Abstract
Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS), a highly invasive and angiogenic tumor of endothelial spindle-shaped cells, is the most common AIDS-associated cancer caused by KS-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) infection. KSHV-encoded viral FLICE-inhibitory protein (vFLIP) is a viral oncogenic protein, but its role in the dissemination and angiogenesis of KSHV-induced cancers remains unknown. Here, we report that vFLIP facilitates cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis by downregulating the SAP18-HDAC1 complex. vFLIP degrades SAP18 through a ubiquitin–proteasome pathway by recruiting E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM56. Further, vFLIP represses HDAC1, a protein partner of SAP18, by inhibiting Nanog occupancy on the HDAC1 promoter. Notably, vFLIP impairs the interaction between the SAP18/HDAC1 complex and p65 subunit, leading to enhancement of p65 acetylation and NF-κB activation. Our data suggest a novel mechanism of vFLIP activation of the NF-κB by decreasing the SAP18/HDAC1 complex to promote the acetylation of p65 subunit, which contributes to vFLIP-induced activation of the NF-κB pathway, cell invasion, and angiogenesis. These findings advance our understanding of the mechanism of KSHV-induced pathogenesis, and providing a rationale for therapeutic targeting of the vFLIP/SAP18/HDAC1 complex as a novel strategy of AIDS-KS.
Subject terms: Oncogenes, Microbiology
Introduction
Approximately 12% of all human cancers worldwide are caused by infections of oncogenic viruses. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is one of the oncogenic viruses, and is etiologically associated with Kaposi's sarcoma (KS), primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), and multicentric Castleman's disease (MCD) [1]. As a multifocal angiosarcoma of spindle endothelial cells, KS is histologically characterized by vast aberrant proliferation of small vessels, lack of the basement membrane, and extravasation of erythrocytes and vast infiltration of the inflammatory cells [2]. KS contains four clinical forms: classic KS, African endemic KS, Iatrogenic KS (post-transplant KS), and AIDS-associated KS (AIDS-KS). AIDS-KS is the most common and aggressive form and frequently occurs throughout the body. Prominently, distal dissemination is often observed in KS and AIDS-KS patients, which causes diffuse lung disease, such as pulmonary KS [3]. Therefore, understanding of the molecular basis underlying KS tumor dissemination and angiogenesis could shed light on the mechanism of KS pathogenesis.
The nuclear factor (NF)-κB signaling pathway is pivotal for immune system function. During infection, pathogenic microorganisms have developed strategies to subvert it for gene expression and cell growth, differentiation, activation, and survival [4]. KSHV modulation of NF-κB signaling is not only important for viral infection and evading the host immune response, but also contributes to the development of malignant neoplasia. So far, six KSHV proteins and one KSHV microRNA (miRNA) have been shown to regulate the NF-κB pathway [5]. KSHV-encoded non-structural membrane proteins vGPCR, K1 and K15 activate the NF-κB pathway, inducing the expression of a range of potent proangiogenic and proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines including VEGF, Cox2, Gro-g, IL-6, and IL-8, which are involved in growth, proliferation, inflammation, and aberrant angiogenesis [6]. Viral IRF3 encoded by KSHV K10.5 and K10.6 inhibits NF-κB transactivation and DNA-binding in response to TNFα treatment through vIRF3-mediated reduction of IKKβ kinase activity and reduced phosphorylation of IκB, resulting in inhibition of antiviral immune response [7]. By manipulating the host survival pathway, KSHV encoded a viral miRNA, miR-K1, controls viral replication and latency by directly targeting IκB and activating the NF-κB pathway [8]. In addition, tegument protein/FGARAT encoded by KSHV ORF75 cooperates in vitro with viral FADD-like interleukin (IL)-1-β-converting enzyme (FLICE/caspase-8) inhibitory protein (vFLIP) for NF-κB activation [9].
As a major NF-κB activator, vFLIP encoded by KSHV K13 is a latently expressed gene with high homology to cellular FLIP (cFLIP). vFLIP harbors two critical domains including the death effector domains (DED) and the TRAF-binding motif, which inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis or accelerates NF-κB activation, respectively [10, 11]. vFLIP can associate with IKKα, IKKβ, and IKKγ/NEMO complex, which destruct IκBα through the ubiquitin–proteasome-dependent pathway following phosphorylation [12]. We have recently confirmed that deletion of K13 gene from KSHV genome partially offsets KSHV-induced NF-κB activity [13]. Membrane lipid raft-associated cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1) interaction with vFLIP is critical for the initiation of IKK kinase complex and NF-κB activation in the PEL cells [14]. The vFLIP-activated NF-κB pathway regulates cell survival, growth, B-cell receptor-mediated apoptosis, proinflammatory cytokines production, along with KSHV lifecycle [10, 15–18]. However, whether vFLIP regulates endothelial cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis remains unclear. Although vFLIP is known to associate with IKK complex to activate the NF-κB pathway, it is possible that vFLIP may activate the NF-κB pathway by other means.
In this study, we report that vFLIP promotes endothelial cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis. Mechanically, vFLIP functions as a scaffolding protein to enhance the interaction between E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM56 and Sin3A-associated protein 18 (SAP18), resulting in ubiquitination and degradation of SAP18. Further, vFLIP inhibits the expression level of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) by negatively regulating the transcription factor Nanog. Subsequently, the reduction of SAP18/HDAC1 complex is responsible for enhancement of p65 acetylation and NF-κB activation. Our results elucidate a novel mechanism of vFLIP activation of the NF-κB pathway, providing better understanding of KSHV pathogenesis and identifying a potential therapeutic target of KSHV-related malignancies.
Results
vFLIP promotes endothelial cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis
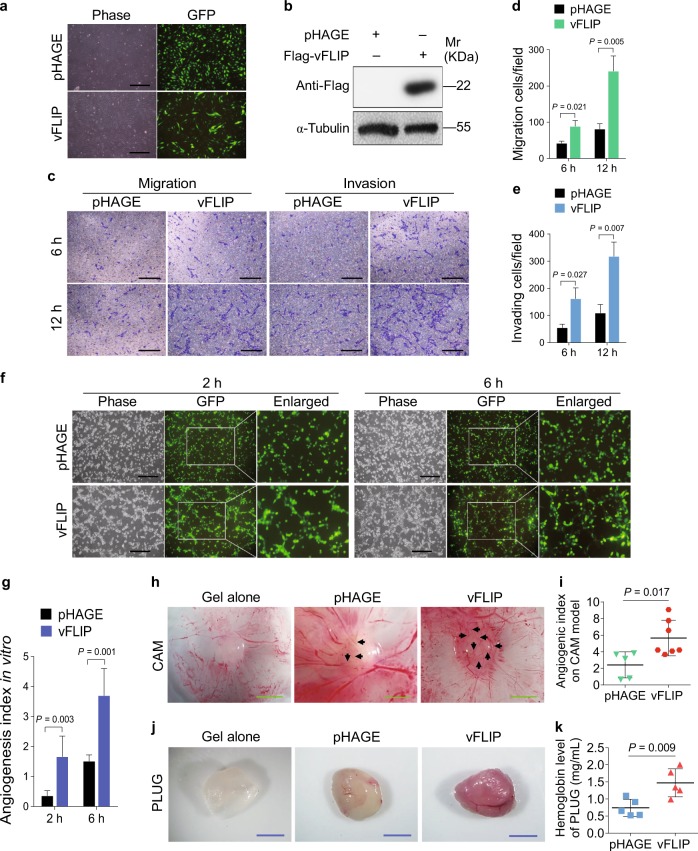
We and others have previously shown that numerous KSHV-encoded proteins and miRNAs promote the migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of endothelial cells [19–26]. However, it is unclear whether KSHV vFLIP regulates these phenotypes. To address this, we transduced HUVECs with lentiviral vFLIP. At day 3 post-transduction, over 95% cells were GFP-positive, and the transduced cells became elongated and acquired a spindle-shape (Fig. 1a), which is in line with a previous report [27]. Western blotting further confirmed the ectopic expression of vFLIP in HUVECs (Fig. 1b). Transwell migration and Matrigel invasion assays revealed that vFLIP significantly increased cell migration and invasion (Fig. 1c–e).
