ABSTRACT
Recent studies show that mitochondria and actin filaments work together in two contexts: (1) increased cytoplasmic calcium induces cytoplasmic actin polymerization that stimulates mitochondrial fission and (2) mitochondrial depolarization causes actin assembly around mitochondria, with roles in mitophagy. It is unclear whether these two processes utilize similar actin assembly mechanisms. Here, we show that these are distinct actin assembly mechanisms in the acute phase after treatment (<10 min). Calcium-induced actin assembly is INF2 dependent and Arp2/3 complex independent, whereas depolarization-induced actin assembly is Arp2/3 complex dependent and INF2 independent. The two types of actin polymerization are morphologically distinct, with calcium-induced filaments throughout the cytosol and depolarization-induced filaments as ‘clouds’ around depolarized mitochondria. We have previously shown that calcium-induced actin stimulates increases in both mitochondrial calcium and recruitment of the dynamin GTPase Drp1 (also known as DNM1L). In contrast, depolarization-induced actin is temporally associated with extensive mitochondrial dynamics that do not result in mitochondrial fission, but in circularization of the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). These dynamics are dependent on the protease OMA1 and independent of Drp1. Actin cloud inhibition causes increased IMM circularization, suggesting that actin clouds limit these dynamics.
This article has an associated First Person interview with the first author of the paper.
KEY WORDS: INF2, Mitochondria, Depolarization, CCCP, OPA1, OMA1, DRP1, Arp2/3 complex
Highlighted Article: Mitochondrial depolarization induces Arp2/3 complex-dependent actin clouds that restrain OMA1-induced mitochondrial shape changes. A distinct actin network stimulates calcium-induced mitochondrial fission.
INTRODUCTION
Mitochondria have traditionally been viewed as energy-generating organelles, through oxidation of metabolic substrates and creation of a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM), with the subsequent passage of protons back into the matrix being coupled to ATP synthesis (Kennedy and Lehninger, 1949; Pagliarini and Rutter, 2013). However, it is increasingly clear that mitochondria communicate frequently with the rest of the cell and are therefore important signaling organelles. For example, mitochondrial release of cytochrome c triggers cell death (Liu et al., 1996), mitochondrially generated reactive oxygen species activate hypoxia-related genes (Al-Mehdi et al., 2012; Chandel et al., 1998) and mitochondrial heat shock proteins promote cytosolic calcium-mediated signaling (Biswas et al., 1999; Martinus et al., 1996). Mitochondria also participate in innate immunity by serving as platforms for downstream signaling to facilitate antimicrobial host cell responses (West et al., 2011). Furthermore, changes in the IMM proton gradient have immediate signaling effects, with IMM depolarization causing stabilization of the PINK1 protein kinase, whose downstream targets include the PARKIN E3 ubiquitin ligase (Pickles et al., 2018). Mitochondrial depolarization also activates an IMM protease, OMA1, which proteolytically cleaves the dynamin-family GTPase optic atrophy type 1 (OPA1) (Ehses et al., 2009; Head et al., 2009; Ishihara et al., 2006).
A growing number of studies suggest that actin polymerization participates in mitochondrial communication and dynamics. During apoptosis, both a C-terminal actin fragment (Utsumi et al., 2003) and the actin-binding protein cofilin translocate to mitochondria, with evidence that translocation of active cofilin is important for downstream cytochrome c release and apoptotic response (Chua et al., 2003). Inhibition of ATP synthase by oligomycin results in mitochondrial fission, which is attenuated by the actin polymerization inhibitors cytochalasin D and latrunculin A (LatA) (De Vos et al., 2005). In another study, actin and myosin II were shown to play a role in translocation of the dynamin GTPase dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1, also known as DNM1L) to mitochondria, resulting in mitochondrial fission (DuBoff et al., 2012).
We have previously found that elevated cytosolic calcium activates the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-bound formin inverted formin-2 (INF2), which stimulates actin polymerization that leads to mitochondrial fission (Chakrabarti et al., 2018; Hatch et al., 2016; Ji et al., 2017, 2015; Korobova et al., 2013). INF2-mediated actin polymerization stimulates constriction of both mitochondrial membranes during fission: IMM constriction is enhanced by increased calcium transfer from ER to mitochondrion, and outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) constriction is enhanced by increased Drp1 recruitment. This pathway also requires non-muscle myosin II (Chakrabarti et al., 2018; Korobova et al., 2014), and the mitochondrially bound SPIRE 1C protein might also participate (Manor et al., 2015).
A somewhat different type of mitochondrially associated actin polymerization has been reported in several studies. Dissipation of the mitochondrial proton gradient using the uncoupler FCCP causes rapid accumulation of an extensive cloud of actin filaments around depolarized mitochondria (Li et al., 2015). Similar actin clouds have been observed in both unstimulated cells and cells treated with the uncoupler carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) and are dependent on both Arp2/3 complex and formin activity (Kruppa et al., 2018; Moore et al., 2016). On a similar time scale as actin cloud formation, mitochondria become less elongated, consistent with an increase in mitochondrial fission (Li et al., 2015; Moore et al., 2016). At a later stage after mitochondrial depolarization, a second wave of actin polymerization encircles depolarized mitochondria and is thought to prevent their fusion with other mitochondria in a myosin VI-dependent manner (Kruppa et al., 2018).
These studies raise a question concerning actin polymerization and mitochondrial function: Are there multiple ways in which actin interacts with mitochondria, or do these studies represent variations on a common actin polymerization pathway? Our present work attempts to clarify this issue. We show that calcium-induced actin polymerization is INF2 dependent and Arp2/3 independent, whereas depolarization-induced actin polymerization is Arp2/3 dependent and INF2 independent. Although both processes are rapid, calcium-induced actin polymerization is faster than depolarization-induced actin polymerization in U2OS cells and is less tightly associated with mitochondria. Spontaneous mitochondrial depolarization causes Arp2/3-dependent actin polymerization around the depolarized mitochondria, similar to that of CCCP-induced actin filaments. Although mitochondrial depolarization results in extensive mitochondrial shape changes on a similar time course to actin polymerization, these shape changes are not dependent on actin polymerization or the Arp2/3 complex. In fact, the shape changes are a result of IMM dynamics and are dependent on the IMM protease OMA1. Inhibition of actin cloud assembly causes an increase in CCCP-induced mitochondrial shape changes, suggesting that actin clouds inhibit these shape changes. In summary, we show that two distinct types of actin filaments, differing in morphology and assembly mechanisms, have differing effects on mitochondria.
RESULTS
Distinct actin polymerization mechanisms induced by mitochondrial depolarization or cytoplasmic calcium
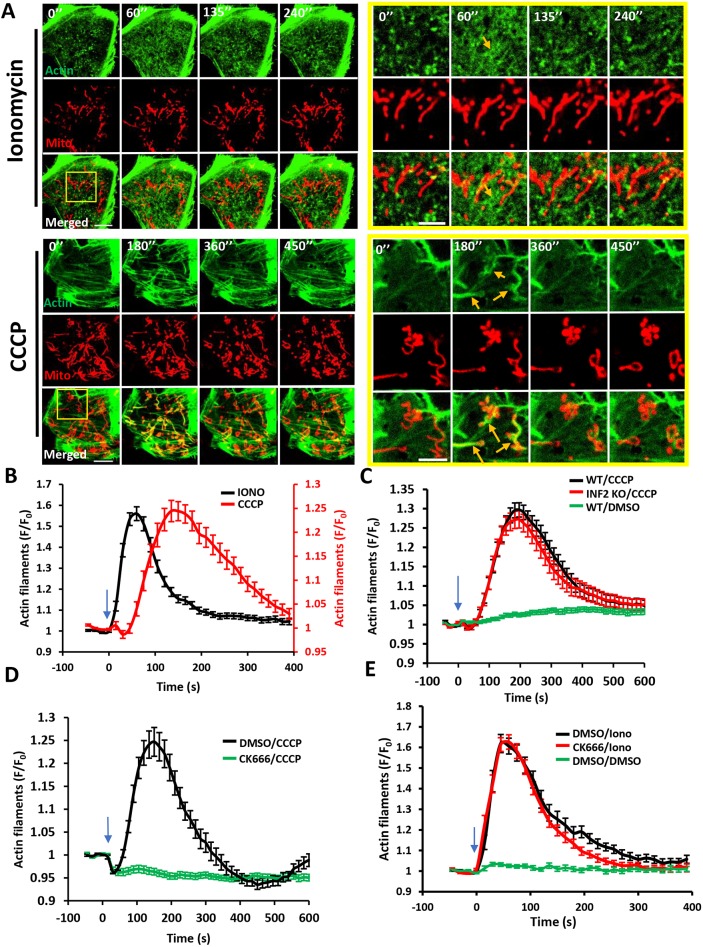
We compared actin bursts stimulated by the calcium ionophore ionomycin with those induced by the mitochondrial depolarizer CCCP in U2OS cells, using live-cell imaging of actin filaments (GFP–F-tractin) and the mitochondrial matrix (mito–BFP). In serum-containing medium, 4 μM ionomycin treatment resulted in a transient increase in cytoplasmic calcium, with a T1/2 of <5 s and a return to baseline within 2 min (Chakrabarti et al., 2018), whereas 20 μM CCCP caused mitochondrial depolarization within 30 s that persisted for at least 10 min, as measured by the polarization marker tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester (TMRE, 20 nM) (Perry et al., 2011) (Fig. S1A). Both stimuli induced transient actin polymerization responses that differed in morphology and kinetics. Morphologically, ionomycin-induced actin polymerization occurred throughout the cytosol, whereas CCCP-induced actin polymerization occurred as ‘clouds’ that were closely associated with mitochondria (Fig. 1A; Fig. S1B). These features are best appreciated in a medial Z-plane (Fig. S1B; Movies 3,4) because there is less interference from basal actin stress fibers. However, actin polymerization in response to both stimuli was also apparent at the basal surface (Fig. 1A; Movies 1,2). Kinetically, ionomycin-induced actin dynamics were more rapid than those induced by CCCP (Fig. 1B), both in the polymerization (T1/2 actin polymerization values, 12.3±5.9 s and 128.1±75.3 s, respectively) and depolymerization (T1/2, 29.4±12.9 s and 79.31±38.9 s, respectively) phases (Fig. S2A).
Fig. 1.
