Abstract
Objective
Animal lifespan is controlled through genetic pathways that are conserved from nematodes to humans. Lifespan-promoting conditions in nematodes include fasting and a reduction of insulin/IGF signaling. Here we aimed to investigate the input of the Caenorhabditis elegans homologue of the mammalian rate-limiting lipolytic enzyme Adipose Triglyceride Lipase, ATGL-1, in longevity control.
Methods
We used a combination of genetic and biochemical approaches to determine the role of ATGL-1 in accumulation of triglycerides and regulation of longevity.
Results
We found that expression of ATGL is increased in the insulin receptor homologue mutant daf-2 in a FoxO/DAF-16-dependent manner. ATGL-1 is also up-regulated by fasting and in the eat-2 loss-of-function mutant strain. Overexpression of ATGL-1 increases basal and maximal oxygen consumption rate and extends lifespan in C. elegans. Reduction of ATGL-1 function suppresses longevity of the long-lived mutants eat-2 and daf-2.
Conclusion
Our results demonstrate that ATGL is required for extended lifespan downstream of both dietary restriction and reduced insulin/IGF signaling.
Keywords: ATGL-1, Dietary restriction, DAF-2, DAF-16, Longevity, C. elegans
Highlights
-
•
Expression of ATGL-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans is regulated by fasting and insulin/IGF1 signaling.
-
•
Over-expression of ATGL-1 extends lifespan while loss-of-function mutant decreases lifespan of long-lived C. elegans models.
-
•
The effect of ATGL-1 on longevity may be mediated by an increase in mitochondrial oxidation.
1. Introduction
In metazoans, the insulin/IGF1 signaling pathway (IIS) coordinates nutrient and energy availability with growth, metabolism, and longevity [1]. Two major “signaling nodes” [2], FoxO- and TORC1-centered, are responsible for the effect of nutrients and IIS on the lifespan [3], [4], [5], [6]. Transcription factor FoxO1 (Forkhead box O 1) that adapts mammalian organisms to starvation is negatively regulated by IIS via Akt-mediated phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion [7], [8]. At the same time, oligomeric Ser/Thr protein kinase TORC1 (Target Of Rapamycin Complex 1) is activated by Akt and nutrients and promotes anabolic processes while inhibiting catabolism [9].
The downstream target(s) of FoxO and TORC1 that transmit longevity signal(s) remain largely unknown. Given that both FoxO and TORC1 are ubiquitously expressed and regulate a plethora of important biological responses, identification of the specific pathway(s) that control longevity is challenging. In fact, we do not even know whether FoxO and mTORC1 are involved in the same pathway or mediate different pathways of the longevity control.
We have recently found that FoxO1 [10], [11] and mTORC1 [12], [13], [14] control the rates of lipolysis in mammalian cells by regulating expression of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL; a.k.a. desnutrin, PNPLA2, TTS2.2, iPLA2ζ). Although complete hydrolysis of triglycerides (TG) to glycerol and fatty acids (FA) is performed jointly by tri- di- and monoacylglyceride lipases, ATGL represents the rate-limiting lipolytic enzyme. In other words, in every mammalian experimental system tested thus far, elevated ATGL expression increases, while attenuated ATGL expression decreases, both basal and cAMP-stimulated lipolysis [12], [15], [16], [17], [18], [19], [20], [21], [22], [23], [24].
Since known biochemical pathways that control longevity converge on the regulation of ATGL expression, we have hypothesized that ATGL may represent the long sought after target of the nutrient and insulin/IGF1 signaling pathways that regulate life span. Here, we utilize the nematode C. elegans, a well-characterized and widely used model for longevity studies, and show that expression of the C. elegans ATGL homologue ATGL-1 (C05D11.7) is controlled by nutrients and the DAF-2/DAF-16 pathway. Moreover, we find that the partial loss-of-function ATGL-1 mutant, ATGL-1 [P87S], blocks the life-extending effects of dietary restriction (in eat-2 loss-of-function model) and DAF-2 deficiency, whereas over-expression of ATGL-1 increases C. elegans lifespan.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. C. elegans strains
All C. elegans strains were maintained at 20 °C using standard methods [25]. The wild-type strain used was the C. elegans Bristol strain N2. The following strains were obtained from the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC): GR1307 daf-16(mgDf50) I, CB1370 daf-2(e1370) III, HT1890 daf-16(mgDf50) I; daf-2(e1370) III, VS20 hjIs67 [atgl-1p::atgl-1::gfp + mec-7::rfp], and VC20458 containing atgl-1 (gk176565) [P87S] III. The atgl-1(gk176565) mutation was outcrossed four times to generate AGK785 atgl-1(gk176565). The AVS518 eat-2(ad465) II strain was obtained from Dr. Andrew Samuelson (University of Rochester).
Other strains produced in this study include:
AGK786: atgl-1(gk176565) daf-2(e1370) III
AGK787: eat-2(ad465) II; atgl-1(gk176565)
AGK788: daf-2(e1370) III; hjIs67
AGK789: daf-16(mgDf50) I; daf-2(e1370) III; hjIs67
2.2. Fasting conditions
L1 larvae were synchronized by treatment of gravid adults with 20% alkaline hypochlorite and allowing embryos to hatch in the M9 buffer (0.3% KH2PO4, 0.6% Na2HPO4, 0.5% NaCl, 1 mM MgSO4) overnight. Hatched worms were grown to the L4 stage on NGM plates, harvested, and washed four times with M9 buffer. The worms were then split into two groups that were grown for 6 h on NGM agar plates either seeded with E. coli OP50 (Fed) or without bacterial food (Fasted).
