Abstract
Background and aim
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are implicated as novel factors in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Although thousands of lncRNAs have been discovered, only a small portion have been functionally determined in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we aimed to comprehensively analyze differentially expressed lncRNAs, evaluate their clinical significance, and explore the functional roles and underlying mechanism in HCC.
Methods
We identified hundreds of lncRNAs which were dysregulated in HCC tissues through performing integrative analyses using the RNA sequencing data and independent gene microarray data from Gene Expression Omnibus and the Cancer Genome Atlas.
Results
Dysregulated DUXAP8, LINC01116, LINC01138, and PCAT6 are significantly associated with HCC patients' poor outcomes. Further experimental validation revealed that down-regulation of lncRNA DUXAP8 inhibited HCC cells proliferation and colony formation ability. Mechanistically, DUXAP8 repressed tumor suppressor KLF2 transcription through interacting with histone-lysine N-methyltransferase enzyme enhancer of zeste homolog 2.
Conclusion
Taken together, our findings can provide a valuable resource of HCC-associated lncRNAs and new insights into the biological functions of lncRNAs in HCC development.
Keywords: HCC, lncRNAs, DUXAP8, EZH2, KLF2
Introduction
Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), one of the most common gastrointestinal malignancies,is a leading cause of tumor-related deaths worldwide.1,2 HCC constitutes ~80% of all new diagnosed liver cancer cases, and approximately 55% of all HCC patients reside in People’s Republic of China.3 In spite of the great improvements of hepatic resection, liver transplantation and comprehensive therapy for HCC have been made, the 5-year overall survival (OS) rate for this disease remains unsatisfactory.4 Therefore, identification of new prognostic molecular biomarkers and a further understanding of underlying molecular mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis is urgently needed to develop novel treatment strategies for this disease.
Recently, the rapid development of high-throughput sequencing technology and bioinformatics has revealed that protein-coding genes account only ~2% of the human genome, the rest of which yields thousands of non-coding RNAs including long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs).5,6 LncRNAs are a class of ncRNAs that are >200 nucleotides in length and lack protein-coding ability.7,8 Recently, increasing evidence have uncovered the critical roles of lncRNAs in the pathogenesis of diverse cancers with variety of cellular functions, such as cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, metastasis, and drug resistance.9,10 For example, Chen et al found that LINC01234 promoted cell proliferation by acting as miR-204-5p sponge to regulate CBFB expression in gastric cancer.11 In addition, a novel TGF-β-1-induced lncRNA ELIT-1 promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition through facilitating TGF-β/Smad signaling by recruiting SMAD3 to the promoters of SNAIL and other TGF-β target genes.12 Recently, some lncRNAs have been found to contribute to the tumorigenesis and progression of HCC.13 Up-regulated Lnc-UCID is associated with HCC patients’ shorter recurrence-free survival of and promotes cell growth and G1/S transition through competitively binding to DHX9 and sequestering it from CDK6 3ʹUTR region, thereby increasing CDK6 expression.14 Additionally, overexpressed MCM3AP-AS1 facilitated HCC cells growth and cell cycle transition via sponging miR-194-5p and promoting its target gene FOXA1 expression.15
Double homeobox A pseudogene 8 (DUXAP8) is a pseudogene derived lncRNA, which is located on chromosome 22q11.1 with 2107 bp in length. A growing number of studies have revealed that DUXAP8 is over expressed and exerts oncogenic function in multiple cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer,16 gastric cancer,17 esophageal squamous cell cancer,18 pancreas cancer,19 etc. Highly expressed DUXAP8 contributes to tumor cells proliferation and invasion through interacting with histone demethylase LSD1 or histone methyltransferase EZH2 to repressing tumor suppressors transcription, such as KLF2, EGR1, and PLEKHO.16,17 However, the potential functional roles of DUXAP8 in HCC remain unclear. In the present study, we conducted a integrative lncRNA profiling analysis using RNA sequencing data and microarray data in HCC from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Moreover, we determined the cancer promotion function and explored molecular mechanism of lncRNA DUXAP8 in HCC. The findings in this study reveal hundreds of dysregulated lncRNAs in HCC and provide potential useful targets for HCC therapy.
