Abstract
We have studied synaptic function in a transgenic mouse strain relevant to Alzheimer's disease (AD), overexpressing the 695 amino acid isoform of human amyloid precursor protein with K670N and M671L mutations (APP695SWE mice), which is associated with early-onset familial AD. Aged-transgenic mice had substantially elevated levels of Aβ (up to 22 μmol/gm) and displayed characteristic Aβ plaques. Hippocampal slices from 12-month-old APP695SWE transgenic animals displayed reduced levels of synaptic transmission in the CA1 region when compared with wild-type littermate controls. Inclusion of the ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonist kynurenate during preparation of brain slices abolished this deficit. At 18 months of age, a selective deficit in basal synaptic transmission was observed in the CA1 region despite treatment with kynurenate. Paired-pulse facilitation and long-term potentiation (LTP) were normal in APP695SWE transgenic mice at both 12 and 18 months of age. Thus, although aged APP695SWE transgenic mice have greatly elevated levels of Aβ protein, increased numbers of plaques, and reduced basal synaptic transmission, LTP can still be induced and expressed normally. We conclude that increased susceptibility to excitotoxicity rather than a specific effect on LTP is the primary cause of cognitive deficits in APP695SWE mice.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease, synaptic plasticity, LTP, hippocampus, APP, transgenic
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive memory loss and personality changes (McKhann et al., 1984). Mutations in the amyloid precursor protein (APP) gene account for ∼2–3% of familial AD cases (Goate et al., 1991) (for review, see Hardy, 1997; Price and Sisodia, 1998; Seabrook and Rosahl, 1999). Such mutations lead to changes in the processing of APP, resulting in either a general increase in production of Aβ or a shift in processing, leading to a greater production of the longer forms of Aβ that lead to plaque deposition. Mutations in other proteins, such as presenilins 1 and 2, also lead to altered APP processing and have been linked to a greater percentage of familial AD cases (Hardy, 1997; Price and Sisodia, 1998;Seabrook and Rosahl, 1999). One mutation in the APP gene that is related to the development of AD is the so-called Swedish mutation, in which the 695 amino acid APP protein contains the two mutations K670N and M671L (APP695SWE mutation). Expression of this mutation in cultured cells leads to an elevation in the formation of all forms of Aβ (Citron et al., 1992).
Mice expressing the human form of the APP695SWE mutation [APP695SWE transgenic mice (Tg mice)] have been shown to develop certain Alzheimer's-like symptoms, such as increased Aβ deposits and plaques, increased glial cell number, and deficits in spatial memory in the Morris water maze and forced T maze tests (Hsiao et al., 1996; Irizarry et al., 1997; Frautschy et al., 1998; Chapman et al., 1999). In electrophysiological studies of the hippocampus, these mice showed normal synaptic transmission but exhibited reduced hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) in the CA1 and dentate regions (Chapman et al., 1999). It was proposed that these alterations in synaptic plasticity underlie some of the cognitive deficits in AD. However, in similar studies using other AD-related mutations in the APP gene, which resulted in Aβ overexpression but not necessarily plaque deposition (Hsia et al., 1999; Larson et al., 1999), synaptic transmission was impaired but LTP in the CA1 region was expressed normally. Given the importance of establishing a cellular correlate of the cognitive dysfunction of AD, it is imperative to resolve this apparent controversy. We have also investigated synaptic transmission and LTP in the hippocampus of the APP695SWE mutant mouse. In contrast to the study of Chapman et al. (1999), we find impaired synaptic transmission but normal levels of LTP. We also find that kynurenate, applied during the slicing procedure, offers protection against this deficit in synaptic transmission. Our data therefore favor excitotoxicity rather than a direct deficit in the LTP process as the major correlate of the cognitive dysfunction in this mouse strain relevant to AD.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Transgenic mice. The generation of the APP695SWE transgenic mice used in this study were described previously (Hsiao et al., 1995, 1996). Tg mice were originally in a hybrid 87.5% C57BL6 × 12.5% SJL genetic background and were subsequently backcrossed to C57BL6 × SJL F1 mice. Four generations of mice were studied (the relative proportion of C57BL6 is cited in parentheses); F2 (87.5%), N1 (69%), N2 (59%), and N4 (52%). All experiments on transgenic mice included wild-type littermate mice controls (Wt mice) in identical genetic backgrounds as appropriate. All animals were genotyped using PCR-based methods for detection of the APP695SWE transgene (Hsiao et al., 1995) and for the rd (retinal degeneration) mutation (Kuenzi et al., 1999). rd homozygous mice were excluded from this study as a precaution, because it has been suggested that this mutation may indirectly affect neuronal number within the hippocampus (Wimer et al., 1991). All experiments and analyses were performed with the experimenters blind as to the genotype of the animal.
Histology. Histology was performed on the brains of mice used for the electrophysiological study. The contralateral hippocampus was immersion fixed in 10% formal saline (Merck Pharmaceuticals, West Drayton, UK) for 24 hr and then processed to paraffin wax, via graded alcohols with chloroform as the clearing agent. Once embedded, 8 μm sagittal sections were collected through the entire ventromedial extent of the hippocampus. APP and plaque deposition were visualized using monoclonal antibodies to human amyloid precursor protein (clone 22C11; Boehringer Ingelheim Limited, Berkshire, UK) or Aβ (clone 6F3D; Dako, High Wycombe, UK), respectively.
Sections were dewaxed, rehydrated, and maintained in 0.1 mPBS. Sections for the demonstration of Aβ were treated first with concentrated formic acid (Merck Pharmaceuticals) for 10 min. After blocking nonspecific binding by incubation in unlabeled horse anti-mouse IgG (1:200; Vector Laboratories, Peterborough, UK) followed by incubation in 5% normal horse serum (Vector Laboratories), slices were incubated with antibody against either APP (1:50) or Aβ (1:100) overnight at +4°C, followed by biotinylated anti-mouse IgG (1:200; Vector Laboratories). Staining was visualized by peroxidase ABC elite reagent (Vector Laboratories) for 30 min, followed by diaminobenzidine solution for 10 min (Menarini Pharmaceuticals, High Wycombe, UK). Sections were counterstained with hematoxylin and mounted in Depex (Merck Pharmaceuticals) for microscopic evaluation.
