Abstract
Background
Two of the most important pathogens contributing to the global rise in antimicrobial resistance (AMR) are Klebsiella pneumoniae and Enterobacter cloacae. Despite this, most of our knowledge about the changing patterns of disease caused by these two pathogens is based on studies with limited timeframes that provide few insights into their population dynamics or the dynamics in AMR elements that they can carry.
Results
We investigate the population dynamics of two priority AMR pathogens over 7 years between 2007 and 2012 in a major UK hospital, spanning changes made to UK national antimicrobial prescribing policy in 2007. Between 2006 and 2012, K. pneumoniae showed epidemiological cycles of multi-drug-resistant (MDR) lineages being replaced approximately every 2 years. This contrasted E. cloacae where there was no temporally changing pattern, but a continuous presence of the mixed population.
Conclusions
The differing patterns of clonal replacement and acquisition of mobile elements shows that the flux in the K. pneumoniae population was linked to the introduction of globally recognized MDR clones carrying drug resistance markers on mobile elements. However, E. cloacae carries a chromosomally encoded ampC conferring resistance to front-line treatments and shows that MDR plasmid acquisition in E. cloacae was not indicative of success in the hospital. This led to markedly different dynamics in the AMR populations of these two pathogens and shows that the mechanism of the resistance and its location in the genome or mobile elements is crucial to predict population dynamics of opportunistic pathogens in clinical settings.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s13059-019-1785-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Resistance mechanisms, Population dynamics, Intrinsic resistance, Plasmid diversity
Background
Since the early 2000s, successive pandemics of bacterial resistance, first- to third-generation cephalosporins and then to carbapenems, have eroded the utility of our most useful antimicrobials (the beta-lactams). Klebsiella pneumoniae and Enterobacter cloacae are amongst the primary threats to human health due to the range of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) that they can cause and their potential for becoming multidrug-resistant [1]. Through the increase of antimicrobial resistance, considerable research has focused on understanding opportunistic pathogens and especially the different mechanisms conferring AMR.
The K. pneumoniae genome encodes for an ancestrally acquired penicillinase leaving it readily treatable with cephalosporins and other antimicrobials. The widespread acquisition of mobile CTX-M and other extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs) encoded on conjugative (transferable) plasmids [2, 3] has been a major driver in the success of K. pneumoniae as hospital pathogen. E. cloacae carry a chromosomally encoded AmpC beta-lactamase which has a wide spectrum of activity conferring intrinsic resistance to many front-line treatment options including penicillins, penicillin-penicillinase inhibitor combinations, and (when ampC becomes derepressed) third-generation cephalosporins, making it a major contributor towards intrinsic resistance for Enterobacter spp.
Both K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae remain largely susceptible to other important groups of antimicrobials in the UK [4]. This includes key drugs such as fluoroquinolones, where resistance can derive from acquired genes but is often caused by chromosomal mutations of the enzymes encoded by gyrA and parC. Other examples of gene acquisitions driving resistance include the aminoglycosides [5, 6] and other antimicrobials such as chloramphenicol or tetracycline, whereby a single resistance cassette or plasmid acquisition can render a bacterium resistant against several classes of antimicrobials with a single acquisition event.
The K. pneumoniae species complex is highly diverse, with three different species predominating amongst human, environmental, and animal isolates [7]. K. pneumoniae comprises four main lineages: K. pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae; K. quasipneumoniae subsp. quasipneumoniae and subsp. similipneumoniae; and K. variicola. The vast majority of hospital isolates belong to K. pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae sensu stricto). From whole-genome sequencing studies comparing outbreaks of drug-resistant K. pneumoniae in both well-resourced and poorly resourced healthcare settings [8, 9], it is clear that there are successful high-risk clones that re-occur in independent settings globally [10]. In common with K. pneumoniae, E. cloacae comprises a diverse species complex with recent reclassification and revision into 18 E. cloacae subspecies clusters [11].
Whilst it is appreciated that both species are highly diverse and multiple lineages and/or clones cause significant health burden, it has become clear that we lack a basic understanding of their population dynamics in clinical settings. Most studies focus on short time frames and provide only short glimpses into the population structure. This significantly limits our understanding of the change in diversity over time and the dynamic gain and loss of antimicrobial resistance genes/mutations over time. To address this, we undertook a 7-year longitudinal study to gain better resolution of the temporal flux of AMR at the Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (CUH), a 1000-bed secondary and tertiary referral hospital in the UK. We examined the relative contributions of the bacterial lineage itself and the mobile AMR determinants towards the temporal flux in the phenotypic patterns of AMR seen in this setting. To provide the context for the changing patterns of disease and AMR in CUH, we relate these data to national AMR surveillance data and global genomic data for these pathogens. We show that K. pneumoniae lineages were successively replaced by new lineages entering CUH that had acquired ESBLs, such as blaCTX-M-15, and were disseminated internationally. E. cloacae isolates on the other hand showed little temporal flux and were highly diverse, largely unlinked to international spread and reliant on intrinsic cephalosporin resistance via the endogenous AmpC enzyme for AMR. Our study highlights the need for more mechanistic pathogen-specific approaches to control antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial-resistant bacteria.
Results
Longitudinal patterns of antimicrobial resistance in K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae
Patient and isolate metadata were collected for the first-recorded K. pneumoniae isolate cultured from 13,379 patients and the first E. cloacae from 5661 patients attending CUH between 2001 and 2012 (summarized in Fig. 1). As such, patients at CUH were 2.4 times more likely to have a positive K. pneumoniae culture compared to E. cloacae during this period. For both species complexes, the sample types were mainly blood, followed by urine, wounds, and sputum, although E. cloacae were isolated from a wider range of body sites (arm/leg, groin, breast, pelvic) compared to K. pneumoniae (Additional file 1: Figure S1).
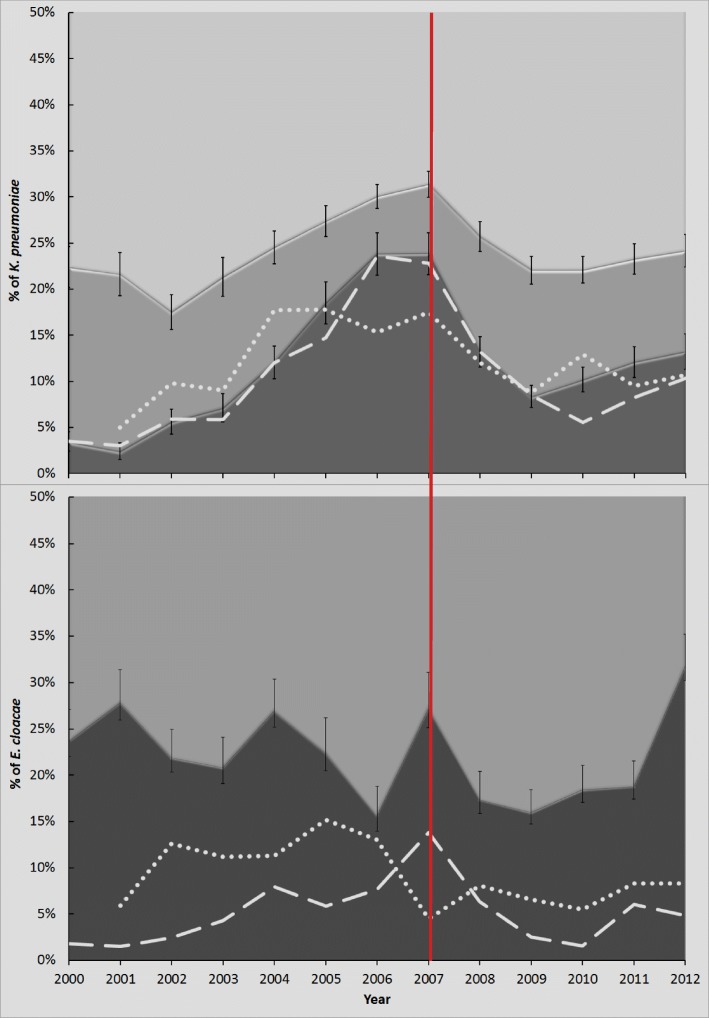
Fig. 1.
