Abstract
Atropisomeric biaryl motifs are ubiquitous in chiral catalysts and ligands. Numerous efficient strategies have been developed for the synthesis of axially chiral biaryls. In contrast, the asymmetric construction of o-quinone-aryl atropisomers has yet to be realized. Inspired by the rapid progress of the chemistry of biaryls, here we present our initial investigations about the atroposelective construction of axially chiral arylquinones by a bifunctional chiral phosphoric acid-catalyzed asymmetric conjugate addition and central-to-axial chirality conversion. With o-naphthoquinone as both the electrophile and the oxidant, three types of arylation counterparts, namely 2-naphthylamines, 2-naphthols and indoles, are utilized to assemble a series of atropisomeric scaffolds in good yields and excellent enantioselectivities. This approach not only expands the axially chiral library but also offers a route to a class of potential, chiral biomimetic catalysts.
Subject terms: Asymmetric catalysis, Organocatalysis, Synthetic chemistry methodology
Axially chiral compounds have widespread use in asymmetric catalysis. Here, the authors disclose a highly enantioselective synthesis of axially chiral o-naphthoquinones by chiral phosphoric acid catalysis and central-to-axial chirality conversion.
Introduction
Enantioenriched axially chiral biaryls are of great significance due to the ubiquitous relevance in natural products1,2, bioactive molecules3,4 and functional materials5,6. They also constitute the core structural motif of various chiral catalysts and ligands for asymmetric transformations7,8. Particularly, the emergence of BINOL9,10 and its derivatives11–13 brought about remarkable improvement of asymmetric catalysis domain and altered the scenario that the acquirement of highly enantioenriched products from prochiral substrates via routinely chemical approaches remained extremely challenging half a century ago. The past couple of decades have witnessed the rapid progress of the biaryls based chemistry and a series of efficient synthetic strategies have been developed for the construction of chiral biaryls (Fig. 1a)14–16. In stark contrast, despite only slight alteration in molecular structure, the o-quinone-aryl atropisomer has been still unrevealed and its asymmetric synthesis has never been materialized till now, to the best of our knowledge. On the other hand, the o-quinones occur prevalently in bioactive natural products17,18 and are widely recognized as cofactors in numerous quinoproteins (Fig. 1b)19–22. Mechanistic studies reveal the role of quinone cofactors as the actual active centers while metals necessitate the regeneration of the quinone cofactors in these transformations. In addition, they were found to be useful synthetic intermediates for many valuable transformations23,24. In this regard, the enantioselective construction of hitherto unknown atropisomeric aryl o-quinone not only brings about a class of axially chiral atropisomers but also may provide a class of potential chiral biomimetic catalysts.
Fig. 1.
Axially chiral biaryls vs. axially chiral arylquinones and their synthesis. a Biaryls as chiral ligands and organocatalysts. b o-Quinone structures in biomimetic catalysts. c Our designed approach to access arylquinone atropisomer
On the basis of the recent advance in the construction of axially chiral backbones25–34 and our continuous understanding of this field35, we envisaged that the atroposelective synthesis of the axially chiral o-quinone is conceivable via arylation of o-naphthoquinone promoted by organocatalyst. First, enantioselective arylation of o-naphthoquinone I with aryl nucleophile II provides central chiral intermediate III in the presence of chiral organocatalyst. Subsequent aromatization and oxidation result in the transfer of central to axial chirality, furnishing the excepted axially chiral aryl o-naphthoquinone IV. Ideally, the oxidative capability of excess o-naphthoquinone I will facilitate the oxidation reaction (Fig. 1c). However, related research becomes more appealing and challenging when the planar aromatic ring was replaced by an o-quinone as compared to biaryls and then several challenges need to be taken into consideration: (1) appropriate substituents should be equipped on o-naphthoquinone and/or nucleophile to enhance the reactivity and restrict the axial rotation; (2) an appropriate bifunctional organocatalyst is essential for simultaneous activation of nucleophile and electrophile in appropriate chiral environment; strong background reaction is detrimental to the stereocontrol; (3) entire oxidation process should proceed under mild conditions to circumvent the racemization of the axial chirality.
Herein we disclose the discovery of axially chiral o-naphthoquinones and their enantioselective construction in the presence of bifunctional chiral phosphoric acid catalyst via central-to-axial chirality conversion. A range of atropisomeric o-naphthoquinone frameworks are synthesized in good yields and excellent enantiocontrol with o-naphthoquinone as the electrophile and oxidant, 2-naphthylamine, 2-naphthol or indole as the arylation reagent.
Results
Optimization of the reaction conditions
Considering the aforementioned factors, we selected o-naphthoquinone 1a–1 with an ester group as the model electrophile and 2-naphthylamine 2a–1 as the aryl donor to construct axially chiral backbone under the activation of chiral phosphoric acid36,37. The introduction of ester group was thought to enhance the interaction between quinone and catalyst while strengthens the stability of chiral axis of the product in line with the reported results38. Also, we expected the excessive o-naphthoquinone to serve as oxidant to de-aromatize naphthol intermediate. To verify the feasibility of our design, 10 mol% of chiral phosphoric acid (CPA1) was utilized to promote the reaction of 1a–1 (2.2 eq.) and 2a–1 (1.0 eq.) in CH2Cl2 at room temperature. Fortunately, the desired product 3a–1 was afforded in 4 h in 32% isolated yield (Table 1, entry 1). Notably, this compound displayed axial chirality based on the chiral stationary high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis. Despite only inapparent enantiomeric excess (4% ee), our proposed hypothesis was substantiated by direct experimental evidence and the enantioenriched atropisomeric o-naphthoquinone was realized. Following optimization focused on the evaluation of various CPA and BINOL-derived CPA4 with a bulky 2,4,6-triisopropylphenyl substituent on the 3,3′-position was found to be the best catalyst, providing 3a–1 in excellent yield and enantioselectivity (87% yield, 99% ee) in only 20 min (Table 1, entries 2–11). Other solvents were surveyed to further improve the reaction but in futile (Table 1, entries 12–16). Further investigations revealed that 1 mol% catalyst loading was optimal to uphold the high yield, as well as enantiocontrol of the current reaction (Table 1, entry 18). The optimized conditions were then concluded as follows: 1a–1 (0.22 mol), 2a–1 (0.10 mol) and CPA4 (1 mol%) in 2 mL of CH2Cl2 and performed at room temperature for 20 min.