2.3. Measurement of triglyceride content
Synchronized L4 stage worms (3000–5000) were pelleted by microcentrifugation at 13,000 rpm for 10 min, re-suspended in 50 μl of 5% Triton X-100 supplied with the protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma, St. Louis, MO), and sonicated by 3 cycles (10 s each) using a Sonic Dismembrator (Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) set at power output “3” at 4 °C. Protein concentration in lysates was determined using the Pierce BCA Protein Assay kit (Fisher Scientific) on a Biotek Synergy™ HT microplate reader (Biotek, Winooski, Vermont). The lysates underwent two cycles of heating to 90 °C for 5 min, each followed by vortexing, cooling to room temperature, and centrifugation at 8000 ×g for 5 min. Triglycerides were measured using Triglyceride Quantification kit (Biovision, Milpitas, CA) according to the manufacturer's protocol.
2.4. Oil-Red-O staining
Synchronized L4 stage worms were harvested, washed with PBS, and fixed in 1 ml of methanol at −20 °C for 5 min. Then, 2 ml of PBST (PBS with 0.01% Tween-20) was added, and worms were pelleted by centrifugation at 1000 rpm for 1 min. Supernatant was removed, and worms were washed twice with PBST in the same regime. Water (60% by volume) was added to Oil Red O (0.5% solution in isopropanol, Sigma) at room temperature, and, in 10 min, the solution was filtered through a 0.4 μm syringe filter. Fixed worms were stained with filtered 40% isopropanol Oil Red O solution (1 ml) for 20 min, washed twice with PBST, and mounted on slides with 3% agar. Images were taken using an inverted epi-fluorescent microscope (Carl Zeiss; Axio Observer D1) with a color camera.
2.5. RT-qPCR
Synchronized L4 stage worms (1000–2000) were washed with PBS, re-suspended in 1 ml of cold TRIzol (Ambion, Austin, TX), incubated at −80 °C for at least 1 h, and RNA was isolated according to the manufacturer's instructions. Reverse transcription (RT) was carried out using a RETROscript kit (Ambion), and quantitative RT-PCR was performed using iTag Universal SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA) according to the protocol of manufacturer with the following primers. atgl-1: forward 5′ GATCGACCGATGATTTATCGAG 3′, reverse 5′ GAGCCAATCCACATTTGGTC 3’; actin-1/3: forward, 5′ CACGAGACTTCTTACAACTCC 3′, reverse, 5′GCATACGATCAGCAATTCCT 3’. Relative expression levels of all mRNAs were normalized to actin-1/3 mRNA.
2.6. Measurement of oxygen consumption rates
OCR was measured by XF96 Extracellular Flux Analyzer - Seahorse (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA) using Seahorse's cartridges and plates (Bioscience). All measurements have been done at 28 °C. Synchronized worms (L3-L4 stage) were washed 3 times with M9 buffer, and ca. 20 worms were placed in a well with 200 μL M9 buffer. For each strain, 10 wells were used. Basal OCR was measured every 5 min. After that, carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone (FCCP, Sigma) was injected to each well to the final concentration of 10 μM, and maximal OCR was measured every 5 min. Finally, sodium azide (Sigma) was injected to the final concentration of 40 mM and non-mitochondrial OCR was measured every 5 min. After all measurements, worms in each well were re-counted, and results were normalized by their exact number.
2.7. Longevity experiments
Young adult worms were allowed to lay eggs for 6 h and then manually removed from the plates. The hatched L1 larvae were plated on ten 6 cm NGM Petri dishes, ca. twenty larvae per plate, and their lifespan was monitored every day. During the gravid adult stage, adult worms were separated from eggs/L1 larva and moved to new plates. The hatching day was considered Day 1. Death was scored if the animal did not move after repeated prodding with a pick. Animals disappearing from the plate or dying due to bursting or internal larva hatching were excluded from scoring, but included in the statistical analysis. Statistical significance (p value) of lifespan differences between the strains was determined by log-rank analysis for a single comparison and log-rank with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons using Oasis-2 software [26]. Time point when 50% of the worm population stays alive was considered mean lifespan. Each lifespan experiment was repeated three times with each group of worms. Combined p value was calculated by the Fisher's combined probability test. Representative life span experiments are shown in the Figures, and all repeats are listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Mean lifespans of C. elegans strains.