Trends in drug resistance amongst K. pneumoniae and Enterobacter spp. isolated from patients attending CUH between 2000 and 2012. The proportion of a Klebsiella pneumoniae and b Enterobacter spp. resistant to one group of antimicrobials or less (pale shading), two groups (mid-shading), or three or more groups (dark shading) are shown, and a major change in national antimicrobial prescribing practice in 2007 is denoted with a red vertical line. Black vertical lines represent 95% confidence intervals. Resistance to cephalosporins and/or aminoglycosides in K. pneumoniae or aminoglycosides in E. cloacae is shown for isolates from Cambridge alone (dashed white line) and the UK (dotted white lines) (UK data from www.bsacsurv.org)
Antimicrobial resistance data showed that K. pneumoniae isolates had reduced susceptibility to penicillins (as expected for the species), whilst 6–19% of isolates in a year were resistant to two of the six antimicrobial groups tested (see the “Materials and methods” section; Fig. 1a). The proportion of K. pneumoniae isolates with phenotypic resistance to three or more groups varied considerably over time (3.5 to 24%), with peaks in resistance occurring in 2006–2007 and 2011–2012 (Fig. 1a). These peaks were associated with flux in the proportion of isolates resistant to third-generation cephalosporins or aminoglycosides (Fig. 1a). For E. cloacae, the background proportions of antimicrobial resistance were higher, with 66–82% of isolates resistant to at least two of the antimicrobial groups tested (Fig. 1b). Unlike K. pneumoniae, multiple peaks in the proportion of isolates resistant to one or more additional groups were seen more often, in 2001, 2004, 2007, and 2012 (Fig. 1b).
The differing trends in proportions of resistant K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae at CUH mirrored trends in national surveillance data during the same time period (71) (Fig. 1). These all had a transient downward trajectory immediately after a change in 2007 to national antimicrobial prescribing policy that aimed to decrease cephalosporin usage [12].
K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae at CUH between 2006 and 2012 reflected the wider diversity of the species
To investigate the basis of these different trends between the species, we selected 162 K. pneumoniae and 132 E. cloacae isolates from 158 and 132 patients, respectively, for sequencing. Isolates were collected between 2006 and 2012 from blood and a range of other body sites (Additional file 1: Figure S1), representing 20–34% of the total invasive K. pneumoniae and 40–45% of invasive E. cloacae isolated at CUH, in any year between 2006 and 2012. The isolates included 114 and 92 isolates that constituted all of the invasive isolates that were resistant to three or more of the six antimicrobial groups tested for K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae, respectively, between 2006 and 2012. Since there were no fully susceptible isolates collected during this period, 48 K. pneumoniae and 40 E. cloacae isolates resistant to no more than two antimicrobial groups were selected at random for inclusion as a (c. 10%) sub-sample of “susceptible” comparators (Table 1).
Table 1.
K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae collected in 2006–2012 that underwent whole-genome sequencing
| Resistance to drug groups | K. pneumoniae isolates (n) | E. cloacae isolates (n) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Available (2006–2012) |
Sequenced | Available (2006–2012) |
Sequenced | |||
| 2006–2012 | Q4 2012 | 2006–2012 | Q4 2012 | |||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 279 | 28 | 3 | 24 | 12 | 3 |
| 2 | 104 | 15 | 2 | 128 | 16 | 9 |
| 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 50 | 44 | 8 |
| 4 | 29 | 28 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 5 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 19 | 19 | 14 |
| 6 | 43 | 43 | 16 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Total | 465 | 124 | 38 | 225 | 95 | 38 |
Isolates were stratified according to the number of antimicrobial groups to which they were phenotypically resistant by routine diagnostic testing
Although all isolates had been classified by the routine microbiology laboratory as K. pneumoniae, the whole genome phylogeny of K. pneumoniae revealed other species within the species complex; 15 isolates were K. quasipneumoniae or K. variicola (Fig. 2a; Additional file 1: Figure S2A; Additional file 2: Table S1). Genotypic resistance predictions indicated that at CUH, the other species were not predominated by multi-drug-resistant isolates (Additional file 1: Figure S3), emphasizing that by contrast, K. pneumoniae sensu stricto were the subspecies comprising the majority of multidrug-resistant isolates.
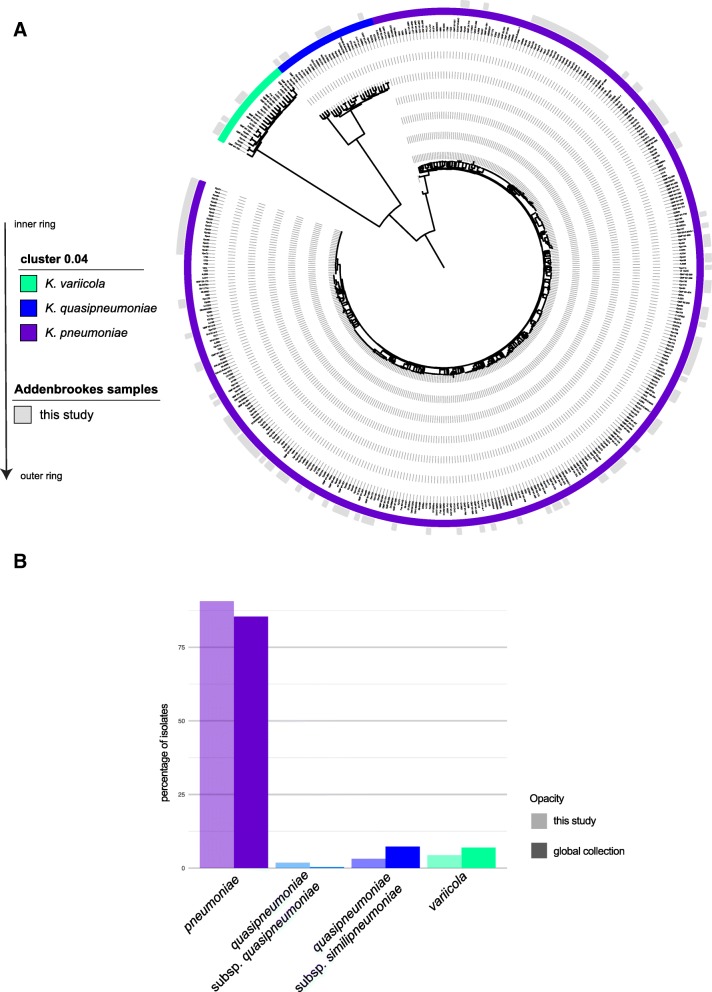
Fig. 2.
K. pneumoniae isolates from CUH within the global population structure. a Phylogenetic tree reconstruction of the core gene alignment again highlights the diversity encountered in routine hospital samples. The inner ring shows mash clusters [13] which split the three species K. pneumoniae, K. quasipneumoniae, and K. variicola, at a cutoff of 0.04 correlating to an ANI of 96%. The outer ring displays which samples are derived from this study, embedded in the global diversity [7]. b Barplot illustrating the numbers of the different lineages observed in our collection compared to the global collection [7]
When combined with a global collection representing the K. pneumoniae population structure [7] (Fig. 2a, Additional file 2: Table S2), our phylogeny showed that the diversity seen at CUH was representative of the global population diversity, with all major lineages represented. This included the relatively rare subspecies: K. q. subsp. quasipneumoniae, K. q. subsp. similipneumoniae, and K. variicola (Fig. 2b). Comparison with a UK collection sampled during a similar time frame [14] (Additional file 1: Figure S2A; Additional file 2: Table S3) showed that the CUH K. pneumoniae reflected the contemporaneous national distributions across the species complex and the diversity of sequence types (Additional file 1: Figure S2A).
