Abstract
Background
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) encompasses various phenotypes that severely limit the applicability of precision respiratory medicine. The present investigation is aimed to assess the circadian rhythm of symptoms in pre-defined clinical COPD phenotypes and its association with health-related quality of life (HR-QoL), the quality of sleep and the level of depression/anxiety in each clinical phenotype.
Methods
The STORICO (NCT03105999) Italian observational prospective cohort study enrolled COPD subjects. A clinical diagnosis of either chronic bronchitis (CB), emphysema (EM) or mixed COPD-asthma (MCA) phenotype was made by clinicians at enrollment. Baseline early-morning, day-time and nocturnal symptoms (gathered via the Night-time, Morning and Day-time Symptoms of COPD questionnaire), HR-QoL (via the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire), anxiety and depression levels (via the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale), quality of sleep (via COPD and Asthma Sleep Impact Scale), physical activity (via the International Physical Activity Questionnaire) as well as lung function were recorded.
Results
606 COPD subjects (age 71.4 ± 8.2 years, male 75.1%) were studied. 57.9, 35.5 5.3 and 1.3% of the sample belonged to the CB, EM, MCA and EM + CB phenotypes respectively. The vast majority of subjects reported early-morning and day-time symptoms (79.5 and 79.2% in the CB and 75.8 and 77.7% in the EM groups); the proportion suffering from night-time symptoms was higher in the CB than in the EM group (53.6% vs. 39.5%, p = 0.0016). In both CB and EM, indiscriminately, the presence of symptoms during the 24-h day was associated with poorer HR-QoL, worse quality of sleep and higher levels of anxiety/depression.
Conclusions
The findings highlight the primary classificatory role of nocturnal symptoms in COPD.
Trial registration
Trial registration number: NCT03105999, date of registration: 10th April 2017.
Keywords: 24-hour symptoms, Clinical phenotype, Respiratory function, Real-world
Background
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable condition characterized by persistent airflow limitation, initiated and sustained by chronic exposure to smoke and other irritants [1]. The complexity and the heterogeneous clinical presentation of the disease, however, requires a more comprehensive approach, obliging physicians to take account of symptoms and exacerbations, and to manage the concomitant occurrence of extra-pulmonary pathological conditions. It is evident, on this basis, that Burrows and Fletcher’s original proposal of emphysematous and bronchitic phenotypes [2] is no longer sufficient to identify the different clinical forms of the disease in clinical practice. A COPD phenotype is considered to be a set of attributes that can help differentiate patients on the basis of clinically meaningful parameters, such as symptoms, exacerbations, progression of disease decline, physical inactivity, response to treatment, and mortality.
One effort to classify COPD individuals according to their clinical presentations is the Spanish COPD guidelines [3], which distinguish the emphysema from the chronic bronchitic phenotype and also consider the rate of exacerbations. In addition, a mixed COPD-asthma phenotype (asthma-COPD overlap [ACO]) has been proposed, although its interpretation and association with exacerbation and mortality are now controversial [4–6]. Distinguishing the bronchitic from the emphysematous phenotype is apparently an easy task. The former is marked by productive cough and early onset of hypoxemia, with high prevalence of respiratory failure and chronic cor pulmonale, whereas the latter displays early and severe dyspnea with late-onset hypoxemia. Hypothetically, these clinical presentations could benefit selectively by the treatment options available, but, in real life settings the spectrum of therapies is variably distributed across the range of severity of COPD, without any distinction in terms of phenotypes, thus making such personalized care treatment more difficult.
Taken together, these observations show the need for deeper understanding of the clinical phenotypes of COPD. The STORICO study (STudio Osservazionale sulla caratteRizzazione dei sIntomi delle 24 ore nei pazienti con broncopneumopatia cronica ostruttiva, Observational study on characterization of 24-h symptoms in patients with COPD) offers a unique opportunity to analyze the clinical characteristics of subjects with COPD in relation to the 24-h day-long variability of symptoms. For example, given that dyspnea depends mainly on physical effort, it is logical to expect this symptom to be far more evident during daytime, and in EM subjects.
To reinforce the classical phenotyping strategy, this paper aims primarily to assess, within the clinical COPD phenotypes, the circadian rhythm of COPD symptoms at baseline (in terms of frequency of early-morning, day-time and night-time symptoms). As secondary objective, for each clinical phenotype, we investigated the potential association at enrollment of the circadian variability of symptoms with both disease severity and selected indicators of health status.
Method
Study design
STORICO (NCT03105999) is an Italian, multicenter observational prospective cohort study conducted in 40 pulmonology referral care centers. The enrollment started in February 2016 and the 1-year longitudinal phase of the study ended in June 2018; a total of three visits (baseline and follow-up at 6-month intervals) were performed. The present paper reports the results of the cross-sectional phase. More details about the STORICO study are available elsewhere [7].
Subjects
Subjects of both sexes aged ≥50, current or former smokers with a smoking history of at least 10 pack-years, with a diagnosis of COPD and in stable conditions for at least 12 months according to GOLD 2014 [8] were enrolled consecutively. Patients provided written, informed consent before participation. Patients participating in a clinical trial and those who had changed their COPD treatment regimen in the 3 months prior to enrolment were excluded, as were patients with recent exacerbations (within 1 month prior to enrollment). Also, patients under continuous use of oxygen therapy or suffering from asthma, sleep apnea syndrome or other chronic diseases that reduced life expectancy to less than 3 years (Charlson index> 3) were excluded. Among enrolled patients, only those with available information on the frequency of COPD symptoms during each part of the 24-h day were analyzed.
The sample size was determined by criteria of feasibility. In fact, given the volume of patients handled by the centers involved in the study, inclusion of approximately 600 subjects with the characteristics defined by the Inclusion/Exclusion criteria was deemed reasonable. An evaluation of the possible precision of the estimates was performed in consideration of the primary objectives, finding that a sample of 100 patients per group (i.e. per class of phenotype) would allow precise estimates of the expected proportion of COPD symptoms ≥30%. More details concerning sample size justification are provided elsewhere [7].
Clinical assessment
On the first assessment day, anthropometric data and clinical history were collected and each subject was assigned a clinical COPD phenotype based on the judgment of the clinician: chronic bronchitis (CB), defined as the presence of productive cough for at least 3 months in two consecutive years; emphysema (EM), for patients whose predominant symptoms are dyspnea and reduced tolerance to exercise; mixed COPD-asthma (MCA) for patients with documented not completely reversible airflow obstruction, accompanied by symptoms or signs of obstruction reversibility [9, 10]. As part of the investigation, local researchers were asked to express their degree of confidence in the choice of clinical phenotype on a scale of 0 to 10, from no confidence at all to maximum of confidence. Disease severity was defined using the combined COPD assessment according to GOLD [11]. Spirometry was performed according to the recommendations of the American Thoracic Society (ATS) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS); forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1) and forced vital capacity (FVC) were retained for analysis. Although not mandatory by protocol, the centers were invited to record static lung volumes, and Residual Volume (RV) and Total Lung Capacity (TLC) were obtained together with diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO), in order to support the clinical assignment of subjects to the phenotypes.
Multidimensional assessment
According to the study design, subjects completed the Night-time, Morning and Day-time Symptoms of COPD questionnaire [12]). This is a 33-item questionnaire developed by Almirall S.A., Barcelona, Spain covering the frequency and severity of COPD symptoms (breathlessness, coughing, bringing up phlegm or mucus, chest tightness, chest congestion and wheezing) during each part of the day. This represented the primary outcome of the study.
