Key Points
Questions
In what proportion of patients can immune suppression medication be successfully discontinued after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation, and what factors are associated with this outcome?
Findings
In this cohort study of 827 patients who underwent allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation, 20.0% of the patients were alive and not receiving immune suppression at 5 years, and several factors were significantly associated with this outcome. A practical system that may estimate the likelihood of successful immune suppression discontinuation based on patient characteristics has been developed for clinical use.
Meaning
These findings may inform patient education, clinical practice, and clinical trial design.
Abstract
Importance
Immune suppression discontinuation is routinely attempted after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) and under current practices may lead to graft-vs-host disease (GVHD)–associated morbidity and death. However, the likelihood and predictive factors associated with successful immune suppression discontinuation after HCT are poorly understood.
Objectives
To examine factors associated with successful immune suppression discontinuation and risk for immune suppression discontinuation failure under conventional HCT approaches and develop a practical tool to estimate successful immune suppression discontinuation likelihood at the clinical point of care.
Design, Setting, and Participants
Using long-term follow-up data from 2 national Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trial Network studies (N = 827), a multistate model was developed to investigate the probability and variables associated with immune suppression discontinuation success. The study began in July 2015, and analyses were completed in August 2019.
Main Outcomes and Measures
Immune suppression discontinuation and immune suppression discontinuation failure.
Results
Of the 827 patients included in the analysis, 456 were men (55.1%). Median age at transplant was 44 (range, <1-67) years. With median follow-up of 72 (range, 11-124) months, 20.0% of the patients were alive and not receiving immune suppression at 5 years. Older recipient age (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] of >50 vs <30 years, 0.27, 99% CI, 0.14-0.50; P < .001), mismatched unrelated donor (aOR, mismatched unrelated vs matched related, 0.37; 99% CI, 0.14-0.97; P = .008), peripheral blood graft (aOR of peripheral blood graft vs bone marrow, 0.46; 99% CI, 0.26-0.82; P < .001), and advanced stage disease (aOR of advanced vs early disease, 0.45; 99% CI, 0.23-0.86, P = 0.002), were significantly associated with decreased odds of immune suppression discontinuation. Failed attempts at immune suppression discontinuation (127 patients [37.1% of total immune suppression discontinuation events]) resulting in GVHD were significantly associated with use of peripheral blood stem cells (HR, 2.62; 99% CI, 1.30-5.29; P < .001), prior GVHD, and earlier immune suppression discontinuation attempts. Earlier immune suppression discontinuation was not associated with protection from cancer relapse after HCT (adjusted hazard ratio for discontinuation vs not, 1.95; 99% CI, 0.88-4.31; P = .03).Dynamic prediction models were developed to provide future immune suppression discontinuation probability according to individual patient characteristics.
Conclusions and Relevance
Successful immune suppression discontinuation is uncommon in the setting of peripheral blood stem cell grafts. The data suggest earlier attempts at ISD conferred no long-term benefit, given frequent ISD failure, limited subsequent success after initial failed ISD attempt, and no evidence of relapse reduction. Using a risk model–based clinical application, physicians may be able to identify individual patients’ probability of successful immune suppression discontinuation.
This cohort analysis examines the factors associated with successful immune suppression discontinuation in patients who undergo allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation and develops a model to estimate the probability of successful discontinuation.
Introduction
The successful outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) includes cure of cancer, immune reconstitution, and freedom from graft-vs-host disease (GVHD), without a continuing need for immune suppression. In contrast to solid organ transplantation, immune suppression discontinuation is commonly attempted after HCT based on the expectation that immune tolerance develops and earlier immune suppression discontinuation will support graft-vs-cancer effects, decrease opportunistic infections, and decrease use of medical resources. However, there are multiple shortcomings in current understanding.
To date, few published data exist regarding successful immune suppression discontinuation rates,1 the required duration of immune suppression therapy is not known,2,3,4,5,6 and clinical or biologic factors in immune tolerance are lacking. This lack of information results in empirical immune suppression discontinuation practice with adverse consequences.7,8 Patients with a history of HCT need improved education on late HCT complications, including chronic GVHD and duration of immune suppression treatment.9 In addition, benchmarks for expected immune suppression discontinuation rates are needed for trials that include immune suppression discontinuation as an end point. Thus, analysis of immune suppression discontinuation and risk for GVHD after immune suppression discontinuation is needed.
Modeling immune suppression discontinuation after HCT requires long-term follow-up data from well-characterized, large populations and must account for multiple health states. Using data from 2 completed Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network (BMT CTN) multicenter, randomized trials, we developed a multistate modeling framework to investigate the likelihood of successful immune suppression discontinuation following HCT and the incidence of GVHD after attempted immune suppression discontinuation. Patient, HCT, and GVHD variables associated with these outcomes were studied, and dynamic prediction models were developed to permit estimation of future outcome according to current status for individual patients.
