Abstract
Monoamines such as noradrenaline and serotonin are stored in secretory vesicles and released by exocytosis. Two related monoamine transporters, VMAT1 and VMAT2, mediate vesicular transmitter uptake. Previously we have reported that in the rat pheochromocytoma cell line PC 12 VMAT1, localized to peptide-containing secretory granules, is controlled by the heterotrimeric G-protein Go2. We now show that in BON cells, a human serotonergic neuroendocrine cell line derived from a pancreatic tumor expressing both transporters on large, dense-core vesicles, VMAT2 is even more sensitive to G-protein regulation than VMAT1. The activity of both transporters is only downregulated by Gαo2, whereas comparable concentrations of Gαo1 are without effect. In serotonergic raphe neurons in primary culture VMAT2 is also downregulated by pertussis toxin-sensitive Go2. By electron microscopic analysis from prefrontal cortex we show that VMAT2 and Gαo2 associate preferentially to locally recycling small synaptic vesicles in serotonergic terminals. In addition, Go2-dependent modulation of VMAT2 also works when using a crude synaptic vesicle preparation from this brain area. We conclude that regulation of monoamine uptake by the heterotrimeric G proteins is a general feature of monoaminergic neurons that controls the content of both large, dense-core and small synaptic vesicles.
Keywords: VMAT2, Go2, neuroendocrine cells, neurons, transmitter uptake, vesicular plasticity
The neurotransmitter content of synaptic vesicles is one of the key parameters in determining the strength of transmission at a given synapse. However, until recently only little information was available concerning the regulation of vesicular transmitter content by means of intracellular signaling pathways not directly linked to synthesis or changes in the proton gradient. Quantal size is known to be rather variable at least in some synapses (van der Kloot, 1991). Thus, upregulation or downregulation of vesicular transmitter content may constitute one of the elements in determining synaptic plasticity.
Transmitter loading of synaptic vesicles is mediated by specific transporters that draw transmitters from cytoplasmic pools and that are driven by an electrochemical proton gradient across the vesicle membrane (for review, see Edwards, 1992). Two structurally related but pharmacologically distinct monoamine transporters are known, VMAT1 and VMAT2 (Liu et al., 1992, 1994), that are responsible for transporting catecholamines, serotonin, and histamine. Although both VMATs recognize monoamines such as serotonin, noradrenaline, and dopamine at almost similar concentrations, VMAT2 can be distinguished from VMAT1 by the ability to use histamine in submillimolar concentrations as substrate and by its 10-fold higher sensitivity to tetrabenazine (Peter et al., 1994). Human VMAT1 is almost insensitive to tetrabenazine (Erickson et al., 1996).
In addition to pharmacological differences, VMAT1 and VMAT2 differ in their tissue distribution. In the rat, VMAT1 is the predominant transporter of the peripheral nervous system and of neuroendocrine cells (Liu et al., 1994; Peter et al., 1995), whereas VMAT2 is preferentially expressed in the CNS (Liu et al., 1994; Peter et al., 1995; Erickson et al., 1996) and in enterochromaffin and enterochromaffin-like cells (Dimaline and Struther, 1995; Erickson et al., 1996). In other species, VMAT2 is also expressed outside the CNS (Krejci et al., 1993; Sagne et al., 1997; Leitner et al., 1999).
More importantly, both transporters are localized to large, dense-core vesicles (LDCV) as well as to small synaptic vesicles (SSV) within neurons or neuroendocrine cells (Liu et al., 1994; Nirenberg et al., 1995). These vesicles share the basic machinery for exocytosis but differ with respect to their intracellular trafficking pathways and with respect to the control of exocytosis. It is not clear at present at which precise step during biogenesis LDCV are loaded with transmitter, how uptake is regulated, and if regulation of uptake resembles that of SSV.
In a previous study we have demonstrated that VMAT1 is downregulated by Go2 (Ahnert-Hilger et al., 1998a), a trimeric G-protein that is associated with both SSV and LDCV (Ahnert-Hilger et al., 1994). In this study, we used the rat pheochromocytoma cell line PC 12, which only contains VMAT1, confined to protein-containing LDCV (Liu et al., 1994; Peter et al., 1995). The current study was undertaken with two aims in mind. First, we wished to clarify whether regulation by Gαo2 is a specific feature of VMAT1 or whether it is also pertinent for the related but pharmacologically distinct VMAT2. These experiments were performed in BON cells, a human neuroendocrine cell line derived from a metastasis of a pancreatic carcinoid tumor (Beauchamp et al., 1991; Ahnert-Hilger et al., 1996), which releases serotonin (Evers et al., 1991) and, as shown here, expresses both VMAT1 and VMAT2. Second, we investigated whether regulation by heterotrimeric G-proteins also occurs in neurons using serotonergic neurons and crude synaptic vesicles where VMAT2 should be predominantly localized to SSV (Liu et al., 1994; Peter et al., 1995; Erickson et al., 1996). Our results show that G-protein-induced downregulation of VMATs represents a feature shared by SSV and LDCV despite their differential trafficking pathways.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Antibodies. Rabbit antisera were raised against glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins with the rat vesicular monoamine transporters VMAT1 (C-terminal, amino acids 468–521) and VMAT2 (N-terminal, amino acids 1–20). When tested against recombinant proteins, both antisera were specific for VMAT1 and VMAT2, respectively, with only negligible cross-reactivity toward the other transporter protein (also see Results). Rabbit and chicken antisera against serotonin were kindly provided by R. Veh (Institut für Anatomie der Charité, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin). A monoclonal antibody against cytochrome b561 was a gift from B. Wiedenmann (Hepatologie und Gastroenterologie, Virchow Klinikum der Charité, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin). A rabbit antiserum against chromogranin B (Kroesen et al., 1996) was a gift from R. Fischer-Colbrie (Department of Pharmacology, University of Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria). The following antibodies were described previously: monoclonal antibodies against synaptobrevin II (clone 69.1;Edelmann et al., 1995) and synaptophysin (clone 7.2; Jahn et al., 1985) and polyclonal antisera against Gαo1 (AS 248;Spicher et al., 1992) and Gαo2 (AS 371;Laugwitz et al., 1996). Peroxidase-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG was obtained from Vector Laboratories (Burlingame, CA). Donkey anti-rabbit and anti-mouse antiserum coupled to Oregon Green or Texas Red, respectively, were obtained from Molecular Probes (Göttingen, Germany). Donkey anti-chicken IgG coupled to Texas Red was obtained from Jackson ImmunoResearch (West Grove, PA).
3H-Labeled transmitters. 5-Hydroxy [3H]tryptamine trifluoroacetate (serotonin; specific activity, 3260 Bq/mmol),l-[7,8-3H]noradrenaline (specific activity, 444 Bq/mmol), and [2,5-3H]histamine dihydrochloride (specific activity, 1550 Bq/mmol) were obtained from Amersham (Dreieich, Germany).
Toxins. Streptolysin O (SLO; Weller et al., 1996) and tetanus toxin (TeNT) as well as its light chain (TeNt/LC) were kindly supplied by U. Weller (Institut Ray-Roecky-Weller, Baden-Baden, Germany) and H. Bigalke (Institut für Toxikologie, Medizinische Hochschule, Hannover, Germany), respectively. Pertussis toxin was obtained from Calbiochem-Novabiochem (Bad Soden/Taunus, Germany).
G-protein α-subunits. Pertussis toxin-sensitive Gα isoforms were purified from bovine brain as described elsewhere (Exner et al., 1999). Purified Gαo- and Gαi-subunits were used in the AlF4−-activated form (also see Ahnert-Hilger et al., 1998a).
Other chemicals. Tetrabenazine was a kind gift from Jean Pierre Henry (Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique UPR 9071, Institut de Biologie Physico-Chimique, Paris, France).
Methods
Cell cultures. BON and PC 12 cells were cultivated as described (Ahnert-Hilger et al., 1996, 1998a, respectively).
Primary neuronal cell cultures of the raphe region were prepared from rats at embryonic day 14 following a recently described protocol for serum-free cultures (Brewer, 1995), which was modified and adapted to raphe neurons (M. Lautenschlager, M. Höltje, G. Ahnert-Hilger, and H. Hörtnagl, unpublished procedures). Briefly, after dissection and dissociation (enzymatically by trypsin and mechanically by pasteur pipettes), neurons were seeded on 48-well plates (precoated with poly-l-lysine and a collagen-containing medium) at a density of 8.5 × 104 cells and were grown in serum-free neurobosal medium (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD) supplemented with B27 (Life Technologies), 0.5 mm glutamine, and 100 U/ml penicillin-streptomycin at 5% CO2 in a humidified atmosphere up to 4 weeks.
Monoamine uptake. The medium was removed, and cells were washed twice with PBS and once with potassium glutamate buffer (KG buffer) containing (in mm): potassium glutamate 150, 1,4-piperazinediethane-sulfonic acid 20, EGTA 4, and MgCl2 1, adjusted to pH 7.0 with KOH, before they were suspended in KG buffer. One volume of this cell suspension (∼107 cells) was mixed with 1 volume of SLO dissolved in KG buffer containing 1 mm dithiothreitol and incubated for 10 min on ice. Unbound SLO was removed by centrifugation (1000 × g, 2 min, 4°C). The cell pellet was resuspended in KG buffer, distributed into individual tubes, and incubated for 10 min at 37°C to induce permeabilization and remove cytosolic components. Permeabilized cells were washed by adding 500 μl of ice-cold KG buffer and spun down for 2 min at 4°C. Uptake was started by adding 100 μl of KG buffer containing 2 mm Mg-ATP supplemented with 1 mm ascorbic acid and 0.5 μCi of [3H]serotonin (90 nm final concentration), [3H]noradrenaline (120 nm final concentration), or [3H]histamine (200 nm final concentration). Substances to be tested were usually applied during this step. Incubation was performed for 10 min (raphe neurons and synaptic vesicles) or 25 min (PC 12 and BON cells) at 37°C and stopped by adding 1 ml of ice-cold KG buffer followed by a rapid centrifugation. The cell pellet was lysed in 0.4% Triton-X-100 to determine radioactivity by scintillation counting and protein content using the bicinchoninic acid method (BCA kit; Pierce, Rockford, IL).
