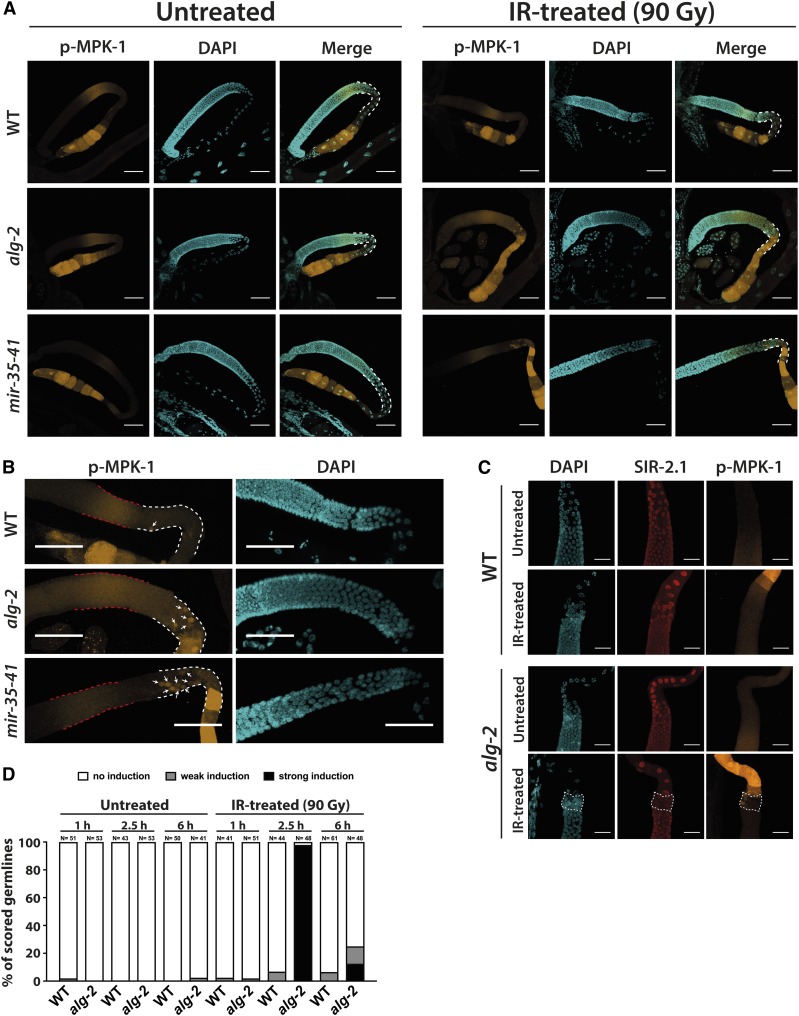
Figure 4.
ERK/MPK-1 is hyperactivated in alg-2 and mir-35-41 mutant germline loops upon IR treatment. (A) IR-treated alg-2(ok304) and mir-35-41(nDf50) mutant germlines exhibited strong MPK-1 phosphorylation 2.5 hr after IR (90 Gy) within the entire gonad loop area (highlighted by white dashed lines). (B) Close-up images of IR-treated WT, alg-2(ok304), and mir-35-41(nDf50) mutant pachytene zones suggested that the activation of MPK-1 in late-pachytene germ cells (white arrows) occurred independently of the phospho-MPK-1 signal in the midpachytene area (red dashed lines). The germline loop is highlighted by white dashed lines. (A and B) Germlines were dissected 2.5 hr post-IR (90 Gy). Representative images were obtained from Z-stacks taken with a confocal microscope. Bars, 40 µm. (C) IR-induced MPK-1 phosphorylation occurred in individual dying late-pachytene germ cells in the alg-2(ok304) mutant gonad. Germlines were dissected 2.5 hr post-IR (90 Gy) or after mock treatment, and were subsequently stained for DAPI, SIR-2.1, and phospho-MPK-1. Representative images were obtained from Z-stacks taken with a confocal microscope. Bars, 20 µm. (D) Quantification of WT and alg-2(ok304) mutant germlines displaying MPK-1 phosphorylation in the late-pachytene zone, or the entire gonad loop, at 1, 2.5, and 6 hr post-IR. Phospho-MPK-1 signals were assessed at 10× and 40× magnification with a fluorescent microscope. Sample sizes are indicated. IR, ionizing radiation; WT, wild-type.