Methods
Study Population
All patients originally enrolled in BMT CTN 0201(NCT00075816) and BMT CTN 0402 (NCT00406393) randomized phase 3 trials (N = 827) were included.10,11 The BMT CTN 0201 trial tested bone marrow vs peripheral blood stem cell grafts from unrelated donors; BMT CTN 0402 examined tacrolimus with methotrexate vs tacrolimus with sirolimus after HLA-identical sibling peripheral blood stem cell transplants. Both trials used myeloablative conditioning and included patients with hematologic cancers. These trials together encompass the major patient, disease, graft source, donor type, conditioning regimen, and GVHD prophylaxis variables relevant to the immune suppression discontinuation study outcomes. Consistent data collection forms and schedules were used to capture data on GVHD development and treatment and immune suppression discontinuation. The data collection schedule and recommended immune suppression taper practices on the BMT CTN 0201 and 0402 trials are provided in the eMethods in the Supplement. Long-term follow-up was performed annually through the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) and included an assessment of GVHD, relapse, date of immune suppression discontinuation (defined as date of discontinuation of all immune suppression), and survival. The study began in July 2015, and analyses were completed in August 2019. This study was reviewed and approved by the institutional review board at the Medical College of Wisconsin, as well as Moffitt Cancer Center (Chesapeake Institutional Review Board). Patients had originally provided informed consent for the parent BMT CTN 0201 and 0402 trials, as well as consent for long-term follow-up data reporting to the CIBMTR. For the purpose of this analysis, certain unique identifiers (study identification number, CIBMTR CRID number) were required for data collection and analysis, but no other unique patient identifiers were used.
For the purpose of our analysis, we modeled immune suppression discontinuation using final discontinuation of all immune suppression as the definition. More granular details on tapering and discontinuation of individual immune suppression agents before the complete stop date of all immune suppression agents were not available. In addition, data on tapering of immune suppression agents owing to mixed chimerism, minimal residual disease, or other scenarios were not available. The aggregate trial and CIBMTR long-term follow-up data were reviewed in full to characterize transitions between health states in this multistate model.
Statistical Analysis
Multistate Modeling
Immune suppression discontinuation after HCT was represented using a multistate model (eFigure 1 in the Supplement) composed of 6 states: (1) receiving initial immune suppression with no GVHD, (2) acute GVHD, (3) chronic GVHD, (4) immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state, (5) resumed immune suppression for GVHD, and (6) death or relapse, or second HCT (combined absorbing state). Patients moving into state 2 or 3 remained there until their date of entry to state 4 or 6 (movement from state 2 to 3 also occurred). Patients in state 4 moved to state 5 for either acute or chronic GVHD requiring resumed immune suppression. The number of patients undergoing each transition was described.12,13,14,15 Descriptive summaries of the timing of immune suppression discontinuation, as well as the time to resume immune suppression for GVHD, were provided using median and interquartile range (IQR) and compared between groups using the Kruskal-Wallis test.
The likelihood of being in each state over time was described using differences in Kaplan-Meier estimators for transient states and the cumulative incidence estimator for the absorbing state.16 The likelihood of immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state as a function of baseline covariates was modeled using pseudo-value regression with results summarized using odds ratios (ORs).17,18,19,20 Pseudo-value regression is an analog of logistic regression to account for incomplete or censored time-to-event data. Pseudo-value regression is particularly useful for multistate models because it allows for direct and interpretable modeling of the likelihood of being in a particular state at a particular time. In contrast, alternatives, such as Markov models, that model transition rates between states must combine multiple models for various transitions to get an aggregate association of covariates with the state probabilities; these combinations typically lead to complex associations that can be difficult to interpret clinically. The immune suppression discontinuation probability can be expressed as a difference in event-free survival probabilities. Therefore, pseudo-values were first obtained for each event-free survival probability on a grid of time points using the SAS macro pseudosurv,21 and pseudo-values for the immune suppression discontinuation probability then were constructed as the corresponding differences in the event-free survival pseudo-values.22 To estimate adjusted ORs (aORs) for the immune suppression discontinuation probability while accounting for the correlation across time points, generalized estimating equation techniques were applied using SAS PROC GENMOD with pseudo-values for the immune suppression discontinuation probability as the response variable and including the covariates described in the Results section. Interactions between time and each covariate were considered.