The questionnaire includes 13 symptom items for night-time (i.e. the time between going to bed and getting up), 10 symptom items for early-morning (i.e. the time from getting up until approximately 11:00 am) and 10 symptom items for day-time (i.e. from approximately 11:00 am until the subject goes to bed).
To address the secondary outcomes of the study the following measures were performed: the level of perceived breathlessness and the extent to which it affected mobility were assessed by the modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea scale ranging from 0 (breathless with strenuous exercise) to 4 (too breathless to leave the house or breathless when dressing or undressing) [13]; health-related quality of life (HR-QoL) was evaluated by the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ), including the subject’s perception of recent respiratory problems (Symptoms component), disturbances to daily physical activity (Activity component) and disturbances of psycho-social function (Impact component); a total score was also calculated. Scores range from 0 (no impairment) to 100 (highest impairment) [14–17], anxiety and depression states were investigated through the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) [18–20], with a total score (emotional distress) ranging from 0 to 42; anxiety and depression subscale scores (range 0–21) were also computed, higher scores indicating more distress; the impact of respiratory symptoms on sleep was assessed by the COPD and Asthma Sleep Impact Scale (CASIS) [21], a self-administered, 7-item scale. The total score range is 0–100, with higher scores indicating greater sleep impairment in the previous week; physical activity was assessed with the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) [22, 23] and a categorical score (low, medium, high level of physical activity) was calculated.
The presence of relevant comorbidities and the number of exacerbations/year in the 5 years before enrollment were recorded. In particular, the presence of anemia was defined as hemoglobin < 13.5 g/dl (for males) and < 12 g/dl (for females), and an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 was considered as indicator of chronic kidney disease [24]. The eGFR was calculated according to the equation proposed by the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration [25].
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were calculated both overall and within each phenotype: mean and standard deviation (SD), median, interquartile range (IQR) for quantitative variables and absolute and relative frequency for categorical variables.
Missing values were not replaced and did not contribute to the analysis of the variable. Frequencies of missing data were given for all analyzed variables.
Primary objective
The frequency of COPD symptoms at enrolment was calculated overall and within each class of phenotype as the ratio between the number of patients with at least 1 (early-morning, day-time and night-time) symptom in the week before enrollment and the total number of evaluable patients in the class. Among the symptomatic patients, the proportion suffering from mild, moderate, severe and very severe symptoms in the week before enrollment was also calculated (overall and by clinical phenotype). The 95% confidence intervals for the proportions were provided when relevant.
Secondary objective
The association between the circadian variability of COPD symptoms and disease severity at enrollment was evaluated by calculating the frequency of patients with early-morning, day-time and night-time symptoms in the groups of patients according to disease severity (groups A to D of Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive lung Disease (GOLD)2014 combined assessment). HR-QoL (SGRQ scores), quality of sleep (CASIS score), anxiety and depression (HADS scores), level of physical activity (IPAQ categorical score) at enrollment in patients with vs without early-morning, day-time and night-time symptoms were described and compared using T-test and Chi-square or Fisher exact test (in the case of non-parametric distribution). The significance threshold was adjusted for multiple comparisons (Bonferroni correction applied) and set to 0.0005 (0.05/number of tests). Site monitoring, data management and statistical analysis were performed by MediNeos an IQVIA Company (Modena, Italy). Statistical analysis was performed using SAS v9.4 and Enterprise Guide v7.1. More details about the STORICO methodology are available elsewhere [7].
Results
Subject characteristics
Among the 683 COPD individuals enrolled in the STORICO study, 606 (88.7%) subjects (age 71.4 ± 8.2 years, 75.1% males) were deemed eligible for the analysis at enrollment; violations causing exclusion are shown in Fig. 1. A total of 351 subjects (57.9%) were classified as CB, 215 (35.5%) as EM and 32 (5.3%) as MCA. In addition, 8 subjects (1.3%) were classified as EM + CB and not retained for analysis due to the paucity of data. When asked for their level of confidence in attributing the phenotype, the vast majority of physicians (77.0% CB, 78.4% EM, 58.6% MCA) rated it at least ≥6 out of 10. Baseline socio-demographic and clinical characteristics (including ongoing therapies for COPD) for each clinical phenotype are shown in Table 1. Table 2 describes the clinical and functional characteristics of subjects according to phenotype. By comparison with EM phenotype, CB patients were more commonly overweight and had more exacerbations/year in the 5 years before baseline (median (IQR): 2 [1–4] in CB vs. 1 (0–2) in EM). As shown in Table 3, the SGRQ components and the total score were similar across phenotypes and, similarly, the CASIS score and the HADS scores did not differ between groups. On the other hand, low levels of physical activity were observed for 35.4% of CB and 18.1% of EM subjects.
Fig. 1.
Patients enrolled and included in the analyses. CB: Chronic Bronchitis; MCA: Mixed-COPD asthma
Table 1.
Socio-demographic, clinical and biological characteristics of the subjects
| Overall (N = 606) | CB (N = 351) | EM (N = 215) | MCA (N = 32) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) (mean ± SD) | 71.4 ± 8.2 | 71.6 ± 8.3 | 71.5 ± 7.9 | 70.1 ± 8.2 |
| Males (N, %) | 455 (75.1) | 256 (72.9) | 174 (80.9) | 20 (62.5) |
| Education (N, %) | ||||
| None | 4 (0.7) | 3 (0.9) | 0 | 0 |
| Primary school | 173 (29.6) | 111 (32.8) | 54 (25.7) | 7 (22.6) |