Incubation of cells with pertussis toxin (100 ng/ml) was performed overnight. In another series of experiments, the cell pellets, after incubation with SLO, were resuspended in 20 μl of KG buffer in the presence or absence of TeNt/LC between 1 μm and 200 nm, which blocked exocytotic events.
Raphe neurons in primary culture were washed once with PBS and once with KG buffer before they were incubated with KG buffer supplemented with SLO, corresponding to ∼1000–2000 hemolytic units for 10 min on ice. This solution was discarded, and the permeabilized neurons were incubated with KG-ATP buffer containing 0.5 μCi of [3H]serotonin (90 nm final concentration) and the substances to be tested. The reaction was stopped after 10 min, and the cells were washed twice with KG buffer before they were lysed with 0.4% Triton-X-100 to determine radioactivity by scintillation counting and protein content using the BCA method.
For pertussis toxin treatment cultures were preincubated with 100 ng/ml for 24–48 hr.
Serotonin secretion. Cultures were preloaded with [3H]serotonin dissolved in serum-free DMEM and supplemented with 1 mm ascorbic acid for 4 hr in the incubator. They were washed three times with Krebs-Ringer-HEPES buffer containing (in mm): NaCl 130, KCl 4.7, MgSO4 1.2, CaCl2 2.5, glucose 11, and HEPES 10, pH 7.4 (KR-HEPES buffer) and preincubated for 10 min at 37°C in KR-HEPES buffer containing 0.1% BSA. The preincubation solution was removed, and cultures were stimulated for 5 min at 37°C by increasing the K+concentration to 50 mm.
Serotonin was measured in the supernatant and in the cells after dissolving them in Triton X-100 (0.4%). Release is given as the percentage of serotonin content present at the beginning of stimulation.
Subcellular fractionation and immunoreplica analysis.Subcellular fractionation of membranes obtained either from BON cells or primary raphe neuronal cultures was performed on continuous sucrose gradients as described previously (Ahnert-Hilger et al., 1998b). Postnuclear supernatants or fractions from gradients were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using the antibodies indicated.
Synaptic vesicles. Crude synaptic vesicles (lysis pellet 2 fraction) were prepared from rat prefrontal cortex following the procedure described by Huttner et al., (1983).
The vesicles were resuspended in KG-ATP buffer, divided to individual tubes, and [3H]serotonin (0.5 μCi, 90 nm final concentration) dissolved in KG/ATP-buffer with or without additions was added. Samples were incubated for 10 min at 37°C followed by centrifugation (30 min, 80,000 rpm; TLA 100.4; Beckman Instruments, Palo Alto, CA) and two washes with KG buffer without ATP. The pellets were lysed with 0.4% Triton X-100 to determine radioactivity by scintillation counting and protein content using the BCA method.
Immunofluorescence microscopy. Cells were grown on glass coverslips, washed twice with PBS, and fixed in 4% formalin in 0.1m phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, for 1 hr on ice. After three rinses with PBS, cells were incubated with a blocking solution containing 5% normal goat serum (Pan System), and 2% BSA (fraction V, pH 7.0; Serva, Heidelberg, Germany) dissolved in PBS supplemented with 0.1% Triton X-100 for 1 hr at room temperature. Incubation with a mixture of chicken and rabbit antibodies against serotonin and VMAT2, respectively, diluted in blocking solution was performed overnight at 4°C. Immunofluorescence was detected with Oregon Green-labeled goat anti-chicken and Texas Red-labeled goat anti-rabbit antibodies.
Electron microscopy. Freshly removed pieces of rat prefrontal cortex were placed in ice-cold PBS (0.1 mphosphate, pH 7.4) and cut into small cubes of ∼8 mm3. These were immersed in a fixative containing 4% formalin, 0.05% glutaraldehyde, and 0.2% picric acid dissolved in 0.1 m phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, for 2 hr on ice and 2 hr at room temperature. The fixed tissue was rinsed for 2 hr with PBS and then embedded in 3% agarose dissolved in PBS to perform vibratome sections of 50 μm. Endogenous peroxidase was blocked by a 30 min incubation with 0.5% H2O2, followed by rinsing with PBS. Pieces were then incubated for 30 min at room temperature with 0.1% Triton-X-100, 5% normal goat serum (NGS), and 2% BSA dissolved in PBS. Tissue pieces were incubated for 24 hr at 4°C with a chicken antiserum against serotonin dissolved in PBS containing NGS, BSA, and 0.05% sodium azide. Immunoreactive structures were visualized by a Vectastain elite kit (Vector Laboratories) according to the manufacturer‘s instructions using 3,3-diaminobenzidine (DAB; Sigma, St. Louis, MO) as chromogen. After several washes with PBS the tissue was incubated for 30 min in 1% OsO4 dissolved in PBS dehydrated by alcohol and subjected to flat embedding using araldite. Ultrathin sections (70 nm) mounted on Formvar-coated (Serva, 21740, in 0.3% dichlorethane) nickel grids were etched two times for 7 min with 1% periodic acid followed by rinsing with double-distilled water and subjected to a postembedding procedure according to the method of Wenzel et al. (1997), using rabbit antisera against VMAT2 or Gαo2. For detection anti-rabbit IgG coupled to 5 nm gold (Amersham) was used.
RESULTS
BON cells contain both VMAT1 and VMAT2
To find out which of the VMATs is expressed in BON cells, we performed both immunocytochemistry and immunoblot analyses. As shown in Figure 1A, immunoreactive bands of an apparent Mrof 55,000 were detected with both antisera in membrane extracts, which correspond to the molecular weight of VMAT proteins (Liu et al., 1994;Peter et al., 1995). When using membrane extracts from PC 12 cells, a protein band of an apparent Mr of 55,000 was recognized by the antiserum against VMAT1, whereas the antiserum against VMAT2 showed no immunoreactivity at all. The antiserum against VMAT1 also stained protein bands at ∼70 and 110 kDa, probably reflecting differentially glycosylated isoforms of VMAT1 and a dimer, respectively (Liu et al., 1994). Double immunofluorescence microscopy revealed that serotonin was present in both VMAT1- and VMAT2-positive cells. VMAT2 was expressed only in a subpopulation of cells, whereas VMAT1 was found in virtually all cells (Fig.1B). The BON cell line is an uncloned cell line, which may explain the heterogeneity with respect to VMAT expression (Townsend et al., 1993).
Fig. 1.
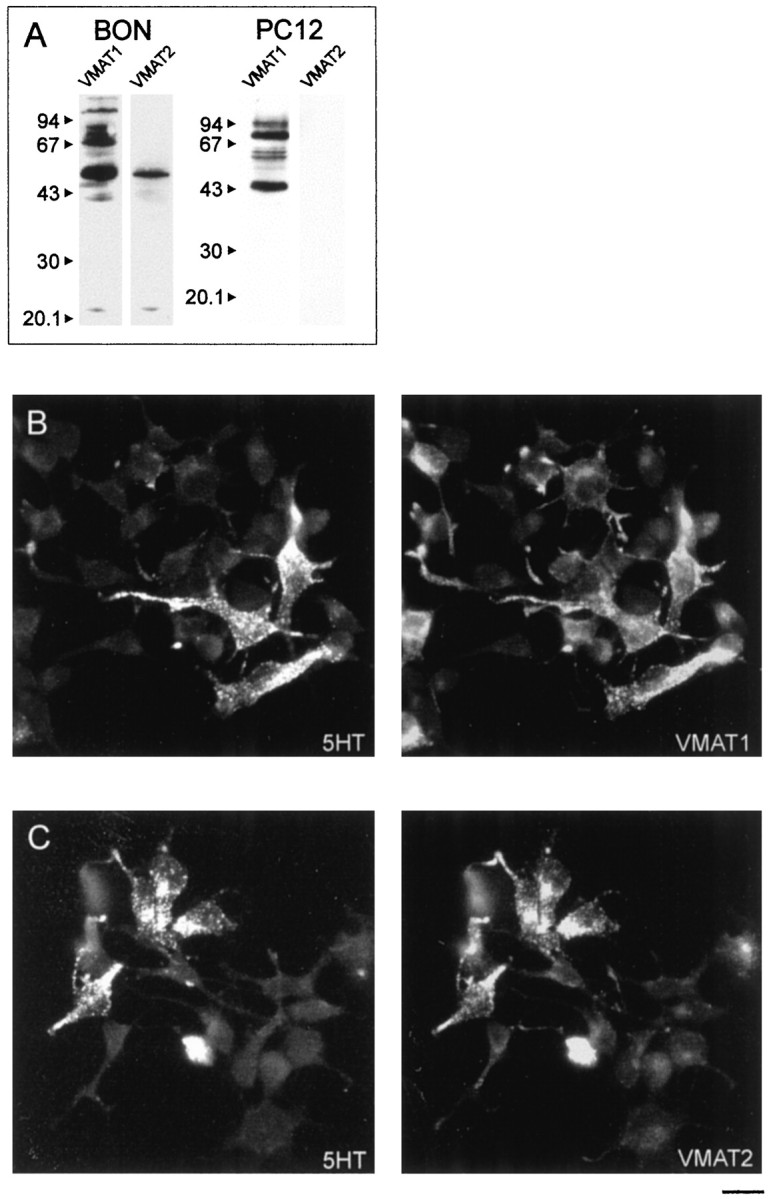
BON cells express both VMAT1 and VMAT2.A, BON or PC 12 cell membranes were subjected to SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and analyzed by polyclonal antisera against VMAT1 or VMAT2. Both antisera recognized proteins at 55 kDa. The higher molecular weight bands stained by the anti-VMAT1 antiserum probably represent glycosylated isoforms. Preincubation with the respective peptide used for immunization abolished the staining with the antisera (results not shown). Note that the antiserum against VMAT2 did not recognize any protein in membranes obtained from PC 12 cells. B, C, Immunofluorescence microscopic analysis revealed that cells contained either VMAT1 (B) or VMAT2 (C), which mostly colocalized with serotonin, detected by a chicken anti-serotonin antiserum. Scale bar, 20 μm.
