by Cytoscape v. 3.6.1 software. Using CentiScape and MCODE plugin in the Cytoscape software to mine the functional modules associated with M. tb infection process, 32 characteristic genes were identified. Gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis was performed on the 32 characteristic genes, and it was demonstrated that these genes were primarily associated with the type I interferon (IFN) pathway. In the established model of THP-1-derived macrophages infected by M. tb, the actual differential expression levels of IFN-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15), 2′-5-oligoadenylate synthetase like (OASL), IFN regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) and DExD/H-box helicase 58 (DDX58), the first 4 genes of the 32 characteristic genes, were verified by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction. The results were consistent with the results of microarray analysis. The association between ISG15, OASL and IRF7 and TB infection was also verified. Although a number of studies have identified that the type I IFN pathway may assist M. tb to achieve immune escape, the present study used a meta-analysis of microarray data and PPI network analysis to examine some of the novel genes identified in the IFN pathway. The results furthered the understanding of the molecular mechanisms of the TB immune response and provided a novel perspective for future therapeutic goals.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, meta-analysis, protein-protein interaction network
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by the bacillus Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tb), one of the most successful bacteria that infects humans (1). TB has existed for millennia and remains a major global health problem (2). In recent years, the emergence and spread of (multi)drug-resistant M. tb along with the limited protection afforded by the current BCG vaccine in a number of populations has made it difficult to effectively control the TB epidemic. TB is one of the top 10 causes of mortality and the leading cause of mortality from a single infectious agent, more than HIV/AIDS, and millions of individuals continue to become infected each year (3). The clinical infection of TB is complicated. The aim of the present study was to reveal the general host response mechanism to TB infection and examine its potential immune mechanism effects through the analysis of the M. tb H37Rv strain.
Macrophages, being professional phagocytes, ingest and degrade dead cells, debris and foreign material, and orchestrate inflammatory processes, which serve an essential role in the control of bacterial infections (4,5). When M. tb infects the host, it first needs to resist the immune response from macrophages (6,7). Paradoxically, macrophages may be the primary long-term environment for M. tb in the host, as M. tb is able to evade the principle antimicrobial mechanism of macrophages through a variety of bacterial immune subversive mechanisms, allowing the bacteria to utilize various intracellular cell resources (8). However, the mechanisms by which M. tb enters the host cell, circumvents host defenses and spreads to neighboring cell are not completely understood. Therefore, an improved understanding of host-pathogen interaction is essential if the global TB pandemic is to be controlled (9). The interaction between macrophages and M. tb alters cellular gene expression profiles, and studies of changes in expression of these genes may assist to understand the immunomodulatory effects of M. tb in macrophages.
With the beginning of the era of big data, the mining and application of high-throughput big data for genes has received more and more attention. Microarray technology is fundamental to generating large amounts of gene expression data. Microarray technology is widely used as it is able to simultaneously detect and express high-throughput expression levels of 10,000's of gene transcription sets (10). Microarray technology can be used to study gene expression more efficiently and in-depth. With the increasing availability of microarray technology, gene expression data associated with various physiological and disease conditions are provided on public platforms, including the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and The Cancer Genome Atlas database (11). The meta-analysis tools for the systematic and comprehensive quantitative analysis of the results of multiple independent studies investigating the same disease have been developed (12). A number of studies have used meta-analysis methods to analyze small sample experimental studies, improving the accuracy of statistical performance and effect estimation (13-19).
The present study used meta-analysis methods to identify overlapping DEGs in THP-1-derived macrophages infected by M. tb, analyze protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks, identify potential central genes, complete functional and pathway enrichment studies and verify pivotal gene differences expression through experiments. The potential effects of the immune mechanism of TB infection was estimated using the aforementioned method.
Materials and methods
Microarray data collection and quality control
The present study used the GEO database at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) to retrieve expression profile datasets. The search terms used were: 'Mycobacterium tuberculosis', 'THP-1' and 'Homo sapiens'. Series Matrix Files of these datasets was downloaded respectively, and the probe IDs were transformed into official gene symbols. In order to obtain more credible results, the MetaQC package in R was applied to implement quality control analysis and directly used the principal component analysis chart to display statistical results. There are 6 quantitative quality control measures in this package, including: i) internal homogeneity of co-expression structure among studies; ii) external consistency of co-expression structure correlating with a pathway database; iii) accuracy of differentially expressed genes (DEG) detection and pathway identification; and iv) consistency of differential expression ranking of genes and pathways. Through quality control, only the data with high quality was included in the subsequent analysis.
DEGs identification
DEGs were screened out with MetaDE v.1.0.5 software package (20), which provides 12 major meta-analysis methods. In the present study, 3 methods, including Fisher, rth-ordered P-value (roP) and random effects model (REM) were selected to filtrate DEGs in high quality data. A false discovery rate (FDR) <0.05 was considered as the cut-off criterion. In addition, the intersection of the required datasets under the three statistical methods was extracted and considered as the most reliable DEGs. DEGs were regressed into high quality data to complete cluster analysis.
PPI network construction
The initial PPI network for the protein products of identified DEGs was constructed using the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins Database (STRING v10; https://string-db.org/) (21), and then the network was visualized and analyzed with Cytoscape v.3.6.1 software (22). To extract the characteristic genes from the DEGs, the CentiScape and MCODE plugins in the Cytoscape software were used. Firstly, the Degree Centrality (DC) of CentiScape reflects hubness of the node in the PPI network by calculating the degree. Nodes with higher centrality were extracted. Secondly, constructing sub-networks through k-core analysis of the MCODE afforded the selection a stable structure from a high-centrality network, and narrowed the scope of the study.
Function and pathway enrichment analysis of characteristic genes
To assess the prospective functions of characteristic genes identified by the meta-analysis and PPI network analysis, Gene Ontology (GO) biological pathways and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways were identified using CluGO from Cytoscape software. P<0.05, subjected to Bonferroni adjustment, were defined as the cut-off criterion.
M. tb H37Rv and THP-1 cell line propagation and infection
The M. tb H37Rv strain (American Type Culture Collection; product no., 27294) was grown at 35°C for 15 days in a Middlebrook 7H9 medium (BD Biosciences), supplemented with 10% (v/v) OADC (BD Biosciences), with the addition of 0.2% glycerol (v/v) and 0.025% Tween-80 (v/v). The human acute monocytic leukemia THP-1 cell line (American Type Culture Collection; cat. no. TIB-202) was cultivated at 37°C in 5% CO2 in RPMI-1640 (Hyclone; GE Healthcare Life Sciences) medium supplemented with 10% FBS (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). Prior to infection, THP-1 cells were treated with 200 nM phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for 24 h to allow for the differentiation into macrophages in 6-well plates. Infections were performed with the M. tb H37Rv strain at a multiplicity of infection of 5. The 7H9 broth was used as a blank control.