| Middle school | 241 (41.2) | 127 (37.6) | 93 (44.3) | 19 (61.3) |
| High school | 133 (22.7) | 76 (22.5) | 51 (24.3) | 4 (12.9) |
| University | 34 (5.8) | 21 (6.2) | 12 (5.7) | 1 (3.2) |
| NK | 21 | 13 | 5 | 1 |
| Occupational status (N, %) | ||||
| Unemployed | 23 (3.8) | 16 (4.6) | 5 (2.4) | 2 (6.5) |
| Employed | 77 (12.8) | 44 (12.6) | 25 (11.7) | 5 (16.1) |
| Retired | 468 (77.9) | 265 (75.9) | 176 (82.6) | 22 (71.0) |
| Housewife/househusband | 33 (5.5) | 24 (6.9) | 7 (3.3) | 2 (6.5) |
| NK | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Smoking status (N, %) | ||||
| Former smoker | 445 (73.4) | 250 (71.2) | 166 (77.2) | 25 (78.1) |
| Current smoker | 161 (26.6) | 101 (28.8) | 49 (22.8) | 7 (21.9) |
| Estimated amount of tobacco consumed (pack/year) (median IQR) | 39.0 (20.0–50.0) | 35.0 (20.0–52.0) | 40.0 (23.0–50.0) | 30.0 (20.0–45.0) |
| Smoking duration (yrs) (median IQR) | 40.0 (30.0–49.5) | 40.0 (30.0–50.0) | 40.0 (32.0–50.0) | 39.0 (30.0–42.0) |
| BMI (N, %) | ||||
| Underweight (BMI < 18.5) | 13 (2.2) | 4 (1.2) | 9 (4.2) | 0 |
| Normal weight (BMI 18.5–24.9) | 183 (30.5) | 90 (26.0) | 81 (37.9) | 11 (34.4) |
| Overweight (BMI 25–29.9) | 272 (45.3) | 163 (47.1) | 91 (42.5) | 16 (50.0) |
| Obese (BMI ≥30) | 132 (22.0) | 89 (25.7) | 33 (15.4) | 5 (15.6) |
| NK | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 |
| Comorbidities (N, %) | ||||
| ≥ 1 comorbidity | 446 (73.6) | 254 (72.4) | 163 (75.8) | 23 (71.9) |
| Anemiaa | 36 (26.7) | 26 (33.8) | 8 (16.0) | 2 (33.3) |
| Arterial Hypertension | 308 (50.8) | 188 (53.6) | 97 (45.1) | 17 (53.1) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 34 (5.6) | 20 (5.7) | 12 (5.6) | 2 (6.3) |
| Cardiac ischemic disease | 63 (10.4) | 35 (10.0) | 21 (9.8) | 6 (18.8) |
| Diabetes | 65 (10.7) | 40 (11.4) | 20 (9.3) | 4 (12.5) |
| GERD | 24 (4.0) | 14 (4.0) | 8 (3.7) | 2 (6.3) |
| Neoplastic disease | 31 (5.1) | 10 (2.8) | 17 (7.9) | 3 (9.4) |
| Osteoporosis | 26 (4.3) | 19 (5.4) | 5 (2.3) | 1 (3.1) |
| Blood tests | ||||
| eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (N, %) | n = 122 | n = 65 | n = 49 | n = 6 |
| 17 (13.9) | 11 (16.9) | 4 (8.2) | 2 (33.3) | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dl) (mean ± SD) | n = 135 | n = 77 | n = 50 | n = 6 |
| 14.0 ± 1.7 | 13.8 ± 1.8 | 14.4 ± 1.4 | 13.2 ± 1.1 | |
| Mean cell volume (fl) (mean ± SD) | n = 106 | n = 64 | n = 35 | n = 6 |
| 90.8 ± 7.9 | 90.4 ± 7.7 | 91.2 ± 7.7 | 93.0 ± 11.4 | |
| Eosinophil count (n/mm3) (median IQR) | n = 129 | n = 75 | n = 47 | n = 6 |
| 2.3 (0.1–166.0) | 3.0 (0.1–190.0) | 4.0 (0.1–166.0) | 0.1 (0.0–0.1) | |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) (median IQR) | n = 122 | n = 65 | n = 49 | n = 6 |
| 0.9 (0.7–1.1) | 0.9 (0.8–1.1) | 0.8 (0.7–1.0) | 0.8 (0.7–1.2) | |
| Ongoing therapies for COPD (N, %) | ||||
| ≥ 1 | 525 (86.6) | 311 (88.6) | 183 (85.1) | 27 (84.4) |
| Triple therapy (LABA, LAMA, ICS) | 187 (30.9) | 116 (33.0) | 62 (28.8) | 7 (21.9) |
| LABA+LAMA | 143 (23.6) | 58 (16.5) | 75 (34.9) | 8 (25.0) |
| LAMA Alone | 90 (14.9) | 66 (18.8) | 23 (10.7) | 1 (3.1) |
| ICS + LABA | 78 (12.9) | 53 (15.1) | 17 (7.9) | 8 (25.0) |
| LABA Alone | 18 (3.0) | 12 (3.4) | 4 (1.9) | 2 (6.3) |
| Other | 9 (1.5) | 6 (1.7) | 2 (0.9) | 1 (3.1) |
Data about EM + CB not shown
BMI body mass index. CB Chronic Bronchitis. eGFR estimated glomerular filtration rate. EM Emphysema. GERD Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. ICS Inhaled corticosteroids. IQR interquartile range. LABA long-acting beta-agonist. LAMA long-acting muscarinic antagonists. MCA Mixed-COPD asthma. NK Unknown. SD standard deviation; Triple therapy includes any combination of LABA, LAMA, ICS
aPresence of anemia was evaluated for 135 patients in the total sample, 77 CB, 50 EM, 6 MCA
Percentages computed out of non-missing responses
Table 2.
COPD medical history, lung function parameters and mMRC Scale score at enrollment
| Overall (N = 606) |
CB (N = 351) |
EM (N = 215) |
MCA (N = 32) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COPD duration (yrs) (mean ± SD) | 7.8 ± 6.5 | 7.7 ± 6.5 | 8.0 ± 6.3 | 8.7 ± 8.9 |
| Age at COPD diagnosis (yrs) (mean ± SD) | 63.6 ± 9.1 | 63.9 ± 9.4 | 63.5 ± 8.1 | 61.4 ± 11.5 |
| N of COPD exacerbations/year (5 years before baseline) median (IQR) | 2.0 (1.0–3.0) | 2.0 (1.0–4.0) | 1.0 (0.0–2.0) | 3.0 (1.0–5.0) |
| COPD assessment (GOLD guidelines) (N, %) | ||||
| group A | 155 (25.6) | 76 (21.7) | 66 (30.7) | 12 (37.5) |
| group B | 187 (30.9) | 133 (37.9) | 43 (20.0) | 7 (21.9) |
| group C | 126 (20.8) | 59 (16.8) | 57 (26.5) | 8 (25.0) |
| group D | 138 (22.8) | 83 (23.6) | 49 (22.8) | 5 (15.6) |
|
FEV1 (L) Median (IQR) |
n = 535 | n = 298 | n = 200 | n = 29 |
| 1.5 (1.2–2.0) | 1.6 (1.2–2.0) | 1.5 (1.1–2.0) | 1.5 (1.2–1.9) | |
|
FEV1 of the predicted (%) Median (IQR) |
n = 537 | n = 300 | n = 200 | n = 29 |
| 63.9 (50.0–80.0) | 66.9 (51.0–81.8) | 61.9 (48.1–78.0) | 58.4 (48.3–77.2) | |
|
FVC (L) Median (IQR) |
n = 536 | n = 299 | n = 200 | n = 29 |
| 2.7 (2.2–3.4) | 2.6 (2.2–3.3) | 2.9 (2.2–3.5) | 2.5 (2.1–3.1) | |
|
FEV1/FVC (%) Median (IQR) |
n = 537 | n = 300 | n = 200 | n = 29 |
| 59.7 (49.0–69.0) | 62.0 (52.0–70.0) | 56.0 (45.0–66.6) | 62.3 (53.0–68.1) | |
|
RV (L) Median (IQR) |
n = 291 | n = 130 | n = 138 | n = 21 |
| 3.2 (2.6–4.2) | 2.9 (2.3–3.7) | 3.5 (2.9–4.8) | 3.4 (2.8–4.9) | |
|
IC (L) Median (IQR) |
n = 306 | n = 143 | n = 138 | n = 24 |
| 2.6 (2.1–3.4) | 2.6 (2.1–3.3) | 2.7 (2.1–3.5) | 2.4 (2.2–3.3) | |
|
TLC (L) Median (IQR) |
n = 286 | n = 128 | n = 135 | n = 21 |
| 6.4 (5.4–7.3) | 6.0 (4.9–6.9) | 6.8 (5.8–7.6) | 6.5 (5.7–7.3) | |
|
RV/TLC Median (IQR) |
n = 289 | n = 128 | n = 138 | n = 21 |
| 0.5 (0.4–0.6) | 0.5 (0.4–0.6) | 0.6 (0.5–0.6) | 0.6 (0.5–0.6) | |
|
DLCO of the predicted (%) Median (IQR) |
n = 205 | n = 98 | n = 92 | n = 15 |
| 68.0 (51.0–83.0) | 69.5 (59.0–87.0) | 63.0 (46.8–76.5) | 76.7 (48.0–81.5) | |
| mMRC Scale score | n = 577 | n = 334 | n = 205 | n = 30 |
| Median (IQR) | 1.0 (1.0–2.0) | 1.0 (1.0–2.0) | 1.0 (1.0–2.0) | 1.0 (1.0–2.0) |
| ≥ 2 (N, %) | 262 (45.4) | 150 (44.9) | 97 (47.3) | 11 (36.7) |
Data about EM + CB not shown
CB Chronic Bronchitis. DLCO diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. EM Emphysema
FEV1 forced expiratory volume in the first second. FVC forced vital capacity. IC Inspiratory capacity. IQR interquartile range. MCA Mixed-COPD asthma. mMRC modified Medical Research Council. RV Residual Volume. SD standard deviation. TLC Total lung capacity
Table 3.