Distinct actin structures assemble in response to two stimuli: increased cytoplasmic calcium and mitochondrial depolarization. (A) Time-lapse image montage of ionomycin-induced (top) and CCCP-induced (bottom) actin polymerization for U2OS cells transfected with GFP–F-tractin (green) and mito–BFP (red). Imaging conducted at the basal cell surface. Ionomycin or CCCP added at time point 0. Scale bars: 10 μm (insets 5 μm). Corresponds to Movies 1 and 2. Movies 3 and 4 show similar time course in medial cell section. Orange arrows indicate actin assembly. (B) Comparison of ionomycin-induced and CCCP-induced actin polymerization time course for U2OS cells (15 s intervals); N=30 cells/60 ROIs for ionomycin (4 μM) treatment, 27 cells/27 ROIs for CCCP (20 μM) treatment. (C) CCCP-induced actin polymerization in U2OS-WT and U2OS-INF2-KO cells (14 s intervals); N=35 cells for WT, 35 cells for INF2-KO and 35 cells for WT cells stimulated with DMSO. (D) Effect of Arp2/3 complex inhibition on CCCP-induced actin polymerization (15 s intervals). U2OS cells were treated with either DMSO or 100 μM CK666 for 30 min and then stimulated with 20 μM CCCP; N=35 cells/35 ROIs for DMSO/CCCP, 41/41 for CK666/CCCP. (E) Effect of Arp2/3 complex inhibition on ionomycin-induced actin polymerization (15 s intervals). U2OS cells were treated with either DMSO or 100 μM CK666 for 30 min and then stimulated with DMSO or 4 μM ionomycin; N=23 cells/46 ROI for DMSO/ionomycin, 25/50 for CK666/ionomycin and 20/40 for DMSO/DMSO. All data (mean±s.e.m.) are from three experiments. Blue arrows denote drug addition.
We next examined the actin assembly factors required for ionomycin- and CCCP-induced actin polymerization. Past results have shown that ionomycin-induced actin polymerization requires the formin INF2 (Chakrabarti et al., 2018; Ji et al., 2015; Shao et al., 2015; Wales et al., 2016). However, INF2 was not required for CCCP-induced actin polymerization, tested using either CRISPR-mediated INF2 knockout (KO) (Fig. 1C) or siRNA-induced INF2 knockdown (KD) (Fig. S2B,C). Control experiments showed that ionomycin-induced actin polymerization was abolished in INF2-KO cells (Fig. S2D). The results show that INF2 is not required for depolarization-induced actin polymerization.
The Arp2/3 complex has been shown to contribute to mitochondrially associated actin polymerization in HeLa cells in the absence of stimulation (Moore et al., 2016) and to actin polymerization that occurs after prolonged CCCP treatment (Kruppa et al., 2018). We used the Arp2/3 complex inhibitor CK666 to test Arp2/3 complex involvement in the rapid actin bursts induced by ionomycin and CCCP. A 30 min pretreatment with 100 μM CK666 abolished the CCCP-induced actin burst (Fig. 1D), but had no clear effect on the ionomycin-induced actin burst (Fig. 1E).
These results show that actin polymerization induced by increased cytoplasmic calcium and by mitochondrial depolarization differ in three ways: kinetically, morphologically and in nucleation mechanism. Calcium-induced actin polymerization is INF2 dependent and Arp2/3 complex independent, whereas depolarization-induced actin polymerization is Arp2/3 complex dependent and INF2 independent.
Spontaneous mitochondrial depolarization triggers Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin clouds
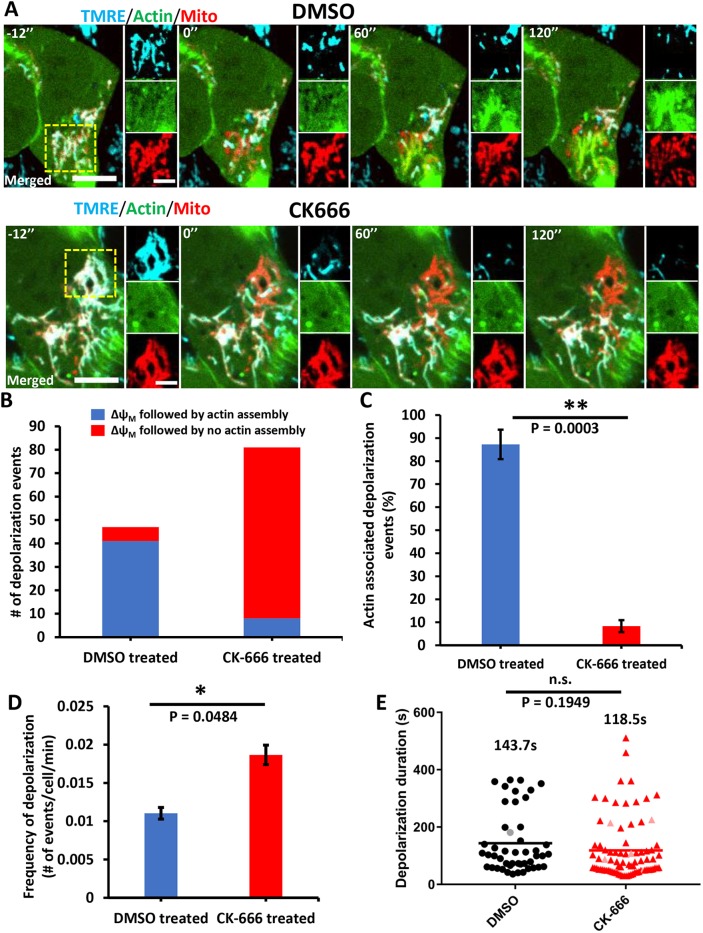
Mitochondria periodically undergo transient depolarization in the absence of uncoupler treatment (Lee and Yoon, 2014). We investigated whether actin polymerization faithfully accompanies such transient depolarization in U2OS cells, using TMRE. Occasional loss of TMRE fluorescence occurred in subpopulations of mitochondria (Fig. 2A; Movie 5). These depolarization events were generally transient, having a mean duration of 143.7±106.5 s (Fig. 2E). Actin polymerization accompanied the majority (87.3±6.3%) of depolarization events (Fig. 2A-C; Movie 5), with an appreciable lag between depolarization and actin polymerization, taking an average time of 129.8±95.0 s (Fig. S2E). The actual polymerization T1/2 (measured from the first detectable polymerization) was 57.2±54.1 s (Fig. S2F).
Fig. 2.
Actin polymerization accompanying transient depolarization of a subset of mitochondria in the absence of CCCP. (A) Time-lapse image montage of changes in mitochondrial polarization (TMRE, blue) and actin polymerization (GFP–F-tractin, green) in U2OS cells in the absence of uncoupler treatment. A mitochondrial matrix marker (mito–BFP, red) is also included. Top panels show a control cell (DMSO) and bottom panels show a CK666-treated cell (100 μM CK666 for 30 min before imaging and 50 μM during imaging). Time 0 denotes start of a depolarization event. Panels to the right of each time point denote zooms of boxed regions. Scale bars: 10 μm (insets 5 μm). Corresponds to Movies 5 and 6. (B) Number of spontaneous depolarization events associated with actin polymerization in either control (DMSO) or CK666-treated cells. Total numbers from three experiments (20 min imaging per cell, 1.2 s intervals): DMSO, 213 cells, 47 depolarization events (41 events accompanied by actin assembly); CK666, 217 cells, 81 depolarization events (8 events accompanied by actin assembly). (C) Percentage of depolarization events accompanied by actin polymerization for DMSO versus CK666 treatment, from same data as in B. Student's unpaired t-test, **P=0.0003. (D) Depolarization frequency (mean±s.e.m.) for DMSO versus CK666 treatment, from data set described in B. Student's unpaired t-test, *P=0.0484. (E) Scatter plot of depolarization duration, from data set described in B. Depolarization durations (mean±s.d.) are given for DMSO group (black line), 143.7 s±106.5 s and CK666 group (red line), 118.5 s±104.4 s. Gray and pink points represent depolarization events that occurred after 16 min of imaging time and failed to repolarize at the end of the 20 min imaging period. Student's unpaired t-test, P=0.1949; n.s., not significant.
We asked whether Arp2/3 complex is involved in actin polymerization induced by spontaneous mitochondrial depolarization. To this end, we pretreated U2OS cells with CK666 for 30 min prior to imaging. Spontaneous depolarization of subpopulations of mitochondria still occurred in CK666 pretreated cells, similar to control cells (Fig. 2A, Movie 6). In fact, the frequency of spontaneous depolarization events was somewhat higher in CK666-treated cells (Fig. 2D), but the average duration of depolarization events was not significantly different (Fig. 2E). CK666 treatment, however, strongly reduced the number of actin polymerization events that occurred after spontaneous depolarization (Fig. 2A–C). These results further support the finding that the actin polymerization occurring around depolarized mitochondria is mediated by the Arp2/3 complex in U2OS cells.
Actin polymerization is not required for depolarization-induced mitochondrial shape change
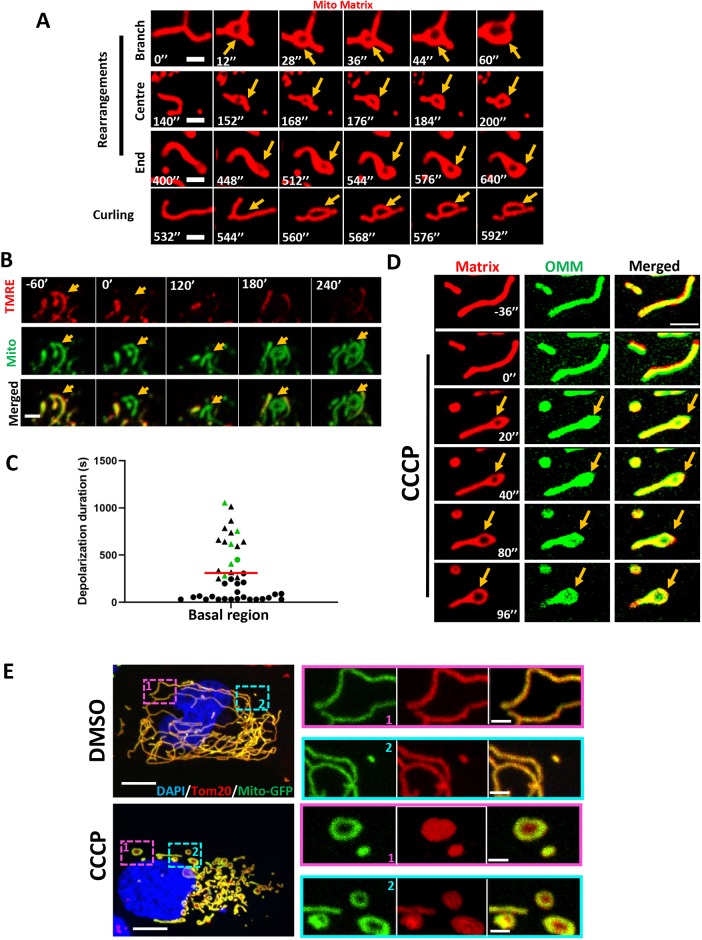
In addition to inducing actin polymerization, CCCP-triggered mitochondrial depolarization induced rapid mitochondrial shape changes (Fig. 1A). Although these shape changes have often been described as mitochondrial fragmentation (Fu and Lippincott-Schwartz, 2018; Kwon et al., 2017), there is also evidence for other changes such as circularization (De Vos et al., 2005; Liu and Hajnóczky, 2011; Miyazono et al., 2018). Using the mitochondrial matrix marker mito–BFP in live-cell microscopy, we observed extensive rearrangement of the matrix compartment, which can occur at any point along the mitochondrion, including at mitochondrial branches (Fig. 3A; Movie 7). The end result of these rearrangements was circularization of the mitochondrion. In the absence of CCCP, circularization occurred in a subset of depolarized mitochondria, typically those that had been depolarized for a prolonged period (Fig. 3B,C).
