Abstract
Status epilepticus (StE) in immature rats causes long-term functional impairment. Whether this is associated with structural alterations remains controversial. The present study was designed to test the hypothesis that StE at an early age results in neuronal loss. StE was induced with lithium–pilocarpine in 12-d-old rats, and the presence of neuronal damage was investigated in the brain from 12 hr up to 1 week later using silver and Fluoro-Jade B staining techniques. Analysis of the sections indicated consistent neuronal damage in the central and lateral segments of the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus, which was confirmed using adjacent cresyl violet-stained preparations. The mechanism of thalamic damage (necrosis vs apoptosis) was investigated further using TUNEL, immunohistochemistry for caspase-3 and cytochrome c, and electron microscopy. Activated microglia were detected using OX-42 immunohistochemistry. The presence of silver and Fluoro-Jade B-positive degenerating neurons in the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus was associated with the appearance of OX-42-immunopositive activated microglia but not with the expression of markers of programmed cell death, caspase-3, or cytochrome c. Electron microscopy revealed necrosis of the ultrastructure of damaged neurons, providing further evidence that the mechanism of StE-induced damage in the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus at postnatal day 12 is necrosis rather than apoptosis. Finally, these data together with previously described functions of the medial and lateral segments of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus suggest that some functions, such as adaptation to novelty, might become compromised after StE early in development.
Keywords: apoptosis, development, microglia, necrosis, pilocarpine, TUNEL
Status epilepticus (StE) and prolonged febrile seizures at an early age are associated with brain damage (Sagar and Oxbury, 1987), increased risk of epilepsy, and cognitive impairment in humans (Aicardi and Chevrie, 1970). Similarly, StE or febrile seizures in immature rats causes functional impairments (Sankar et al., 1998; Dubé et al., 2000b; Kubová et al., 2000). For example, uptake of [14C]2-deoxyglucose is reduced in the dorsal and ventral hippocampus and the mammillary bodies in rats with pentylenetetrazol-induced StE 2 months earlier at postnatal day 10 (P10) (Hussenet et al., 1995). An association of early StE with a lower seizure threshold and spontaneous seizures was reported by Babb et al. (1995), who injected kainic acid into the hippocampus at P7 and recorded spontaneous seizures with video-EEG (electroencephalogram) 5 months later. More recently, Sankar et al. (1998) recorded spontaneous seizures in 3-month-old rats with lithium–pilocarpine-induced StE during the second week of life. Furthermore, Dubé et al. (2000b)demonstrated that rats with febrile convulsions lasting for ∼20 min at P10 have a lower seizure threshold for kainate as adults. Furthermore, as a result of febrile seizures, these animals exhibit increased inhibitory synaptic transmission that lasts into adulthood (Chen et al., 1999). Finally, rats with lithium–pilocarpine-induced StE at P12 exhibit motor impairment in the rotarod and open-field tests at the age of 3 months (Kubová et al., 2000).
Whether the long-term functional consequences induced by StE at an early age in rats (≤P12: corresponds to infancy in humans; Dobbing, 1970) are associated with structural damage has remained controversial. In one study, analysis of hematoxylin–eosin-stained preparations of rats with lithium–pilocarpine-induced StE during the second week of life revealed damage in the hippocampus, amygdala, thalamus, and septum (Sankar et al., 1997). Further analysis of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells demonstrated DNA fragmentation [terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated biotinylated UTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)] and apoptotic bodies in electron micrographs of damaged neurons, favoring the idea that apoptosis contributes to the damage (Sankar et al., 1998). In other studies, permanent neuronal damage was not observed in rats experiencing StE or prolonged febrile seizures at or before P12 (Chang and Baram, 1994; Dubé et al., 2000a).
We hypothesized that it is unlikely that widespread long-term sequelae of StE in the immature brain can be attributable merely to the hippocampal damage previously described in detail. Therefore, we investigated the neuronal degeneration in the entire brain 12 hr, 24 hr, 48 hr, and 1 week after induction of StE with lithium–pilocarpine at P12 using both silver and Fluoro-Jade B staining. Damage was most prominent in the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus and, therefore, we focused on the mechanisms of damage in the thalamus (apoptosis vs necrosis) using TUNEL (DNA fragmentation), immunohistochemistry for caspase-3 (cysteine protease participating in programmed cell death), cytochrome c (mitochondrial electron carrier protein released during programmed cell death), and OX-42 (microglial marker), and electron microscopy (ultrastructure of damaged neurons).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Induction of status epilepticus
Male Wistar albino rats (12-d-old; n = 76; from the facilities of the Institute of Physiology) were used. The day of birth was taken as day 0. Animals were housed in a controlled environment (temperature 22 ± 1°C; humidity 50–60%; lights on 6:00 A.M. to 6:00 P.M.) with ad libitum access to food and water. Experiments were approved by the Animal Care Committee of the Institute of Physiology of the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic. Animal care and experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the European Community Council directives 86/609/EEC.