The association between post-HCT characteristics, including development of GVHD, and immune suppression discontinuation was examined using separate Cox Markov models for each transition into the immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state, left truncated at the time of entry into the preceding state. Markov model assumptions were tested using covariates representing the time until development of GVHD. Hazard ratios for the risk of resuming immune suppression for GVHD were estimated using left-truncated Cox regression, estimating this outcome from the starting point of the time of immune suppression discontinuation. Adjusted cumulative incidences for resuming immune suppression were summarized for the effect of GVHD history and timing of immune suppression discontinuation owing to nonproportional hazards.23
Dynamic prediction models for a patient’s likelihood of immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state at post-HCT horizon times given their current status used landmarking supermodels with pseudo-value regression.24 These landmarking supermodels considered linear and quadratic associations with landmark time, as well as interactions with covariates. Regression coefficients from these models were used to develop a scoring system for the likelihood of immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state at a future horizon time given a patient’s current status. Owing to limited sample size available for complex multistate modeling, it was not feasible to split the data set into separate training and validation sets; therefore, an independent validation of the dynamic prediction model will need to be conducted in the future. All statistical analysis was performed using 2-sided, unpaired testing at a significance level of .01 owing to the number of variables and models being considered. All analyses were conducted using SAS, version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc).
Variables Analyzed
Baseline variables included patient age, disease, and CIBMTR disease risk, donor-recipient HLA match, donor type (sibling, unrelated), donor-recipient sex match, graft source (bone marrow, peripheral blood stem cells), GVHD prophylaxis (cyclosporine with methotrexate, tacrolimus with methotrexate, or tacrolimus with sirolimus), and antithymocyte globulin use. For transitions from acute and chronic GVHD states to immune suppression discontinuation, acute and chronic GVHD overall grade or score and organ-specific involvement and severity were examined. Graft-vs-host disease variables were assessed both as fixed covariates (value at GVHD diagnosis) and time-dependent covariates (history and current state). Acute GVHD scoring followed consensus guidelines,25 while chronic GVHD overall score was an overall severity measure used in BMT CTN 0201 and 0402 and CIBMTR forms at the time of these studies. For modeling the rate of GVHD development after immune suppression discontinuation, prior GVHD characteristics and timing of immune suppression discontinuation were also considered.
Results
Patient Characteristics
A summary of baseline characteristics is provided in eTable 1 in the Supplement. Of the 827 patients included in the analysis, 456 were men (55.1%). Median age at transplant was 44 (range, <1-67) years. Median follow-up for the entire population was 72 (range, 11-124) months; 20.0% of the patients were alive and not receiving immune suppression at 5 years.
Multistate Model
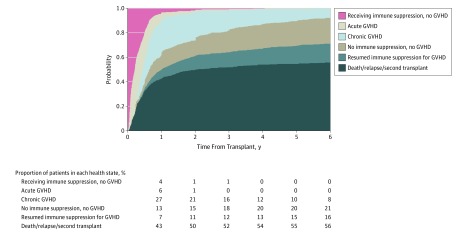
A diagram of the model is provided in eFigure 1 in the Supplement. A total of 342 patients (41.4% of the total population) were able to stop immune suppression, yet 127 of those (37.1% of patients who discontinued immune suppression) had to resume immune suppression for treatment of GVHD (immune suppression discontinuation failure). An additional 47 patients (13.7%) died or experienced relapse after immune suppression discontinuation, which was a competing risk event for the immune suppression discontinuation failure outcome. Thus, 174 of the 342 initial immune suppression discontinuation attempts (50.9%) resulted in adverse outcomes. Of the original 827 patients, 135 individuals (16.3%) reached immune suppression discontinuation without GVHD, while 82 patients (9.9%) first experienced acute GVHD and 125 patients (15.1%) first experienced chronic GVHD, with or without acute GVHD, before reaching immune suppression discontinuation.
Median time to immune suppression discontinuation among those who achieved that outcome was 343 (IQR, 189-746) days; this time varied by whether they discontinued immune suppression without prior GVHD (median [IQR], 190 [145-276] days), had prior acute GVHD (median, 276 [IQR, 202-372] days), or had chronic GVHD (median, 871 [IQR, 535-1443] days) (P < .001). The probability of each state over time is summarized in Figure 1. Among the 127 patients with immune suppression discontinuation failure, 50 patients (39.4%) subsequently discontinued immune suppression, with immune suppression discontinuation failing again in 6 patients (12.0%).
Figure 1. Probability of Health States From Time of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation .
The percentages presented indicate the proportion of patients in each health state at each year following transplant. GVHD indicates graft-vs-host disease.
Baseline Indicators of Discontinuation
The Table provides the multivariable pseudo-value regression model for the likelihood of immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state at any time. Peripheral blood grafts (aOR, 0.46; 99% CI, 0.26-0.82; P<.001) and mismatched, unrelated donors (aOR, 0.37; 99% CI, 0.14-0.97; P = .008) were associated with lower odds of immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state. Increasing age (aOR, 0.27, 99% CI, 0.14-0.50; P<.001) and advanced stage disease (aOR, 0.45; 99% CI, 0.23-0.86, P = 0.002) were also associated with lower odds of immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state. Antithymocyte globulin use vs no use did not associate with immune suppression discontinuation probability (aOR, 1.26; 99% CI, 0.73-2.18; P = .27).