| Figure | Individual Experiments | Genotypes Compared | # of Worms | Mean Lifespan ± SEM (days) | % Lifespan Change compared to N2 or as noted | p Value | Combined p Value compared to N2 or as noted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1H | 1 | N2 | 206 | 14.07 ± 0.35 | |||
| atgl-1::gfp | 202 | 18.62 ± 0.44 | +32.3 | <1.0e-10 | |||
| 2 | N2 | 132 | 15.74 ± 0.44 | ||||
| atgl-1::gfp | 82 | 20.20 ± 0.78 | +28.3 | 7.8e-8 | |||
| 3 | N2 | 90 | 14.78 ± 0.39 | ||||
| atgl-1::gfp | 112 | 20.87 ± 0.67 | +41.2 | <1.0e-10 | <1.0e-4 | ||
| 2F | 1 | N2 | 146 | 13.90 ± 0.35 | |||
| eat-2(ad453) | 104 | 18.81 ± 0.80 | +35.3 | 1.0e-3 | |||
| atgl-1(P87S) | 156 | 13.8 ± 0.30 | −0.7 | 0.5495 | |||
| eat-2(ad453); atgl-1(P87S) | 166 | 12.58 ± 0.18 | −9.5 −33.1 (comp. to eat-2) |
1.0e-3 <1.0e-10 (comp. to eat-2) |
|||
| 2 | N2 | 216 | 13.20 ± 0.33 | ||||
| eat-2(ad453) | 187 | 18.77 ± 0.45 | +42.2 | <1.0e-10 | |||
| atgl-1(P87S) | 180 | 14.26 ± 0.24 | −8.0 | 0.0326 | |||
| eat-2(ad453); atgl-1(P87S) | 206 | 12.58 ± 0.28 | −4.7 −33.0 (comp. to eat-2) |
0.7903 <1.0e-10 (comp. to eat-2) |
|||
| 3 | N2 | 217 | 13.3 ± 0.34 | ||||
| eat-2(ad453) | 202 | 20.33 ± 0.51 | +52.9 | <1.0e-10 | <1.0e-4 | ||
| atgl-1(P87S) | 255 | 12.52 ± 0.17 | −5.9 | 0.85 | 0.21 | ||
| eat-2(ad453); atgl-1(P87S) | 251 | 15.43 ± 0.41 | +16.0 −24.1 (comp. to eat-2) |
4.3e-6 <1.0e-10 (comp. to eat-2) |
<1.0e-4 (comp. to eat-2) | ||
| 3D | 1 | N2 | 100 | 12.0 ± 0.39 | |||
| daf-2(e1370) | 90 | 27.73 ± 1.7 | +131.1 | <1.0e-10 | |||
| atgl-1(P87S) | 102 | 10.92 ± 0.30 | −9.0 | 0.1268 | |||
| daf-2(e1370); atgl-1(P87S) | 110 | 14.90 ± 0.89 | +24.2 −46.3 (comp. to daf-2) |
3.3e-3 <1.0e-10 (comp. to daf-2) |
|||
| 2 | N2 | 189 | 14.46 ± 0.29 | ||||
| daf-2(e1370) | 171 | 28.22 ± 0.81 | +95.2 | <1.0e-10 | |||
| atgl-1(P87S) | 174 | 14.16 ± 0.30 | −2.1 | 1 | |||
| daf-2(e1370); atgl-1(P87S) | 155 | 16.87 ± 0.63 | +16.7 −40.2 (comp. to daf-2) |
3.0e-4 <1.0e-10 (comp. to daf-2) |
|||
| 3 | N2 | 194 | 14.07 ± 0.35 | ||||
| daf-2(e1370) | 113 | 29.99 ± 1.65 | +113.1 | <1.0e-10 | <1.0e-4 | ||
| atgl-1(P87S) | 180 | 14.26 ± 0.24 | +1.4 | 1 | 0.66 | ||
| daf-2(e1370); atgl-1(P87S) | 134 | 16.84 ± 0.63 | +19.7 −43.8 (comp. to daf-2) |
4.1e-3 <1.0e-10 (comp. to daf-2) |
<1.0e-4 <1.0e-4 (comp. to daf-2) |
2.8. Fluorescence microscopy
Live animals were mounted on 2% agarose pads and immobilized with sodium azide. Images were taken either using Axiovert 200 or Zeiss AxioImager Z1 (Carl Zeiss, Germany) with a 20X objective. Identical exposure times were used when GFP intensity was compared between different conditions. ImageJ software was used to assess the level of fluorescence.
3. Results
3.1. ATGL-1 increases oxygen consumption and longevity
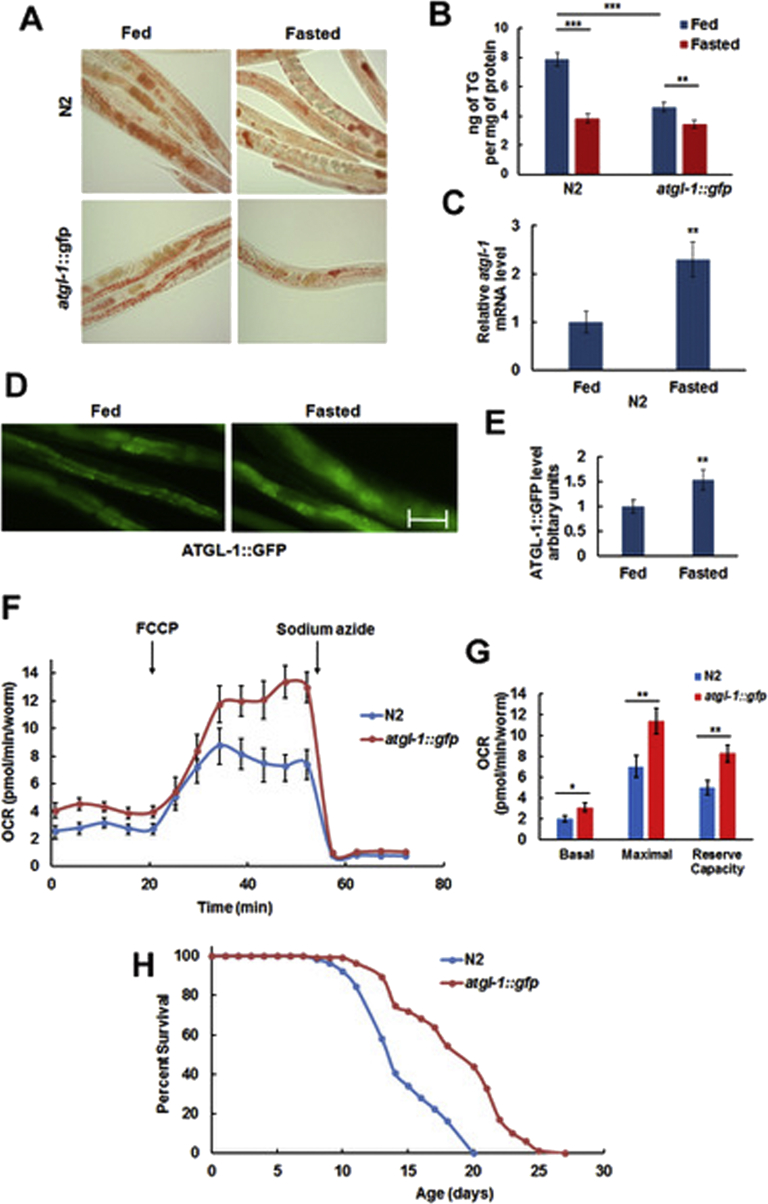
Fasting of wild type (N2) worms for 6 h depletes their TG reserves (Figure 1A (top) & B (left)) and up-regulates the atgl-1 mRNA (Figure 1C). To analyze expression of the ATGL-1 protein, we have utilized the VS20 strain that contains chromosome-integrated transgenic array hjIs67 [atgl-1p::atgl-1::GFP + mec-7p::RFP] [27] (that will be further referred to as atgl-1::gfp). As shown in Figure 1D,E, fasting increases ATGL-1 protein levels. Also, overexpression of atgl-1::gfp decreases TG reserves in both fed and, to a lesser extent, fasted worms (Figure 1A bottom & 1B right). In agreement with these results, it has been shown previously that down-regulation of atgl-1 by RNAi prevents TG depletion in adult worms subjected to fasting [28].