To induce StE, rat pups (n = 54) were injected with an aqueous solution of lithium chloride (3 mmol · ml−1 · kg−1, i.p.; catalog #L-0505; Sigma, St. Louis, MO) on P11 followed by pilocarpine (40 mg · ml−1 · kg−1, i.p.; catalog #P-6503; Sigma; made in saline) 24 hr later (Hirsch et al., 1992). After pilocarpine injection, motor manifestations of seizure activity (twitching of facial muscles, chewing, head bobbing, forelimb clonus, tail erection, “swimming” movements) were monitored by an experienced observer for 2 hr. Latency to the first motor seizure manifestations after pilocarpine injection was measured, and this time point was considered the beginning of StE. Two hours later, seizure activity was interrupted with paraldehyde (0.3 ml/kg, i.p.; catalog #76260; Fluka Chemie AG, Buchs, Switzerland). To standardize the experimental groups, only 50 animals with motor StE lasting at least 2 hr were used in the experiments; 16 of these rats died within 24 hr after pilocarpine. Control animals (n= 22) were treated with equal volumes of lithium chloride, but pilocarpine solution was replaced with saline. Paraldehyde was administered 2 hr after saline injection. Animals from each nest were randomly assigned to the experimental and control groups.
Histologic processing of tissue
Fixation. Rats were killed at 12 hr (n = 2), 24 hr (n = 11), 48 hr (n = 17), or 1 week (n = 13) after StE. The animals were deeply anesthetized with 20% urethane (2 gm/kg, i.p.; catalog #U-2500; Sigma) and perfused as follows: 20 ml of 0.01m sodium PBS, pH 7.4, room temperature, followed by 4% paraformaldehyde and 0.1% glutaraldehyde in 0.1m sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 (2 ml/gm of body weight, +4°C). The brains were removed from the skull, post-fixed for 3 hr in the fixative, and then cryoprotected in a solution containing 20% glycerol in 0.02 mpotassium buffered saline (KPBS) for 24 hr (+4°C). Then, the brains were frozen in dry ice and stored at −70°C. They were sectioned in the coronal plane (30 μm, one-in-five series) with a sliding microtome. The sections were stored in a cryoprotectant tissue-collecting solution (30% ethylene glycol, 25% glycerol in 0.05m sodium phosphate buffer) at −20°C until processed. An adjacent series of sections was used for cresyl violet staining (17 controls, 25 with StE), silver impregnation (11 controls: 5 at 48 hr and 6 at 1 week; 14 rats with StE: 2 at 12 hr, 2 at 24 hr, 5 at 48 hr, 7 at 1 week), Fluoro-Jade B staining (6 rats with StE: 2 at 12 hr, 2 at 24 hr, 2 at 48 hr), and/or immunohistochemistry for antibodies raised against caspase-3, cytochrome c, or OX-42 (6 controls: 3 at 24 hr, 3 at 48 hr; 11 rats with StE: 2 at 12 hr, 5 at 24 hr, 4 at 48 hr).
Cresyl violet staining. To identify the cytoarchitectonic boundaries and to detect neuronal damage, the first series of one in five sections was stained with cresyl violet.
Silver impregnation. Degeneration of neurons was determined using the silver impregnation techniques described by Gallyas et al. (1980). Briefly, the series of sections adjacent to those used for cresyl violet staining were incubated for 10 min in a pretreatment solution containing 2% NaOH and 2.5% NH4OH. Thereafter, the sections were incubated in an impregnating solution containing 0–0.8% NaOH, 2.5% NH4OH, and 0.5% AgNO3. Sections were washed three times (5 min each time) in a solution containing 0.4–0.6% formaldehyde and 0.01% citric acid in 10% ethanol, pH 5.0–5.5, for 1 min and washed three times (10 min each) in 0.5% acetic acid. All steps were performed at room temperature. Sections were mounted on gelatin-coated slides, dehydrated, and coverslipped.
Sections from different treatment groups were analyzed in a blinded manner using a light microscope equipped with bright-field and dark-field optics. All sections (one-in-five series, 30 μm) throughout the entire rostrocaudal extent of the brain back to the occipital pole were inspected. Only shrunken argyrophilic neurons with granular silver deposits were considered to be irreversibly damaged (Fig. 1D). Neuronal damage in silver-stained sections was analyzed side-by-side with adjacent cresyl violet-stained sections.
Fig. 1.
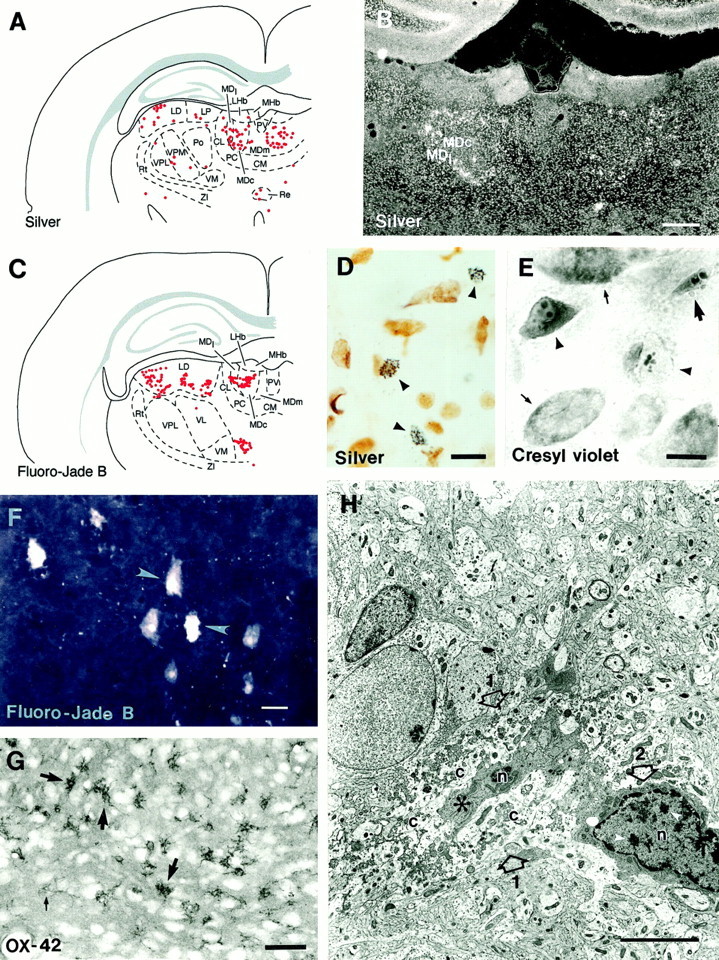
