Abstract
Background
Mucormycosis is an invasive fungal infection (IFI) most commonly seen in immunocompromised patients. Diabetic ketoacidosis, haematopoietic transplantation, iron overload states, and deferoxamine therapy are considered to be some of the classical risk factors. While cutaneous and rhino-sinusoidal forms may be seen in immunocompetent (IC) individuals, cardiac and mediastinal involvement is rare. In this report, we describe a young patient without predisposing factors who presented as mediastinal mucormycosis with extensive cardiac involvement.
Case summary
A 19-year-old male presented with complaints of dry cough and dyspnoea on exertion over the last 4 months. Echocardiography showed diffuse infiltration of both atria along with multiple pedunculated freely mobile masses. A computed tomography chest was done to further delineate the true extent of the disease and revealed diffuse infiltration of the mediastinum, bilateral atria and interatrial septum, pulmonary veins, and superior vena cava. A fine needle aspiration cytology from a mediastinal mass revealed broad aseptate fungal hyphae with right angled branching consistent with Mucor. Extensive evaluation could not find any predisposing factors. The patient was started on Amphotericin B and surgical debridement was contemplated. However, owing to the diffuse infiltration around the heart and mediastinal vasculature, debridement could not be performed and the patient eventually succumbed to the illness.
Discussion
Mediastinal mucormycosis though rare in IC patients, is a rapidly progressive condition with a high fatality. A high index of suspicion needs to be maintained in individuals presenting with infiltrative disorders of the mediastinum for early diagnosis and prompt treatment.
Keywords: Invasive fungal infection, Mediastinal mucormycosis, Cardiac mucormycosis, Immunocompetent, Immunocompromise, Case report
Learning points
In endemic geographical regions, invasive mucormycosis can occur even in individuals without predisposition.
It has to be considered in the differential diagnosis of a infiltrating mass lesion involving heart and mediastinum.
Invasive mucormycosis can present with imaging findings that can mimic sclerosing mediastinitis, other infiltrating fungal infections and neoplasms.
Introduction
Mucormycosis is an invasive fungal infection (IFI), usually seen in individuals with underlying predisposing conditions including diabetes mellitus, iron overload states and haematological malignancies. While rhino-sinusoidal and cutaneous forms may occur in all individuals, disseminated forms are usually seen in individuals with these risk factors. Isolated mediastinal involvement is rare and when it occurs usually presents as sclerosing mediastinitis. In this report, we describe a young patient without predisposing factors who presented with isolated mediastinal mucormycosis (MM) with predominant cardiac infiltration.
Timeline
| Time | Events |
|---|---|
| 4 months prior to presentation | Dry cough and dyspnoea on exertion which was gradually progressive and unattended. |
| Day 1 | Admitted at our centre for evaluation. Chest X-ray showed minimal right sided pleural effusion and echocardiography revealed soft tissue mass infiltrating bilateral atria. |
| Differentials considered in life time were lymphoma and other solid malignancies, clots, infiltrating fungal infections, primary cardiac neoplasms. | |
| Day 3 | CECT chest was performed that showed mediastinal and cardiac infiltration, infiltration of superior venacava and pulmonary veins. |
| Day 5 | Clinical deterioration and worsening of breathlessness requiring oxygen support. |
| Day 6 | Computed tomography-guided fine needle aspiration was done from the mass lesion. |
| Day 7 | Smears confirmed to be Mucor hyphae. Prognosis explained to the patient family. |
| Day 8 | After extensive discussions with infectious disease team and surgical team, surgical debridement was deferred and was started on amphotericin. |
| Day 11 | Cardio embolic stroke and right sided hemiparesis and loss of vision in left eye. |
| Day 14 | Clinical condition worsened and finally succumbed to his illness. |
Case presentation
A 19-year-old gentleman presented to our centre with complaints of non-productive cough and dyspnoea on exertion for the past 4 months. Clinical examination was unremarkable while a chest X-ray was significant for a small right sided pleural effusion. Laboratory investigations showed neutrophilic leucocytosis, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 30 mm/h (0–20 mm/h) and fasting blood sugars within the normal range. A transthoracic echocardiogram was performed which showed a soft tissue mass with diffuse infiltration of the right and left atria along with multiple pedunculated masses attached to the lateral and superior wall of the left atrium (Figure 1A–C, Supplementary material online, Video S1 and S2). The mass was also seen to be infiltrating into the ostia of the superior pulmonary veins. On colour Doppler, he also had moderate tricuspid regurgitation with severe pulmonary hypertension.