Methods and materials
lncRNA profiling analyses in HCC
RNA sequencing data of HCC tissues and normal tissues RNA sequencing data and related pathological features were obtained from the https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/. In addition, three public HCC and non-tumor tissues RNA sequencing and microarray profiling data (GSE70880,20 GSE113850,21 and GSE12453522) were obtained from GEO. To re-analyze the microarray data, we conducted differential gene analysis by using the limma’s eBayes method according to the Agilent-038314 CBC Homo sapiens lncRNA+mRNA microarray V2.0, Invitrogen NCode Human Non-coding RNA Microarray platforms. Meanwhile, Mann–Whitney U-test was used to get the FPKM values normalized with upper-quantile for each RNA sequencing sample. Benjamini–Hochberg correction method was used to adjust the p-values.
Analyze survival-related lncRNAs in HCC
Univariate Cox regression analyses were used to evaluate the significance of dysregulated lncRNAs in assessing the OS and progression-free survival (PFS) in HCC patients. Next, we conducted multivariate Cox regression analyses on Bioconductor and R software to explore whether these lncRNAs can be dependent variable factors for predicting PFS and OS in HCC patients.Then, HCC patients were grouped into relative high- or low-lncRNAs expression groups based on each lncRNA’s median expression. Finally, lncRNAs with log-rank p≤0.05 were considered as significant.
Cell culture and siRNA transfection
Human HCC cell lines and normal cell line were purchased from Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the American Type Culture Collection. The cells were maintained with Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (Gibco, NY, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), 100 μ/mL streptomycin and penicillin (Sigma, MO, USA) in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 at 37°C. The RNAiMAX (Invitrogen) regent was used to transfect DUXAP8, EZH2, and scrambled siRNAs (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) into HepG2 and Hep3B cells according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The DUXAP8 siRNAs sequences are: 1#,5ʹ-AAGAUAAAGGUGGUUUCCACAAGAA-3ʹ 2#, 5ʹ- CAGCAUACUUCAAAUUCACAGCAAA-3ʹ. The sequence of EZH2 siRNA is 5ʹ-AAGACUCUGAAUGCAGUUGCU-3ʹ.
qRT-PCR assays
The RNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN) was used to extract the total RNA of HCC tissues and cells, and 1 μg RNA was reverse-transcribed using the PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit (TaKaRa, Dalian, People’s Republic of China) following the manual. For qRT-PCR analysis, we used SYBR Premix Ex Taq regent (TaKaRa) to examine DUXAP8, EZH2, and KLF2 expression levels according to instructions. The sequences of DUXAP8, EZH2, KLF2, and GAPDH primers are: DUXAP8, forward 5ʹ-AGGATGGAGTCTCGCTGTATTGC-3ʹ, reverse 5ʹ- GGAGGTTTGTTTTCTTCTTTTTT-3ʹ; EZH2, forward 5′-TGCACATCCTGACTTCTGTG-3′, reverse 5′-AAGGGCATTCACCAACTCC-3′; KLF2, forward 5′-TTCGGTCTCTTCGACGACG-3′, reverse 5′-TGCGAACTCTTGGTGTAGGTC-3′; GAPDH, forward 5′-AGAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTTG-3′, reverse 5′-AGGGGCCATCCACAGTCTTC-3′.
Cell proliferation assays
The cell proliferation capacity of DUXAP8 or control siRNAs-transfected HCC cells was evaluated with a CCK-8 kit (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, People’s Republic of China) according to manual. HepG2 and Hep3B cells transfected with DUXAP8 or scrambled siRNAs were plated into 96-well plates, and 10 μL CCK8 reagent was added in each well.Next, 450 nm absorbance value was measured after incubation for 2 hrs every day. For colony formation assay, HepG2 and Hep3B cells were plated into six-well plates, and cultured for 2 weeks. Finally, 4% paraformaldehyde was used to fix the colonies, which was further stained by 0.1% crystal violet solution.
Subcellular fractionation
The PARIS Kit (Life Technologies) was used to detect the distribution of DUXAP8 in the cytoplasm and nucleus of HepG2 and Hep3B cells according to the manufacturer’s manual.
RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP)
The RIP assay was conducted by using the Magna RIP RNA-Binding Protein Immunoprecipitation Kit (Millipore, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The IgG antibody was used as a negative control. The SUZ12 and EZH2 antibodies were obtained from the Millipore.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)assay
ChIP experiment was performed with the EZ-ChIP Kit (Millipore) according to the manual, and anti-rabbit IgG was used as a negative control. H3K27me3 and EZH2 antibodies were obtained from Millipore. The primer sequence of KLF2 promoter region is: forward, 5′-ACGGGCTTATTGAGGTTGG-3′; reverse, 5′-GCCTGGGTGACAGAGGAGAC-3′.
Statistical analyses
The Mann–Whitney U-test, Student's t-test (two-tailed), and one-way analysis were used to analyze the in vitro experimental data on SPSS 18.0. p-value ≤0.05 was determined as significant.
Results
Identification of dysregulated lncRNAs in HCC
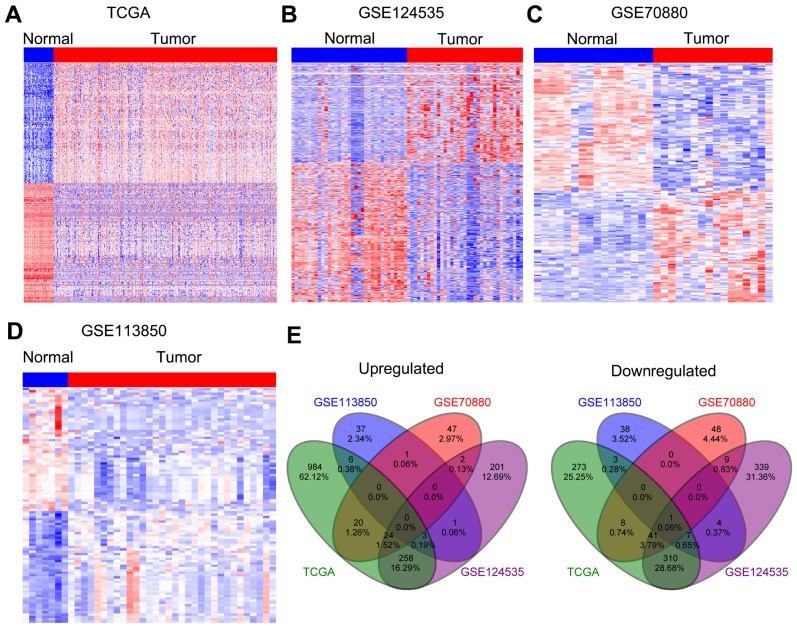
To identify more dysregulated lncRNAs in HCC, we downloaded the HCC tissues and normal tissues microarray profiling RNA sequencing data (GSE70880, GSE113850, and GSE124535) from TCGA and GEO. The results of differential profiling analysis indicated that 1938 lncRNAs were altered in TCGA dataset (1295 increased and 643 decreased); 201 lncRNAs were dysregulated in GSE70880 dataset (94 increased and 107 decreased); 101 lncRNAs’ expression was altered in GSE113850 dataset (48 increased and 53 decreased); 2162 lncRNAs’ expression was altered in GSE124535 dataset (1007 increased and 1155 decreased) (Figure 1A–D). Furthermore, Venn analyses indicated that 315 lncRNAs were increased and 383 lncRNAs were decreased in at least two datasets (Figure 1E ).
Figure 1.
Differential profiling analyses of lncRNAs expression in human HCC tissues and normal tissues. (A) A heatmap was drawn to show the dysregulated lncRNAs in HCC specimen with normal samples from TCGA. (B–D) Heatmaps were drawn to show the upregulated or downregulated lncRNAs in HCC compared with normal tissues in the GSE70880, GSE113850, and GSE124535 datasets. (E) Venn diagram of dysregulated lncRNAs in TCGA, GSE70880, GSE113850, and GSE124535 datasets.
Abbreviations: IncRNAs, long non-coding RNAs; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; TCGA, the Cancer Genome Atlas.