A, Computer-generated plot demonstrating the distribution of silver-positive cells in the different nuclei of the thalamus. Each red dotrepresents one silver-positive cell. B, A dark-field photomicrograph demonstrating the silver-positive cells (appear aswhite dots) in the thalamus in a rat that experienced StE 48 hr earlier (case StE10). Note the large number of silver-positive cells in the periphery of the central segment and also in the dorsal aspect of the lateral segment. C,Computer-generated plot demonstrating the distribution of Fluoro-Jade B-positive cells in the different nuclei of the thalamus. Eachred dot represents one labeled cell (case StE21). Note the similarity in the distribution with silver-positive cells in A. D, Color photomicrograph showing the appearance of silver-positive cells under bright-field illumination (arrowheads; case StE 10). Note the granular accumulation of silver deposits and shrunken appearance of the remains of the cell. Most of the undamaged cells are glial cells. E, High-power bright-field photomicrograph of neurons in the posterior pole of the anteromedial nucleus in cresyl violet staining (StE11). Note the fragmented appearance of nuclei in cells with pyknotic (arrowhead) or shrunken (large arrow) somata. Under fluorescence light (FITC filters) these same neurons had a pale appearance and could be easily distinguished from surrounding neurons (data not shown).F, A confocal image showing the appearance of Fluoro-Jade B-positive cells in the mediodorsal nucleus (arrowheads; case StE21). G,Ameboid-shaped activated microglia (thick arrows) in the central segment of the mediodorsal nucleus in preparations stained with an antibody raised against OX-42. Thin arrow points to an inactive OX-42-positive microglia. H, An electron micrograph showing a cell body (1 with open arrows) undergoing lysis. In the center, there is a small part of the nucleus (n) and condensed cytoplasm (asterisk), which are surrounded by lysed cytoplasm (c). Note the disintegration of cellular components, which is a sign of irreversible (necrotic) neuronal damage. Adjacent to the lysed cell on the right(2 with open arrow) there is a microglial cell with an irregular shape, dense cytoplasm, and clumped chromatin in the nucleus (n, white arrowheads) and on the nuclear membrane. CL, Centrolateral nucleus; CM, central medial nucleus; LD, laterodorsal nucleus;LHb, latreal habenula; LP, lateral posterior nucleus; MDc, central segment of the mediodorsal nucleus; MDl, lateral segment of the mediodorsal nucleus; MDm, medial segment of the mediodorsal nucleus; MHb, medial habenula;PC, paracentral nucleus; Po, posterior thalamic nuclear group; PV, paraventricular nucleus;Re, reuniens nucleus; Rt, reticular nucleus; VL, ventrolateral nucleus; VM, ventromedial nucleus; VPL, ventral posterolateral nucleus; VPM, ventral posteromedial nucleus;ZI, zona incerta. Scale bars: B, 500 μm;D–F, 10 μm; G, 50 μm;H, 5 μm.
Fluoro-Jade B staining. In one series of sections (30 μm; one-in-five series), degenerating neurons were stained with Fluoro-Jade B using the method described by Schmued et al. (1997). Briefly, sections were mounted from 0.1 m sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, onto gelatin-coated slides and dried at 37°C overnight. Then they were immersed in absolute alcohol for 3 min, followed by 70% ethanol for 2 min, and distilled water for 2 min. The slides were transferred to 0.06% potassium permanganate for 15 min. After rinsing with distilled water for 2 min, the slides were incubated for 30 min in 0.001% Fluoro-Jade B solution (Histo-Chem, Inc., Jefferson, AR) made in 0.1% acetic acid. Slides were rinsed in water, dried at 37°C, dehydrated in xylene, and coverslipped. Sections throughout the entire rostrocaudal extent of the brain were examined using a Leica DMRD fluorescent microscope (I3 filter cube for FITC, excitation band 450–490 nm).
Immunohistochemistry. Adjacent sections were processed immunohistochemically with antibodies raised against caspase-3 (goat polyclonal, dilution 1:2000; detects p20 subunit and precursor of caspase-3; catalog #sc-1225; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), cytochrome c (mouse monoclonal, 1:14,000; catalog #G7421; Promega, Madison, WI), or OX-42 (mouse monoclonal, 1:4000; catalog #NCA275G; Serotec, Oxford, UK) using the avidin–biotin method described previously in detail (Tuunanen et al., 1996). As a positive control, a thalamic section from an adult rat that experienced StE 24 hr earlier was included into each set of immunostainings.