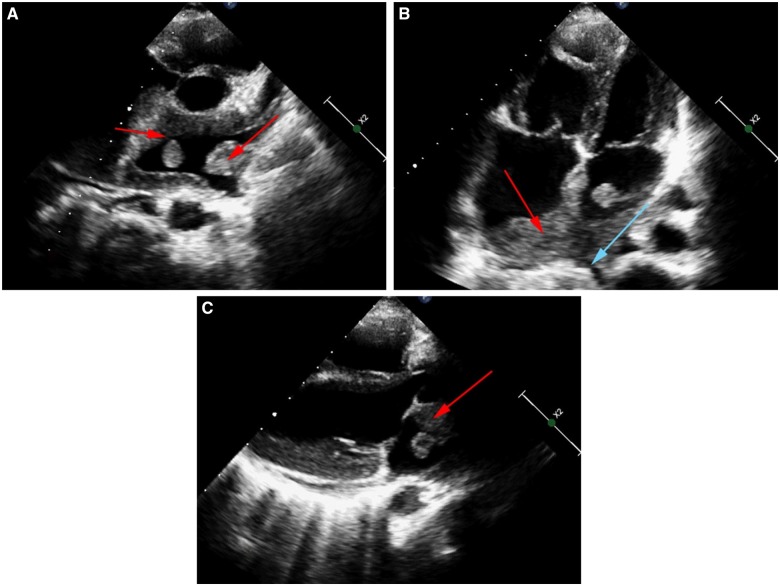
Figure 1.
(A) Transthoracic echocardiogram in parasternal short-axis view showing mass protruding (red arrow) and infiltrating all walls of left atrium (red arrow). (B) Apical four chamber view, showing diffuse infiltration of both atria, interatrial septum (red arrows), extending into the pulmonary vein ostium (blue arrow) with hanging mass in left atrium. (C) Parasternal long-axis view showing a pedunculated soft tissue mass in the left atrium (red arrow).
Computed tomography (CT) chest showed extensive mediastinal infiltration by a soft tissue mass, encasing both bronchi, superior vena cava, pulmonary veins and was seen extending into and enveloping the arch of the aorta (Figure 2B, C). The mass was also seen infiltrating the right atrium and extending through the interatrial septum into the left atrium (Figure 2A).
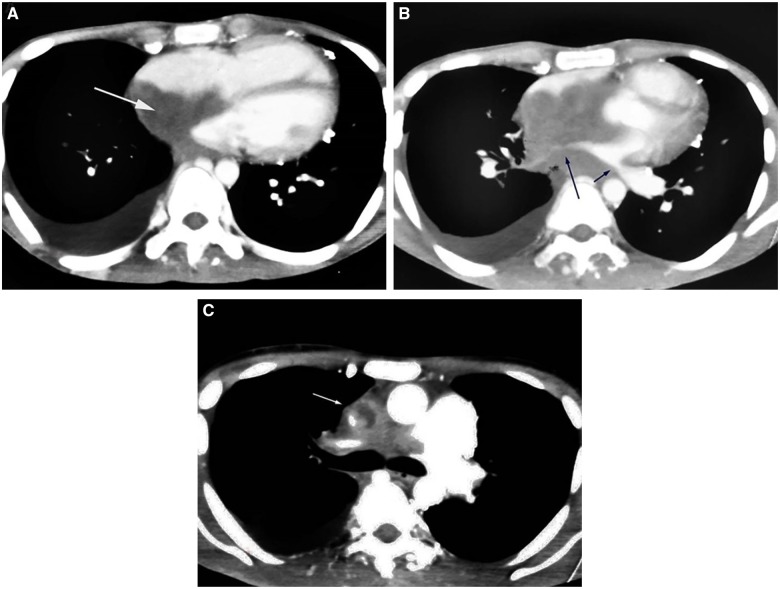
Figure 2.
Computed tomography chest showing similar findings of (A) tissue infiltration in bilateral atria and interatrial septum (white arrow), (B) right and left pulmonary vein infiltration (blue arrows), and (C) superior venacava infiltration (white arrow).
The differential diagnosis considered included lymphoproliferative disorders and other primary cardiac tumours, IFI, sclerosing mediastinitis due to tuberculosis, histoplasmosis, aspergillosis, and clots. Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) from the mediastinal mass showed broad, thin walled, aseptate fungal profiles with right angle branching consistent with Mucormycosis (Figure 3A–C).