Identifying HCC survival-related lncRNAs
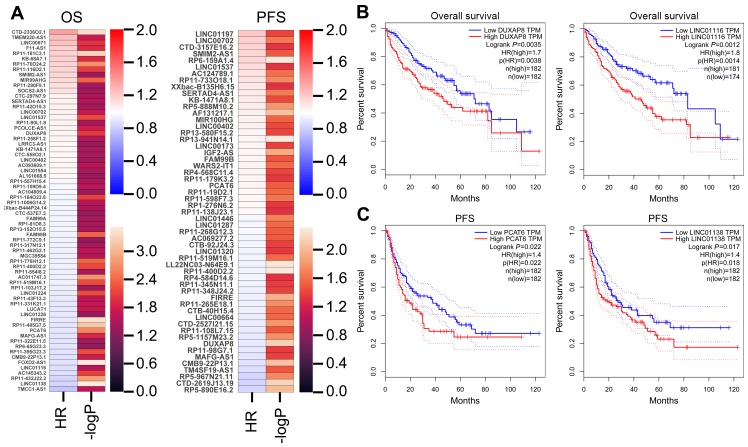
To date, increasing evidence have uncovered that lots of lncRNAs are closely related to the outcome of diverse cancers, and can be used as independent predicting factors of patients’ prognosis. To identify more HCC outcome-related lncRNAs, we conducted univariable Cox regression analysis. As showing in Figure 2A, several over expressed and decreased lncRNAs are related to HCC patients shorter OS and PFS (log-rank p<0.05). Taken DUXAP8, LINC01116, LINC01138, and PCAT6, for example, HCC patients with higher expression levels of LINC01116 and DUXAP8 had poorer OS, and HCC patients with higher expression levels of LINC01138 and PCAT6 had poorer PFS (Figure 2B and C). These findings suggest that these HCC survival-associated lncRNAs may be potential valuable candidates for HCC patients prognosis prediction.
Figure 2.
Analyzing HCC patients’ survival-related lncRNAs. (A) A heatmap was drawn to show the PFS and OS associated lncRNAs-log P-value and hazard ratio value in HCC using the TCGA clinical data. (B) The Kaplan–Meier curve for HCC patients overall survival in high- or low-DUXAP8 and LINC01116 groups using the TCGA data was conducted with two-sided log-rank test. (C) The Kaplan–Meier curve for HCC patients PFS in high- or low-PCAT6 and LINC01138 groups using the TCGA data was conducted with two-sided log-rank test.
Abbreviations: IncRNAs, long non-coding RNAs; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; TCGA, the Cancer Genome Atlas; PFS, progression-free survival; OS, overall survival.
Down-regulation of DUXAP8 impairs HCC cells proliferation
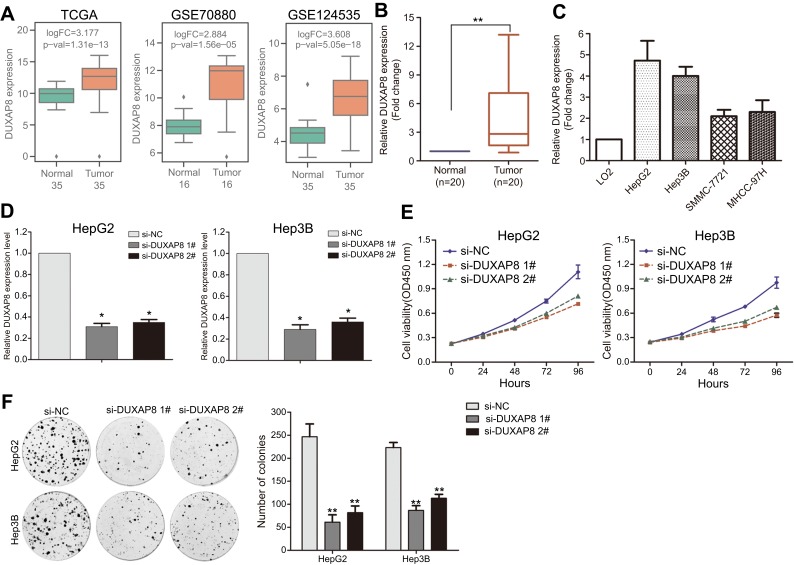
To further determine whether those altered lncRNAs have function in HCC, we chose the over expressed lncRNAs which may be potential biomarkers. We found that DUXAP8 is significantly over expressed in TCGA, GSE70880, and GSE124535 datasets (Figure 3A). Moreover, high DUXAP8 level is related to HCC patients' shorter OS. Therefore, DUXAP8 was chosen as a candidate for further validation. Next, the results of qPCR revealed that DUXAP8 expression was significantly up-regulated in HCC tissues which is consistent with our analyses results (Figure 3B). Moreover, DUXAP8 expression was also increased in HCC cell lines (Figure 3C). Next, two siRNAs were used to knock down DUXAP8 expression and the results of qRT-PCR revealed that DUXAP8 expression was decreased by both two siRNAs in HepG2 and Hep3B cells (Figure 3D). Furthermore, the results of CCK8 and colony formation assays revealed that DUXAP8 down-regulation impaired HepG2 and Hep3B cells growth and colony formation capacity (Figure 3E–F).