Fig. 3.
Depolarization-induced mitochondrial shape changes in U2OS cells. (A) Examples of mitochondrial matrix dynamics after depolarization, leading to circularization. Three examples show matrix rearrangement and one example shows the mitochondrion curling back on itself to form the circle. U2OS cells were transfected with the mitochondrial matrix marker Mito–DsRed and treated with 20 μM CCCP at time point 0. Confocal imaging was conducted at the basal region of the cell at 4 s intervals, starting 10 frames before CCCP treatment. Corresponds to Movie 7. Orange arrows indicate mitochondrial circularization. (B) Example of mitochondrial circularization after transient depolarization in the absence of CCCP. Time indicates the time after depolarization. Time-lapse images taken at the basal region of the cell. (C) Quantification of depolarization time for depolarization events, with events resulting in mitochondrial circularization in green. Triangles indicate events in which no re-polarization was observed at the end of the imaging period (20 min). Red line indicates depolarization duration (mean±s.d.) of 310.2 s±308.1 s. Total numbers from two experiments, 144 cells and 41 depolarization events. (D) Dynamics of the OMM and mitochondrial matrix upon depolarization. U2OS cell transfected with Mito–DsRed (red) and Tom20–GFP (green) was treated with 20 μM CCCP at time point 0. Airyscan images (basal region) were acquired at 4 s intervals starting 10 frames before CCCP treatment. Corresponds to Movie 8. (E) Maximum intensity projections of glutaraldehyde-fixed U2OS cells (transfected with mito–GFP, green) after treatment with either DMSO (top) or 20 μM CCCP (bottom) for 20 min. Cells were stained with anti-Tom20 (OMM, red) and DAPI (nucleus, blue). Z-stacks were taken at step size of 0.4 μm. Zoomed images show representative examples of mitochondrial circularization after CCCP treatment. Scale bars: 2 μm in A; 2.5 μm in B,D; 10 μm in E (insets, 2 μm).
We also used dual-color live-cell imaging to observe the dynamics of both the OMM (Tom20–GFP) and the matrix (Mito–dsRed) in the same cell. Interestingly, the matrix marker underwent circularization, whereas the OMM marker remained intact across the center of this circularized region (Fig. 3D; Movie 8). This result was consistent in all cases analyzed (Fig. S3A) and was similar to those previously reported by others (Miyazono et al., 2018), suggesting that the IMM is the primary membrane undergoing rearrangement during depolarization-induced mitochondrial circularization.
To verify this result, we used fixed cell microscopy, using glutaraldehyde as a fixative. Upon CCCP treatment for 20 min, numerous circular mitochondria were observed (Fig. 3E). The mitochondrial matrix marker (transfected mito–GFP) displayed a characteristic hollow donut shape, whereas the OMM marker (anti-Tom20) was intact throughout the circle. A similar pattern occurred upon formaldehyde fixation, although OMM staining was less regular in this case (Fig. S3B). Using an antibody against the β-subunit of ATP synthase (an IMM protein) gave a similar result, although ATP synthase staining was more irregular than the GFP-labeled matrix protein (Fig. S3C).
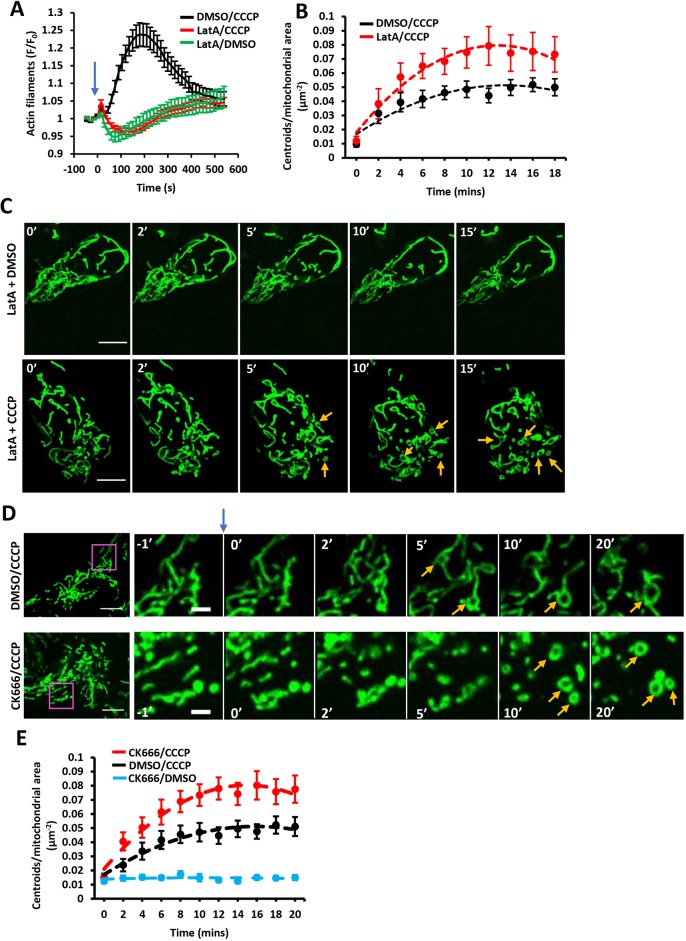
We asked whether actin polymerization is required for these mitochondrial shape changes, quantifying shape change as the number of circular matrix structures (‘centroids’) present per overall mitochondrial area at specific time points after CCCP addition. Interestingly, although the actin sequestering drug LatA eliminated CCCP-induced actin polymerization (Fig. 4A), it did not inhibit mitochondrial rearrangement (Fig. 4B,C). In fact, the number of CCCP-induced centroids was moderately increased by 500 nM LatA treatment. Similarly, Arp2/3 complex inhibition by CK666 also increased CCCP-induced mitochondrial shape change (Fig. 4D,E; Movie 9). CCCP-induced mitochondrial shape change also occurred in INF2-KO cells (Fig. S3D; Movie 10). We also examined the presence of actin filaments around mitochondria at the time of circularization for CCCP-treated cells. Of 96 circularization events examined, actin polymerization preceded 93 of these events, but had fully depolymerized prior to circularization for 85 events. These results suggest that actin polymerization is not required for the acute mitochondrial shape changes that occur upon CCCP treatment and might even be inhibitory to these shape changes.
Fig. 4.
Effect of LatA and Arp2/3 complex inhibition on depolarization-induced mitochondrial shape changes. (A) Effect of LatA on CCCP-induced actin polymerization. U2OS cells were treated with combinations of LatA (500 nM) and CCCP (20 μM) at time 0 (blue arrow). Confocal images (medial section) were acquired at 15 s intervals starting four frames before treatment. Data (mean±s.e.m.) are from three experiments; N=23 cells/23 ROIs for LatA/DMSO, 38/38 for LatA/CCCP and 31/31 for DMSO/CCCP. (B) Effect of LatA on CCCP-induced mitochondrial matrix circularization (‘centroids’). U2OS cells were transfected with mito–BFP and GFP–F-tractin. CCCP (20 μM) was added at time point 0, simultaneously with LatA addition (500 nM). Data (mean±s.e.m.) are from three experiments; N=22 cells/4354 μm2 total mitochondrial area for DMSO/CCCP control cells; 18 cells/3823 μm2 for LatA/CCCP. Mean±s.e.m. P-value for time points 4–18 min post-treatment was 0.0115±0.0119 for DMSO versus LatA. (C) Time-course montage of LatA-treated cells under control conditions (DMSO treatment, top) or CCCP treatment (20 μM, bottom). U2OS cells transfected with F-tractin (not shown) and mito–BFP (green) were treated with 500 nM LatA and CCCP or DMSO simultaneously at 0 min. Confocal images (basal section) acquired at 15 s intervals starting four frames before treatment. Orange arrows denote centroids (circular mitochondrial matrix). (D) Time-course montage of CCCP-induced mitochondrial matrix circularization in the absence (top) or presence (bottom) of CK666 pretreatment. U2OS cells transfected with GFP–F-tractin (not shown) and mito–BFP (green) were treated with DMSO or CK666 (100 μM) for 30 min before stimulation with 20 μM CCCP at time point 0 (blue arrow). Confocal images (basal section) were acquired at 15 s intervals starting four frames before CCCP treatment. Orange arrows denote centroids (circular mitochondrial matrix). Corresponds to Movie 9. (E) Change in mitochondrial matrix circularization (defined as centroids per total mitochondrial area in the region of interest) from time-courses as described in A. Data (mean±s.e.m.) from three experiments. The three conditions tested were CK666 pretreatment followed by CCCP stimulation (N=46 cells/8539 μm2 total mitochondrial area), DMSO pretreatment, followed by CCCP stimulation (58 cells/11473 total mitochondrial area) and CK666 pretreatment followed by DMSO stimulation (36 cells/6655 total mitochondrial area). Mean±s.e.m. P-value for time points 4–18 min post-treatment was 0.00141±0.00217 for CK666/CCCP versus DMSO/CCCP. Scale bars: 10 μm in C; 10 μm in D (insets 2.5 μm).
We also assessed whether mitochondrial fission was upregulated during the early stages of CCCP-induced mitochondrial depolarization. For this purpose, we used a live-cell assay to quantify fission rate (Chakrabarti et al., 2018; Ji et al., 2017, 2015), because fixed-cell methods to assess fission based on change in mitochondrial length are confounded by the apparent length change induced by circularization. Our results suggest that CCCP treatment does not increase the number of fission events in the first 30 min, in contrast to the fission increase induced by ionomycin (Fig. S4A). In addition, we evaluated the effect of Drp1 depletion on CCCP-induced actin clouds and mitochondrial circularization. Drp1 suppression by siRNA had no clear effect on actin cloud assembly (Fig. S4B,C) and caused a slight increase in mitochondrial circularization both prior to and at all time points during CCCP treatment (Fig. S4D,E). The constitutive nature of the circularization increase suggests that acute CCCP-induced mitochondrial shape changes are not due to Drp1-dependent mitochondrial dynamics. The increase in circularization upon Drp1-KD might be explained by a constitutive elevation in OPA1 processing (Fig. S4B). Combined, these results suggest that the major morphological change to mitochondria in response to depolarization is remodeling of the IMM, resulting in circular mitochondria in which the OMM remains intact.