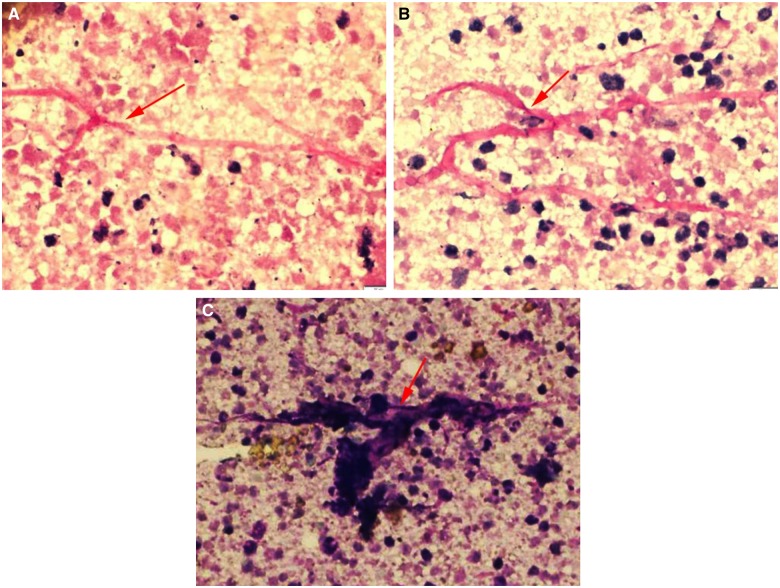
Figure 3.
PAS, periodic acid schiff (A, B) and MGG, May–Grunwald–Giemsa (C) stained images showing broad, aseptate, foldable fungal hyphae (red arrows) with right angled branching consistent with Mucor.
Blood cultures were sterile. He had no underlying risk factors like iron overload states, diabetes mellitus, intake of steroids, or other immunosuppressive drugs. There was no evidence of neutropenia, while the CD4 count was 670/µL. Serum galactomannan index was 0.63 and there was no histological evidence of aspergillosis. Nasal scrapings were negative for fungal hyphae. He was started on Amphotericin B and was initially considered for surgical debridement, which was later deferred in view of diffuse infiltration into and around the heart and great vessels. During the course of hospitalization, the patient developed right sided hemiparesis, facial palsy of the upper motor neuron type, and loss of vision in the left eye. A CT angiogram of the neck vessels showed occlusion of the left common carotid artery likely due to embolization. Pulmonary vein involvement led to pulmonary oedema with worsening respiratory failure and the patient eventually succumbed to the illness.
Discussion
Mucormycosis is one of the most common IFIs after candidiasis and aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients.1,2 Its rise in incidence parallels the rise in incidence of diabetes, cancer and need for organ transplantation. Classical risk factors include diabetes (with or without ketoacidosis), haematological malignancies, solid organ and bone marrow transplant recipients, deferoxamine therapy, intravenous drug use, and renal failure.1,2 However, occasionally it also occurs in the absence of risk factors.2 It is caused by angioinvasive moulds of the mucorales order.3 Inhalation of spores and cutaneous seeding at sites of epithelial breach are main portals of entry.2 It can manifest in various forms such as rhinocerebral, pulmonary, cutaneous, gastrointestinal, cerebral, and disseminated forms.4,5 Patients without any predisposition commonly present with cutaneous and rhino-sinusoidal involvement.2,4 Cardiac involvement in mucormycosis, although less common, can occur in invasive infections. It commonly occurs in patients with predisposing conditions or following cardiac surgery.5 It can present with a myriad of symptoms like myocardial infarction, new onset heart failure, endocarditis and valvular insufficiency, pericarditis, rhythm disturbances, or an abscess.6–9 In immunocompetent (IC) individuals, case reports of mucormycosis presenting as fibrosing mediastinitis with cardiac involvement and as mediastinal granuloma have been reported.7,10,11 Diagnosis needs high index of suspicion, especially in patients without predisposition and presentation other than rhinocerebral and cutaneous forms. Definitive diagnosis is made by tissue sampling and isolation of fungus or demonstration of typical broad, wide angled branching, aseptate hyphae with evidence of tissue invasion and necrosis.1 The standard therapy for mucormycosis is surgery along with Amphotericin B. Patients with invasive infection and cardiac involvement have a very poor prognosis with mortality up to 100%.12
Our index case described was a immunocompetent patient with mediastinal involvement (heart and great vessels) with angioinvasion (superior vena cava, pulmonary vein, and carotid involvement). Echocardiography demonstrated diffuse infiltration of both atria and provided the first clue to the presence of a systemic disease and CT imaging provided further insights. Definitive diagnosis was established by tissue sampling and demonstration of broad aseptate hyphae. Subsequently, the patient had a fulminant course during the hospital stay and died due to hypoxic respiratory failure (pulmonary vein invasion) and septic shock.