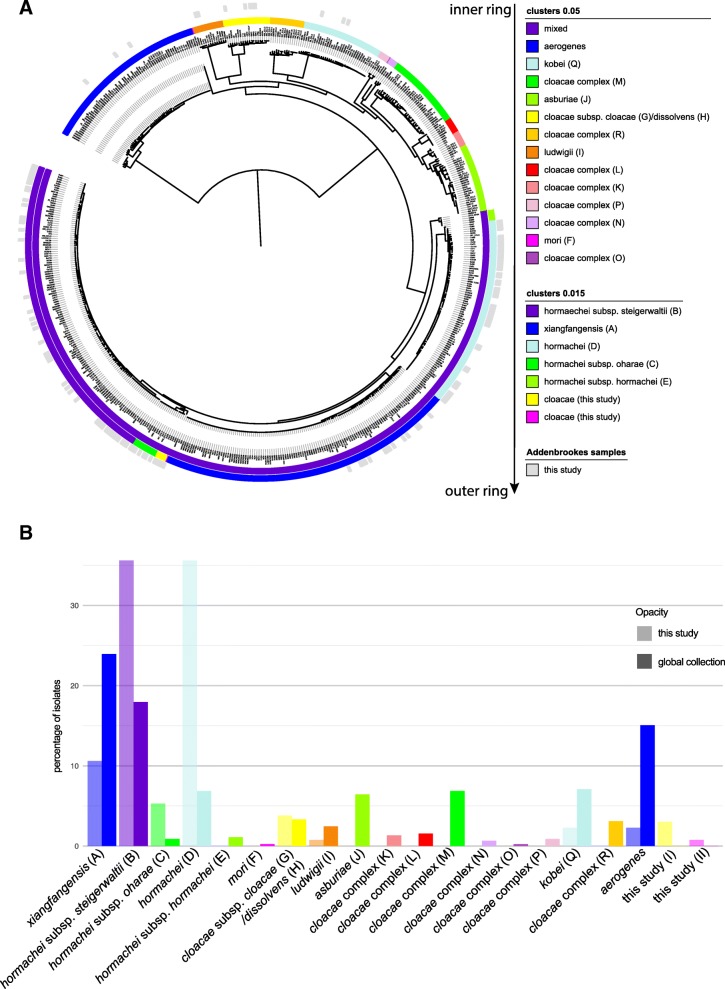
E. cloacae contained two separate species (E. aerogenes, recently reclassified as Klebsiella aerogenes [15], and E. kobei), as well as several subspecies and clusters. Using the revised E. cloacae taxonomy [11], we observed high levels of genomic similarity. Clustering using a distance matrix (mash [13]) at the cutoff of 0.05% which is representative of the species cutoff ANI 0.95% [13] showed a large group comprised of several previously described subgroups [11] that were resolved when a finer distance cutoff (0.015) was used (excepting group G/H; Fig. 3a, Additional file 2: Table S4). The CUH population diversity was comparable to that observed for isolates from across the UK [16] (Additional file 1: Figure S3B; Additional file 2: Table S3), but unlike K. pneumoniae, there were clear differences evident when compared with the global collection [11] (Fig. 3b, Additional file 2: Table S5). We identified 8 out of the 18 clusters described previously [11] and discovered two new clusters nested in the widely distributed E. xianfangensis and E. hormaechei subgroups (Fig. 3a). We also observed a far lower percentage of E. xiangfangensis that expanded with the spread of KPC-type carbapenemases, which is consistent with our dataset lacking carbapenem-resistant isolates (Fig. 3b). Analysis of the deep branching lineages showed E. kobei and E. ludwigii were exclusively isolated from blood, whereas E. aerogenes and groups G/H were from a wider variety of isolation sites, possibly more indicative of opportunistic infections (Additional file 1: Figure S3C). These differences were also reflected in the predicted (genotypic) resistance profiles, with E. kobeii showing resistance to two or three antimicrobial classes, whereas the other deep lineages showed no (E. aerogenes, E. ludwigii) or only a low proportion (groups G/H) of MDR isolates (Additional file 1: Figure S3D).
Fig. 3.
E. cloacae isolates from CUH within the global population structure. a Phylogenetic tree reconstruction from the core gene alignment highlights the diversity encountered in routine hospital samples. The inner and middle rings show the same clustering information at 0.05 and 0.015, respectively. The outer ring displays which samples are derived from this study, embedded in the global diversity [11]. Accession numbers and cluster annotation are given in Additional file 2: Tables S2 and S5 for the global collection and the samples from this study, respectively. b Barplot illustrating the numbers of the different lineages observed in our collection compared to the global collection [11]
K. pneumoniae and Enterobacter represented flowing vs static populations in CUH between 2006 and 2012
The dominance of four globally important clones (STs: 15; 101; 307; 874) amongst the K. pneumoniae at CUH (41%) (Additional file 1: Figure S3A; Additional file 2: Table S1) was led by ST15 which is strongly linked to outbreaks in hospitals [8, 17, 18]. ST101 has been highlighted for its association with extensive resistance and KPC carbapenemases [19], and ST307 was reported in a recent large-scale analysis of carbapenem-resistant isolates [20, 21]. By contrast in E. cloacae, the main four sequence types constituted only 27% of the isolates (Additional file 1: Figure S3B; Additional file 2: Table S4), suggestive of different population dynamics for these two genera in a hospital setting.
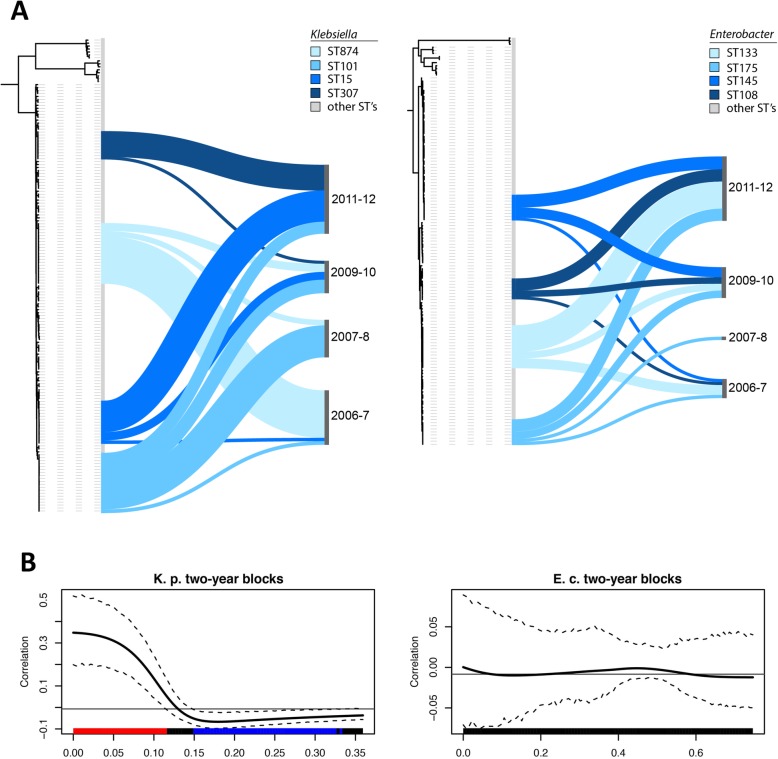
Successive replacements of the K. pneumoniae STs occurred over time (Fig. 4a). Testing for the correlation between genetic distance using whole-genome SNP data (after removing recombination) and the date of isolation showed a strong correlation between phylogenetic signal and the temporal information, using month, year, and the observed 2-year span as a trait (Fig. 4b; Additional file 1: Figure S4). This trend was not apparent for Enterobacter isolates (Fig. 4b), with all clones represented across the study period. These temporal signals for strain flow vs stasis between the species were not perturbed after 2007 when the change in antimicrobial prescribing policy occurred.
Fig. 4.
Population structures of Klebsiella and Enterobacter over time. a Visualizing the occurrence of the four main sequence types for Klebsiella (left tree) and Enterobacter (right tree) highlights a consecutive replacement of the different Klebsiella sequence types, whereas the main Enterobacter sequence types occur continuously as mixed population during all time frames. b Test for the correlation of the distance on the tree between two samples using SNP data from whole-genome trees after removing recombination and sharing or difference of a trait (2-year spans of isolation as given in Additional file 2: Tables S1 and S4). This shows a strong positive correlation (similar trait is more likely) for very close strains and negative correlation (similar traits are more unlikely) for large distances on the tree for Klebsiella (left panel); no signal can be observed for Enterobacter (right panel)
Sharing of the same composite and dynamic resistance elements differed across the genera
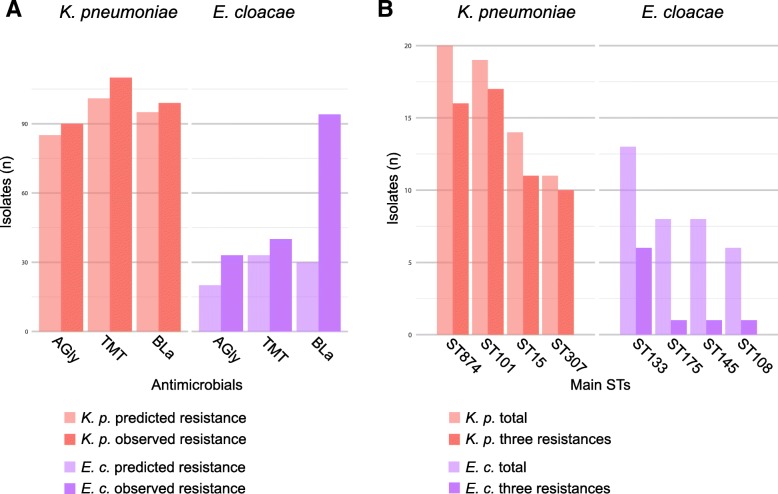
To gain insight into the contrasting population and resistance dynamics between K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae, we compared the patterns of genotypic to phenotypic resistance, i.e., how well-predicted resistance genes could explain the observed resistance patterns (Fig. 5a).