Quality of life, quality of sleep, level of physical activity and anxiety/depression at enrollment
| Overall | CB | EM | MCA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 582 | 339 | 204 | 32 |
| SGRQ symptoms score | 42.5 ± 22.2 | 43.3 ± 22.7 | 40.7 ± 21.1 | 44.4 ± 25.3 |
| activity score | 49.8 ± 21.3 | 50.4 ± 21.4 | 49.1 ± 21.2 | 48.5 ± 22.1 |
| impacts score | 23.5 ± 18.7 | 24.0 ± 18.7 | 22.7 ± 18.8 | 22.5 ± 18.2 |
| total score | 34.5 ± 18.1 | 35.1 ± 18.2 | 33.5 ± 18.1 | 33.9 ± 18.5 |
| N | 597 | 344 | 213 | 32 |
| CASIS total score | 17.4 ± 16.2 | 19.3 ± 16.6 | 14.5 ± 14.9 | 14.3 ± 17.1 |
| N | 566 | 332 | 196 | 30 |
| HADS Total score | 9.5 ± 6.8 | 9.9 ± 6.9 | 8.9 ± 6.4 | 8.8 ± 7.1 |
| Anxiety score | 4.9 ± 3.7 | 5.1 ± 3.9 | 4.4 ± 3.3 | 4.8 ± 3.9 |
| Depression score | 4.7 ± 3.7 | 4.8 ± 3.6 | 4.5 ± 3.8 | 4.0 ± 3.6 |
| N | 199 | 113 | 72 | 11 |
| IPAQ Level of physical activity (N, %) | ||||
| Low | 57 (28.6) | 40 (35.4) | 13 (18.1) | 3 (27.3) |
| Moderate | 139 (69.8) | 72 (63.7) | 57 (79.2) | 8 (72.7) |
| High | 3 (1.5) | 1 (0.9) | 2 (2.8) | 0 (0.0) |
Data about EM + CB not shown
Mean ± SD (standard deviation) were shown
CASIS COPD and Asthma Sleep Impact Scale. CB Chronic Bronchitis. EM Emphysema. HADS Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. IPAQ International Physical Activity Questionnaire. MCA Mixed-COPD asthma. SGRQ St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire
Circadian rhythm of symptoms in the clinical COPD phenotypes
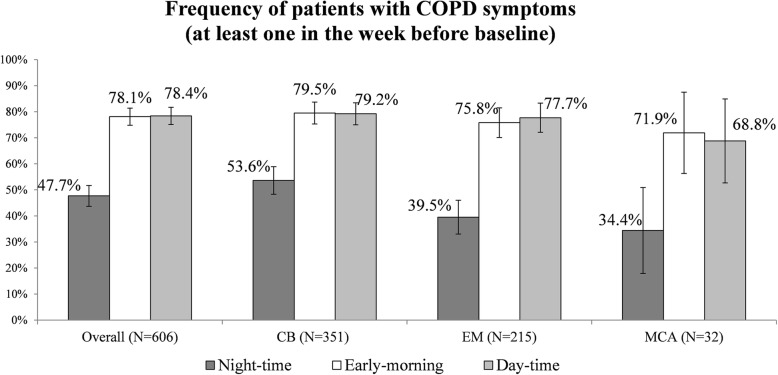
A higher proportion of patients suffered from respiratory symptoms in the early-morning and day-time (79.5 and 79.2% in CB and 75.8 and 77.7% in EM groups reported early-morning and day-time symptoms, respectively) than during night-time..
Interestingly, the proportion of subjects suffering from night-time symptoms was higher in the CB group (53.6%) than in the EM (39.5%) or MCA (34.4%) groups (Chi-square test p-value presence/absence of night-time symptoms vs clinical phenotype = 0.0016 – see Fig. 2). In the subsample of patients reporting night-time symptoms, the frequency of current smokers was not significantly higher in CB (n = 53, 28.2%) than in EM (n = 22, 25.9%) patients (Chi-square test smoke vs clinical phenotype p-value > 0.05). In addition, the prevalence of current smokers was unrelated to nocturnal symptoms in either CB (n = 53, 28.2% and n = 48, 29.4%, symptomatic vs asymptomatic patients), EM (n = 22, 25.9% and n = 27, 20.8%), or CB/EM (n = 75, 27.5% and n = 75, 25.6%).
Fig. 2.
Frequency of patients with COPD symptoms (in the week before baseline). CB: Chronic Bronchitis; EM: Emphysema; MCA: Mixed-COPD asthma. 95% confidence intervals are shown
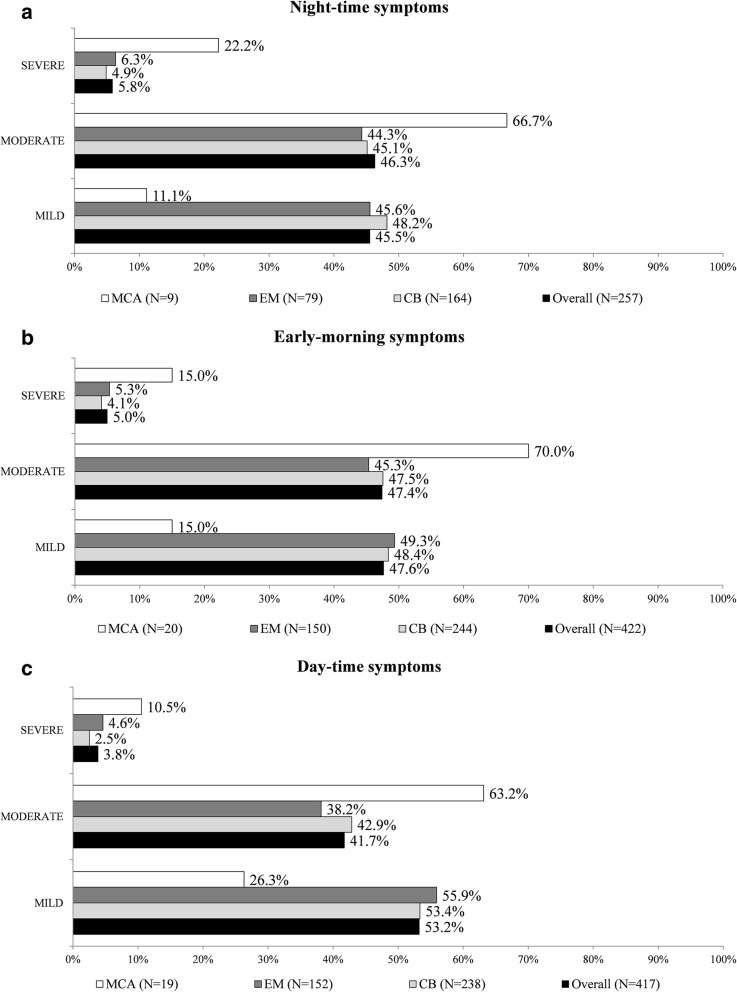
As shown in Fig. 3a, b and c, the CB and EM phenotypes did not differ in terms of severity of respiratory symptoms for any portion of the 24-h day. The higher proportion of MCA patients with severe and moderate symptoms in each portion of the day may depend on the small sample size.