M. tb infection confocal microscopy
The success of the M. tb infection model was verified by observing the co-localization of M. tb with THP-1 cell lysosomes. Firstly, M. tb was labeled with fluorescent isothiocyanate (FITC) solution (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) according to the manufacturer's protocol. M. tb was washed 3 times with PBS buffer, resuspended in carbonate buffer, and added to FITC (10 mg/ml) to a final concentration of 100 µg/ml. Following incubation for 2 h at room temperature, the supernatant was isolated by centrifugation at 1,000 × g for 2 min at 4°C, and inoculated into THP-1 cells previously induced to adhere to slides in a 6-well plate, and the whole procedure was performed in the dark. Then, according to the manufacturer's protocol, the Lyso Tracker Red99 (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) solution was prepared with RPMI-1640 medium, mixed and stored at 4°C, and preheated at 37°C prior to use. After 24 h, the cell culture solution of infection was discarded, washed 3 times with PBS, and 1 ml Lyso Tracker Red99 solution was added to each well to label the lysosomal component of the macrophage, and incubated at room temperature for 30 min. Finally, the supernatant was directly discarded using a pipette and the slides were washed 3 times with PBS. Then, the slides were removed, fixed on a glass slide with 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 min at room temperature, observed under a confocal microscope (magnification, ×20) and visualized by FV10-ASW 2.1 Viewer software (Olympus Europa Holding GmbH) to observe the co-localization.
Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
To validate the accuracy of DEGs microarray analysis results, the total RNA of cells from the infection model was extracted using Trizol® (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and 2 µg RNA was transcribed into cDNA by PrimeScript™ RT reagent kit with gDNA Eraser (Perfect Real Time) (Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). Relative expression levels of mRNA were quantitatively normalized and analyzed by RT-qPCR using FastStart Universal SYBR Green Master (ROX; Roche Diagnostics) against the expression of β-actin, using the 2−ΔΔCq method (23). The primer sequences were derived from PrimerBank (https://pga.mgh.harvard.edu/prim-erbank/) (24) (Table SI). The thermocycling conditions for RT-qPCR are presented in Table SII.
Statistical analysis
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to analyze the differentially expressed genes [interferon (IFN)-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15), 2′-5-oligoad-enylate synthetase like (OASL), IFN regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) and DExD/H-box helicase 58 (DDX58)] between TB infected group and control group. Quantitative data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. GraphPad Prism 6 software (GraphPad Software, Inc.) was utilized to draw the ROC curves and calculated the sensitivity, specificity and area under the curve (AUC). The AUC of the ROC curve >0.7 was regarded as significant. Data from multiple groups were analyzed using analysis of variance followed by a Student-Newman-Keuls post-hoc test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Identification of DEGs with microarray meta-analysis
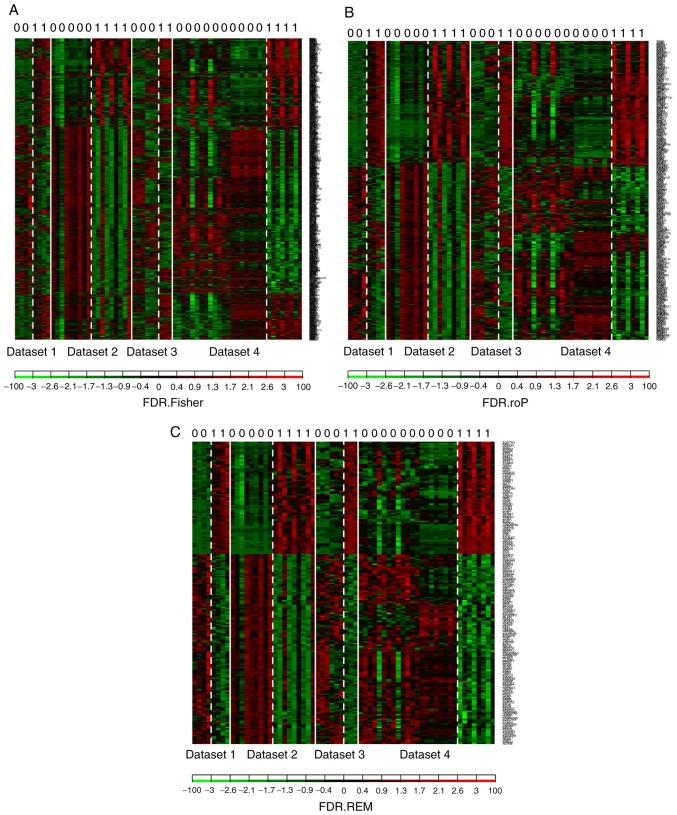
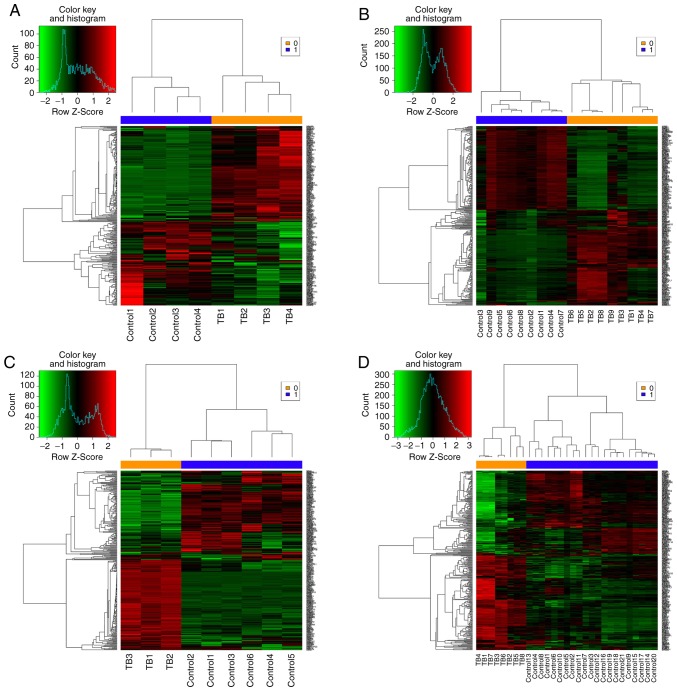
A total of 6 microarray datasets were downloaded from the GEO using the aforementioned search method (Table I). These datasets were analyzed by MetaQC package and visualized by principle component analysis (PCA; Table II; Fig. 1). The results of the comprehensive PCA indicate that the datasets GSE17477, GSE51029, GSE57028 and GSE89391 were rated as high quality data. The raw data of these 4 high quality datasets were analyzed using the R package MetaDE, for a total of 76 independent samples (30 H37Rv-infected samples and 46 controls). The shared genes from the 4 datasets were analyzed by 3 methods: Fisher; roP; and REM (Fig. 2A-C). During the analysis, the non-DEGs, and those exhibiting small variation and expression intensities across the majority of datasets were filtered out. Through the same three statistical methods (Fisher, roP and REM), 1,190, 426 and 927 differentially expressed genes were identified, respectively. The intersection of the 3 datasets yielded 306 common DEGs (Fig. 3). These 306 DEGs were arranged into 4 high-quality datasets for hierarchical cluster analysis (Fig. 4A-D). It was clear that these genes were well-differentiated between the M. tb infection and control groups. The top 20 shared DEGs identified in the meta-analysis are summarized in Table III, ranked by average log2 fold change.