Fig. 5.
Different population and resistance profiles in the two data collections. a A comparison of the number of isolates to be resistant according to the genes as predicted (light bars) and measured to be resistant in physical tests (dark bars). b The distribution of MDR isolates across the main STs for Klebsiella and Enterobacter spp., with the total number of isolates for the ST in lighter and the number of isolates resistant against all three classes in darker color
For K. pneumoniae, resistance to aminoglycosides, trimethoprim, and the beta-lactams was closely linked with horizontally acquired genes (Fig. 5a; Additional file 1: Figure S5; Additional file 2: Table S1). Amongst the beta-lactams, ESBLs were detected in almost all cephalosporin-resistant isolates (95 out of 99), most often blaCTX-M-15 (85 isolates). Only three isolates encoded carbapenemases (Additional file 2: Table S1). For the same three antimicrobial classes in E. cloacae, gene presence predicted resistance in 20 out of 33 aminoglycoside-resistant and 33 out of 40 trimethoprim-resistant isolates (Fig. 5a, Additional file 2: Table S1 and Table S4). The poor correlation between resistance to third-generation cephalosporins and the presence of ESBL genes (30 of 94 resistant isolates acquired ESBL genes) (Additional file 2: Table S2) in E. cloacae could be explained by the upregulation of the endogenous AmpC beta-lactamase [22–29].
Differences are also clearly apparent when assessing the most dominant STs. Whilst in K. pneumoniae, the four dominant STs are almost exclusively comprised of multidrug-resistant isolates, the opposite was true for E. cloacae (Fig. 5b).
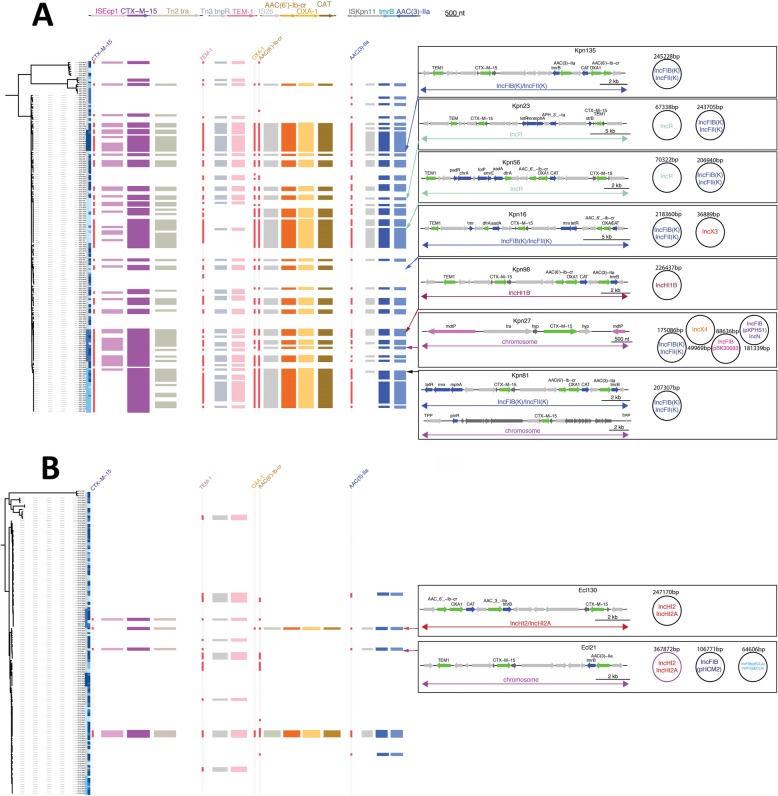
When analyzing co-occurrence of resistance elements, we noticed that the main resistance cassettes were shared between K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae and almost always show perfect co-occurrence (Fig. 6, left panels). This includes the comparatively few E. cloacae encoding ESBL genes (blaCTX-M-15), which were identified with the same pattern of aminoglycoside and trimethoprim resistance genes that was found in K. pneumoniae, indicating both species access the same shared gene pool, but the distribution across the populations is clearly different between the two species. To resolve this, we performed long-read (PacBio) sequencing on selected isolates, which confirmed that the resistance genes shared related genetic environments, suggesting that both genera were acquiring a similar pool of resistance genes. However, there is an extensive pool of mobile elements being sampled, with no two isolates sharing the same plasmid repertoire (Fig. 6 right panels). The key ESBL gene blaCTX-M-15 was found integrated at an array of different chromosomal sites or carried on a diverse set of plasmid replicons in K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae alike (Fig. 6a, b), with no two strains sharing it at the same location. A comparison against a curated large-scale plasmid database showed that these elements co-occur (Additional file 1: Figure S6), but less frequently as seen in our examples. This is most likely since similar geographic and temporal isolation sources seem to reflect a dynamic pool of transposable elements and plasmids shared between K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae, and potentially also other members of the Enterobacterales occurring at the same time in the area.
Fig. 6.
The conservation of integrons and mobile units across the species vs the dynamic broader genetic context. The guidance trees are based on the core gene alignment for Klebsiella pneumoniae (a) and Enterobacter cloacae (b). The conservation of the genetic environment of the main acquired resistance genes blaCTX-M-15, blaTEM1, blaOXA1, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, and aac(3)-IIa was tested by mapping against the predominantly observed cassettes surrounding these genes as mobile units. Whilst blaCTX-M-15 moves by itself in the Tn2021 structure, and blaTEM-1 moves with a tnpR gene, the blaOXA-1, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, and cat (chloramphenicol-resistance) genes are conserved in an integron element and the aac(3)-IIa and tmrB (tunicamycin resistance) genes are conserved together. This highlights that even though there is high variability in the plasmid content, there is a core set of resistance gene cassettes that is stable in both populations, and strains very often carry all of them combined. Long-read assemblies (Pacbio) resolved the plasmid content and location of the CTX-M-15 gene in several representatives of Enterobacter spp. and Klebsiella spp., as indicated by the arrows to the core gene guide trees. The respective boxes illustrate the plasmid content with the Inc-type and their respective sizes. The arrow diagrams illustrate the location of the CTX-M-15 gene, which is highly mobile, and can be seen to be integrated into the chromosomes in three out of our nine examples, each at different locations, as well as on plasmids belonging to the IncR, IncFIB(K)/IncFIIK, IncHI2/IncHI2A, and IncHIB types
Discussion
WGS highlighted the contrasting AMR populations of these species in our hospital across 6 years from 2006. The K. pneumoniae population was dominated by clonal replacements of major STs with the majority of isolates multidrug-resistant due to uptake of resistance plasmids (STs 874, 101 and 307), whilst the E. cloacae hospital population reflected a continuous sampling from the whole diversity without temporal signal and without apparent fitness advantage for strains carrying mobile elements conferring resistance. For Klebsiella, this indicated the importance of horizontal acquisition of ESBLs, like blaCTX-M-15, whilst for Enterobacter, it emphasized the capacity for intrinsic cephalosporin resistance via the endogenous AmpC enzyme [30].
We observed four successive introductions of highly cephalosporin-resistant K. pneumoniae clones. Three of the four (excepting ST307) are known to be widespread in the UK [14], and all four have been seen to be resistant lineages disseminated internationally [20]. In contrast, for Enterobacter, there were differences between this cephalosporin resistance-focussed study and a recent global study. The main difference was due to an under-representation E. xiangfangensis, a major Enterobacter lineage associated with plasmid-acquired KPC-based carbapenem resistance. This is in accordance with our sampling time frame, which are derived from times before carbapenems were widely used, and strongly indicates that the shift from intrinsic resistance to advanced cephalosporins (in our study) to relying on acquired resistance mechanisms for carbapenem resistance (via plasmid-derived KPC) changed the E. cloacae population structure towards few dominating clones, as discussed in [16].
The finding that small numbers of diverse Enterobacter acquired the same collection of mobile resistance elements found across K. pneumoniae demonstrated a similarity between the species in their use of a linked network of mobile resistance genes, which, based on reports on E. coli [3], is widely shared with other Enterobacterales. For this study, the consistent profile of the numerous resistance genes present alongside blaCTX-M-15 detected from short-read data masked the extensive plasticity and variability of the complex resistance elements acquired by both species. Despite this plasticity of different plasmids and chromosomal integration sites, the presence and absence of the resistance genes themselves remained stable across the major K. pneumoniae clones found in 2012 (ST307) or in 2006 (i.e., ST874). The lack of association between the persistent or successful lineages of E. cloacae indicated that AMR alone did not explain the success of major clones in either genus, a point that will form the basis of ongoing and future work.