TUNEL. A separate group of animals (n = 9; five with StE) was prepared for TUNEL staining. Brains were removed from the skull 48 hr after StE, frozen in dry ice, and coronal sections were cut with the cryostat (20-μm-thick). Sections were incubated in 0.1 m sodium citrate at +70°C for 30 min for permeabilization, washed with H2O (3 × 10 min), and dried. Subsequently, 100 μl of solution containing 1 μl of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT; Promega) and 0.5 μl of fluorescein-12-dUTP (Boehringer Mannheim GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) in TdT buffer was applied on each slide, and sections were incubated for 1 hr at +37°C. Thereafter, sections were washed with 0.02m KPBS, pH 7.4, and incubated for 2 hr in 10% normal horse serum (NHS) and 0.25% Triton X-100 in 0.02m KPBS. Then, sections were incubated overnight in a solution containing anti-fluorescein monoclonal antibody (1:200; Boehringer Mannheim), 1% NHS, and 0.25% Triton X-100 in 0.02m KPBS. After washing (3 × 10 min) with 1% NHS and 0.25% Triton X-100 in 0.02 m KPBS, sections were incubated with biotinylated anti-mouse IgG (1:200; Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA), 1% NHS, 0.01% Triton in KPBS for 2 hr, and then washed with KPBS and incubated with avidin–biotin solution (Vectastain ABC kit; Vector Laboratories) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The reaction was developed with 0.05% 3′, 3′-diaminobenzidine (Pierce, Rockford, IL) and 0.04% H2O2 in KBPS. For a TUNEL-positive control, some sections were treated with DNAase (1 mg/ml in 100 mm Tris, pH 7.4, 100 mm NaCl, 1 mmCaCl2, and 250 mm KCl; 10 min at 37°C), processed as described above.
To analyze the distribution of TUNEL-positive nuclei, labeled nuclei were plotted from sections with a computer-aided digitizing system (Minnesota Datametrics, St. Paul, MN). The anatomic boundaries were drawn from adjacent cresyl violet-stained sections using a stereomicroscope equipped with a drawing tube.
Electron microscopy. An additional group of animals (two controls and two with StE) was perfused 48 hr after StE with 20 ml of 0.01 m sodium PBS, pH 7.4, (room temperature) followed by 2% paraformaldehyde and 2% glutaraldehyde in 0.1m sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 (2 ml/gm of body weight, +4°C). The brains were post-fixed for 24 hr in the same fixative. Thereafter, the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus was dissected, and the tissue blocks were post-fixed in 2% osmium tetroxide (Electron Microscopy Sciences, Fort Washington, PA) for 2 hr, dehydrated in an ascending ethanol series, and embedded in Durcupan (Fluka, Switzerland). Semithin sections (1 μm) were cut on Reichert Ultracut E and LKB ultramicrotomes and stained with Toluidine blue. After a light microscopic identification of damaged neurons, ultrathin sections (50 nm) were cut and stained with 1% uranyl acetate (Electron Microscopy Sciences) in ethanol following by 0.1% lead citrate (Electron Microscopy Sciences) dissolved in 0.1 msodium hydroxide. Finally, sections were analyzed using a Philips CM 100 electron microscope (Philips, Eindhoven, The Netherlands).
Photography. Higher power photomicrographs were taken with a Leica DMRB microscope and lower power photomicrographs with a Nikon 6 × 8 cm system. Confocal images were captured with a Bio-Rad (Hercules, CA) MRC600 confocal laser microscope using a krypton–argon laser.
RESULTS
Development and severity of status epilepticus
The development of StE correlated well with the original description by Hirsch et al. (1992). The latency to the first behavioral seizure was 519 ± 151 sec (n = 50). Motor StE lasting for at least 2 hr was observed in 50 of 54 rats, and only these animals were included into the analysis. In this group, 16 of 50 rats died within the first 24 hr. Typically, it was preceded by the loss of a righting reflex and the occurrence of a tonic phase of generalized tonic–clonic seizure. Body weight of experimental animals did not differ from that in control siblings (1 week follow-up).
Distribution of damage in silver staining
Initially, the entire brain back to the level of the brainstem was analyzed (n = 16). The mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus contained damaged neurons in 13 of 16 rats, and the damaged neurons were present in cases analyzed 12 hr (two of two animals), 24 hr (two of two animals), 48 hr (five of five animals), or 1 week (four of seven animals) after StE (Table 1). The anterior cortical and/or medial nuclei of the amygdala contained damaged neurons in 9 of 16 cases. Cells with granular silver deposits were rare in other brain areas, including the hippocampus. Therefore, the distribution and mechanisms of neuronal damage were explored further in the thalamus. There were no silver-positive neurons observed in the controls.
Table 1.
Distribution of silver-positive cells in the different nuclei of the thalamus in rats that experienced pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus 12, 24, 48 hr or 1 week earlier at the age of 12 d
| Thalamic nucleus | 12 hr | 24 hr | 48 hr | 1 week after status epilepticus | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE 17 | SE 16 | SE 14 | SE 15 | SE 6 | SE 8 | SE 9 | SE 10 | SE 11 | SE 1 | SE 2 | SE 3 | SE 4 | SE 5 | SE 7 | SE 13 | |
| Mediodorsal nucleus (MD) | ||||||||||||||||
| Medial segment | o | o | o | o | o | o | o | o | o | o | o | o | o | o | o | o |
| Central segment | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | o | ++ | o | o | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Lateral segment | + | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | o | + | o | o | + | + | + |
| Lateral dorsal nucleus (LD) | + | + | ++ | ++ | o | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | o | o | o | o | + | + | + |
| Lateral posterior nucleus (LP) | + | + | ++ | + | o | + | ++ | + | + | o | o | o | o | o | o | o |
| Anteroventral nucleus (AV) | o | o | o | o | o | o | + | + | + | o | o | o | o | o | o | o |
| Anteromedial nucleus (AM) | o | o | o | o | o | o | + | + | + | o | o | o | o | o | o | o |
| Ventrolateral nucleus (VL) | o | + | + | + | o | + | + | + | ++ | o | o | o | o | + | + | + |
| Ventroposterior nucleus | ||||||||||||||||
| Medial part (VPM) | o | o | + | + | o | + | + | + | + | o | o | o | o | + | o | o |
| Lateral part (VPL) | o | o | + | + | o | + | + | + | + | o | o | o | o | + | o | o |
| Posterior thalamic nuclear | o | o | + | + | o | + | + | + | + | + | o | + | o | o | + | o |
| Ventromedial nucleus (VM) | o | + | ++ | o | + | ++ | o | + | o | o | o | o | o | o | o | + |
| Dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (DLG) | o | o | o | o | o | + | + | + | ++ | o | o | o | o | o | o | o |
Density of silver-stained neurons was scored as follows: o, no damaged neurons; +, <5 silver-positive neurons per nucleus; ++, 5–10 silver-positive neurons per nucleus; +++, >20 silver-positive neurons per nucleus.