Mitochondrial shape changes depend on the IMM protease OMA1
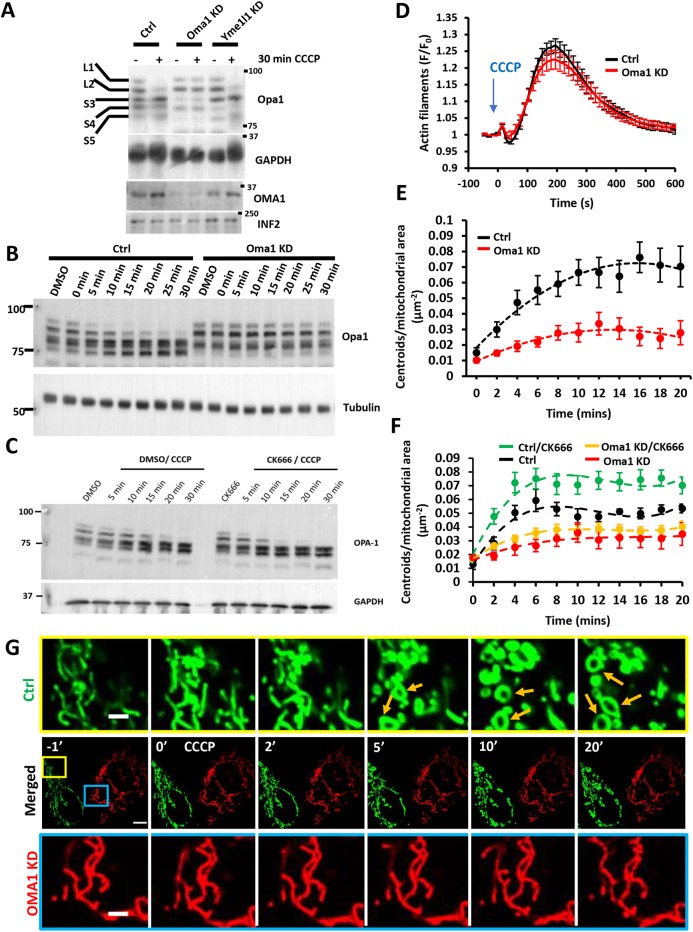
Because CCCP-induced mitochondrial shape change appears to be largely a result of IMM rearrangement, we asked which IMM proteins mediate these changes. One candidate is the IMM dynamin family protein OPA1, because OPA1 mediates fusion of IMM (Song et al., 2007), is important for cristae structure (Anand et al., 2014; Patten et al., 2014; Varanita et al., 2015) and might also play a role mitochondrial fission (Anand et al., 2014). OPA1 can be proteolytically processed by two IMM proteases, OMA1 and Yme1 (also known as YME1L1), with consequences for mitochondrial fission/fusion balance and for cristae ultrastructure (MacVicar and Langer, 2016). Five distinct bands for OPA1 can be resolved by SDS-PAGE, resulting both from splice variation and differential proteolytic processing (Fig. 5A).
Fig. 5.
Role of OMA1 in depolarization-induced mitochondrial shape change. (A) Western blots of OPA1 and OMA1 in control, OMA1-KD and Yme1-KD U2OS cells before and after treatment with 20 μM CCCP for 30 min. The positions of the five OPA1 forms (L1, L2, S1–S3) are indicated. GAPDH was INF2 loading control. (B) Western blots of OPA1 in control and OMA1-KD U2OS cells during time course of CCCP treatment (20 μM). Tubulin was loading control. (C) Western blot of OPA1 in control and CK666-treated U2OS-WT cells during the time course of CCCP treatment (20 μM). GAPDH was loading control. (D) CCCP-induced actin polymerization for control and OMA1-KD U2OS cells, transfected with GFP–F-tractin and mito–BFP, and stimulated with 20 μM CCCP (blue arrow). Data (mean±s.e.m.) from three experiments; N=40 cells/40 ROIs for scrambled control, 28/28 for OMA1-KD. (E) Change in mitochondrial matrix circularization (‘centroids’) over time for control and OMA1-KD U2OS cells transfected with mito–BFP and GFP–F-tractin. CCCP (20 μM) added at time point 0. Data (mean±s.e.m.) from three experiments; N=36 cells/4733 μm2 total mitochondrial area for control cells; 53 cells/9519 μm2 for OMA1-KD cells. Mean±s.e.m. P-value for time points 4–20 min post-treatment was 0.000185±0.000171 for control versus OMA1-KD. (F) Change in mitochondrial matrix circularization upon CCCP treatment for control-KD and OMA1-KD U2OS cells in the presence or absence of CK666. Data (mean±s.e.m.) from three experiments; N=87 cells/11,778.29 μm2 total mitochondrial area for control-KD/CK666 cells; 28 cells/4010.9 μm2 for control-KD cells; 81 cells/10,691.47 μm2 for OMA1-KD/CK666 cells; 28 cells/3126.79 μm2 for OMA1-KD cells. Mean±s.e.m. P-value for time points 4–20 min post-treatment was 0.00590±0.0103 for control KD versus control KD/CK666, and 0.256±0.229 for OMA1-KD versus OMA1-KD/CK666. (G) Time-course montage of CCCP-induced mitochondrial shape change (orange arrows) in control (green) and OMA1-KD U2OS cells (red), imaged in the same field. Control cells (scrambled siRNA) were transfected with mito–GFP whereas OMA1-KD cells were transfected with Mito–DsRed. The two cell populations were trypsinized, mixed and plated 24 h before imaging. Confocal images (basal cell section) were acquired at 15 s intervals starting four frames before CCCP treatment. CCCP (20 μM) was added at time point 0. Corresponds to Movie 11. Scale bar: 10 μm in G (insets 2.5 μm).
CCCP treatment induced OPA1 proteolytic processing on a similar time scale to both actin polymerization and mitochondrial rearrangement, with increases in short OPA1 bands (S3, S4 and S5) within 5 min and almost complete disappearance of long forms (L1 and L2) by 30 min (Fig. 5A,B), similar to past results (Ehses et al., 2009; Head et al., 2009; Ishihara et al., 2006). CK666 treatment caused accelerated CCCP-induced OPA1 proteolytic processing (Fig. 5C). Conversely, CCCP-induced OPA1 processing was abolished by siRNA-mediated KD of OMA1 (Fig. 5A,B), similar to past results (Head et al., 2009; MacVicar and Lane, 2014). In contrast, Yme1-KD had no effect on depolarization-induced OPA1 processing (Fig. 5A). Therefore, we reasoned that OMA1 processing of OPA1 might be involved in mediating depolarization-induced mitochondrial shape changes.
We assessed the effect of OMA1-KD or OPA1-KD on CCCP-induced actin polymerization and mitochondrial shape changes. CCCP-induced actin polymerization was unaffected by either OMA1-KD (Fig. 5D) or OPA1-KD (Fig. S5A,D). Due to the presence of highly fragmented mitochondria resulting from OPA1-KD (Fig. S5C), it was difficult to assess the role of OPA1 in CCCP-induced mitochondrial shape change. However, mitochondria in OMA1-KD cells were similar in morphology to those in control cells, allowing examination of shape change upon CCCP treatment. OMA1-KD cells failed to undergo significant CCCP-induced shape change, as judged by quantifying circularization for 20 min after stimulation (Fig. 5E). In addition, the increase in CCCP-induced circles caused by CK666 treatment was strongly suppressed by OMA1-KD (Fig. 5F). As a further test of this effect, we mixed control cells (transfected with mito–GFP marker) and OMA1-KD cells (transfected with Mito–DsRed marker) and imaged the two cell types in the same field after CCCP treatment. Although mitochondria in the control cells underwent CCCP-induced shape changes, mitochondria in the OMA1-KD cells did not (Fig. 5G; Movie 11).
These results suggest that the rapid changes in mitochondrial morphology induced by CCCP are a result of changes in IMM structure through OMA1-mediated proteolysis, rather than through actin-mediated effects on the OMM.
DISCUSSION
A growing number of studies show that actin can functionally interact with mitochondria (Chakrabarti et al., 2018; Chua et al., 2003; De Vos et al., 2005; DuBoff et al., 2012; Ji et al., 2015; Korobova et al., 2013; Kruppa et al., 2018; Li et al., 2015; Moore et al., 2016; Utsumi et al., 2003). In this paper, we show that there are at least two distinct types of mitochondrially associated actin, differing in cellular stimulus, assembly mechanisms and functional consequences. Mitochondrial depolarization triggers assembly of a dense cloud of actin filaments around the depolarized mitochondria, whereas increased cytosolic calcium triggers actin polymerization throughout the cytosol. Both actin filament populations are transient, with the calcium-induced actin being more rapid both in assembly and disassembly. Depolarization-induced actin is Arp2/3 complex dependent and INF2 independent, whereas calcium-induced actin is INF2 dependent and Arp2/3 complex independent. Inhibition of depolarization-induced actin polymerization causes a greater degree of OMA1-dependent mitochondrial shape change, suggesting that actin polymerization inhibits these changes. Inhibition of calcium-induced actin polymerization causes reduced mitochondrial calcium entry and Drp1 recruitment, with downstream inhibition of mitochondrial fission, which we have shown previously (Chakrabarti et al., 2018; Korobova et al., 2013).
Several studies have shown similar types of actin clouds to those that we observed after depolarization (Kruppa et al., 2018; Li et al., 2015; Moore et al., 2016). In two cases, these clouds were triggered after mitochondrial depolarization (Kruppa et al., 2018; Li et al., 2015); however, in one case, the clouds assembled without stimulation, were not associated with depolarization and progressed in a cyclic pattern around the cell (Moore et al., 2016). Both the depolarization-induced and the depolarization-independent clouds were blocked by Arp2/3 complex inhibition (Kruppa et al., 2018; Moore et al., 2016). Therefore, multiple mechanisms could exist to activate the Arp2/3 complex around mitochondria. In addition, these studies show that formins are involved in Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin assembly around mitochondria (Kruppa et al., 2018; Moore et al., 2016). In our work, we found that INF2 is not the responsible formin in the case of depolarization-induced clouds. Mammals possess 15 distinct formin proteins (Higgs and Peterson, 2005; Pruyne, 2016) and it will be interesting to identify which formin(s) participate(s) in actin cloud assembly.