Table. Pseudo-Value Regression Model of Immune Suppression Discontinuation Using Baseline Factors.
| Variable | No. | Adjusted OR (99% CI) | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time, mo | <.001 (8 df) | ||
| 6 | NAa | 1 [Reference] | |
| 12 | 3.30 (2.00-5.49) | <.001 | |
| 18 | 3.65 (2.17-6.12) | <.001 | |
| 24 | 4.05 (2.35-6.96) | <.001 | |
| 30 | 4.77 (2.77-8.22) | <.001 | |
| 36 | 5.21 (3.02-8.99) | <.001 | |
| 48 | 6.00 (3.47-10.37) | <.001 | |
| 60 | 6.12 (3.52-10.62) | <.001 | |
| 72 | 6.32 (3.63-11.02) | <.001 | |
| Graft type (unrelated only) | |||
| Bone marrow | 264 | 1 [Reference] | |
| Peripheral blood | 262 | 0.46 (0.26-0.82) | <.001 |
| Donor source | .003 (2 df) | ||
| Matched sibling | 301 | 1 [Reference] | |
| Unrelated, well matched | 409 | 1.05 (0.57-1.92) | .84 |
| Unrelated, mismatched | 117 | 0.37 (0.14-0.97) | .008 |
| Age, y | <.001 (2 df) | ||
| 0-30 | 194 | 1 [Reference] | |
| 31-50 | 381 | 0.51 (0.31-0.85) | <.001 |
| >50 | 252 | 0.27 (0.14-0.50) | <.001 |
| Disease risk | .003 (2 df) | ||
| Early | 476 | 1 [Reference] | |
| Intermediate | 177 | 0.66 (0.38-1.16) | .06 |
| Advanced | 174 | 0.45 (0.23-0.86) | .002 |
Abbreviations: df, degrees of freedom; NA, not applicable; OR, odds ratio.
Numbers of patients are not given for the times because each patient can contribute to the model at multiple follow-up times, depending on how long they survived and/or remained on study.
Discontinuation and Cancer Relapse
We examined the association of immune suppression discontinuation as a time-dependent covariate with relapse, focusing on initial immune suppression discontinuation without intervening GVHD by considering both GVHD and death or second HCT as competing risk events. Disease and disease risk characteristics did not significantly differ according to time to immune suppression discontinuation dichotomized by median time to immune suppression discontinuation. In multivariable analysis, discontinuation of immune suppression was not significantly associated with a decreased risk of relapse (HR for off vs receiving immune suppression as a time-varying covariate among patients without the competing event of GVHD was 1.95; 99% CI, 0.88-4.31; P = .03).
GVHD History and Discontinuation
Separate models were considered to examine the association between GVHD-related variables and the transition from either prior acute GVHD or chronic GVHD to immune suppression discontinuation. No acute GVHD variables were significantly associated with the time to immune suppression discontinuation after development of acute GVHD. Current (active) skin involvement (HR, 0.33; 99% CI, 0.14-0.80; P = .001) and unrelated donors (unrelated well-matched vs matched sibling donor: HR, 0.29; 99% CI, 0.10-0.79; P = .001; unrelated mismatched vs matched sibling donor: HR, 0.17; 99% CI, 0.03-0.95; P = .008) were associated with a lower likelihood of immune suppression discontinuation after chronic GVHD in a multivariable model.
Immune Suppression Discontinuation Failure
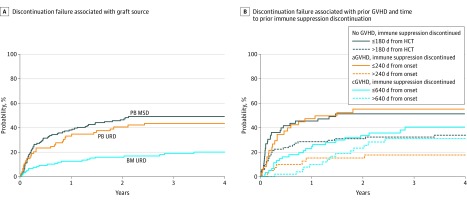
Overall, 127 patients (37.1%) resumed immune suppression for GVHD after initial immune suppression discontinuation (immune suppression discontinuation failure). The median time from immune suppression discontinuation to subsequent GVHD was 113 (IQR, 42-371) days. The time from immune suppression discontinuation to subsequent GVHD varied by whether patients discontinued immune suppression without prior GVHD (n = 60; median, 56 [IQR, 28-181] days), had prior acute GVHD (n = 28; median, 107 [IQR, 55-284] days), or had chronic GVHD (n = 39; median, 366 [IQR, 135-643] days) (P < .001). In a multivariable Cox proportional hazards model, use of peripheral blood stem cells vs bone marrow in unrelated donor HCT was associated with a greater likelihood of immune suppression discontinuation failure (HR, 2.62; 99% CI, 1.30-5.29; P < .001) (Figure 2). A history of GVHD before immune suppression discontinuation, namely, the presence and timing of any acute or chronic GVHD onset before immune suppression discontinuation, was also associated with immune suppression discontinuation failure. Owing to nonproportional hazards, outcomes are summarized as adjusted cumulative incidence curves in Figure 2. Overall, the risk of resuming immune suppression for GVHD was highest (approximately 50%) for patients who discontinued immune suppression with no prior GVHD 180 days or less after HCT or who discontinued immune suppression after acute GVHD at 240 days or less after acute GVHD onset. eFigure 2 in the Supplement shows the subsequent state probabilities of 127 patients with immune suppression discontinuation failure. By 5 years after immune suppression discontinuation failure, only 24.8% of the patients successfully reached immune suppression discontinuation (99% CI, 15.4%-34.6%), while 41.0% continued to receive immune suppression (99% CI, 28.6%-53.4%) and 27.0% experienced death, relapse, or second HCT (99% CI, 16.9%-38.1%).