Fig. 1.
vFLIP enhances endothelial cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis. a HUVECs were transduced with lentiviral vFLIP and control pHAGE, respectively. Cells were photographed in phase and GFP modes under fluorescence microscope 3 days post-transduction (×100). b Exogenous expression of vFLIP taq was determined by western blotting in HUVECs treated as in (a) with the indicated antibodies. c Transwell migration and Matrigel invasion assays were employed to evaluate cell motility. The representative images of migrated and invaded HUVECs treated as in (a) were collected at 6 h and 12 h post-seeding (×100). Scar bars, 40 μm. d Quantification of transwell migration assay in (c). Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results. Three independent experiments, each with sextic technical replicates, were performed. e Quantification of Matrigel invasion assay in (c). Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results. Three independent experiments, each with sextic technical replicates, were performed. f Cells treated as in (a) were subjected to microtubule-formation assay. The GFP-labeled cells indicated higher than 95% of lentivirus transduction efficiency. The images were captured 2 h and 6 h post-seeding to reflect in vitro angiogenesis capability by counting sprouted cells, connected cells, and polygonal cells (×100). Scar bars, 40 μm. g Quantification of microtubule-formation assay in (f). Data are shown as mean ± s.d. Three independent experiments, each with quintic technical replicates, were performed. h Cells treated as in (a) were mixed with the high concentration Matrigel, and further inoculated onto CAMs to examine in vivo angiogenesis capability. The CAMs were separated and examined under stereomicroscope. Representational graphs of angiogenesis are shown. Black arrows indicate vessels and their branches. Scar bars, 1 cm. i Quantification of the angiogenesis index on CAM model in (h). Data are represented as mean ± s.d. Each group with at least five tumors. j The mixture containing high concentration Matrigel and cells treated as in (a) was injected into nude mice. Representational photographs of plugs are exhibited. Scar bars, 1 cm. k The level of hemoglobin in plug tissues treated in (j) was measured by comparing the standard curve. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results, with five tumors for each group
We performed microtubule formation assay to examine the effect of vFLIP on angiogenesis in vitro. We observed that vFLIP promoted the formation of capillary tubes when compared with the control group (Fig. 1f, g). Consistently, ectopic expression of vFLIP increased the angiogenic index in an in vivo chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) model (Fig. 1h, i). In another in vivo angiogenesis model of Matrigel plug assay in mice, vFLIP also promoted angiogenesis with the increased hemoglobin content compared with the control group (Fig. 1j, k). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of the plugs exhibited abnormal neovascular distribution along with erythrocyte infiltration in the vFLIP-expressing group (Figure S1). The proangiogenic factors including smooth muscle actin (SMA), VEGFA, and basic fibroblast growth factor (b-FGF) were further examined by immunohistochemistry (IHC). There were indeed more SMA-, VEGFA-, and b-FGF-positive cells in the vFLIP plugs than the control group (Figure S1). These results indicated that vFLIP promoted endothelial cell motility, invasion, and angiogenesis.
vFLIP enhances cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis by downregulating SAP18
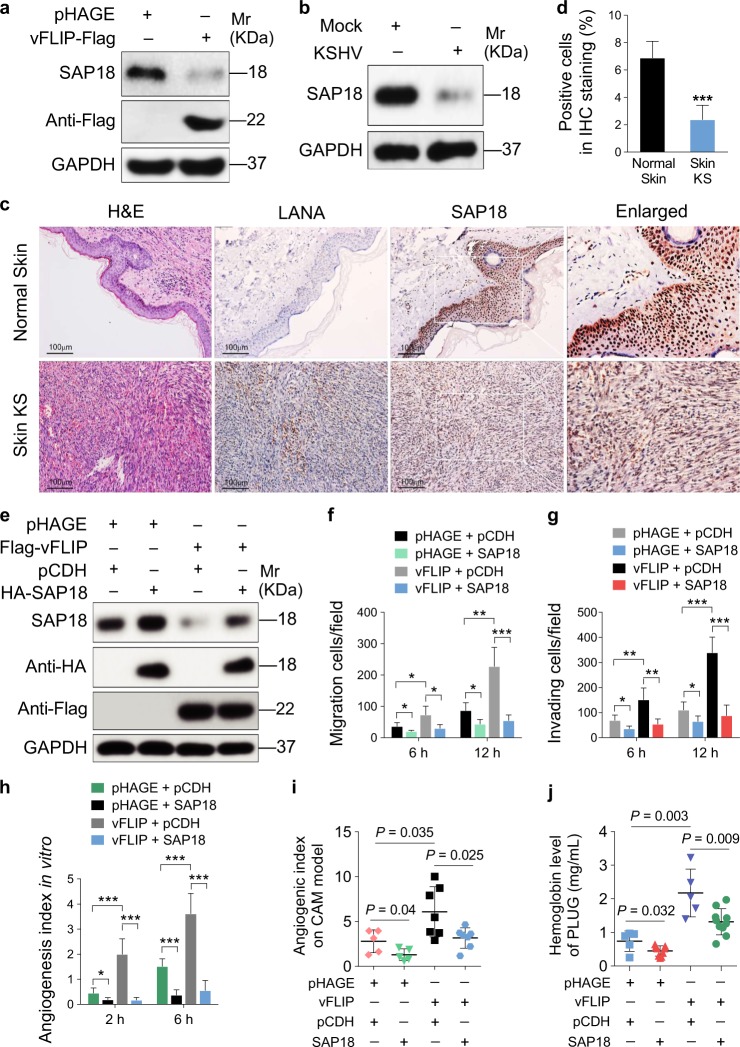
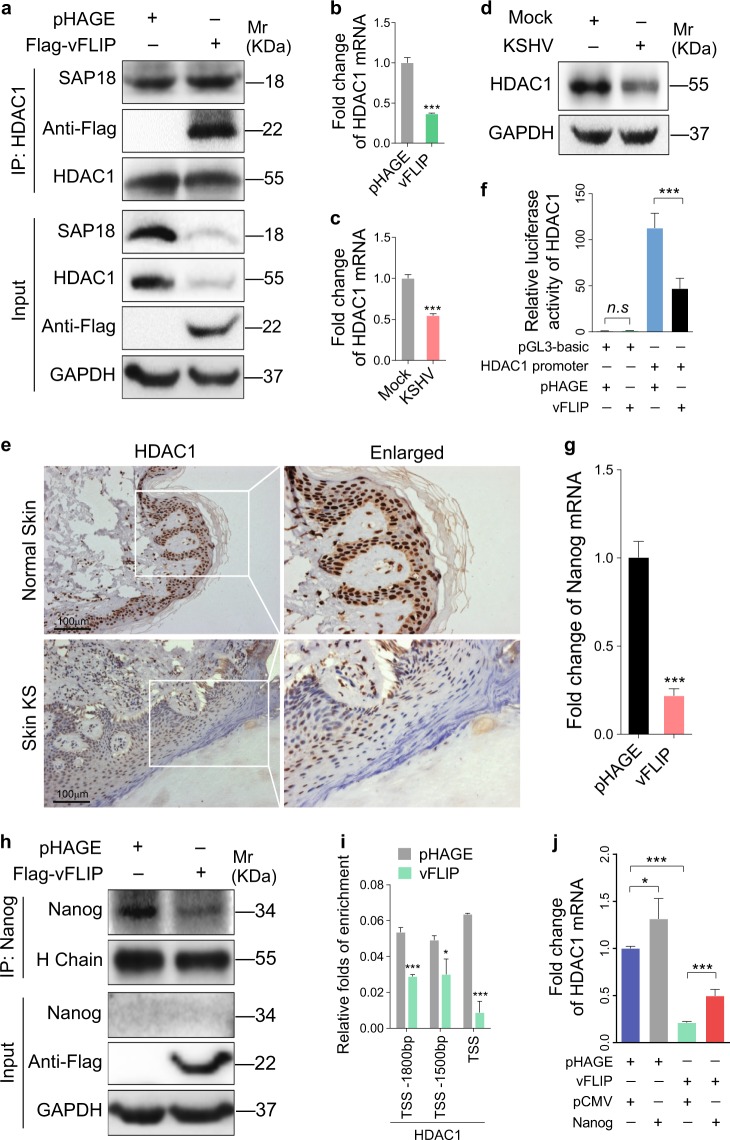
To elucidate the underlying mechanism of vFLIP promotion of endothelial cell motility, invasion, and angiogenesis, we examined vFLIP-induced differential expression of proteins by mass spectrometry analysis. Among the altered cellular proteins, we observed that SAP18, the component of histone deacetylase complex, was prominently downregulated (Table S1). We further validated the expression levels of SAP18 in vFLIP-transduced and KSHV-infected HUVECs by western blotting. We found that both ectopic expression of vFLIP and KSHV infection strongly inhibited the expression of SAP18 (Fig. 2a, b). Consistent with these observations, there were less SAP18-postive cells in KS lesion compared with the normal skin tissue as shown by IHC staining (Fig. 2c, d).