Table I.
Characteristics of gene expression datasets from Gene Expression Omnibus database.
Table II.
Quality control test of the gene expression datasets.
| Study | IQC | EQC C | QCg C | QCp | AQCg | AQCp | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE17477 | 4.4 | 3.3 | 25.52 | 146.88 | 6.08 | 94.1 | 1.67 |
| GSE51029 | 4.84 | 3.19 | 21.13 | 127.06 | 2.88 | 79.93 | 2.83 |
| GSE57028 | 4.4 | 3.4 | 17.81 | 57.94 | 4.66 | 29.26 | 3.33 |
| GSE89391 | 4.4 | 2.77 | 19.03 | 106.29 | 3.9 | 64.74 | 3.5 |
| GSE52819 | 3.97 | 0.4 | 16.34 | 151.75 | 3.52 | 85.18 | 3.83 |
| GSE65714 | 0.26 | 0.75 | 0.58 | 0.96 | 0.26 | 0.49 | 5.83 |
IQC, internal quality control; EQC, external quality control; CQCg, consistency quality control of genes; CQCp, consistency quality control of pathways; AQCg, accuracy quality control of genes; AQCp, accuracy quality control of pathways.
Figure 1.
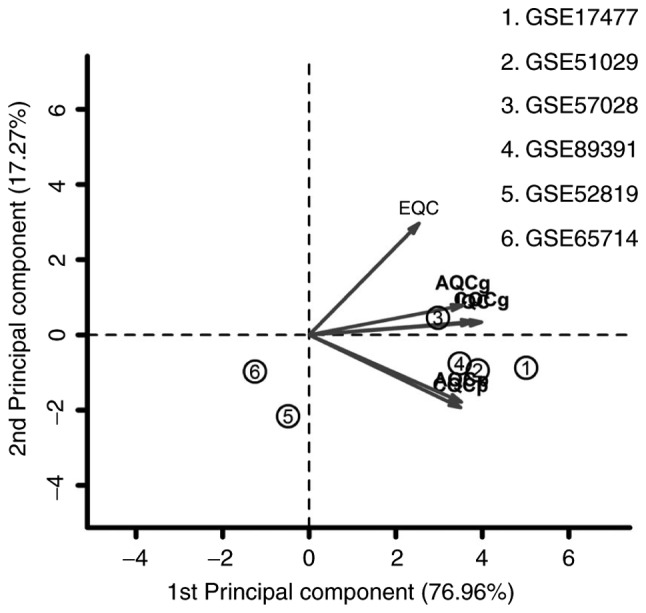
Principal component analysis results of the 6 gene expression datasets. IQC, internal quality control; EQC, external quality control; CQCg, consistency quality control of genes; CQCp, consistency quality control of pathways; AQCg, accuracy quality control of genes; AQCp, accuracy quality control of pathways.
Figure 2.
Results of the (A) Fisher, (B) rth-ordered p-value and (C) random effects model analyses in MetaDE software package of the 4 high quality datasets.
Figure 3.
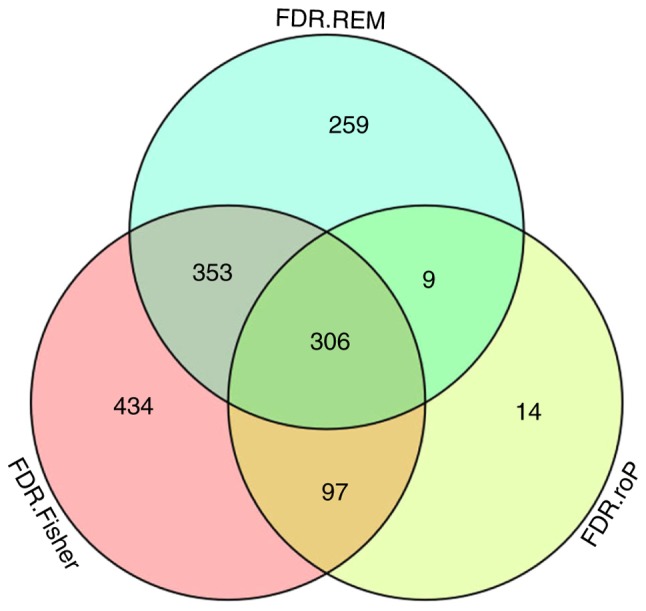
Venn diagram of the Fisher, roP and REM analysis results. FDR, false discovery rate; roP, rth-ordered p-value; REM, random effects model.
Figure 4.
Hierarchical cluster analysis of 306 differentially expressed genes in four high quality datasets. (A) GSE17477 dataset. (B) GSE51029 dataset. (C) GSE57028 dataset. (D) GSE89391 dataset. Each row represents mRNA and each column represents a sample. Red indicates higher expression in TB as compared with that in normal subjects. Green indicates low expression in TB compared to that in normal subjects. TB, THP-1 derived macrophages infected by Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv strain; control, normal THP-1 derived macrophages.
Table III.
