In the article “Properties of Synaptically Evoked Astrocyte Calcium Signal Reveal Synaptic Information Processing by Astrocytes,” by Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque, which appeared on pages 2192-2203 of the March 2, 2005 issue, Figure 7 was erroneously processed as a black and white figure. The correct color version of the figure, as well as the legend, is printed here.
Figure 7.
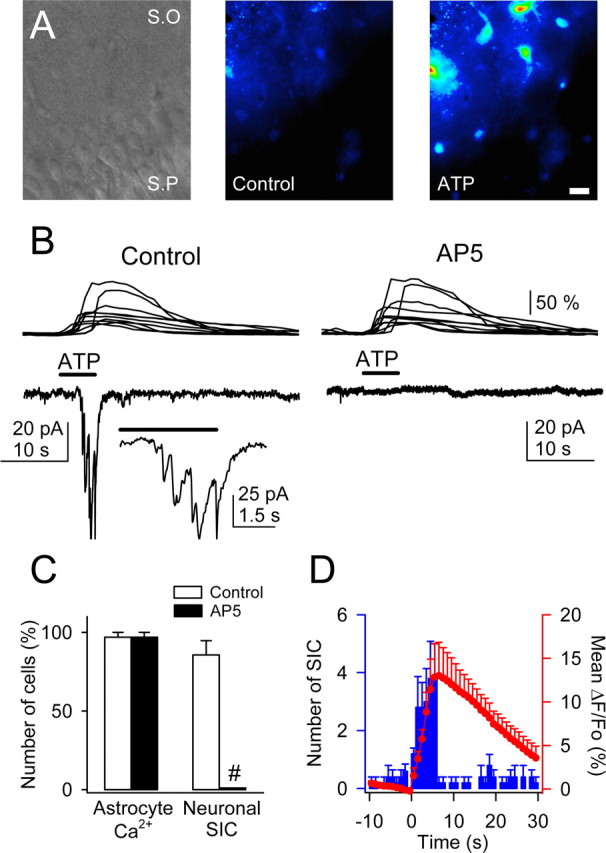
ATP-induced Ca2+ elevations in astrocytes evoked NMDAR-mediated SICs in pyramidal neurons. A, Infrared differential interference contrast image and pseudocolor images representing fluorescence intensities of a fluo-3-filled slice before and after ionophoretical application of ATP for 5 s. Note the lower relative fluorescence at the pyramidal layer. S.O, Stratum oriens; S.P, stratum pyramidale. Scale bar, 30 μm. B, Astrocyte Ca2+ levels (top traces) and whole-cell neuronal currents (bottom traces) during ionophoretical application of ATP (horizontal bar) in TTX and without Mg2+ (control and after perfusion with 50 μm AP-5). Inset, Expanded current trace illustrating the multiple NMDAR-mediated SICs. C, Relative number of astrocytes and neurons that showed Ca2+ elevations and SICs, respectively, after application of ATP in controls and after perfusion with AP-5 (n = 35 astrocytes and 5 neurons from 5 slices). Significant differences were established by the Student's t test at #p < 0.001. D, Mean number of neuronal SICs (blue bars) and averaged astrocyte Ca2+ elevations (red circles) versus time (n = 5 slices). Time 0 corresponds to the beginning of the ATP application (5 s).