Figure 1.
ATGL-1 is up-regulated by fasting and increases oxygen consumption rate as well as longevity of C. elegans. (A) Wild type (N2) and atgl-1::gfp worms were split into control (Fed) and Fasted groups and stained with Oil Red O. (B) Triglyceride content was measured in Fed and Fasted groups of N2 and atgl-1::gfp worms. (C) RNA was extracted from Fed and Fasted groups, and atgl-1 mRNA levels were measured by qRT-PCR; actin-1/3 was used for normalization. (D) Fed and Fasted L4 stage atgl-1::gfp worms were visualized by fluorescence microscopy (200X, equal exposure times). Bar – 50 μM. (E) Quantification of the results shown in panel D by ImageJ (10 randomly selected worms per group). (F) Oxygen Consumption Rate (OCR) of N2 and atgl-1::gfp L4 worms was measured by XF96 Extracellular Flux Analyzer Seahorse, as described in Experimental Procedures. Each experiment was performed with ca. 200 worms and repeated 3 times. (G) Average basal OCR was calculated as the mean of the first five measurements after subtraction of average non-mitochondrial OCR; average maximal OCR is the mean of the last (before addition of sodium azide) five measurements after subtraction of average non-mitochondrial OCR; reserve respiratory capacity is the difference between average maximal and basal OCR. (H) The lifespan of atgl-1::gfp worms is extended by 32% in comparison to N2 (p value < 1.0e-10, log-rank analysis). Panels B, C, E-G show an average result of three independent experiments ±SEM, p values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
In mammals, ATGL-mediated lipolysis produces endogenous ligands for PPARα, its isotype PPARδ, and co-activator PGC-1α to control mitochondrial biogenesis and functions [29], [30], [31], [32], [33], [34]. In agreement with these results, we have found that overexpression of atgl-1::gfp increases both basal and maximal oxygen consumption rate as well as reserve respiratory capacity (Figure 1F,G). As healthy mitochondria are essential for longevity in both mammals [35] and C. elegans [36], we decided to determine the effect of atgl-1::gfp on longevity. Interestingly, the life span of the VS20 strain is significantly longer compared to that of N2 (Figure 1H and Table 1).
The latter result may seem to contradict a reported negative effect of ATGL-1 on the lifespan of aak-2 (the C. elegans AMP-activated kinase α2 catalytic subunit) mutant dauer larvae [37]. However, dauer represents an arrested dormant state that nematodes convert to in the absence of food. Dauer larvae do not feed and rely on stored energy for their survival. Therefore, in this case, the lipolytic activity of ATGL-1 appears to be suppressed by AMPK, and ATGL-1 de-repression in aak-2 mutant worms leads to faster depletion of nutrient stores and lifespan reduction.