Fig. 3.
a Frequency of patients according to severity of night-time COPD symptoms (in the week before baseline). CB: Chronic Bronchitis; EM: Emphysema; MCA: Mixed-COPD asthma. Percentages computed out of patients with symptoms and with non-missing severity. b Frequency of patients according to severity of early-morning COPD symptoms (in the week before baseline). CB: Chronic Bronchitis; EM: Emphysema; MCA: Mixed-COPD asthma. Percentages computed out of patients with symptoms and with non-missing severity. c Frequency of patients according to severity of day-time COPD symptoms (in the week before baseline). CB: Chronic Bronchitis; EM: Emphysema; MCA: Mixed-COPD asthma. Percentages computed out of patients with symptoms and with non-missing severity
Association between circadian variability of symptoms in each clinical phenotype and severity of disease, HR-QoL, quality of sleep, level of physical activity and depression/anxiety
In each clinical phenotype, the frequency of symptoms increased significantly with the severity of COPD (in CB GOLD A-D vs. presence/absence of symptoms p-values < 0.0005 – see Table 4). In EM, the proportions of patients of groups A to D with early-morning, day-time and night-time symptoms were similar to those observed in CB, although the association between GOLD classification and symptoms was not statistically significant.
Table 4.
Symptoms and severity of disease, HR-QoL, quality of sleep, level of physical activity and depression/anxiety
| EARLY-MORNING SYMPTOMS | DAY-TIME SYMPTOMS | NIGHT-TIME SYMPTOMS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | p-value | No | Yes | p-value | No | Yes | p-value | |
| A. CB (N = 351) | |||||||||
| GOLD combined COPD assessment (N, %) | |||||||||
| n | 72 | 279 | 73 | 278 | 163 | 188 | |||
| GROUP A | 28 (36.8) | 48 (63.2) | <.0001 | 25 (32.9) | 51 (67.1) | 0.0002 | 52 (68.4) | 24 (31.6) | <.0001 |
| GROUP B | 29 (21.8) | 104 (78.2) | 34 (25.6) | 99 (74.4) | 65 (48.9) | 68 (51.1) | |||
| GROUP C | 6 (10.2) | 53 (89.8) | 8 (13.6) | 51 (86.4) | 24 (40.7) | 35 (59.3) | |||
| GROUP D | 9 (10.8) | 74 (89.2) | 6 (7.2) | 77 (92.8) | 22 (26.5) | 61 (73.5) | |||
| SGRQ scores (mean ± SD) | |||||||||
| n | 71 | 268 | 71 | 268 | 159 | 180 | |||
| symptoms | 19.4 ± 16.2 | 49.7 ± 19.7 | <.0001 | 18.5 ± 14.7 | 49.9 ± 19.6 | <.0001 | 31.4 ± 20.3 | 53.9 ± 19.2 | <.0001 |
| activity | 40.4 ± 17.6 | 53.0 ± 21.6 | <.0001 | 39.0 ± 17.6 | 53.4 ± 21.4 | <.0001 | 42.2 ± 19.0 | 57.6 ± 20.9 | <.0001 |
| impacts | 14.6 ± 12.0 | 26.5 ± 19.4 | <.0001 | 13.4 ± 12.0 | 26.8 ± 19.2 | <.0001 | 15.7 ± 13.1 | 31.3 ± 19.9 | <.0001 |
| total | 23.4 ± 12.6 | 38.2 ± 18.2 | <.0001 | 22.1 ± 12.4 | 38.5 ± 17.9 | <.0001 | 26.3 ± 13.8 | 42.9 ± 18.0 | <.0001 |
| CASIS scores (mean ± SD) | |||||||||
| n | 70 | 274 | 70 | 274 | 161 | 183 | |||
| total | 10.7 ± 12.3 | 21.5 ± 16.8 | <.0001 | 9.1 ± 11.1 | 21.9 ± 16.7 | < 0.0001 | 9.3 ± 9.7 | 28.1 ± 16.4 | <.0001 |
| HADS scores (mean ± SD) | |||||||||
| n | 69 | 263 | 69 | 263 | 156 | 176 | |||
| total | 8.3 ± 6.2 | 10.4 ± 7.0 | 0.0279 | 7.1 ± 5.9 | 10.7 ± 7.0 | < 0.0001 | 8.0 ± 6.2 | 11.7 ± 7.1 | < 0.0001 |
| n | 70 | 266 | 70 | 266 | 157 | 179 | |||
| anxiety | 4.4 ± 3.5 | 5.3 ± 4.0 | > 0.05 | 3.8 ± 3.4 | 5.5 ± 4.0 | 0.0018 | 4.1 ± 3.5 | 6.0 ± 4.0 | < 0.0001 |
| n | 69 | 265 | 69 | 265 | 156 | 178 | |||
| depression | 3.8 ± 3.0 | 5.1 ± 3.7 | 0.009 | 3.3 ± 3.0 | 5.2 ± 3.6 | < 0.0001 | 3.9 ± 3.1 | 5.6 ± 3.8 | < 0.0001 |
| IPAQ Level of physical activity (N, %) | |||||||||
| n | 17 | 96 | 19 | 94 | 50 | 63 | |||
| Low | 4 (10.0) | 36 (90.0) | > 0.05 | 4 (10.0) | 36 (90.0) | > 0.05 | 19 (47.5) | 21 (52.5) | > 0.05 |
| Moderate | 12 (16.7) | 60 (83.3) | 14 (19.4) | 58 (80.6) | 30 (41.7) | 42 (58.3) | |||
| High | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0) | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0) | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0) | |||
| B. EM (N = 215) | |||||||||
| GOLD combined COPD assessment (N, %) | |||||||||
| n | 52 | 163 | 48 | 167 | 130 | 85 | |||
| GROUP A | 24 (36.4) | 42 (63.6) | 0.0009 | 23 (34.8) | 43 (65.2) | 0.0075 | 48 (72.7) | 18 (27.3) | 0.0035 |
| GROUP B | 14 (32.6) | 29 (67.4) | 10 (23.3) | 33 (76.7) | 22 (51.2) | 21 (48.8) | |||
| GROUP C | 11 (19.3) | 46 (80.7) | 11 (19.3) | 46 (80.7) | 39 (68.4) | 18 (31.6) | |||
| GROUP D | 3 (6.1) | 46 (93.9) | 4 (8.2) | 45 (91.8) | 21 (42.9) | 28 (57.1) | |||
| SGRQ scores (mean ± SD) | |||||||||
| n | 50 | 154 | 46 | 158 | 122 | 82 | |||
| symptoms | 20.8 ± 14.7 | 47.1 ± 18.6 | <.0001 | 23.7 ± 17.8 | 45.6 ± 19.3 | <.0001 | 33.2 ± 18.9 | 51.7 ± 19.2 | <.0001 |
| activity | 39.7 ± 20.8 | 52.2 ± 20.5 | 0.0003 | 34.8 ± 17.4 | 53.3 ± 20.4 | <.0001 | 43.7 ± 18.7 | 57.2 ± 22.3 | <.0001 |
| impacts | 13.9 ± 11.5 | 25.5 ± 19.9 | <.0001 | 11.1 ± 8.7 | 26.0 ± 19.7 | <.0001 | 16.1 ± 12.7 | 32.5 ± 22.0 | <.0001 |
| total | 22.7 ± 13.0 | 37.0 ± 18.1 | <.0001 | 20.3 ± 10.6 | 37.4 ± 18.0 | <.0001 | 27.1 ± 13.3 | 43.0 ± 20.0 | <.0001 |
| CASIS scores (mean ± SD) | |||||||||
| n | 51 | 162 | 47 | 166 | 129 | 84 | |||
| total | 7.2 ± 8.2 | 16.8 ± 15.8 | <.0001 | 7.1 ± 10.0 | 16.6 ± 15.4 | < 0.0001 | 8.0 ± 8.7 | 24.6 ± 16.8 | <.0001 |
| HADS scores (mean ± SD) | |||||||||
| n | 45 | 151 | 42 | 154 | 121 | 75 | |||
| total | 6.5 ± 5.5 | 9.6 ± 6.5 | 0.0039 | 5.1 ± 5.1 | 9.9 ± 6.3 | < 0.0001 | 7.2 ± 5.6 | 11.7 ± 6.6 | < 0.0001 |
| n | 46 | 153 | 44 | 155 | 123 | 76 | |||
| anxiety | 3.4 ± 3.0 | 4.8 ± 3.3 | 0.0079 | 2.7 ± 2.4 | 4.9 ± 3.3 | < 0.0001 | 3.8 ± 3.0 | 5.5 ± 3.5 | 0.0002 |
| n | 48 | 152 | 43 | 157 | 123 | 77 | |||
| depression | 3.3 ± 3.3 | 4.9 ± 3.9 | 0.0107 | 2.6 ± 3.2 | 5.0 ± 3.8 | 0.0002 | 3.4 ± 3.3 | 6.2 ± 3.9 | < 0.0001 |
| IPAQ Level of physical activity (N, %) | |||||||||
| n | 17 | 55 | 15 | 57 | 54 | 18 | |||
| Low | 2 (15.4) | 11 (84.6) | > 0.05 | 1 (7.7) | 12 (92.3) | 0.0265 | 8 (61.5) | 5 (38.5) | > 0.05 |
| Moderate | 14 (24.6) | 43 (75.4) | 12 (21.1) | 45 (78.9) | 44 (77.2) | 13 (22.8) | |||
| High | 1 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) | 2 (100.0) | 0 (0) | 2 (100.0) | 0 (0) | |||
The percentages of the GOLD combined COPD assessment are computed by row, i.e. over the total number of patients in Groups A, B, C, D respectively. Similarly, the percentages of IPAQ Level of physical activity are computed by row, i.e. over the total number of patients in the low, moderate, severe classes respectively