One question concerns the activation mechanisms for INF2 and the Arp2/3 complex in these processes. We recently showed that cytosolic calcium activates INF2 through a mechanism involving HDAC6-mediated deacetylation of actin (A et al., 2019). The mechanism by which mitochondrial depolarization activates the Arp2/3 complex is less clear. The Arp2/3 complex is directly activated by members of the nucleation-promoting factor (NPF) family, which includes WASP/N-WASP, WAVE proteins, WASH, Dip/WISH, WHAMM, JMY and cortactin (Campellone and Welch, 2010). The NPF responsible for depolarization-induced Arp2/3 complex activation has yet to be identified. WHAMM is an attractive candidate, being recruited to early autophagosomes to promote Arp2/3 complex activity during starvation-induced nonspecific autophagy (Kast et al., 2015). Because long-term CCCP incubation leads to mitophagy and an overall increase in autophagosomes (Li et al., 2018; Matsuda et al., 2010; Park et al., 2018; Tanaka et al., 2010; Vives-Bauza et al., 2010), WHAMM might also regulate actin clouds around mitochondria. JMY is another strong candidate, due to its role in autophagosome formation after cell stress (Coutts and La Thangue, 2015). Furthermore, previous results show that downregulation of cortactin results in elongated and interconnected mitochondria (Li et al., 2015), so cortactin is also a candidate Arp2/3 complex activator.
A second question is how IMM depolarization can activate the NPF involved in actin cloud assembly. One protein activated by depolarization is the IMM protease OMA1, but we have shown that neither OMA1 suppression nor suppression of the OMA1 substrate OPA1 inhibits actin cloud assembly. Another interesting candidate to relay the depolarization signal is the protein kinase PINK1, which is stabilized on the OMM of depolarized mitochondria (Narendra et al., 2010). An important role of PINK1 is to initiate PARKIN-mediated mitophagy and other processes by phosphorylating both PARKIN and ubiquitin (Okatsu et al., 2013; Pickles et al., 2018; Yamano et al., 2018). PINK1 is expressed in U2OS cells (McLelland et al., 2018), whereas PARKIN has not been detected (Durcan et al., 2014), so it is possible that stabilized PINK1 phosphorylates other substrates that control Arp2/3 complex activation. Candidates include the recently discovered PINK1 substrate Paris (Lee et al., 2017), or possibly direct phosphorylation of an NPF.
A third question concerns the roles for actin clouds around mitochondria. There is evidence that actin filaments are involved in mitochondrial quality control (Kruppa et al., 2018; Li et al., 2015). A recent paper (Kruppa et al., 2018) showed evidence that ‘cages’ of actin and myosin VI assemble around CCCP-depolarized mitochondria and inhibit mitochondrial fusion after washing out CCCP. These cages assemble later (approximately 2 h) than the actin clouds shown here. Because mitochondrial fusion has been shown to require membrane potential (Hoppins et al., 2011; Legros et al., 2002; Song et al., 2007) and mitochondria remain depolarized for at least 10 min after CCCP treatment in U2OS cells (Fig. S1A), it is unlikely that the rapidly assembled actin clouds act as a mitochondrial fusion barrier.
Another possibility is that actin polymerization mediates changes in mitochondrial morphology, as CCCP treatment results in significant changes in mitochondrial structure on a similar time course as actin cloud assembly. However, we found that these rapid mitochondrial shape changes still occurred under conditions that prevent actin cloud assembly. In fact, the shape changes were actually increased in the absence of actin clouds. Possibly, actin clouds serve to confine the depolarized mitochondria in order to reduce mitochondrial dynamics.
Our work provides insights into the mechanisms behind these shape changes. A number of studies suggest that depolarization-induced shape changes are the result of massive mitochondrial fragmentation, which is generally observed after mitochondria have been depolarized for an hour or longer (Duvezin-Caubet et al., 2006; Fu and Lippincott-Schwartz, 2018; Kwon et al., 2017; Li et al., 2018). However, others show that in the first 20 min of depolarization the major change in mitochondria is circularization, which is the result of changes in the IMM but not the OMM (De Vos et al., 2005; Liu and Hajnóczky, 2011; Miyazono et al., 2018).
Our live-cell imaging agrees with these observations, showing that the IMM circularizes whereas the OMM remains intact. IMM circularization depends upon OMA1 and is independent of Drp1. The exact nature of the IMM dynamic rearrangements that lead to circularization remains to be determined, but it is our impression that the matrix compartment seems to ‘split’ in most cases to form the circle. We also show that inhibition of Arp2/3 complex increases the rate of OMA1-mediated OPA1 processing after mitochondrial depolarization. It is therefore possible that signaling occurs in both directions in this system, with mitochondrial depolarization triggering cytosolic Arp2/3 complex activation and the resulting actin clouds inhibiting OMA1 activity. Subsequent actin cloud disassembly might then allow OMA1 to mediate IMM rearrangement. Although OPA1 is likely to be the relevant OMA1 substrate in these rearrangements, other OMA1 substrates have also been identified, including PINK1 (Sekine et al., 2019), C11orf83 (Desmurs et al., 2015) and even OMA1 itself (Zhang et al., 2014). Reciprocal communication from and to the mitochondrial matrix, through actin polymerization, could serve as another form of interaction between the mitochondrion and its cellular environment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture
Wild-type U2OS (U2OS-WT) cells were procured from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and INF2-KO human osteosarcoma U2OS cells were prepared in our laboratory using CRISPR-Cas9 and are described elsewhere (Chakrabarti et al., 2018). Both cell types were grown in DMEM (Corning, 10-013-CV) supplemented with 10% newborn calf serum (Hyclone, SH30118.03) at 37°C with 5% CO2. Cell lines routinely tested negative for mycoplasma contamination using the Universal Mycoplasma Detection Kit (ATCC, 30-1012K) or LookOut Mycoplasma Detection Kit (Sigma-Aldrich, MP0035).
DNA transfections
For plasmid transfections, cells were seeded at 4×105 cells per well in a 35 mm dish at ∼16 h before transfection. Transfections were performed in OPTI-MEM medium (Gibco, 31985062) with 2 μl lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, 11668) per well for 6 h, followed by trypsinization and re-plating onto glass-bottomed dishes (MatTek Corporation, P35G-1.5-14-C) at ∼3.5×105 cells per well. Cells were imaged ∼16–24 h after transfection.
The following expression constructs were used: Mito–DsRed and mito–BFP, previously described (Korobova et al., 2014), consisting of amino acids 1–22 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae COX4 N-terminal to the respective fusion protein. GFP–F-tractin was a gift from Clare Waterman and Ana Pasapera (NIH, Bethseda, MD) (Johnson and Schell, 2009). GFP–Mito was purchased from Clontech (pAcGFP1-Mito, #632432) and consists of the mitochondrial targeting sequence derived from the precursor of subunit VIII of human cytochrome c oxidase. Tom20–GFP was made by restriction digest of Tom20 from Tom20–mCherry (a gift from Andrew G. York, NIH, Bethseda, MD) with NheI and BamHI, and then cloned into eGFP–N1 (Clontech) (Chakrabarti et al., 2018). Mito–R-GECO1 (Addgene, #46021) is previously described (Wu et al., 2014). H2B-mCherry (Addgene #20972) is previously described (Nam and Benezra, 2009).
The following amounts of DNA were transfected per well (individually or combined for co-transfection): 500 ng for mito–BFP, Mito–DsRed, GFP–Mito, Mito–R-GECO1, H2B–mCherry and GFP–F-tractin; 600 ng for the Tom20–GFP construct.
For siRNA transfections, 1×105 cells were plated onto a 35 mm dish and 2 μl RNAimax (Invitrogen, 13778) with 63 pg siRNA were used per well. Cells were analyzed 96 h post siRNA transfection. For live-cell imaging, plasmids containing fluorescent markers were transfected into siRNA-treated cells 18–24 h prior to imaging, as described above. All siRNAs were purchased from IDT, including human INF2 (custom synthesized, HSS.RNAI.N001031714.12.7, 5′-GGAUCAACCUGGAGAUCAUCCGC-3′); human OMA1 (hs.Ri.OMA1.13.1, 5′-GGAUAUUCAGGGUCAAAUGUACAUGAUUUGACCCUG-3′); human YME1L1 (hs.Ri.YME1L1.13.1, 5′-GGUGGAGGAAGCUAAACAAGAAUUA-3′); human OPA1 (hs.Ri.OPA1.13.1, 5′-CCACAGUGGAUAUCAAGCUUAAACA-3′); human Drp1 (custom synthesized, HSC.RNAI.N005690.12.1, 5′-GCCAGCUAGAUAUUAACAACAAGAA-3′); and negative control (#51-01-14-04, 5′-CGUUAAUCGCGUAUAAUACGCGUAU-3′).
Antibodies
Anti-INF2 (rabbit polyclonal against amino acids 941–1249 of human INF2) (Ramabhadran et al., 2011) was used at 3.75 μg/ml. Anti-Opa1 (BD Biosciences, 612606, mouse monoclonal, clone 18/OPA1) was used at 1:2000. Anti-Oma1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-515788, mouse monoclonal, clone H-11/OMA1) was used at 1:500. Anti-Drp1 (BD Transduction Laboratories, 611112, mouse, clone 8/DLP1) was used at 1:500. Anti-tubulin (Sigma-Aldrich, T9026, mouse, clone DM1-α) was used at 1:10,000. Anti-GAPDH (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-365062, G-9, mouse) was used at 1:1500. Anti-Tom20 (Abcam, ab78547) was used at 1:500 for immunofluorescence. Anti-ATP synthase beta monoclonal antibody (Invitrogen, A-21351, mouse, 3D5AB1) was used at 1:500 for immunofluorescence. Secondary antibodies used for western blots were goat anti-mouse IgG horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugate (Bio-Rad, 1705047) at 1:2000 and goat anti-rabbit IgG HRP conjugate (Bio-Rad, 1706515) at 1:5000. For immunofluorescence, we used goat anti-rabbit IgG Texas Red secondary (Vector Laboratories, TI-1000) at 1:500 and horse anti-mouse IgG fluorescein secondary (Vector Laboratories, FI-2000) at 1:500.
Western blot analysis
Cells from a 35 mm dish were trypsinized, pelleted by centrifugation at 300 g for 5 min and resuspended in 400 μl of 1× DB (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 2 mM EDTA, 20% glycerol, 0.8% SDS, 0.02% Bromophenol Blue, 1000 mM NaCl, 4 M urea). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE in a Bio-Rad mini-gel system (7×8.4 cm) and transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (EMD Millipore, IPFL00010). The membrane was blocked with TBS-T (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 136 mM NaCl, 0.1% Tween-20) containing 3% BSA (VWR Life Science, VWRV0332) for 1 h, then incubated with primary antibody solution at 4°C overnight. After washing with TBS-T, the membrane was incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibody for 1 h at 23°C. Signals were detected by chemiluminescence. For western blots of OPA1, samples were prepared and separated by SDS-PAGE on a Hoefer SE600 (14 cm×14 cm) apparatus and transferred using a Hoefer transfer apparatus. The rest of the procedure was similar to that listed above.