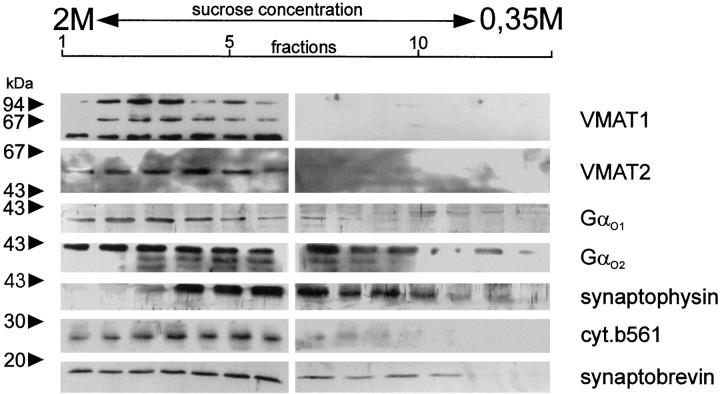
Next we investigated whether VMAT1 and VMAT2 are localized to LDCV or SSV or to both types of organelles. For this purpose, a postnuclear supernatant was separated by density gradient centrifugation on a continuous sucrose gradient. The distribution of VMAT1 and VMAT2 was then determined by immunoblot analysis and compared with that of established markers cytochrome b561 and synaptophysin for LDCV or SSV, respectively. Both VMATs were found in the LDCV fraction in a distribution similar to cytochrome b561. SSV analogs, identified by their synaptophysin content, were largely separated from the LDCV fractions but contain only minor amounts of both transporters. As expected, synaptobrevin, which localizes to both types of secretory vesicles, was found in both parts of the gradient.
Gαo and Gαi have been recently shown to localize to LDCV as well as SSV in neurons and chromaffin cells (Ahnert-Hilger et al., 1994). In addition, Gαo2 has been shown to regulate LDCV-located VMAT1 (Ahnert-Hilger et al., 1998a). We therefore analyzed the distribution of Gαo proteins in our gradients. Besides a distribution in both parts of the gradient, considerable amounts especially of Gαo2 associated with the dense fraction, consistent with a presumed localization to LDCV (Fig.2).
Fig. 2.
Localization of VMAT1, VMAT2, and Gαo-subunits to subcellular fractions from BON cells. Subcellular fractionation was performed using a continuous sucrose gradient. Fractions were spun down, dissolved in Laemmli buffer, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using the indicated antibodies.
Monoamine uptake by VMAT1 and VMAT2 can be differentiated in permeabilized BON cells
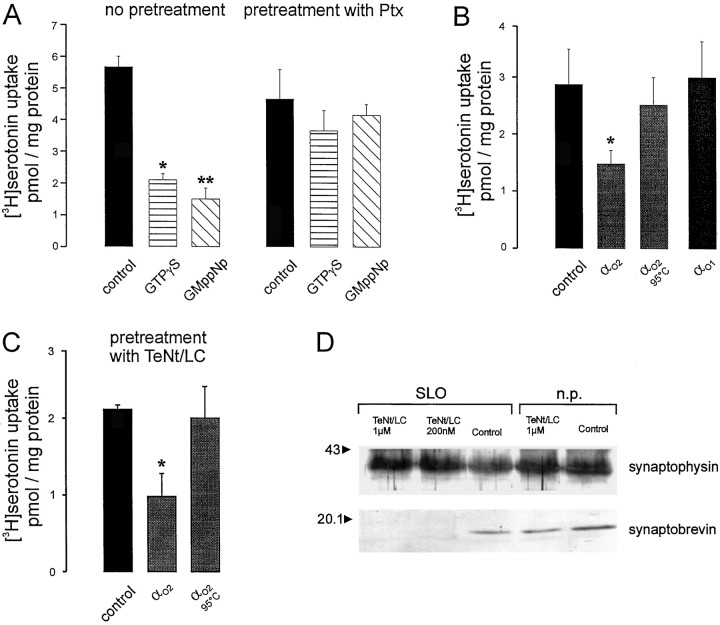
For measurement of VMAT activity, BON cells were permeabilized with SLO according to standard procedures (see Materials and Methods). When [3H]serotonin was added, an ATP-dependent and reserpine-sensitive uptake was observed, as expected for vesicular monoamine transport. Poorly hydrolyzable GTP analogs significantly inhibited serotonin uptake, and their inhibitory effects could be prevented by pertussis toxin treatment (Fig.3A). Purified Gαo2 but not heat-denatured Gαo2 or Gαo1 also inhibited serotonin uptake (Fig. 3B). Other purified Gα-subunits (Gαi1 or Gαi2) did not specifically interfere with VMAT activity, because their effects could not be prevented by heat denaturation and were probably artifacts attributable to detergent contaminations (Table 1). The effects of Gαo2 were insensitive to tetanus toxin treatment, which strongly excludes exocytotic events and suggests that Gαo2 regulates vesicular monoamine transport in these cells (Fig. 3C,D).
Fig. 3.
Activators of heterotrimeric G proteins and Gαo2 inhibit uptake of [3H]serotonin by permeabilized BON cells.A, SLO-treated and washed cells (see Materials and Methods) were resuspended in KG buffer containing 2 mmMg-ATP with additions as indicated and incubated for 25 min at 36°C. The reserpine-sensitive serotonin uptake was inhibited by addition of the GTP analogs GMppNp and GTPγS each at a final concentration of 50 μm. Their effects were statistically significant, calculated by Students’ t test (*,**p < 0.003). Preincubating the cells with pertussis toxin (100 ng/ml) prevented the inhibition of serotonin uptake by GTP analogs. Values (n = 3 ± SD) represent the reserpine-sensitive uptake. Unspecific accumulation (picomoles per milligram of protein) in the presence of 2 μm reserpine was 0.93 ± 0.05 and 0.82 ± 0.08 for untreated and pertussis toxin-treated samples, respectively.B, Permeabilized cells were incubated as given inA with purified Gαo1 (20 nm), Gαo2 (10 nm), or Gαo2 that had been denatured by heating to 100°C. Only effects of Gαo2 were statistically significant (*p < 0.05). Unspecific accumulation in the presence of reserpine was 0.83 ± 0.1 pmol/mg of protein.C, Permeabilized BON cells were preincubated for 20 min with KG buffer in the absence or presence of TeNt/LC (200 nm final concentration) before uptake was started by addition of fresh KG buffer plus Mg-ATP supplemented with 10 nm AlF4−-activated or heat-denaturated Gαo2. Only effects of Gαo2 were statistically significant (*p < 0.02). Values (n = 3 ± SD) represent reserpine-sensitive uptake. Uptake in the presence of reserpine (2 μm) was 0.28 ± 0.2 pmol/mg of protein. D, Under the experimental conditions given in C, addition of TeNt/LC between 200 nm and 1 μm completely cleaved synaptobrevin without affecting synaptophysin analyzed for comparison.n.p., Nonpermeabilized.
Table 1.
Failure of Gαi subunits to specifically downregulate VMATs in BON cells
| [3H]Serotonin uptake (pmol/mg protein) | |
|---|---|
| Control | 1.58 ± 0.06 |
| Reserpine | 0.55 ± 0.01 |
| Gαi110 nm | 1.06 ± 0.02 |
| Gαi1 heat denatured | 1.11 ± 0.06 |
| Gαi2 10 nm | 1.04 ± 0.1 |
| Gαi2 heat denatured | 1.08 ± 0.11 |
Permeabilized BON cells were incubated with purified ALF4−-activated Gαi subunits. The effects observed by the added proteins could not be overcome after prolonged heating to 100°C, which contrasts with the effects observed after application of Gαo2 and must be attributed to solvent contaminants.
To distinguish between transport activities mediated by VMAT1 and VMAT2, we exploited pharmacological differences between the two transporters (see introductory remarks). Because VMAT2 has an ∼30-fold higher affinity for histamine than VMAT1, we monitored [3H]serotonin uptake in the presence of increasing concentrations of histamine. Serotonin uptake into BON cells can be partially inhibited by 0.5–2 mm histamine, whereas a complete inhibition was observed with 10 mm histamine (data not shown). These data are consistent with the presence of both transporter activities in BON cells, VMAT2 with aKi value of ∼0.2 mm for histamine and VMAT1, which can be blocked only by histamine concentrations >5 mm (Erickson et al., 1996).
