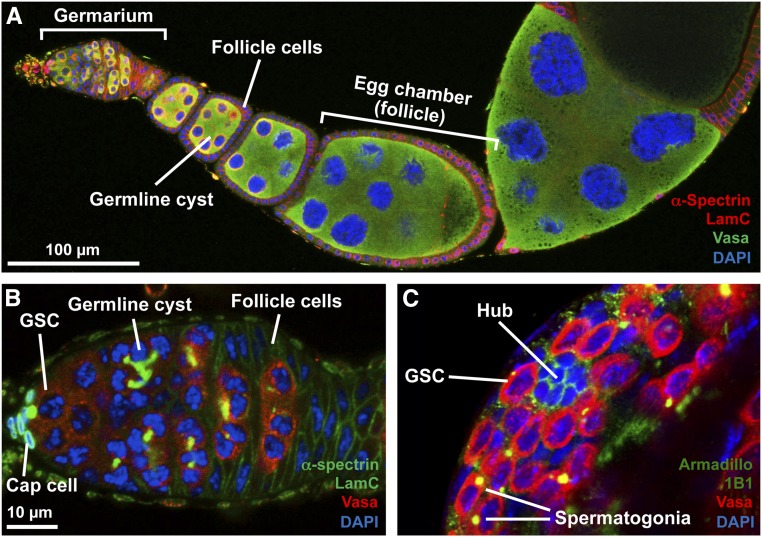
Figure 1.
Drosophila GSC lineages. (A) Confocal image of an ovariole showing the anterior germarium followed by developing egg chambers (or follicles). Each egg chamber is composed of a 16-cell germline cyst surrounded by a monolayer of follicle cells. (B) Image of germarium showing GSCs juxtaposed to cap cells. GSCs give rise to cystoblasts that divide to give rise to 2-, 4-, 8-, and 16-cell germline cysts. Follicle cells surround each 16-cell germline cyst to form an egg chamber that buds off the germarium. (C) Anterior tip of a testis showing the hub surrounded by GSCs. GSCs give rise to gonialblasts that divide to form germline cysts collectively called spermatogonia. α-Spectrin [red in (A); green in (B)] labels fusomes and follicle cell membranes; LamC [red in (A); green in (B)] labels cap cell nuclear envelopes; Armadillo [green in (C)] labels hub cells; 1B1 [green in (C)] labels fusomes; Vasa [green in (A) and red in (B and C)] labels germ cells; and DAPI (blue) labels nuclei. (B and C) are shown at the same magnification. GSC, germline stem cell.