Quantification of Aβ levels by homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence. Amyloid was extracted from the contralateral hemispheres by homogenization in 10 vol of 5m GnHCl, 50 mm HEPES, pH 7.3, 5 mm EDTA, and 1× protease inhibitor cocktail (Complete; Roche Diagnostics, Hertforshire, UK). After 3 hr rotation at room temperature, the homogenate was diluted 10-fold into ice-cold 25 mm HEPES, pH 7.3, 1 mm EDTA, 0.1% BSA, and 1× protease inhibitor cocktail and centrifuged (16,000 × g for 20 min at 4°C). Aliquots of the supernatant were stored at −20°C to prevent degradation.
The levels of amyloid peptides Aβ(40) and Aβ(42) were detected by homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF). All peptides (of >95% purity; California Peptide Research Inc., Napa, CA) were frozen at 100 μm in 100% DMSO and serially diluted in buffer whose composition reflects that of the extracted samples (1 part GnHCl extraction buffer:9 parts dilution buffer, as above). The HTRF signal was generated as a result of nonradiative transfer from europium cryptate-labeled Aβ(40)- or Aβ(42)-specific antibodies (G2–10 and G2–11, respectively; licensed from the University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany; labeled at CIS bio international, Marcoule, France) to streptavidin-conjugated allophycocyanin (SA-XL665) (ProZyme, San Leandro, CA). The latter was brought into the complex by interaction with biotinylated antibody 4G8 (Senetek, Maryland Heights, MO), which is specific for residues 17–24 of Aβ. Final reagent concentrations in a typical 96-well plate assay were as follows: G2–10K (0.75 nm) or G2–11K (0.6 nm), 4G8 with or without biotin (1.0 nm), SA-XL665 (2.0 nm), and KF (0.1–0.2 m). Sample or synthetic peptide standard (50 μl) was assayed, and a total volume of 200 μl/well was made up with dilution buffer. Blank values were determined by the use of nonbiotinylated 4G8 antibody. The reaction mixture was left at 4°C for 20 hr and then read on the Discovery HTRF microplate analyzer, providing simultaneous measurement at 665 nm (SA-XL665 fluorescence) and 620 nm (europium cryptate fluorescence). The ΔR ratio [ΔR ratio = Ratio (sample) − Ratio (blank)] was used to extrapolate the amyloid concentrations of the brain extracts from the synthetic peptide standard curves.
Electrophysiology. Recordings were made form 350-μm-thick parasagittal hippocampal slices prepared from 12- and 18-month-old Tg and Wt mice. Animals were killed by decapitation, or cervical dislocation, in accordance with the UK Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986, and the brains were rapidly removed in ice-cold artificial CSF (aCSF). The composition of this aCSF was (in mm): 126 NaCl, 1.2 NaH2PO4, 1.3 MgCl2, 2.4 CaCl2, 2.5 KCl, 26 NaHCO3, and 10 glucose. Brains were cut along the midline and parasagittal whole brain slices prepared from one hemisphere using a vibratome. The hippocampus was then dissected out of these slices. The contralateral hemisphere was used for histology or determination of Aβ levels. Kynurenate (1 mm) was included in the aCSF used for dissection where indicated, and slices were then transferred to nonkynurenate containing aCSF either immediately after dissection or half an hour later, with no difference seen between the two methods. Slices were allowed to recover for at least 1 hr before being transferred to a submerged recording chamber perfused with aCSF at 2 ml/min and maintained at 32°C.
Field EPSPs (fEPSPs) were recorded from the CA1 region and the dentate gyrus. In the CA1 region, recordings were made using glass microelectrodes filled with 4 m NaCl placed in stratum radiatum, and Schaffer collateral–commissural fibers were stimulated using a bipolar nickel–chromium electrode. In the dentate gyrus, recordings were made by stimulating and recording from the medial perforant path. The initial slope of the rising phase of the fEPSP was used as a measure of synaptic efficacy. Recordings were made using the LTP program (Anderson and Collingridge, 1997) or a SPIKE 2 script running on a CED1401plus interface (Cambridge Electronic Design, Cambridge, UK). Stimulus–response curves were constructed by using stimulus intensities from 0 to 45 V in increments of 5 V. Responses were subsequently set to a level that gave a slope value 20% of the maximum obtained. Baseline responses were obtained every 30 sec. Paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) was assessed using a succession of paired pulses separated by intervals of 25, 50, 100, 200, and 300 msec. An additional 30 min baseline period was obtained before attempting to induce LTP.
LTP was induced by delivery of a theta burst stimulation paradigm (TBS), consisting of 10 bursts each of four stimuli delivered at a frequency of 100 Hz, with bursts delivered at a frequency of 5 Hz, given at the test stimulus intensity. In some experiments, LTP was induced using a stronger stimulation, whereby TBS was delivered a total of three times, each delivery separated by 15 sec. For LTP experiments in the dentate gyrus, slices were incubated in 50 μmpicrotoxin, and TBS was delivered at 10 times the test strength. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
RESULTS
Aβ levels and amyloid plaque deposition
Expression of the APP695SWE gene produced a dramatic increase in both short [Aβ(40)] and long [Aβ(42)] forms of the Aβ peptide, of ∼1000-fold (Table1). This was evident at 12 months, and the increase was even greater at 18 months of age. Plaques were also evident in both age groups of APP695SWE Tg mice throughout the hippocampus but were not evident in Wt animals (Fig.1).
Table 1.
Elevated levels of Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 in human APP695SWE transgenic mice at 12 versus 18 months of age
| 12 months | 18 months | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt | Tg | Wt | Tg | |
| Aβ1–40 | 3 ± 2* (9) | 5159 ± 784 (6) | 19 ± 11* (7) | 22,609 ± 1102 (6) |
| Aβ1–42 | 2 ± 1* (9) | 3058 ± 681 (6) | 14 ± 13* (7) | 11,085 ± 678 (6) |
The Aβ load of the contralateral hemisphere of mice used for electrophysiological studies was quantified using a homogenous time-resolved fluorescence assay. Values are in picomoles per gram wet weight tissue, with the number of animals in parentheses.
indicates background levels of detection.
Fig. 1.