Figure 2. Association of Graft Source, Previous Graft-vs-Host Disease (GVHD), and Time to Prior Immune Suppression Discontinuation With Probability of Resuming Immune Suppression for GVHD (Immune Suppression Discontinuation Failure).
Associations with graft source (A) and prior GVHD and time to prior immune suppression discontinuation (B). Cumulative incidence of immune suppression discontinuation failure is presented in years from time of immune suppression discontinuation. aGVHD indicates acute GVHD; cGVHD, chronic GVHD; BM, bone marrow; MSD, matched-sibling donor; PB, peripheral blood; and URD, unrelated donor.
Dynamic Prediction Model
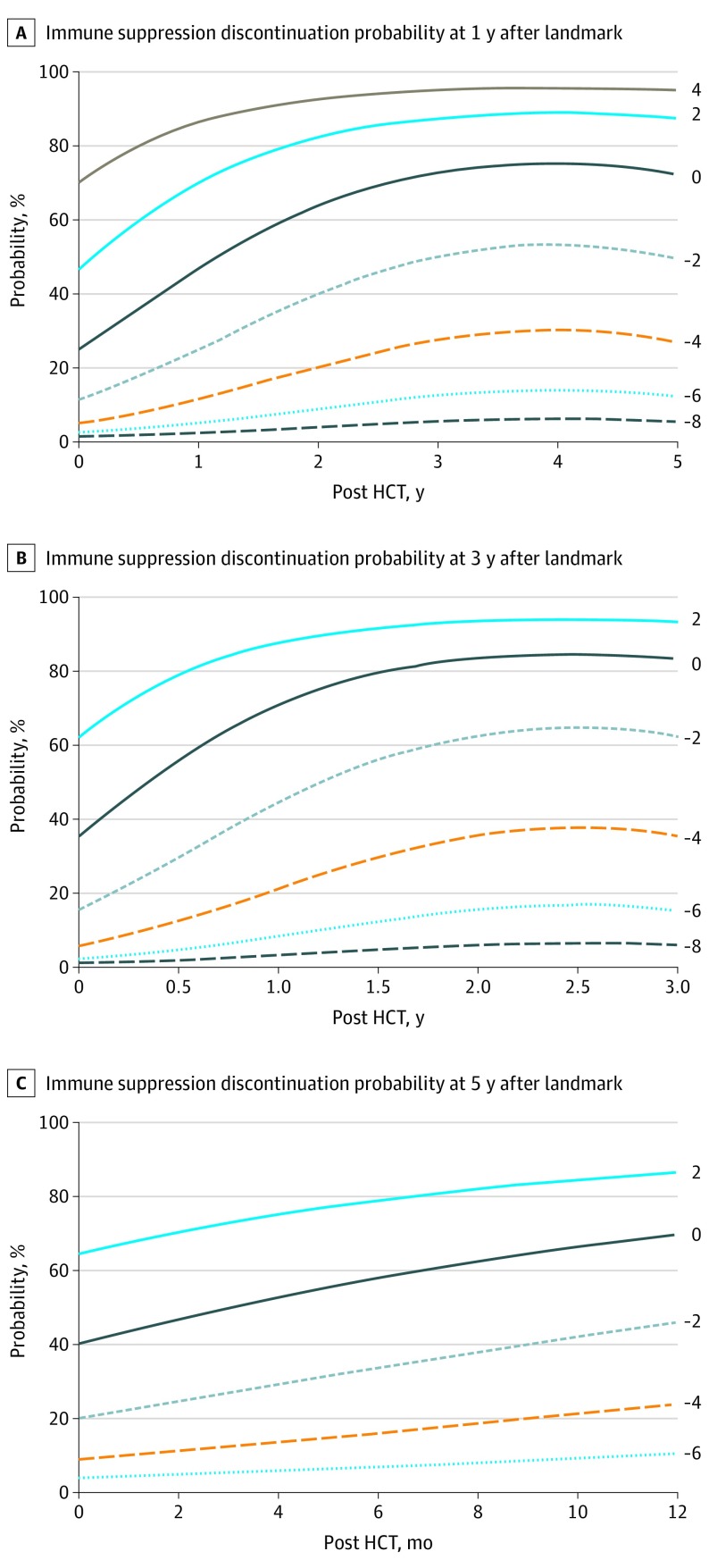
Dynamic prediction models for the probability of immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state were developed for 3 different time horizons: 1, 3, and 5 years in the future. Graft type, donor type, age, state history, and timing of immune suppression discontinuation were associated with the likelihood of immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state at 1, 3, or 5 years (eTables 2, 3, and 4 in the Supplement); disease risk was only associated with immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state for the 1-year horizon. No interactions of any factors with the landmark time were significant. Coefficients for a scoring system for the likelihood of immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state are reported in eTable 5 in the Supplement, based on the log OR coefficients. After refitting the dynamic prediction model with the scoring system, a 1-U increase in the score was associated with ORs for immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state of 1.64 (99% CI, 1.53-1.75; P < .001) at 1 year, 1.74 (99% CI, 1.53-1.98; P < .001) at 3 years, and 1.66 (99% CI, 1.35-2.03; P < .001) at 5 years. Plots of the probability of immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state by score and landmark time post HCT are shown in Figure 3, assuming the score has a linear association with the log odds. These plots can be used to provide patients with specific information about their 1-, 3-, and 5-year likelihood of immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state, depending on their clinical condition at a particular time post HCT. A web application is also available for directly computing the probability of immune suppression discontinuation from these prediction models.26
Figure 3. Probability of Immune Suppression-Free and Graft-vs-Host Disease-Free State by Risk Score and Posttransplant Landmark Time.