In the following different approaches were used to selectively measure VMAT1 and VMAT2 activities. First, using PC 12 cells as a reference for VMAT1, we confirmed that only serotonin and noradrenaline but not histamine were taken up in a reserpine-sensitive way under our experimental conditions (Fig.4A). Second, tetrabenazine, which is selective for VMAT2, partially inhibited serotonin uptake by BON cells but failed to do so when applied to PC 12 cells (Fig. 4B). Third, when measuring serotonin uptake in the presence of 2 mm histamine, a reserpine-sensitive uptake was observed, which was no longer affected by tetrabenazine and thus represents VMAT1 activity (Fig. 4C, left panel). Conversely [3H]histamine was taken up in a reserpine- and tetrabenazine-sensitive manner, which thus reflected VMAT2 activity (Fig. 4C, right panel). As expected, histamine uptake was dependent on ATP (data not shown). Histamine uptake by VMAT2 was less pronounced than serotonin uptake by VMAT1 (Fig. 4C), which is probably attributable to the fact that fewer BON cells express VMAT2 (see above).
Fig. 4.
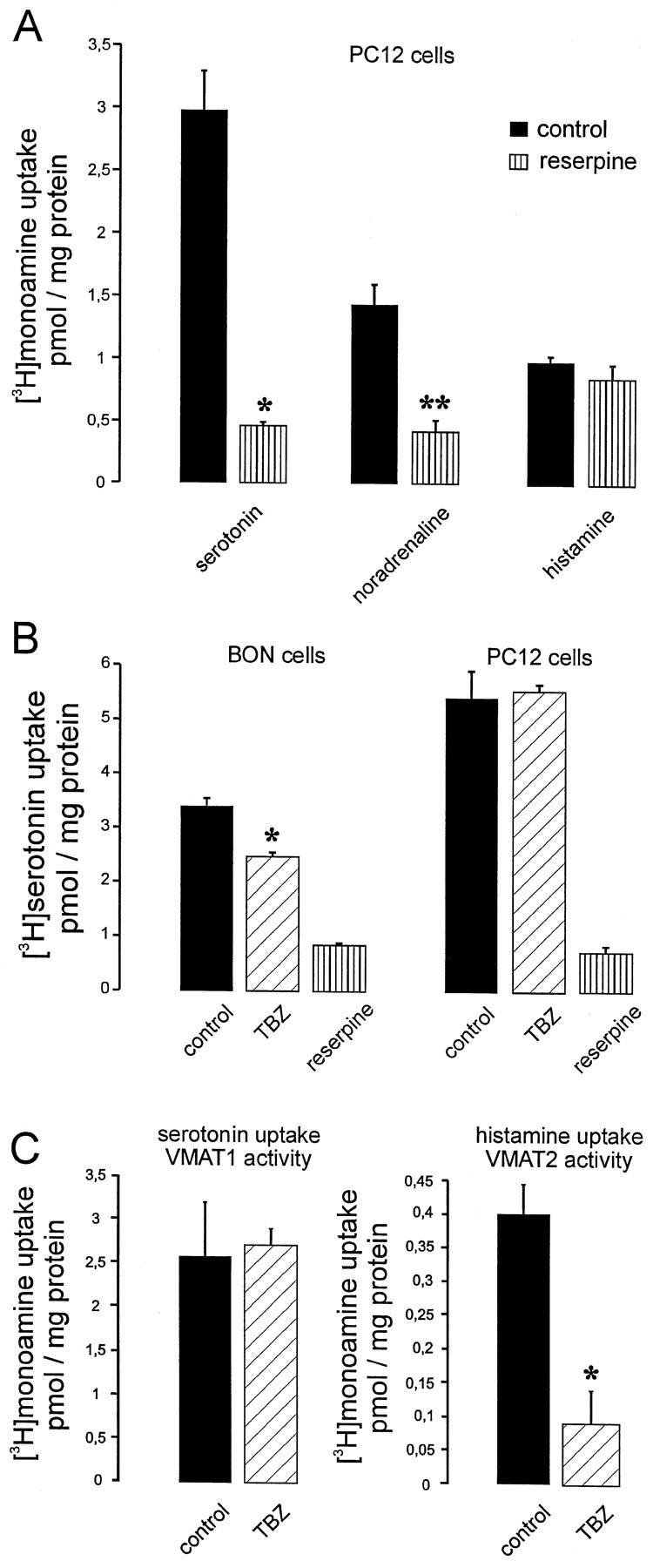
Monoamine uptake by VMAT1 and VMAT2 can be differentiated in permeabilized cells. A, Monoamine uptake was performed with permeabilized PC 12 cells using [3H]serotonin, [3H]noradrenaline, or [3H]histamine as substrates. Note that the serotonin and the noradrenaline uptake was reserpine-sensitive (*,**p < 0.001 or 0.002, respectively, calculated by Students' t test), whereas histamine uptake could not be blocked. B, [3H]Serotonin uptake into permeabilized BON cells could be partially inhibited by 1 μm tetrabenazine (TBZ) (*p < 0.04). Tetrabenazine had no effect on serotonin uptake when using permeabilized PC 12 cells.C, [3H]Serotonin uptake was performed in the presence of 2 mm histamine, which is transported only by VMAT2 and therefore blocks [3H]serotonin transport by this transporter activity. The uptake observed under these conditions is consistent to be exclusively attributable to VMAT1 activity, because it was reserpine-sensitive but could not be inhibited by tetrabenazine. Reserpine-sensitive uptake of [3H]histamine into permeabilized BON cells was inhibited by 1 μmtetrabenazine to ∼80% (*p < 0.04). This uptake is attributable to VMAT2 activity. Values (n = 3 ± SD) represent the reserpine uptake in picomoles per milligram of protein. Monoamine uptake in the presence of reserpine (5 μm) was 2.2 ± 1.3 and 1.23 ± 0.006 pmol/mg of protein for VMAT1 and VMAT2 activity, respectively.
Gαo2 inhibits VMAT2 in BON cells more potently than VMAT1
A pronounced inhibition of monoamine uptake into BON cells by Gαo2 was observed when measuring serotonin uptake by VMAT1 activity or histamine uptake by VMAT2. Again, heat-denatured Gαo2 was ineffective, as shown for histamine uptake (Fig.5A). The concentration–response curve revealed that VMAT2 could be inhibited by subnanomolar concentrations of Gαo2(half-maximal effect at ∼0.5 nm), whereas for VMAT1 half-maximal effects were observed at 1.5 nm (Fig. 5B). The different sensitivities were also reflected when using 5′-guanylylimidodiphosphate (GMppNp), which almost completely inhibited VMAT2 at 50 μm, a concentration at which VMAT1 was only partially downregulated (Fig. 5C). For both transporters Gαo1 as well as Gαi1 and Gαi2 were ineffective even when a concentration of 10 nmwas applied (Fig. 5B; data not shown).
Fig. 5.
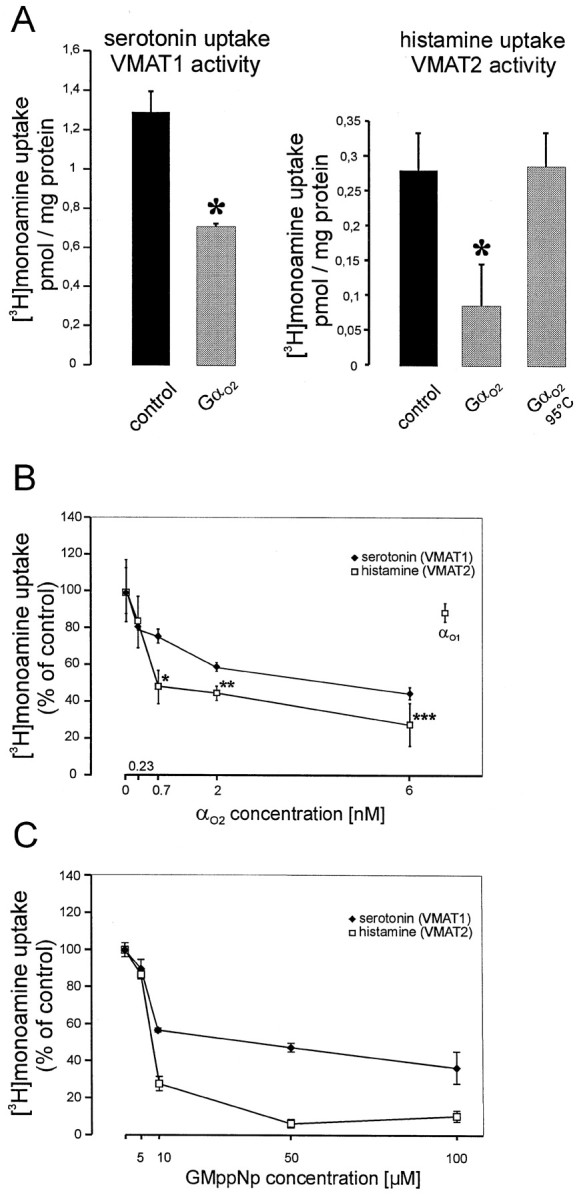
Inhibition of VMAT1 and VMAT2 activity by Gαo2 or GMppNp in permeabilized BON cells.A, [3H]Serotonin uptake performed in the presence of 2 mm histamine (VMAT1 condition) was inhibited by 10 nmAlF4−-activated Gαo2 (*,p < 0.004). [3H] histamine uptake (200 nm final concentration of histamine) was inhibited by 10 nm AlF4−-activated Gαo2, whereas heat-denaturated protein had no effect or (*p < 0.02, calculated by Students't test). Values (n = 3 ± SD) represent the reserpine-sensitive uptake. Monoamine uptake in the presence of reserpine was 0.42 ± 0.035 and 0.33 ± 0.001 pmol/mg of protein for VMAT1 and VMAT2 activity, respectively.B, Increasing concentrations of AlF4−-activated Gαo2 and 10 nm AlF4−-activated Gαo1 were applied to permeabilized BON cells measuring either VMAT1 or VMAT2 activity. Note that Gαo2 downregulates VMATs at concentrations between 0.2 and 2 nmm whereas Gαo1 had no effect on the activity VMAT2. Values (n = 3 ± SD) are expressed as percent of control of the reserpine-sensitive monoamine uptake, which was 1.86 ± 0.2 and 0.33 ± 0.033 pmol/mg of protein for VMAT1 and VMAT2, respectively. Note that VMAT2 activity is more affected by Gαo2 between 0.7 and 6 nm than VMAT1 (*p < 0.008; **p < 0.02; ***p < 0.04, calculated by students't test). C, Increasing concentrations of GMppNp between 5 and 100 μm were applied to permeabilized BON cells. VMAT1 or VMAT2 activity was measured. Values (n = 3 ± SD) are expressed as percent of control of the reserpine-sensitive monoamine uptake, which was 1.03 ± 0.02 and 0.53 ± 0.01 pmol/mg of protein for VMAT1 and VMAT2, respectively.