Table 1.
Reaction optimization with 2-naphthylaminea

| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | CPA | solvent | time (min) | yield (%)b | ee (%)c |
| 1 | (R)-CPA1 | CH2Cl2 | 240 | 32 | –4 |
| 2 | (R)-CPA2 | CH2Cl2 | 240 | 38 | –36 |
| 3 | (R)-CPA3 | CH2Cl2 | 240 | 27 | –51 |
| 4 | (S)-CPA4 | CH2Cl2 | 20 | 87 | 99 |
| 5 | (R)-CPA5 | CH2Cl2 | 20 | 85 | 99 |
| 6 | (R)-CPA6 | CH2Cl2 | 240 | 36 | –83 |
| 7 | (R)-CPA7 | CH2Cl2 | 240 | 57 | –47 |
| 8 | (R)-CPA8 | CH2Cl2 | 240 | 52 | –30 |
| 9 | (R)-CPA9 | CH2Cl2 | 240 | 24 | –28 |
| 10 | (R)-CPA10 | CH2Cl2 | 240 | 35 | –14 |
| 11 | (R)-CPA11 | CH2Cl2 | 240 | 38 | –42 |
| 12 | (S)-CPA4 | toluene | 20 | 60 | 99 |
| 13 | (S)-CPA4 | CHCl3 | 20 | 82 | 99 |
| 14 | (S)-CPA4 | EtOAc | 20 | 43 | 68 |
| 15 | (S)-CPA4 | DCE | 20 | 86 | 99 |
| 16 | (S)-CPA4 | ether | 20 | 62 | 83 |
| 17d | (S)-CPA4 | CH2Cl2 | 20 | 86 | 99 |
| 18e | (S)-CPA4 | CH2Cl2 | 20 | 86 | 99 |
aReaction conditions: 1a–1 (0.22 mmol), 2a–1 (0.10 mmol), solvent (2 mL) under Ar atmosphere, unless noted otherwise. bIsolated yields. cDetermined by HPLC analysis on a chiral stationary phase. dConducted with 5 mol% of CPA4. eConducted with 1 mol% of CPA4
Substrate scope
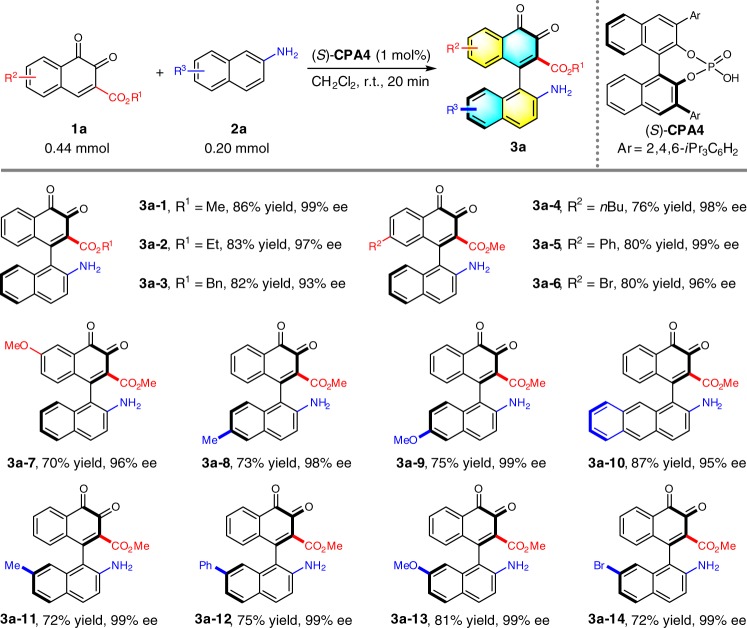
With the optimized conditions in hand, we next set out to explore the substrate scope of this reaction by examining derivatives of 2-naphthylamine and o-naphthoquinone. Overall, all the tested substrates gave the expected axially chiral arylquinones in good yields with excellent atroposelectivities (Table 2). Firstly, replacement of methyl group on ester by an ethyl or benzyl group provided the adduct 3a–2 or 3a–3 in lower yield and enantioselectivity. The introduction of a substituent on the aromatic ring of o-naphthoquinones (3a–4~3a–7) led to slight yield reduction. A wide range of 2-naphthylamines with different substituents or substitution patterns were evaluated under the standard conditions. In most cases, the desired axially chiral arylquinones (3a–8~3a–14) could be furnished with up to 99% ee. A certain degree of variation in chemical yield was detected for each reaction. Notably, no desired product was obtained under standard conditions when N,N-dimethyl-2-naphthylamine was used, indicating the importance of N–H bond for this reaction.
Table 2.