Amyloid plaque load and APP expression in hippocampus of 18-month-old Wt and Tg mice. Tissue was immersion fixed, sectioned at 6 μm, and counter-stained with hematoxylin. A and B show amyloid plaques labeled with anti-human β amyloid (6F3D). No plaques are present in Wt animals (A) and can be seen localized to the subiculum, stratum oriens, and stratum moleculare of Tg animals (B). Reactive microgliosis and astrocytosis were also associated with plaques (data not shown). C andD illustrate endogenous expression of APP in Wt animals (C) detected with a supraoptimal dilution of anti- human APP695 (22C11). D illustrates a high level of intraneuronal accumulation of APP in CA1 through CA4 cell body layers. Heavy labeling of plaques was also evident in subiculum, stratum oriens, stratum moleculare, and stratum granulosum of the dentate gyrus. Evident with plaque structures were intense punctate labeling indicative of type I dystrophic neurites (data not shown). Scale bar, 200 μm.
Electrophysiology
Basal synaptic transmission in the CA1 region
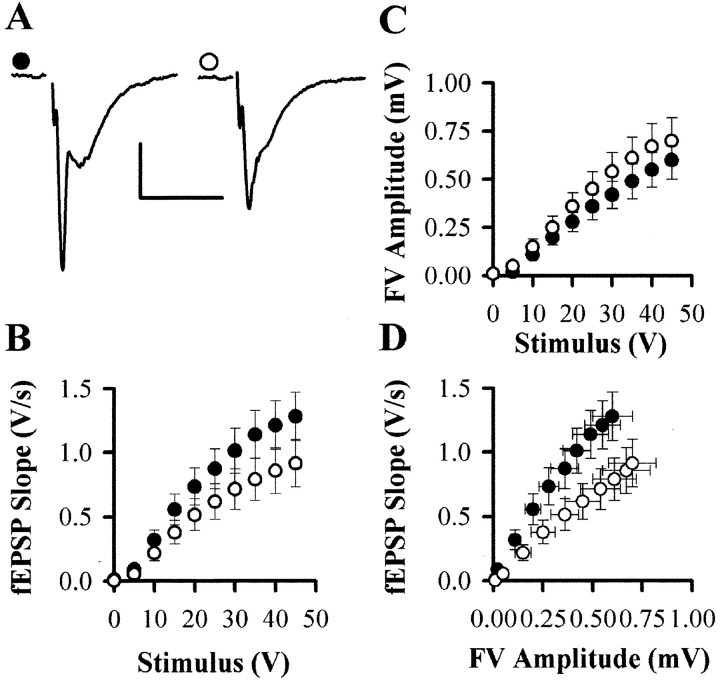
Initial experiments were performed on slices from 12-month-old animals prepared without the use of kynurenate in the dissection media (Fig. 2A–D). In general, it was difficult to obtain good synaptic responses in the CA1 region of hippocampal slices obtained from these mice compared with other mouse strains on which we have worked (Kuenzi et al., 1999;Morton et al., 1999; Seabrook et al., 1999; Fitzjohn et al., 2000), and this is reflected in the mean low-amplitude responses in the fEPSP slope versus stimulus intensity plot (Fig. 2B). Excluded from this analysis are many slices from which it was not possible to evoke reasonable synaptic responses. When these data were analyzed in terms of fiber volley (FV) amplitude versus stimulus intensity (Fig. 2C) and fEPSP slope versus FV amplitude (Fig. 2D), a clear deficit in synaptic transmission was evident in the Tg mice. The slope of the input–output plot was reduced from 1.03 ± 0.16 V · sec−1 · mV−1(n = 47 slices from 23 animals) in Wt mice to 0.72 ± 0.10 V · sec−1 · mV−1(n = 47 slices from 27 animals) in Tg mice (p < 0.05). The reason that the deficit was not apparent in the fEPSP versus stimulus intensity plot is probably attributable to the method used to optimize the electrode placements and stimulus parameters; this was done by maximizing the size of the fEPSP. Presumably, more time was spent searching for usable synaptic responses in the Tg mice, and this is reflected in the larger FV amplitudes, as a result of either closer electrode placements or damage to the slice by repeated movement of electrodes (Fig.2C).
Fig. 2.

Basal synaptic transmission is reduced in the CA1 region of 12-month-old APP695SWE Tg mice. A, Individual examples of fEPSPs recorded with a stimulus intensity of 35 V from the CA1 region of slices prepared from 12-month-old Wt (●;n = 47 slices from 23 animals) and Tg (○;n = 47 slices from 27 animals) animals without the use of kynurenate, showing a reduction in Tg animals. Calibration: 0.5 mV, 10 msec. B–D, Pooled data (mean ± SEM) showing the relationship between fEPSP slope and stimulus intensity (B), FV amplitude and stimulus intensity (C), and fEPSP slope and fiber volley amplitude (D). E–H, Equivalent data for experiments performed on slices prepared in the presence of kynurenate (Wt, n = 24 slices from 6 animals; Tg,n = 22 slices from 6 animals).
It has been suggested that the inclusion of kynurenate in the dissection medium may improve slice viability in this strain of mice (Chapman et al., 1999) (P. F. Chapman personal communication). We therefore repeated these experiments using 1 mm kynurenate (Fig. 2E–H). Under these conditions, synaptic viability was greatly improved in both Tg and Wt mice (Fig. 2F), and the deficit in synaptic transmission in the Tg mice was no longer apparent (Fig.2H). Thus, under these conditions, the slopes of the input–output plots were 2.42 ± 0.22 V · sec−1 · mV−1(n = 24 slices from 6 animals) and 2.97 ± 0.40 V · sec−1 · mV−1(n = 22 slices from 6 animals) for Wt and Tg mice, respectively (p > 0.05).
Given the beneficial effects of kynurenate, we performed all of the experiments using the 18-month-old age group using kynurenate treatment. In these experiments, however, a deficit in the Tg mice was apparent (Fig. 3A–D). Thus, the slopes of the input–output plots were reduced from 2.35 ± 0.23 V · sec−1 · mV−1(n = 25 slices from 10 animals) in the Wt to 1.22 ± 0.14 V · sec−1 · mV−1in the Tg mice (n = 29 slices from 12 animals;p < 0.01).
Fig. 3.
Basal synaptic transmission is reduced in the CA1 region of 18-month-old APP695SWE Tg mice, prepared in the presence of kynurenate. A, Single examples of fEPSPs recorded with a stimulus intensity of 35 V from the CA1 region of slices prepared from 18-month-old Wt (●; n = 25 slices from 10 animals) and Tg (○; n = 29 slices from 12 animals) animals. Calibration: 0.5 mV, 10 msec.B–D, Pooled data showing the relationship between fEPSP slope and stimulus intensity (B), fiber volley amplitude and stimulus intensity (C), and fEPSP slope and fiber volley amplitude (D).