Fig. 2.
vFLIP downregulates SAP18 expression to promote cell motility and angiogenesis. a Western blotting analysis of SAP18 in HUVECs transduced with lentiviral vFLIP or its control pHAGE with the indicated antibodies. b Western blotting analysis of SAP18 in KSHV-infected or PBS-treated (Mock) HUVECs with the indicated antibodies. c Histologic features of KS lesion tissues (lower) and normal skin tissues (upper) were presented by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining (×200), the expression levels of KSHV LANA and SAP18 in the tissues were examined by immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay (×200). d Results were quantified in (c) (***P < 0.001). e Western blotting analysis of SAP18 in lentiviral vFLIP- or control pHAGE-transduced HUVECs infected with lentiviral SAP18 (HA-SAP18) or its control pCDH (pCDH), respectively, with the indicated antibodies. f Cells treated as in (e) were subjected to transwell migration assay. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results. Three independent experiments, each with quantic technical replicates, were performed. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. g Cells treated as in (e) were subjected to Matrigel invasion assay. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results. Three independent experiments, each with quantic technical replicates, were performed. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. h Cells treated as in (e) were subjected to microtubule-formation assay. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results. Three independent experiments, each with quantic technical replicates, were performed. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. i Cells treated as in (e) were mixed with the high concentration Matrigel, and further inoculated onto CAMs to examine in vivo angiogenesis capability. The angiogenesis index on CAM model was quantified, and data are represented as mean ± s.d. Each group with at least five tumors. j The mixture containing high concentration Matrigel and cells treated as in (e) was injected into nude mice. The level of hemoglobin in plug tissues treated was measured by comparing the standard curve. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results, with at least five tumors for each group
We next transduced vFLIP-expressing HUVECs with lentiviral SAP18 to determine whether downregulation of SAP18 was required for vFLIP promotion of endothelial cell motility, invasion, and angiogenesis. Overexpression of SAP18 significantly inhibited vFLIP-induced endothelial cell migration and invasion (Fig. 2e–g, Figure S2). Consistently, overexpression of SAP18 impeded vFLIP-induced angiogenesis both in vitro (Fig. 2h; Figure S3) and in vivo (Fig. 2i, j).
Taken together, these results indicated that downregulation of SAP18 is required for vFLIP promotion of endothelial cell motility, invasion, and angiogenesis.
vFLIP recruits E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM56 to degrade SAP18
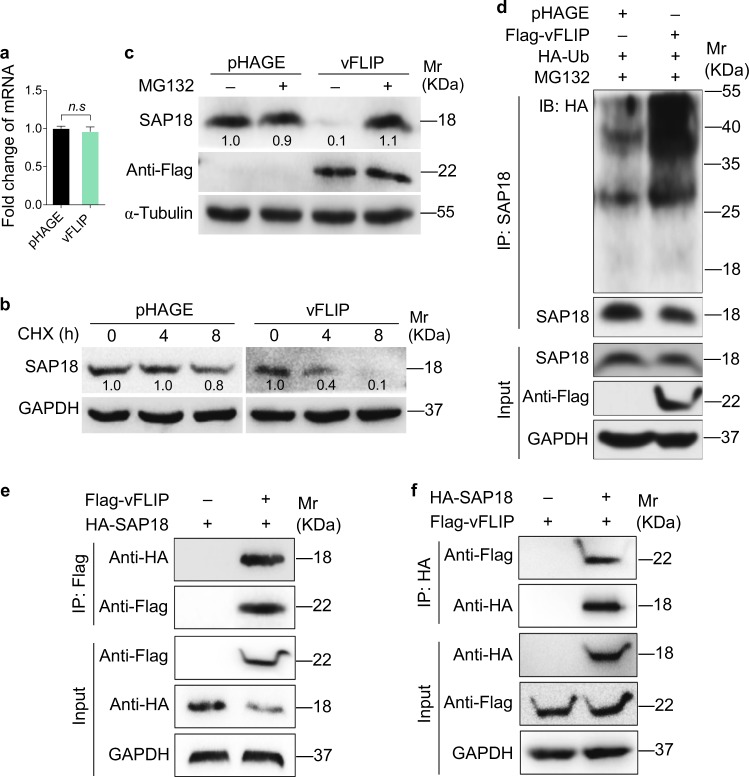
To explore the molecular mechanism by which vFLIP downregulated SAP18 expression, we examined SAP18 mRNA level in vFLIP-expressing HUVECs. We found that ectopic expression of vFLIP did not alter SAP18 mRNA level (Fig. 3a). We further determined whether vFLIP might reduce SAP18 protein level by promoting its degradation. We examined SAP18 degradation in the presence of cycloheximide (CHX), a de novo protein biosynthesis inhibitor. vFLIP-expressing HUVECs exhibited an increased SAP18 degradation rate than the control group in the presence of CHX (Fig. 3b), indicating that vFLIP accelerated SAP18 protein degradation. Since the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway is the most ubiquitous way for protein degradation, we treated the cells with the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway inhibitor MG132. We found that MG132 inhibited vFLIP induction of SAP18 degradation (Fig. 3c), indicating that vFLIP mediated SAP18 degradation via the proteasome-dependent pathway. Furthermore, we detected more polyubiquitinated SAP18 with and without overexpressing exogenous ubiquitin and K48-linked ubiquitin in vFLIP-overexpressing cells than the control cells (Fig. 3d, Figure S4a). We generated SAP18 mutants by replacing Lys with Arg and then examined their expression and ubiquitination by transfecting these mutants together with vFLIP, respectively. We found that overexpression of vFLIP did not induce the degradation of SAP18_102KR (Figure S4b), and the ubiquitination of SAP18_102KR was attenuated compared with that of wild type SAP18 (Figure S4c). Co-immunoprecipitation assay showed that vFLIP directly interacted with SAP18 (Fig. 3e, f).
Fig. 3.
vFLIP degrades SAP18 through ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. a RT-qPCR was performed to examine the mRNA level of SA18 in HUVECs transduced with lentiviral vFLIP and its control pHAGE. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. (n.s., not significant). b Lentiviral pHAGE- and vFLIP-transduced HUVECs were treated with CHX (20 μg/ml) for 0 h, 4 h, and 8 h. Cells were lysed and then subjected to western blotting with indicated antibodies to monitor the stability of SAP18 protein. c Lentiviral pHAGE- and vFLIP-transduced HUVECs were treated with MG132 (20 μM) for 6 h and then subjected to western blotting with indicated antibodies to verify the SAP18 degradation pathway. d Lentiviral pHAGE- and vFLIP-transduced HUVECs were transfected with the HA-Ub construct, and then treated with MG132 (20 μM) for 6 h. Cells were subjected to anti-SAP18 immunoprecipitation assay (IP) for detection of SAP18 ubiquitination. e HUVECs were transfected with Flag-vFLIP construct alone, or co-transfected with HA-SAP18 construct. The interaction between vFLIP and SAP18 proteins was examined by immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody. f HUVECs were transfected with HA-SAP18 construct alone, or co-transfected with Flag-vFLIP construct. The interaction between vFLIP and SAP18 proteins was examined by immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibody
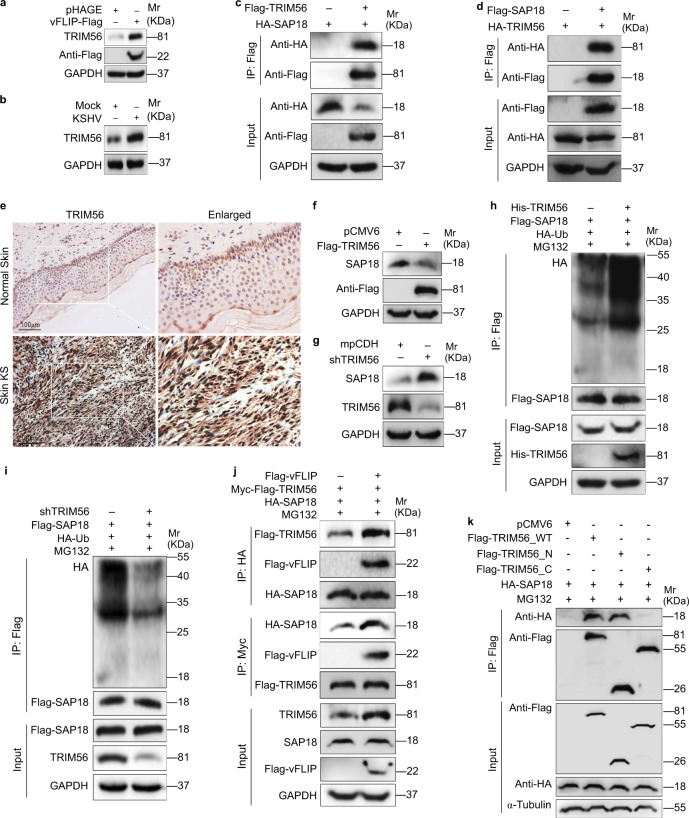
The critical step in the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway is the specific binding of E3 ubiquitin ligase to the substrate. Therefore, we performed Co-IP combined with mass spectrometry (MS) analysis to screen for the E3 ubiquitin ligase that might bind to SAP18. The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM56 was revealed to bind to SAP18 in three independent IP-MS experiments (Table S2). Ectopic expression of vFLIP led to increased levels of TRIM56 mRNA and protein (Fig. 4a, Figure S5a). KSHV infection also upregulated TRIM56 protein and mRNA (Fig. 4b, Figure S5b). Together, these results suggest that TRIM56 is a potential candidate that mediates vFLIP-induced degradation of SAP18. Co-IP assays indeed confirmed the interaction between SAP18 and TRIM56 (Fig. 4c, d). Importantly, there were more TRIM56-postive cells in KS lesions compared with the normal skin tissues as shown by IHC staining (Fig. 4e).