3.2. Reduction of ATGL-1 function suppresses longevity of the eat-2 loss-of-function mutant strain
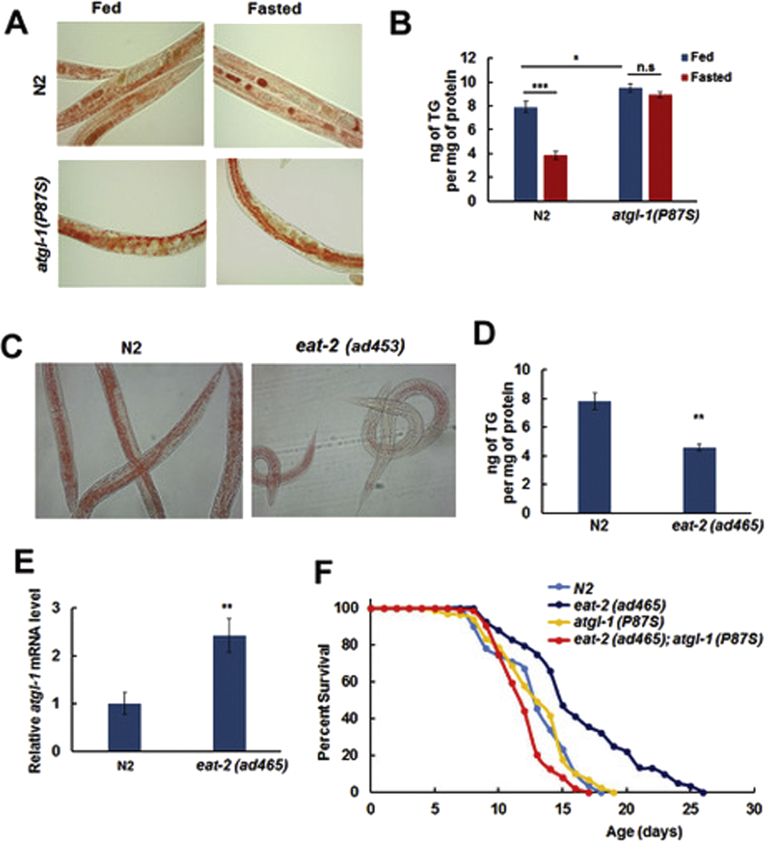
As deletion of the atgl-1 gene (the tm3116 allele) is lethal [38], we used a partial loss-of-function atgl-1 mutant for further experiments. To obtain a viable atgl-1 mutant allele we searched a list of strains generated by the Million Mutation Project [39] and identified atgl-1(gk176565 [P87S]) as a potential candidate. We reasoned that substitution of a proline by a serine in the extended conserved catalytic domain of ATGL [40] should impact ATGL function, through reducing ATGL catalytic activity and/or protein stability. Importantly, this mutation did not change levels of the atgl-1 mRNA (not shown). The atgl-1(gk176565) allele was outcrossed four times prior to its use in experiments described below.
In agreement with our expectations, the atgl-1(P87S) mutant accumulated significantly more TG than N2. Furthermore, fasting of the atgl-1(P87S) strain does not decrease its TG reserves (Figure 2A,B), which supports our hypothesis that P87S is a reduction-of-function ATGL-1 mutation.
Figure 2.
Increased longevity of the eat-2(ad465) strain is suppressed by atgl-1(P87S). (A) N2 and atgl-1(P87S) worms were split into Fed and Fasted groups and stained with Oil Red O. (B) Triglyceride content was measured in Fed and Fasted groups of N2 and atgl-1(P87S) worms. (C) N2 and eat-2(ad465) worms were stained with Oil Red O. (D) Triglyceride content was measured in N2 and eat-2(ad465) worms. (E) RNA was extracted from N2 and eat-2(ad465) worms, and atgl-1 mRNA levels were measured by qRT-PCR; actin-1/3 was used for normalization. (F) The lifespan of eat-2(ad465) worms is extended by 35.3% in comparison to N2 (p value 1.0e-3, log-rank with Boneferroni correction), while the lifespan of eat-2(ad465); atgl-1(P97S) worms is decreased by 33.1% in comparison to eat-2(ad465) (p value < 1.0e-10, log-rank with Bonferroni correction). Panels B, D, and E show an average result of three independent experiments ±SEM, p values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed t-test. *p< 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
To test whether or not ATGL-1 mediates the effect of fasting on longevity, we took advantage of a long lived strain eat-2(ad465) that mimics several aspects of dietary restriction due to the defect in pharyngeal function hence insufficient food uptake [41]. As expected, eat-2 mutant worms accumulated less TG than N2 (Figure 2C,D). Interestingly, the levels of atgl-1 mRNA in fed eat-2(ad465) worms were twice as high as in fed N2 strain (Figure 2E), and similar to the fasted N2 (Figure 1C). We then combined atgl-1(P87S) with eat-2(ad465) to obtain the eat-2(ad465); atgl-1(P87S) double mutant strain and used it in longevity experiments along with N2, atgl-1(P87S), and eat-2(ad465). As shown in Figure 2F and Table 1, atgl-1(P87S) completely suppressed the extended life span of eat-2(ad465). Therefore, ATGL-1 is required for the life span extension in this model of dietary restriction.
