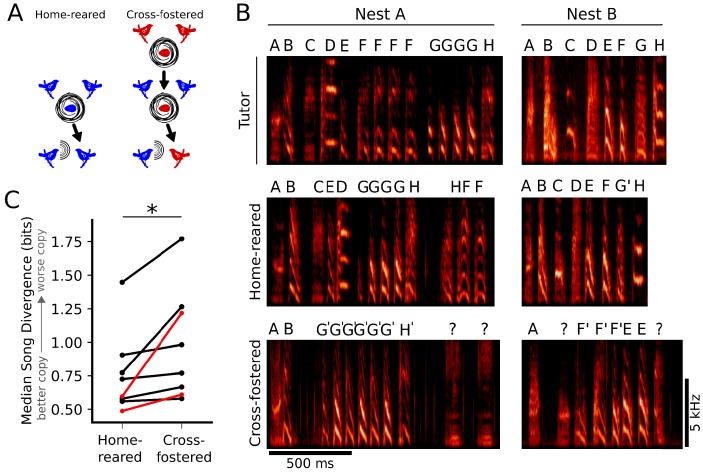
Figure 2. Learning outcomes are better when juveniles are tutored by their genetic fathers.
(A) Schematic representation of the experimental design. Parental pairs (middle row, blue birds) reared both their own genetic offspring (home-reared, left), and foster birds from different genetic backgrounds (cross-fostered, right). (B) Examples of learning outcomes for two nests. (B, top) Example songs from the resident male tutors in each nest. (B, middle, bottom) Example songs from birds that were either home-reared (B, middle) or cross-fostered (B, bottom) in nests where males sang the tutor songs indicated in B, top. The examples of learned songs are from birds that had the median Song Divergence (SD) scores for their cohort (home-reared or cross-fostered). Syllable labels are provided to facilitate comparisons, but do not reflect automated SD scores used to quantify song similarity. (C) Paired plot of median SD scores for home-reared and cross-fostered cohorts. Across eight nests, birds that were home-reared learned significantly better than birds that were cross-fostered (n = 8 parental pairs, 52 cross-fostered birds, 45 home-reared birds; Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p<0.005). Median SD scores for nests corresponding to spectrograms in panel B are shown in red.