Probability of discontinuation at 1 (A), 3 (B), and 5 (C) years into the future past the landmark time after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). Each line corresponds to a risk score (indicated with the graph lines) as computed from eTable 4 in the Supplement. The x-axis represents the landmark time point. To use the figure to determine the immune suppression discontinuation probability at a particular landmark time, identify the landmark time point on the x-axis, select the line corresponding to the patient’s risk score at that landmark time point, and then read off the corresponding probability where they cross. For example, a patient with a risk score of −2 at a landmark time of 2 years post HCT would have a 40% probability of immune suppression discontinuation 1 year past the landmark (eg, at 3 years) (A). These figures should not be read from left to right, as a patient’s risk score can change as the landmark time is varied.
Discussion
The results of this analysis suggest that, in the context of HCT with standard calcineurin inhibitor–based GVHD prophylaxis and myeloablative conditioning, tolerance is not rapidly achieved for most patients, and earlier immune suppression discontinuation does not protect from cancer relapse and is associated with high risk of immune suppression discontinuation failure. These data appear to call for critical reappraisal of current practices and appear to demonstrate the need for clinical and biomarker-based tools to tailor practice for individual patients.
In total, only 20.0% of patients were immune suppression–free survivors by 5 years after HCT. Among the variables associated with successful immune suppression discontinuation, usually, only the graft source is modifiable. In particular, use of peripheral blood stem cells vs bone marrow grafts in the unrelated donor context had an adverse association with immune suppression discontinuation. These data expand the body of evidence supporting the adverse association of peripheral blood stem cells with GVHD and quality of life from the parent BMT CTN 0201 trial,10,27 which to date has not influenced practices.28 There are major applications of our present analysis. These data may provide a robust immune suppression discontinuation benchmark for trial design and counseling of HCT recipients. The dynamic prediction models provide a clinically useful tool to assess a given patient’s immune suppression discontinuation likelihood. Our scoring system is straightforward to apply and has been implemented in a web application for use at the point of care.26
The analysis also provides insight into the state of immune suppression discontinuation failure, quantitatively presenting the clinical challenges faced owing to empirical immune suppression discontinuation practice. In total, 37.1% of attempted immune suppression discontinuation fails, and this failure risk appears to be significantly affected by the use of peripheral blood stem cells, GVHD history, and timing of attempted immune suppression discontinuation. Only 25% of patients who experienced immune suppression discontinuation failure subsequently achieved discontinuation 5 years later; most patients continued to receive prolonged immune suppression, died, or experienced relapse. Among potentially modifiable practices, longer initial exposure to immune suppression may mitigate risk: immune suppression discontinuation failure was consistently more likely when discontinuation had been attempted earlier (either with reference to time from HCT or from time of prior GVHD). This possibility is supported in part by interventional trial data demonstrating decreased GVHD risk after intentionally prolonged immune suppression duration,3,4,5,6,29 yet appears to require further study regarding the specific outcome of immune suppression discontinuation. In contrast to some published data,30 the cancer relapse risk did not appear to be significantly associated with timing of immune suppression discontinuation in our analysis.