These data show that Gαo2 downregulates VMAT2 even more efficiently than VMAT1 in these human neuroendocrine cells.
VMAT2 of serotonergic neurons is downregulated by Gαo2
The data described above show that in neuroendocrine cells both VMAT1 and VMAT2 are sensitive to downregulation by the trimeric G-protein Gαo2. We therefore examined whether a similar downregulation also occurs in serotonergic neurons.
Rat raphe neurons were grown in primary culture and assayed for their ability to sequester and release [3H]serotonin. Depolarization of preloaded neurons by elevating extracellular potassium resulted in serotonin release. As expected for exocytotic release, basal as well as stimulated release was inhibited by pretreating the neurons with 10 nm TeNT for 48 hr (Table2).
Table 2.
Serotonin secretion from rat raphe neurons in primary culture
| [3H]Serotonin secretion (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| No pretreatment | Pretreatment with TeNt | |
| Control | 13.0 ± 1.4 | 7.3 ± 0.47 |
| 50 mm K+ | 33.0 ± 1 | 12.3 ± 0.48 |
Raphe neurons (11 d in vitro) were treated with solvent or with 1 nm TeNt and further cultivated for another 2 d. [3H]Serotonin secretion was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Release is given as percentage of total [3H]serotonin present at the start of the experiment and represents the mean of three individual cultures ± SD. Note that TeNt pretreatment reduced basal as well as stimulated release.
Primary cultures of raphe represent a mixture of different types of neurons. Therefore, we estimated the proportion of serotonergic neurons present in our culture system by immunofluorescence microscopy. As shown in Figure 6, some (∼5%) of the cultivated neurons were positive for both VMAT2 and serotonin.
Fig. 6.
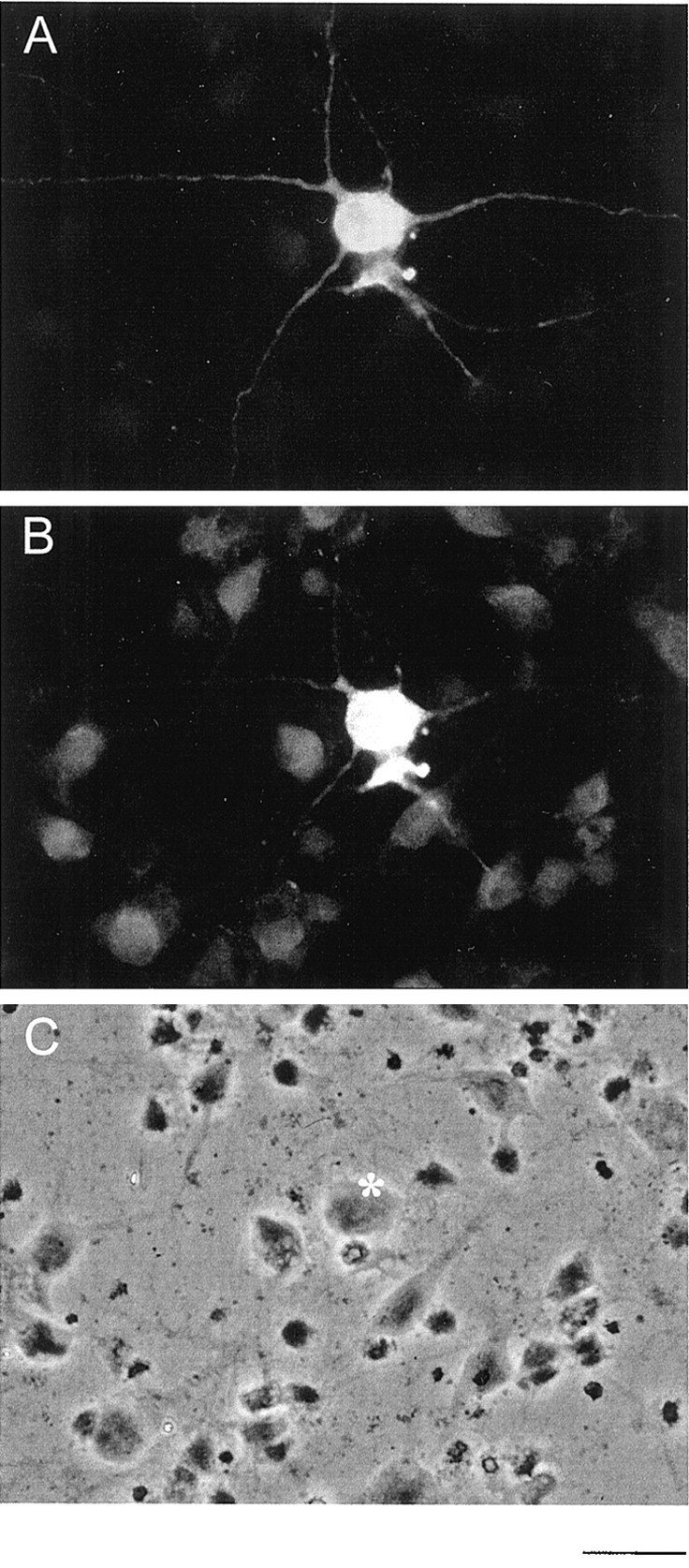
Immunofluorescence microscopic analysis of serotonergic neurons in raphe primary culture. Raphe neurons cultivated for 10 d in vitro were fixed and incubated using a mixture of chicken anti-serotonin antiserum and rabbit anti-VMAT2 antiserum. Of a couple of neurons shown in C, only one neuron labeled by an asterisk was positively stained for serotonin (A) or VMAT2 (B). Scale bar, 10 μm.
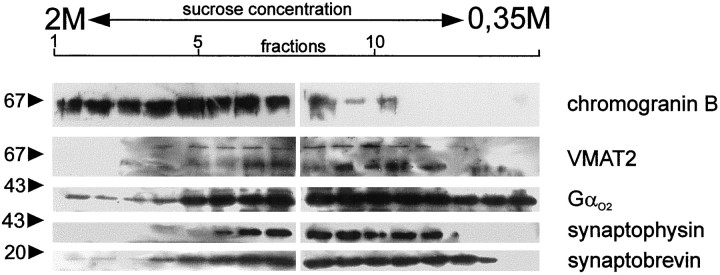
Because serotonergic neurons predominantly contain SSV besides some LDCV (Smiley et al., 1996), we first analyzed the subcellular distribution of VMAT2 in these cultures using subcellular fractionation. When separating postnuclear supernatants by density gradient centrifugation on a continuous sucrose gradient, VMAT2 was preferentially associated with lighter membrane fractions identified by their synaptophysin content. LDCV, identified by their chromogranin B content, were largely separated from the SSV fractions and almost devoid of VMAT2. As expected, synaptobrevin, which localizes to both types of secretory vesicles, was found in both parts of the gradient (Fig. 7). These data indicate that VMAT2 preferentially localizes to SSV in these serotonergic neurons and thus offer the opportunity to investigate whether G-protein-mediated regulation of transmitter loading is a feature of neuronal SSV.
Fig. 7.
Localization of VMAT1, VMAT2, and Gαo subunits to subcellular fractions from raphe neurons. Raphe neurons were cultivated for 14 d. Subcellular fractionation was performed using a continuous sucrose gradient. Fractions were spun down, dissolved in Laemmli buffer, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using the indicated antibodies.
