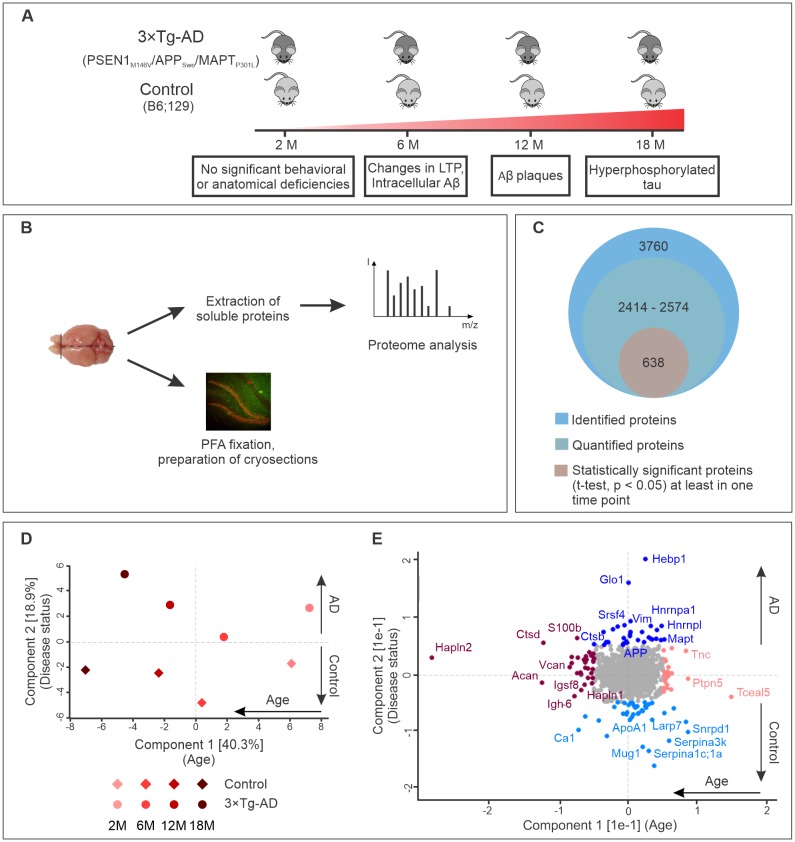
Figure 1. Progression of Alzheimer’s disease at molecular level in the triple transgenic mouse model (PSEN1M146V/APPSwe/MAPTP301L).
(A) Disease progression in 3×Tg-AD mice and corresponding time points (2, 6, 12, 18 months) of sample collection. Four biological replicates per group were collected at each time point. (B) Experimental workflow and sample processing. Half of the collected brain sample was used for preparation of the cryosections for immunohistochemistry. Soluble proteins of the other half were extracted for proteomics analysis. (C) Number of identified, quantified and statistically significant proteins in the dataset. (D) Principal component analysis of soluble brain proteome of 3×Tg-AD and control mice based on their protein expression profile. Principal component one segregates mice by age and accounts for 40.3% of variability in the dataset, while principal component two clusters mice according to their disease status (18.9% of variance). (E) Proteins driving the differences in proteomes between aged, young, diseased and control mice depicted in brown, pink, navy and light blue colors, respectively.