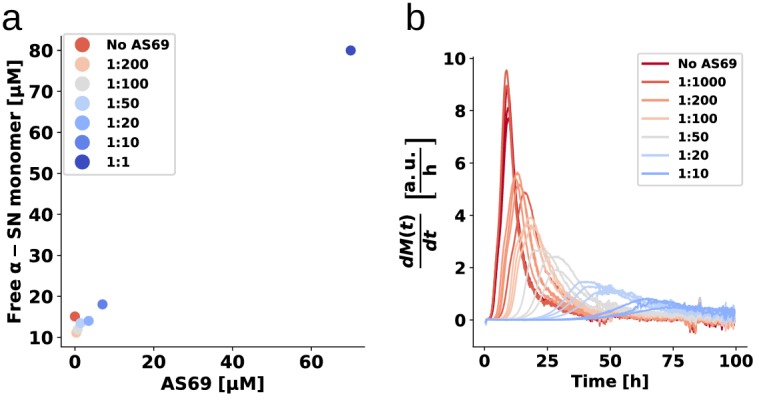
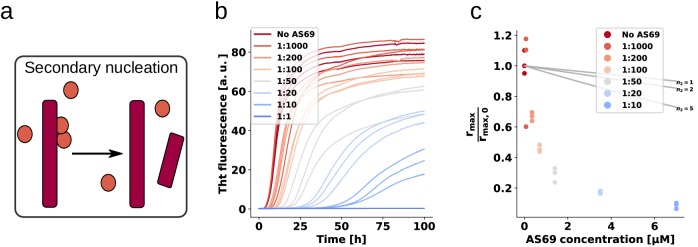
Figure 6. AS69 inhibits -synuclein fibril amplification.
(a) Schematic representation of fibril amplification through secondary nucleation Buell et al. (2014a). (b) Change in ThT fluorescence intensity when a 70 μM solution of monomeric -synuclein was incubated with increasing concentrations of AS69 in acetate buffer (pH 5.0) under quiescent conditions and weak seeding. (c) Relative rate of fibril amplification as a function of the concentration of AS69. The solid lines correspond to simulations based on the assumption that AS69 acts only through monomer sequestration, for different values of the monomer dependence (reaction order) of secondary nucleation (see Appendix 2 for details).
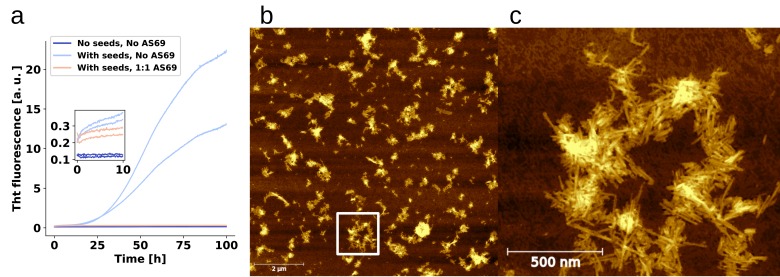
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Seeds are required for aggregation under quiescent conditions.
Figure 6—figure supplement 2. Weakly seeded aggregation experiments at pH 5.0.