Substrate scope with 2-naphthylaminea
aReaction conditions: 1a (0.44 mmol), 2a (0.20 mmol), (S)-CPA4 (1 mol%), CH2Cl2 (4 mL), room temperature for 20 min under Ar atmosphere. Isolated yields were provided and ee values were determined by HPLC analysis on a chiral stationary phase
To further expand the generality of this strategy, we applied the optimized conditions to the reaction of o-naphthoquinone 1a–1 and phenyl protected 2-naphthylamine 2b–1. Disappointedly, less than 10% of conversion was detected after 10 h under this set of conditions. While previous studies suggested the indicative effects of CPA catalyst on reaction outcomes, the re-optimization was initiated by screening of various CPA. Our optimization efforts revealed that H8–BINOL derived CPA6 could provide the most optimal results at room temperature for 10 h, affording the product 3b–1 in 93% yield and 99% ee. Further studies showed CH2Cl2 remained as the most efficient reaction solvent. While 10 mol% catalyst loading could not bring about any improvement for the reaction results, 1 mol% catalyst loading resulted in chemical yield decrement of 3 mol% (Supplementary Table 2). The re-optimized conditions were then applied to a wide spectrum of o-naphthoquinones and phenyl protected 2-naphthylamines (Table 3). The influence of the ester groups on the o-naphthoquinone was first investigated. Slightly compromised reaction yield and selectivity were observed when methyl group was replaced with bulkier ethyl (3b–2), benzyl (3b–3) or isopropyl group (3b–4). Nonetheless, additional substituent introduced on the aromatic ring of o-naphthoquinone exerted limited effects to the reaction outcomes (3b–5~3b–8). Halide functionality (3b–9 to 3b–11), electron-donating (3b–12 and 3b–13) and electron-withdrawing groups (3b–14) on phenyl protecting group were all well tolerated to give the corresponding products in satisfactory results. To verify the utility of the current organocatalytic atroposelective reaction, a gram-scale synthesis of 3b–7 was performed under the standard reaction conditions. As presented in Table 3, the desired axially chiral product was furnished with the same enantiocontrol but in higher yield, inferring this protocol is suitable for the large-scale production.
Table 3.
Substrate scope with N-arylnaphthalen-2-aminea
aReaction conditions: 1a (0.44 mmol), 2b (0.20 mmol), (R)-CPA6 (5 mol%), CH2Cl2 (4 mL), room temperature for 10 h under Ar atmosphere. Isolated yields were provided and ee values were determined by HPLC analysis on a chiral stationary phase. bGram-scale reaction: 1a–6 (4.4 mmol), 2b–1 (2.0 mmol)
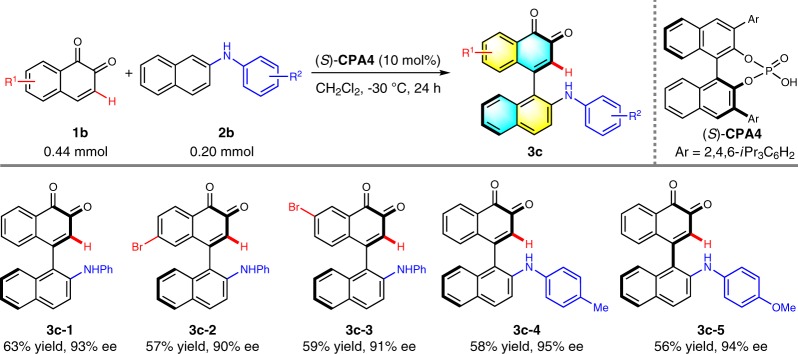
In our original design, the ester group was proposed to enhance the interaction between CPA and substrate as well as the stability of the chiral axis. However, the C-3 substituent of o-naphthoquinones has been demonstrated to reduce the catalytic capability significantly39. Encouraged by our initial results, we then attempted to explore the practicability for the synthesis of axially chiral arylquinones without an ester group. The more challenging and rewarding project commenced with o-naphthoquinone 1b–1 as the model electrophile. Compound 2b–1 was anticipated to be an appropriate nucleophile since the bulky protecting group might be conducive to restrict the axial rotation. The reaction was conducted in CH2Cl2 with 10 mol% CPA4 as the catalyst. Gratifyingly, the desired product 3c–1 was provided in 92% yield and 83% ee. No improved result arose by screening a variety of CPAs including CPA6 (78% yield, 46% ee), the optimal catalyst for the reaction of phenyl protected 2-naphthylamines and o-naphthoquinones with an ester group. Not surprisingly, CH2Cl2 proved to be the most efficient solvent. The enantioselectivity was augmented to 93% when the reaction was performed at –30 °C, albeit lower yield (63%). The reduction of the catalyst loading led to obvious yield and enantioselectivity depletion (Supplementary Table 3). The optimal reaction conditions were then applied to other four substrates. As depicted in Table 4, all these reactions could deliver the desired products (3c–2 to 3c–5) in excellent stereocontrol at the expense of lower yields. Although limited substrate scope was established at this stage, the successful construction of this axially chiral backbone offered more possibility to realize the application in catalysis.
Table 4.
