Figure 1.
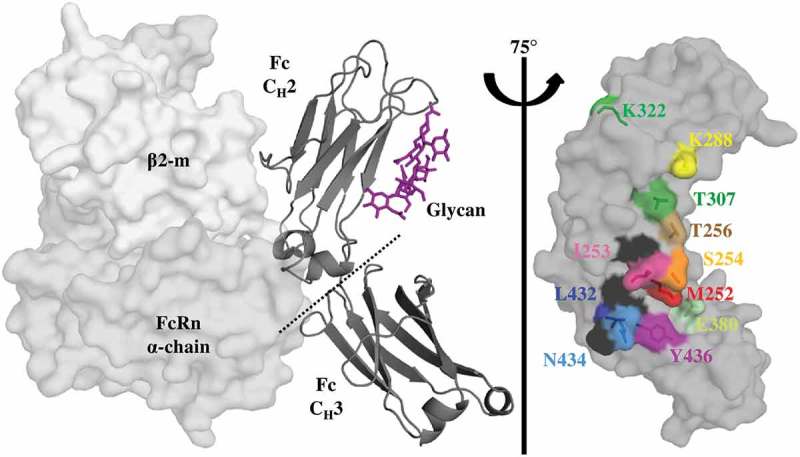
Key Residues at the Fc-FcRn Interface. Crystal structure (pdb: 4n0u) showing one Fc monomer and its glycosylation (dark gray ribbon), in complex with the α-domain (gray) and β2-m (light gray) hFcRn subunits. FcRn interacts with the Fc region at the CH2-CH3 interface with a pH-dependent affinity as a result of key surface histidine residues (black). The glycosylation of the CH2 domain is not required for FcRn binding. A saturation library of key residues was created at the Fc-FcRn interface and each position investigated in this study is shown as sticks and uniquely colored.