The thalamus was partitioned into subnuclei according to Paxinos and Watson (1982). The density of silver-positive neurons was highest in the mediodorsal nucleus (>20 silver-positive cells per 30-μm-thick section), next highest in the lateral dorsal nucleus, lateral posterior nucleus, ventrolateral nucleus, ventromedial nucleus, and dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (5–10 silver-positive cells per 30-μm-thick section), and next highest anteroventral nucleus, anteromedial nucleus, ventroposterior nucleus, posterior thalamic nuclear group (<5) (Fig. 1A, Table 1).
The mediodorsal nucleus was partitioned into the medial, central, and lateral segments (Krettek and Price, 1977). Most of the silver-positive cells were located at the periphery of the central segment (Fig.1A,B, Table 1) throughout its rostrocaudal extent. Some damaged neurons with granular silver deposits were also observed in the lateral segment. The density of silver-positive neurons appeared slightly lower (20–25 silver-positive neurons per section) in animals that were perfused 1 week after StE rather than 48 hr. The distribution of damaged neurons within the mediodorsal nucleus was similar in both groups (Table 1).
Distribution of damage in Fluoro-Jade B staining
In general, the distribution of Fluoro-Jade B-stained neurons was similar to that of silver-positive cells (Fig. 1C,F). Twelve hours after StE (two of two animals), Fluoro-Jade B-stained neurons were observed throughout the entire rostrocaudal extent of the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus, most of which (5–10 neurons per section) were located in the central segment, and occasionally in the lateral segment. At this time point, there was no labeling in the other thalamic nuclei. At 24 hr after StE, the density of Fluoro-Jade B-positive neurons in the mediodorsal nucleus increased to 20–30 labeled neurons per section, and at 48 hr, to 30–40 per section. Approximately 80% of the Fluoro-Jade B-positive neurons in the mediodorsal nucleus were located in the central segment and the rest in the lateral segment. In addition, there was a lower density of labeled neurons in the lateral dorsal nucleus and the lateral posterior nucleus (5–10 neurons per section). There were a few positive neurons in the ventromedial nucleus, the ventrolateral nucleus, and the posterior thalamic nuclear group (<5 neurons per section).
TUNEL
TUNEL-positive nuclei were rare in the thalamus in rats with StE 48 hr earlier (n = 5; 5 ± 1 cells per section) as well as in controls (n = 3; 9 ± 2 cells per section). Furthermore, unlike in silver preparations, the few TUNEL-positive nuclei appeared randomly scattered without any accumulation in the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus.
Caspase-3, cytochrome c, and OX-42 immunohistochemistry
We did not observe any caspase-3 or cytochrome c-immunopositive cells in the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus (analysis 12, 24, or 48 hr after StE). There were, however, a substantial number of OX-42-positive microglial cells with amoeboid morphology (activated microglia) in the central and lateral segments (Fig. 1G). Activated microglia were also observed in other thalamic areas with silver-positive neurons (data not shown).
Electron microscopy
Ultrastructural analysis of neurons with a damaged appearance after light microscopic inspection revealed that the damaged cells had a condensed or lysed cytoplasm, and the cellular components were undergoing disintegration (Fig. 1H). In many cases, cells with microglial characteristics were observed in close proximity to lysed neurons (Fig. 1H). We did not identify any neurons with an apoptotic ultrastructure (nuclear condensation and fragmentation, cell surface protrusions, and formation of membrane-bounded apoptotic bodies) in the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus.
DISCUSSION
Recent data demonstrate that StE or recurrent febrile seizures occurring at an early age in rats (<P14) cause long-term functional impairment without any clear histologically assessed neuronal loss (de Feo et al., 1986; Nehlig and Pereira de Vasconcelos, 1996; Dubéet al., 2000a,b) except in the hippocampus (Sankar et al., 1998). The present study was designed to test the hypothesis that StE at an early age leads to neuronal degeneration in brain areas that have not previously been explored in such detail. There was no hippocampal damage in animals that were perfused for histology from 24 hr up to 1 week after StE, and there was only an occasional degenerating cell in the granule cell layer of the dentate gyrus 12 hr after StE. There was consistent neuronal degeneration, however, in the thalamus, which is consistent with the findings of Sankar et al. (1997). The results of the present study extend previous observations by demonstrating that the damage is already present at 12 hr and can still be detected up to 1 week after StE. Second, neuronal degeneration is most prominent in the central and lateral segments of the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus. Third, the mechanism of thalamic damage in 12-d-old rats with StE is necrosis rather than apoptosis.
