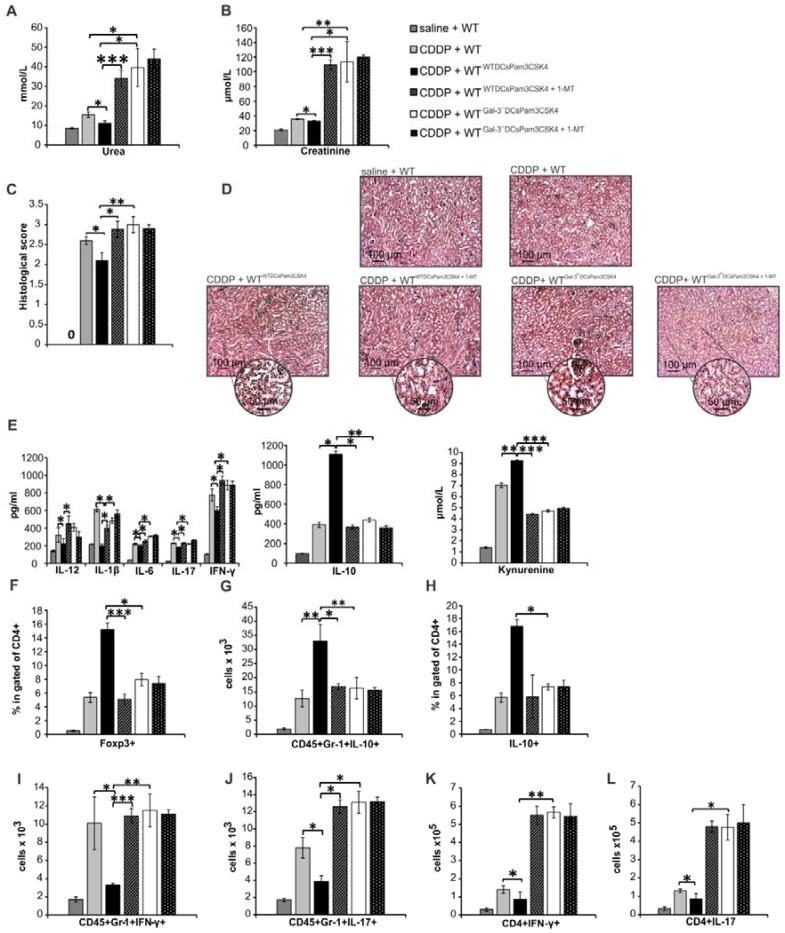
Figure 8.
Transfer of WTDCsPam3CSK4 significantly attenuated CDDP-induced AKI in WT recipients by promoting expansion of immunosuppressive Tregs in IDO1/KYN-dependent manner. TLR-2-primed DCs, isolated from the kidneys of untreated WT and Gal‐3-/- mice (WTDCsPam3CSK4 and Gal‐3-/-DCsPam3CSK4), were intravenously injected (5×105cells/mouse) in CDDP-treated WT recipients (WTWTDCsPam3CSK4 and WTGal‐3-/-DCsPam3CSK4) two days prior CDDP administration (16 mg/kg body weight). IDO1 was inhibited in TLR-2-primed renal DCs (WTDCsPam3CSK4+1-MT) and Gal-3-/-DCs (Gal-3-/-DCsPam3CSK4+1-MT) by using 1-methyl tryptophan (1-MT; 2 mM). Transfer of WTDCsPam3CSK4 managed to attenuate CDDP-injured AKI and inflammation in CDDP-treated WT recipients, as evidenced by notably lower serum levels of urea (A), creatinine (B), decreased histological score (C), reduced extent of renal injury in the cortex of CDDP-injured kidneys (D), decreased serum levels of inflammatory, Th1/Th17-related cytokines and increased serum levels of immunosuppressive IL-10 and KYN (E), significantly higher presence of Tregs (F), and IL-10-producing neutrophils (G) and CD4+T cells (H), but notably decreased of IFN-γ (I) and IL-17-producing neutrophils (J) as well as IFN-γ (K) and IL-17-producing CD4+T cells (L). Transfer of WTDCsPam3CSK4+1-MT or Gal-3-/-DCsPam3CSK4 did not expand immunosuppressive Tregs (F), IL-10-producing neutrophils (G) and CD4+Tcells (H) in CDDP-injured kidneys, but promoted polarization of renal-infiltrating neutrophils (I-J) and CD4+T cells (K-L) towards IFN-γ-producing (I, K) and IL-17-producing cells (J, L), resulting in significant aggravation of CDDP-induced AKI in WT recipients (A-D). There was no significant difference between CDDP-treated WT recipients of Gal-3-/-DCsPam3CSK4+1-MT and Gal-3-/-DCsPam3CSK4 (A-L). Data from two individual experiments with 8 mice per group are shown as Mean ± SEM; *p<0.05, **p<0.01;***p<0.001.