Substrate scope with o-naphthoquinone without ester groupa
aReaction conditions: 1b (0.44 mmol), 2b (0.20 mmol), (S)-CPA4 (10 mol%), CH2Cl2 (4 mL), –30 °C for 24 h under Ar atmosphere. Isolated yields were provided and ee values were determined by HPLC analysis on a chiral stationary phase
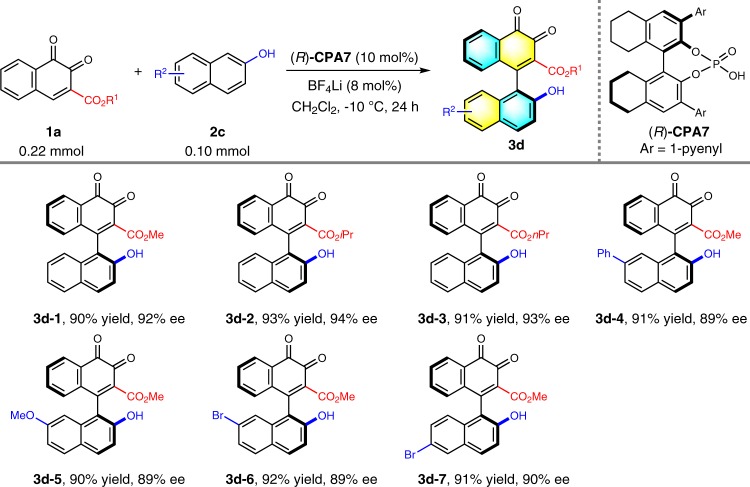
To further broaden the scope of axially chiral arylquinone family, we moved to seek other applicable nucleophiles upon accomplishing the investigation with 2-naphthylamine and its derivatives. 2-Naphthol, which has proven impressive ability to act as aryl nucleophiles for construction of BINOL derivatives40,41, then came to our mind. Employing 2-naphthol 2c as the aryl donor, we again envisaged the prohibitory role of an ester moiety on o-naphthoquinone for hindering the rotation of chiral axis. Careful screening of the conditions presented the following optimal system: H8–BINOL-derived CPA7 as the catalyst, BF4Li as the additive, and the reaction was conducted in CH2Cl2 at −10 °C for 24 h to give the desired product 3d–1 in 90% yield and 92% ee (Supplementary Table 5). This protocol has shown excellent applicability and compatibility to several analogs (Table 5). All products (3d–2~3d–7) were obtained in excellent yields and enantioselectivities respectively.
Table 5.
Substrate scope with 2-naphthola
aReaction conditions: 1a (0.22 mmol), 2c (0.10 mmol), (R)-CPA7 (10 mol%), CH2Cl2 (4 mL), BF4Li (8 mol%), –10 °C for 24 h under Ar atmosphere. Isolated yields were provided and ee values were determined by HPLC analysis on a chiral stationary phase
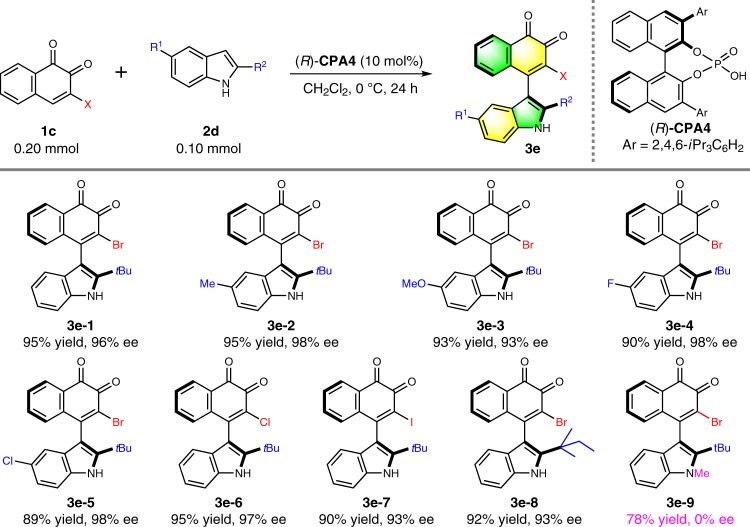
Besides, indole has been validated to be a competent nucleophile42,43 under acidic conditions for the synthesis of indolylbenzoquinone44,45, which is widespread in various natural products with remarkable bioactivity. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no facile asymmetric construction of axially chiral indolyl-o-naphthoquinone to-date. To test the relevance of indole nucleophile in our protocol, CPA4 (10 mol%) was utilized to promote the reaction of 1a–1 and 2d–1 in CH2Cl2 for 24 h under Ar atmosphere which led to the corresponding product in 44% ee. Extensive efforts dedicated in a massive parallel screening of conditions were unfruitful with only moderate enantiocontrol (76% ee) attained. Interestingly, the bromide-containing substrate 1c–1 provided the product 3e–1 efficiently with 89% ee with the optimal catalyst CPA4 in CH2Cl2. Subsequent optimization further affirmed the superior reaction competency of CH2Cl2 compared to other solvents in the presence of CPA4. The reaction selectivity was dictated by catalyst loading in which lower catalyst loading gave lower reaction efficiency in return. Notably, the enantioselectivity was improved to 96% ee when the reaction was performed at 0 °C without diminution of the yield (95%). On the contrary, alteration of other factors such as reaction time and molarity proved futile. The optimized conditions were then concluded as follows: 1c–1 0.20 mol, 2d–1 0.10 mol, 10 mol% CPA4 in CH2Cl2 and the reaction was performed at 0 °C for 24 h under air atmosphere (Supplementary Table 6).