Top 20 shared differentially expressed genes identified in the meta-analysis, ranked by average Log2FC.
| A, Top 10 upregulated genes
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | FDR.Fisher | FDR.roP | FDR.REM | Average Log2FC |
| CXCL10 | 1.62×10−19 | 7.52×10−04 | 1.86×10−02 | 4.46 |
| IFI44L | 1.62×10−19 | 5.41×10−19 | 5.74×10−03 | 4.00 |
| RSAD2 | 1.62×10−19 | 5.41×10−19 | 4.35×10−03 | 3.89 |
| ISG20 | 1.62×10−19 | 4.63×10−05 | 2.43×10−19 | 3.59 |
| IFIT2 | 1.62×10−19 | 5.41×10−19 | 2.43×10−19 | 3.58328139 |
| IFIT1 | 1.62×10−19 | 5.41×10−19 | 2.43×10−19 | 3.58 |
| IFIT3 | 1.62×10−19 | 5.41×10−19 | 2.43×10−19 | 3.22 |
| OASL | 1.62×10−19 | 5.41×10−19 | 5.65×10−05 | 3.15 |
| HERC5 | 1.62×10−19 | 5.41×10−19 | 3.74×10−04 | 3.01 |
| IFITM1 | 1.62×10−19 | 5.41×10−19 | 1.96×10−05 | 2.78 |
| B, Top 10 downregulated genes
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | FDR.Fisher | FDR.roP | FDR.REM | Average Log2FC |
| CX3CR1 | 1.62×10−19 | 1.94×10−04 | 8.65×10−05 | −1.17 |
| MYB | 1.62×10−19 | 1.31×10−03 | 1.50×10−02 | −1.09 |
| RASGRP2 | 7.10×10−04 | 1.20×10−04 | 3.21×10−02 | −1.00 |
| LMNB1 | 1.62×10−19 | 4.63×10−05 | 1.48×10−05 | −0.98 |
| ABI2 | 1.13×10−03 | 4.63×10−05 | 3.92×10−03 | −0.96 |
| PHGDH | 1.54×10−04 | 1.51×10−03 | 3.04×10−03 | −0.95 |
| RECK | 3.21×10−03 | 2.35×10−02 | 2.43×10−19 | −0.93 |
| DOCK10 | 1.62×10−19 | 5.41×10−19 | 7.87×10−03 | −0.90 |
| DTL | 1.75×10−03 | 4.46×10−02 | 5.07×10−04 | −0.89 |
| BUB1 | 6.61×10−03 | 2.56×10−02 | 5.74×10−03 | −0.89 |
FDR, false discovery rate; FC, fold change.
Prioritization of DEGs by PPI network analysis
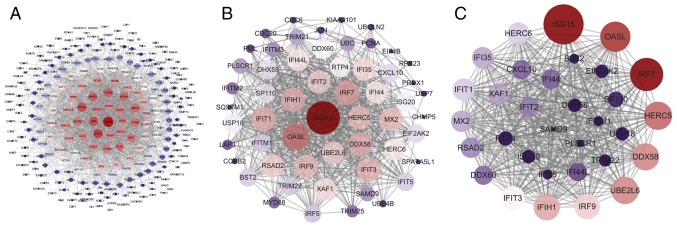
The PPI network of these DEGs was established using STRING database, and the node and edge relationships were imported into Cytoscape software for visualization, and then the DC evaluation was completed. The degree result is demonstrated by the size of the point and the thickness of the edge (Fig. 5A). The first 56 genes were selected as hub genes (Fig. 5B) as a focus for subsequent examination. Using the k-core decomposition function of MCODE with average MCODE score =28.774, nodes =32 and edges =446, a variety of sub-networks were obtained and a new network was created (Fig. 5C). This resulted in 32 remaining differentially expressed genes in the new network. These 32 differentially expressed genes were therefore selected for further research to narrow the scope of the present study. The association between the three PPI networks is demonstrated in Fig. S1. The results of DC and MCODE of DEGs analysis are summarized in Table IV.
Figure 5.
PPI networks of the DEGs in THP-1-derived macrophages infected by Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. (A) The PPI network of all DEGs in the meta-analysis, consisting of 275 nodes and 2,038 edges. (B) PPI network extracted from A by Degree Centrality, consisting of 56 nodes and 644 edges. (C) The PPI network extracted from B by MCODE, consisting of 32 nodes and 446 edges. PPI, protein-protein interaction; DEGs, differentially expressed genes.
Table IV.
Results of Degree Centrality and MCODE analysis.
| Symbol | BC | Degree | MCODE_Score | MCODE_Cluster |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISG15 | 0.27257001 | 55 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| OASL | 0.05886982 | 42 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| IRF7 | 0.01632719 | 38 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| DDX58 | 0.01029361 | 38 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| IFIH1 | 0.00863645 | 37 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| IFIT1 | 0.00773668 | 37 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| IFIT3 | 0.01031726 | 37 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| HERC5 | 0.01926602 | 36 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| IRF9 | 0.0092487 | 36 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| MX2 | 0.00610183 | 36 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| IFIT2 | 0.00542212 | 35 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| RSAD2 | 0.00566624 | 35 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| UBE2L6 | 0.01919648 | 35 | 21.70666667 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| IFI35 | 0.00540913 | 34 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| XAF1 | 0.0038621 | 34 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| HERC6 | 0.01571431 | 33 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| IFI44 | 0.00381869 | 33 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| IFI44L | 0.00381869 | 33 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| DDX60 | 0.00236545 | 30 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| RTP4 | 0.00168655 | 30 | 20.69950739 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| ISG20 | 0.0054854 | 29 | 20.77173913 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| USP18 | 0.00142348 | 29 | 22.77 | Cluster 1 |
| DHX58 | 0.00224466 | 28 | 21.52615385 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| SP110 | 0.00130771 | 28 | 21.84057971 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| CXCL10 | 0.00634646 | 27 | 20.91699605 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| EIF2AK2 | 0.0022294 | 27 | 21.84057971 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| BST2 | 0.00201042 | 26 | 20 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| IFIT5 | 6.43E-04 | 26 | 21.84057971 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| IFITM1 | 0.00123016 | 26 | 19.42028986 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| TRIM22 | 0.00324214 | 26 | 18.75324675 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| PLSCR1 | 7.11E-04 | 21 | 18.90952381 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
| SAMD9 | 5.86E-05 | 20 | 19 | Cluster 2|Cluster 1 |
Function and pathway enrichment analyses of hub genes
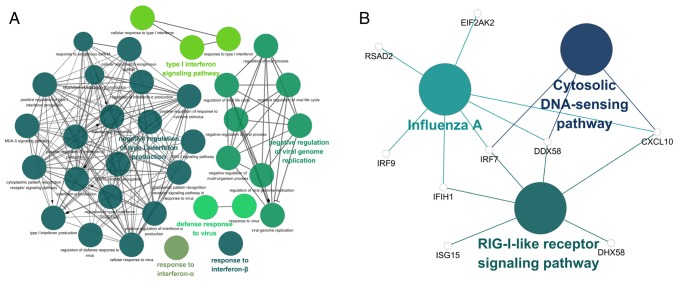
The GO and KEGG term enrichment analyses were performed using CluGO. There were a total of 35 GO terms within the 'Biological Process' (BP) group and 3 KEGG pathways with P<0.05 (including Bonferroni adjustment) identified within the analysis of the 32 characteristic genes.