Immunofluorescence
U2OS-WT cells (1×105, either transfected with mito–GFP or untransfected) were plated onto MatTek dishes (MatTek Corporation, P35G-1.5-14-C) 16 h prior to fixation and staining. Cells were treated with DMSO or 20 μM CCCP for 20 min at 37°C and 5% CO2, washed twice in PBS (23°C) and fixed either for 10 min in 1% glutaraldehyde (EMS, 16020) prepared in BRB80 buffer (80 mM PIPES pH 6.9, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA) or for 20 min in 4% prewarmed paraformaldehyde (EMS, 15170). The glutaraldehyde-fixed samples were additionally washed for 3×10 min with NaBH4 (1 mg/ml in PBS) prior to permeabilization. The cells were then permeabilized in 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 10 min and blocked in PBS containing 10% calf serum for 30 min. These cells were then stained with anti-Tom20 antibody and/or ATP synthase (mitochondria), appropriate secondary antibodies and DAPI (to stain the nucleus) in PBS containing 1% calf serum. Imaging was carried out in PBS on the Mat-Tek dish using a Dragonfly 302 spinning disk confocal (Andor Technology) with CFI Plan Apochromat Lambda 100×1.45 NA oil objective. Z-stacks were taken from the basal region to the apical top at 0.4 μm step size. Maximum intensity projections were generated from z-stack images and background subtracted in ImageJ Fiji (rolling ball 20.0).
Live imaging by confocal microscopy and Airyscan microscopy
All live-cell imaging was conducted in DMEM (Gibco, 21063-029) with 25 mM D-glucose, 4 mM L-glutamine and 25 mM HEPES, supplemented with 10% newborn calf serum, hence referred to as ‘live-cell imaging medium’. Cells (∼3.5×105) were plated onto MatTek dishes 16 h prior to imaging. Medium was pre-equilibrated at 37°C and 5% CO2 before use.
For confocal microscopy, dishes were imaged using the Dragonfly 302 spinning disk confocal (Andor Technology) on a Nikon Ti-E base, equipped with an iXon Ultra 888 EMCCD camera, a Zyla 4.2 Mpixel sCMOS camera and a Tokai Hit stage-top incubator set at 37°C. A solid-state 405 smart diode 100 mW laser, solid state 560 OPSL smart laser 50 mW laser and solid state 637 OPSL smart laser 140 mW laser were used. Objectives used were the CFI Plan Apochromat Lambda 100×1.45 NA oil (Nikon, MRD01905) for all drug treatment live-cell assays and the CFI Plan Apochromat 60×1.4 NA oil (Nikon, MRD01605) to observe transient depolarization events during live-cell imaging. Images were acquired using Fusion software (Andor Technology, version 2.0.0.15). For actin burst and TMRE quantifications, cells were imaged at a single confocal slice at the medial region, approximately 2 μm above the basal surface, to avoid stress fibers. To observe mitochondrial morphological changes, cells were imaged at a single confocal slice at the basal surface.
For ionomycin treatments, cells were treated with 4 μM ionomycin (Sigma-Aldrich, I0634, from 1 mM stock in DMSO) at the start of the fifth image frame (∼1 min, time interval set at 15 s) during imaging and continued for another 5–10 min. INF2-KO cells were used as negative control (Chakrabarti et al., 2018). For CCCP (Sigma-Aldrich, C2759) treatments, cells were treated with 20 μM CCCP (from a 100 mM stock in DMSO) at the start of the fifth frame (∼1 min, with time interval set at 14 s or 15 s) during imaging and continued for another 15–20 min. Equal volume DMSO (Invitrogen, D12345) was used as the negative control. For TMRE (Sigma-Aldrich, 87917) staining before CCCP treatment, cells were loaded with 20 nM TMRE (from a 30 mM stock in DMSO) for 30 min in live-cell imaging medium. Cells were subsequently washed twice with live-cell medium and fresh live-cell medium added prior to imaging. During imaging, cells were treated with 20 μM CCCP at the start of the fifth frame (∼1 min, with time interval set at 15 s) and continued for another 15–20 min. As negative control, an equal volume of DMSO was added during imaging (in place of CCCP) for cells loaded with 20 nM TMRE.
To observe transient depolarization in U2OS cells in the absence of CCCP, cells were loaded with 20 nM TMRE (with or without CK666) for 30 min in live-cell imaging medium at 37°C and 5% CO2. CK666- and TMRE-treated cells were rinsed twice with fresh live-cell medium; live-cell medium containing 50 μM CK666 was added prior to imaging. Single field confocal imaging in the medial region was conducted at 1.2 s time intervals and continued for 1000 frames (20 min). To visualize more cells in the field, the 60×1.4 NA objective was used. Equal volume DMSO was used as a negative control in place of CK666 while retaining TMRE. To observe mitochondrial rearrangements after transient depolarization, multiple field confocal imaging with the 100×1.4 NA objective was conducted in the basal region at 6 s time intervals and continued for 200 frames (20 min).
For LatA (Millipore-Sigma, 428021) coupled with CCCP treatment, cells were treated with live-cell medium containing 500 nM LatA (from a 1 mM stock in DMSO) and 20 μM CCCP simultaneously at the start of the fifth frame (1 min, time interval set at 15 s). Imaging was continued for 10–20 min. Cells simultaneously treated with DMSO (replacing LatA) and 20 μM CCCP were the positive control; cells simultaneously treated with 500 nM LatA and DMSO (replacing CCCP) were used as the negative control.
For CK666 (Sigma-Aldrich, SML006) pretreatment before CCCP addition, cells were pretreated with 1 ml of live-cell medium containing 100 μM CK666 (from a 20 mM stock in DMSO) for 30 min before the start of imaging. During imaging, cells were treated with 1 ml live-cell medium containing 40 μM CCCP at the start of the fifth frame (1 min, time interval set at 15 s). Imaging was continued for 15–20 min with cells in medium containing a final concentration of 20 μM CCCP and 50 μM CK666. Control cells were pretreated with an equal volume of DMSO (replacing CK666) and stimulated with 20 µM CCCP during imaging. As a negative control, cells were pretreated with 100 μM CK666, and an equal volume of DMSO (replacing CCCP) was added during imaging.
For CK666 pretreatment before ionomycin addition, cells were pretreated with 1 ml of live-cell medium containing 100 μM CK666 for 30 min. After which, cells were directly taken for imaging. During imaging, cells were treated with 1 ml of live-cell medium containing 8 μM ionomycin at the start of the fifth frame (1 min, time interval set at 15 s). Imaging was continued for 5–10 min with cells in medium containing a final concentration of 4 μM ionomycin and 50 μM CK666. Control cells were pretreated with an equal volume of DMSO (replacing CK666) and stimulated with 4 µM ionomycin during imaging. As a negative control, cells were pretreated with DMSO (replacing CK666) and additional DMSO (replacing ionomycin) was added during imaging.
For Airyscan imaging, dishes were imaged on the LSM 880 equipped with a 100×1.4 NA Apochromat oil objective using the Airyscan detectors (Carl Zeiss Microscopy). The Airyscan uses a 32-channel array of GaAsP detector configured as 0.2 airy units per channel. Cells were imaged with the 488 nm laser and band pass (BP) 420–480/BP 495–620 filter for GFP. The 561 nm laser and BP 495–550/long pass 570 filter was used for RFP. For live-cell microscopy, U2OS-WT cells were co-transfected with 500 ng of Mito–DsRed and 600 ng Tom20–GFP; INF2-KO cells were co-transfected with 500 ng Mito–R-GECO1 and 600 ng Tom20–GFP. All imaging was conducted at 37°C and 5% CO2, with a single basal slice acquired at a frame interval of 4.1 s. Images were subsequently processed using Zen2 software. Raw data were processed using Airyscan processing with Zen Black software (Carl Zeiss, version 2.3).
For mixing experiments, control cells were transfected with 500 ng Mito–DsRed and OMA1-KD cells were transfected with 500 ng mito–BFP 72 h after knock down. After 4 h transfection, control cells were mixed with OMA1-KD cells in a 1:2 (control was OMA1-KD) volume ratio. Mixed cells were re-plated onto MatTek dishes at ∼3.5×105 cells per dish and allowed to adhere for ∼18 h. During live-cell imaging with CCCP, fields were selected with both OMA1-KD and control cells visible.
Quantification from live-cell imaging experiments
Unless otherwise stated, all image analysis was performed on ImageJ Fiji (version 1.51n, National Institutes of Health). Cells that shrunk during imaging or exhibited signs of phototoxicity such as blebbing or vacuolization were excluded from analysis.
Actin burst measurements
Mean actin fluorescence was calculated by selecting two region of interests (ROIs) (for ionomycin treatments) per cell or one ROI per cell (for CCCP treatments). The ROI selected for CCCP encompassed the entire area at the height of actin assembly after CCCP treatment. Fluorescence values for each time point (F) were normalized with the mean initial fluorescence before drug treatment (first four frames−F0) and plotted against time as F/F0. For DMSO control or cells that did not exhibit actin burst, the ROI was selected as the bulk region of the cytoplasm containing mitochondria using the mito–BFP channel.
Centroid measurements
Every eighth frame was analyzed (2 min intervals). Imaging fields were coded and scrambled by one investigator (T.S.F.) and given to the other investigator (R.C.) for blind analysis. Centroids were counted manually for every time point. To normalize the data, the number of centroids was divided by the total mitochondrial area in the field (μm2). The results were then decoded by the first investigator.
Mitochondrial division rate measurements
Mitochondrial division rate has been described in detail previously (Ji et al., 2015). Suitable ROIs were selected based on whether individual mitochondria were resolvable and did not leave the focal plane. One ROI was selected per cell. Files of the ROIs were coded and scrambled by one investigator (R.C.) and analyzed for division by a second investigator (W.K.J.) in a blinded manner. The second investigator manually scanned the ROIs frame by frame for division events and determined total mitochondrial length in the ROI using the ImageJ macro Mitochondrial Morphology. The results were then returned to the first investigator for decoding.
Depolarization measurements
Mean TMRE fluorescence was calculated from the entire mitochondrial area determined in the mito–BFP channel, for which the fluorescent intensity did not change appreciably during imaging. TMRE fluorescence values for each time point (F) were normalized with the mean initial fluorescence before drug treatment (first four frames−F0) and plotted against time as F/F0.
