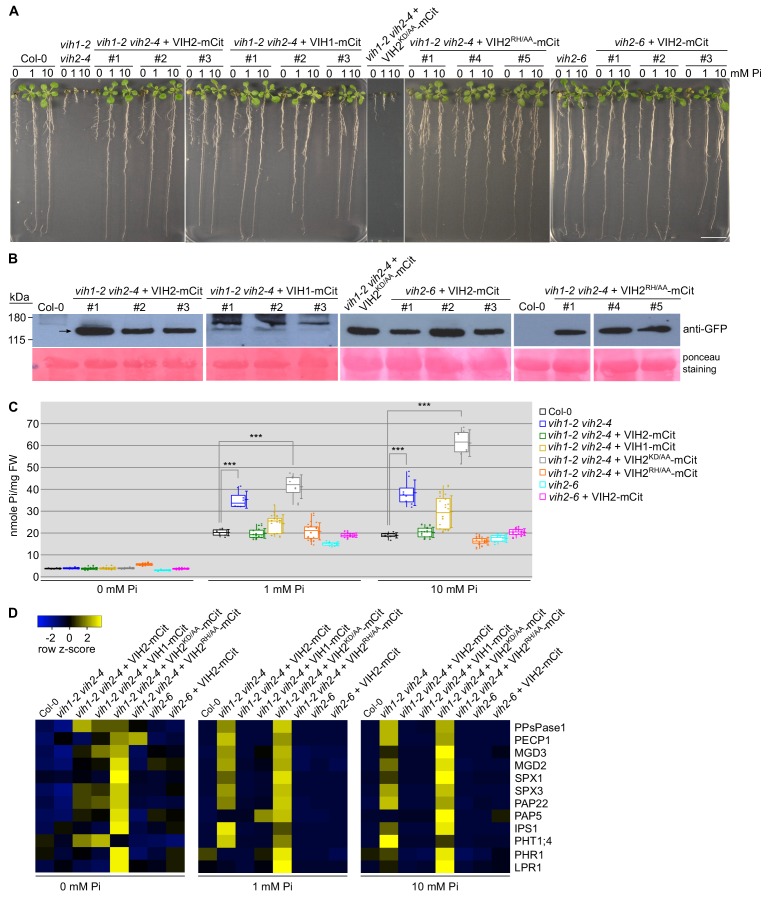
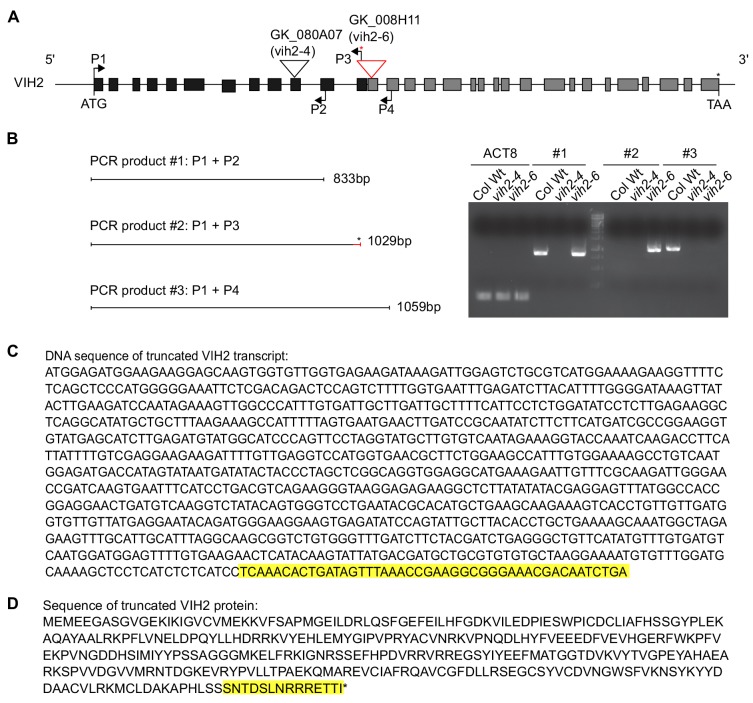
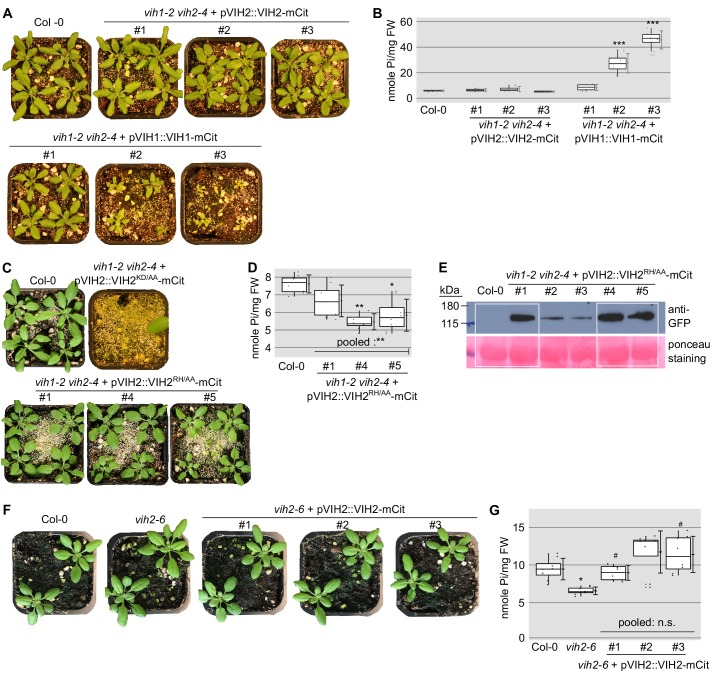
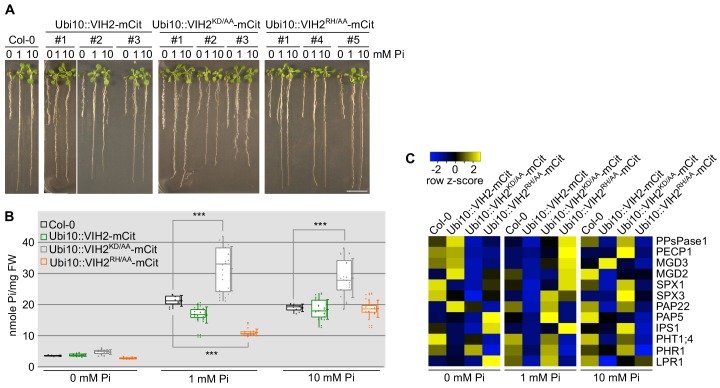
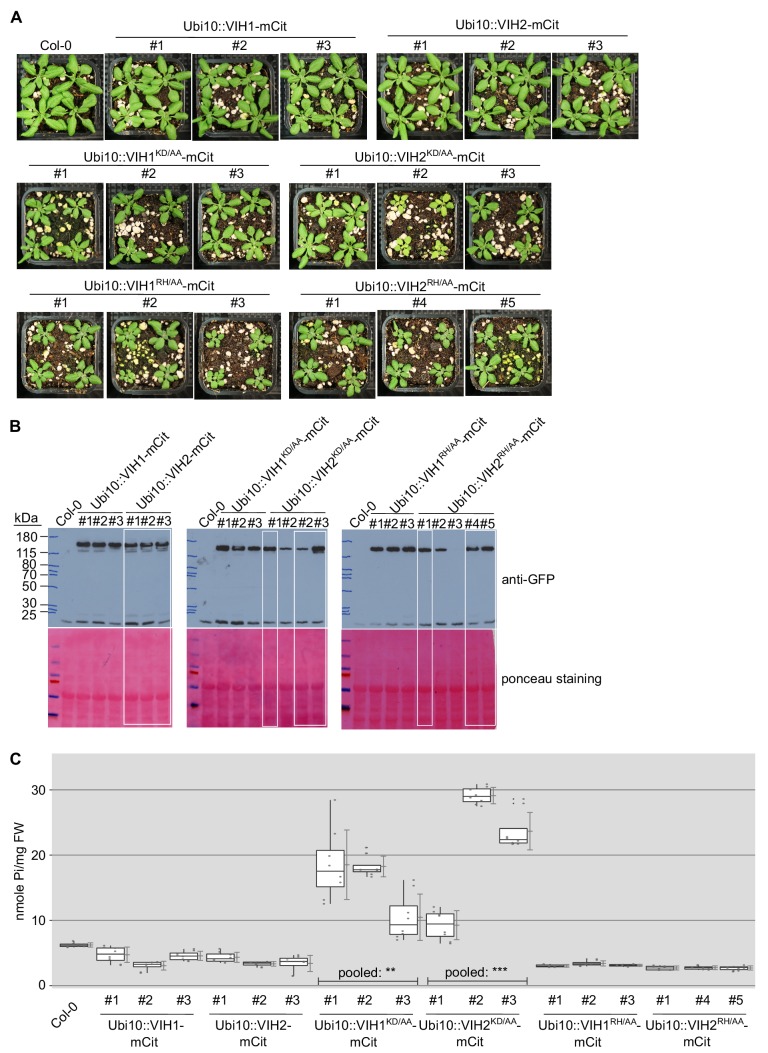
Figure 2. VIH kinase and phosphatase activities regulate plant Pi homeostasis.
(A) Complementation of vih1 vih2 growth phenotypes. Shown are three independent lines for each construct grown in different Pi regimes. Plants were germinated in vertical 1/2MS plates for 8 d, transferred to Pi-free 1/2MS plates supplemented with either 0 mM, 1 mM or 10 mM Pi and grown for additional 6 d. Scale bars correspond to 2 cm. (B) Western blot showing the expression of VIH2-mCit, VIH1-mCit, VIH2KD/AA-mCit, VIH2RH/AA-mCit proteins (indicated by arrow heads) in the transgenic lines from (A) using an anti-GFP antibody. A Ponceau stain of the membrane is shown as loading control below. (C) Pooled Pi content of seedlings 14 DAG as shown in (A). For each position, four independent plants from each trangenic line were measured with two technical replicates. (D) qRT-PCR quantification of the PSI marker genes in seedlings shown in (A). Expression levels are represented as Z-scores. The original qRT-PCR data are shown in Supplementary file 3b.