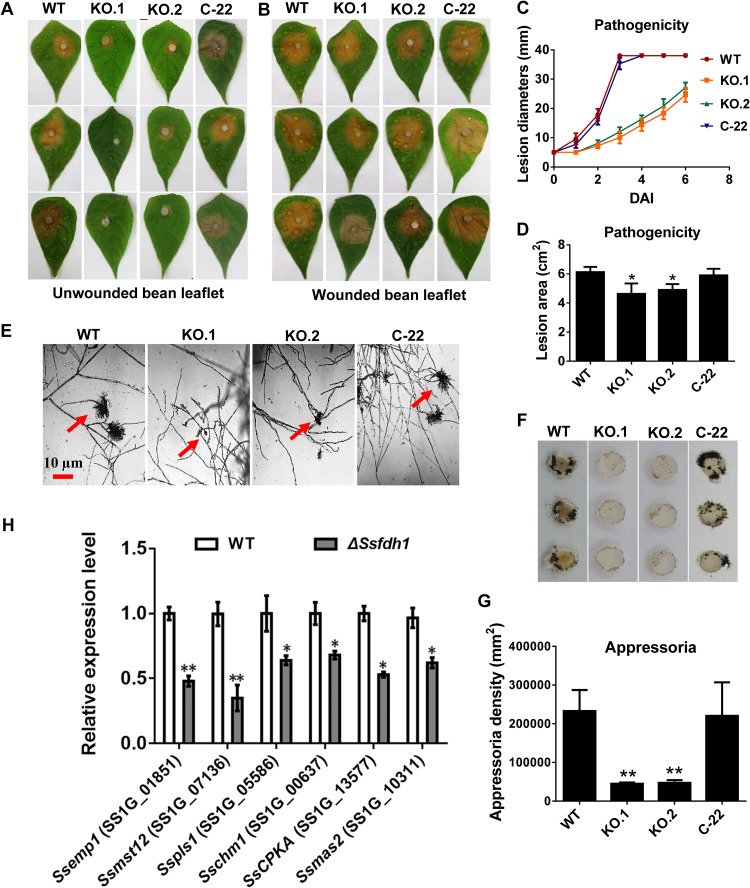
FIG 2.
Deletion of Ssfdh1 attenuates pathogenicity mainly by a deficiency in compound appressoria. (A) WT, KO, and C-22 strains were inoculated on unwounded common bean leaves and photographed 2 days after inoculation (DAI). (B) Pathogenicity phenotype of WT, KO, and C-22 strains on wounded common bean leaves. Pictures were taken by 2 DAI. (C) Lesion diameters were measured on unwounded leaves daily until 6 DAI. (D) Lesion areas were measured on unwounded leaves by 2 DAI. (E) Compound appressoria (red arrows) of WT, KO, and C-22 strains on glass sides were observed by light microscopy at 1 DAI. (F) Compound appressorium development of WT, KO, and C-22 strains on parafilm. Pigmented compound appressoria were observed on parafilm at 1 DAI using 5-mm-diameter mycelial plugs. (G) Quantities of compound appressoria calculated by ImageJ pixel density analysis compared among different strains. (H) Relative expression levels of compound appressorium-associated genes were investigated in hyphal tissue in Ssfdh1 deletion mutant and WT strains. The constitutively expressed histone H3 gene was used as the reference gene to standardize data (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 [Student's t test, n = 3]).