Synaptic plasticity in the CA1 region
A measure of short-term synaptic plasticity, PPF was examined in both 12-month-old, without kynurenate treatment, and 18-month-old mice. In both age groups, there was no difference between Tg and Wt mice (Fig. 4). For example, at an interstimulus interval of 50 msec, the paired-pulse ratio (slope of second response/slope of first response) observed in 12-month-old Wt and Tg animals was 1.72 ± 0.05 (n = 34 slices from 17 animals) and 1.73 ± 0.05 (n = 43 slices from 16 animals; p > 0.1), respectively. In 18-month-old animals, the paired-pulse ratio at this interval was 1.60 ± 0.04 (n = 18 slices from six animals) and 1.54 ± 0.10 (n = 11 slices from four animals;p > 0.1) in Wt and Tg animals, respectively.
Fig. 4.
Paired-pulse facilitation is normal in the CA1 region of APP695SWE Tg mice. A, Example traces taken from 18-month-old Wt (●) and Tg (○) animals showing paired-pulse facilitation at interstimulus intervals of 25 and 100 msec. Calibration: 0.5 mV, 20 msec. B, Pooled data for 12-month-old animals (Wt, n = 34 slices from 17 animals; Tg, n = 43 slices from 16 animals).C, Pooled data for 18-month-old animals (Wt,n = 18 slices from 6 animals; Tg,n = 11 slices from 4 animals).
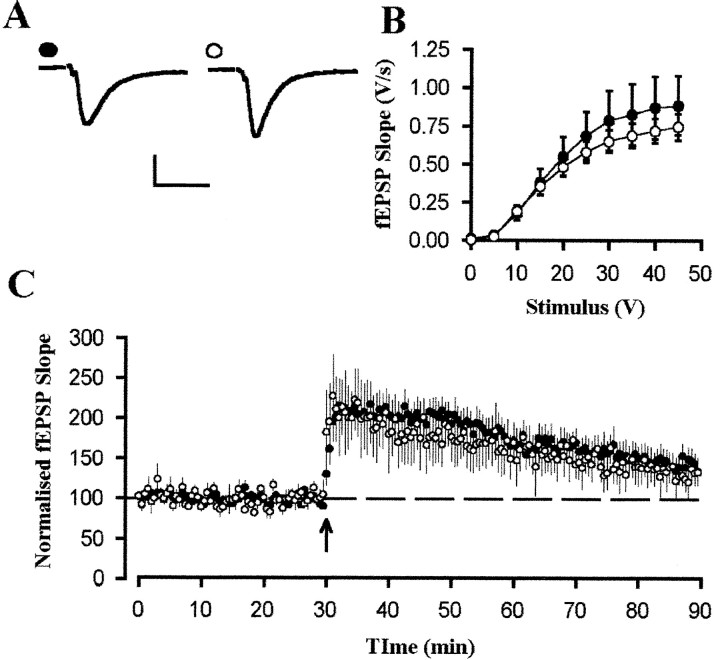
LTP was also studied in the CA1 region of hippocampal slices. Despite the reduced level of basal synaptic transmission in slices prepared without the use of kynurenate from 12-month-old Tg compared with Wt animals, LTP in these mice was normal (Fig.5). Thus, in Wt and Tg mice, 60 min after a theta burst stimulus, responses were 171 ± 10% (n = 26 slices from 17 animals) and 164 ± 11% (n = 22 slices from 18 animals) of control. Normal levels of LTP in hippocampal slices from Tg mice was apparent regardless of the genetic background of the animals used. In F2 generation mice, the relative amplitude of LTP at 1 hr after a theta burst (expressed as a percentage of LTP in Wt mice) was 98% (n = 10 slices from 4 Wt animals and 8 slices from 6 Tg animals; p > 0.1) compared with 78% (n = 11 slices from 8 Wt animals and 9 slices from 7 Tg animals; p > 0.1) in N1 and 114% in N2 animals (n = 5 slices from 5 Wt animals and 5 slices from 5 Tg animals; p > 0.1). Likewise, in slices prepared from 18-month-old animals, the magnitude of LTP observed 60 min after theta burst stimulation was 166 ± 11% (n = 22 slices from 12 animals) and 179 ± 7% (n = 13 slices from 8 animals) of control for Wt and Tg mice, respectively (Fig.6A–C).
Fig. 5.

LTP is normal in area CA1 of 12-month-old APP695SWE Tg mice. A, Example experiment from a slice prepared without the use of kynurenate from a Wt animal. Examples traces are taken from the time points immediately before and 60 min after the induction of LTP. LTP was induced by the delivery of theta burst stimulation at the time indicated by thearrow. Calibration: 0.25 mV, 10 msec. B, Similar data taken from a Tg animal. C, Pooled data for 12-month-old animals from slices prepared without the use of kynurenate, showing no difference in the levels of LTP between Wt (●;n = 26 slices from 17 animals) and Tg (○;n = 22 slices from 18 animals) animals.
Fig. 6.