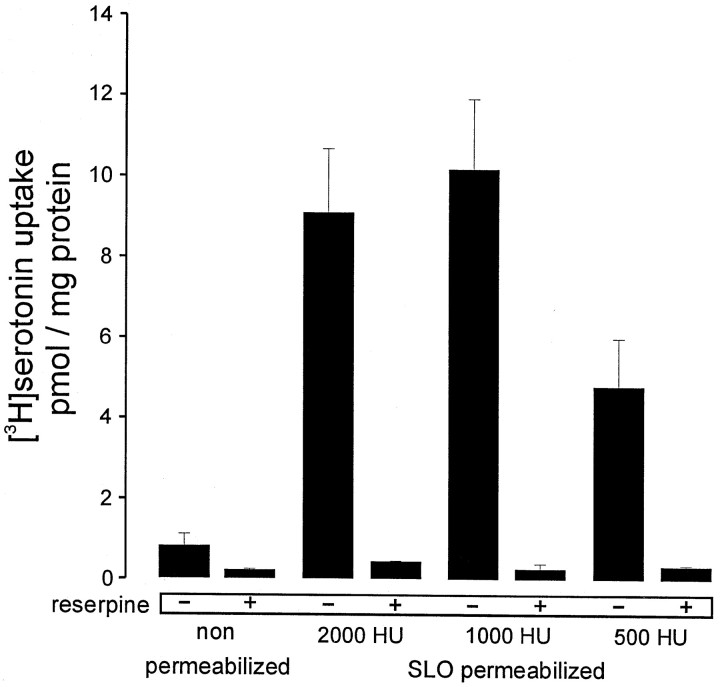
Next we applied our permeabilization technique to these neurons using various concentrations of SLO. As can been seen in Figure8, a reserpine-sensitive uptake of serotonin was observed after permeabilizing the neurons with SLO concentrations corresponding to 500–2000 hemolytic units (Ahnert-Hilger and Weller, 1998). In the intracellular buffer used for these kind of experiments, only minute amounts of serotonin uptake were observed without permeabilization. When GMppNp or guanosine 5′-3-O-(thio)triphosphate (GTPγS) in micromolar concentrations were applied to permeabilized neurons, the reserpine-sensitive serotonin uptake was inhibited by ∼40%. Pretreating the neurons with pertussis toxin overnight abolished the inhibitory action of the GTP analogs (Fig.9A). In an experimental design similar to the one in Table 2, neurons were pretreated with TeNt for 48 hr, which did not influence the inhibition of serotonin uptake by GMppNp or GTPγS, demonstrating that inhibition is not a consequence of exocytosis (Fig. 9B). When AlF4−-activated Gαo2 was applied to permeabilized neurons an ∼40% inhibition of uptake was observed (Fig. 9C). The data support the idea that in rat raphe neurons a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein, presumably Gαo2, regulates vesicular storage of serotonin. Thus not only monoamine storage of LDCV in neuroendocrine cells but also transmitter storage of neuronal SSV may be controlled by Gαo2 residing on the vesicle surface.
Fig. 8.
Reserpine-sensitive serotonin uptake into SLO-permeabilized serotonergic neurons. Raphe neurons cultivated for 10 d in vitro were washed twice with PBS and once with KG buffer. Cultures were incubated on ice for 10 min with various dilutions of SLO [between 2000 and 500 hemolytic units (HU)/ml] dissolved in KG buffer or with KG buffer alone. The permeabilization solution was replaced by fresh KG buffer, and neurons were preincubated for 5 min at 37°C. After removal of this solution, uptake was started by applying [3H]serotonin dissolved in KG-ATP buffer in the absence or presence of 2 μm reserpine. The incubation was stopped after 10 min at 37°C, and cultures were lysed in Triton X-100 for determination of radioactivity and protein content. Values are the mean of three individual culture wells ± SD. Note that reserpine-sensitive uptake dramatically increased in SLO-treated neurons.
Fig. 9.
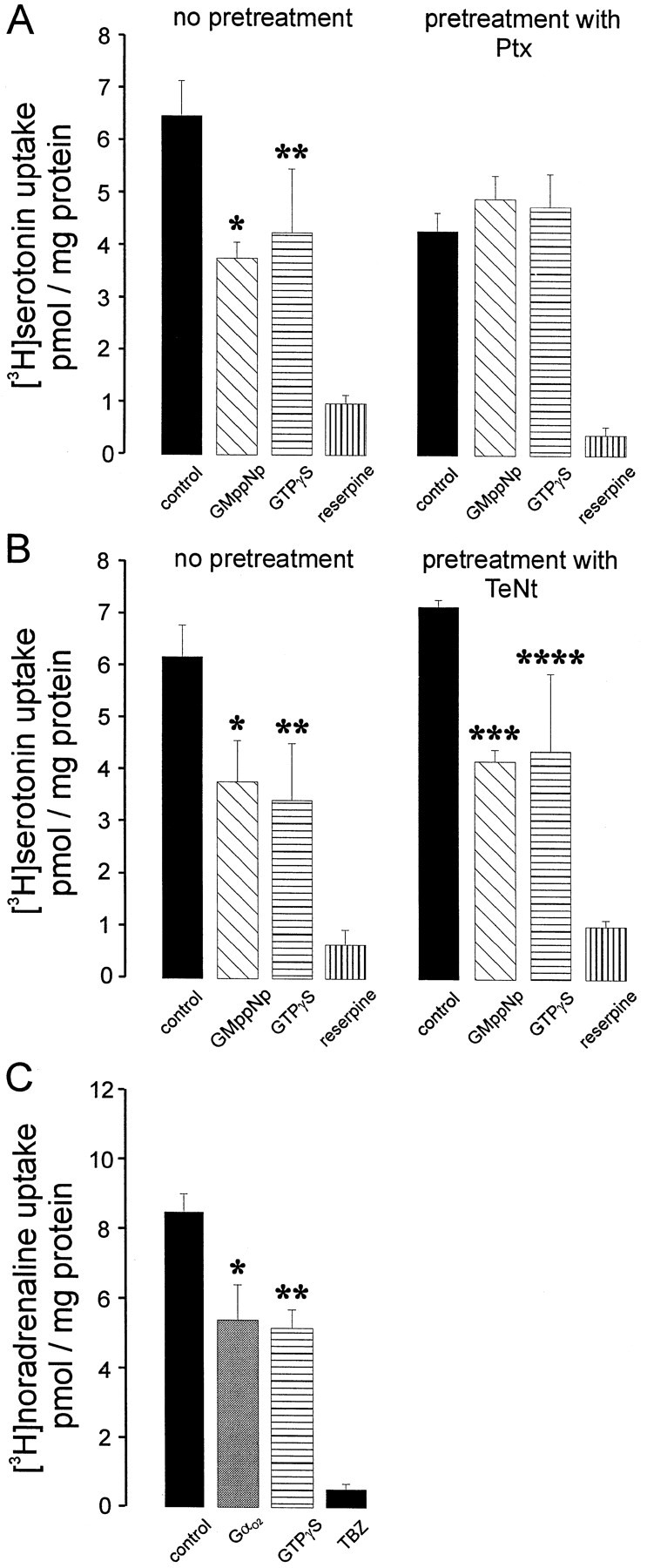
Gαo2 downregulates monoamine uptake into permeabilized raphe neurons. A, Raphe neurons cultivated for 25 d in vitro were treated with either buffer or pertussis toxin (Ptx; 100 ng/ml) 2 d before the experiment. The experiment followed the protocol described in Figure 8. GMppNp or GTPγS was applied at 50 μmtogether with [3H]serotonin, and incubation was stopped after 10 min (*,**p < 0.04 or 0.05, respectively). B, This experiment followed a similar experimental design, with the exception that cultures were treated with TeNt (1 nm) 2 d before the experiment (*p < 0.02; **p < 0.03; ***p < 0.004; ****p < 0.05, calculated by Students' t test). Values are the mean of three cultures ± SD. C, The experiment was performed as stated in A, with the exception that noradrenaline as substrate and 1 μm tetrabenazine (TBZ) were used to specifically block VMAT2. Gαo2 (10 nm final concentration) was applied in the AlF4−-activated form, and the incubation was stopped after 10 min (*,**p < 0.003, p< 0.002, respectively). Values represent the mean of three individual culture wells ± SD. In the experiments given in A,values were calculated referring to the mean protein content of all samples.
VMAT2 of SSV is downregulated by Gαo2
To get a direct proof for the localization of VMAT2 and Gαo2 on SSV, a double immunoelectron microscopic analysis was performed using a combination of pre- and postembedding techniques. For this purpose serotonergic terminals in the rat prefrontal cortex were first labeled by a chicken serotonin antiserum using the DAB technique and then subjected to postembedding procedure using rabbit antisera against VMAT2 or Gαo2 detected by gold-labeled anti-rabbit IgG. This technique allows identification of serotonergic terminals with VMAT2 or Gαo2 localized to SSV. Serotonin was found in thin neuronal processes showing terminals typical for serotonergic neurons processing to the prefrontal cortex (Fig.10A). The electron microscopic analysis of these terminals revealed that they were filled exclusively with SSV containing the DAB reaction product and worked by an antibody against synaptophysin (Fig. 10B). VMAT2 could be detected almost exclusively in SSV-containing terminals (Fig. 10C,C′, arrows); some of them were devoid of DAB and may originate from dopaminergic neurons (Fig.10C′, arrowheads). The serotonergic terminals clearly marked by DAB were also decorated with gold particles indicating Gαo2 (Fig. 10D, arrows) on serotonin-containing SSV. As expected, Gαo2 was also found on other membranes besides SSV (data not shown) and on SSV from nonserotonergic terminals (Fig.10D′, arrowheads).
Fig. 10.
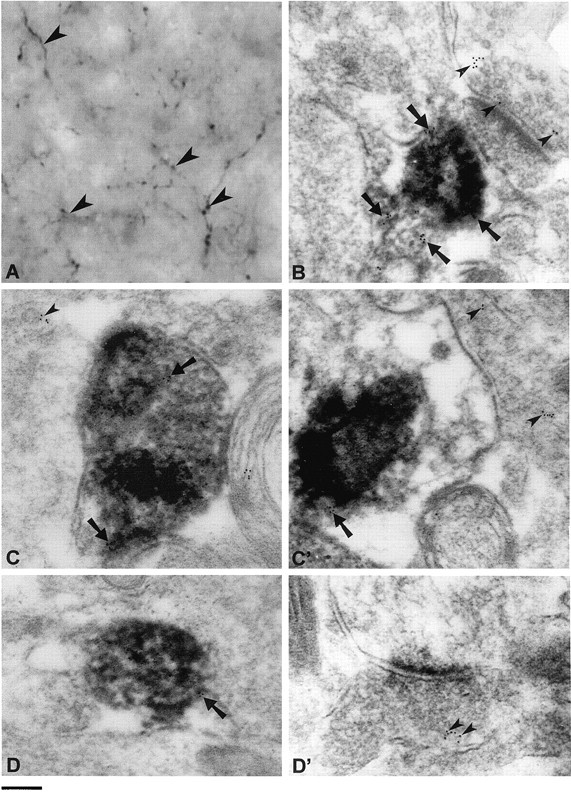
Immunoelectron microscopic localization of VMAT2 and Gαo2 in serotonergic terminals from rat prefrontal cortex. A, The micrograph shows serotonergic terminals (arrowheads) labeled by a chicken antiserum against serotonin and visualized by DAB. From this tissue ultrathin sections were performed and subjected to postembedding procedures using antisera against synaptophysin, VMAT2 or Gαo2 and anti-rabbit IgG coupled to 5 nm gold particles. B,Electronmicroscopic details from an area showing two terminals, one of them being serotonergic, identified by the DAB precipitate. Synaptophysin is present on SSV of the serotonergic or the other terminal, as indicated by arrows orarrowheads, respectively. C,C′, Electronmicroscopic details from two serotonergic terminals (C, C′), identified by DAB containing SSV, where VMAT2 is clearly visible on some SSV (arrows). Arrowheads denote gold particles on SSV from an adjacent monoaminergic terminal, probably originating from a dopaminergic neuron. D,D′, In a serotonergic terminal (D) identified by its DAB content, Gαo2 is also detected on SSV (arrows). D′, Presence of Gαo2 on synaptic vesicles (arrowheads) in a not further identified synaptic terminal. Scale bar:A, 1 μm; B–D, 150 nm.
