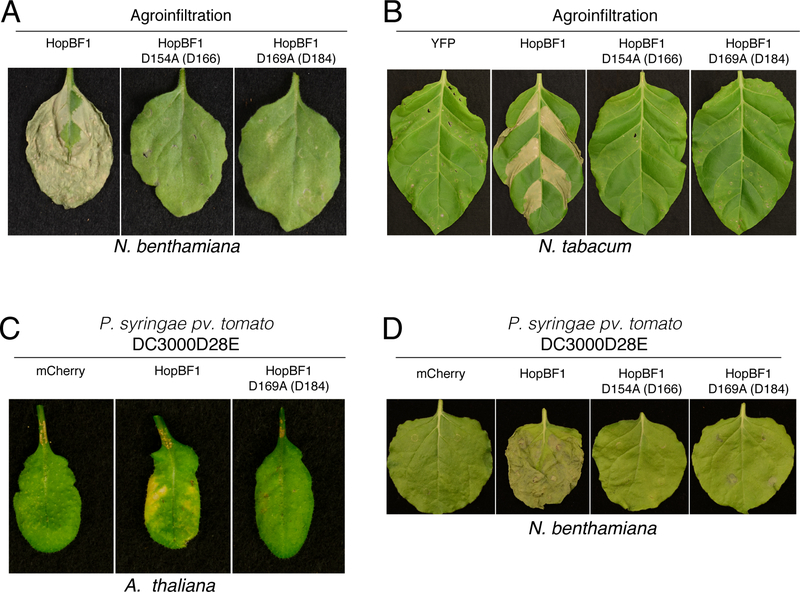
Figure 2. HopBF1 induces severe disease symptoms in plants (Related to Figure S2).
(A) Agrobacterium-mediated expression of HopBF1 leads to leaf tissue collapse. Leaves of N. benthamiana plants were infiltrated with A. tumefaciens carrying HopBF1 or the predicted kinase inactive mutants D154A and D169A. PKA numbering is in parentheses. Photos were taken 7 days post infiltration.
(B) Agrobacterium-mediated expression of HopBF1 induces tissue collapse in N. tabacum. Sections of tobacco leaves were infiltrated with A. tumefaciens carrying HopBF1 or the predicted kinase inactive mutants D154A and D169A. YFP was used as a negative control. Tissue collapse in the infiltrated zones developed within 4 days.
(C) HopBF1 evokes leaf tissue collapse in Arabidopsis plants after infection with P. syringae. Three adult leaves were infiltrated with P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 strain with 28 effectors deleted expressing HopBF1, the D169A mutant or mCherry as a control. Representative leaves were photographed 6 days post inoculation.
(D) HopBF1 evokes N. benthamiana leaf tissue collapse after infection with P. syringae. Leaves of N. benthamiana plants were infiltrated with P. syringae strain pv. tomato DC3000 with 28 effectors deleted expressing HopBF1, the D154A and D169A mutants or mCherry as a control. Representative leaves were photographed 7 days post inoculation.