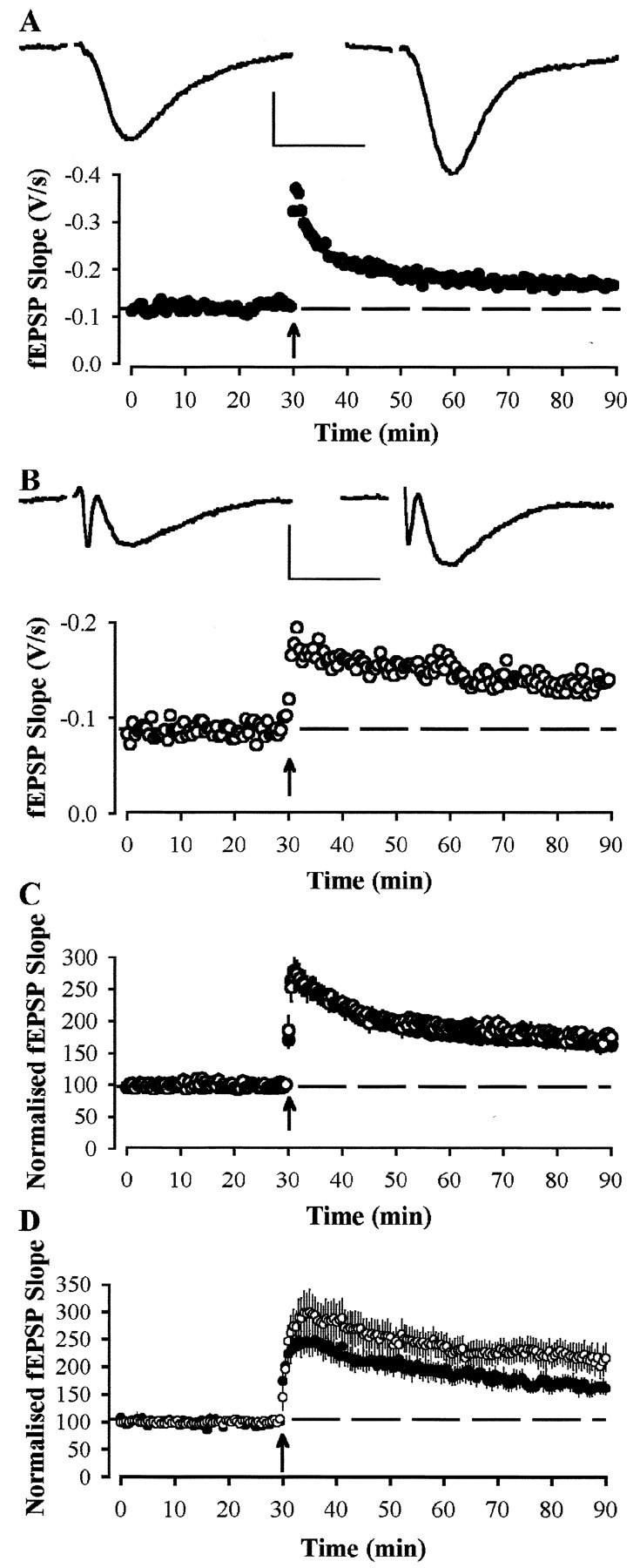
Long-term potentiation is normal in area CA1 of 18-month-old APP695SWE transgenic mice. A, Example experiment from a slice, prepared with the use of kynurenate, from a Wt animal. Examples traces are taken from the time points immediately before and 60 min after the induction of LTP. LTP was induced by the delivery of theta burst stimulation at the time indicated by the arrow. Calibration: 0.25 mV, 10 msec.B, Similar data taken from a Tg animal.C, Pooled data for 18-month-old animals from slices prepared with the use of kynurenate, showing no difference in the levels of LTP between Wt (●; n = 22 slices from 12 animals) and Tg (○; n = 13 slices from 8 animals) mice. D, Pooled data showing LTP induced by strong theta burst stimulation (3 theta burst trains, separated by 15 sec) in Wt (●; n = 8 slices from 4 animals) and Tg (○; n = 8 slices from 4 animals) mice.
Finally, we used a stronger stimulus (three times theta burst stimulation) to induce LTP in the CA1 region of slices from 18-month-old animals (Fig. 6D). In these experiments, the LTP observed 60 min after inducing LTP was 165 ± 14% (n = 8 slices from 4 animals) in Wt mice compared with 211 ± 27% (n = 8 slices from 4 animals) in Tg mice (p > 0.1).
Synaptic transmission and plasticity in the dentate gyrus
Stimulus–response curves were obtained from the dentate gyrus region of mice aged 18 months (with kynurenate during slice preparation). In all cases, Tg mice showed normal synaptic transmission compared with Wt controls (Fig.7A). Thus, a 40 V stimulus elicited responses of 0.9 ± 0.2 V/sec (n = 30 slices from 15 animals) and 0.7 ± 0.1 mV/sec (n = 28 slices from 12 animals) in Wt and Tg mice, respectively (p > 0.05). We were unable to construct fEPSP slope versus FV amplitude plots for experiments performed in the dentate gyrus region because the majority of responses failed to show a visible fiber volley. This was true for both wild-type and transgenic animals, and no obvious difference between the two groups in terms of fiber volley amplitude was observed.
Fig. 7.
Synaptic transmission and long-term plasticity in the dentate gyrus of 18-month-old APP695SWE transgenic mice are normal. A, Example traces show the response to a 30 V stimulus from a Wt (●) and a Tg (○) mouse. Calibration: 0.5 V, 10 msec. These slices were prepared in the presence of kynurenic acid (1 mm). B, Pooled data showing stimulus response curves for Wt (●; n = 30 slices from 15 animals) and Tg (○; n = 28 slices from 12 animals) mice. C, Pooled data showing LTP in Wt (●;n = 8 slices from 6 animals) and Tg (○;n = 4 slices from 4 animals) mice. LTP was induced by a strong theta burst stimulus (see Materials and Methods) given at the time indicated by the arrow. Eachpoint represents the response to a single stimulus. Slices were bathed in picrotoxin (50 μm) throughout.
LTP in the dentate gyrus was studied in 18-month-old animals after blockade of GABAA receptor function with picrotoxin (see Materials and Methods). Strong theta burst stimulation induced a similar increase in response size in both Wt and Tg animals (Fig. 7B). Thus, 60 min after theta stimulation, responses were 135 ± 18% (n = 8 slices from 6 animals) and 134 ± 12% (n = 4 slices from 4 animals) of control for Wt and Tg mice, respectively.
DISCUSSION
The primary findings of the present study are that (1) basal synaptic transmission in area CA1 is impaired and (2) normal levels of LTP can be induced in mice that overexpress the human APP695SWE mutant form of APP in both the CA1 and dentate gyrus regions. These results would seem to directly contradict the previous conclusion that in the same strain of transgenic mouse (Hsiao et al., 1996) this mutation leads to a dramatic reduction in LTP but no alteration in basal synaptic transmission (Chapman et al., 1999). Given the potential usefulness of this mouse strain for the understanding of the etiology of AD, it is important to understand the basis of this apparent controversy.