Fig. 4.
vFLIP increases and recruits TRIM56 to interact with and degrade SAP18. a Western blotting analysis of TRIM56 in HUVECs transduced with lentiviral vFLIP and its control pHAGE. b Western blotting analysis of TRIM56 in HUVECs infected with KSHV and its control PBS (Mock). c HUVECs were transfected with HA-SAP18 construct alone, or co-transfected with Flag-TRIM56 construct. The interaction between TRIM56 and SAP18 proteins was examined by immunoprecipitating with anti-Flag antibody. d HUVECs were transfected with HA-TRIM56 construct alone, or co-transfected with Flag-SAP18. The interaction between TRIM56 and SAP18 proteins was examined by immunoprecipitating with anti-Flag antibody. e The expression levels of TRIM56 in KS lesions and normal tissues were examined by immunohistochemistry assay (×200). f Western blotting analysis of SAP18 in HUVECs transfected with TRIM56 or its control pCMV6. g Western blotting analysis of SAP18 in HUVECs transduced with TRIM56 shRNA pool or its control mpCDH. h The HA-Ub and Flag-SAP18 plasmids were co-transfected with or without His-TRIM56 into HUVECs. The ubiquitinated SAP18 was detected by immunoprecipitating with anti-Flag antibody. i The HA-Ub and Flag-SAP18 plasmids were co-transduced with or without TRIM56 shRNA pool in HUVECs. The ubiquitinated SAP18 was detected by immunoprecipitating with anti-Flag antibody. j Immunoprecipitation analysis was adopted to examine the effect of vFLIP on the interaction between TRIM56 and SAP18 proteins. Cells were incubated with 20 μM MG132 for 6 h before immunoprecipitating the taq of TRIM56 or SAP18. k TRIM56_N and TRIM56_C were generated and used to examine the TRIM56-binding region with SAP18 by immunoprecipitation
Next, we investigate the effect of TRIM56 on SAP18 expression in HUVECs, and found that overexpression of TRIM56 effectively downregulated SAP18 protein level (Fig. 4f), while knockdown of TRIM56 by using shRNAs increased the protein level of SAP18 (Fig. 4g, Figure S6). To verify TRIM56 modulation of SAP18 ubiquitination, we immunoprecipitated Flag-SAP18 in TRIM56-overexpressed and TRIM56-knocked down cells. The results revealed that TRIM56 promoted SAP18 ubiquitination (Fig. 4h, i). We further investigated whether vFLIP regulated the interaction between TRIM56 and SAP18. We found that vFLIP enhanced the interaction of TRIM56 and SAP18 by Co-IP assay (Fig. 4j). This observation might explain why vFLIP facilitated TRIM56-mediated degradation of SAP18. It is known that the RING-finger domain of E3 ligase transfer ubiquitin directly from E2 to the substrate. Since TRIM56 is a RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase and the RING finger is located at 8-214 aa according to NCBI annotation, we constructed the TRIM56-N (1–250 aa) and TRIM56-C (251–755 aa) plasmids to verify whether the TRIM56 RING domain is responsible for SAP18 interaction. We co-transfected SAP18 with TRIM56_WT or TRIM56_N or TRIM56_C in 293T cells. As expected TRIM56_N bound to SAP18 (Fig. 4k), indicating that TRIM56 RING domain was critical for SAP18-binding. These results collectively indicated that vFLIP increased the expression of TRIM56 and further recruited TRIM56 to SAP18 to promote its degradation via the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway.
vFLIP decreases HDAC1 by downregulating transcript factor Nanog
It has been reported that SAP18 interacts with histone deacetylases HDAC1 and the mammalian transcriptional repressor Sin3 (mSin3) to form a complex, which regulates gene transcription [28]. Co-immunoprecipitation assay showed that SAP18 could interact with HDAC1 in vFLIP-expressing HUVECs (Fig. 5a). Intriguingly, ectopic expression of vFLIP not only downregulated SAP18 but also inhibited the expression of HDAC1 at both mRNA and protein levels (Fig. 5a, b). KSHV infection also downregulated HDAC1 expression (Fig. 5c, d). Furthermore, there were less HDAC1-postive cells in KS lesions compared with the normal skin tissues (Fig. 5e). In line with these observations, we found that the activity of HDAC1 promoter was dramatically repressed by vFLIP (Fig. 5f). Nanog has been reported as a transcription factor that promotes HDAC1 transcription via promoter occupancy [29]. We speculated that vFLIP might inhibit HDAC1 transcription through regulating Nanog. As expected, ectopic expression of vFLIP decreased Nanog mRNA and protein (Fig. 5g, h). ChIP-qPCR results revealed that vFLIP suppressed HDAC1 transcription by releasing Nanog from HDAC1 promoter (Fig. 5i). Overexpression of Nanog attenuated vFLIP suppression of HDAC1 (Fig. 5j). Together these data suggested that vFLIP downregulated HDAC1 transcription by inhibiting the expression of its transcriptional activator Nanog.
Fig. 5.
vFLIP decreases HDAC1 by downregulating Nanog. a The interaction between HDAC1 and SAP18 was examined by immunoprecipitating with anti-HDAC1 antibody in vFLIP and pHAGE-transduced HUVECs. Western blotting was adopted to detect HDAC1 and SAP18 with indicated antibodies. b RT-qPCR was performed to examine HDAC1 mRNA in vFLIP and pHAGE-transduced HUVECs. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. (***P < 0.001). c RT-qPCR was performed to examine HDAC1 mRNA in HUVECs infected with KSHV and its control PBS (Mock). Data are shown as mean ± s.d. (***P < 0.001). d Western blotting analysis of HDAC1 in KSHV-infected HUVECs. e The expression levels of HDAC1 in KS lesion and normal tissues were examined by immunohistochemistry assay (×200). f HEK293T cells were transfected with vFLIP or its control pHAGE, together with pGL-Basic-HDAC1 promoter. pRL-TK plasmids were also transfected into HEK293T cells to normalize the values of luciferase activity. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. (n.s., not significant, ***P < 0.001). g RT-qPCR was employed to examine Nanog mRNA level in vFLIP and pHAGE-transduced HUVECs. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. (***P < 0.001). h Western blotting and immunoprecipitation analysis with indicated antibodies were performed to analyze the protein level of Nanog in HUVECs transduced with lentiviral vFLIP and its control pHAGE. i ChIP assays were performed in vFLIP- and pHAGE-transfected HUVECs. HDAC1 promoter fragments which bind to Nanog were immunoprecipitated with anti-Nanog antibodies. Immunoprecipitated DNA was purified and amplified for HDAC1 promoter with specific primers which are listed in the Table S4. j The expression of HDAC1 was examined by RT-qPCR analysis in vFLIP and Nanog co-overexpressed HUVECs. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001)
vFLIP decreases SAP18 and HDAC1 complex resulting in enhancement of acetylation of p65 subunit and NF-κB activation
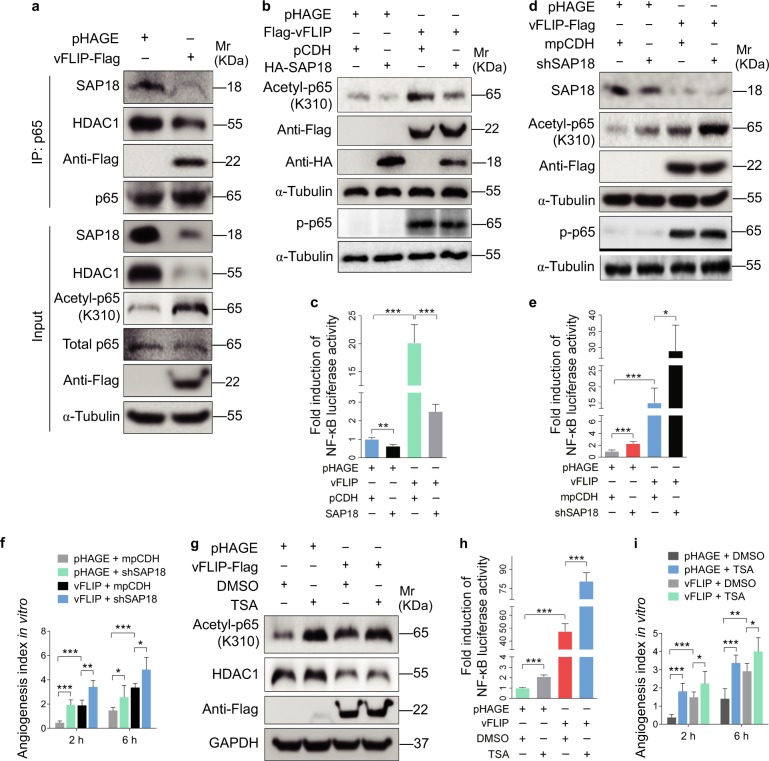
It has been reported that HDAC1 can directly interact with the Rel/p65 subunit of NF-κB to exert its corepressor function [30, 31]. We performed Co-IP assay to examine whether SAP18/HDAC1 complex is associated with the p65 of NF-κB. We found that the p65 subunit could indeed interact with SAP18/HDAC1 complex and vFLIP markedly suppressed the interaction of p65 with SAP18 and HDAC1 (Fig. 6a). Because HDAC1 bound to p65 to deacetylate its lysine K310, resulting in suppression of p65 transcriptional activity [30–35], we examined the acetylation level of p65. Indeed, the K310 acetylation level of p65 subunit was dramatically increased by vFLIP transduction (Fig. 6a). Meanwhile, overexpression of vFLIP facilitated endogenous association of TRIM56 and SAP18-HDAC1 complex in the presence of MG132 (Figure S7). Overexpression of SAP18 not only downregulated acetylated p65, but also inhibited NF-κB reporter activity in vFLIP-expressing HUVECs (Fig. 6b, c). Furthermore, knockdown of SAP18 enhanced vFLIP-induced p65 acetylation and NF-κB activity (Fig. 6d, e, Figure S8a), thus promoting endothelial cell motility, invasion, and angiogenesis in vFLIP-transduced HUVECs (Fig. 6f, Figures S8b and 8c). However, SAP18 had no effect on p65 phosphorylation (Fig. 6b, d). Treatment with HDAC1 inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA) not only increased p65 acetylation and activated NF-κB activity (Fig. 6g, h) but also increased the vFLIP-induced cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis (Fig. 6i, Figure S9a and S9b).