For SGRQ, CASIS and HADS scores T-test p-values (pts with symptoms vs. pts. without symptoms) are shown. Chi-square test p-values of GOLD combined COPD assessment vs. presence/absence of (early-morning, day-time, night-time) symptoms are shown. Fisher exact test p-values of IPAQ Level of physical activity vs. presence/absence of (early-morning, day-time, night-time) symptoms are shown. P-values < 0.0005 (alpha adjusted for multiple comparisons) are in bold
CASIS COPD and Asthma Sleep Impact Scale. CB Chronic Bronchitis. EM Emphysema. HADS Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. IPAQ International Physical Activity Questionnaire. SGRQ St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire
As Table 4 shows, independently of clinical phenotype, the presence of symptoms during the 24-h day was associated with lower QoL (T-test p-values SGRQ scores for patients with vs. without symptoms < 0.0005) and worse quality of sleep (T-test p-values CASIS score patients with vs without symptoms < 0.0005).
In both the CB and EM phenotypes, mood disturbances were significantly worse in patients with day-time and night-time symptoms: higher HADS scores were observed, in fact, in patients with vs. without symptoms (T-test p-values HADS scores patients with vs. without symptoms < 0.0005). Lastly, the level of physical activity did not differ significantly between CB or EM patients with early-morning, day-time or night-time symptoms and those without them (see Table 4).
Discussion
The observations reported here indicate that a very high proportion of individuals suffering from COPD and under chronic inhaled medication nevertheless still show symptoms during some parts of the day. In particular, almost 80% of COPD subjects experienced symptoms during day-time or early-morning, and half had nocturnal symptoms. The novelty of this study is the relationship between circadian rhythm of symptoms and the pre-defined clinical phenotypes. Night-time symptoms, alone or in combination with symptoms during other parts of the day, appear to characterize the CB phenotype specifically.
A previous multicenter observational investigation (ASSESS study) was conducted in European clinical practice centers to determine the prevalence and severity of respiratory symptoms during different parts of the 24-h day and other patient-reported outcomes (PROs) [12]. That study found that more than half of COPD patients had symptoms during the 24-h day, which were associated with worse PROs; interestingly, two thirds of these patients experienced night-time symptoms. The present study confirms and extends these observations: in a similar cohort of COPD subjects, nocturnal symptoms were confirmed to be very common and more frequent in the CB than in the EM phenotype. This finding advances our knowledge on the distinctive clinical appearance of COPD patients. Whether this is of clinical importance has yet to be demonstrated, and future confirmatory studies are required. In both CB and EM groups, night-time symptoms were associated with worse quality of life and quality of sleep and higher levels of anxiety/depression.
From a clinical standpoint, there is an urgent need to move away from the simplistic definition of COPD embracing the entire spectrum of individuals with chronic, non-reversible airway obstruction and to develop instead a classification of subgroups on the basis of common pathogenetic mechanisms and similar clinical manifestations. The commonly accepted concept of COPD is well described by the Venn diagram, which covers different clinical phenotypes and their overlap conditions [25], in the effort to classify COPD patients into distinct clinical manifestations, each of which requires specific treatment. In the present study, researchers were asked for a clinical diagnosis of the phenotype of consecutively enrolled COPD individuals based on their judgment (according to medical history and clinical characteristics). Chest imaging and lung function, when available, helped to determine or confirm the clinical decision. In this respect, the GOLD document [11] focuses mainly on symptoms and future risk in order to determine the proper treatment, with no distinction into clinical phenotypes. This missing information is likely have been a factor in the failure of large interventional clinical trials. There is no doubt that COPD patients may respond selectively to different treatments, depending on their functional and clinical manifestations, and the recent literature offers evidence in support of this concept [26–29]. The identification of clinical phenotypes, therefore, may entail prognostic consequences at the individual patient level. Since current treatment is not sufficient to control nocturnal symptoms, specific actions are strongly advocated, either a more aggressive pharmacological approach or tests of the efficacy of non-pharmacological interventions, such as pulmonary rehabilitation or non-invasive ventilation; the latter have never been investigated and warrant specially designed ad hoc studies.
The reasons for the greater prevalence of nighttime symptoms in CB individuals are unclear. Bronchial hypersecretion and the consequent accumulation of mucus during the night probably explains, at least in part, the more frequent occurrence of nocturnal symptoms. Also, the occurrence of expiratory flow limitation (EFL) at night could contribute to the respiratory symptoms. Indeed, increased bronchial vagal hypertone, typically occurring at night, and chronic inflammation and mucus, together with changes in lung volume owing to the supine position, can favor EFL, which in turn causes air trapping and pulmonary hyperinflation. In addition, cough – which is the cardinal symptom of CB – is a common cause of nocturnal awakening. On the other hand, dyspnea is typically effort-related in mild to moderate EM and is accordingly less severe, when the patient is at rest. Finally, one cannot rule out report bias on the part of EM patients. Indeed, night-time respiratory distress, by increasing the abdominal pressure, might induce nicturia, and this (rather than dyspnea) might, in turn, be perceived as the cause of night-time awakening, along the lines of what has been observed in elderly OSAS patients [30].