Effects on basal synaptic transmission and LTP
There are two reasons why in the study of Chapman et al. (1999) a deficit in basal synaptic transmission was not observed. First, they performed all of their in vitro experiments using kynurenate-treated slices and, as we have demonstrated here, the deficit is less pronounced in slices prepared using this approach. Indeed, when we used kynurenate treatment, the deficit in synaptic transmission was only apparent in the 18 month age group and not in the 12 month age group. In this context, Chapman et al. (1999) used two age groups (2–8 months and 15–17 months), and so the deficit may not have developed in their animals. Furthermore, Chapman et al. incubated slices in kynurenate until they were transferred to the recording chamber, whereas in the present study, slices were maintained for only 30 min or less after dissection in kynurenate-containing medium. Second, they quantified synaptic transmission by plotting fEPSP slope versus stimulus intensity and, as we show here, using this approach it is possible to miss deficits in synaptic transmission that are apparent in fEPSP versus FV amplitude plots. Indeed, initial observations byChapman et al. (1997) did suggest a deficit in basal synaptic transmission in APP695SWE mutant mice.
The reason for the difference in the LTP results is more difficult to explain. Chapman et al. (1999) found a substantial impairment in LTP in their older age group at both CA1 and dentate synapses. In our group of comparable age, we observed substantial LTP at CA1 synapses in every slice tested, and the pooled data sets were superimposable. In subsequent experiments using the same induction protocol as that used by Chapman et al. (1999), we found no deficit in LTP in the CA1 region, nor have we observed any differences in the level of basal synaptic transmission or LTP expressed in the dentate gyrus. We conclude that LTP can be readily obtained in these aged APP695SWE mice; however, factors such as alterations in basal synaptic transmission might affect LTP induction under certain experimental conditions.
Relationship to other mouse strains relevant to Alzheimer's disease
The conclusions of the present study are in broad agreement with studies using transgenic mice that overexpress the V717F mutant form of APP (APPInd; Games et al., 1995). In the study ofHsia et al. (1999), there was very pronounced deficits in synaptic transmission that developed over the first year of life. Despite this, LTP at CA1 synapses of 8- to 10-month-old mice was normal. In the study of Larson et al. (1999), pronounced age-related deficits in synaptic transmission were also observed. Deficits in LTP at CA1 synapses were observed in the young animals (4–5 months) but not the older animals (27–29 months). These LTP deficits were attributed to changes in circuitry affecting induction indirectly rather than an alteration in the LTP process per se. In the London mutation (V642I), there was a substantial reduction in LTP at CA1 synapses (Moechars et al., 1999). Similar effects were observed in transgenic mice expressing a C-terminal 104 amino acid fragment of APP (Nalbantoglu et al., 1997). Our finding that the APP695SWE mutant mouse resembles the APPInd mouse in both the age-related impairment in synaptic transmission and its capacity to express LTP normally suggests that this phenotype is relevant to the overexpression of Aβ rather than some other unique feature of either of these strains of mice.
A number of studies have also examined the effects of other AD-linked mutations on synaptic plasticity (Seabrook and Rosahl, 1999). In contrast to overexpression of human APP mutants, disruption of the mouse APP gene causes a small reduction in LTP (Dawson et al., 1999;Seabrook et al., 1999) that may be attributable to an indirect effect on inhibitory transmission (Fitzjohn et al., 2000). Overexpression of the A246E mutation in the presenilin 1 gene (Parent et al., 1999), or expression of a PS1 exon 9 deletion mutant (Zaman et al., 2000), treatments, which also elevates production of Aβ1–42 (Borchelt et al., 1996), caused an increase in the magnitude of LTP at hippocampal CA1 synapses. Clearly, no obvious correlation exists between Aβ levels and LTP.
On the mechanism of the deficit
In the present study, at 18 months of age, Aβ levels were over 1000-fold higher than in wild-type mice, and there was the deposition of plaques in all areas of the hippocampus and other brain regions. Although the elevated production of Aβ protein, and associated plaques, are characteristic of AD pathology, it is still not known whether declines in cognitive function are caused (1) directly by toxic action of Aβ protein or its fragments, (2) whether it is an indirect effect caused by an immune response triggered by plaque deposition, or (3) the production of Aβ is a by-product rather than a causative factor in the disease process (Hardy, 1997; Neve and Robakis, 1998).
In the study of Hsia et al. (1999), it was concluded that there is a reduction in the number of functional synaptic connections in the APPInd mouse. Although we have not explored this issue directly in the APP695SWE mouse, our results are entirely consistent with such a mechanism. In the study ofLarson et al. (1999), it was suggested that altered presynaptic Ca2+ kinetics contributed to the deficit in the APPInd mouse because PPF was altered (Hsia et al., 1999). However, we observed no alteration in PPF.
It has been shown that the APP695SWE mouse brain is more susceptible to ischemic injury (Zhang et al., 1997). Interestingly, in the present study, kynurenate, added during the dissection procedure, prevented the deficit in synaptic transmission at 12 months of age. The ability of kynurenate to protect is not absolute because impairments were still observed in APP695SWE mice at 18 months of age, despite the use of kynurenate. This partial effect of kynurenate pretreatment may explain why no protection was observed in other studies using APPInd mice (Hsia et al., 1999; Larson et al., 1999). During the slicing process, brain tissue is unavoidably exposed to a brief hypoxic period, which will lead to excitotoxic processes that decrease neuronal health (Choi, 1990; Martin et al., 1994). Inclusion of kynurenate during slicing presumably limits the extent of this excitotoxicity by preventing activation of glutamate receptors. It should be noted that responses in these wild-type mice are reduced compared with other strains of mice used previously in this laboratory (Kuenzi et al., 1999; Morton et al., 1999; Seabrook et al., 1999;Fitzjohn et al., 2000). Thus, it is possible that the background strain of mice we have used in the present study is particularly susceptible to this kind of excitotoxicity, which may accentuate the effects of Aβ overexpression. It is, nevertheless, entirely consistent with excitotoxicity resulting from hypoxic insult as the underlying pathological change. Indeed, in agreement with the results presented here, it has been reported that C-terminal fragments of Aβ increase the risk of excitotoxicity and damage by hypoxia (Ghribi et al., 1999;Kim et al. 2000) and that neuronal cultures from APP695SWE mice show increased sensitivity to oxidative neurotoxicity (Takahashi et al., 2000). There could be several possible explanations for increased sensitivity to excitotoxicity in transgenic compared with wild-type animals. For example, AD (and elevated Aβ and other proteolytic products of APP) has been associated with decreased glutamate transporter expression and function (Cowburn et al., 1990; Li et al., 1997), increased free radical production (Klegeris and McGeer, 1997), altered calcium homeostasis (Mattson et al., 1993, 2000; Wu et al., 1997; Kim et al., 2000), and inhibition of heme oxygenase (Takahashi et al., 2000).
