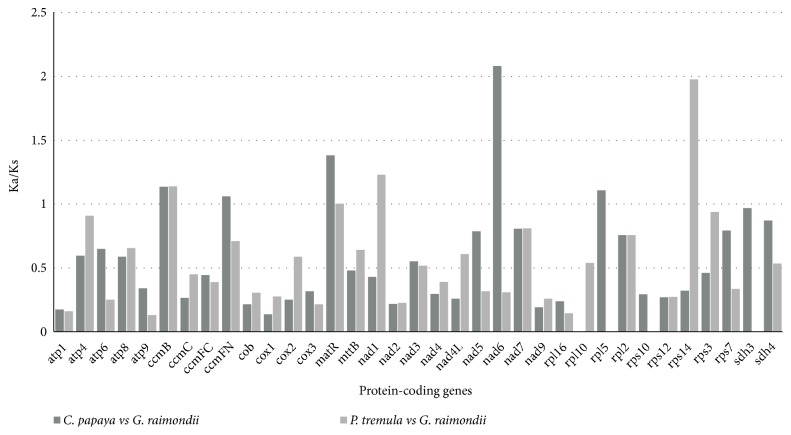
In the article titled “Analysis of the Complete Mitochondrial Genome Sequence of the Diploid Cotton Gossypium raimondii by Comparative Genomics Approaches” [1], there were several errors that should be corrected as follows: (i) the references in the text to Figures 4 and 5 are reversed and should be exchanged; (ii) in Figure 5, the Ka/Ks values for C. papaya versus G. raimondii for ccmFC are inaccurate; (iii) in Figure 5, the gene ccmFC should be replaced by ccmFN. The correct Ka/Ks values for each protein-coding gene between C. papaya and G. raimondii and between P. tremula and G. raimondii are available in a supplementary file.
Supplementary Materials
The raw Ka/Ks values for each protein-coding gene in C. papaya, G. raimondii, and P. tremula.
Figure 5.
Ka/Ks values of 36 protein-coding genes of G. raimondii, C. papaya, and P. tremula. Deep brown and light brown boxes indicate the Ka/Ks ratio of C. papaya vs. G. raimondii and P. tremula vs. G. raimondii, respectively.
References
- 1.Bi C., Paterson A. H., Wang X., et al. Analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the diploid cotton Gossypium raimondii by Comparative genomics approaches. BioMed Research International. 2016;2016:18. doi: 10.1155/2016/5040598.5040598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The raw Ka/Ks values for each protein-coding gene in C. papaya, G. raimondii, and P. tremula.