Transient depolarization events in untreated cells are defined as an abrupt loss in mitochondrial TMRE fluorescence signal that persists for ≥30 s without an appreciable decrease in fluorescence signal of the mito–BFP marker. Individual transient depolarization events were manually identified by scrolling through images frame by frame. Clear increases in actin fluorescence signal after transient depolarization were considered as ‘Δψm followed by actin assembly’; depolarization events that demonstrated no appreciable actin fluorescence increase were considered as ‘Δψm followed by no actin assembly’. To determine the frequency of depolarization, the total number of depolarization events was normalized to the total cell count and the total duration of the imaging (in minutes). For depolarization duration, suitable ROIs were selected for mitochondria that had undergone depolarization. TMRE fluorescence values for each time point were normalized to the mean initial fluorescence (ten frames before transient depolarization) and plotted against time. Depolarization events that occurred 16 min into imaging and did not recover at the end of 20 min imaging were separately noted.
T1/2 analysis of actin assembly and disassembly
Mean actin fluorescence was calculated by selecting one ROI (for ionomycin and CCCP treatments). The ROI selected for CCCP encompassed the entire cell area at a medial cell section, whereas for ionomycin treatment one ROI at the perinuclear region (free from stress fibers for all time frames) per cell was selected. Fluorescence values for each time point (F) were normalized with the mean initial fluorescence before drug treatment (first 30 frames−F0) and plotted against time as F/F0. The half-maximum value was calculated after establishing the peak value; the time was determined from the ascending slope (actin assembly) for each cell. For actin disassembly, the time (in seconds) was determined for the half-maximum value from the descending slope and deducted from the peak time. For ionomycin analysis, all the cells were used for assembly, peak and disassembly calculations. For CCCP, five cells were removed for disassembly calculations because of stress fiber interference. The numbers of individual cells were 18 (ionomycin), 25 (CCCP/actin assembly and actin peak) and 20 (CCCP actin disassembly). Data were compiled from three independent experiments.
Statistical analysis and graph plotting software
All statistical analyses and P-value determinations were conducted using GraphPad Prism QuickCalcs or GraphPad Prism 8 (version 8.2.0, GraphPad Software). To determine P-values, an unpaired Student's t-test was performed between two groups of data, comparing full datasets as stated in the figure legends. For P-values in multiple comparisons (unpaired), Sidak's multiple comparisons test and Dunnett's multiple comparison test were performed in GraphPad Prism 8. Mean P-values were calculated with multiple t-tests (without correction) in GraphPad Prism 8. All data, along with the standard errors of the mean (s.e.m.) were plotted using Microsoft Excel for Office 365 (version 16.0.11231.20164, Microsoft Corporation), with the exception of scatter plots. Fig. 2E, Fig. 3C and Fig. S2A,E,F were plotted with GraphPad Prism 8 and Fig. S4A was plotted with KaleidaGraph (version 4.01, Synergy Software).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank past and present members of the Higgs laboratory, especially Lori Schoenfeld for generating the U2OS INF2-KO cell line. We also thank Zdenek Svindrych and Ann Lavanway for microscopy help and valuable tips. Being ever-present, the importance of Uli Toppanos cannot be overstated.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Author contributions
Conceptualization: T.S.F., H.N.H., R.C.; Methodology: T.S.F., R.C.; Software: T.S.F., R.C.; Validation: T.S.F., R.C.; Formal analysis: T.S.F., W.-K.J., R.C.; Investigation: T.S.F., R.C.; Writing - original draft: T.S.F., H.N.H., R.C.; Writing - review & editing: T.S.F., H.N.H., R.C.; Visualization: T.S.F., H.N.H., R.C.; Supervision: H.N.H.; Project administration: H.N.H.; Funding acquisition: H.N.H.
Funding
This work supported by National Institutes of Health grants R35 GM122545 and DK088826, and National Institute of General Medical Sciences grant P20 GM113132. Deposited in PMC for release after 12 months.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information available online at http://jcs.biologists.org/lookup/doi/10.1242/jcs.234435.supplemental
References
- A M., Fung T. S., Kettenbach A. N., Chakrabarti R. and Higgs H. N. (2019). A complex containing lysine-acetylated actin inhibits the formin INF2. Nat. Cell Biol. 21, 592-602. 10.1038/s41556-019-0307-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mehdi A.-B., Pastukh V. M., Swiger B. M., Reed D. J., Patel M. R., Bardwell G. C., Pastukh V. V., Alexeyev M. F. and Gillespie M. N. (2012). Perinuclear mitochondrial clustering creates an oxidant-rich nuclear domain required for hypoxia-induced transcription. Sci. Signal. 5, ra47 10.1126/scisignal.2002712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anand R., Wai T., Baker M. J., Kladt N., Schauss A. C., Rugarli E. and Langer T. (2014). The i-AAA protease YME1L and OMA1 cleave OPA1 to balance mitochondrial fusion and fission. J. Cell Biol. 204, 919-929. 10.1083/jcb.201308006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas G., Adebanjo O. A., Freedman B. D., Anandatheerthavarada H. K., Vijayasarathy C., Zaidi M., Kotlikoff M. and Avadhani N. G. (1999). Retrograde Ca2+ signaling in C2C12 skeletal myocytes in response to mitochondrial genetic and metabolic stress: a novel mode of inter-organelle crosstalk. EMBO J. 18, 522-533. 10.1093/emboj/18.3.522 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campellone K. G. and Welch M. D. (2010). A nucleator arms race: cellular control of actin assembly. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 237-251. 10.1038/nrm2867 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti R., Ji W.-K., Stan R. V., de Juan Sanz J., Ryan T. A. and Higgs H. N. (2018). INF2-mediated actin polymerization at the ER stimulates mitochondrial calcium uptake, inner membrane constriction, and division. J. Cell Biol. 217, 251-268. 10.1083/jcb.201709111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandel N. S., Maltepe E., Goldwasser E., Mathieu C. E., Simon M. C. and Schumacker P. T. (1998). Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species trigger hypoxia-induced transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 11715-11720. 10.1073/pnas.95.20.11715 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua B. T., Volbracht C., Tan K. O., Li R., Yu V. C. and Li P. (2003). Mitochondrial translocation of cofilin is an early step in apoptosis induction. Nat. Cell Biol. 5, 1083-1089. 10.1038/ncb1070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutts A. S. and La Thangue N. B. (2015). Actin nucleation by WH2 domains at the autophagosome. Nat. Commun. 6, 7888 10.1038/ncomms8888 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos K. J., Allan V. J., Grierson A. J. and Sheetz M. P. (2005). Mitochondrial function and actin regulate dynamin-related protein 1-dependent mitochondrial fission. Curr. Biol. 15, 678-683. 10.1016/j.cub.2005.02.064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmurs M., Foti M., Raemy E., Vaz F. M., Martinou J.-C., Bairoch A. and Lane L. (2015). C11orf83, a mitochondrial cardiolipin-binding protein involved in bc1 complex assembly and supercomplex stabilization. Mol. Cell. Biol. 35, 1139-1156. 10.1128/MCB.01047-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBoff B., Götz J. and Feany M. B. (2012). Tau promotes neurodegeneration via DRP1 mislocalization in vivo. Neuron 75, 618-632. 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.06.026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durcan T. M., Tang M. Y., Pérusse J. R., Dashti E. A., Aguileta M. A., McLelland G. L., Gros P., Shaler T. A., Faubert D., Coulombe B. et al. (2014). USP8 regulates mitophagy by removing K6-linked ubiquitin conjugates from parkin. EMBO J. 33, 2473-2491. 10.15252/embj.201489729 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvezin-Caubet S., Jagasia R., Wagener J., Hofmann S., Trifunovic A., Hansson A., Chomyn A., Bauer M. F., Attardi G., Larsson N.-G. et al. (2006). Proteolytic processing of OPA1 links mitochondrial dysfunction to alterations in mitochondrial morphology. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 37972-37979. 10.1074/jbc.M606059200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehses S., Raschke I., Mancuso G., Bernacchia A., Geimer S., Tondera D., Martinou J.-C., Westermann B., Rugarli E. I. and Langer T. (2009). Regulation of OPA1 processing and mitochondrial fusion by m-AAA protease isoenzymes and OMA1. J. Cell Biol. 187, 1023-1036. 10.1083/jcb.200906084 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu D. and Lippincott-Schwartz J. (2018). Monitoring the effects of pharmacological reagents on mitochondrial morphology. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 79, e45 10.1002/cpcb.45 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch A. L., Ji W.-K., Merrill R. A., Strack S. and Higgs H. N. (2016). Actin filaments as dynamic reservoirs for Drp1 recruitment. Mol. Biol. Cell 27, 3109-3121. 10.1091/mbc.e16-03-0193 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head B., Griparic L., Amiri M., Gandre-Babbe S. and van der Bliek A. M. (2009). Inducible proteolytic inactivation of OPA1 mediated by the OMA1 protease in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 187, 959-966. 10.1083/jcb.200906083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs H. N. and Peterson K. J. (2005). Phylogenetic analysis of the formin homology 2 domain. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 1-13. 10.1091/mbc.e04-07-0565 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppins S., Edlich F., Cleland M. M., Banerjee S., McCaffery J. M., Youle R. J. and Nunnari J. (2011). The soluble form of Bax regulates mitochondrial fusion via MFN2 homotypic complexes. Mol. Cell 41, 150-160. 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.11.030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara N., Fujita Y., Oka T. and Mihara K. (2006). Regulation of mitochondrial morphology through proteolytic cleavage of OPA1. EMBO J. 25, 2966-2977. 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji W.-K., Hatch A. L., Merrill R. A., Strack S. and Higgs H. N. (2015). Actin filaments target the oligomeric maturation of the dynamin GTPase Drp1 to mitochondrial fission sites. eLife 4, e11553 10.7554/eLife.11553 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji W.-K., Chakrabarti R., Fan X., Schoenfeld L., Strack S. and Higgs H. N. (2017). Receptor-mediated Drp1 oligomerization on endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 216, 4123-4139. 10.1083/jcb.201610057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. W. and Schell M. J. (2009). Neuronal IP3 3-kinase is an F-actin-bundling protein: role in dendritic targeting and regulation of spine morphology. Mol. Biol. Cell 20, 5166-5180. 10.1091/mbc.e09-01-0083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast D. J., Zajac A. L., Holzbaur E. L. F., Ostap E. M. and Dominguez R. (2015). WHAMM directs the Arp2/3 complex to the ER for autophagosome biogenesis through an actin comet tail mechanism. Curr. Biol. 25, 1791-1797. 10.1016/j.cub.2015.05.042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. P. and Lehninger A. L. (1949). Oxidation of fatty acids and tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates by isolated rat liver mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 179, 957-972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korobova F., Ramabhadran V. and Higgs H. N. (2013). An actin-dependent step in mitochondrial fission mediated by the ER-associated formin INF2. Science 339, 464-467. 