Figure 3.
Down-regulation of DUXAP8 inhibits HCC cells proliferation. (A) The box plots show the relative DUXAP8 expression in HCC and normal tissues in TCGA/GTEx, GSE70880, GSE113850, and GSE124535. (B) The relative DUXAP8 expression was evaluated in HCC and normal tissues by qRT-PCR. (C) The relative DUXAP8 expression was evaluated in HCC and normal cell lines by qRT-PCR. (D) The relative DUXAP8 expression was evaluated by qRT-PCR in HepG2 and Hep3B cells after transfection with DUXAP8 or negative control siRNAs. (E) CCK8 assays were performed to examine the cell proliferation capacity of DUXAP8 or negative control siRNA transfected HepG2 and Hep3B cells. (F) Colony formation assay was performed to determine the cell colony formation ability of DUXAP8 or negative control siRNA transfected HepG2 and Hep3B cells. **p<0.01; *p<0.05.
Abbreviations: HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; TCGA, the Cancer Genome Atlas; DUXAP8, double homeobox A pseudogene 8.
DUXAP8 represses KLF2 expression via binding with EZH2
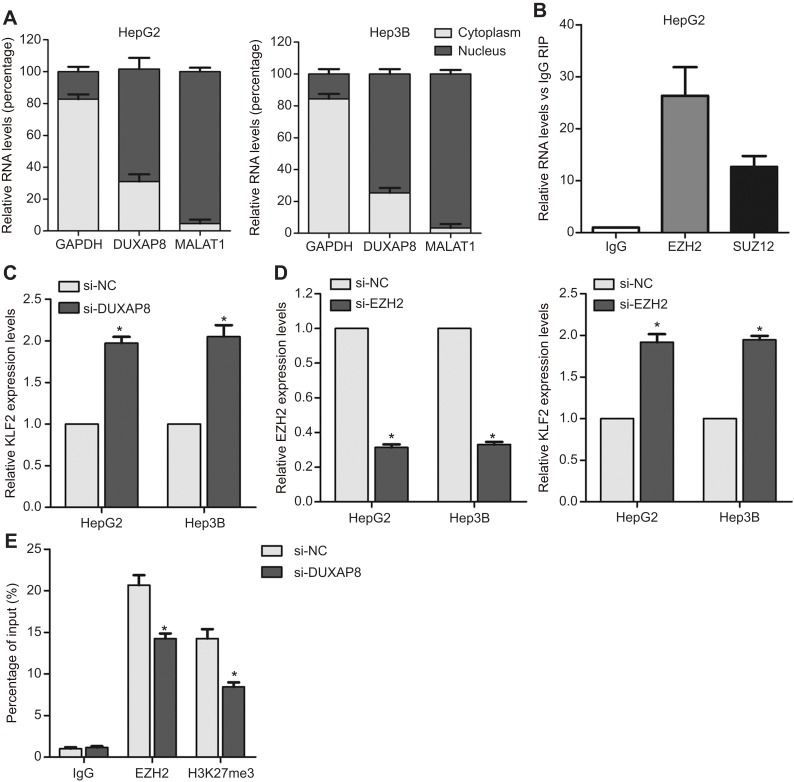
To elucidate the molecular mechanism by which DUXAP8 regulates downstream target genes, we firstly examined distribution of DUXAP8 in HCC cells. The results of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions showed that DUXAP8 is mainly distributed in HCC cell’s nucleus (Figure 4A). Furthermore, the results of RIP experiment revealed that DUXAP8 could bind with EZH2 in HCC cells (Figure 4B). A lot of studies have demonstrated that lncRNAs inhibit some tumor suppressors expression (such as P21 and P51) through binding with EZH2. We found that DUXAP8 down-regulation up-regulated KLF2 expression in HCC cells (Figure 4C). Meanwhile, down-regulation of EZH2 also up-regulated KLF2 (Figure 4D). Furthermore, the results of ChIP experiments revealed that EZH2 could bind to the promoter region of KLF2, and DUXAP8 down-regulation decreased EZH2’s binding to KLF2 promoter and H3K27me3 occupancy (Figure 4E).