The lack of differences between the clinical phenotypes examined with specific regard to quality of life, mood changes and physical performance is somewhat surprising, and it implies clinical consequences. However, the similarities in terms of lung function impairment and dyspnea perception may have played at least some role in explaining the observed findings. It cannot be excluded that missing data for each variable explored affected the outcomes. Our present findings should improve awareness of night-time symptoms in COPD individuals. Thus, in clinical practice the occurrence of symptoms such as wheezing and coughing during the night should be subjected to routine investigation. The automated systems of long-term monitoring of respiratory symptoms now available can record respiratory symptoms during the nocturnal hours that would otherwise go unnoticed [31].
Interestingly, the present study found no significant difference in level of physical activity, in either the CB or the EM group, between subjects with and without early-morning, day-time or night-time symptoms. This conflicts with previous studies according to which morning symptoms are responsible for limitations of physical activity and a consequent sedentary lifestyle [32, 33]. Differences between the tools used to assess morning symptoms and those used to assess the level of physical activity, as well as the items derived by the latter to perform the analysis, may help to explain the discordance between this study and those others.
The main limitation of the present study is that the STORICO study was not specifically designed to investigate differences between clinical phenotypes, so no hypotheses on the proper sizes of the groups were made a priori. As a consequence, only the CB and EM phenotypes had a large enough sample and no conclusions could be drawn with regard to MCA. Another limitation is the lack of available spirometries in a minority of the subjects enrolled. The careful evaluation of the medical history and previous functional assessment of these subjects enhanced the probability of diagnosis of COPD. Furthermore, since lung function assessment was not included among the primary outcomes of the protocol, the main findings of the study were not affected by it. Recall bias could also have affected data collection: this is why the Night-time, Morning and Day-time Symptoms of COPD questionnaire, with its short recall period of only 1 week, was chosen to evaluate the primary objectives. Other information was usually available in medical charts or could be drawn from routine questionnaires filled out during visits.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the findings of this study indicate that the circadian rhythm of symptoms can supplement the classical phenotyping of COPD patients by revealing the prevalent phenotype-specific patterns of symptoms. Pending a confirmatory study, these findings seem robust enough to recommend systematic assessment of nocturnal symptoms and their correlates, mainly anxiety and depression, in the clinical assessment of COPD patients. This would improve our knowledge of patients’ health status and, hopefully, would help to tailor COPD therapy to the individual patient.
Acknowledgments
The members of the Steering Committee (Scichilone N., Antonelli Incalzi R., Blasi F., Canonica G.W.) designed the study protocol and are responsible for the conduction of the study and the interpretation of the results; they and the other authors (Shino P., Cuttitta G., Zullo A., Ori A.) fulfil the criteria for authorship as recommended by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) and were fully responsible for all aspects of manuscript development. We are grateful to Sara Rizzoli for her help in drafting the manuscript.
STORICO study group - Participating Centers.
Pietro Schino (Acquaviva delle Fonti); Giuseppina Cuttitta (Palermo); Maria Pia Foschino (Foggia); Renato Prediletto (Pisa); Carmelindo Mario Enrico Tranfa (Naples); Maria Cristina Zappa (Rome); Pasquale Patriciello (Pollena Trocchia); Luciana Labate (Bari); Salvatore Mariotta (Rome); Stefano Nava (Bologna); Alessandro Vatrella (Salerno); Michele Mastroberardino (Avellino); Riccardo Sarzani (Ancona); Antonio Iuliano (Milan); Lamberto Maggi (Bergamo); Anna Zedda (Casoria); Alberto Pesci (Monza); Giuseppe Sera (Turin); Antonello Nicolini (Sestri Levante); Di Donato Salvatore Walter (Mondragone); Silvia Forte (Rome); Del Donno Mario (Benevento); Federica Rivolta (Abbiategrasso); Mauro Ferliga (Chiari); Antonio Filippo Raco (Menaggio); Di Re Luigi (Teramo); Gaetano Cabibbo (Modica); Rosario Maselli (Catanzaro); Carlo Gulotta (Orbassano); Stefano Nardini (Vittorio Veneto); Enrico Eugenio Guffanti (Casatenovo); Walter Castellani (Florence); Luca Triolo (Rome); Giovanni Passalacqua (Messina); Bianca Beghè (Modena); Lo Cicero Salvatore (Milan); Enzo Faccini (Dolo); Elena Atzeni (Nuoro); Roberto Tazza (Terni); Piercarlo Giamesio (Asti).
Abbreviations
- ACO
Asthma-COPD overlap
- ATS
American Thoracic Society
- BMI
Body mass index
- CASIS
COPD and Asthma Sleep Impact Scale
- CB
Chronic bronchitis
- COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- DLCO
Diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide
- EFL
Expiratory flow limitation
- eGFR
estimated glomerular filtration rate
- EM
Emphysema
- ERS
European Respiratory Society
- FEV1
Forced expiratory volume in the first second
- FVC
Forced vital capacity
- GERD
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- GOLD
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
- HADS
Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale
- HR-QoL
Health-related quality of life
- IC
Inspiratory capacity
- ICS
Inhaled corticosteroids
- IPAQ
International Physical Activity Questionnaire
- IQR
Interquartile range
- LABA
Long-acting beta-agonist
- LAMA
Long-acting muscarinic antagonists
- MCA
Mixed COPD-asthma
- mMRC
Modified Medical Research Council
- NK
Unknown
- PROs
Patient reported outcomes
- RV
Residual Volume
- SD
Standard deviation
- SGRQ
St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire
- TLC
Total Lung Capacity
Authors’ contributions
SN, AIR, BF, CGW contributed substantially to the conception and design of the work, to data analysis and interpretation, and to the drafting and substantial revision of the work. SP and CG have made contribution to acquisition of data. ZA, OA revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Laboratori Guidotti and Malesci, Italy provided unconditional financial support to the study. No other support was provided for the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from authors and Laboratori Guidotti and Malesci but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors and Laboratori Guidotti upon reasonable request. Data request may be sent to the first author (nicola.scichilone@unipa.it) and to Stefania Barsanti (Laboratori Guidotti, sbarsanti@labguidotti.it).
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Ethic Committee of the coordinating center (Fondazione Toscana G. Monasterio Pisa, Italy) and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and the Good Clinical Practices guidelines for observational studies, complying with all requirements of local regulations. Patients provided written, informed consent before participation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
B.F. reports grants and personal fees from ASTRAZENECA, grants and personal fees from BAYER, personal fees from CHIESI, personal fees from GSK, personal fees from GUIDOTTI, grants and personal fees from GRIFOLS, grants from INSMED, personal fees from MENARINI, personal fees from NOVARTIS, grants and personal fees from PFIZER, personal fees from TEVA, personal fees from ZAMBON, outside the scope of the work submitted.
Z.A. and O.A. are employees of Medineos Observational Research.
The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Scichilone Nicola, Email: nicola.scichilone@unipa.it, Email: medidata@medineos.com.
Antonelli Incalzi Raffaele, Email: R.Antonelli@unicampus.it.
