Abstract
Cervical radiography showed subglottic narrowing of the trachea suggestive of steeple sign.
1. IMAGES
A 50‐year‐old woman presented at our emergency department with fever, coryza, and barking cough. Physical examination revealed stridor, neck lymphadenopathy, and tachypnea with the use of accessory muscles of respiration on admission.
We found that she was positive for influenza type A. Arterial blood gas analysis showed: pH 7.271; PaO2 82.5 mm Hg (FiO2:1.0); PaCO2 57.6 mm Hg; HCO3 − 25.6 mmol/L; base excess −1.8 mmol/L; and lactate level 1.1 mmol/L. Other laboratory findings were unremarkable. Cervical radiography showed subglottic narrowing of the trachea suggestive of steeple sign (Figure 1A,B). A diagnosis of influenza A‐induced croup was established. The clinical condition improved symptomatically following intubation with a 6‐mm endotracheal tube and inhaled epinephrine. The cervical computed tomography revealed narrow subglottic lesion causing significant airway problem (Figure 1C). She was transferred to another hospital with an otolaryngology unit on the same day. Croup and influenza A‐induced croup are seen most commonly in childhood, rarely in adults1. We present the case of influenza A‐induced croup in an adult, with early intubation to prevent respiratory problems.
Figure 1.
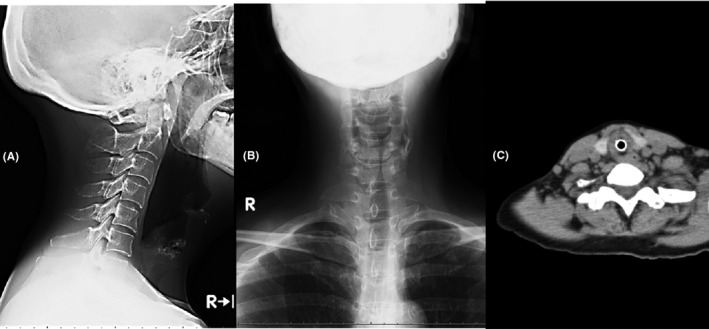
A and B showed Xp in sagittal and coronal section. C showed cervical computed tomography
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
None
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have stated explicitly that there are no conflicts of interest in connection with this article.
Hongo T, Fujiwara T. Influenza A‐induced croup in an adult. J Gen Fam Med. 2019;20:213–214. 10.1002/jgf2.266
REFERENCES
- 1. Shaikh N, Dy P, Basnet A, et al. Uncommon presentation of a common disease: Influenza A presenting as adult. BMJ Case Rep. 2018;6:4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