Figure 4.
DUXAP8 represses KLF2 expression by interacting with EZH2. (A) The distribution of DUXAP8 in HepG2 and Hep3B cells cytoplasm and nucleus fractions. (B) The RNA level of DUXAP8 in EZH2-immunoprecipitate was examined by qRT-PCR in HepG2 and Hep3B cells and presented as fold change compared with IgG-immunoprecipitate. (C–D) qRT-PCR analysis of EZH2 and KLF2 expression in HepG2 and Hep3B cells after transfection with DUXAP8, EZH2 or negative control siRNAs. (E) ChIP-qRT-PCR analysis of EZH2 and H3K27me3 occupancy in KLF2 promoter region in HepG2 cells after transfection with DUXAP8 or negative control siRNA. *p<0.05.
Abbreviations: DUXAP8, double homeobox A pseudogene 8; EZH2, enhancer of zeste homolog 2.
Discussion
Recently, a lot of large-scale transcriptomics studies using next-generation sequencing and microarray have identified hundreds of dysregulated lncRNAs in multiple cancers.23,24 In addition, many evidence demonstrated the involvement of lncRNAs in the biological behavior of tumor cells, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, metastasis, and drug resistance.25,26 In this study, we performed an integrated lncRNAs differential profiling analysis in HCC, and identified hundreds of dysregulated lncRNAs in HCC. Moreover, our findings indicated that some lncRNAs expression levels are correlated with HCC patients shorter survival time, such as DUXAP8, LINC01116, LINC01138, and PCAT6. Our findings identified a lot of abnormally expressed lncRNAs in HCC, and might provide a useful list of lncRNAs for further studies.
Among those dysregulated lncRNAs, DUXAP8 was significantly over expressed in HCC and increased DUXAP8 expression is associated with HCC patients poor outcome. Our further experimental validation determined the oncogenic roles of DUXAP8 in HCC cells. In addition to HCC, DUXAP8 has been reported to be over expression in other cancers. Sun et al found that increased DUXAP8 facilitates cells growth and invasion through interacting with EZH2 and LSD1 to suppress RHOB and EGR1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer.16 Moreover, elevated DUXAP8 contributes to renal cell carcinoma development and progression via enhances cells growth through sponging miR-126 to antagonize its repression of CED-9.27 However, the underlying molecular mechanism of DUXAP8 response for its oncogenic function in HCC remains unclear.
Generally, lncRNAs can regulate cancer cells biological behavior through diverse mechanisms, such as acting as microRNAs sponge, binding with RNA-binding proteins and inducing the epigenetic modification, and influencing mRNA stability and translation.28–30 Here, our findings indicate that DUXAP8 is mostly located in the cytoplasmic fraction of HCC cells and can bind with histone methyltransferase EZH2, which is consistent with previous studies. Moreover, we found that down-regulation of DUXAP8 or EZH2 could increase tumor suppressor KLF2 expression in HCC cells. Moreover, ChIP assays determined the occupancy of EZH2 and in the promoter regions of KLF2. EZH2 (enhancer of zeste homolog 2) is a subunit of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2, which is involved in the transcriptional repression of genes. Recently, dysregulation of EZH2 has been frequently observed in multiple cancers, which promotes tumorigenesis through repressing the transcription of numerous tumor suppressor genes.31 Our findings suggest that the DUXAP8/EZH2/KLF2 axis may be a key molecular mechanism of HCC tumorigenesis and progression. Taken together, this study uncovers hundreds of differentially expressed lncRNAs in HCC, while majority of these lncRNAs biological functions remain unclear. In addition, a small part of those lncRNAs is related to the HCC patients prognosis. Our findings may provide potential valuable lncRNA candidates as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for HCC.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81602003 to XS), the Project of Zhejiang Basic Public Benefit Research of Zhejiang Province (No. LGF18H160005 to GY), the Medical and Health Research Project of Zhejiang Province (No. 2019315440 to YX), and the Project of Huzhou Municipal Science (No. 2017GY25 to YX).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):9–29. doi: 10.3322/caac.21208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21387 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–132. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21442 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2009;136(4):629–641. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nagano T, Fraser P. No-nonsense functions for long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2011;145(2):178–181. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kung JT, Colognori D, Lee JT. Long noncoding RNAs: past, present, and future. Genetics. 2013;193(3):651–669. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.146704 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chu C, Spitale RC, Chang HY. Technologies to probe functions and mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22(1):29–35. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2921 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sahu A, Singhal U, Chinnaiyan AM. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer: from function to translation. Trends Cancer. 2015;1(2):93–109. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2015.08.