Blasi Francesco, Email: francesco.blasi@unimi.it.
Schino Pietro, Email: p.schino@miulli.it.
Cuttitta Giuseppina, Email: cuttitta@ibim.cnr.it.
Zullo Alessandro, Email: medidata@medineos.com.
Ori Alessandra, Email: medidata@medineos.com.
Canonica Giorgio Walter, Email: canonica@unige.it.
on behalf of STORICO study group:
Pietro Schino, Giuseppina Cuttitta, Maria Pia Foschino, Renato Prediletto, Carmelindo Mario Enrico Tranfa, Maria Cristina Zappa, Pasquale Patriciello, Luciana Labate, Salvatore Mariotta, Stefano Nava, Alessandro Vatrella, Michele Mastroberardino, Riccardo Sarzani, Antonio Iuliano, Lamberto Maggi, Anna Zedda, Alberto Pesci, Giuseppe Sera, Antonello Nicolini, Di Donato Salvatore Walter, Silvia Forte, Del Donno Mario, Federica Rivolta, Mauro Ferliga, Antonio Filippo Raco, Di Re Luigi, Gaetano Cabibbo, Rosario Maselli, Carlo Gulotta, Stefano Nardini, Enrico Eugenio Guffanti, Walter Castellani, Luca Triolo, Giovanni Passalacqua, Bianca Beghè, Lo Cicero Salvatore, Enzo Faccini, Elena Atzeni, Roberto Tazza, and Piercarlo Giamesio
References
- 1.Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD, Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). 2017. Available from: http://goldcopd.org. Accessed 15 Jan 2019.
- 2.Burrows B., Fletcher C.M., Heard B.E., Jones N.L., Wootliff J.S. THE EMPHYSEMATOUS AND BRONCHIAL TYPES OF CHRONIC AIRWAYS OBSTRUCTION. The Lancet. 1966;287(7442):830–835. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(66)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Miravitlles M, Soler-Cataluña JJ, Calle M, Molina J, Almagro P, Quintano JA, Riesco JA, et al. Spanish COPD guidelines (GesEPOC). Update 2014. Arch Bronconeumol. 2014;50(Suppl 1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/S0300-2896(14)70070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Orie NGM, Sluiter HJ, De Vries K, Tammeling GJ, Witkop J. The host factor in bronchitis. In: Orie NGM, Sluiter HJ, editors. Bronchitis. Assen: Royal Van Gorcum; 1961. pp. 43–59. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Barnes PJ. Against the Dutch hypothesis: asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are distinct diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;174(3):240–243. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2604008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bonten TN, Kasteleyn MJ, de Mutsert R, Hiemstra PS, Rosendaal FR. Chavannes NH et al, defining asthma–COPD overlap syndrome: a population-based study. Eur Respir J. 2017;49:160. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02008-2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Canonica GW, Blasi F, Scichilone N, Simoni L, Zullo A, Giovannetti C, et al. On behalf of STORICO study group characterization of circadian COPD symptoms by phenotype: methodology of the STORICO observational study. Eur J of Intern Med. 2017;43:62–68. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2017.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Miravitlles M, Soler-Cataluña JJ, Calle M, Molina J, Almagro P, Quintano JA, et al. Spanish COPD guidelines (GesEPOC): pharmacological treatment of stable COPD. Arch Bronconeumol. 2012;48(7):247–257. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2012.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lange P, Halpin DM, O'Donnell DE, MacNee W. Diagnosis, assessment, and phenotyping of COPD: beyond FEV1. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016;11:3–12. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S85976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Miravitlles M, Worth H, Soler Catalauña JJ, Price D, De Benedetto F, Roche N, Godtfredsen NS, et al. Observational study to characterize 24-hour COPD symptoms and their relationship with patient-reported outcomes; results from the ASSESS study. Respir Res. 2014;15:122. doi: 10.1186/s12931-014-0122-1.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Charlson M, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jones P, Lareau S, Mahler DA. Measuring the effects of COPD on the patient. Respir Med. 2005;99(Suppl B):S11–S18. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2005.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jones PW, Quirk FH, Baveystock CM. The St George's respiratory questionnaire. Respir Med. 1991;85(Suppl. B):25–31. doi: 10.1016/S0954-6111(06)80166-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jones PW, Quirk FH, Baveystock CM, Littlejohns P. A self-complete measure for chronic airflow limitation - the St George's respiratory questionnaire. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;145:1321–1327. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.6.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Meguro M, Barley EA, Spencer S, Jones PW. Development and validation of an improved COPD-specific version of the St George's respiratory questionnaire. Chest. 2006;132:456–463. doi: 10.1378/chest.06-0702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1983;67:361–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb09716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Herrmann C. International experiences with the hospital anxiety and depression scale - a review of validation data and clinical results. J Psychosom Res. 1997;42:17–41. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3999(96)00216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Barth J, Martin CR. Factor structure of the hospital anxiety and depression scale (HADS) in German coronary heart disease patients. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2005;3:15. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-3-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pokrzywinski RF, Meads DM, McKenna SP, Glendenning GA, Revicki DA. Development and psychometric assessment of the COPD and asthma sleep impact scale (CASIS) Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2009;7:98. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-7-98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ainsworth BE, Bassett DR, Jr, Strath SJ, Swartz AM, O'Brien WL, Thompson RW, et al. Comparison of three methods for measuring the time spent in physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32:S457–S464. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200009001-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Guidelines for Data Processing and Analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) Short and Long Forms. 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 24.National Kidney Foundation KDOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39(2 Suppl 1):S1–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Soriano JB, Alfageme I, Almagro P, Casanova C, Esteban C, Soler-Cataluña JJ, et al. Distribution and prognostic validity of the new Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease grading classification. Chest. 2013;143(3):694–702. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rabe KF, Wedzicha JA. Controversies in treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 2011;378(9795):1038–1047. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61295-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Miravitlles M, Soler-Cataluña JJ, Calle M, Soriano JB. Treatment of COPD by clinical phenotypes: putting old evidence into clinical practice. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(6):1252–1256. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00118912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cheng SL, Wang HH, Lin CH. Effect of allergic phenotype on treatment response to inhaled bronchodilators with or without inhaled corticosteroids in patients with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:2231–2238. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S140748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pavord ID, Chanez P, Criner GJ, Kerstjens HAM, Korn S, Lugogo N, et al. Mepolizumab for eosinophilic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(17):1613–1162. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1708208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Endeshaw YW, Johnson TM, Kutner MH, Ouslander JG, Bliwise DL. Sleep-disordered breathing and nocturia in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52(6):957–960. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Krönig J, Hildebrandt O, Weissflog A, Cassel W, Gross V, Sohrabi K, Fischer P, Koehler U. Long-term recording of night-time respiratory symptoms in patients with stable COPD II-IV. COPD. 2017;14(5):498–503. doi: 10.1080/15412555.2017.1338681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.van Buul AR, Kasteleyn MJ, Chavannes NH, Taube C. Physical activity in the morning and afternoon is lower in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with morning symptoms. Respir Res. 2018;19(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0749-4.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.van Buul AR, Kasteleyn MJ, Chavannes NH, Taube C. The association between objectively measured physical activity and morning symptoms in COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:2831–2840. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S143387.eCollection2017.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from authors and Laboratori Guidotti and Malesci but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors and Laboratori Guidotti upon reasonable request. Data request may be sent to the first author (nicola.scichilone@unipa.it) and to Stefania Barsanti (Laboratori Guidotti, sbarsanti@labguidotti.it).