Among the top significant GO BP terms identified were those associated with response to IFN-α and IFN-β, the IFN-γ-mediated signaling pathway and the type I IFN signaling pathway (Fig. 6A). Only 3 significant KEGG pathways, the retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I)-like receptor signaling pathway, cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway and influenza A were identified (Fig. 6B). Detailed enrichment information for the GO and KEGG pathways is summarized in Tables V and VI. Based on the results of the function and pathway enrichment analyses, the result that M. tb infection was closely associated with virus-associated pathways, including the type I IFN signaling pathway, is consistent with the characteristics of M. tb as an intracellular pathogen. Among these pathways, it was hypothesized that genes which serve a significant role include bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 (BST2), IRF7, IFN induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 1 (IFIT1), C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10), ISG15, DDX58 and OASL.
Figure 6.
GO and KEGG analysis of the 32 characteristic genes. (A) A total of 35 GO biological pathways were identified (B) A total of 3 KEGG pathways with P<0.05 (with Bonferroni adjustment). GO, Gene ontology; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
Table V.
Most significant GO pathway of the 32 nodes in the protein-protein interaction network.
| GO ID | Term | P-value | Associated genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0035455 | Response to interferon-α | 3.23899×10−12 | BST2, EIF2AK2, IFIT2, IFIT3, IFITM1, MX2 |
| GO:0035456 | Response to interferon-β | 8.3886×10−8 | BST2, IFITM1, PLSCR1, XAF1 |
| GO:0060337 | Type I interferon signaling pathway | 5.06394×10−27 | BST2, IFI35, IFIT1, IFIT2, IFIT3, IFITM1, IRF7, IRF9, ISG15, ISG20, MX2, OASL, RSAD2, USP18, XAF1 |
| GO:0051607 | Defense response to virus | 4.21784×10−39 | BST2, CXCL10, DDX58, DDX60, DHX58, EIF2AK2, HERC5, IFI44L, IFIH1, IFIT1, IFIT2, IFIT3, IFIT5, IFITM1, IRF7, IRF9, ISG15, ISG20, MX2, OASL, PLSCR1, RSAD2, RTP4, TRIM22 |
| GO:0045069 | Negative regulation of viral genome replication | 2.22495×10−16 | BST2, EIF2AK2, IFIT1, IFIT5, IFITM1, ISG15, ISG20, OASL, PLSCR1, RSAD2 |
| GO:0032480 | Negative regulation of type I interferon production | 3.69762×10−10 | DDX58, DHX58, HERC5, IFIH1, ISG15, UBE2L6 |
GO, gene ontology.
Table VI.
Most significant KEGG pathway of the 32 nodes in the protein-protein interaction network.
| KEGG ID | Term | P-value | Associated genes identified |
|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG:04622 | Retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-like receptor signaling pathway | 1.0325×10−9 | CXCL10, DDX58, DHX58, IFIH1, IRF7, ISG15 |
| KEGG:04623 | Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | 0.000173925 | CXCL10, DDX58, IRF7 |
| KEGG:05164 | Influenza A | 5.76×10−9 | CXCL10, DDX58, EIF2AK2, IFIH1, IRF7, IRF9, RSAD2 |
KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
M. tb successfully enters THP-1-derived macrophage lysosomes
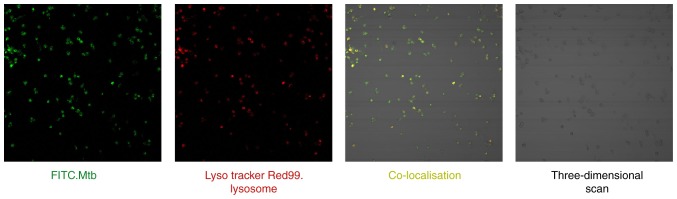
Co-localization of the lysosome specific-acido-tropic dye Lyso Tracker Red99 with live virulent M. tb in macrophages was examined by confocal microscopy (Fig. 7). A total of 2 sets of images were recorded: Firstly, the localization of the FITC-labeled Mycobacterium-positive compartment (green) and secondly, the Lyso Tracker Red99 lysosome-positive compartment (red). Following merging of the 2 image sets, the sections in which M. tb was co-localized with the lysosomes appeared yellow. Finally, a three-dimensional scan of THP-1 derived macrophages was obtained. These results demonstrated that THP-1 cells were successfully cultured and induced into macrophages, and that an M. tb infection model was established to verify the reliability of the previous bioinformatics analysis.
Figure 7.
Co-localization of M. tb and lysosomes in macrophages (magnification, ×20). Macrophages were infected with FITC-labelled (green) M. tb H37Rv and stained with Lyso Tracker Red99 for identification of the acidic lysosomes. M. tb, Mycobacterium tuberculosis; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate.
Analysis of relative expression levels of ISG15, OASL, IRF7 and DDX58 in the infection model
A total of 4 genes, ISG15, OASL, IRF7 and DDX58, were selected from the important genes identified, and their differential expression levels between the infected and control groups was verified by RT-qPCR. Using the 2−ΔΔCq method, the difference in expression levels of the 4 genes relative to β-actin was calculated, and it was identified that the expression of these 4 genes was significantly upregulated following M. tb infection. Then, GraphPad Prism 6 software was used to visually demonstrate the comparison between RT-qPCR results and microarray meta-analysis results, and it was identified that the experimental verification results were consistent with bioinformatics analysis data (Fig. 8). These genes were differentially expressed following M. tb infection of the host and are associated with the response mechanism of the host to M. tb, which requires additional study.
Figure 8.
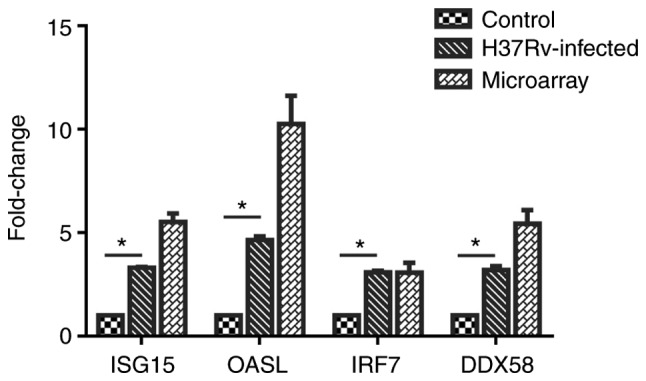
Expression levels of ISG15, OASL, IRF7 and DDX58. Validation is based on the expression levels in infected and uninfected cells, measured by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and then compared with the microarray results. Experiments were performed in triplicate, *P<0.05 by ANOVA.
ROC curve analysis of the expression of ISG15, OASL, IRF7 and DDX58
The ROC curve analysis of ISG15, OASL, IRF7 and DDX58 identified that the AUC values were 0.9691, 0.9228, 0.8488 and 0.679, respectively (Fig. 9). Among the 4 genes, only the AUC of the ROC curve of DDX58 was <0.7, indicating that DDX58 did not have good specificity and sensitivity, while ISG15, OASL and IRF7 were statistically significant, and may be able to distinguish between infected and uninfected cells.
