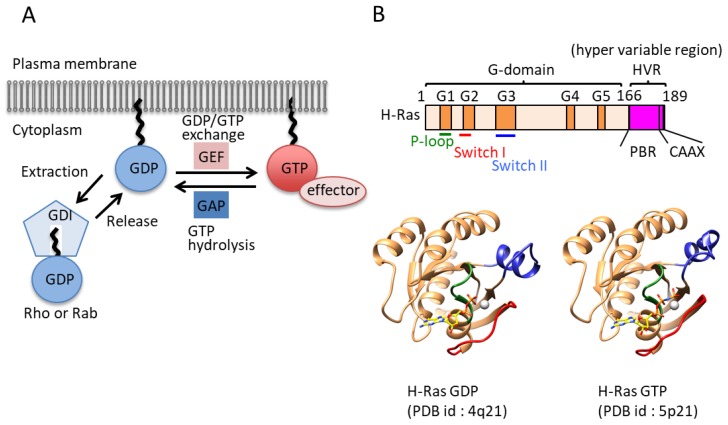
Figure 1.
Regulation mechanism of small GTPases: (A) Schematic diagram of the small GTPase switching mechanism. Guanine-nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) enhance the exchange reaction. The guanine dissociation inhibitor (GDI) and effector are also shown. Guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-bound and guanosine diphosphate (GDP)-bound GTPases (lipidated forms) are shown as red and blue circles, respectively. GAP and GEF are shown as red and blue boxes, respectively. Several GTPase families combine their GDP/GTP switch with alternations in cytosolic/membrane localization in a process regulated by GDIs or GDI-like proteins. (B) General structural information of small GTPases. Upper: The domain architecture of H-Ras. G boxes of the G domain are highlighted with orange boxes. The hyper variable region, including a polybasic region and a CAAX motif, is highlighted with pink boxes. The P-loop, switch I, and switch II are shown as bars colored green, red, and blue, respectively. Lower: Crystal structures of GDP-bound and GTP-bound H-Ras. The P-loop, switch I, and switch II are colored green, red, and blue, respectively.