Fig. 6.
vFLIP decreases SAP18 and HDAC1 complex to promote cell motility and angiogenesis by enhancing acetylation of p65 subunit and NF-κB activation. a The interaction between p65 subunit and SAP18, or p65 subunit and HDAC1 was examined by immunoprecipitating with anti-p65 antibody in vFLIP and pHAGE-transduced HUVECs. Western blotting was adopted to examine SAP18, HDAC1, and acetylated p65 with indicated antibodies. b Western blotting analysis of acetylated and phosphorylated p65 in lentiviral vFLIP (Flag-vFLIP)- or its control pHAGE-infected HUVECs, followed by transduction with lentiviral SAP18 (HA-SAP18) or its control pCDH (pCDH), respectively, with the indicated antibodies. c NF-κB activity was assessed by using NF-κB reporter luciferase plasmid in HUVECs transfected with pHAGE or vFLIP plasmid, together with pCDH or SAP18 plasmid. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. (**P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001). d Lentiviral vFLIP-transduced HUVECs were transduced with lentivirus expressing a mixture of shRNA1 and shRNA2 that target SAP18. Cells were subjected to western blotting for examination of acetylated and phosphorylated p65, SAP18. e NF-κB activity was assessed by using NF-κB reporter luciferase plasmid in HUVECs treated as in (d). Data are shown as mean ± s.d. (*P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001). f Microtubule-formation assay was adopted in cells treated as in (d). Data are represented as mean ± s.d. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001). g Western blotting analysis of acetylated p65 level in lentiviral vFLIP-transduced HUVECs treated with HDAC inhibitor TSA or DMSO. h NF-κB activity was measured in cells as treated in (g). Data are shown as mean ± s.d. (***P < 0.001). i The in vitro angiogenesis capability was examined by microtubule-formation assay in cells treated as in (g). Data are represented as mean ± s.d. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001)
Taken together, these results collectively demonstrated that vFLIP promoted acetylation of p65 subunit and activated NF-κB signaling by suppressing the SAP18 and HDAC1 complex, resulting in enhanced endothelial cell motility, invasion, and angiogenesis.
Deletion of vFLIP gene attenuates cell motility, invasion, and angiogenesis induced by KSHV
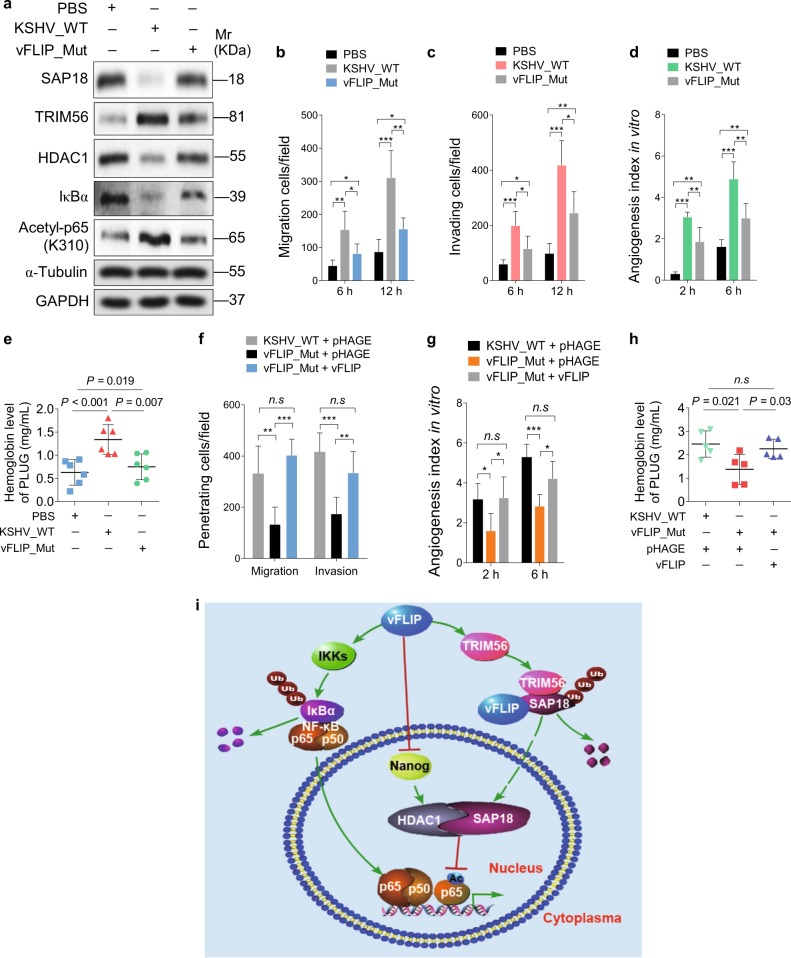
To further confirm that vFLIP induced endothelial cell motility, invasion, and angiogenesis during KSHV infection, we infected HUVECs with a BAC16 vFLIP_mut virus with K13 deleted from the KSHV genome [13]. We found that KSHV infection downregulated SAP18, HDAC1, and IκBα, and upregulated TRIM56 and acetylated p65 (Fig. 7a), which were consistent with the results of single gene expression (Figs. 2b, 4b, and 5d). As expected, infection of vFLIP_mut virus increased the levels of SAP18, HDAC1, and IκBα, and decreased the levels of TRIM56 and acetylated p65 compared with KSHV_WT infection (Fig. 7a). More importantly, deletion of vFLIP attenuated KSHV-induced cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis (Fig. 7b–e). To examine whether overexpression vFLIP could rescue the reduced cell motility, invasion, and angiogenesis of the K13 mutant, we transduced vFLIP into vFLIP_mut virus-infected cells. Ectopic vFLIP significantly rescued vFLIP_mut virus-mediated cell motility, invasion, and angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo (Fig. 7f–h).
Fig. 7.
Lack of vFLIP restrains cell invasion and angiogenesis induced by KSHV. a Western blotting was performed with indicated antibodies to detect SAP18, TRIM56, HDAC1, IκBα, and acetylated p65 HUVECs treated with PBS (PBS), infected with wild-type KSHV (KSHV_WT) or vFLIP mutant virus (vFLIP-Mut). b Cells treated as in (a) were subjected to transwell migration assay. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001). c Cells treated as in (a) were subjected to Matrigel invasion assay. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001). d Cells treated as in (a) were subjected to microtubule-formation assay. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results. (**P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001). e Cells treated as in (a) were adopted to Matrigel plug assay in mice. The level of hemoglobin in plug tissues treated was measured by comparing the standard curve. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results, with six tumors for each group. f Transwell migration and Matrigel invasion assays were performed in HUVECs infected with wild-type KSHV or vFLIP mutant virus, followed by transduction of lentiviral vFLIP at 12 h post-seeding. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results (n.s., not significant, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001). g Cells treated as in (f) were subjected to microtubule-formation assay. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results (n.s., not significant, *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001). h Cells treated as in (f) were adopted to Matrigel plug assay in mice. The level of hemoglobin in plug tissues treated in (f) was measured by comparing the standard curve. Mean ± s.d. is adopted to quantify the results, with five tumors for each group. i Schematic illustration for the mechanism of vFLIP-induced endothelial cell motility and angiogenesis. During KSHV latent infection, vFLIP recruits E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM56, leading to the ubiquitination and degradation of SAP18. Meanwhile, vFLIP inhibits HDAC1 promoter by suppressing transcription factor Nanog, resulting in downregulation of HDAC1. The decreased SAP18/HDAC1 complex enhances acetylation of p65 subunit and activates the NF-κB signal pathway
Discussion
SAP18 was first identified by immunopurification of mammalian Sin3 (mSin3)-associated proteins; it was further demonstrated to be a component of the Sin3-HDAC1 complex, which enhanced Sin3-mediated repression of transcription [28]. It is now well-recognized that the SAP18/Sin3/HDAC1 complex acts as a transcriptional repressor and that its function is regulated by several proteins. For instance, tribbles homolog 1 (TRIB1) recruits mSin3A to microsomal TG transfer protein (MTTP) regulatory elements through associating with SAP18, and promotes MTTP expression to further regulate blood lipid levels [36]. Furthermore, SAP18 utilizes its ubiquitin-like domain to assemble RNA splicing regulatory proteins, including RNPS1 (RNA-binding protein prevalent during the S phase) and acinus, forming apoptosis and splicing-associated protein (ASAP) complex, which is involved in the regulation of both RNA splicing and apoptosis [37, 38]. Finally, SAP18 in ASAP complex cooperates with HDAC1 to inhibit transcriptional activity and has a potent effect on splicing regulation [39].