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yarmishyn AA, Kurochkin IV. Long noncoding RNAs: a potential novel class of cancer biomarkers. Front Genet. 2015;6:145. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chen X, Chen Z, Yu S, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC01234 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate CBFB expression by sponging miR-204-5p in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(8):2002–2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sakai S, Ohhata T, Kitagawa K, et al. Long noncoding RNA ELIT-1 acts as a Smad3 cofactor to facilitate TGF-beta/Smad signaling and promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2019;79(11):2821–2838. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yang Y, Chen L, Gu J, et al. Recurrently deregulated lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14421. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14421 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang YL, Liu JY, Yang JE, et al. Lnc-UCID promotes G1/S transition and hepatoma growth by preventing DHX9-mediated CDK6 downregulation. Hepatology. 2019;70(1):259-275. doi: 10.1002/hep.30613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang Y, Yang L, Chen T, et al. A novel lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting miR-194-5p/FOXA1 axis. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1010-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sun M, Nie FQ, Zang C, et al. The pseudogene DUXAP8 promotes non-small-cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion by epigenetically silencing EGR1 and RHOB. Mol Ther. 2017;25(3):739–751. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.12.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 17.Ma HW, Xie M, Sun M, et al. The pseudogene derived long noncoding RNA DUXAP8 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration via epigenetically silencing PLEKHO1 expression. Oncotarget. 2017;8(32):52211–52224. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11075 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xu LJ, Yu XJ, Wei B, et al. Long non-coding RNA DUXAP8 regulates proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(9):2646–2652. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201805_14959 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lian Y, Yang J, Xiao C, Hu X, Xu H. DUXAP8, a pseudogene derived lncRNA, promotes growth of pancreatic carcinoma cells by epigenetically silencing CDKN1A and KLF2. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018;38(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0333-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yuan J, Yue H, Zhang M, et al. Transcriptional profiling analysis and functional prediction of long noncoding RNAs in cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(7):8131–8142. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6993 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Klingenberg M, Gross M, Goyal A, et al. The long noncoding RNA cancer susceptibility 9 and RNA binding protein heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L form a complex and coregulate genes linked to AKT signaling. Hepatology. 2018;68(5):1817–1832. doi: 10.1002/hep.30102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jiang Y, Sun A, Zhao Y, et al. Proteomics identifies new therapeutic targets of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 2019;567(7747):257–261. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0987-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li J, Han L, Roebuck P, et al. TANRIC: an interactive open platform to explore the function of lncRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 2015;75(18):3728–3737. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0273 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.He Y, Meng XM, Huang C, et al. Long noncoding RNAs: novel insights into hepatocelluar carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2014;344(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.10.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS. Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017;77(15):3965–3981. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2634 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lin C, Yang L. Long noncoding RNA in cancer: wiring signaling circuitry. Trends Cell Biol. 2018;28(4):287–301. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.11.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Huang T, Wang X, Yang X, et al. Long non-coding RNA DUXAP8 enhances renal cell carcinoma progression via downregulating miR-126. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:7340–7347. doi: 10.12659/MSM.910054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Huarte M. LncRNAs have a say in protein translation. Cell Res. 2013;23(4):449–451. doi: 10.1038/cr.2012.169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rinn JL. lncRNAs: linking RNA to chromatin. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014;6(8):a018614. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018614 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang KC, Chang HY. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2011;43(6):904–914. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim KH, Roberts CW. Targeting EZH2 in cancer. Nat Med. 2016;22(2):128–134. doi: 10.1038/nm.4036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]