The highest density of degenerating neurons was observed in the periphery of the central segment and in the lateral segment of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus. A question arises whether the damaged neurons are local inhibitory neurons or projection neurons. Previous studies indicated that the central and lateral segments contain very few glutamic acid decarboxylase-immunopositive neurons (Kuroda and Price, 1991), which suggests that the damaged silver-positive cells are projection neurons rather than inhibitory interneurons. Tract-tracing studies show that the central segment provides substantial inputs to various regions of the ventrolateral prefrontal cortex, including the lateral orbital cortex and the ventral agranular insula (Krettek and Price, 1977; Groenewegen, 1988; Ray and Price, 1993). The lateral segment innervates nonoverlapping portions of the prefrontal cortex, including the dorsolateral orbital cortex, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, medial precentral cortex, and the lateral frontal polar cortex (Krettek and Price, 1977; Groenewegen, 1988; Ray and Price, 1993). Reciprocal connections between the thalamus and the cortex develop prenatally or during early postnatal life in rodents (Lund and Mustari, 1977; Crandall and Caviness, 1984a,b; Minciacchi and Granato, 1988). Therefore, the somata of neurons in the central and lateral segments of the mediodorsal nucleus innervating the prefrontal cortex form a candidate neuronal population damaged by StE at P12.
Why are the thalamic neurons so sensitive to damage in the lithium–pilocarpine model of StE? One explanation could be a direct toxic effect of cholinergic muscarinic receptor activation by pilocarpine. An anatomic basis supporting this idea comes from electron microscopic studies demonstrating that an input from the dorsal tegmental region to the lateral segment of the mediodorsal nucleus is cholinergic and makes asymmetric, presumably excitatory, contacts with the proximal dendrites of target neurons (Kuroda and Price, 1991). Indirect evidence arguing against cholinergic toxicity comes from experiments in which hippocampal cultures were exposed to the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, soman, and no effect was observed on neuronal viability (Deshpande et al., 1995). Furthermore, using dissociated retinal ganglion cells, direct toxicity of pilocarpine was documented only after incubation at a very high concentration (>0.4 mm; Vorwerk et al., 1999). In addition, rats that were treated with a high dose of pilocarpine without the development of StE, did not exhibit any behavioral impairment in the Morris water maze (Hort et al., 2000). These data provide further evidence that the neuronal damage is caused by StE rather than pilocarpine administration alone.
Another possibility underlying thalamic damage after lithium–pilocarpine-induced StE is glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. By administering atropine at different times after pilocarpine injection,Morrisett et al. (1987) demonstrated that cholinergic activation is important only for the initiation of StE. At later stages of StE, pilocarpine-induced activation of cholinergic muscarinic receptors excites glutamatergic pathways, which eventually causes the neuronal damage (Turski et al., 1983). Tracer studies with3H-aspartate demonstrated that the central segment receives inputs containing excitatory amino acids from the piriform cortex and the amygdala, and the lateral segment from the superior colliculus (Ray et al., 1992). In addition, there are several other putative glutamatergic inputs to these areas (Krettek and Price, 1977; Groenewegen, 1988; Ray et al., 1992) that become activated during lithium–pilocarpine-induced StE at P10 (da Silva Fernandes et al., 1999). Therefore, we propose that the degenerated somata with granular silver deposits in the central and lateral segments of the mediodorsal nucleus belong to the population of neurons innervated by the glutamatergic inputs.
Previous studies investigating thalamic damage after StE in immature animals have provided somewhat contradictory results.Dubé et al. (2000a) did not report any silver-positive neurons in the mediodorsal thalamus 6 hr after StE induced in rats at P10. The discrepancy with the present findings might be explained by the slightly different time courses of the experiments (6 hr vs 12 hr to 1 week). This idea is supported by the observations of Pineau et al. (1999), who reported no positive acid fuchsin staining in the mediodorsal thalamus in rats that experienced StE at P10 and were analyzed 4 hr after StE. A large number of positive neurons were, however, detected 24 hr after the onset of StE. According to the present findings, damaged neurons can be detected up to 1 week after StE. The age of animals at the time of StE (P10 vs P12) might also contribute to the variability of results between the studies.
The silver and Fluoro-Jade B stain “degenerating neurons” (Gallyas et al., 1980; Schmued et al., 1997), but are the stained neurons irreversibly damaged and is the damage apoptotic or necrotic? The study of Sankar et al. (1998) provides evidence that apoptosis contributes to the damage of hippocampal neurons after StE in rats 2 weeks old. In the present study, we did not observe any TUNEL-positive neurons in the thalamus. It is unlikely that we missed the TUNEL positivity because of the timing of sampling. As demonstrated previously, TUNEL positivity can be detected from 12 hr up to 48 hr after StE (Tuunanen et al., 1999). The two other markers used to investigate the occurrence of programmed cell death were cytochrome c and caspase-3 immunoreactivities. As many recent studies demonstrate, the release of a mitochondrial electron carrier protein cytochrome c is one of the early steps in the sequence of events that eventually lead to the activation of caspases, including caspase-3 (for review, seeThornberry and Lazebnik, 1998). In the present study, we did not observe increased neuronal expression of either marker after StE in the thalamus. This was somewhat unexpected because at the same age hypoxia–ischemia causes caspase activation (Hu et al., 2000), and therefore our data cannot be explained by the inability of the developing brain to activate caspase pathways. OX-42-positive activated microglial cells, however, were observed in the central and lateral segments of the mediodorsal nucleus in most of the rats with StE, which supports the idea of inflammation at the damaged area, most probably caused by necrotic neuronal damage. This conclusion is supported by the electron microscopic analysis of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus. All damaged neurons analyzed ultrastructurally, so far, have had a lysed cytoplasm and disintegration of organelles, which are characteristic of irreversible necrotic damage. Therefore, these data suggest that the damage to the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus after lithium–pilocarpine-induced StE at P12 is irreversible and occurs via necrotic rather than apoptotic mechanisms.