If the deficit that we and others (Hsia et al., 1999; Larson et al., 1999) have observed in synaptic transmission was solely the result of increased susceptibility to hypoxia during the preparation of slices, then there would not be expected to be a deficit in synaptic transmission in vivo. Although synaptic transmission was normal in the dentate gyrus of APP695SWE in vivo (Chapman et al., 1999), it was impaired in the dentate gyrus of APPInd in vivo (Giacchino et al., 2000). We interpret this to mean that APP overexpression leads to an increased susceptibility to neuronal damage that may, or may not, be detectedin vivo but that becomes evident when the tissue is challenged by a hypoxic insult during the preparation of brain slices. The corollary in man is that overexpression of APP increases the likelihood of hypoxic or other forms of neuronal damage over the lifespan.
In conclusion, we have demonstrated that the APP695SWE mutation causes a selective reduction in basal synaptic transmission in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, which may be related to an increased susceptibility to excitotoxic damage that can be partially protected against using the ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonist kynurenate. However, overexpression of the human APP695SWE mutation, and the subsequent accumulation of Aβ, does not alter either short- or long-term plasticity in the CA1 region of the hippocampus.
Footnotes
This work was supported by Merck Sharp and Dohme–Medical Research Council LINK Grant G9710681.
Correspondence should be addressed to Dr. Stephen M. Fitzjohn, Medical Research Council Centre for Synaptic Plasticity, Department of Anatomy, School of Medical Sciences, University Walk, Bristol, BS8 1TD, UK. E-mail: stephen.fitzjohn@man.ac.uk.
R. A. Morton's present address: Novartis Institute for Medical Sciences, 5 Gower Place, London, WCE 6BS, UK.
C. H. Davies' present address: SmithKline Beecham Pharmaceuticals, The Pinnacles, Harlow, Essex, CM19 5AW, UK.
REFERENCES
- 1.Anderson WW, Collingridge GL. A data acquisition program for on-line analysis of long-term potentiation and long-term depression. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1997;23:665. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0270(01)00374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Borchelt DR, Thinakaran G, Eckman CB, Lee MK, Davenport F, Ratovitsky T, Prada CM, Kim G, Seekins S, Yager D, Slunt HH, Wang R, Seeger M, Levey AI, Gandy SE, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Price DL, Younkin SG, Sisodia SS. Familial Alzheimer's disease-linked presenilin 1 variants elevate Aβ1–42/1–40 ratio in vitro and in vivo. Neuron. 1996;17:1005–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chapman PF, Irizarri MC, Nilsen S, Hyman BT, Hsiao KK. Abnormal synaptic transmission in aged APP transgenic mice. J Physiol (Lond) 1997;501:95.P. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chapman PF, White GL, Jones MW, Cooper-Blacketer D, Marshal VJ, Irizarry M, Younkin L, Good MA, Bliss TVP, Hyman BT, Younkin SG, Hsiao KK. Impaired synaptic plasticity and learning in aged amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:271–276. doi: 10.1038/6374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Choi DW. Cerebral hypoxia: some new approaches and unanswered questions. J Neurosci. 1990;10:2493–2501. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-08-02493.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Citron M, Oltersdorf T, Haass C, McConlogue L, Hung AY, Seubert P, Vigo-Pelfry C, Lieberburg I, Selkoe DJ. Mutation of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in familial Alzheimer's disease increases beta-protein production. Nature. 1992;360:672–674. doi: 10.1038/360672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cowburn RF, Hardy JA, Roberts PJ. Glutamatergic neurotransmission in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990;18:390–392. doi: 10.1042/bst0180390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dawson GR, Seabrook GR, Zheng H, Smith DW, Graham S, O'Dowd G, Bowey BJ, Boyce S, Trumbauer ME, Chen HY, Van der Ploeg LHT, Sirinathsinghji DJS. Age-related cognitive deficits, impaired long-term potentiation and reduction in synaptic marker density in mice lacking the β-amyloid precursor protein. Neuroscience. 1999;90:1–13. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fitzjohn SM, Morton RA, Kuenzi F, Seabrook GR, Collingridge GL. Normal levels of long-term potentiation in hippocampal brain slices from mice lacking amyloid precursor protein after blockade of GABAA receptors. Neurosci Lett. 2000;288:9–12. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(00)01204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Frautschy SA, Yang F, Irizarry M, Hyman B, Saido TC, Hsiao K, Cole GM. Microglial response to amyloid plaques in APPSW transgenic mice. Am J Pathol. 1998;152:307–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Games D, Adams D, Alessandrini R, Barbour R, Berthelette P, Blackwell C, Carr T, Clemens J, Donaldson T, Gillespie F, Guido T, Hagoplan S, Johnson-Wood K, Khan K, Lee M, Leibowitz P, Lieberburg I, Little S, Masliah E, McConlogue L, Montoya-Zavala M, Mucke L, Paganini L, Penniman E, Power M. Alzheimer-type neuropathology in transgenic mice overexpressing V717F beta-amyloid precursor protein. Nature. 1995;373:523–527. doi: 10.1038/373523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ghribi O, Lapierre L, Girard M, Ohayon M, Nalbantoglu J, Massicotte G. Hypoxia-induced loss of synaptic transmission is exacerbated in hippocampal slices of transgenic mice expressing C-terminal fragments of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein. Hippocampus. 1999;9:201–205. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1999)9:3<201::AID-HIPO1>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Giacchino J, Criado JR, Games D, Henriksen S. In vivo synaptic transmission in young and aged amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Brain Res. 2000;876:185–190. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02615-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Goate A, Chartier-Harlin M-C, Mullan M, Brown J, Crawford F, Fidani L, Giuffra L, Haynes A, Irving N, James L, Mant R, Newton P, Rooke K, Roques P, Talbot C, Pericak-Vance M, Roses A, Williamson R, Rosser M, Owen M, Hardy J. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991;349:704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hardy J. Amyloid, the presenilins and Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci. 1997;20:154–159. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(96)01030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hsia AY, Masliah E, McConlogue L, Yu G-Q, Tatsuno G, Hu K, Kholondenko D, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA, Mucke L. Plaque-independent disruption of neural circuits in Alzheimer's disease mouse models. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:3228–3233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.6.3228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hsiao KK, Borchelt DR, Olson K, Johannsdottir R, Kitt C, Yunis W, Xu S, Eckman C, Younkin S, Price D, Iadecola C, Brent Clark H, Carlson G. Age-related CNS disorder and early death in transgenic FVB/N mice overexpressing Alzheimer amyloid precursor proteins. Neuron. 