10.1126/science.1228360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korobova F., Gauvin T. J. and Higgs H. N. (2014). A role for myosin II in mammalian mitochondrial fission. Curr. Biol. 24, 409-414. 10.1016/j.cub.2013.12.032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruppa A. J., Kishi-Itakura C., Masters T. A., Rorbach J. E., Grice G. L., Kendrick-Jones J., Nathan J. A., Minczuk M. and Buss F. (2018). Myosin VI-dependent actin cages encapsulate Parkin-positive damaged mitochondria. Dev. Cell 44, 484-499.e6. 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.01.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon D., Park E., Sesaki H. and Kang S.-J. (2017). Carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) suppresses STING-mediated DNA sensing pathway through inducing mitochondrial fission. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 493, 737-743. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.08.121 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. and Yoon Y. (2014). Transient contraction of mitochondria induces depolarization through the inner membrane dynamin OPA1 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 11862-11872. 10.1074/jbc.M113.533299 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y., Stevens D. A., Kang S.-U., Jiang H., Lee Y.-I., Ko H. S., Scarffe L. A., Umanah G. E., Kang H., Ham S. et al. (2017). PINK1 primes Parkin-mediated ubiquitination of PARIS in dopaminergic neuronal survival. Cell Rep. 18, 918-932. 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.090 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legros F., Lombès A., Frachon P. and Rojo M. (2002). Mitochondrial fusion in human cells is efficient, requires the inner membrane potential, and is mediated by mitofusins. Mol. Biol. Cell 13, 4343-4354. 10.1091/mbc.e02-06-0330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Xu S., Roelofs B. A., Boyman L., Lederer W. J., Sesaki H. and Karbowski M. (2015). Transient assembly of F-actin on the outer mitochondrial membrane contributes to mitochondrial fission. J. Cell Biol. 208, 109-123. 10.1083/jcb.201404050 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G.-B., Zhang H.-W., Fu R.-Q., Hu X.-Y., Liu L., Li Y.-N., Liu Y.-X., Liu X., Hu J.-J., Deng Q. et al. (2018). Mitochondrial fission and mitophagy depend on cofilin-mediated actin depolymerization activity at the mitochondrial fission site. Oncogene 37, 1485-1502. 10.1038/s41388-017-0064-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. and Hajnóczky G. (2011). Altered fusion dynamics underlie unique morphological changes in mitochondria during hypoxia-reoxygenation stress. Cell Death Differ. 18, 1561-1572. 10.1038/cdd.2011.13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Kim C. N., Yang J., Jemmerson R. and Wang X. (1996). Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell 86, 147-157. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80085-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacVicar T. D. B. and Lane J. D. (2014). Impaired OMA1-dependent cleavage of OPA1 and reduced DRP1 fission activity combine to prevent mitophagy in cells that are dependent on oxidative phosphorylation. J. Cell Sci. 127, 2313-2325. 10.1242/jcs.144337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacVicar T. and Langer T. (2016). OPA1 processing in cell death and disease - the long and short of it. J. Cell Sci. 129, 2297-2306. 10.1242/jcs.159186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manor U., Bartholomew S., Golani G., Christenson E., Kozlov M., Higgs H., Spudich J. and Lippincott-Schwartz J. (2015). A mitochondria-anchored isoform of the actin-nucleating spire protein regulates mitochondrial division. eLife 4, e08828 10.7554/eLife.08828 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinus R. D., Garth G. P., Webster T. L., Cartwright P., Naylor D. J., Høj P. B. and Hoogenraad N. J. (1996). Selective induction of mitochondrial chaperones in response to loss of the mitochondrial genome. Eur. J. Biochem. 240, 98-103. 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0098h.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda N., Sato S., Shiba K., Okatsu K., Saisho K., Gautier C. A., Sou Y.-S., Saiki S., Kawajiri S., Sato F. et al. (2010). PINK1 stabilized by mitochondrial depolarization recruits Parkin to damaged mitochondria and activates latent Parkin for mitophagy. J. Cell Biol. 189, 211-221. 10.1083/jcb.200910140 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLelland G.-L., Goiran T., Yi W., Dorval G., Chen C. X., Lauinger N. D., Krahn A. I., Valimehr S., Rakovic A., Rouiller I. et al. (2018). Mfn2 ubiquitination by PINK1/parkin gates the p97-dependent release of ER from mitochondria to drive mitophagy. eLife 7, e32866 10.7554/eLife.32866 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazono Y., Hirashima S., Ishihara N., Kusukawa J., Nakamura K.-I. and Ohta K. (2018). Uncoupled mitochondria quickly shorten along their long axis to form indented spheroids, instead of rings, in a fission-independent manner. Sci. Rep. 8, 350 10.1038/s41598-017-18582-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore A. S., Wong Y. C., Simpson C. L. and Holzbaur E. L. F. (2016). Dynamic actin cycling through mitochondrial subpopulations locally regulates the fission-fusion balance within mitochondrial networks. Nat. Commun. 7, 12886 10.1038/ncomms12886 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nam H.-S. and Benezra R. (2009). High levels of Id1 expression define B1 type adult neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 5, 515-526. 10.1016/j.stem.2009.08.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narendra D. P., Jin S. M., Tanaka A., Suen D.-F., Gautier C. A., Shen J., Cookson M. R. and Youle R. J. (2010). PINK1 is selectively stabilized on impaired mitochondria to activate Parkin. PLoS Biol. 8, e1000298 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000298 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okatsu K., Uno M., Koyano F., Go E., Kimura M., Oka T., Tanaka K. and Matsuda N. (2013). A dimeric PINK1-containing complex on depolarized mitochondria stimulates Parkin recruitment. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 36372-36384. 10.1074/jbc.M113.509653 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagliarini D. J. and Rutter J. (2013). Hallmarks of a new era in mitochondrial biochemistry. Genes Dev. 27, 2615-2627. 10.1101/gad.229724.113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park Y. S., Choi S. E. and Koh H. C. (2018). PGAM5 regulates PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy via DRP1 in CCCP-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol. Lett. 284, 120-128. 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.12.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patten D. A., Wong J., Khacho M., Soubannier V., Mailloux R. J., Pilon-Larose K., MacLaurin J. G., Park D. S., McBride H. M., Trinkle-Mulcahy L. et al. (2014). OPA1-dependent cristae modulation is essential for cellular adaptation to metabolic demand. EMBO J. 33, 2676-2691. 10.15252/embj.201488349 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. W., Norman J. P., Barbieri J., Brown E. B. and Gelbard H. A. (2011). Mitochondrial membrane potential probes and the proton gradient: a practical usage guide. BioTechniques 50, 98-115. 10.2144/000113610 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickles S., Vigié P. and Youle R. J. (2018). Mitophagy and Quality Control Mechanisms in Mitochondrial Maintenance. Curr. Biol. 28, R170-R185. 10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruyne D. (2016). Revisiting the phylogeny of the animal formins: two new subtypes, relationships with multiple wing hairs proteins, and a lost human formin. PLoS ONE 11, e0164067 10.1371/journal.pone.0164067 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramabhadran V., Korobova F., Rahme G. J. and Higgs H. N. (2011). Splice variant-specific cellular function of the formin INF2 in maintenance of Golgi architecture. Mol. Biol. Cell 22, 4822-4833. 10.1091/mbc.e11-05-0457 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekine S., Wang C., Sideris D. P., Bunker E., Zhang Z. and Youle R. J. (2019). Reciprocal roles of Tom7 and OMA1 during mitochondrial import and activation of PINK1. Mol. Cell 73, 1028-1043.e5. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.01.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shao X., Li Q., Mogilner A., Bershadsky A. D. and Shivashankar G. V. (2015). Mechanical stimulation induces formin-dependent assembly of a perinuclear actin rim. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, E2595-E2601. 10.1073/pnas.1504837112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Z., Chen H., Fiket M., Alexander C. and Chan D. C. (2007). OPA1 processing controls mitochondrial fusion and is regulated by mRNA splicing, membrane potential, and Yme1L. J. Cell Biol. 178, 749-755. 10.1083/jcb.200704110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Cleland M. M., Xu S., Narendra D. P., Suen D.-F., Karbowski M. and Youle R. J. (2010). Proteasome and p97 mediate mitophagy and degradation of mitofusins induced by Parkin. J. Cell Biol. 191, 1367-1380. 10.1083/jcb.201007013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi T., Sakurai N., Nakano K. and Ishisaka R. (2003). C-terminal 15 kDa fragment of cytoskeletal actin is posttranslationally N-myristoylated upon caspase-mediated cleavage and targeted to mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 539, 37-44. 10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00180-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varanita T., Soriano M. E., Romanello V., Zaglia T., Quintana-Cabrera R., Semenzato M., Menabò R., Costa V., Civiletto G., Pesce P. et al. (2015). The OPA1-dependent mitochondrial cristae remodeling pathway controls atrophic, apoptotic, and ischemic tissue damage. Cell Metab. 21, 834-844. 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.05.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vives-Bauza C., Zhou C., Huang Y., Cui M., de Vries R. L. A., Kim J., May J., Tocilescu M. A., Liu W., Ko H. S. et al. (2010). PINK1-dependent recruitment of Parkin to mitochondria in mitophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 378-383. 10.1073/pnas.0911187107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wales P., Schuberth C. E., Aufschnaiter R., Fels J., Garcia-Aguilar I., Janning A., Dlugos C. P., Schäfer-Herte M., Klingner C., Walte M. et al. (2016). Calcium-mediated actin reset (CaAR) mediates acute cell adaptations. eLife 5, e19850 10.7554/eLife.19850 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West A. P., Shadel G. S. and Ghosh S. (2011). Mitochondria in innate immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 389-402. 10.1038/nri2975 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Prole D. L., Shen Y., Lin Z., Gnanasekaran A., Liu Y., Chen L., Zhou H., Chen S. R. W., Usachev Y. M. et al. (2014). Red fluorescent genetically encoded Ca2+ indicators for use in mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem. J. 464, 13-22. 10.1042/BJ20140931 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamano K., Wang C., Sarraf S. A., Münch C., Kikuchi R., Noda N. N., Hizukuri Y., Kanemaki M. T., Harper W., Tanaka K. et al. (2018). Endosomal Rab cycles regulate Parkin-mediated mitophagy. eLife 7, e31326 10.7554/eLife.31326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., Li H. and Song Z. (2014). Membrane depolarization activates the mitochondrial protease OMA1 by stimulating self-cleavage. EMBO Rep. 15, 576-585. 10.1002/embr.201338240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.