What are the implications of the damage caused by StE to the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus in immature brain for the long-term functional outcome? A local infusion of glutamate receptor antagonists or GABAA agonists into the mediodorsal nucleus leads to seizure suppression in adult rats (Patel et al., 1988; Cassidy and Gale, 1998). Therefore, the presumed loss of projection neurons in the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, which converge both glutamatergic and GABAergic inputs (Ray et al., 1992) and are proposed to be involved in suppression of seizure activity (Cassidy and Gale, 1998), might result in a change in the seizure threshold. Otherwise, the mediodorsal nucleus acts as a critical link between the basal forebrain and the prefrontal cortex (Krettek and Price, 1977). Particularly, tasks assigned to the central and lateral segments of the mediodorsal nucleus include the olfactory-related functions, memory, and eye movements (McCrea and Baker, 1985). Adult rats surviving lithium–pilocarpine-induced StE have impaired learning and retention in radial maze, which is related to the severity of seizure-induced damage of the mediodorsal nucleus (Harrigan et al., 1991). These data are consistent with our recent findings in immature rats showing that animals surviving StE at P12 exhibit learning deficits in Morris water maze when tested 2–3 months later (H. Kubová, unpublished observations).
In conclusion, the present study provides evidence that pilocarpine-induced StE causes neuronal damage in selective populations of neurons in the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus as early as on P12. The mechanism of neuronal damage appears to be necrosis rather than apoptosis.
Footnotes
This work was supported by the Exchange Visitor Program between the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic and the Academy of Finland (H.K., A.P.), by Grant A7011603 of the Grant Agency of the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, and by Grant309/00/1643 of the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic. We gratefully acknowledge the expert technical help Blanka Čejková and Merja Lukkari. The expert help of Dr. Riita Miettinen is greatly appreciated in the interpretation of the electron microscopic data. We also thank Dr. Lucie Kubinová for help with confocal microscopy and Eija Antikainen for photographic processing.
Correspondence should be addressed to Dr. Hana Kubová, Institute of Physiology, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Vídeňská 1083, Prague 4, CZ-142 20, Czech Republic. E-mail: kubova@biomed.cas.cz.
REFERENCES
- 1.Aicardi J, Chevrie JJ. Convulsive status epilepticus in infants and children: a study of 239 cases. Epilepsia. 1970;11:187–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1970.tb03880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Babb TL, Leite JP, Mathern GW, Pretorius JK. Kainic acid induced hippocampal seizures in rats: comparison of acute and chronic seizures using intrahippocampal versus systemic injection. Ital J Neurol Sci. 1995;16:39–44. doi: 10.1007/BF02229073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cassidy RM, Gale K. Mediodorsal thalamus plays a critical role in the development of limbic motor seizures. J Neurosci. 1998;18:9002–9009. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-21-09002.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chang D, Baram TZ. Status epilepticus results in reversible neuronal injury in infant rat hippocampus. Dev Brain Res. 1994;77:133–136. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(94)90220-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chen K, Baram TZ, Soltesz I. Febrile seizures in the developing brain result in persistent modification of neuronal excitability in limbic circuits. Nat Med. 1999;5:888–894. doi: 10.1038/11330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Crandall JE, Caviness VS., Jr Axon strata of the cerebral wall in embryonic mice. Brain Res. 1984a;316:185–195. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(84)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Crandall JE, Caviness VS., Jr Thalamocortical connections in newborn mice. J Comp Neurol. 1984b;228:542–556. doi: 10.1002/cne.902280407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.da Silva Fernandes MJ, Dubé C, Boyet S, Marescaux C, Nehlig A. Correlation between hypermetabolism and neural damage during status epilepticus induced by lithium and pilocarpine in immature and adult rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:195–209. doi: 10.1097/00004647-199902000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.de Feo MR, Mecarelli O, Palladini G, Ricci GF. Long-term effects of status epilepticus on the acquisition of conditioned avoidance behavior in rats. Epilepsia. 1986;27:476–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1986.tb03571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Deshpande SS, Smith CD, Filbert MG. Assessment of primary neuronal culture as a model for soman-induced neurotoxicity and effectiveness of memantine as a neuroprotective drug. Arch Toxicol. 1995;69:384–390. doi: 10.1007/s002040050188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dobbing J. Undernutrition and the developing brain. In: Himwich WA, editor. Developmental neurobiology. Charles C Thomas; Springfield: 1970. pp. 241–261. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dubé C, Boyet S, Marescaux C, Nehlig A. Progressive metabolic changes underlying the chronic reorganization of brain circuits during the silent phase of the lithium-pilocarpine model of epilepsy in the immature and adult rat. Exp Neurol. 2000a;162:146–157. doi: 10.1006/exnr.2000.7324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dubé C, Chen K, Eghbal-Ahmadi M, Brunson K, Soltesz I, Baram TZ. Prolonged febrile seizures in the immature rat model enhance hippocampal excitability long term. Ann Neurol. 2000b;47:336–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gallyas F, Wolff H, Bottcher H, Zaborszky L. A reliable and sensitive method to localize terminal degeneration and lysozymes in the central nervous system. Stain Technol. 1980;55:299–306. doi: 10.3109/10520298009067258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Groenewegen HJ. Organization of the afferent connections of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus in the rat, related to the mediodorsal-prefrontal topography. Neuroscience. 1988;24:379–431. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Harrigan T, Peredery O, Persinger M. Radial maze learning deficits and mediodorsal thalamic damage in context of multifocal seizure-induced brain lesions. Behav Neurosci. 1991;105:482–486. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.105.3.