Conclusions
We demonstrated the stark contrast of the MDR population dynamics between two major pathogens in a major UK hospital. Whilst cephalosporin resistance in K. pneumoniae is plasmid driven, E. cloacae can rely on its chromosomal resistance mechanism. This leads to a markedly different population structure and shows that plasmid-derived resistance leads to the shift from a highly diverse population to the dominance of a few major lineages, whilst chromosomal resistance mechanisms do not bias the population, with a similar composition observed throughout the 7-year time frame.
Materials and methods
Surveillance data for national context
The annual national context for cephalosporin and aminoglycoside resistance in K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae was analyzed using antimicrobial susceptibility data from the BSAC Bacteraemia Resistance Surveillance Programme (www.bsacsurv.org, accessed April 2018). Susceptibility data for gentamicin, cefotaxime, and ceftazidime from the first seven isolates of both species collected at each of 30 sentinel laboratories each year between 2001 and 2012 was included.
Clinical setting, patient data, and isolate collections
Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (CUH) is a 1000-bed secondary and tertiary referral hospital. The on-site Public Health England Clinical Microbiology Laboratory processes ca. 1,000,000 specimens per annum for CUH. Linked anonymized patient demographic and routine microbiology laboratory data (NHS research ethics committee approval 12/SC/0431), including species identifications by API (bioMérieux, Marcy L’Etoile, France) or MALDI Biotyper (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, GmbH) indicated that between 2006 and 2012, 13,379 patients were positive for K. pneumoniae (from any specimen type) and 5661 patients were positive for E. cloacae (from any specimen type). We included and analyzed antimicrobial susceptibility data, determined according to the BSAC disc diffusion method [31] for the first isolate of these two species from each patient.
Between 2006 and 2012, K. pneumoniae and/or E. cloacae associated with invasive disease (isolated via sterile site cultures) in patients at CUH was stored at − 80 °C. To understand the populations of sensitive and resistant isolates of each species by WGS, we first stratified the 465 invasive K. pneumoniae and 225 invasive E. cloacae according to their routine laboratory antimicrobial susceptibility results for six groups of antimicrobials that were tested each year between 2006 and 2012 (penicillins, amoxicillin-clavulanate, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, trimethoprim, and third-generation cephalosporins). To enrich for drug-resistant isolates, we included all of the available invasive isolates that were resistant to three or more groups for both species (Table 1). From amongst the invasive isolates that were resistant to two groups of antimicrobials or fewer, we randomly selected 44 K. pneumoniae isolates (11.5% of the available isolates) and 28 (18.4%) of the available E. cloacae isolates (Table 1), which for the invasive isolates, represented 20–34% of K. pneumoniae and 40–45% of E. cloacae isolated in any year being included for study. Where a patient had an isolate of both species that was resistant to three or more groups of antimicrobial, we included one isolate of both species. Isolates of the same species were de-duplicated to represent one isolate per species per patient except four patients for whom two isolates of K. pneumoniae were included due to differences in initial phenotypic susceptibilities that were considered suggestive of different strain types. From this collection of invasive isolates, we included 124 K. pneumoniae from 120 patients and 94 E. cloacae from 94 patients for further study. Additionally, a prospective collection (during the last half of 2012) of K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae isolated from samples taken from any body site yielded a further 38 isolates of K. pneumoniae and 35 isolates of E. cloacae from a total of 73 patients. Of these, 33 K. pneumoniae and 26 E. cloacae isolates were resistant to three or more groups of antimicrobials (Table 1).
Of the isolates included for study, four carbapenemase-producing E. cloacae were identified by Public Health England’s (PHE) national Antimicrobial Resistance and Healthcare Associated Infections (AMRHAI) Reference Unit to produce IMP-1 carbapenemase (as well as other co-acquired resistance genes). One K. pneumoniae was identified later to carry the NDM-1 carbapenemase gene, one to carry the KPC-2 gene, and one the CARB-12 gene. In total, 162 K. pneumoniae from 158 patients and 133 E. cloacae from 133 patients were sequenced (Additional file 2: Table S1 and S4).
Bacterial culture and antimicrobial susceptibility testing
Clinical specimens had been previously processed according to standard operating procedures, including antimicrobial susceptibility testing using the BSAC disc diffusion method [31] with results interpreted using EUCAST breakpoints. For this study, bacteria were re-identified using MALDI-ToF (Bruker Daltonics) and antimicrobial susceptibilities confirmed with the VITEK-2 instrument (BioMérieux). MICs were determined by agar dilution methodology for three NDM carbapenemase-producing E. cloacae in Public Health England’s AntiMicrobial Resistance and Healthcare Associated Infections (AMRHAI) Reference Unit.
DNA sequencing
Isolates were cultured overnight on Brilliance UTI chromogenic agar (Oxoid, UK), then inoculated into Brain Heart Infusion broth (Oxoid, UK) and grown to stationary phase. DNA was extracted and quantified [8]. Whole-genome sequencing was performed on a HiSeq 2000, and 150 bp paired-end Illumina sequencing reads were produced [32]. Selected samples were also sequenced on a PacBio RSII using P6/C4 sequencing chemistry. High molecular weight DNA for long-read sequencing was prepared from bacterial cultures by phenol-chloroform extraction from overnight cultures; phases were separated by centrifugation using MaXtract phase lock tubes (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Libraries were made using the SMRTbell Template Prep Kit 1.0. Sequence data have been deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive (Additional file 2: Table S1 and S2).
Annotated assemblies of short-read Illumina data were produced [33]: briefly, for each sample, multiple assemblies were created using VelvetOptimiser v2.2.5 [34] and Velvet v1.2 [35], assembly improvement using the best N50 and contigs in scaffolds via SSPACE [36] was followed by sequence gap filling using GapFiller [37]. For PacBio, sequence reads were assembled using Canu (v1.1) [38] with filtered subreads generated through the SMRT analysis software v2.3.0. Assemblies were circularized using Circlator v1.1.3 [39] using the corrected reads generated during the Canu assembly. Finally, the circularized assembly was polished with the short-reads and pilon as implemented in the unicycler-polish script [40]. If not all resulting contigs were circularized, assemblies combining the Illumina and PacBio reads were performed using unicycler [40], followed by Circulator with the corrected reads generated in the previous Canu assembly, and unicycler-polish. The assemblies used were based on Canu for Kpn135, Kpn23, Kpn27, Kpn56, Kpn81, Kpn98, Ecl21, and Ecl55; the hybrid assembly was used for Kpn16 and Ecl130. All assemblies were controlled by mapping back the PacBio and Illumina reads of the respective strain using bwa mem (default options; -x pacbio for the pacbio reads), as well as Mauve alignments of the Illumina assemblies to the final assemblies. Automated annotation of all assemblies was performed using PROKKA v1.11 [41] and genus-specific databases from RefSeq [42].
Sequence analyses
Multi-locus sequence typing was performed using blast against the sequence types available at PubMLST [43]. The resistance gene content and plasmid replicon types carried by each isolate were predicted using the short-read search software ariba [44] with the implemented arg-annot as provided for SRST2 [45, 46] and PlasmidFinder [47] databases respectively. K. pneumoniae capsule and O-antigen type was predicted using Kaptive [48], using the capsule type database provided with Kaptive and an in-house generated database based on the different O-antigen operons described [49] (Additional file 2: Table S2); the distinction between different O-types was revised according to the recently published updated typing online platform (http://kaptive.holtlab.net) [50].
We combined our K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae datasets with a global collection and a UK-focused collection (Additional file 2: Table S3), for each species [7, 11, 14, 16]. Roary [51] was used to determine the core, soft core, and shell components of the pan-genome for the respective datasets (Additional file 2: Tables S1 - S5). For core gene tree-based phylogeny, the core gene alignment from roary was retrieved and informative sites were chosen using snp_sites [52] and trimal [53] as detailed in the respective figure legends, and RAxML (v 8.2.8) was used to construct phylogenetic trees using the general time-reversible (GTR) model with 100 bootstrap support calculations. iTOL was used for tree and metadata visualization [54]. Clustering was performed using mash (as an approximation of ANI [13]), and cutoffs were chosen as indicated in the figure legend (Fig. 3). Reference sequences for the mash clustering to define (sub)species and further groups were used as given in Additional file 2: Table S5. (Pro)Phages in the PacBio assemblies were predicted using Phaster [55].
