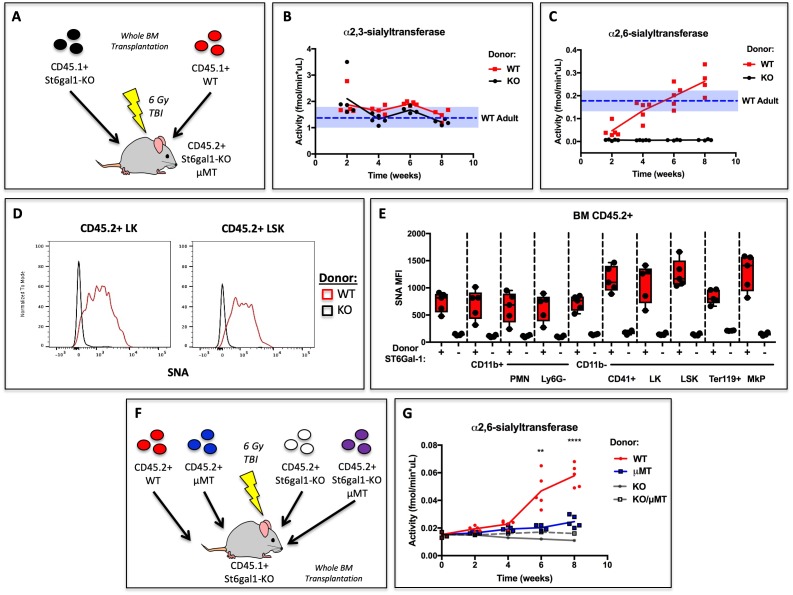
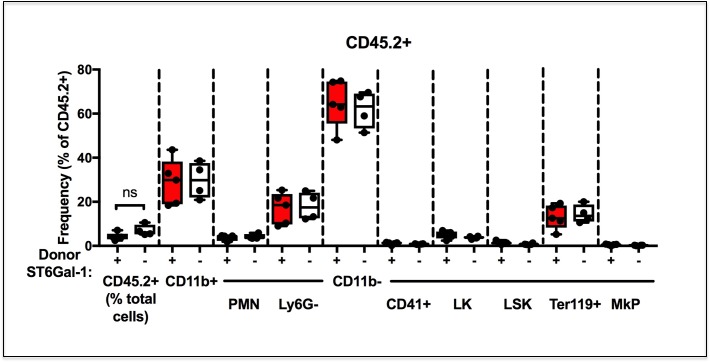
Figure 4. Hematopoietic Cells Supply Extracellular ST6GAL1 for Extrinsic Sialylation in vivo.
(A) CD45.1 + St6gal1 sufficient (WT) or deficient (KO) whole bone marrow was used to reconstitute irradiated CD45.2+/St6gal1KO/μMT mice. (B) α2,3 and (C) α2,6-sialyltransferase activity was quantified in serum of bone marrow chimeras at indicated time points. (D) Representative histograms of SNA-reactivity are shown for Lin-/c-kit+/Sca-1- (LK) and Lin-/c-kit+/Sca-1+ (LSK) progenitor compartments in the bone marrow, 8 weeks post-transplant. (E) Mean fluorescence intensity of SNA in CD45.2+ recipient bone marrow cell subsets was quantified by flow cytometry (n = 5). All cell types were significantly (p<0.01) different between WT and KO donor chimeras by student’s T-test. (F) CD45.2+ WT, μMT, St6gal1KO, or St6gal1KO/μMT bone marrow was used to reconstitute irradiated CD45.1+ St6gal1KO recipients. (G) α2,6-sialyltransferase activity was quantified in serum of bone marrow chimeras at indicated time points. Statistical significance is indicated in comparisons of WT and μMT cohorts for student’s T-test (**p<0.01, ****p<0.0001).