Figure 9.
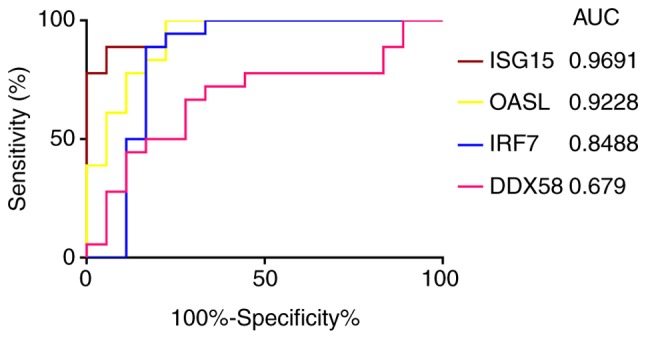
Receiver operating characteristics curve of the expression of ISG15, OASL, IRF7 and DDX58. AUC, area under the curve.
Discussion
In the present study, a meta-analysis was conducted using microarray-based gene expression studies that were previously published and are available for public reuse. Under the premise of reducing research bias and individual heterogeneity, a total of 306 DEGs with high credibility were identified, including 178 upregulated and 128 downregulated genes with FDR<0.05. Based on these DEGs, a PPI network was constructed, including 275 nodes and 2038 edges, and 32 characteristic genes were obtained through DC sorting and k-core analysis, including ISG15, OASL, IRF7, DDX58, IFN induced with helicase C domain 1, IFIT1, IFN induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3, HECT and RLD domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 5, IFN regulatory factor 9, MX dynamin like GTPase 2, IFN induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 2, radical S-adenosyl methionine domain containing 2, ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 L6, IFN induced protein 35, XIAP associated factor 1, HECT and RLD domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase family member 6, IFN induced protein 44 (IFI44), IFI44 like, DExD/H-box helicase 60, receptor transporter protein 4, IFN stimulated exonuclease gene 20, ubiquitin specific peptidase 18 and sterile α motif domain containing 9.
A THP-1-derived macrophage model of M. tb infection was constructed, and the co-localization association between M. tb and lysosome was confirmed by confocal microscopy to determine the success of infection. Among the 32 characteristic genes identified, the genes with the top 4 DC values in the PPI network and associations with type I IFN were selected as the verification targets. The expression of these 4 genes extracted by bioinformatics analysis was verified, and the RT-qPCR results were consistent with the microarray data analysis, which suggested that the results of the analyses were reliable.
These characteristic genes were primarily enriched in BP pathways including responses to IFN-α and IFN-β, the IFN-γ-mediated signaling pathway, the type I IFN signaling pathway, defense response to virus and regulation of viral genome replication. Analysis of the KEGG pathways revealed that the characteristic genes were involved in the RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway, cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway, and influenza A pathways. These results are consistent with the intracellular parasite characteristics of M. tb. This species is known to possess a specific secretion system, early secretory antigenic target-6 secretion system 1 (ESX-1), which serves a key role in mycobacterial virulence by promoting the release of M. tb products into the cytoplasm of macrophages (25-28). We hypothesized that the double-stranded DNA of M. tb enters the host cell via the ESX-1 system, stimulating the response recognition of the cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway, which triggers downstream type I IFN-associated signaling pathways.
The type I IFN system, as the first important line of defense against viral infection, detects viruses by pattern-recognition receptor recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns, and then expresses >300 IFN-stimulated genes to mediate multiple antiviral mechanisms to exert antiviral and immunomodulatory effects (29). However, viruses have developed an impressive array of strategies to circumvent IFN responses, for example, by disrupting Toll-like receptors or RIG-I-like receptors to prevent initial virus detection, and the degradation of transcription factors involved in IFN expression, in order to prevent IFN production (30). The interaction between viruses and the type I IFN system requires additional study. The present study only focused on the role of the type I IFN system in M. tb infection, as it has been suggested previously that the type I IFN pathway may promote the survival and replication of M. tb in host cells, and that this is a common strategy of a number of intracellular pathogenic bacteria to promote virulence (28,31-38). Understanding the role of type I IFN signaling is critical to understanding the pathology and outcome of TB. Therefore, the present study focused on the most important first-line genes identified in the PPI network, which were associated with type I IFNs and validated by biological experiments and ROC curve analysis, ISG15, OASL and IRF7.
ISG15 is one of the most commonly induced proteins by type I IFN (39) and during M. tb infection (40). It is a ubiquitin-like protein that is conjugated to intracellular target proteins upon activation by IFN-α and IFN-β (41). It has been demonstrated to have several functions, including promoting T cell-dependent natural killer cell proliferation, augmenting lymphokine activated killer activity, serving as a chemotactic factor that enhances neutrophil chemotactic activity, directing ligated target proteins to intermediate filaments, cell-to-cell signaling and antiviral activity during viral infections (42-45).
It was suggested that type I IFN and ISG15 serve transient roles in promoting bacterial replication. However, as the disease progresses, ISGylation deviates from the overall effect of type I IFN and, ultimately, mice deficient in ISGylation are significantly more susceptible than IFNAR mice (46). In the study conducted by Keller et al (47), differences in gene expression in M. tb-infected susceptible and resistant mouse strains were investigated, and ISG15 expression was also significantly increased following infection with M. tb for 28 days. However, to the best of our knowledge, no studies have been conducted in patients with TB; ISG15 may lead to different disease outcomes during the development of TB infection in humans, and the actual role requires additional study.
The data from the study by Sambarey et al (48), involving whole blood samples from patients with TB, indicated that OASL was significantly upregulated in blood samples from patients with active TB compared with patients with latent TB, and the expression level in the blood samples of patients after 6 months of treatment was significantly downregulated. However, to the best of our knowledge, no in-depth study of the role of OASL in the infection process has been performed as of yet. OASL belongs to the type I IFN-induced antiviral protein OAS family consisting of OAS1, OAS2, OAS3 and OASL (49). OASL is associated with the OAS family through the N-terminal OAS-like domain but lacks synthetase activity (50). Although OASL lacks enzymatic activity, recently identified functions appear to be critical for viral innate and adaptive immune responses (51). In response to viral infections, OASL serves 2 distinct roles. In the case of RNA virus infection, OASL may enhance the ability of type I IFN signaling to exert antiviral effects (51). However, when challenged with DNA viruses, OASL exerts a pro-survival function by inhibiting type I IFN signaling (52,53). Nonetheless, its biological role in microbial infection is not clear. As M. tb is phagocytosed by macrophages, it is able to release contents including dsDNA into host cell solute, which is similar to DNA virus attack. A recent study identified that when the host was infected with M. leprae, OASL was able to inhibit antimicrobial peptides expression, impair the mechanism of bacterial kill activation and inhibit the autophagy process of host cells, thereby preventing microbial clearance (54). In view of these data and the similarity between the physiological state and infection process of M. tb and M. leprae, it is reasonable to conclude that OASL may serve a similar role in M. tb infection, relying on the type I IFN pathway to inhibit autophagy of macrophages, provide sites and raw materials for M. tb, and promote the progression of TB.