With the optimal conditions in hand, we next explored the substrate scope and the limitation of this reaction. Firstly, the effect of the substituent on the indole ring was tested. As summarized in Table 6, indole nucleophile with either an electron donating group (3e–2, 3e–3) or a halide group (3e–4, 3e–5) could be utilized to give the desired product in excellent yields and enantioselectivities. Likewise, both chlorine (3e–6) and iodine group (3e–7) substituted o-naphthoquinone electrophiles were very well tolerated under the conditions to give the axially chiral products with similar outcome and high chemical stability apart from the bromine counterpart. The isopentyl group could also act as the axial rotation resistance group to furnish product 3e–8 in consistently excellent enantioselectivity. Noteworthy, the stereoselectivity was completely lost (0% ee) when 2-tert-butyl-1-methylindole 2d–7 was used as the nucleophile for this reaction, indicating that the N–H bond of indole is crucial on the stereocontrol.
Table 6.
Substrate Scope with Indolea
aReaction conditions: 1c (0.20 mmol), 2d (0.10 mmol), (R)-CPA4 (10 mol%) in CH2Cl2 (1 mL) at 0 °C for 24 h under Ar atmosphere. Isolated yields were provided and ee values were determined by HPLC analysis on a chiral stationary phase
Transformations and asymmetric catalysis applications
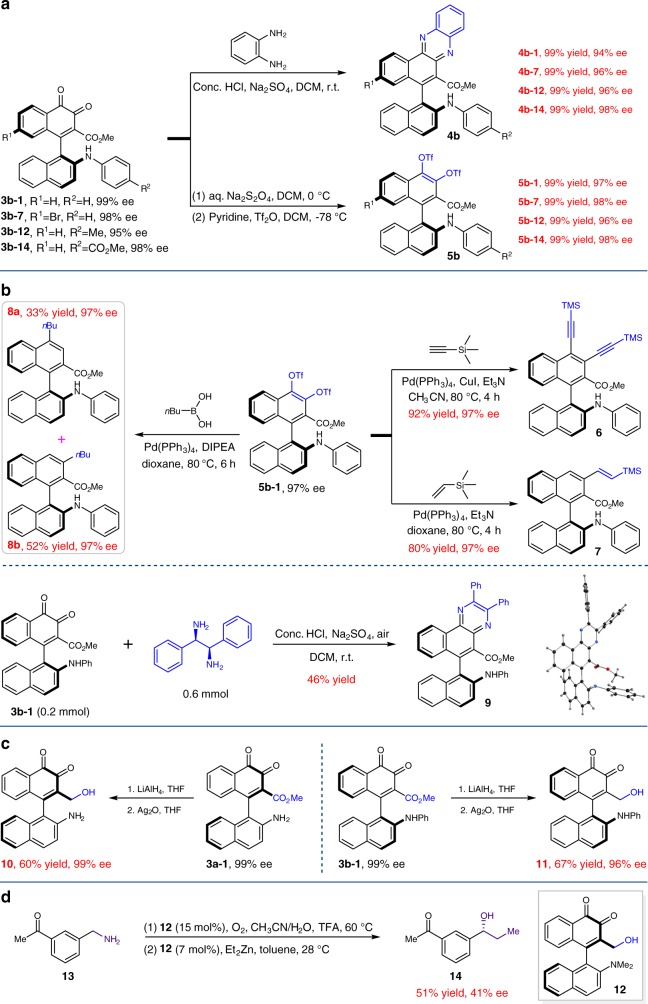
To demonstrate the potential of the developed approach, synthetic transformations were then performed based on the generated products 3b. Phenazine scaffold constitutes the core structures of various natural products with attractive bioactivities46–48. Moreover, it could sever as essential backbone for synthetic dyes. Accordingly, the synthesis of phenazine containing molecules to enrich the diversity of the library is of significant importance. Gratifyingly, the expected phenazine could be readily attained from o-quinone. The reactions of representative 3b with benzene-1,2-diamine in the presence of concentrated HCl and sodium sulfate proceeded smoothly to yield the corresponding products 4b in quantitative yields with almost identical enantioselectivities (Fig. 2a). Subsequently, sodium dithionite was utilized to reduce the o-quinone moiety. The generated o-dihydroxybenzene intermediates were then trapped by Tf2O to give the more stable structures 5b in quantitative yields. Negligible deteriorations of stereochemical integrity were detected for all these reactions (Fig. 2a). Notably, the resultant phenyl trifluoromethanesulfonate provides opportunities for downstream coupling reactions, allowing quick access to a variety of structurally diversified atropisomeric binaphthyls. Interestingly, utilizing 5b–1 as the starting material, the Sonogashira coupling reaction proceeded smoothly to give bis-substituted product 6 with ethynyltrimethylsilane in 92% yield, while axially chiral molecule 7 with one olefinic group was produced efficiently by the Heck reaction. Apart from that, the Suzuki coupling reaction provided a mixture of 8a and 8b with n-butylboronic acid as the coupling partner. Likewise, no stereochemical integrity loss was observed for all these reactions (Fig. 2b). Next, the absolute configuration of 3b–1 was deduced to be (S) by X-ray crystallographic analysis of its derivative 9, which could be prepared by the treatment of 3b–1 with (1 R,2 R)-1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-diamine under the identical conditions for the synthesis of compounds 4 (CCDC: 1833698), and those of other products (3a–3e) were assigned by analogy in accordance with the corresponding absolute configuration of CPAs. Subsequently, the ester group could be readily converted to alcohol with lithium aluminum hydride as the reductive agent, affording arylquinone 10 or 11 with acceptable yield, respectively (Fig. 2c). Finally, the synthetic and catalytic applications of the obtained axially chiral o-naphthoquinones were investigated. As shown in Fig. 2d, compound 12, prepared from compound 10 by reductive amination, acted as an oxidant for the transformation of benzylamine 13 to corresponding aldehyde. Subsequently, it severed as a chiral ligand in the presence of reducing agent for the asymmetric addition of ZnEt2 to the generated aldehyde, give the desired chiral alcohol 14 in moderate yield for two steps, albeit low enantioselectivity.