3.3. ATGL-1 is regulated by the DAF-2/DAF-16 axis and is required for extended lifespan of daf-2 mutants
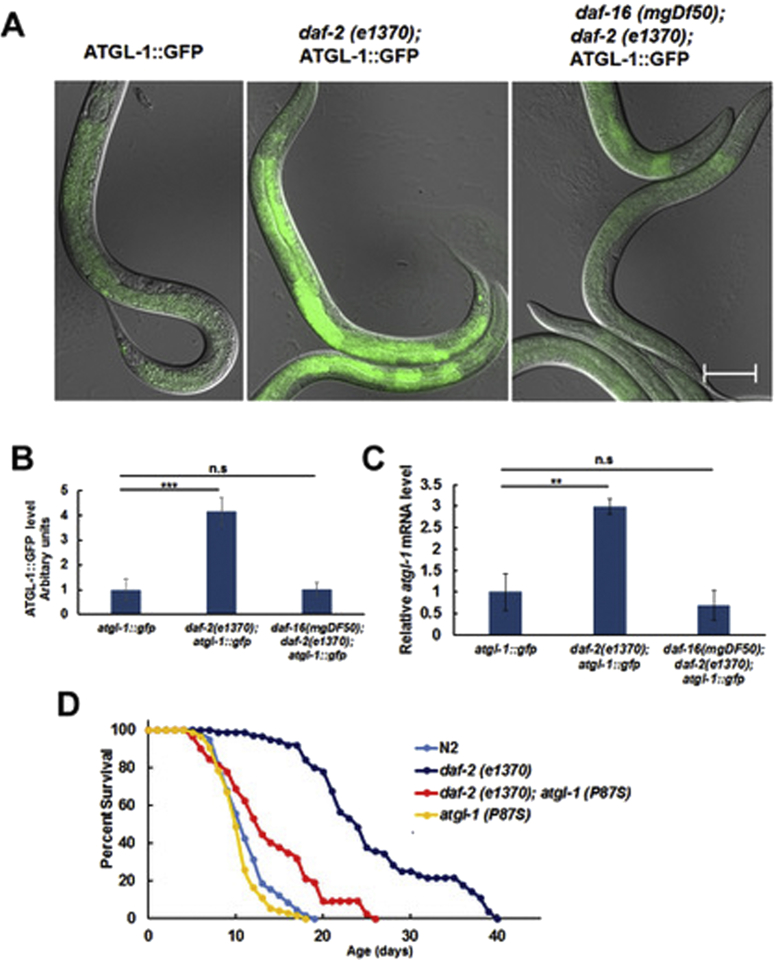
In mammalian adipocytes, expression of ATGL is suppressed by insulin via inhibition of FoxO1 [11]. The worm expresses homologues of the insulin receptor (DAF-2) and FoxO (DAF-16), but it is unknown whether expression of ATGL-1 in C. elegans is controlled by DAF-2 and DAF-16. Supporting this possibility, bioinformatics analysis shows a canonical DAF-16 binding site in the promoter of the atgl-1 gene (not shown). Therefore, we generated daf-2(e1370) and daf-2(e1370); daf-16(mgDf50) strains containing the atgl-1::gfp translational fusion reporter. Indeed, we observed elevated ATGL-1::GFP protein (Figure 3A,B) and atgl-1 mRNA (Figure 3C) expression in daf-2(e1370) compared to the background transgenic strain. Importantly, this effect was suppressed by the daf-16(mgDf50) null allele (Figure 3A–C). These results confirm the evolutionary conservation of ATGL regulation via the insulin receptor/FoxO1 axis from C. elegans to mammals.
Figure 3.
Expression of ATGL-1 is regulated by the daf-2/daf-16 pathway, and atgl-1(P87S) suppresses longevity of the daf-2 mutant. (A) L4 stage worms were visualized by fluorescence microscopy (200X, equal exposure times). Bar – 50 μM. (B) Quantification of the results shown in panel A by ImageJ (10 randomly selected worms per group). (C) Expression of the atgl-1 mRNA was measured by RT-qPCR; actin-1/3 was used for normalization. (D) The lifespan of daf-2(e1370) worms is increased by 131.1% in comparison to N2 (p value < 1.0e-10, log-rank with Boneferroni correction), while the lifespan of daf-2(e1370); atgl-1(P97S) worms is decreased by 46.3% in comparison to daf-2(e1370) (p value < 1.0e-10, log-rank with Boneferroni correction). Panel D shows an average result of three independent experiments ±SEM, p values were calculated by unpaired two-tailed t-test. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, n.s. – not significant.
To determine whether or not increased life span of the daf-2(e1370) mutant was dependent on atgl-1, we have crossed it with the atgl-1(P87S) strain. Our longevity experiments demonstrate that the life span of daf-2(e1370); atgl-1(P87S) was significantly (by ca. 46%) shorter compared to that of daf-2(e1370) alone (Figure 3D and Table 1). Therefore, ATGL-1 function is required downstream of both dietary restriction (Figure 2F) and DAF-16/FoxO pathways to extend life.
4. Discussion
Wang et al. [42] have previously identified another “life extending” lipase, LIPL-4 (K04A8.5) that shares a high degree of homology with mammalian lysosomal acid lipase and, therefore, is likely to be localized in lysosomes. Similar to cytosolic ATGL-1, LIPL-4 increases mitochondrial oxidation and reduces lipid storage [43]. In C. elegans, expression of both LIPL-4 [42] and ATGL-1 (this report) is activated by DAF-16; in mammalian cells, lysosomal acid lipase and ATGL are also co-regulated by FoxO1 [44]. Thus, both lysosomal and cytoplasmic lipases are regulated by the same evolutionary conserved signaling pathway and are essential for the life span control in C. elegans.
Adipose tissue plays a very special role in the control of the life span in mammals [45]. In particular, caloric restriction decreases TG stores in adipocytes and increases longevity, while obesity has the opposite effect [46]. Genetic ablation of the insulin receptor specifically in adipose tissue suppresses TG accumulation and significantly extends life span in mice [47]. Knock out of IRS-1 produces a similar outcome [48]. As regulatory pathways of ATGL expression are conserved from yeast [14] through C. elegans (this report) and Drosophila [49] to mammals [11], [14], it is feasible that ATGL may have a systemic life extending effect in higher eukaryotes.
5. Conclusions
Our results suggest that (a) evolutionary conserved dietary restriction and the IIS pathways converge on ATGL-1 expression, and (b) ATGL-1 is required for the extension of life span in response to dietary restriction and reduced IIS.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research grants from the NIH DK52057 & DK107498 to K.V.K., the research grant from the American Diabetes Association 1-18-IBS-266 to K.V.K., the BU-CTSI Pilot Award 1UL1TR001430 to K.V.K. and A.G., and by Boston Obesity Nutrition Research Center supported by P30DK046200 to Dr. Corkey. Strains used in this study were obtained from the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center, which is funded by NIH Office of Research Infrastructure Programs (P40 OD010440). The VC20458 strain was provided by the C. elegans Reverse Genetics Core Facility at the University of British Columbia, which is part of the International C. elegans Gene Knockout Consortium. We thank Dr. Andrew Samuelson (University of Rochester) for sharing the AVS518 eat-2(ad465) II strain.