Using a synaptic vesicle preparation from prefrontal cortex, a tetrabenazine-sensitive uptake of [3H]serotonin was observed, which coud be downregulated by the addition of GMppNp. Again, purified Gαo2 but not Gαo1inhibited serotonin uptake from this vesicular preparation (Fig.11). These data strongly support the idea that VMAT2 residing on SSV is also modulated by Go2.
Fig. 11.
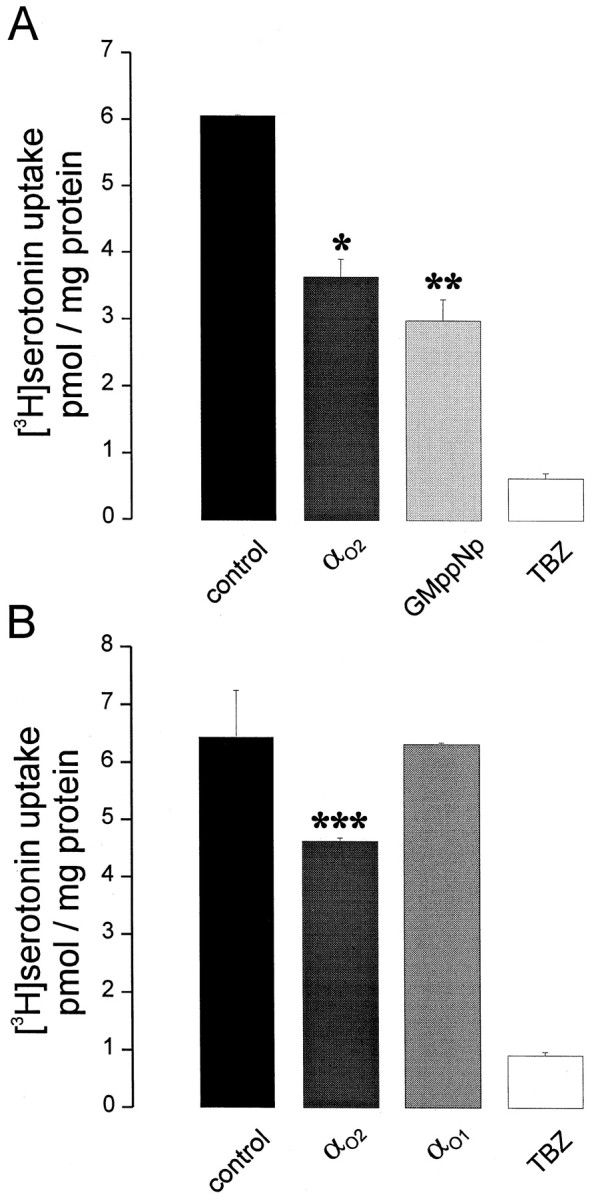
Gαo2 downregulates monoamine uptake into synaptic vesicles. A, B, Crude synaptic vesicles from rat prefrontal cortex were incubated for 10 min at 37°C with KG-ATP buffer containing [3H]serotonin (90 nm final concentration), supplemented with 10 nm purified AlF4−-activated Gαo1 (B), Gαo2(A, B), 50 μm GmppNp (A), or 10 μm tetrabenazine (TBZ; A, B), as indicated (*,**,***p < 0.003, p < 0.003, or p < 0.04, respectively, calculated by Students' t test). Values represent the mean of three samples ± SD.
DISCUSSION
In the present study we show that VMAT2 is highly sensitive to regulation by Gαo2. These data extend our previous findings concerning the regulation of VMAT1 in PC 12 cells (Ahnert-Hilger et al., 1998a). Together they lend strong support to the view that vesicular monoamine transporters are regulated by Go2 in neurons and neuroendocrine cells, regardless of whether the transporter is localized to LDCV or SSV. The presence of both VMAT1 and VMAT2 in the neuroendocrine cell line BON allowed for a direct comparison of the two transporters. Because the transport activities can be distinguished pharmacologically, we were able to demonstrate that VMAT2 is even more sensitive to downregulation than VMAT1. Although representing a valuable model for directly comparing the regulation of both transporters on dense-core vesicles, BON cells cannot substitute for neurons. This issue was addressed by two different neuronal preparations. VMAT2 was also downregulated in raphe neurons in primary culture, demonstrating that this type of control is not confined to neuroendocrine cells. Even more, downregulation was also clearly visible when using synaptic vesicles. The reason for the differential sensitivity of the two transporters remains unclear. However, VMAT2 but not VMAT1 is phosphorylated (Krantz et al., 1997) suggesting that the transporters may have more differences in their regulation. The recently described association of Gαo2 with membranes of both LDCV and SSV (Ahnert-Hilger et al., 1994; this paper) favors a role in controlling neurotransmitter uptake, although we do not know the factors involved in the upstream regulation. In addition to Gα-subunits, Gβγ subunits also were found to colocalize with secretory vesicle proteins (Ahnert-Hilger et al., 1994; Brunk et al., 1999), assuming a signal transduction from the luminal site over the vesicle membrane by an unknown receptor (Nürnberg and Ahnert-Hilger, 1996). So far, only one example of an endomembrane protein with characteristics of classical G-protein-coupled receptors has been described. This KDEL receptor locates on Golgi membranes and is involved in the retrograde transport from Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum (Scheel and Pelham, 1998).
Although we do not know how the G-protein is turned on, its general feature in regulating VMATs allows speculations toward the physiological relevance of a regulation of transmitter storage by intracellular signaling pathways.
There is increasing evidence from electrophysiological studies that vesicular content is variable and may be subject to both short- and long-term regulation. Overexpression of vesicular acetylcholine transporter resulted in a 10-fold increase of vesicular acetylcholine content (Song et al., 1997). Drugs that interfere with acetylcholine metabolism decrease quantal size at the neuromuscular junction (Parsons et al., 1993), whereas β-adrenergic stimulation increases quantal release at least in the frog (van der Kloot 1991; Williams, 1997). In this line, it has recently been shown that activation of dopamine D2 autoreceptors reduces quantal release of dopamine from PC 12 cells (Pothos et al., 1998b). In addition, the neurotrophic factor glial-derived neurotrophic factor as well as changes in the metabolism of dopaminergic neurons affected quantal dopamine release (Pothos et al., 1998a). These data support the idea that intracellular signaling pathways may modulate vesicular storage. The regulation of VMATs by the heterotrimeric G protein Go2 described here could be one of the missing links in intracellular signaling pathways regulating the filling of secretory vesicles and may represent the contribution of the vesicle to synaptic plasticity. Whether these regulations could be better explained by a “steady-state” model or a “set-point” model (Williams, 1997) or whether switches between these two models may be regulated by heterotrimeric G proteins is an open discussion.
Besides being a regulator of vesicle filling in monoaminergic and presumably other neurons, regulation by G-proteins may be of additional pathophysiological relevance specific for monoaminergic neurons. Monoamine transporters are characterized by a lowKm value quite different from the higher Km values of vesicular acetylcholine transporter and the transporters for GABA/glycine and glutamate (Liu and Edwards, 1997). IncreasingKm of the transporter for monoamines by Go may therefore have two functions. It may enable the cell to rapidly refill secretory vesicles for another cycle and in addition to get rid of high amounts of probably toxic monoamines and their oxidation products in the cytoplasm. The idea that VMATs may help clean the cell from hazardous compounds is supported by their phylogenetic relationship with bacterial toxin-extruding transporters (Schuldiner et al., 1995). Furthermore, the absence of VMATs in periglomerular dopaminergic neurons of the olfactory bulb (Peter et al., 1995) makes these neurons the first affected in the beginning of Parkinson‘s disease (Daniel and Hawkes, 1992). On the other hand, elevated VMAT2 and reduced dopamine plasma membrane transporter expression appeared to decrease the vulnerability of dopaminergic neurons (Uhl et al., 1994). Whether an impaired regulation of VMAT2 by Gao2is crucial for the development of Parkinson’s disease, especially in the mostly affected large dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta, remains to be found out.
Footnotes
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and Fonds der Chemischen Industrie. We thank Evelyn Heuckendorf for expert technical assistance and Anja Becher for critically reading this manuscript. Portions of this work were completed as part of the PhD thesis of M.H.