Conclusion
Mediastinal mucormycosis usually occurs as a disseminated form predominantly in individuals with predisposing factors. However, rarely it can occur in individuals without risk factors and should be considered in the differential diagnosis in all individuals presenting with infiltrating cardiac and mediastinal masses.
Lead author biography

Dr Ganesh Kasinadhuni, MD, DM is senior resident, cardiology at Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh. His area of interest is to excel in complex percutaneous coronary interventions. He started his academic and research under the able mentorship of Prof. Rajesh Vijayvergiya, Department of Cardiology at PGIMER. His future endeavour is to continue his academic research and publications.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary material
Supplementary material is available at European Heart Journal - Case Reports online.
Slide sets: A fully edited slide set detailing this case and suitable for local presentation is available online as Supplementary data.
Consent: The authors confirm that written consent for submission and publication of this case report including image(s) and associated text has been obtained from the patient in line with COPE guidance.
Conflict of interest: none declared.
References
- 1. Chayakulkeeree M, Ghannoum MA, Perfect JR.. Zygomycosis: the re-emerging fungal infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2006;25:215–229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Mignogna MD, Fortuna G, Leuci S, Adamo D, Ruoppo E, Siano M, Mariani U.. Mucormycosis in immunocompetent patients: a case-series of patients with maxillary sinus involvement and a critical review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis 2011;15:e533–e540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Hibbett DS, Binder M, Bischoff JF, Blackwell M, Cannon PF, Eriksson OE, Huhndorf S, James T, Kirk PM, Lücking R, Thorsten Lumbsch H, Lutzoni F, Matheny PB, McLaughlin DJ, Powell MJ, Redhead S, Schoch CL, Spatafora JW, Stalpers JA, Vilgalys R, Aime MC, Aptroot A, Bauer R, Begerow D, Benny GL, Castlebury LA, Crous PW, Dai Y-C, Gams W, Geiser DM, Griffith GW, Gueidan C, Hawksworth DL, Hestmark G, Hosaka K, Humber RA, Hyde KD, Ironside JE, Kõljalg U, Kurtzman CP, Larsson K-H, Lichtwardt R, Longcore J, Miądlikowska J, Miller A, Moncalvo J-M, Mozley-Standridge S, Oberwinkler F, Parmasto E, Reeb V, Rogers JD, Roux C, Ryvarden L, Sampaio JP, Schüßler A, Sugiyama J, Thorn RG, Tibell L, Untereiner WA, Walker C, Wang Z, Weir A, Weiss M, White MM, Winka K, Yao Y-J, Zhang N.. A higher-level phylogenetic classification of the fungi. Mycol Res 2007;111:509–547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Roden MM, Zaoutis TE, Buchanan WL, Knudsen TA, Sarkisova TA, Schaufele RL, Sein M, Sein T, Chiou CC, Chu JH, Kontoyiannis DP, Walsh TJ.. Epidemiology and outcome of zygomycosis: a review of 929 reported cases. Clin Infect Dis 2005;41:634–653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Virmani R, Connor DH, McAllister HA.. Cardiac mucormycosis. A report of five patients and review of 14 previously reported cases. Am J Clin Pathol 1982;78:42–47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Jackman JD, Simonsen RL.. The clinical manifestations of cardiac mucormycosis. Chest 1992;101:1733–1736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Connor BA, Anderson RJ, Smith JW.. Mucor mediastinitis. Chest 1979;75:525–526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Ferreira D, Davies A, Thiruchelvam T, Wark P.. Acute myocardial infarction in disseminated mucormycosis infection. Eur Heart J 2017;38:838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Nam Y, Jung J, Park SS, Kim SJ, Shin SJ, Choi JH, Kim M, Yoon HE.. Disseminated mucormycosis with myocardial involvement in a renal transplant recipient. Transpl Infect Dis 2015;17:890–896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Bharadwaj R, Madakshira MG, Bharadwaj P, Sidhu HS.. Sclerosing mediastinitis presenting as complete heart block. J Clin Diagn Res 2017;11:ED12–ED14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Leong AS. Granulomatous mediastinitis due to rhizopus species. Am J Clin Pathol 1978;70:103–107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Spellberg B, Edwards J, Ibrahim A.. Novel perspectives on mucormycosis: pathophysiology, presentation, and management. Clin Microbiol Rev 2005;18:556–569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.