Previous studies have shown that KSHV vFLIP activates the canonical and noncononical NF-κB pathways. In this study, we have shown that vFLIP markedly downregulates SAP18 to promote endothelial cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis. Mechanically, vFLIP represses SAP18 via the TRIM56-dependent ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. TRIM56 termed as tripartite-motif-containing protein 56, predominantly participated in the process of antiviral immunity and tumorigenesis using its RING domain and C-terminal structure [40, 41]. The RING domain conferred TRIM56 the E3 ligase activity, while its C-terminal structure affected the interaction between TRIM56 and multiproteins. In terms of antiviral immunity, TRIM56 bound TLR3 ligands TRIF, cGAS, and STING, respectively, activating the TLR3 and cGAS-STING signaling pathway to promote IFN response [42–45]. TRIM56 bound substrate proteins such as NEMO and vimentin for ubiquitin-mediated degradation, regulating NF-κB activation and tumor progression [46, 47]. Herein, our study has demonstrated that, by serving as a scaffold protein, vFLIP upregulates TRIM56 and promotes TRIM56 to bind substrate protein SAP18. TRIM56 subsequently exerts its function as an E3 ligase for SAP18 degradation, resulting in activation of the NF-κB pathway. Importantly, besides in lentiviral vFLIP-transduced HUVECs, TRIM56 is also increased in KSHV-infected HUVECs and KS tissues, however, the precise mechanism remains unknown.
Nanog is a transcription factor involved in the self-renewal of embryonic stem cells (ES) and a critical factor for the maintenance of the undifferentiated state of pluripotent cells, such as cancer stem cells (CSCs) and ES. Nanog can function as an epigenetic regulator to promote transcription activity of HDAC1 via promoter occupancy [29]. In line with this report, we have revealed that vFLIP impairs the occupancy of Nanog to HDAC1 promoter through downregulating Nanog. It is worth mentioning that Nanog is expressed at a lower level in the native cells of adult organisms [48], therefore, we have examined its protein using immunoprecipitation rather than western blotting (Fig. 5h).
As an epigenetic modifier, HDAC1 exerts transcriptional repression by regulating the deacetylation of histones [49]. HDAC1 presented in several multiprotein repressor complexes including Sin3, NuRD, and N-CoR/SMRT, of which the Sin3-HDAC1 complex is the most common repressor complex. For instance, HIV-1 integrase and host factor INI1/hSNF5 associate with SAP18 and selectively recruit Sin3-HDAC1 complex to facilitate the infection and replication of HIV-1 [50]. Inhibition of deacetylase activity of HDAC1 impairs the phosphorylation of STAT1 and the expression of IFITM3 and ISG15, thus repressing influenza A virus (IAV) infection [51]. In this study, we revealed that the expression of HDAC1 was suppressed by ectopic expression of vFLIP and KSHV infection. We also detected a lower level of HDAC1 in KS lesions compared with normal control tissues. vFLIP inhibited the promoter activity of HDAC1 indicating a transcriptional regulation. HDAC1 is considered as an oncogenic protein and HDAC inhibitors exert anticancer activity [52]. However, it has been reported that IAV and human papillomavirus virus 16 (HPV16) negatively regulate HDAC1 expression [53, 54], which are in line with our current study. These results suggest that HDAC1 may play a different role in the pathogenesis of virus-induced cancers and other cancers.
vFLIP is known to interact with IKKγ/NEMO to phosphorylate IκBa, leading to translocation of phosphorylated p65 to the nucleus and activation of the NF-κB pathway [12]. HDAC1 has been reported to inactivate NF-κB signaling by binding and deacetylating p65 [30, 31]. Acetylation of p65, like its phosphorylation, is important for the nuclear function of NF-κB [32–35]. In fact, the acetylation of lysine(K) 310 of the p65 subunit is required for full transactivation by NF-κB complex [32]. The effect of HDAC1 on p65 could be enlarged by co-repressors, such as LZAP and BRMS1, respectively [55, 56]. In this study, our results have revealed another mechanism by which vFLIP activates the NF-κB pathway. By suppressing the SAP18/HDAC1 complex, vFLIP attenuates the associations between p65 and SAP18/HDAC1 complex, resulting in enhancement of the p65 acetylation and NF-κB activation.
In conclusion, following KSHV infection, vFLIP is constitutively expressed during latency and might serve as a scaffold protein to assemble E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM56 to SAP18. Meanwhile, vFLIP downregulates HDAC1, a protein partner of SAP18, by suppressing Nanog for HDAC1 promoter occupancy. The impaired SAP18 and HDAC1 further mediates vFLIP-induced NF-κB activation by enhancing p65 acetylation (Fig. 7i). Our findings illustrate a novel mechanism of vFLIP activation of the NF-κB pathway, hence demonstrating the significance of vFLIP and its regulatory proteins and pathways in the pathogenesis of KSHV-associated cancers, and providing potential therapeutic targets for KSHV-induced cancers.
Materials and methods
Cell lines and reagents
Primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were isolated from the umbilical cord of healthy newborn fetuses delivered by cesarean section and isolated under aseptic conditions [57]. The isolated HUVECs were cultured in complete EBM-2 media (LONZA, USA). The HUVECs used in this study ranged from passage 3 to passage 6. The culture conditions of HEK293T were previously described [58]. Effectence transfection reagent (Qiagen) and LipofectamineTM 2000 (Invitrogen) were used for transfection of HUVECs and HEK293T cells, respectively. Cycloheximide (CHX) and HDAC inhibitor TSA were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, while MG132, a proteasome inhibitor was obtained from Selleck Chemicals. Anti-flag affinity gel, protein A/G, anti-HA, and anti-myc Immunomagnetic beads were from Bimake.
Lentivirus packaging and infection
The packaging plasmid, psPAX2, together with the envelope plasmid, pMD2.G, and the lentivirus plasmids were co-transfected into pre-inoculated HEK293T cells as previously described [20]. Lentivirus was collected and used to infect HUVECs. The infection efficiency was monitored at 48 to 72 h post infection, and the infected cells were collected at the indicated time points for further analyses.
Generation of KSHV_WT and K13_mutant recombinant virus
KSHV_WT and vFLIP_mutant constructs were previously described [13, 59]. The production of KSHV_WT virus and vFLIP_mutant virus were induced by sodium butyrate and doxycycline as previously described [59].
Cycloheximide (CHX) and MG132 treatments
To monitor the protein stability, each group of cells were treated with 20 μg/ml CHX for 0 h, 4 h, and 8 h. The proteasome inhibitor MG132 was also incubated with cells at 20 μM for 6 h. Cells were collected for further validation after CHX and MG132 treatments.
Knockdown of SAP18 and TRIM56
The short hairpin RNAs (shRNA) targeting SAP18 and TRIM56 were designed and then inserted into lentiviral vector mpCDH, which was modified according to pCDH-CMV-MCS-EF1-copGFP plasmid [22]. SAP18 and TRIM56 silenced plasmids were subjected to lentivirus packaging and infection. The complementary sequences of shRNA were shown in Table S3.
Western blotting and antibodies
Western blotting was performed as previously described [60]. Briefly, cellular protein was extracted and separated by SDS-PAGE, and transferred to the PVDF membrane. The membranes were blocked and incubated with specific primary antibodies to examine each protein. Anti-GAPDH, anti-HA, anti-Flag, anti-IκBα, anti-Ub, anti-VEGF, and anti-basic FGF (b-FGF) were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Antibodies against SAP18, HDAC1, NF-κB p65 (acetylation K310), TRIM56, and Nanog were supplied by Abcam. Anti-NF-κB p65 antibody and anti-K48-Ub was from Cell Signaling Technology. Anti-KSHV LANA rat antibody was purchased from Advanced Biotechnologies Inc. (Columbia, MD, USA). Anti-His and anti-GST antibodies were from Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology (Nantong, Jiangsu, China). Anti-smooth muscle actin (SMA) rabbit antibody was purchased from Abbiotec TM (San Diego, CA, USA). The blots incubated with secondary antibodies were further developed by ECL.