Finally, IRF7 encodes IFN regulatory factor 7, a member of the IFN regulatory transcription factor family. IRF7 was also demonstrated to be upregulated in a host RNA sequencing study in response to M. tb infection (55). Cheng and Schorey (56) indicated that M. tb may rely on cytoplasmic DNA and RNA sensing pathways to mediate IFN-βproduction by IRF7, thereby assisting the host in the identification of bacterial infection. In the study by Lin et al (57), involving whole blood gene expression profiles in patients with active and latent TB, a transcription factor gene regulatory network was constructed and IRF7 was revealed to be significantly upregulated and enriched in the immune and infection pathways, which was hypothesized to help patients resist TB infection (57).
In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that the type I interferon signaling pathway serves a significant role in the infection of macrophages by M. tb. In addition, the mechanism of a number IFN-stimulated genes in TB infection remains uncertain, but ISG15 and OASL are likely to become a potential target for TB treatment, creating new possibilities for TB treatment. However, the results from the present study were obtained via bioinformatics analysis, and require additional confirmation using animal model studies.
Supplementary Data
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no., 81672109), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, JLU and Program for JLU Science and Technology Innovative Research Team.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Authors' contributions
FL, YWZ and YL designed the current study. YWZ, YL and RNT performed the experiments and acquired/analyzed the data. HYY and RNT analyzed experimental data. YWZ and YL wrote the manuscript. The final version of the manuscript was read and approved by all authors.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Goldberg MF, Saini NK, Porcelli SA. Evasion of innate and adaptive immunity by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Microbiol Spectr. 2014;5 doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MGM2-0005-2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Comas I, Coscolla M, Luo T, Borrell S, Holt KE, Kato-Maeda M, Parkhill J, Malla B, Berg S, Thwaites G, et al. Out-of-Africa migration and Neolithic coexpansion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with modern humans. Nat Genet. 2013;45:1176–1182. doi: 10.1038/ng.2744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Organization WH Global Tuberculosis Report. 2018 https://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/. Accessed September 18, 2018.
- 4.Aderem A, Underhill DM. Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:593–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.17.1.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Weiss G, Schaible UE. Macrophage defense mechanisms against intracellular bacteria. Immunol Rev. 2015;264:182–203. doi: 10.1111/imr.12266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bhatt K, Salgame P. Host innate immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Immunol. 2007;27:347–362. doi: 10.1007/s10875-007-9084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hmama Z, Peña-Díaz S, Joseph S, Av-Gay Y. Immunoevasion and immunosuppression of the macrophage by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Immunol Rev. 2015;264:220–232. doi: 10.1111/imr.12268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Meena LS, Rajni Survival mechanisms of pathogenic Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. FEBS J. 2010;277:2416–2427. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N, Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A, Chinnaiyan AM. Large-scale meta-analysis of cancer microarray data identifies common transcriptional profiles of neoplastic transformation and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:9309–9314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401994101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rung J, Brazma A. Reuse of public genome-wide gene expression data. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14:89–99. doi: 10.1038/nrg3394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang X, Kang DD, Shen K, Song C, Lu S, Chang LC, Liao SG, Huo Z, Tang S, Ding Y, et al. An R package suite for microarray meta-analysis in quality control, differentially expressed gene analysis and pathway enrichment detection. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:2534–2536. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Smid M, Dorssers LC, Jenster G. Venn mapping: Clustering of heterologous microarray data based on the number of co-occurring differentially expressed genes. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:2065–2071. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.DeConde RP, Hawley S, Falcon S, Clegg N, Knudsen B, Etzioni R. Combining results of microarray experiments: A rank aggregation approach. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 2006;5:Article15. doi: 10.2202/1544-6115.1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xia J, Fjell CD, Mayer ML, Pena OM, Wishart DS, Hancock RE. INMEX-a web-based tool for integrative meta-analysis of expression data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:W63–W70. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Xia J, Gill EE, Hancock RE. NetworkAnalyst for statistical, visual and network-based meta-analysis of gene expression data. Nat Protoc. 2015;10:823–844. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2015.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang R, Cai Y, Zhang B, Wu Z. A 16-gene expression signature to distinguish stage I from stage II lung squamous carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41:1377–1384. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shao K, Shen LS, Li HH, Huang S, Zhang Y. Systematic-analysis of mRNA expression profiles in skeletal muscle of patients with type II diabetes: The glucocorticoid was central in pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:4068–4076. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tuo Y, An N, Zhang M. Feature genes in metastatic breast cancer identified by MetaDE and SVM classifier methods. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17:4281–4290. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tseng GC, Ghosh D, Feingold E. Comprehensive literature review and statistical considerations for microarray meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:3785–3799. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos A, Tsafou KP, et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D447–D452. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13:2498–2504. doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Spandidos A, Wang X, Wang H, Seed B. PrimerBank: A resource of human and mouse PCR primer pairs for gene expression detection and quantification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:D792–D799. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stanley SA, Raghavan S, Hwang WW, Cox JS. Acute infection and macrophage subversion by Mycobacterium tuberculosis require a specialized secretion system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:13001–13006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2235593100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hsu T, Hingley-Wilson SM, Chen B, Chen M, Dai AZ, Morin PM, Marks CB, Padiyar J, Goulding C, Gingery M, et al. The primary mechanism of attenuation of bacillus Calmette-Guerin is a loss of secreted lytic function required for invasion of lung interstitial tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:12420–12425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1635213100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Guinn KM, Hickey MJ, Mathur SK, Zakel KL, Grotzke JE, Lewinsohn DM, Smith S, Sherman DR. Individual RD1-region genes are required for export of ESAT-6/CFP-10 and for virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mol Microbiol. 2004;51:359–370. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03844.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Stanley SA, Johndrow JE, Manzanillo P, Cox JS. The type I IFN response to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis requires ESX-1-mediated secretion and contributes to pathogenesis. J Immunol. 2007;178:3143–3152. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.5.3143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.de Veer MJ, Holko M, Frevel M, Walker E, Der S, Paranjape JM, Silverman RH, Williams BR. Functional classification of interferon-stimulated genes identified using microarrays. J Leukoc Biol. 2001;69:912–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Taylor KE, Mossman KL. Recent advances in understanding viral evasion of type I interferon. Immunology. 2013;138:190–197. doi: 10.1111/imm.12038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Manca C, Tsenova L, Bergtold A, Freeman S, Tovey M, Musser JM, Barry CE, III, Freedman VH, Kaplan G. Virulence of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolate in mice is determined by failure to induce Th1 type immunity and is associated with induction of IFN-alpha/beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:5752–5757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091096998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Flynn JL, Chan J. What's good for the host is good for the bug. Trends Microbiol. 2005;13:98–102. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2005.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ordway D, Henao-Tamayo M, Harton M, Palanisamy G, Troudt J, Shanley C, Basaraba RJ, Orme IM. The hypervirulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain HN878 induces a potent TH1 response followed by rapid down-regulation. J Immunol. 2007;179:522–531. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.1.522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Antonelli LR, Gigliotti Rothfuchs A, Gonçalves R, Roffê E, Cheever AW, Bafica A, Salazar AM, Feng CG, Sher A. Intranasal Poly-IC treatment exacerbates tuberculosis in mice through the pulmonary recruitment of a pathogen-permissive monocyte/macrophage population. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:1674–1682. doi: 10.1172/JCI40817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Berry MP, Graham CM, McNab FW, Xu Z, Bloch SA, Oni T, Wilkinson KA, Banchereau R, Skinner J, Wilkinson RJ, et al. An interferon-inducible neutrophil-driven blood transcriptional signature in human tuberculosis. Nature. 2010;466:973–977. doi: 10.1038/nature09247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Desvignes L, Wolf AJ, Ernst JD. Dynamic roles of type I and type II IFNs in early infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 2012;188:6205–6215. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.McNab FW, Ewbank J, Rajsbaum R, Stavropoulos E, Martirosyan A, Redford PS, Wu X, Graham CM, Saraiva M, Tsichlis P, et al. TPL-2-ERK1/2 signaling promotes host resistance against intracellular bacterial infection by negative regulation of type I IFN production. J Immunol. 2013;191:1732–1743. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Dorhoi A, Yeremeev V, Nouailles G, Weiner J, III, Jörg S, Heinemann E, Oberbeck-Müller D, Knaul JK, Vogelzang A, Reece ST, et al. Type I IFN signaling triggers immunopathology in tuberculosis-susceptible mice by modulating lung phagocyte dynamics. Eur J Immunol. 2014;44:2380–2393. doi: 10.1002/eji.201344219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Der SD, Zhou A, Williams BR, Silverman RH. Identification of genes differentially regulated by interferon alpha, beta, or gamma using oligonucleotide arrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:15623–15628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chaussabel D, Semnani RT, McDowell MA, Sacks D, Sher A, Nutman TB. Unique gene expression profiles of human macrophages and dendritic cells to phylogenetically distinct parasites. Blood. 2003;102:672–681. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-10-3232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hermann M, Bogunovic D. ISG15: In sickness and in health. Trends Immunol. 2017;38:79–93. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chua PK, McCown MF, Rajyaguru S, Kular S, Varma R, Symons J, Chiu SS, Cammack N, Nájera I. Modulation of alpha interferon anti-hepatitis C virus activity by ISG15. J Gen Virol. 2009;90:2929–2939. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.013128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang D, Zhang DE. Interferon-stimulated gene 15 and the protein ISGylation system. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011;31:119–130. doi: 10.1089/jir.2010.0110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Speer SD, Li Z, Buta S, Payelle-Brogard B, Qian L, Vigant F, Rubino E, Gardner TJ, Wedeking T, Hermann M, et al. ISG15 deficiency and increased viral resistance in humans but not mice. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11496. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sooryanarain H, Rogers AJ, Cao D, Haac MER, Karpe YA, Meng XJ. ISG15 modulates type I interferon signaling and the antiviral response during Hepatitis E virus replication. J Virol. 2017;91:e00621–17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00621-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kimmey JM, Campbell JA, Weiss LA, Monte KJ, Lenschow DJ, Stallings CL. The impact of ISGylation during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice. Microbes Infect. 2017;19:249–258. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2016.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Keller C, Hoffmann R, Lang R, Brandau S, Hermann C, Ehlers S. Genetically determined susceptibility to tuberculosis in mice causally involves accelerated and enhanced recruitment of granulocytes. Infect Immun. 2006;74:4295–4309. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00057-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sambarey A, Devaprasad A, Mohan A, Ahmed A, Nayak S, Swaminathan S, D'Souza G, Jesuraj A, Dhar C, Babu S, et al. Unbiased identification of blood-based biomarkers for pulmonary tuberculosis by modeling and mining molecular interaction networks. EBioMedicine. 2017;15:112–126. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sadler AJ, Williams BR. Interferon-inducible antiviral effectors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:559–568. doi: 10.1038/nri2314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hancks DC, Hartley MK, Hagan C, Clark NL, Elde NC. Overlapping patterns of rapid evolution in the nucleic acid sensors cGAS and OAS1 suggest a common mechanism of pathogen antagonism and escape. PLoS Genet. 2015;11:e1005203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Choi UY, Kang JS, Hwang YS, Kim YJ. Oligoadenylate synthase-like (OASL) proteins: Dual functions and associations with diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2015;47:e144. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lee MS, Kim B, Oh GT, Kim YJ. OASL1 inhibits translation of the type I interferon-regulating transcription factor IRF7. Nat Immunol. 2013;14:346–355. doi: 10.1038/ni.2535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lee MS, Park CH, Jeong YH, Kim YJ, Ha SJ. Negative regulation of type I IFN expression by OASL1 permits chronic viral infection and CD8(+) T-cell exhaustion. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003478. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.de Toledo-Pinto TG, Ferreira AB, Ribeiro-Alves M, Rodrigues LS, Batista-Silva LR, Silva BJ, Lemes RM, Martinez AN, Sandoval FG, Alvarado-Arnez LE, et al. STING-dependent 2′-5′ oligoadenylate synthetase-like production is required for intracellular Mycobacterium leprae survival. J Infect Dis. 2016;214:311–320. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Leisching G, Pietersen RD, van Heerden C, van Helden P, Wiid I, Baker B. RNAseq reveals hypervirulence-specific host responses to M. tuberculosis infection. Virulence. 2017;8:848–858. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1250994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Cheng Y, Schorey JS. Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced IFN-β production requires cytosolic DNA and RNA sensing pathways. J Exp Med. 2018;215:2919–2935. doi: 10.1084/jem.20180508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lin Y, Duan Z, Xu F, Zhang J, Shulgina MV, Li F. Construction and analysis of the transcription factor-microRNA co-regulatory network response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A view from the blood. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9:1962–1976. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.