Fig. 2.
Synthetic transformations and catalytic applications. a Synthetic transformations of 3b. b Cross-coupling reactions with 5b–1, the synthesis of compound 9 and its X-ray structure. c The reduction of the ester group on 3a–1 and 3b–1. d Applications in asymmetric catalysis
Plausible mechanism
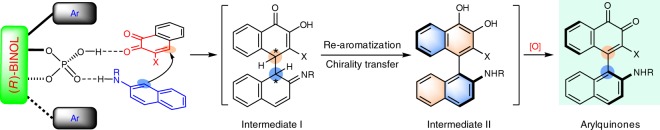
Based on the experimental results and the elegant work of Rodriguez and Bonne involving central-to-axial chirality conversion strategy49,50, a plausible reaction pathway was proposed in Fig. 3. The first step of this reaction is the chiral phosphoric acid catalyzed asymmetric conjugate addition to form intermediate I with two chiral centers. The following re-aromatization with central-to-axial chirality conversion gives atropisomeric intermediate II. Finally, oxidation by the use of excessive o-quinone furnished the excepted axially chiral arylquinone. Chiral phosphoric acid performed as a bifunctional organocatalyst to simultaneously activate 2-naphthylamine/2-naphthol/indole and o-naphthoquinone by multiple H-bonding and promote the first step of enantioselective nucleophilic addition to produce intermediate I. The rapid re-aromatization of this intermediate leads to the axially chiral intermediate II and eventually to the final product.
Fig. 3.
Proposed reaction pathway. The reaction sequence follows chiral phosphoric acid catalyzed asymmetric conjugate addition, re-aromatization with central-to-axial chirality conversion and oxidation
Discussion
In summary, we have discovered the axial chirality of o-naphthoquinones and provided the enantioselective conjugate addition strategy for the construction of axially chiral arylquinones with chiral phosphoric acid as the catalyst via sequential conjugated addition, chirality transfer and oxidation. With o-naphthoquinone as the electrophile and oxidant, three types of arylation nucleophiles, 2-naphthylamines, 2-naphthols, as well as indoles, were efficiently employed to outline the spectrum for axially chiral skeletons in good yields and excellent enantioselectivities. The resulted products could be converted to phenazine containing molecules and other useful axial chiral binaphthyls by downstream transformations. The arylquinone is not only an efficient reagent for the oxidation of amine, but also an applicable chiral ligand in asymmetric catalysis. Further investigations are underway to exploit the catalytic and synthetic applications in our laboratory.
Methods
General procedure for asymmetric synthesis (R)-3a
To a mixture of (S)-CPA4 (1 mol%), o-naphthoquinone 1a (0.44 mmol) and nucleophile 2a (0.20 mmol) in 10 mL Schlenk tube was added CH2Cl2 (4.0 mL) under Ar atmosphere. Then the reaction mixture was stirred vigorously at room temperature until 2a was completely consumed. Typical reaction time was about 20 min. The resulting mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure and purified by flash chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PE/EA = 4/1) to afford the corresponding axially chiral arylquinones (R)−3a.
General procedure for asymmetric synthesis of (S)-3b
To a mixture of (R)-CPA6 (5 mol%), o-naphthoquinone 1a (0.44 mmol) and nucleophile 2b (0.20 mmol) in 10 mL Schlenk tube was added CH2Cl2 (4.0 mL) under Ar atmosphere. Then the reaction mixture was stirred vigorously at room temperature until 2b was completely consumed. Typical reaction time was about 10 h. The resulting mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure and purified by flash chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PE/EA = 6/1) to yield the corresponding axially chiral arylquinones (S)-3b.
General procedure for asymmetric synthesis of (R)-3c
To a mixture of (S)-CPA4 (10 mol%) and nucleophile 2b (0.20 mmol) in 10 mL Schlenk tube was added CH2Cl2 (4.0 mL) under Ar atmosphere. The reaction mixture was stirred for 15 min at −30 °C before o-naphthoquinone 1b (0.44 mmol) was added under Ar atmosphere. Then the reaction was stirred vigorously at −30 °C until 2b was completely consumed. Typical reaction time was about 24 h. The resulting mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure and purified by flash chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PE/EA = 6/1) to give rise to the corresponding axially chiral arylquinones (R)-3c.
General procedure for asymmetric synthesis of (S)-3d
To a mixture of (R)-CPA7 (10 mol%) and BF4Li (8 mol%) in 10 mL Schlenk tube was added CH2Cl2 (4.0 mL) under Ar atmosphere. The reaction mixture was stirred for 1 h at room temperature. After that, o-naphthoquinone 1a (0.22 mmol) and 2c (0.10 mmol) were added and the mixture was stirred vigorously at −10 °C until 2c was completely consumed. Typical reaction time was about 24 h. The resulting mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure and purified by flash chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PE/EA = 6/1) to produce the corresponding axially chiral arylquinones (S)-3d.