Correspondence should be addressed to Gudrun Ahnert-Hilger, Institut für Anatomie der Charité, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, Philippstrasse 12, 10115 Berlin, Germany. E-mail:gudrun.ahnert@charite.de.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ahnert-Hilger G, Weller U (1998) Alpha-toxin and streptolysin O as tools in cell biological research. In: Cell biology, a laboratory handbook (Celio E, ed), Ed 2, Vol 4, pp 103–110. New York: Academic.
- 2.Ahnert-Hilger G, Schäfer T, Spicher K, Grund C, Schultz G, Wiedenmann B. Detection of G-protein heterotrimers on large dense core and small synaptic vesicles of neuroendocrine and neuronal cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994;65:26–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ahnert-Hilger G, Stadtbäumer A, Strübing C, Scherübl H, Schultz G, Riecken EO, Wiedenmann B. γ-Aminobutyric acid secretion from pancreatic neuroendocrine cells. Gastroenterology. 1996;110:1595–1604. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8613067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ahnert-Hilger G, Nürnberg B, Exner T, Schäfer T, Jahn R. The heterotrimeric G protein Go2 regulates catecholamine uptake by secretory vesicles. EMBO J. 1998a;17:406–413. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ahnert-Hilger G, John M, Kistner U, Wiedenmann B, Jarry H. Immortalized gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons secrete γ-amino acid—evidence for an autocrine regulation. Eur J Neurosci. 1998b;10:1145–1152. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1998.00129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Beauchamp DR, Coffey RJ, Jr, Lyons RM, Perkett EA, Townsend CM, Jr, Moses HL. Human carcinoid cell production of paracrine growth factors that can stimulate fibroblast and endothelial cell growth. Cancer Res. 1991;51:5253–5260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Brewer GJ. Serum-free B27/neurobasal medium supports differentiated growth of neurons from the striatum, substantia nigra, septum, cerebral cortex, cerebellum and dentate gyrus. J Neurosci Res. 1995;42:674–683. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490420510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brunk I, Pahner I, Maier U, Jenner B, Veh RW, Nürnberg B, Ahnert-Hilger G. Differential distribution of G-protein β-subunits in brain: an immunocytochemical analysis. Eur J Cell Biol. 1999;78:311–322. doi: 10.1016/s0171-9335(99)80065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Daniel SE, Hawkes CH. Preliminary diagnosis of Parkinson's disease by olfactory bulb pathology. Lancet. 1992;340:186. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93275-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dimaline R, Struther J. Expression and regulation of a vesicular monoamine transporter in rat stomach: a putative histamine transporter. J Physiol (Lond) 1995;490.1:249–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Edelmann L, Hanson PI, Chapman ER, Jahn R. Synaptobrevin binding to synaptophysin: a potential mechanism for controlling exocytotic fusion machine. EMBO J. 1995;14:224–231. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06995.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Edwards RH. The transport of neurotransmitters into synaptic vesicles. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992;2:586–594. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90023-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Erickson JD, Schäfer MKH, Bonner TI, Eiden LE, Weihe E. Distinct pharmacological properties and distribution in neurons and endocrine cells of two isoforms of the human vesicular monoamine transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:5166–5171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.5166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Evers BM, Townsend CM, Jr, Upp JR, Allen E, Hurlbut SC, Kim SW, Rajaraman S, Singh P, Reubi JC, Thompson JC. Establishment and characterization of a human carcinoid in nude mice and effects of various agents on tumor growth. Gastroenterology. 1991;101:303–311. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Exner T, Jensen ON, Kleuss C, Mann M, Nürnberg B. Posttranslational modification of Galphao1 generates Galphao3, an abundant G protein in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:1327–1332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.4.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Huttner WB, Schiebler W, Greengard P, DeCamilli P. Synapsin I (Protein I) a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983;96:1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jahn R, Schiebler W, Oimet C, Greengard P. A 38,000 dalton membrane protein (p38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1985;82:4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Krantz DE, Peter D, Liu Y, Edwards R. Phosphorylation of a vesicular monoamine transporter by casein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:6752–6759. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.10.6752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Krejci E, Gasnier B, Botton D, Sambert MF, Sagne C, Gagnon J, Massoulie J, Henry JP. Expression and regulation of the bovine vesicular monoamine transporter gene. FEBS Lett. 1993;335:227–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80432-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kroesen S, Marksteiner J, Leitner B, Hogue-Angeletti R, Fischer-Colbrie R, Winkler H. Rat brain: distribution of immunoreactivity of Pe-11, a peptide derived from chromogranin B. Eur J Neurosci. 1996;8:2679–2689. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1996.tb01563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Laugwitz KL, Allgeier A, Offermanns S, Spicher K, van Sande J, Dumont JE, Schultz G. The human thyrotropin receptor: a heptahelical receptor capable of stimulating members of all four G protein families. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:116–120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Leitner B, Lovisetti-Scamihorn P, Heilmann J, Striessnig J, Blakely RD, Eiden LE, Winkler H. Subcellular localization of chromogranins, calcium channels, amine carriers, and proteins of the exocytotic machinery in bovine splenic nerve. J Neurochem. 1999;72:1110–1116. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0721110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liu Y, Edwards R. The role of vesicular transport proteins in synaptic transmission and neural degeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1997;20:125–156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.20.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liu Y, Peter A, Roghani A, Schuldiner S, Prive GG, Eisenberg D, Brecha N, Edwards R. A cDNA that suppresses MPP+ toxicity encodes a vesicular amine transporter. Cell. 1992;70:539–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90425-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Liu Y, Schweitzer E, Nirenberg MJ, Pickel VM, Evans CJ, Edwards RH. Preferential localization of a vesicular monoamine transporter to dense core vesicles in PC 12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1994;127:1419–1433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.5.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nirenberg MJ, Liu Y, Peter D, Edwards RH, Pickel VM. The vesicular monoamine transporter 2 is present in small synaptic vesicles and preferentially localizes to large dense core vesicles in rat solitary tract nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:8773–8777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nürnberg B, Ahnert-Hilger G. Potential roles of heterotrimeric G proteins of the endomembrane system. FEBS Lett. 1996;389:61–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00584-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Parsons SM, Bahr BA, Rogers GA, Clarkson ED, Noremberg K, Hicks BW. Acetylcholine transporter—vesamicol receptor pharmacology and structure. Prog Brain Res. 1993;98:175–181. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Peter D, Jiminez J, Liu Y, Kim J, Edwards RH. The chromaffin granule and synaptic vesicle amine transporters differ in substrate recognition and sensitivity to inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:7231–7237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Peter D, Liu Y, Sternini C, de Giorgio R, Brecha N, Edwards RH. Differential expression of twi vesicular monoamine transporters. J Neurosci. 1995;15:6179–6188. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-09-06179.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pothos EN, Davial V, Sulzer D. Presynaptic recording of quantal from midbrain dopamine neurons and modulation of quantal size. J Neurosci. 1998a;18:4106–4118. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-11-04106.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pothos EN, Przedborski S, Davila V, Schmitz Y, Sulzer D. D2-like dopamine autoreceptor activation reduces quantal size in PC 12 cells. J Neurosci. 1998b;18:5575–5585. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-15-05575.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sagne C, Isambert M-F, Vandekerckhove J, Henry JP, Gasnier B. The photoactive inhibitor 7-azido-8-iodoketanserin labels the N-terminus of the vesicular monoamine transporter from bovine chromaffin granules. Biochemistry. 1997;36:3345–3352. doi: 10.1021/bi9623439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Scheel AA, Pelham HR. Identification of amino acids in the binding pocket of the human KDEL receptor. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:2467–2472. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.4.2467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schuldiner S, Shirvan A, Linial M. Vesicular neurotransmitter transporters: from bacteria to humans. Physiol Rev. 1995;75:369–392. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1995.75.2.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Smiley JF, Goldman-Rakic PS. Serotonergic axons in monkey prefrontal cerebral cortex synapse predominantly on interneurons as demonstrated by serial section electron microscopy. J Comp. Neurol. 1996;367:431–443. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960408)367:3<431::AID-CNE8>3.0.CO;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Song HJ, Ming GL, Fon E, Bellocchio E, Edwards RH, Poo MM. Expression of a putative vesicular acetylcholine transporter facilitates quantal transmitter packaging. Neuron. 1997;18:815–826. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Spicher K, Nürnberg B, Jäger B, Rosenthal W, Schultz G. Heterogeneity of three electrophoretically distinct Go α-subunits in mammalian brain. FEBS Lett. 1992;307:215–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80770-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Townsend CM, Jr, Ishizuka J, Thomplson JC. Studies of growth regulation in a neuroendocrine cell line. Acta Oncol. 1993;32:125–130. doi: 10.3109/02841869309083900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Uhl GR, Walther D, Mash D, Faucheux B, Javoy-Agid F. Dopamine transporter messenger RNA in Parkinson‘s disease control substantia nigra neurons. Ann Neurol. 1994;35:494–498. doi: 10.1002/ana.410350421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.van der Kloot W. The regulation of quantal size. Prog Neurobiol. 1991;36:93–103. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(91)90019-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Weller U, Müller L, Meßner M, Bhakdi S. Expression of active streptolysin-O in E. coli as maltose-binding protein-streptolysin-O fusion protein: the N-terminal 70 amino acids are not required for hemolytic activity. Eur J Biochem. 1996;236:34–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.00034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wenzel HJ, Buckmaster PS, Anderson NL, Wenzel ME, Schwartzkroin PA. Ultrastructural localization of neurotransmitter immunoreactivity in mossy cell axons and their synaptic targets in the rat dentate gyrus. Hippocampus. 1997;7:559–570. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1997)7:5<559::AID-HIPO11>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Williams J. How does a vesicle know it is full? Neuron. 1997;18:683–686. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]