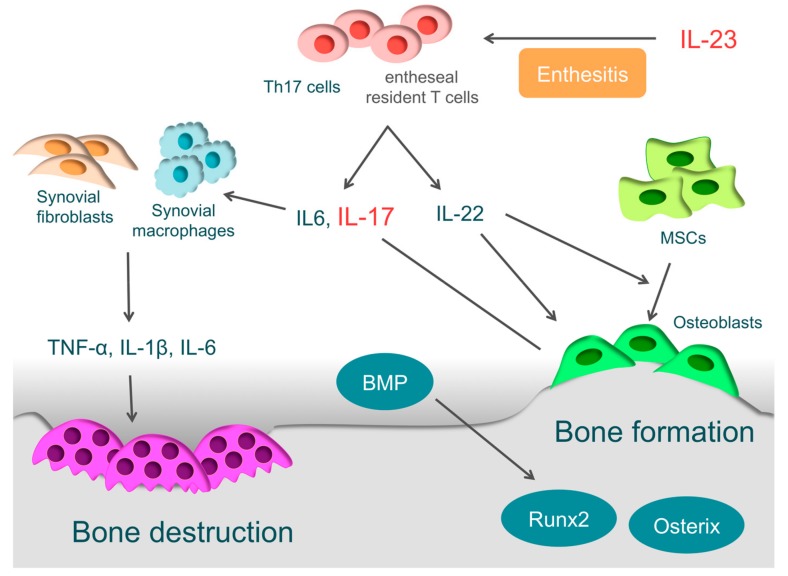
Figure 4.
The pathology of psoriatic arthritis. In the pathology of psoriatic arthritis (PsA), T-helper (Th) 17 cells and the associated interleukin-23 (IL-23)/IL-17 axis are important. IL-23 is closely involved in the enthesitis. IL-23 drives entheseal resident T-cells expressing the IL-23 receptor to produce inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-17, and IL-22. IL-17 drives synovial fibroblasts and macrophages to promote inflammatory cytokines, such as IL1-β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and it ultimately causes bone destruction. IL-22 is involved in new bone formation in entheses or around articular cartilages. IL-22 promotes the proliferation of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and induces differentiation to osteoblasts. Furthermore, it activates osteoblasts via the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), which strongly induces the expression of osteogenic transcription factors such as Runx2 and osterix, is also involved.