Limitations
This study has limitations. Although the existing long-term follow-up seemed to provide an unparalleled view into late immune suppression discontinuation events, additional immune suppression discontinuation events may occur beyond this time. As well, both certain GVHD features (National Institutes of Health consensus-based chronic GVHD severity scoring)31 and other validated tools relevant to post-HCT outcome32,33 could not be used in our analysis because of the data collection methods performed by the BMT CTN 0201 and 0402 trials and CIBMTR at the time these patients were treated. We also could not discern specific immune suppression discontinuation or its failure outcomes according to specific individual immune suppression agents, because data on type and timing of each immune suppression agent taper and discontinuation were lacking. In addition, the population represented herein included few children and lacks representation of reduced-intensity conditioning, alternative donor sources (related haploidentical or umbilical cord blood transplants), and approaches that powerfully deplete donor alloreactive T cells (eg, antithymocyte globulin, CD34+ selection, or posttransplant use of cyclophosphamide). For example, several randomized trials have demonstrated improved rates of immune suppression discontinuation when antithymocyte globulin is used.34,35 Thus, conclusions from this analysis cannot be applied to these approaches. In addition, all of the sibling transplants in this analysis used peripheral blood stem cell grafts, so the risk factors with sibling bone marrow grafts could not be evaluated.
Regarding the statistical approach, we focused on novel dynamic prediction models using landmarking and pseudo-value regression. Although this approach has been used previously with survival and competing risks analyses, we are the first, to our knowledge, to apply it in a multistate model setting. Other approaches, such as Markov modeling of each transition, are available; however, we found the Markov modeling approach to be impractical in this setting for 2 reasons: first, the Markov assumptions are not tenable for our multistate model, necessitating creation of additional time-dependent states and increasing model complexity to allow Markov modeling; and second, some transitions had an insufficient number of events to permit regression modeling on the corresponding transition rates. In contrast, our approach is more direct because it offers simple interpretability of covariate effects and the risk score on the probability of interest: immune suppression-free and GVHD-free state. A limitation of our analysis is that we focused on modeling initial immune suppression discontinuation and did not incorporate subsequent transitions to immune suppression discontinuation after initial failure of discontinuation as part of our dynamic prediction model, owing to the limited number of these events available.
Conclusions
Validation of our model in an independent patient cohort is warranted as a next step. Following this validation, we recommend that a prospective interventional trial be conducted to examine immune suppression discontinuation and risk of immune suppression discontinuation failure according to a risk-adapted immune suppression taper schedule.
eMethods. Detailed Methodology
eFigure 1. Multistate Model for Discontinuation of IS
eFigure 2. State Probability From Time of ISD Failure
eTable 1. Characteristics of Patients From CTN 0201 and CTN 0402
eTable 2. Dynamic Prediction Model of Likelihood of Being off IS Without GVHD at 1 Year Time Horizon
eTable 3. Dynamic Prediction Model of Likelihood of Being off IS Without GVHD at 3 Year Time Horizon
eTable 4. Dynamic Prediction Model of Likelihood of Being off IS Without GVHD at 5 Year Time Horizon
eTable 5. Proposed Scoring Algorithm for Each Landmark Time
References
- 1.Stewart BL, Storer B, Storek J, et al. Duration of immunosuppressive treatment for chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2004;104(12):-. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-01-0200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Burroughs L, Mielcarek M, Leisenring W, et al. Extending postgrafting cyclosporine decreases the risk of severe graft-versus-host disease after nonmyeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation. Transplantation. 2006;81(6):818-825. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000203556.06145.5b [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kansu E, Gooley T, Flowers ME, et al. Administration of cyclosporine for 24 months compared with 6 months for prevention of chronic graft-versus-host disease: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Blood. 2001;98(13):3868-3870. doi: 10.1182/blood.V98.13.3868 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lönnqvist B, Aschan J, Ljungman P, Ringdén O. Long-term cyclosporin therapy may decrease the risk of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 1990;74(4):547-548. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb06356.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mengarelli A, Iori AP, Romano A, et al. One-year cyclosporine prophylaxis reduces the risk of developing extensive chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. 2003;88(3):315-323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ruutu T, Volin L, Elonen E. Low incidence of severe acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease as a result of prolonged cyclosporine prophylaxis and early aggressive treatment with corticosteroids. Transplant Proc. 1988;20(3):491-493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pidala J, Bloom GC, Enkemann S, Eschrich S, Lancaster J, Anasetti C. Biomarkers to discern transplantation tolerance after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16(6):729-738. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.11.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pidala J, Lee SJ, Quinn G, Jim H, Kim J, Anasetti C. Variation in management of immune suppression after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011;17(10):1528-1536. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2011.03.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jim HS, Quinn GP, Gwede CK, et al. Patient education in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant: what patients wish they had known about quality of life. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49(2):299-303. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2013.158 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Anasetti C, Logan BR, Lee SJ, et al. ; Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network . Peripheral-blood stem cells versus bone marrow from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(16):1487-1496. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1203517 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cutler C, Logan B, Nakamura R, et al. Tacrolimus/sirolimus vs tacrolimus/methotrexate as GVHD prophylaxis after matched, related donor allogeneic HCT. Blood. 