1995;25:1203–1218. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hsiao KK, Chapman P, Nilsen S, Eckman C, Harigaya Y, Younkin S, Yang F, Cole G. Correlative memory deficits, Aβ elevation and amyloid plaques in transgenic mice. Science. 1996;274:99–102. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5284.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Irizarry MC, McNamarra M, Fedorchak K, Hsiao KK, Hyman BT. APPSW transgenic mice develop age-related Aβ deposits and neuropil abnormalities, but no neuronal loss in CA1. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1997;56:965–973. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199709000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kim H-S, Park CH, Cha SH, Lee J-H, Lee S, Kim Y, Rah J-C, Jeong S-J, Suh Y-H. Carboxyl-terminal fragment of Alzheimer's APP destabilizes calcium homeostasis and renders neuronal cells vulnerable to excitotoxicity. FASEB J. 2000;14:1508–1517. doi: 10.1096/fj.14.11.1508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Klegeris A, McGeer PL. Beta-amyloid protein enhances macrophage production of oxygen free radicals and glutamate. J Neurosci Res. 1997;49:229–235. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4547(19970715)49:2<229::aid-jnr11>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kuenzi F, Thomsit F, Rosahl TW, Whiting PJ, Morton RA, Fitzjohn SM, Collingridge GL, Seabrook GR. The rd mutation in cGMP PDE-IV does not affect synaptic plasticity in mouse hippocampus. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1999;25:398.9. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Larson J, Lynch G, Games D, Seubert P. Alterations in synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation in hippocampal slices from young and aged PDAPP mice. Brain Res. 1999;840:23–35. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01698-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li S, Mallory M, Alford M, Tanaka S, Masilah E. Glutamate transporter alterations in Alzheimer disease are possibly associated with abnormal APP expression. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1997;56:901–911. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199708000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Martin RL, Lloyd HG, Cowan AI. The early events of oxygen and glucose deprivation: setting the scene for neuronal death? Trends Neurosci. 1994;17:251–257. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mattson MP, Cheng B, Culwell AR, Esch FS, Lieberburg I, Rydel RE. Evidence for excitoprotective and intraneuronal calcium-regulating roles for secreted forms of the beta-amyloid precursor protein. Neuron. 1993;10:243–254. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90315-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mattson MP, Zhu H, Yu J, Kindy MS. Presenilin-1 mutation increases neuronal vulnerability to focal ischemia in vivo and to hypoxia and glucose deprivation in cell culture: involvement of perturbed calcium homeostasis. J Neurosci. 2000;20:1358–1364. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-04-01358.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984;34:939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Moechars D, Dewachter I, Lorent K, Reversé D, Baekelandt V, Naidu A, Tesseur I, Spittaels K, van den Haute C, Checler F, Godaux E, Cordell B, van Leuven F. Early phenotypic changes in transgenic mice that overexpress different mutants of amyloid precursor protein in the brain. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:6483–6492. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.10.6483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Morton RA, Kuenzi F, Fitzjohn SM, Rosahl TW, Zheng H, Coan EJ, Collingridge GL, Seabrook GR. Selective disruption of late-phase LTP in mice under-expressing presenilin-1. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1999;25:398.10. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nalbantoglu J, Tirado-Santiago G, Lahsaini A, Poirier J, Goncalves O, Verge G, Momoli F, Welner SA, Massicotte G, Julien JP, Shapiro ML. Impaired learning and LTP in mice expressing the carboxy terminus of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein. Nature. 1997;387:500–505. doi: 10.1038/387500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Neve RL, Robakis NK. Alzheimer's disease: a re-examination of the amyloid hypothesis. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21:15–19. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(97)01168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Parent A, Linden DJ, Sisodia SS, Borchelt DR. Synaptic transmission and hippocampal long-term potentiation in transgenic mice expressing FAD-linked presenilin 1. Neurobiol Dis. 1999;6:56–62. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.1998.0207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Price DL, Sisodia SS. Mutant genes in familial Alzheimer's disease and transgenic models. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1998;21:479–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.21.1.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Seabrook GR, Rosahl TW. Transgenic animals relevant to Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(98)00170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Seabrook GR, Smith DW, Bowery BJ, Easter A, Reynolds T, Fitzjohn SM, Morton RA, Zheng H, Dawson GR, Sirinathsinghji DJS, Davies CH, Collingridge GL, Hill RG. Mechanisms contributing to the deficits in hippocampal synaptic plasticity in mice lacking amyloid precursor protein. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(98)00204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Takahashi M, Doré S, Ferris CD, Tomita T, Sawa A, Wlosker H, Borchelt DR, Iwatsubo T, Kim S-H, Thinakaran G, Sisodia SS, Snyder SH. Amyloid precursor proteins inhibit heme oxygenase activity and augment neurotoxicity in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 2000;28:461–473. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wimer RE, Wimer CC, Alameddine L, Cohen AJ. The mouse gene retinal degeneration (rd) may reduce the number of neurons present in the adult hippocampal dentate gyrus. Brain Res. 1991;547:275–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90971-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wu A, Derrico CA, Hatem L, Colvin RA. Alzheimer's amyloid-beta peptide inhibits sodium/calcium exchange measured in rat and human brain plasma membrane vesicles. Neurosci. 1997;80:675–684. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zaman SH, Parent A, Laskey A, Lee MK, Borchelt DR, Sisodia SS, Malinow R. Enhanced synaptic potentiation in transgenic mice expressing presenilin 1 familial Alzheimer's disease is normalized with a benzodiazepine. Neurobiol Dis. 2000;7:54–63. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.1999.0271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zhang F, Eckman C, Younkin S, Hsiao KK, Iadecola C. Increased susceptibility to ischemic brain damage in transgenic mice overexpressing the amyloid precursor protein. J Neurosci. 1997;17:7655–7661. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-20-07655.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]