Bacteria mapping and variant detection
For each sample of K. pneumoniae or E. cloacae, sequence reads were mapped against the reference genome (Enterobacter hormaechei subsp. steigerwaltii DSM 16691, Genbank accession CP017179.1, for Enterobacter; K. pneumoniae subsp. pneumoniae MGH 78578, Genbank accession CP000647.1, for Klebsiella) using SMALT v0.7.4 [56, 57] to produce a BAM file. Variation detection was performed using SAMtools mpileup v0.1.19 [58] with parameters “-d 1000 -DSugBf” and bcftools v0.1.19 [59] to produce a BCF file of all variant sites. The option to call genotypes at variant sites was passed to the bcftools call. All bases were filtered to remove those with uncertainty in the base call. The bcftools variant quality score was required to be greater than 50 (quality < 50) and mapping quality greater than 30 (map_quality < 30). If not all reads gave the same base call, the allele frequency, as calculated by bcftools, was required to be either 0 for bases called the same as the reference, or 1 for bases called as a SNP (af1 < 0.95). The majority base call was required to be present in at least 75% of reads mapping at the base (ratio < 0.75), and the minimum mapping depth required was 4 reads, at least two of which had to map to each strand (depth < 4, depth_strand < 2). Finally, strand_bias was required to be less than 0.001, map_bias less than 0.001, and tail_bias less than 0.001. If any of these filters were not met, the base was called as uncertain.
A pseudo-genome was constructed by substituting the base call at each site (variant and non-variant) in the BCF file into the reference genome, and any site called as uncertain was substituted with an N. Insertions with respect to the reference genome were ignored, and deletions with respect to the reference genome were filled with N’s in the pseudo-genome to keep it aligned and the same length as the reference genome used for read mapping. Gubbins [57] was then used to remove recombinant/highly variable regions from the alignment, and the resulting reduced alignment was used as input for tree calculations as well as pairwise SNP comparisons. These were performed with the dist.alignment() function in the R package seqinr [60], which gives relative values and therefore enables plotting both organisms onto one y-axis. We tested for relative enrichment of organisms of the same sequence type vs. different sequence type in the same or different 2-year time span using the chi.square() function as implemented in R (v3.4.2). The contingency matrix consisted of numbers of isolates of same vs. different ST occurring in the same vs. different 2-year span, which was significant for K. pneumoniae and not significant for E. cloacae (p values < 2.2e−16 and p = 0.03, respectively).
The masked alignment was used as input for phylogenetic tree calculation using RAxML as described above, disregarding positions with more than 5% N content, to perform tests for phylogenetic signal, where 10 maximum likelihood trees were generated as described above. For branch length comparisons and testing for phylogenetic signal, we used the phylosignal package in R and calculated correlation plots using either month, year, or 2-year span as trait information [61]. To ensure that enough signal is in these three traits, for each correlation, we also performed a randomization step using the sample() function in R. All tree files and alignments as well as the R script used to assess phylogenetic signal, SNP distances, and the chi-square test are available for download at the figshare link [https://figshare.com/s/830209f84c587c28813e].
Plasmid/integron analyses
Pacbio plasmids were annotated using the online plasmidfinder database to annotate the assembled sequences. The integron/mobile cassette sequence(s) were identified manually by searching for the main beta-lactam and aminoglycoside resistance conferring genes (blaOXA, blaCTX, blaTEM, aac(3)IIa, aac(6′)-Ib-cr), and annotation was performed by using the ISFinder resource [62] as well as blast against the non-redundant genbank database [63, 64]. Annotating the identified mobile units in the Illumina samples was performed by blasting the DNA sequences derived from pacbio against the Illumina assemblies with an e value cutoff of 1e−90; partial hits were identified as encoding the respective resistance genes, but truncated mobile elements due to frameshifts or other elements inserting within them. Comparison of the operons was depicted using GenePlotR [65] with the respective closest reference contigs as templates; replicons were identified using the plasmidfinder resource as described above. For a comparison against the plasmid database, the assemblies of the database were downloaded (16. 04. 2019; 10.15146/R33X2J) [66], and blast runs performed using the same elements as in the ariba search as input. To account for less closely related organisms, we accepted hits with over 99% similarity. If several hits of the same cassette on one plasmid were reported, the longest element was chosen; if two elements were still of the same length, the element with the higher similarity was chosen; if this still did not distinguish the hits, the first one in the sequence was chosen for representation. The plasmids were clustered using the heatmap.2() command in R using the percentage of similarity to the different cassettes as data matrix for clustering. The region of coverage on the cassettes was displayed using the ggtree package and the facetplot function in R [67].
Additional files
Figure S1. Comparison of sources of isolation for K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae datasets. Figure S2. Addenbrookes hospital isolates reflect the UK-wide diversity of isolates. Figure S3. K. quasipneumoniae and K. variicola are mostly part of the sensitive population of Klebsiella, amongst Enterobacter E. aerogenes, E. kobei, E. ludwigii and E. dissolvans show varying patterns of isolation site and drug resistance. Figure S4. Testing for phylogenetic signal. Figure S5. Number of resistance genes in sensitive and resistant populations. Figure S6. Comparison of study isolates against a curated large-scale plasmid database. (DOCX 1489 kb)
Table S1. Accession numbers, isolation site, study month of isolation, detected acquired resistance genes, antimicrobial resistance phenotypes, of Klebsiella pneumoniae in this study. Table S2. Accession numbers and metadata for the global K. pneumoniae collection [7]. Table S3. Accession numbers and metadata for UK K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae [14, 16]. Table S4. Accession numbers, isolation site, study month of isolation, detected acquired resistance genes, antimicrobial resistance phenotypes, of Enterobacter cloacae in this study. Table S5. Accession numbers and metadata for the global E. cloacae collection [11]. (XLSX 176 kb)
Review history. (DOCX 15 kb)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the staff of the Cambridge PHE Public Health Laboratory for access to bacterial isolates and the staff of the AMRHAI Reference Unit for confirming carbapenemase producers. The authors are grateful for assistance from library construction, sequencing and core informatics teams at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute (WTSI).
Review history
The review history is available as Additional file 3.
Authors’ contributions
MJE and NRT designed and coordinated the project, EH and MJE performed the WGS analysis and wrote the first draft of the manuscript, AMW and MdG performed the data analysis, MD and NG undertook the laboratory work, EMT applied for research ethics approval, and all other authors contributed to drafting the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the following grants: to N.R.T, E.H., A.M.W., S.P.H., J.P., and S.J.P were supported by the Wellcome Trust [grant no. 098051 awarded to the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute]; from the Health Protection Agency (now PHE) (project grant no. 108077) to M.J.E.; to S.J.P from the UKCRC Translational Infection Research Initiative and the Medical Research Council [grant no. G1000803]; contributions to the grant were from the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the National Institute for Health Research on behalf of the Department of Health, and the Chief Scientist Office of the Scottish Government Health Directorate (to Prof. Peacock); by the Health Protection Agency (to Prof. Peacock); and by the NIHR Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre (to Dr. Török and Prof. Peacock). M.J.D. was supported by a Wellcome Sanger Institute PhD studentship. A.K.C. was supported by a Australian Research Council DECRA fellowship [grant no. DE180100929]. G.D. was supported by the NIHR Biomedical Research Centres in Cambridge (in particular the NIHR Cambridge BRC AMR Theme). M.E.T. is a Clinician Scientist Fellow funded by the Academy of Medical Sciences and the Health Foundation.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its additional files. The sequence data generated in this study are publicly available in the NCBI Archive under the accession code PRJEB1271 [68]. Accession numbers for all genomes sequenced in this study are available in Additional file 2 S1 (K. pneumoniae) and S4 (Enterobacter).
The accessions are given alongside key metadata including clinical isolation site, year of isolation, bacterial MLST assignations, and resistance gene detections in the Additional file 2 and FIGSHARE dataset [69].