2014;124(8):1372-1377. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-567164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Andersen PK, Keiding N. Multi-state models for event history analysis. Stat Methods Med Res. 2002;11(2):91-115. doi: 10.1191/0962280202SM276ra [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Klein JP, Shu Y. Multi-state models for bone marrow transplantation studies. Stat Methods Med Res. 2002;11(2):117-139. doi: 10.1191/0962280202sm277ra [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Logan BR. Review of multistate models in hematopoietic cell transplantation studies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(1)(suppl):S84-S87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2012.10.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Meira-Machado L, de Uña-Alvarez J, Cadarso-Suárez C, Andersen PK. Multi-state models for the analysis of time-to-event data. Stat Methods Med Res. 2009;18(2):195-222. doi: 10.1177/0962280208092301 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pepe MS. Inference for events with dependent risks in multiple end point studies. J Am Stat Assoc. 1991;86:770-778. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1991.10475108 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Andersen PK, Klein JP, Rosthoj S. Generalised linear models for correlated pseudo-observations, with applications to multi-state models. Biometrika. 2002;90:15-27. doi: 10.1093/biomet/90.1.15 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Andersen PK, Klein JP. Regression analysis for multistate models based on a pseudo-value approach, with applications to bone marrow transplantation studies. Scand J Stat. 2007;34(1):3-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9469.2006.00526.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Andersen PK, Perme MP. Pseudo-observations in survival analysis. Stat Methods Med Res. 2010;19(1):71-99. doi: 10.1177/0962280209105020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Logan BR, Wang T Pseudo-value regression models. In: Klein JP, Van Houwelingen HC, Ibrahim JG, Scheike TH, eds. Handbook of Survival Analysis Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pseudosurv. https://www.mcw.edu/-/media/MCW/Departments/Biostatistics/sas_macros_to_find_pseudo-values.txt?la=en. Accessed August 23, 2019.
- 22.Klein JP, Gerster M, Andersen PK, Tarima S, Perme MP. SAS and R functions to compute pseudo-values for censored data regression. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2008;89(3):289-300. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2007.11.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang X, Zhang MJ. SAS macros for estimation of direct adjusted cumulative incidence curves under proportional subdistribution hazards models. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2011;101(1):87-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2010.07.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nicolaie MA, van Houwelingen JC, de Witte TM, Putter H. Dynamic pseudo-observations: a robust approach to dynamic prediction in competing risks. Biometrics. 2013;69(4):1043-1052. doi: 10.1111/biom.12061 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15(6):825-828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Landmark prediction of immune suppression discontinuation (ISD). https://discis.shinyapps.io/discis/. Accessed August 23, 2019.
- 27.Lee SJ, Logan B, Westervelt P, et al. Comparison of patient-reported outcomes in 5-year survivors who received bone marrow vs peripheral blood unrelated donor transplantation: long-term follow-up of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2(12):1583-1589. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.2520 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Khera N, Mau LW, Denzen EM, et al. Translation of clinical research into practice: an impact assessment of the results from the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network Protocol 0201 on unrelated graft source utilization. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018;24(11):2204-2210. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.06.028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pidala J, Kim J, Alsina M, et al. Prolonged sirolimus administration after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation is associated with decreased risk for moderate-severe chronic graft-versus-host disease. Haematologica. 2015;100(7):970-977. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2015.123588 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Inamoto Y, Flowers ME, Lee SJ, et al. Influence of immunosuppressive treatment on risk of recurrent malignancy after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2011;118(2):456-463. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-330217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jagasia MH, Greinix HT, Arora M, et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: I. The 2014 Diagnosis and Staging Working Group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(3):389-401.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.12.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Armand P, Kim HT, Logan BR, et al. Validation and refinement of the Disease Risk Index for allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2014;123(23):3664-3671. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-552984 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood. 2005;106(8):2912-2919. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Walker I, Panzarella T, Couban S, et al. ; Canadian Blood and Marrow Transplant Group . Pretreatment with anti-thymocyte globulin versus no anti-thymocyte globulin in patients with haematological malignancies undergoing haemopoietic cell transplantation from unrelated donors: a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(2):164-173. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00462-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Finke J, Schmoor C, Bethge WA, et al. Long-term outcomes after standard graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis with or without anti–human-T-lymphocyte immunoglobulin in haemopoietic cell transplantation from matched unrelated donors: final results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Haematol. 2017;4(6):e293-e301. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(17)30081-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eMethods. Detailed Methodology
eFigure 1. Multistate Model for Discontinuation of IS
eFigure 2. State Probability From Time of ISD Failure
eTable 1. Characteristics of Patients From CTN 0201 and CTN 0402
eTable 2. Dynamic Prediction Model of Likelihood of Being off IS Without GVHD at 1 Year Time Horizon
eTable 3. Dynamic Prediction Model of Likelihood of Being off IS Without GVHD at 3 Year Time Horizon
eTable 4. Dynamic Prediction Model of Likelihood of Being off IS Without GVHD at 5 Year Time Horizon
eTable 5. Proposed Scoring Algorithm for Each Landmark Time