Contributor Information
Alla Grishok, Email: agrishok@bu.edu.
Konstantin V. Kandror, Email: kkandror@bu.edu.
Conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Templeman N.M., Murphy C.T. Regulation of reproduction and longevity by nutrient-sensing pathways. The Journal of Cell Biology. 2018;217(1):93–106. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201707168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Taniguchi C.M., Emanuelli B., Kahn C.R. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2006;7(2):85–96. doi: 10.1038/nrm1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Riera C.E., Dillin A. Tipping the metabolic scales towards increased longevity in mammals. Nature Cell Biology. 2015;17(3):196–203. doi: 10.1038/ncb3107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kenyon C.J. The genetics of ageing. Nature. 2010;464(7288):504–512. doi: 10.1038/nature08980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Johnson S.C., Rabinovitch P.S., Kaeberlein M. mTOR is a key modulator of ageing and age-related disease. Nature. 2013;493(7432):338–345. doi: 10.1038/nature11861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Singh P.P., Demmitt B.A., Nath R.D., Brunet A. The genetics of aging: a vertebrate perspective. Cell. 2019;177(1):200–220. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Calnan D.R., Brunet A. The FoxO code. Oncogene. 2008;27(16):2276–2288. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gross D.N., van den Heuvel A.P., Birnbaum M.J. The role of FoxO in the regulation of metabolism. Oncogene. 2008;27(16):2320–2336. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Saxton R.A., Sabatini D.M. mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell. 2017;168(6):960–976. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chakrabarti P., English T., Karki S., Qiang L., Tao R., Kim J. SIRT1 controls lipolysis in adipocytes via FOXO1-mediated expression of ATGL. The Journal of Lipid Research. 2011;52(9):1693–1701. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M014647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chakrabarti P., Kandror K.V. FoxO1 controls insulin-dependent adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) expression and lipolysis in adipocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2009;284(20):13296–13300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C800241200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chakrabarti P., English T., Shi J., Smas C.M., Kandror K.V. Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 suppresses lipolysis, stimulates lipogenesis, and promotes fat storage. Diabetes. 2010;59(4):775–781. doi: 10.2337/db09-1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chakrabarti P., Kandror K.V. The role of mTOR in lipid homeostasis and diabetes progression. Current Opinion in Endocrinology Diabetes and Obesity. 2015;22(5):340–346. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chakrabarti P., Kim J.Y., Singh M., Shin Y.K., Kim J., Kumbrink J. Insulin inhibits lipolysis in adipocytes via the evolutionarily conserved mTORC1-Egr1-ATGL-mediated pathway. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2013;33(18):3659–3666. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01584-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Smirnova E., Goldberg E.B., Makarova K.S., Lin L., Brown W.J., Jackson C.L. ATGL has a key role in lipid droplet/adiposome degradation in mammalian cells. EMBO Reports. 2006;7(1):106–113. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zimmermann R., Strauss J.G., Haemmerle G., Schoiswohl G., Birner-Gruenberger R., Riederer M. Fat mobilization in adipose tissue is promoted by adipose triglyceride lipase. Science. 2004;306(5700):1383–1386. doi: 10.1126/science.1100747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Villena J.A., Roy S., Sarkadi-Nagy E., Kim K.H., Sul H.S. Desnutrin, an adipocyte gene encoding a novel patatin domain-containing protein, is induced by fasting and glucocorticoids: ectopic expression of desnutrin increases triglyceride hydrolysis. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279(45):47066–47075. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403855200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jenkins C.M., Mancuso D.J., Yan W., Sims H.F., Gibson B., Gross R.W. Identification, cloning, expression, and purification of three novel human calcium-independent phospholipase A2 family members possessing triacylglycerol lipase and acylglycerol transacylase activities. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279(47):48968–48975. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407841200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Haemmerle G., Lass A., Zimmermann R., Gorkiewicz G., Meyer C., Rozman J. Defective lipolysis and altered energy metabolism in mice lacking adipose triglyceride lipase. Science. 2006;312(5774):734–737. doi: 10.1126/science.1123965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bezaire V., Mairal A., Ribet C., Lefort C., Girousse A., Jocken J. Contribution of adipose triglyceride lipase and hormone-sensitive lipase to lipolysis in hMADS adipocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2009;284(27):18282–18291. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.008631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Miyoshi H., Perfield J.W., 2nd, Obin M.S., Greenberg A.S. Adipose triglyceride lipase regulates basal lipolysis and lipid droplet size in adipocytes. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 2008;105(6):1430–1436. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kershaw E.E., Hamm J.K., Verhagen L.A., Peroni O., Katic M., Flier J.S. Adipose triglyceride lipase: function, regulation by insulin, and comparison with adiponutrin. Diabetes. 2006;55(1):148–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gronke S., Mildner A., Fellert S., Tennagels N., Petry S., Muller G. Brummer lipase is an evolutionary conserved fat storage regulator in Drosophila. Cell Metabolism. 2005;1(5):323–330. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kurat C.F., Natter K., Petschnigg J., Wolinski H., Scheuringer K., Scholz H. Obese yeast: triglyceride lipolysis is functionally conserved from mammals to yeast. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2006;281(1):491–500. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508414200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974;77(1):71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Han S.K., Lee D., Lee H., Kim D., Son H.G., Yang J.S. OASIS 2: online application for survival analysis 2 with features for the analysis of maximal lifespan and healthspan in aging research. Oncotarget. 2016;7(35):56147–56152. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhang S.O., Box A.C., Xu N., Le Men J., Yu J., Guo F. Genetic and dietary regulation of lipid droplet expansion in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107(10):4640–4645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912308107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee J.H., Kong J., Jang J.Y., Han J.S., Ji Y., Lee J. Lipid droplet protein LID-1 mediates ATGL-1-dependent lipolysis during fasting in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2014;34(22):4165–4176. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00722-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Haemmerle G., Moustafa T., Woelkart G., Buttner S., Schmidt A., van de Weijer T. ATGL-mediated fat catabolism regulates cardiac mitochondrial function via PPAR-alpha and PGC-1. Nature Medicine. 2011;17(9):1076–1085. doi: 10.1038/nm.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Khan S.A., Sathyanarayan A., Mashek M.T., Ong K.T., Wollaston-Hayden E.E., Mashek D.G. ATGL-catalyzed lipolysis regulates SIRT1 to control PGC-1alpha/PPAR-alpha signaling. Diabetes. 2015;64(2):418–426. doi: 10.2337/db14-0325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mottillo E.P., Bloch A.E., Leff T., Granneman J.G. Lipolytic products activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha and delta in brown adipocytes to match fatty acid oxidation with supply. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2012;287(30):25038–25048. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.374041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tang T., Abbott M.J., Ahmadian M., Lopes A.B., Wang Y., Sul H.S. Desnutrin/ATGL activates PPARdelta to promote mitochondrial function for insulin secretion in islet beta cells. Cell Metabolism. 2013;18(6):883–895. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.10.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Biswas D., Ghosh M., Kumar S., Chakrabarti P. PPARalpha-ATGL pathway improves muscle mitochondrial metabolism: implication in aging. The FASEB Journal. 2016;30(11):3822–3834. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600571RR. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schreiber R., Diwoky C., Schoiswohl G., Feiler U., Wongsiriroj N., Abdellatif M. Cold-Induced thermogenesis depends on ATGL-mediated lipolysis in cardiac muscle, but not Brown adipose tissue. Cell Metabolism. 2017;26(5):753–763. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.09.004. e757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kauppila T.E.S., Kauppila J.H.K., Larsson N.G. Mammalian mitochondria and aging: an update. Cell Metabolism. 2017;25(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chaudhari S.N., Kipreos E.T. The energy maintenance theory of aging: maintaining energy metabolism to allow longevity. Bioessays. 2018 doi: 10.1002/bies.201800005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Narbonne P., Roy R. Caenorhabditis elegans dauers need LKB1/AMPK to ration lipid reserves and ensure long-term survival. Nature. 2009;457(7226):210–214. doi: 10.1038/nature07536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Consortium C.E.D.M. large-scale screening for targeted knockouts in the Caenorhabditis elegans genome. G3 (Bethesda) 2012;2(11):1415–1425. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.003830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Thompson O., Edgley M., Strasbourger P., Flibotte S., Ewing B., Adair R. The million mutation project: a new approach to genetics in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genome Research. 2013;23(10):1749–1762. doi: 10.1101/gr.157651.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cornaciu I., Boeszoermenyi A., Lindermuth H., Nagy H.M., Cerk I.K., Ebner C. The minimal domain of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) ranges until leucine 254 and can be activated and inhibited by CGI-58 and G0S2, respectively. PLoS One. 2011;6(10) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lakowski B., Hekimi S. The genetics of caloric restriction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95(22):13091–13096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.13091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang M.C., O'Rourke E.J., Ruvkun G. Fat metabolism links germline stem cells and longevity in C. elegans. Science. 2008;322(5903):957–960. doi: 10.1126/science.1162011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ramachandran P.V., Savini M., Folick A.K., Hu K., Masand R., Graham B.H. Lysosomal signaling promotes longevity by adjusting mitochondrial activity. Developmental Cell. 2019;48(5):685–696. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.12.022. e685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Barbato D.L., Aquilano K., Ciriolo M.R. FoxO1 at the nexus between fat catabolism and longevity pathways. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 2014;1841(10):1555–1560. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Picard F., Guarente L. Molecular links between aging and adipose tissue. International Journal of Obesity (London) 2005;29(Suppl. 1):S36–S39. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tchkonia T., Morbeck D.E., Von Zglinicki T., Van Deursen J., Lustgarten J., Scrable H. Fat tissue, aging, and cellular senescence. Aging Cell. 2010;9(5):667–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bluher M., Kahn B.B., Kahn C.R. Extended longevity in mice lacking the insulin receptor in adipose tissue. Science. 2003;299(5606):572–574. doi: 10.1126/science.1078223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Selman C., Lingard S., Choudhury A.I., Batterham R.L., Claret M., Clements M. Evidence for lifespan extension and delayed age-related biomarkers in insulin receptor substrate 1 null mice. The FASEB Journal. 2008;22(3):807–818. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-9261com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Birse R.T., Choi J., Reardon K., Rodriguez J., Graham S., Diop S. High-fat-diet-induced obesity and heart dysfunction are regulated by the TOR pathway in Drosophila. Cell Metabolism. 2010;12(5):533–544. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.09.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]