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The retrospective use of linked anonymized clinical and routine microbiology laboratory data was approved by the South Cambridgeshire Local NHS Research Ethics Committee (12/SC/0431). Research and Development (R&D) approval for whole-genome sequencing of bacteria was granted by the R&D Department at Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
M.J.E. and N.W. perform work for Public Health Englands AMRHAI Reference Unit which has received financial support for conference attendance, lectures, research projects, or contracted evaluations from numerous sources, including Accelerate Diagnostics, Achaogen Inc., Allecra Therapeutics, Amplex, AstraZeneca UK Ltd., Basilea Pharmaceutica, Becton Dickinson Diagnostics, BioMérieux, Bio-Rad Laboratories, The BSAC, Cepheid, Check-Points B.V., Cubist Pharmaceuticals, Department of Health, Enigma Diagnostics, Food Standards Agency, GlaxoSmithKline Services Ltd., Henry Stewart Talks, IHMA Ltd., Kalidex Pharmaceuticals, Melinta Therapeutics, Merck Sharpe & Dohme Corp, Meiji Seika Pharma Co, Mobidiag, Momentum Biosciences Ltd., Nordic Pharma Ltd., Norgine Pharmaceuticals, Rempex Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Roche, Rokitan Ltd., Smith & Nephew UK Ltd., Trius Therapeutics, VenatoRx Pharmaceuticals, and Wockhardt Ltd. J.P. and S.J.P. are consultants to Next Gen Diagnostics.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Matthew J. Ellington and Eva Heinz contributed equally to this work.
References
- 1.Boucher HW, Talbot GH, Bradley JS, Edwards JE, Gilbert D, Rice LB, et al. Bad bugs, no drugs: no ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48(1):1–12. doi: 10.1086/595011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Karisik E, Ellington MJ, Pike R, Warren RE, Livermore DM, Woodford N. Molecular characterization of plasmids encoding CTX-M-15 beta-lactamases from Escherichia coli strains in the United Kingdom. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006;58(3):665–668. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Woodford N, Carattoli A, Karisik E, Underwood A, Ellington MJ, Livermore DM. Complete nucleotide sequences of plasmids pEK204, pEK499, and pEK516, encoding CTX-M enzymes in three major Escherichia coli lineages from the United Kingdom, all belonging to the international O25:H4-ST131 clone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53(10):4472–4482. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00688-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Public Health England. English surveillance programme antimicrobial utilisation and resistance (ESPAUR) report: Internet. London: Public Health England; 2014.
- 5.Leverstein-van Hall MA, Box AT, Blok HE, Paauw A, Fluit AC, Verhoef J. Evidence of extensive interspecies transfer of integron-mediated antimicrobial resistance genes among multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in a clinical setting. J Infect Dis. 2002;186(1):49–56. doi: 10.1086/341078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Luzzaro F, Docquier JD, Colinon C, Endimiani A, Lombardi G, Amicosante G, et al. Emergence in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Enterobacter cloacae clinical isolates of the VIM-4 metallo-beta-lactamase encoded by a conjugative plasmid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48(2):648–650. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.2.648-650.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Holt KE, Wertheim H, Zadoks RN, Baker S, Whitehouse CA, Dance D, et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(27):E3574–E3581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1501049112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chung The H, Karkey A, Pham Thanh D, Boinett CJ, Cain AK, Ellington M, et al. A high-resolution genomic analysis of multidrug-resistant hospital outbreaks of Klebsiella pneumoniae. EMBO Mol Med. 2015;7(3):227–239. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201404767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mathers AJ, Stoesser N, Sheppard AE, Pankhurst L, Giess A, Yeh AJ, et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)-producing K. pneumoniae at a single institution: insights into endemicity from whole-genome sequencing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(3):1656–1663. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04292-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Woodford N, Turton JF, Livermore DM. Multiresistant Gram-negative bacteria: the role of high-risk clones in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011;35(5):736–755. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chavda KD, Chen L, Fouts DE, Sutton G, Brinkac L, Jenkins SG, et al. Comprehensive genome analysis of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacter spp.: new insights into phylogeny, population structure, and resistance mechanisms. MBio. 2016;7(6):e02093–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.Livermore DM, Hope R, Reynolds R, Blackburn R, Johnson AP, Woodford N. Declining cephalosporin and fluoroquinolone non-susceptibility among bloodstream Enterobacteriaceae from the UK: links to prescribing change? J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;68(11):2667–2674. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ondov BD, Treangen TJ, Melsted P, Mallonee AB, Bergman NH, Koren S, et al. Mash: fast genome and metagenome distance estimation using MinHash. Genome Biol. 2016;17(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-0997-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Moradigaravand D, Martin V, Peacock SJ, Parkhill J. Evolution and epidemiology of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in the United Kingdom and Ireland. MBio. 2017;8(1):e01976–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Tindall BJ, Sutton G, Garrity GM. Enterobacter aerogenes Hormaeche and Edwards 1960 (approved lists 1980) and Klebsiella mobilis Bascomb et al. 1971 (approved lists 1980) share the same nomenclatural type (ATCC 13048) on the approved lists and are homotypic synonyms, with consequences for the name Klebsiella mobilis Bascomb et al. 1971 (approved lists 1980) Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017;67(2):502–504. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Moradigaravand D, Reuter S, Martin V, Peacock SJ, Parkhill J. The dissemination of multidrug-resistant Enterobacter cloacae throughout the UK and Ireland. Nat Microbiol. 2016;1:16173. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ejaz H, Wang N, Wilksch JJ, Page AJ, Cao H, Gujaran S, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae from hospitalized children, Pakistan. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23(11):1872–1875. doi: 10.3201/eid2311.170833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stoesser N, Giess A, Batty EM, Sheppard AE, Walker AS, Wilson DJ, et al. Genome sequencing of an extended series of NDM-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from neonatal infections in a Nepali hospital characterizes the extent of community- versus hospital-associated transmission in an endemic setting. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(12):7347–7357. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03900-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Oteo J, Perez-Vazquez M, Bautista V, Ortega A, Zamarron P, Saez D, et al. The spread of KPC-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Spain: WGS analysis of the emerging high-risk clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11/KPC-2, ST101/KPC-2 and ST512/KPC-3. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(12):3392–3399. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Long SW, Olsen RJ, Eagar TN, Beres SB, Zhao P, Davis JJ, et al. Population genomic analysis of 1,777 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates, Houston, Texas: unexpected abundance of clonal group 307. MBio. 2017;8(3):e00489–17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 21.Villa L, Feudi C, Fortini D, Brisse S, Passet V, Bonura C, et al. Diversity, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance of the KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 clone. Microb Genom. 2017;3(4):e000110. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Babouee Flury B, Ellington MJ, Hopkins KL, Turton JF, Doumith M, Loy R, et al. Association of novel nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in ampD with cephalosporin resistance and phylogenetic variations in ampC, ampR, ompF, and ompC in Enterobacter cloacae isolates that are highly resistant to carbapenems. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(4):2383–2390. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02835-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Babouee Flury B, Ellington MJ, Hopkins KL, Turton JF, Doumith M, Woodford N. The differential importance of mutations within AmpD in cephalosporin resistance of Enterobacter aerogenes and Enterobacter cloacae. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016;48(5):555–558. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.07.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Barnaud G, Labia R, Raskine L, Sanson-Le Pors MJ, Philippon A, Arlet G. Extension of resistance to cefepime and cefpirome associated to a six amino acid deletion in the H-10 helix of the cephalosporinase of an Enterobacter cloacae clinical isolate. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001;195(2):185–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Guerin F, Isnard C, Cattoir V, Giard JC. Complex regulation pathways of AmpC-mediated beta-lactam resistance in Enterobacter cloacae Complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(12):7753–7761. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01729-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kaneko K, Okamoto R, Nakano R, Kawakami S, Inoue M. Gene mutations responsible for overexpression of AmpC beta-lactamase in some clinical isolates of Enterobacter cloacae. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43(6):2955–2958. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.6.2955-2958.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kuga A, Okamoto R, Inoue M. ampR gene mutations that greatly increase class C beta-lactamase activity in Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000;44(3):561–567. doi: 10.1128/aac.44.3.561-567.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nakano R, Nakano A, Yano H, Okamoto R. Role of AmpR in the high expression of the plasmid-encoded AmpC beta-lactamase CFE-1. mSphere. 2017;2(4):e00192–17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Porres-Osante N, Saenz Y, Somalo S, Torres C. Characterization of beta-lactamases in faecal Enterobacteriaceae recovered from healthy humans in Spain: focusing on AmpC polymorphisms. Microb Ecol. 2015;70(1):132–140. doi: 10.1007/s00248-014-0544-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yang YJ, Livermore DM, Williams RJ. Chromosomal beta-lactamase expression and antibiotic resistance in Enterobacter cloacae. J Med Microbiol. 