General procedure for asymmetric synthesis of (S)-3e
To a mixture of (R)-CPA4 (10 mol%) and indole derivative 2d (0.10 mmol) in 10 mL Schlenk tube was added CH2Cl2 (1.0 mL) under Ar atmosphere. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 20 min. After that, a solution of o-naphthoquinone 1c (0.20 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (1.0 mL) was added dropwise at 0 °C. Then the reaction mixture was stirred vigorously at 0 °C until 2d was completely consumed (monitored by thin-layer chromatography). Typical reaction time was about 24 h. The resulting mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure and purified by flash chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PE/DCM = 1/2) to give the corresponding axially chiral arylquinones (S)-3e.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21772081 and 21825105), Shenzhen Nobel Prize Scientists Laboratory Project (C17213101), Shenzhen Special Funds for the Development of Biomedicine, Internet, New Energy, and New Material Industries (JCYJ20170412151701379, KQJSCX20170328153203) is greatly appreciated.
Author contributions
S.Z., Y.-H.C., and Y.-B.W. designed and performed experiments and prepared the supplementary information. S.-H.X. and S.-Y.L. helped with characterizing some new compounds. B.T., J.-Q.W., and J.X. conceived and directed the project and S.-H.X., P.Y., and B.T. wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Data availability
The X-ray crystallographic coordinates for structures reported in this Article have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC), under deposition number CCDC 1833698. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif. Supplementary information and chemical compound information are available in the online version of the paper. For NMR analysis and HPLC traces of the compounds in this article, see Supplementary Figures. Reprints and permissions information is available online at www.nature.com/reprints. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to B.T.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Shuai Zhu, Ye-Hui Chen, Yong-Bin Wang.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41467-019-12269-4.
References
- 1.Kozlowski MC, Morgan BJ, Linton EC. Total synthesis of chiral biaryl natural products by asymmetric biaryl coupling. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009;38:3193–3207. doi: 10.1039/b821092f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bringmann G, Gulder T, Gulder TAM, Breuning M. Atroposelective total synthesis of axially chiral biaryl natural products. Chem. Rev. 2011;111:563–639. doi: 10.1021/cr100155e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Clayden J, Moran WJ, Edwards PJ, LaPlante SR. The challenge of atropisomerism in drug discovery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009;48:6398–6401. doi: 10.1002/anie.200901719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.LaPlante SR, et al. Assessing atropisomer axial chirality in drug discovery and development. J. Med. Chem. 2011;54:7005–7022. doi: 10.1021/jm200584g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pu L. 1,1’-Binaphthyl dimers, oligomers, and polymers: molecular recognition, asymmetric catalysis, and new materials. Chem. Rev. 1998;98:2405–2494. doi: 10.1021/cr970463w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pu L. Enantioselective fluorescent sensors: a tale of BINOL. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012;45:150–163. doi: 10.1021/ar200048d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kočovský P, Vyskočil Š, Smrčina M. Non-symmetrically substituted 1,1′-binaphthyls in enantioselective catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2003;103:3213-–33246. doi: 10.1021/cr9900230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ding K, Li X, Ji B, Guo H, Kitamura M. Ten years of research on NOBIN chemistry. Curr. Org. Syn. 2005;2:499–545. doi: 10.2174/157017905774322631. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen Y, Yekta S, Yudin AK. Modified BINOL ligands in asymmetric catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2003;103:3155–3212. doi: 10.1021/cr020025b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brunel JM. BINOL: a versatile chiral reagent. Chem. Rev. 2005;105:857–898. doi: 10.1021/cr040079g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Noyori R, Takaya H. BINAP: an efficient chiral element for asymmetric catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 1990;23:345–350. doi: 10.1021/ar00178a005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Akiyama T. Stronger Brønsted acids. Chem. Rev. 2007;107:5744–5758. doi: 10.1021/cr068374j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Terada M. Binaphthol-derived phosphoric acid as a versatile catalyst for enantioselective carbon-carbon bond forming reactions. Chem. Commun. 2008;35:4097–4112. doi: 10.1039/b807577h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wencel-Delord J, Panossian A, Leroux FR, Colobert F. Recent advances and new concepts for the synthesis of axially stereoenriched biaryls. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015;44:3418–3430. doi: 10.1039/C5CS00012B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kumarasamy E, Raghunathan R, Sibi MP, Sivaguru J. Nonbiaryl and heterobiaryl atropisomers: molecular templates with promise for atropselective chemical transformations. Chem. Rev. 2015;115:11239–11300. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lv F, Yao Z-J. Recent advances in direct dehydrogenative biphenyl couplings. Sci. China Chem. 2017;60:701–720. doi: 10.1007/s11426-016-0435-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sairafianpour M, et al. Leishmanicidal, Antiplasmodial, and cytotoxic activity of novel diterpenoid 1,2-duinones from perovskia abrotanoides: new source of tanshinones. J. Nat. Prod. 2001;64:1398–1403. doi: 10.1021/np010032f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xu SW, Liu PQ. Tanshinone II-A: new perspectives for old remedies. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013;23:149–153. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2013.743995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mure M. Tyrosine-derived quinone cofactors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004;37:131–139. doi: 10.1021/ar9703342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Klinman JP, Boonot F. Intrigues and intricacies of the biosynthetic pathways for the enzymatic quinocofactors: PQQ, TTQ, CTQ, TPQ, and LTQ. Chem. Rev. 2014;114:4343–4365. doi: 10.1021/cr400475g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Largeron M. Protocols for the catalytic oxidation of primary amines to imines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013;2013:5225–5235. doi: 10.1002/ejoc.201300315. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wendlandt AE, Stahl SS. Quinone-catalyzed selective oxidation of organic molecules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015;54:14638–14658. doi: 10.1002/anie.201505017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hussain HH, et al. Development of novel antioxidants: design, synthesis, and reactivity. J. Org. Chem. 2003;68:7023–7032. doi: 10.1021/jo0301090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hung CH, et al. Experimental and theoretical studies on iron-promoted oxidative annulation of arylglyoxal with alkyne: unusual addition and migration on the aryl ring. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017;139:17015–17021. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b05981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li GQ, et al. Organocatalytic aryl-aryl bond formation: an atroposelective [3,3]-rearrangement approach to BINAM derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013;135:7414–7417. doi: 10.1021/ja401709k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.De CK, Pesciaioli F, List B. Catalytic asymmetric Benzidine rearrangement. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013;52:9293–9295. doi: 10.1002/anie.201304039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Barrett KT, Metrano AJ, Rablen PR, Miller SJ. Spontaneous transfer of chirality in an atropisomerically enriched two-axis system. Nature. 2014;509:71–75. doi: 10.1038/nature13189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Link A, Sparr C. Organocatalytic atroposelective aldol condensation: synthesis of axially chiral biaryls by arene formation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014;53:5458–5461. doi: 10.1002/anie.201402441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hazra CK, Dherbassy Q, Wencel-Delord J, Colobert F. Synthesis of axially chiral biaryls through sulfoxide-directed asymmetric mild C-H activation and dynamic kinetic resolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014;53:13871–13875. doi: 10.1002/anie.201407865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Feng J, Li B, He Y, Gu Z-H. Enantioselective synthesis of atropisomeric vinyl arene compounds by palladium catalysis: a carbene strategy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016;55:2186–2190. doi: 10.1002/anie.201509571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yu C-G, Huang H, Li X-M, Zhang Y-T, Wang W. Dynamic kinetic resolution of biaryl lactones via a chiral bifunctional amine thiourea-catalyzed highly atropo-enantioselective transesterification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016;138:6956–6959. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b03609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mori K, Itakura T, Akiyama T. Enantiodivergent atroposelective synthesis of chiral biaryls by asymmetric transfer hydrogenation: chiral phosphoric acid catalyzed dynamic kinetic resolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016;55:11642–11646. doi: 10.1002/anie.201606063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang J, Chen M-W, Ji Y, Hu S-B, Zhou Y-G. Kinetic resolution of axially chiral 5- or 8-substituted quinolines via asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016;138:10413–10416. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b06009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Olliffe JD, Armstrong RJ, Smith MD. Catalytic enantioselective synthesis of atropisomeric biaryls by a cation-directed O-alkylation. Nat. Chem. 2017;9:558–562. doi: 10.1038/nchem.2710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang Y-B, Tan B. Construction of axially chiral compounds via asymmetric organocatalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018;51:534–547. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Akiyama T, Itoh J, Yokota K, Fuchibe K. Enantioselective Mannich-type reaction catalyzed by a chiral Brønsted acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004;43:1566–1568. doi: 10.1002/anie.200353240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Uraguchi D, Terada M. Chiral Brønsted acid-catalyzed direct Mannich reactions via electrophilic activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:5356–5357. doi: 10.1021/ja0491533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chen Y-H, et al. Atroposelective synthesis of axially chiral biaryldiols via organocatalytic arylation of 2-naphthols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015;137:15062–15065. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b10152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Goriya. Y, Kim H-Y, Oh K. o-Naphthoquinone-catalyzed aerobic oxidation of amines to (ket)imines: a modular catalyst approach. Org. Lett. 2016;18:5174–5177. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b02697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Moliterno M, et al. Quinine-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of 2,2’-binaphthol-type biaryls under mild reaction conditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016;55:6525–6529. doi: 10.1002/anie.201601660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wang J-Z, et al. Symmetry in cascade chirality-transfer processes: a catalytic atroposelective direct arylation approach to BINOL derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016;138:5202–5205. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b01458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.You S-L, Cai Q, Zeng M. Chiral Brønsted acid catalyzed Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009;38:2190–2201. doi: 10.1039/b817310a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bartoli G, Bencivenni G, Dalpozzo R. Organocatalytic strategies for the asymmetric functionalization of indoles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010;39:4449–4465. doi: 10.1039/b923063g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Harris GD, et al. A one-pot, two-step synthesis of tetrahydro Asterriquinone E. Org. Lett. 1999;1:431–434. doi: 10.1021/ol990075b. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pirrung MC, Park K, Li Z-T. Synthesis of 3-indolyl-2,5-dihydroxybenzoquinones. Org. Lett. 2001;3:365–367. doi: 10.1021/ol006852l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Laursen JB, Nielsen J. Phenazine natural products: biosynthesis, synthetic analogues, and biological activity. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:1663–1686. doi: 10.1021/cr020473j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Beifuss U, Tietze M. Methanophenazine and other natural biologically active phenazines. Top. Curr. Chem. 2005;244:77–113. doi: 10.1007/b96889. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Guttenberger N, Blankenfeldt W, Breinbauer R. Recent developments in the isolation, biological function, biosynthesis, and synthesis of phenazine natural products. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017;25:6149–6166. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Quinonero O, et al. Combining organocatalysis with central-to-axial chirality conversion: atroposelective Hantzsch-type synthesis of 4-arylpyridines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016;55:1401–1405. doi: 10.1002/anie.201509967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Raut VS, et al. Enantioselective syntheses of furan atropisomers by an oxidative central-to-axial chirality conversion strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017;139:2140–2143. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b11079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The X-ray crystallographic coordinates for structures reported in this Article have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC), under deposition number CCDC 1833698. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif. Supplementary information and chemical compound information are available in the online version of the paper. For NMR analysis and HPLC traces of the compounds in this article, see Supplementary Figures. Reprints and permissions information is available online at www.nature.com/reprints. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to B.T.