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hirsch E, Baram TZ, Snead OC., III Ontogenic study of lithium-pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in rats. Brain Res. 1992;583:120–126. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(10)80015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hort J, Brožek G, Komárek V, Langmeier M, Mareš P. Interstrain differences in cognitive functions in rats in relation to status epilepticus. Behav Brain Res. 2000;112:77–83. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(00)00163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hu BR, Liu CL, Ouyang Y, Blomgren K, Siesjö BK. Involvement of caspase-3 in cell death after hypoxia-ischemia declines brain maturation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:1294–1300. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200009000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hussenet F, Boyet S, Nehlig A. Long-term metabolic effects of pentylenetetrazol-induced status epilepticus in the immature brain. Neuroscience. 1995;67:455–461. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00062-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Krettek JE, Price JL. The cortical projections of the mediodorsal nucleus and adjacent thalamic nuclei in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1977;171:157–192. doi: 10.1002/cne.901710204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kubová H, Haugvicová R, Suchomelová L, Mareš P. Does status epilepticus influence motor development of immature rats? Epilepsia. 2000;41 [Suppl 6]:S64–S69. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.2000.tb01559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kuroda M, Price JL. Synaptic organization of projections from basal forebrain structures to the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1991;303:513–533. doi: 10.1002/cne.903030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lund RD, Mustari MJ. Development of the geniculocortical pathway in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1977;173:289–306. doi: 10.1002/cne.901730206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.McCrea RA, Baker R. Anatomical connection of the nucleus prepositus of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1985;237:377–407. doi: 10.1002/cne.902370308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Minciacchi D, Granato A. Developmental remodeling of thalamic projections to the frontal cortex in rats. In: Bentivoglio M, Spreafico R, editors. Cellular thalamic mechanisms. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 1988. pp. 502–516. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Morrisett RA, Jope RJ, Snead OC., III Effects of drugs on the initiation and maintenance of status epilepticus induced by administration of pilocarpine to lithium-pretreated rats. Exp Neurol. 1987;97:193–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(87)90293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nehlig A, Pereira de Vasconcelos A. The model of pentylenetetrazol-induced status epilepticus in the immature rat: short- and long-term effects. Epilepsy Res. 1996;26:93–103. doi: 10.1016/s0920-1211(96)00045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Patel S, Millan MH, Meldrum BS. Decrease in excitatory transmission within the lateral habenula and the mediodorsal thalamus protects against limbic seizures in rats. Exp Neurol. 1988;101:63–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(88)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic; New York: 1982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pineau N, Charriaut-Marlangue C, Motte J, Nehlig A. Pentylenetetrazol induced seizures induce cell suffering but not death in the immature brain. Dev Brain Res. 1999;112:139–144. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(98)00158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ray JP, Price JL. The organization of projections from the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus to orbital and medial prefrontal cortex in macaque monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1993;337:1–31. doi: 10.1002/cne.903370102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ray JP, Russchen FT, Fuller TA, Price JL. Sources of presumptive glutamatergic/aspartatergic afferents to the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1992;320:435–456. doi: 10.1002/cne.903200403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sagar HJ, Oxbury JM. Hippocampal neuron loss in temporal lobe epilepsy: correlation with early childhood convulsions. Ann Neurol. 1987;22:334–340. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sankar R, Shin DH, Wasterlain CG. Serum neuron-specific enolase is a marker for neuronal damage following status epilepticus in the rat. Epilepsy Res. 1997;28:129–136. doi: 10.1016/s0920-1211(97)00040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sankar R, Shin DH, Liu H, Mazarati A, Pereira de Vasconcelos A, Wasterlain CG. Patterns of status epilepticus-induced neuronal injury during development and long-term consequences. J Neurosci. 1998;18:8382–8393. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-20-08382.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schmued LCY, Albertson C, Slikker W., Jr Fluoro-Jade: a novel fluorochrome for the sensitive and reliable histochemical localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res. 1997;751:37–46. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(96)01387-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y. Caspases: enemies within. Science. 1998;281:1312–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5381.1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Turski WA, Cavalheiro EA, Schwartz M, Czuczwar SJ, Kleinrok Z, Turski L. Limbic seizures produced by pilocarpine in rats: behavioral, electroencephalographic and neuropathological study. Behav Brain Res. 1983;32:778–782. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(83)90136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tuunanen J, Halonen T, Pitkanen A. Status epilepticus causes selective regional damage and loss of GABAergic neurons in the rat amygdaloid complex. Eur J Neurosci. 1996;8:2711–2725. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1996.tb01566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tuunanen J, Lukasiuk K, Halonen T, Pitkanen A. Status epilepticus-induced neuronal damage in the rat amygdaloid complex: distribution, time-course and mechanisms. Neuroscience. 1999;94:473–495. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(99)00251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Vorwerk CK, Simon P, Gorla M, Katowitz W, Zurakowski D, Levin LA, Dreyer EB. Pilocarpine toxicity in retinal ganglion cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999;40:813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