RNA extraction and RT-qPCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted with TRIzol (Invitrogen) followed by the manufacturer's instructions, and subsequently was reverse-transcribed (RT) into cDNA. RT-qPCR analysis was performed to detect the expression level of mRNA as previously described [61]. qPCR primers for specific gene amplification were listed in Table S4. HiScript II Q RT SuperMix for qPCR and AceQ qPCR SYBR Green Master Mix were purchased from Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd.
Luciferase reporter assay and transfection
The HEK293T cells were transfected with HDAC1 promoter reporter or NF-κB reporter. To normalize transfection efficiency, renilla vector pRL-TK was co-transfected into HEK293T cells using LipofectamineTM 2000 transfection regent. Relative luciferase activity of firefly and Renilla was measured through the dual-luciferase reporter assay according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Dual-Luciferase® Reporter Assay System was purchased from Promega.
IHC analysis
The KS lesion tissues and normal skin tissues adopted in this study were offered by The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. The application of the clinical specimens for H&E staining and IHC analysis was approved by the Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. All the paraffin-embedded histological sections were deparaffinized, and incubated with specific antibodies following standard methodology.
Transwell migration and Matrigel invasion assays
Transwell migration and Matrigel invasion assays were performed as previous described [21–23]. The chambers were coated with 60 μL of diluted Matrigel. Cells were seeded into upper chambers, and placed in culture incubators under the condition of 37 ℃ and 5% CO2. At 6 h and 12 h post-seeding, cells which migrated to underside of the chamber were fixed with methanol, stained with crystal violet, and counted following double-blinded principle.
Microtubule-formation assay
Microtubule-formation assay was performed as previously described [20, 24]. A total of 15 μL of Matrigel was spread on the ibiTreat plate (ibidi). After the Matrigel was coagulated, 7 × 103 cells were plated on the Matrigel. The number of sprouted cells, connected cells, and polygonal cells were counted by Image J.
Chicken chorioallantoic membranes (CAMs) assay
The specific pathogen-free chick embryos were used for CAM assay as previously described [25, 26]. Briefly, artificial gas chambers were created avoiding blood vessels on chicken eggs. The cells were mixed with a high concentration of Matrigel and further injected onto CAMs of 9-day-old embryos via the artificial gas chambers. The CAMs were harvested, photographed, and counted to monitor blood vessels at 4 days post-implantation. All statistical processes followed the double-blinded principle.
Matrigel plug assay
Male BALB/c nude mice (4-week-old) were chosen for Matrigel plug assay as previously described [20]. All animal studies were performed in accordance with Laboratory Animal Management Regulations, and were approved by Nanjing Medical University Experimental Animal Welfare Ethics Committee. The cells containing a high concentration of Matrigel were then subcutaneously injected into the flanks of mice. The Matrigel plug tissues were harvested and photographed after 10 days. The hemoglobin content in the plug tissues was detected with Drabkin's reagent kit.
Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) and mass spectrometry (MS)
Co-IP assay was executed according to the standard protocol for detecting protein–protein interactions. The IP lysis/wash buffer containing protein inhibitor cocktail was employed to collect protein lysates, which were then centrifuged and incubated with 10 μL of anti-HA or anti-myc immunomagnetic beads, or anti-Flag gel for overnight at 4 ℃. To identify binding proteins, the beads were washed and eluted for MS analysis (Shanghai Applied Protein Technology Co., Ltd.) on Q Exactive mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) or western blotting.
Chromosome immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
ChIP assay was performed following the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, the anti-Nanog antibody immunoprecipitated DNA was obtained by eluting the magnetic beads with ChIP elution buffer, and was purified for analysis using the HDAC1 promoter-specific primers through RT-qPCR. Meanwhile, anti-RNA polymerase II antibody, served as positive control, were applied into ChIP assay and detected by GAPDH promoter primers. The sequences of HDAC1 promoter primers were provided in Table S4.
Statistical analysis
All statistical results are presented as mean ± s.d. Two-tailed Student’s t test was adopted to analyze differences and associations among varied groups. P-value < 0.05 represented statistically significant. All the experiments were repeated at least for three times, unless otherwise stated.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to members from Dr. Lu laboratory for helpful discussion. This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81730062, 81761128003, 31800148 and 81871642), grants from NIH (R01CA213275, R01CA177377 and R01CA132637), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (18KJB310004), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20180084) and Nanjing Medical University (KY101RC1710).
Author contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: CL. Performed the experiments: XD, JX, CW, QF, QW, YY, FW and KZ. Providing reagents: HL. Analyzed the data: CW, WL, QY, SJG and CL. Wrote the paper: XD, JX, SJG and CL.
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally to this work: Xiangya Ding, Jingyun Xu, Cong Wang
Edited by H. Ichijo
Supplementary information
The online version of this article (10.1038/s41418-018-0268-3) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
References
- 1.Mesri EA, Cesarman E, Boshoff C. Kaposi's sarcoma and its associated herpesvirus. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:707–19. doi: 10.1038/nrc2888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Giffin L, Damania B. KSHV: pathways to tumorigenesis and persistent infection. Adv Virus Res. 2014;88:111–59. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800098-4.00002-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cheung TW. AIDS-related cancer in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART): a model of the interplay of the immune system, virus, and cancer. "On the offensive--the Trojan Horse is being destroyed"--Part A: Kaposi's sarcoma. Cancer Invest. 2004;22:774–86. doi: 10.1081/CNV-200032788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hayden MS, Ghosh S. NF-kappaB, the first quarter-century: remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev. 2012;26:203–34. doi: 10.1101/gad.183434.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.de Oliveira DE, Ballon G, Cesarman E. NF-kappaB signaling modulation by EBV and KSHV. Trends Microbiol. 2010;18:248–57. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2010.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Abere B, Schulz TF. KSHV non-structural membrane proteins involved in the activation of intracellular signaling pathways and the pathogenesis of Kaposi's sarcoma. Curr Opin Virol. 2016;20:11–9. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2016.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Seo T, Park J, Lim C, Choe J. Inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB activity by viral interferon regulatory factor 3 of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Oncogene. 2004;23:6146–55. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lei X, Bai Z, Ye F, Xie J, Kim CG, Huang Y, et al. Regulation of NF-kappaB inhibitor IkappaBalpha and viral replication by a KSHV microRNA. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:193–9. doi: 10.1038/ncb2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Konrad A, Wies E, Thurau M, Marquardt G, Naschberger E, Hentschel S, et al. A systems biology approach to identify the combination effects of human herpesvirus 8 genes on NF-kappaB activation. J Virol. 2009;83:2563–74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01512-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Guasparri I, Keller SA, Cesarman E. KSHV vFLIP is essential for the survival of infected lymphoma cells. J Exp Med. 2004;199:993–1003. doi: 10.1084/jem.20031467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 11.Guasparri I, Wu H, Cesarman E. The KSHV oncoprotein vFLIP contains a TRAF-interacting motif and requires TRAF2 and TRAF3 for signalling. EMBO Rep. 2006;7:114–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Liu L, Eby MT, Rathore N, Sinha SK, Kumar A, Chaudhary PM. The human herpes virus 8-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein physically associates with and persistently activates the Ikappa B kinase complex. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:13745–51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110480200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wang F, Guo Y, Li W, Lu C, Yan Q. Generation of a KSHV K13 deletion mutant for vFLIP function study. J Med Virol. 2018;90:753–60. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hunte R, Alonso P, Thomas R, Bazile CA, Ramos JC, van der Weyden L, et al. CADM1 is essential for KSHV-encoded vGPCR-and vFLIP-mediated chronic NF-kappaB activation. PLoS Pathog. 2018;14:e1006968. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Keller SA, Schattner EJ, Cesarman E. Inhibition of NF-kappaB induces apoptosis of KSHV-infected primary effusion lymphoma cells. Blood. 2000;96:2537–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Graham C, Matta H, Yang Y, Yi H, Suo Y, Tolani B, et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus oncoprotein K13 protects against B cell receptor-induced growth arrest and apoptosis through NF-kappaB activation. J Virol. 2013;87:2242–52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01393-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ballon G, Akar G, Cesarman E. Systemic expression of Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV) Vflip in endothelial cells leads to a profound proinflammatory phenotype and myeloid lineage remodeling in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1004581. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ye FC, Zhou FC, Xie JP, Kang T, Greene W, Kuhne K, et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latent gene vFLIP inhibits viral lytic replication through NF-kappaB-mediated suppression of the AP-1 pathway: a novel mechanism of virus control of latency. J Virol. 2008;82:4235–49. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02370-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Giffin L, West JA, Damania B. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus interleukin-6 modulates endothelial cell movement by upregulating cellular genes involved in migration. MBio. 2015;6:e01499–15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01499-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Xue M, Yao S, Hu M, Li W, Hao T, Zhou F, et al. HIV-1 Nef and KSHV oncogene K1 synergistically promote angiogenesis by inducing cellular miR-718 to regulate the PTEN/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:9862–79. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li W, Yan Q, Ding X, Shen C, Hu M, Zhu Y, et al. The SH3BGR/STAT3 pathway regulates cell migration and angiogenesis induced by a gammaherpesvirus MicroRNA. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:e1005605. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hu M, Wang C, Li W, Lu W, Bai Z, Qin D, et al. A KSHV microRNA directly targets G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 to promote the migration and invasion of endothelial cells by inducing CXCR2 and activating AKT signaling. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1005171. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li W, Hu M, Wang C, Lu H, Chen F, Xu J, et al. A viral microRNA downregulates metastasis suppressor CD82 and induces cell invasion and angiogenesis by activating the c-Met signaling. Oncogene. 2017;36:5407–20. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yao S, Hu M, Hao T, Li W, Xue X, Xue M, et al. MiRNA-891a-5p mediates HIV-1 Tat and KSHV Orf-K1 synergistic induction of angiogenesis by activating NF-kappaB signaling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:9362–78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhu X, Guo Y, Yao S, Yan Q, Xue M, Hao T, et al. Synergy between Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) vIL-6 and HIV-1 Nef protein in promotion of angiogenesis and oncogenesis: role of the AKT signaling pathway. Oncogene. 2014;33:1986–96. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhou F, Xue M, Qin D, Zhu X, Wang C, Zhu J, et al. HIV-1 Tat promotes Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) vIL-6-induced angiogenesis and tumorigenesis by regulating PI3K/PTEN/AKT/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2013;8:e53145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Grossmann C, Podgrabinska S, Skobe M, Ganem D. Activation of NF-kappaB by the latent vFLIP gene of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is required for the spindle shape of virus-infected endothelial cells and contributes to their proinflammatory phenotype. J Virol. 2006;80:7179–85. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01603-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhang Y, Iratni R, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Reinberg D. Histone deacetylases and SAP18, a novel polypeptide, are components of a human Sin3 complex. Cell. 1997;89:357–64. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Song KH, Choi CH, Lee HJ, Oh SJ, Woo SR, Hong SO, et al. HDAC1 upregulation by NANOG promotes multidrug resistance and a stem-like phenotype in immune edited tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2017;77:5039–53. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ashburner BP, Westerheide SD, Baldwin AS., Jr. The p65 (RelA) subunit of NF-kappaB interacts with the histone deacetylase (HDAC) corepressors HDAC1 and HDAC2 to negatively regulate gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:7065–77. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.20.7065-7077.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Liu Y, Smith PW, Jones DR. Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 functions as a corepressor by enhancing histone deacetylase 1-mediated deacetylation of RelA/p65 and promoting apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:8683–96. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00940-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chen LF, Mu Y, Greene WC. Acetylation of RelA at discrete sites regulates distinct nuclear functions of NF-kappaB. EMBO J. 2002;21:6539–48. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chen LF, Williams SA, Mu Y, Nakano H, Duerr JM, Buckbinder L, et al. NF-kappaB RelA phosphorylation regulates RelA acetylation. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:7966–75. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.18.7966-7975.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kiernan R, Bres V, Ng RW, Coudart MP, El Messaoudi S, Sardet C, et al. Post-activation turn-off of NF-kappa B-dependent transcription is regulated by acetylation of p65. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:2758–66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209572200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hoberg JE, Popko AE, Ramsey CS, Mayo MW. IkappaB kinase alpha-mediated derepression of SMRT potentiates acetylation of RelA/p65 by p300. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:457–71. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.2.457-471.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Makishima S, Boonvisut S, Ishizuka Y, Watanabe K, Nakayama K, Iwamoto S. Sin3A-associated protein, 18 kDa, a novel binding partner of TRIB1, regulates MTTP expression. J Lipid Res. 2015;56:1145–52. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M057802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Singh KK, Erkelenz S, Rattay S, Dehof AK, Hildebrandt A, Schulze-Osthoff K, et al. Human SAP18 mediates assembly of a splicing regulatory multiprotein complex via its ubiquitin-like fold. RNA. 2010;16:2442–54. doi: 10.1261/rna.2304410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Schwerk C, Prasad J, Degenhardt K, Erdjument-Bromage H, White E, Tempst P, et al. ASAP, a novel protein complex involved in RNA processing and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:2981–90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.8.2981-2990.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Deka B, Singh KK. Multifaceted regulation of gene expression by the apoptosis- and splicing-associated protein complex and its components. Int J Biol Sci. 2017;13:545–60. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.18649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ozato K, Shin DM, Chang TH, Morse HC., III TRIM family proteins and their emerging roles in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:849–60. doi: 10.1038/nri2413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wang J, Liu B, Wang N, Lee YM, Liu C, Li K. TRIM56 is a virus- and interferon-inducible E3 ubiquitin ligase that restricts pestivirus infection. J Virol. 2011;85:3733–45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02546-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chen Y, Zhao J, Li D, Hao J, He P, Wang H, et al. TRIM56 suppresses multiple myeloma progression by activating TLR3/TRIF signaling. Yonsei Med J. 2018;59:43–50. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shen Y, Li NL, Wang J, Liu B, Lester S, Li K. TRIM56 is an essential component of the TLR3 antiviral signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:36404–13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.397075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Seo GJ, Kim C, Shin WJ, Sklan EH, Eoh H, Jung JU. TRIM56-mediated monoubiquitination of cGAS for cytosolic DNA sensing. Nat Commun. 2018;9:613. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-02936-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tsuchida T, Zou J, Saitoh T, Kumar H, Abe T, Matsuura Y, et al. The ubiquitin ligase TRIM56 regulates innate immune responses to intracellular double-stranded DNA. Immunity. 2010;33:765–76. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fang R, Wang C, Jiang Q, Lv M, Gao P, Yu X, et al. NEMO-IKKbeta are essential for IRF3 and NF-kappaB activation in the cGAS-STING pathway. J Immunol. 2017;199:3222–33. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhao L, Zhang P, Su XJ, Zhang B. The ubiquitin ligase TRIM56 inhibits ovarian cancer progression by targeting vimentin. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:2420–5. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chang DF, Tsai SC, Wang XC, Xia P, Senadheera D, Lutzko C. Molecular characterization of the human NANOG protein. Stem Cells. 2009;27:812–21. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2008-0657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hassig CA, Tong JK, Fleischer TC, Owa T, Grable PG, Ayer DE, et al. A role for histone deacetylase activity in HDAC1-mediated transcriptional repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:3519–24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.7.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sorin M, Cano J, Das S, Mathew S, Wu X, Davies KP, et al. Recruitment of a SAP18-HDAC1 complex into HIV-1 virions and its requirement for viral replication. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000463. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Nagesh PT, Husain M. Influenza A virus dysregulates host histone deacetylase 1 That inhibits viral infection in lung epithelial cells. J Virol. 2016;90:4614–25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00126-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lakshmaiah KC, Jacob LA, Aparna S, Lokanatha D, Saldanha SC. Epigenetic therapy of cancer with histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014;10:469–78. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.137937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Buggele WA, Krause KE, Horvath CM. Small RNA profiling of influenza A virus-infected cells identifies miR-449b as a regulator of histone deacetylase 1 and interferon beta. PLoS One. 2013;8:e76560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Liu D, Zhou P, Zhang L, Zheng Y, He F. HPV16 activates the promoter of Oct4 gene by sequestering HDAC1 from repressor complex to target it to proteasomal degradation. Med Hypotheses. 2012;79:531–4. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2012.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wang J, An H, Mayo MW, Baldwin AS, Yarbrough WG. LZAP, a putative tumor suppressor, selectively inhibits NF-kappaB. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:239–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Cicek M, Fukuyama R, Cicek MS, Sizemore S, Welch DR, Sizemore N, et al. BRMS1 contributes to the negative regulation of uPA gene expression through recruitment of HDAC1 to the NF-kappaB binding site of the uPA promoter. Clin Exp Metastas- 2009;26:229–37. doi: 10.1007/s10585-009-9235-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Poon M, Zhang X, Dunsky KG, Taubman MB, Harpel PC. Apolipoprotein(a) induces monocyte chemotactic activity in human vascular endothelial cells. Circulation. 1997;96:2514–9. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.96.8.2514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Yan Q, Ma X, Shen C, Cao X, Feng N, Qin D, et al. Inhibition of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic replication by HIV-1 Nef and cellular microRNA hsa-miR-1258. J Virol. 2014;88:4987–5000. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00025-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Brulois KF, Chang H, Lee AS, Ensser A, Wong LY, Toth Z, et al. Construction and manipulation of a new Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus bacterial artificial chromosome clone. J Virol. 2012;86:9708–20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01019-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zeng Y, Zhang X, Huang Z, Cheng L, Yao S, Qin D, et al. Intracellular Tat of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activates lytic cycle replication of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: role of JAK/STAT signaling. J Virol. 2007;81:2401–17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02024-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hu H, Dong J, Liang D, Gao Z, Bai L, Sun R, et al. Genome-wide mapping of the binding sites and structural analysis of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus viral interferon regulatory factor 2 reveal that it is a dna-binding transcription factor. J Virol. 2016;90:1158–68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01392-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.