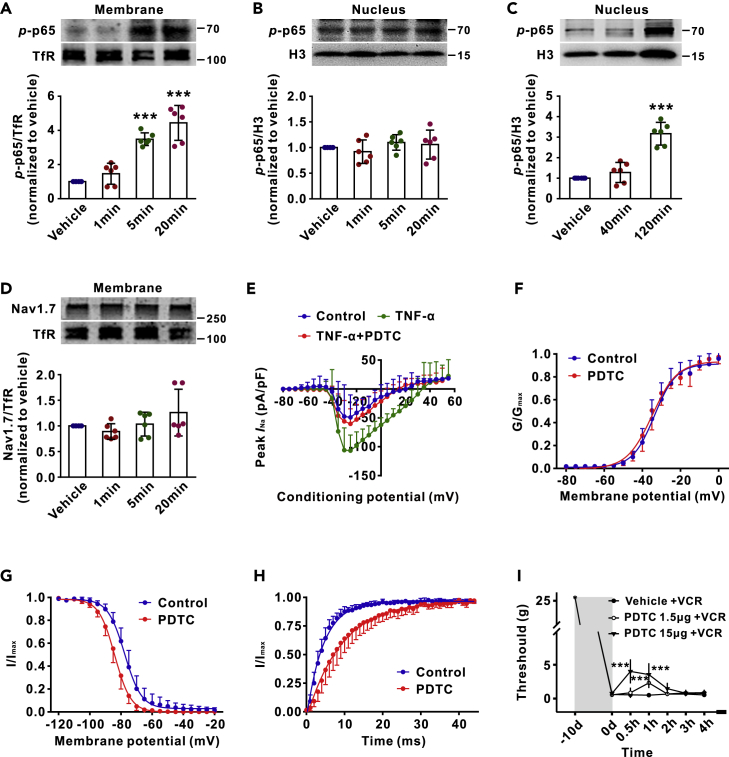
Figure 6.
TNF-α Enhances Membrane p-p65 (s311) and Nav1.7 Currents in Cultured DRG Neurons without Affecting Nuclear p-p65 and Membrane Nav1.7 within Minutes
(A–D) The western blots show the levels of p-p65 and Nav1.7 in membrane (A and D) or nucleus (B and C) of DRG neurons at indicated time points after application of rrTNF-α (100 ng/mL). n = 6 in each group. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with vehicle group.
(E) The I-V curves show the peak Nav1.7 currents recorded under different potentials in indicated groups. n = 9, 8, and 9 in control, TNF-α, and TNF-α + PDTC group.
(F–H) The effects of PDTC (10 nM) on activation (F), inactivation (G), and recovery (H) of Nav1.7 channels in HEK293 cells. n = 6–7 in each group.
(I) Intrathecal injection of NF-κB inhibitor PDTC (10 μL) reduces mechanical allodynia in vincristine (VCR)-treated rats within 30 min. n = 5 in each group. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with vehicle + VCR group. The data in A, B, C, D, and E were analyzed with one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test, and in F, G, and H with two-tailed t test. I, two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test. Data expressed as mean ± SD. The control of nuclear fractionation process was shown in Figure S2C.