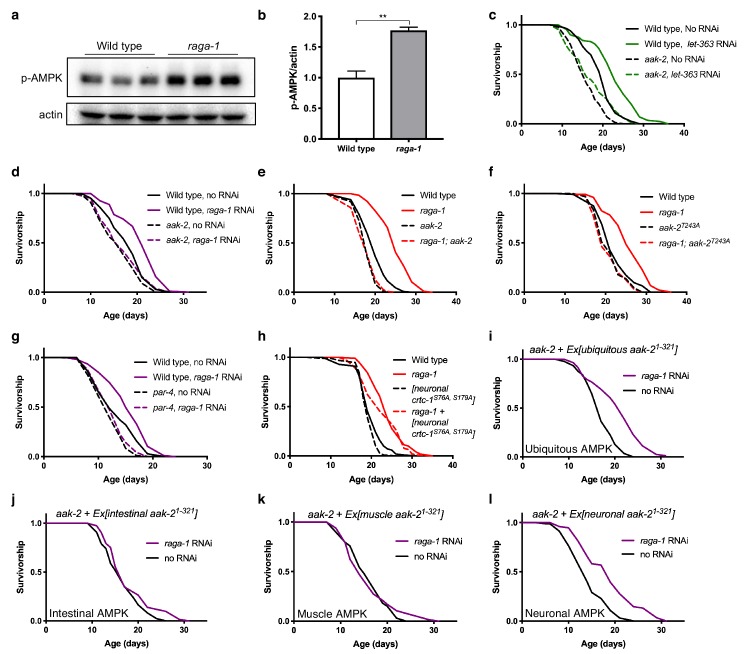
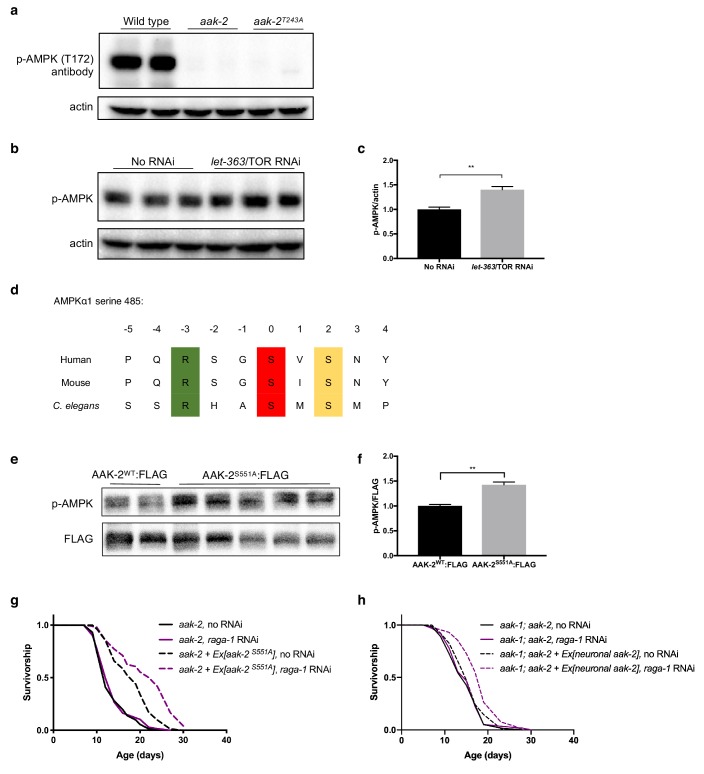
Figure 1. Neuronal AMPK is required for TORC1-mediated longevity.
(a, b) AMPK T172 phosphorylation is increased in raga-1(ok386) null mutants compared to wild type animals. Actin levels are used as loading controls (representative immunoblot and corresponding quantification, n = 3 independent blots). Source data for Figure 1b are provided in Figure 1—source data 1. (c, d) Knockdown of (c) let-363 (TOR) (n = 3 independent biological replicates) or (d) raga-1 from day 1 of adulthood extends lifespan in wild type animals (p<0.0001), but not in aak-2(ok524) null mutants (n = 8 independent biological replicates). P values: wild type on no RNAi vs let-363 RNAi (p<0.0001), aak-2(ok524) on no RNAi vs let-363 RNAi (p=0.0122), wild type vs aak-2(ok524) on let-363 RNAi (p<0.0001); wild type on no RNAi vs raga-1 RNAi (p<0.0001), aak-2(ok524) on no RNAi vs raga-1 RNAi (p=0.1968). Sample size ranges between 62–115 deaths per treatment each replicate. P values are calculated with Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Details on strains and lifespan replicates can be found in Supplementary file 6. (e) raga-1(ok386) mutants live longer than wild type (p<0.0001). raga-1(ok386); aak-2(ok524) double mutant animals do not live significantly longer than aak-2(ok524) single mutants (p=0.9735). n = 5 independent biological replicates, sample size ranges between 90–129 deaths per treatment each replicate. P values are calculated with Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Details on strains and lifespan replicates can be found in Supplementary file 6. (f) raga-1(ok386) mutants live longer than wild type (p<0.0001). raga-1(ok386) does not extend lifespan in an aak-2(wbm20) [AAK-2 (T243A)] CRISPR-generated allele background (p=0.5354). n = 3 independent biological replicates, sample size ranges between 93–119 deaths per treatment each replicate. P values are calculated with Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Details on strains and lifespan replicates can be found in Supplementary file 6. (g) At the restrictive temperature 22.5°C to induce par-4 loss-of-function, raga-1 RNAi from adulthood extends lifespan in wild type animals (p<0.0001) but does not extend lifespan of par-4(it57) mutant animals (p=0.206). Worms were grown at 15°C until L4 stage before shifting to restrictive temperature. n = 3 independent biological replicates, sample size 68–115 deaths per treatment each replicate. P values are calculated with Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Details on strains and lifespan replicates can be found in Supplementary file 6. (h) raga-1(ok386) null allele extends lifespan in animals expressing the non-phosphorylatable CRTC-1S76A, S179A driven by a pan-neuronal rab-3 promoter (p<0.0001). n = 3 independent biological replicates; sample size ranges between 90–121 deaths per treatment each replicate. P values are calculated with Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Details on strains and lifespan replicates can be found in Supplementary file 6. (i) raga-1 RNAi from adulthood extends median lifespan of animals overexpressing aak-2aa1-321 driven by the ubiquitous sur-5 promoter in aak-2 mutant background (p<0.0001). n = 3 independent biological replicates; sample size ranges between 78–109 deaths per treatment. P values are calculated with Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Details on strains and lifespan replicates can be found in Supplementary file 6. (j, k) raga-1 RNAi from adulthood does not extend median lifespan of animals overexpressing aak-2 aa1-321 driven by (j) an intestine-specific gly-19 promoter (p=0.0342) or (k) a muscle-specific myo-3 promoter in aak-2 mutant background (p=0.9827). n = 3 independent biological replicates; sample size ranges between 72–102 (intestine) and 44–107 (muscle) deaths per treatment each replicate. P values are calculated with Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Details on strains and lifespan replicates can be found in Supplementary file 6. (l) raga-1 RNAi from adulthood can extend median lifespan of animals overexpressing aak-2 aa1-321 driven by the pan-neuronal rab-3 promoter in an aak-2 mutant background (p<0.0001). n = 4 independent biological replicates, sample size ranges between 66–117 deaths per treatment each replicate. P values are calculated with Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Details on strains and lifespan replicates can be found in Supplementary file 6.