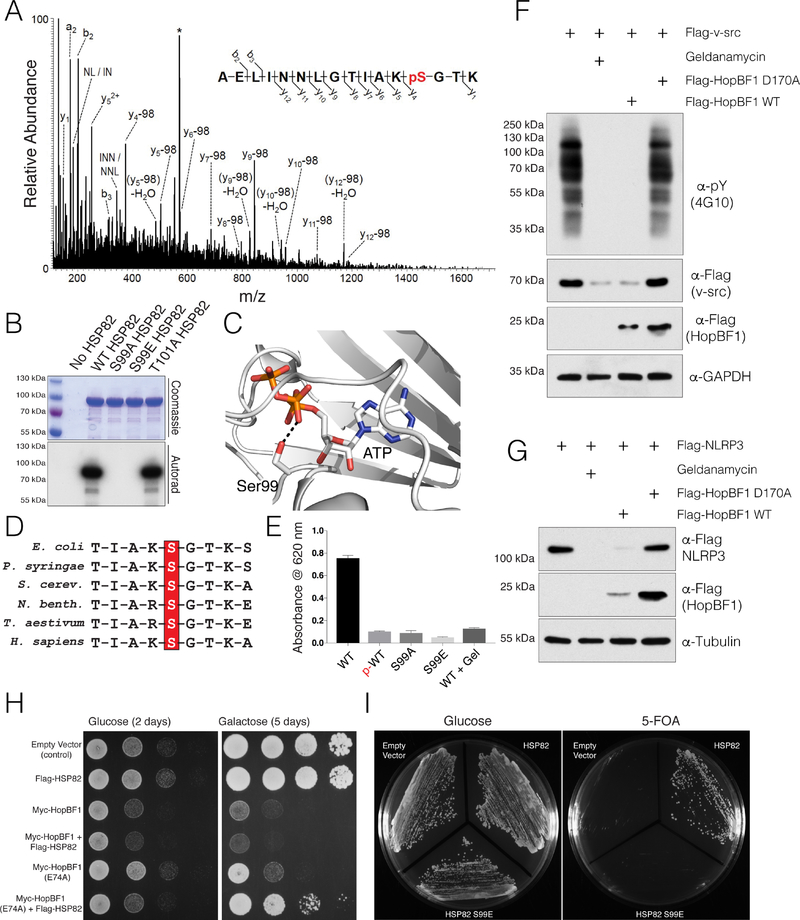
Figure 4. HopBF1 inactivates HSP90 ATPase and chaperoning activity (Related to Figure S4).
(A) Representative MS/MS fragmentation spectra of a tryptic peptide (HSP82 87–102) depicting Ser99 phosphorylation of HSP82. Recombinant HSP82 was incubated with ATP and P. syringae HopBF1, separated by SDS PAGE and subjected to MS. Control experiments were performed in parallel using P. syringae HopBF1 D169A but no phosphopeptides were identified.
(B) Incorporation of 32P from [γ32P]ATP into S. cerevisiae HSP82 and the Thr101Ala mutant but not the Ser99Ala or the Ser99Glu mutants by recombinant P. syringae HopBF1. Reaction products were analyzed as in Figure 3B.
(C) Zoomed in view of the active site of HSP90, PDB: 2CG9 (Ali et al., 2006) depicting the interaction between the β-phosphate of ATP and the HopBF1 target Ser (Ser99 in yeast; Ser108 in human HSP90β).
(D) Multiple sequence alignment depicting the conservation of the HopBF1 target Ser in the HSP90 family of chaperones. HSP90 sequences from E. coli, P. syringae, S. cerevisiae, N. benthamiana, T. aestivum and H. sapiens are shown.
(E) ATPase activity of unphosphorylated (WT) and HopBF1-phosphorylated (p-WT) HSP82 was assayed by measuring free phosphate release from ATP using the Malachite Green method. The activities of the S99A and S99E mutants are also shown. The HSP90 inhibitor geldanamycin (Gel) was used as a control.
(F) Protein immunoblotting of HEK293A cell extracts expressing Flag-v-src with E. americana HopBF1 or the D170A mutant. Cells were also pretreated with geldanamycin. Extracts were analyzed for v-src activity as judged by global phospho-Tyr immunoblotting (α-pY; 4G10). Levels of Flag-v-src and HopBF1 are also shown. GAPDH is included as a loading control.
(G) Protein immunoblotting of HEK293A cell extracts expressing Flag-NLRP3 with E. americana HopBF1 or the D170A mutant. Cells were also pretreated with geldanamycin. Levels of Flag-NLRP3 and HopBF1 are also shown. Tubulin is included as a loading control.
(H) Spot assay depicting the growth of S. cerevisiae expressing Flag-tagged S. cerevisiae HSP82 (Flag-HSP82) with Myc-tagged P. syringae HopBF1 (Myc-HopBF1) or the hypomorphic E74A mutant. Images were taken 2 days after spotting (glucose) and 5 days after spotting (galactose, induced).
(I) Viability of HSP90 null yeast expressing empty vector, WT HSP82 or the Ser99Glu (S99E) phosphomimetic mutant deduced by a 5-fluoroorotic acid (5-FOA) shuffling assay (Nathan and Lindquist, 1995).