1988;25(3):227–233. doi: 10.1099/00222615-25-3-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Andrews JM, Howe RA, Testing BWPS. BSAC standardized disc susceptibility testing method (version 10) J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66(12):2726–2757. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Harris SR, Feil EJ, Holden MT, Quail MA, Nickerson EK, Chantratita N, et al. Evolution of MRSA during hospital transmission and intercontinental spread. Science. 2010;327(5964):469–474. doi: 10.1126/science.1182395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Page AJ, De Silva N, Hunt M, Quail MA, Parkhill J, Harris SR, et al. Robust high-throughput prokaryote de novo assembly and improvement pipeline for Illumina data. Microb Genom. 2016;2(8):e000083. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gladman S, Seemann T. Velvet Optimiser: for automatically optimising the primary parameter options for the Velvet de novo sequence assembler. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zerbino DR, Birney E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008;18(5):821–829. doi: 10.1101/gr.074492.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Boetzer M, Henkel CV, Jansen HJ, Butler D, Pirovano W. Scaffolding pre-assembled contigs using SSPACE. Bioinformatics. 2011;27(4):578–579. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Boetzer M, Pirovano W. Toward almost closed genomes with GapFiller. Genome Biol. 2012;13(6):R56. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-6-r56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Koren S, Walenz BP, Berlin K, Miller JR, Bergman NH, Phillippy AM. Canu: scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017;27(5):722–736. doi: 10.1101/gr.215087.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hunt M, Silva ND, Otto TD, Parkhill J, Keane JA, Harris SR. Circlator: automated circularization of genome assemblies using long sequencing reads. Genome Biol. 2015;16:294. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0849-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wick RR, Judd LM, Gorrie CL, Holt KE. Unicycler: resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017;13(6):e1005595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Seemann T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(14):2068–2069. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pruitt KD, Tatusova T, Brown GR, Maglott DR. NCBI Reference Sequences (RefSeq): current status, new features and genome annotation policy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(Database issue):D130–D135. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Page AJ, Taylor B, Keane JA. Multilocus sequence typing by blast from de novo assemblies against PubMLST. J Open Source Softw. 2016;1(8):118. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hunt M, Mather AE, Sanchez-Buso L, Page AJ, Parkhill J, Keane JA, et al. ARIBA: rapid antimicrobial resistance genotyping directly from sequencing reads. Microb Genom. 2017;3(10):e000131. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gupta SK, Padmanabhan BR, Diene SM, Lopez-Rojas R, Kempf M, Landraud L, et al. ARG-ANNOT, a new bioinformatic tool to discover antibiotic resistance genes in bacterial genomes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(1):212–220. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01310-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Inouye M, Dashnow H, Raven LA, Schultz MB, Pope BJ, Tomita T, et al. SRST2: rapid genomic surveillance for public health and hospital microbiology labs. Genome Med. 2014;6(11):90. doi: 10.1186/s13073-014-0090-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Carattoli A, Zankari E, Garcia-Fernandez A, Voldby Larsen M, Lund O, Villa L, et al. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(7):3895–3903. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02412-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wyres KL, Wick RR, Gorrie C, Jenney A, Follador R, Thomson NR, et al. Identification of Klebsiella capsule synthesis loci from whole genome data. Microb Genom. 2016;2(12):e000102. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Follador R, Heinz E, Wyres KL, Ellington MJ, Kowarik M, Holt KE, et al. The diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae surface polysaccharides. Microb Genom. 2016;2(8):e000073. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wick RR, Heinz E, Holt KE, Wyres KL. Kaptive Web: user-friendly capsule and lipopolysaccharide serotype prediction for Klebsiella genomes. J Clin Microbiol. 2018;56(6):e00197–18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 51.Page AJ, Cummins CA, Hunt M, Wong VK, Reuter S, Holden MT, et al. Roary: rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(22):3691–3693. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Page AJ, Taylor B, Delaney AJ, Soares J, Seemann T, Keane JA, et al. SNP-sites: rapid efficient extraction of SNPs from multi-FASTA alignments. Microb Genom. 2016;2(4):e000056. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Capella-Gutierrez S, Silla-Martinez JM, Gabaldon T. trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(15):1972–1973. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive Tree Of Life v2: online annotation and display of phylogenetic trees made easy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:W475–W478. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Arndt D, Grant JR, Marcu A, Sajed T, Pon A, Liang Y, et al. PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(W1):W16–W21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.SMALT: A mapper for DNA sequencing reads. Available from: https://sourceforge.net/projects/smalt/.
- 57.Croucher NJ, Page AJ, Connor TR, Delaney AJ, Keane JA, Bentley SD, et al. Rapid phylogenetic analysis of large samples of recombinant bacterial whole genome sequences using Gubbins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(3):e15. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(16):2078–2079. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bcftools: Utilities for variant calling and manipulating VCFs and BCFs. Available from: http://samtools.github.io/bcftools/.
- 60.Charif DL, Lobry JR. Seqin{R} 1.0-2: a contributed package to the {R} project for statistical computing devoted to biological sequences retrieval and analysis. In: Bastolla UP, Porto M, Roman HE, Vendruscol M, editors. Structural approaches to sequence evolution: molecules, networks, populations. Biological and medical physics, biomedical engineering. New York: Springer Verlag; 2007. pp. 207–232. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Keck F, Rimet F, Bouchez A, Franc A. Phylosignal: an R package to measure, test, and explore the phylogenetic signal. Ecol Evol. 2016;6(9):2774–2780. doi: 10.1002/ece3.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Siguier P, Perochon J, Lestrade L, Mahillon J, Chandler M. ISfinder: the reference Centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(Database issue):D32–D36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Coordinators NR. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D12–DD7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Guy L, Kultima JR, Andersson SG. genoPlotR: comparative gene and genome visualization in R. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(18):2334–2335. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Brooks L, Kaze M, Sistrom M. A curated, comprehensive database of plasmid sequences. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2019;8(1):e01325–18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 67.Yu G, Lam TT, Zhu H, Guan Y. Two methods for mapping and visualizing associated data on phylogeny using Ggtree. Mol Biol Evol. 2018;35(12):3041–3043. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Ellington, Matthew; Heinz, Eva; Wailan, Alexander M.; Dorman, Matthew J; Goffau, Marcus de; Cain, Amy K.; Henson, Sonal P; Gleadall, Nicholas; Boinett, Christine, Dougan, Gordon; Brown, Nicholas M; Wooford, Neil; Parkhill, Julian; Török, Estee M; Peacock, Sharon J; Thomson Nicholas R.: Additional data for: contrasting patterns of longitudinal population dynamics and antimicrobial resistance mechanisms in two priority bacterial pathogens over seven years in a single center. European Nucleotide Archive. Dataset. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/data/view/PRJEB1271 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 69.Ellington, Matthew; Heinz, Eva; Wailan, Alexander M.; Dorman, Matthew J; Goffau, Marcus de; Cain, Amy K.; Henson, Sonal P; Gleadall, Nicholas; Boinett, Christine, Dougan, Gordon; Brown, Nicholas M; Wooford, Neil; Parkhill, Julian; Török, Estee M; Peacock, Sharon J; Thomson Nicholas R.: Additional data for: contrasting patterns of longitudinal population dynamics and antimicrobial resistance mechanisms in two priority bacterial pathogens over seven years in a single center. Figshare. Dataset. 10.6084/m9.figshare.9171674.v1 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Comparison of sources of isolation for K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae datasets. Figure S2. Addenbrookes hospital isolates reflect the UK-wide diversity of isolates. Figure S3. K. quasipneumoniae and K. variicola are mostly part of the sensitive population of Klebsiella, amongst Enterobacter E. aerogenes, E. kobei, E. ludwigii and E. dissolvans show varying patterns of isolation site and drug resistance. Figure S4. Testing for phylogenetic signal. Figure S5. Number of resistance genes in sensitive and resistant populations. Figure S6. Comparison of study isolates against a curated large-scale plasmid database. (DOCX 1489 kb)
Table S1. Accession numbers, isolation site, study month of isolation, detected acquired resistance genes, antimicrobial resistance phenotypes, of Klebsiella pneumoniae in this study. Table S2. Accession numbers and metadata for the global K. pneumoniae collection [7]. Table S3. Accession numbers and metadata for UK K. pneumoniae and E. cloacae [14, 16]. Table S4. Accession numbers, isolation site, study month of isolation, detected acquired resistance genes, antimicrobial resistance phenotypes, of Enterobacter cloacae in this study. Table S5. Accession numbers and metadata for the global E. cloacae collection [11]. (XLSX 176 kb)
Review history. (DOCX 15 kb)
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its additional files. The sequence data generated in this study are publicly available in the NCBI Archive under the accession code PRJEB1271 [68]. Accession numbers for all genomes sequenced in this study are available in Additional file 2 S1 (K. pneumoniae) and S4 (Enterobacter).
The accessions are given alongside key metadata including clinical isolation site, year of isolation, bacterial MLST assignations, and resistance gene detections in the Additional file 2 and FIGSHARE dataset [69].